L28 Prokaryotic Cells Structural Components and Their Roles
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the structural components of prokaryotic cells and their roles, Gram staining, bacterial movement, adherence factors, glycocalyx, and endospores.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Prokaryotic Cell
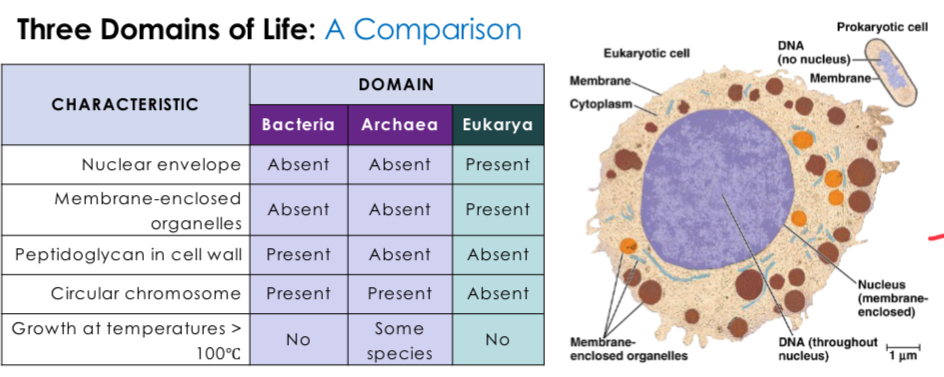
A cell lacking a nuclear envelope and other membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the Bacteria and Archaea domains.
Prokaryotic cell components and structure
Fimbriae/Pili, nucleoid, Plasma membrane, cell wall, ribosomes, Flagella, glycocalyx.
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic
Prokaryotes don’t have nuclear envelope, or membrane enclosed organelles and are very resistant. Eukaryotes don’t have peptidoglycan in cell wall, or circular chromosome.
Bacterial genome
Typivally a single circular ds chromosome with no nuclear envelope, however it is restricted to a defined region (nucleoid). Other small circular self replicating DNA molecules in cytosol (Plasmids)
Peptidoglycan
A mesh-like structure, provides strength to the cell wall, protects from osmotic lysis and conferrs cell shape (rods, cocci, spiral). Prokaryotes that lack cell wall= Mycoplasmas.
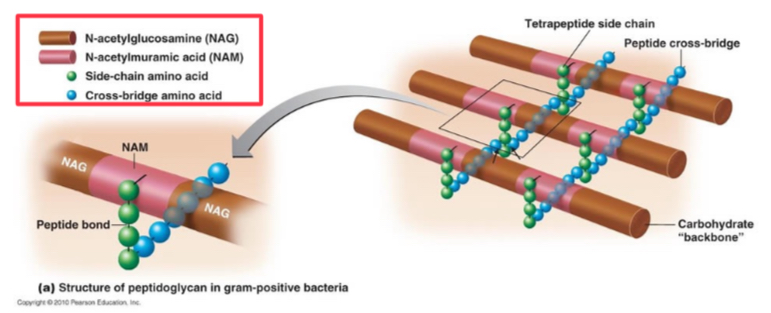
Peptidoglycan structure
Made of NAG, NAM, sidechain amino acid, and crossbridge amino acid. Transpetidase= the enzyme that cross link peptidoblycan chains. Forming rigid cell walls.
Gram stain procedure
Put culture on slide, stain with crystal violet, then iodine, then rinse with alcohol. Purple stain remains for gram positive. Stain with safranin, gram negative is revealed.
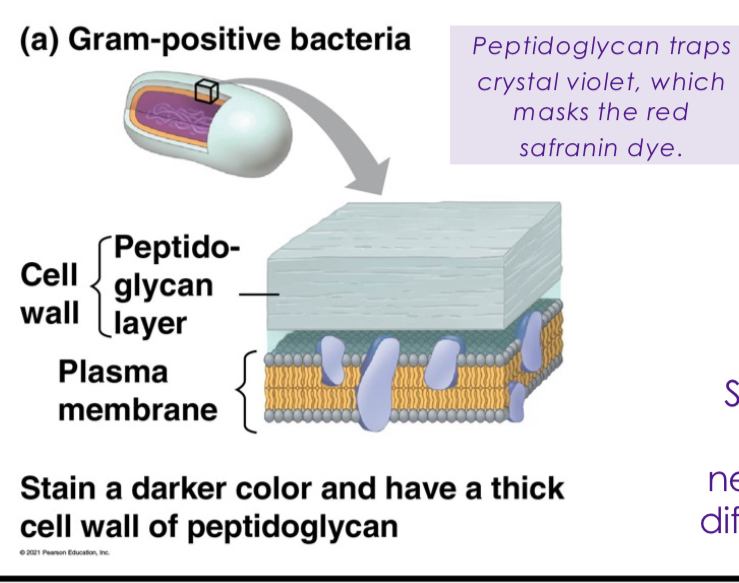
Gram-positive Bacteria
Cocci bacteria with a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall and no outer membrane, which traps crystal violet stain, purple color after Gram staining.
Gram-negative Bacteria
Rod bacteria with a thin peptidoglycan layer between an inner and outer membrane, so crystal violet is rinsed away during Gram staining, restained with red safranin dye.

Flagella (tails)
Long, flexible appendages that enable motile bacteria to move through liquid medium by rotating like a propeller. Number and location vary, 10-20 nm in diameter.
