Lab 1 Practical
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
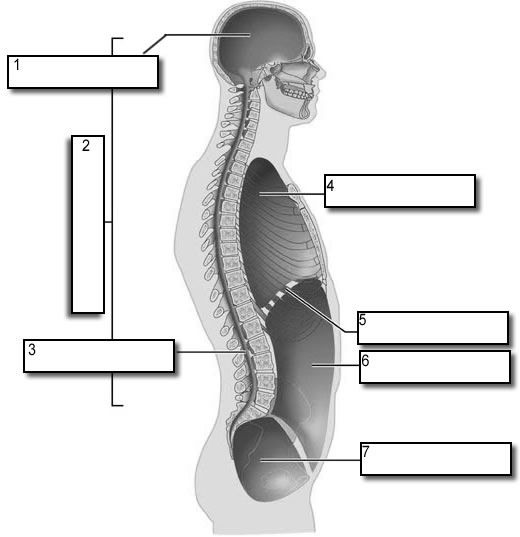
what number is the dorsal body cavity
2
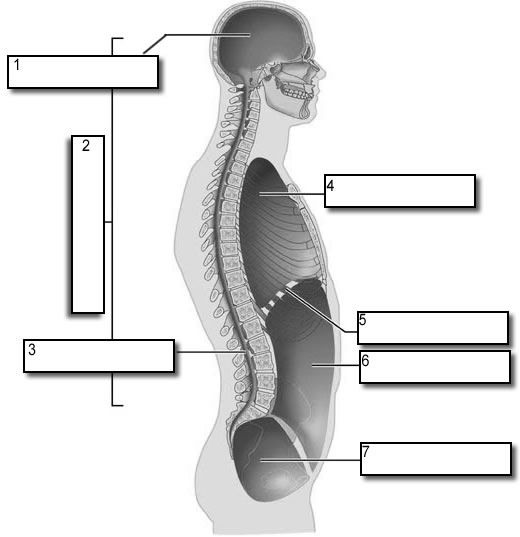
what number is the cranial cavity
1
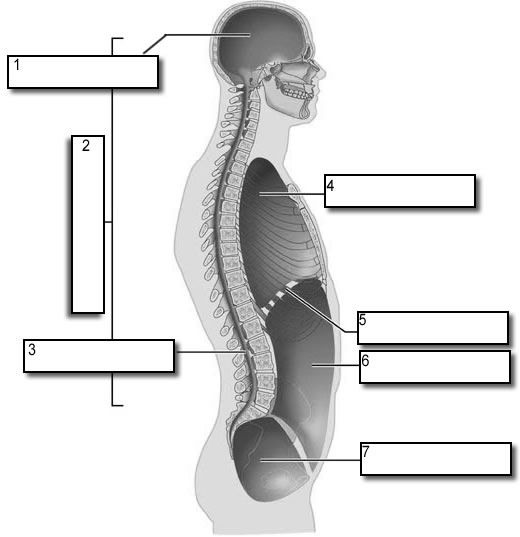
what number is the vertebral cavity
3
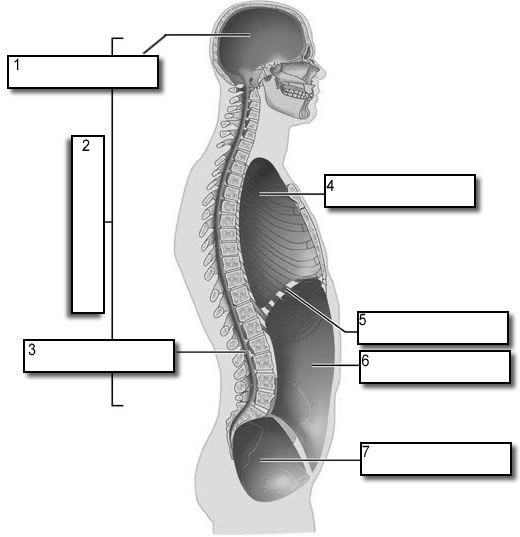