Chemotaxis
The movement of bacteria along a concentration gradient towards a chemical attractant (positive eg glucos/energy) or away from a chemical repellent (negative). Bacteria spin then tumble, triggered by presence of attractant.
Fimbriae
An inherited hair-like structures on bacteria that facilitate adhesion to surfaces; shorter and more numerous than flagella and not involved in motility.
Pili (Sex Pili/F Pili)
Attachment to other bacteria like gap junction, transfer of genetic material from one bacterial cell to another through a process called conjugation (horizontal gene transfer)
Glycocalyx (capsules and slime layers)
A gelatinous polysaccharide or polypeptide outer covering on bacteria that forms a sticky meshwork of fibers for protection.
Capsule
A glycocalyx that is organized into a defined structure and firmly attached to the cell wall, providing protection against phagocytosis and englofment by immune cells and desiccation (cell drying out).
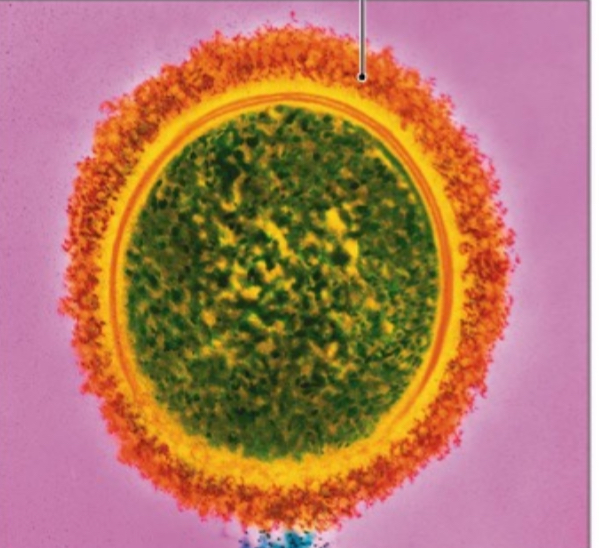
Slime Layer
A glycocalyx that is disorganized, without cell shape, and loosely attached to the cell wall.
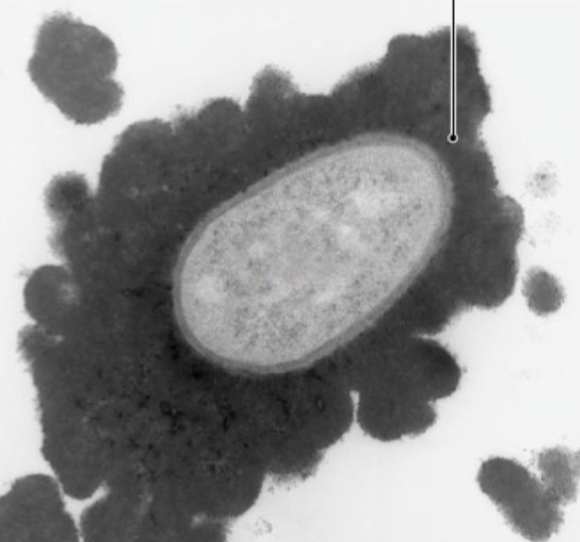
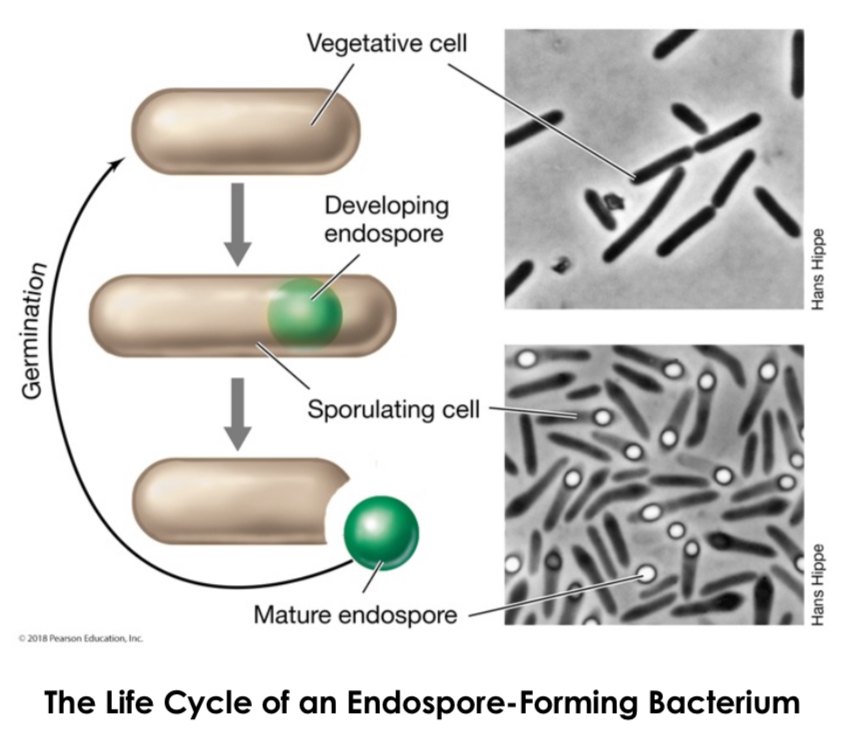
Endospores
Highly differentiated, dormant cells formed in some gram+ bacteria under unfavorable conditions (high cell density or nutrient starvation) that protect cells from stress. Members of genus Bacillus and Clostridium.