what number is the thoracic cavity
4
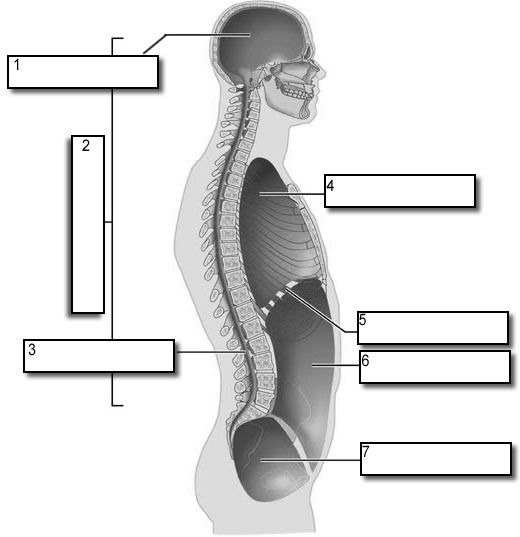
what number is the abdominal cavity
6
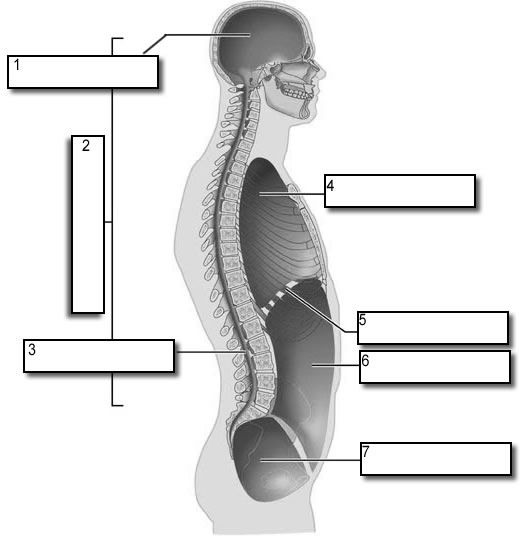
what number is the pelvic cavity
7
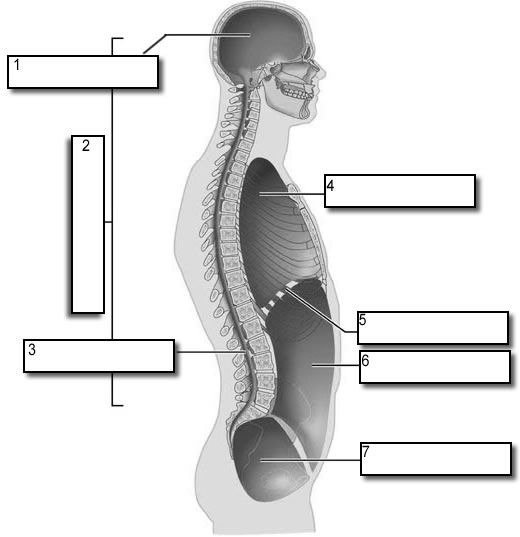
what number is the diaphragm
5
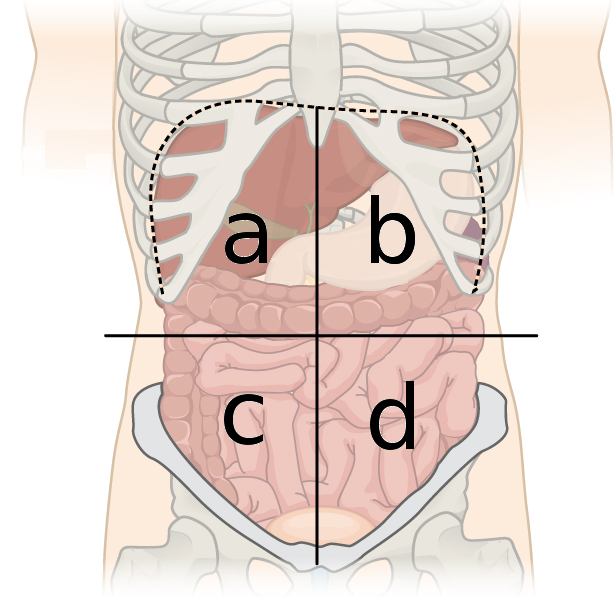
right upper quadrant organs (A)
liver
pancreas
gallbladder
duodenum
transverse colon
right adrenal gland
right kidney
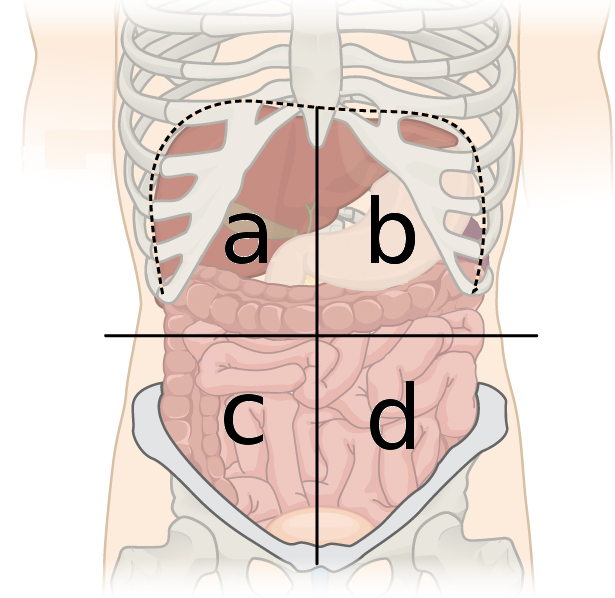
left upper quadrant organs (B)
liver
stomach
spleen
pancreas
transverse colon
left adrenal gland
left kidney
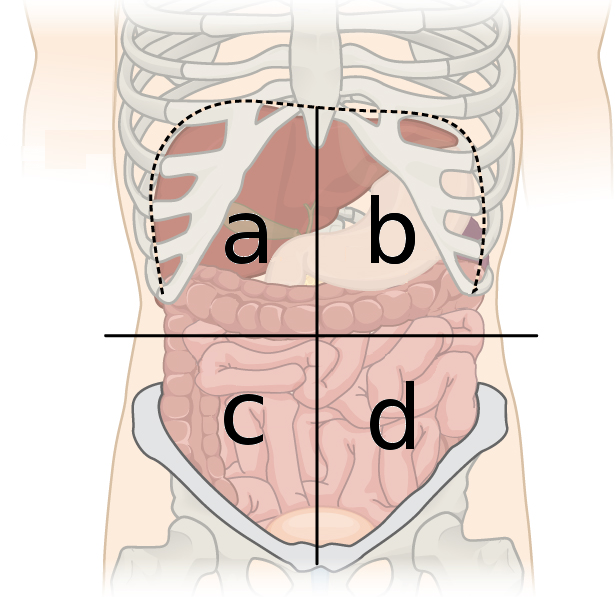
left lower quad organs (D)
small intestine
descending colon
urinary bladder
part of left kidney
left ureter
left ovary and uterine tube
left spermatic cord
signmoid colon
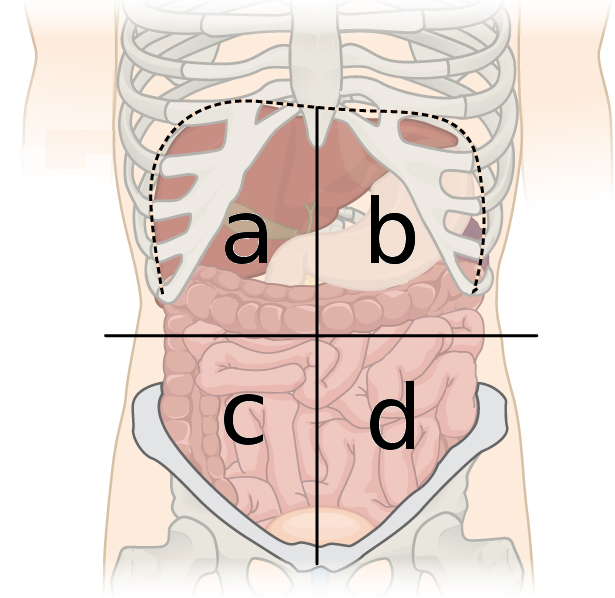
Right lower quad (C)
small intestine
ascending colon
appendix
urinary bladder
part of right kidney
right ureter
right ovary and uterine tube
right spermatic cord
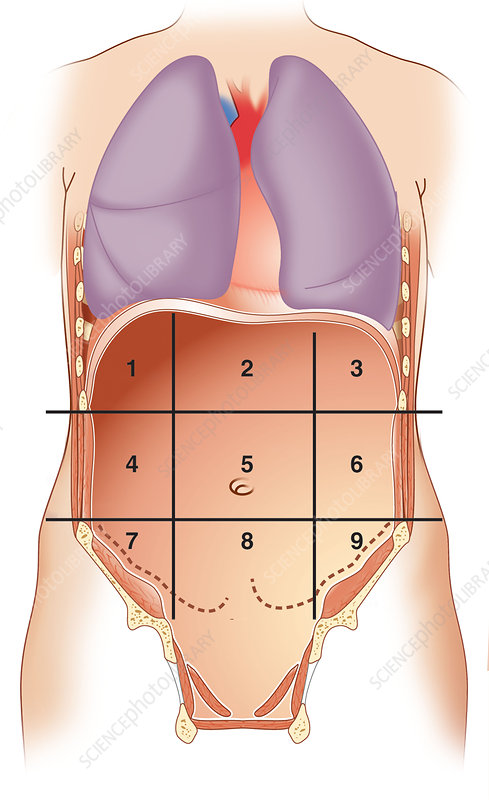
what number is right hypochondriac region
1
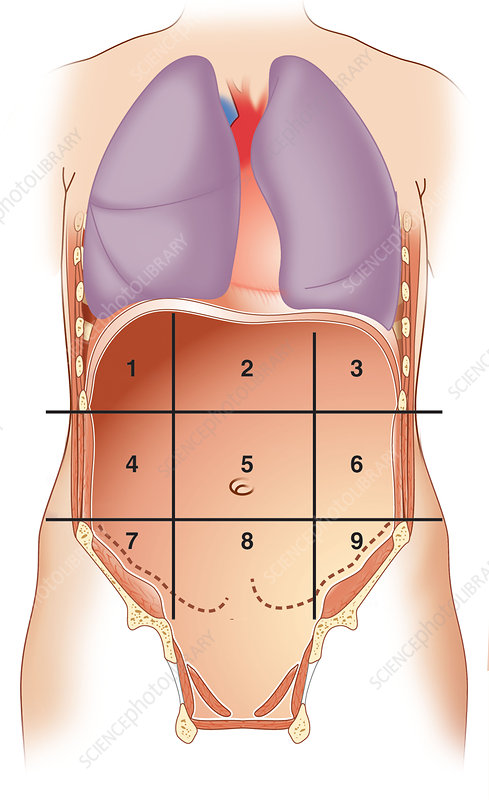
what number is epigastric region
2
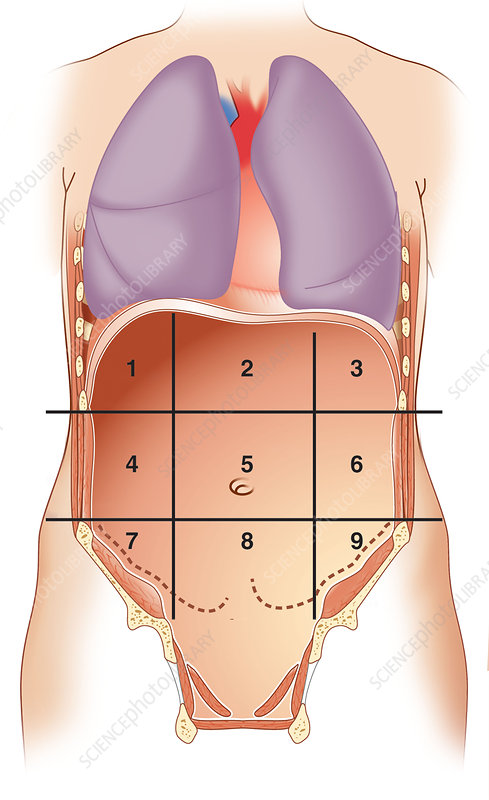
what number is left hypochondriac region
3
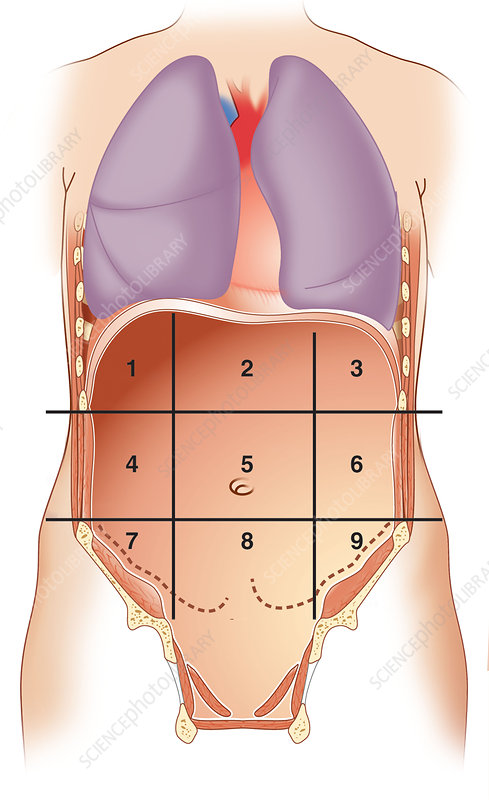
what number is right lumbar region
4
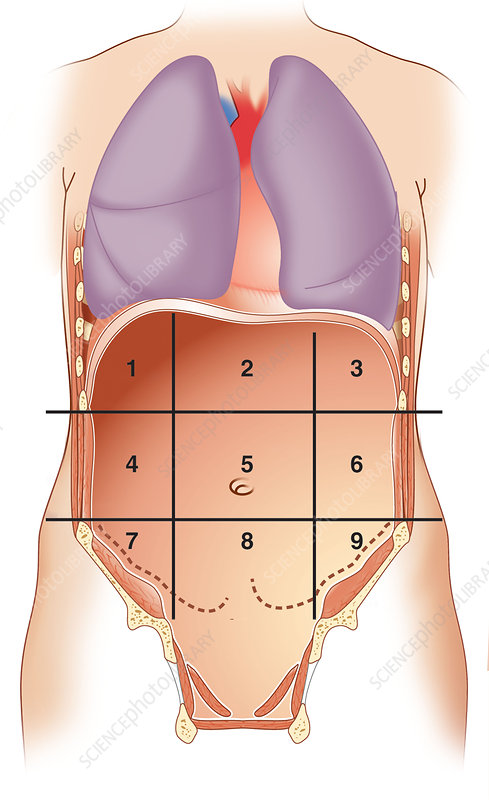
what number is umbilical region
5
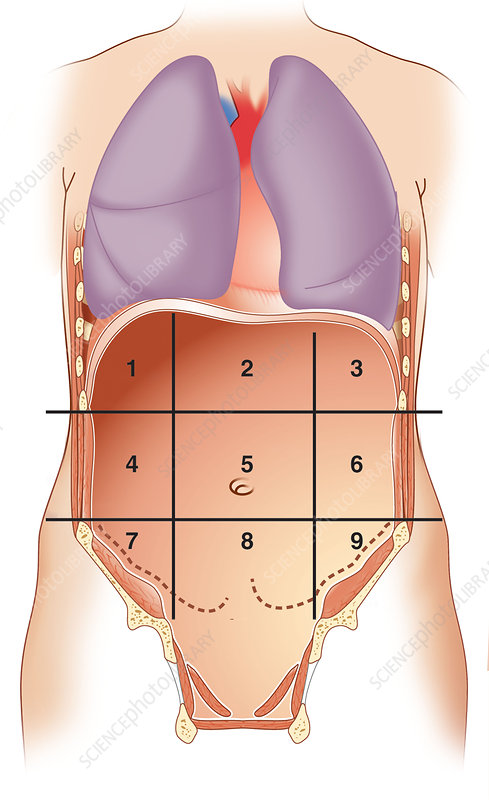
what number is left lumbar region
6
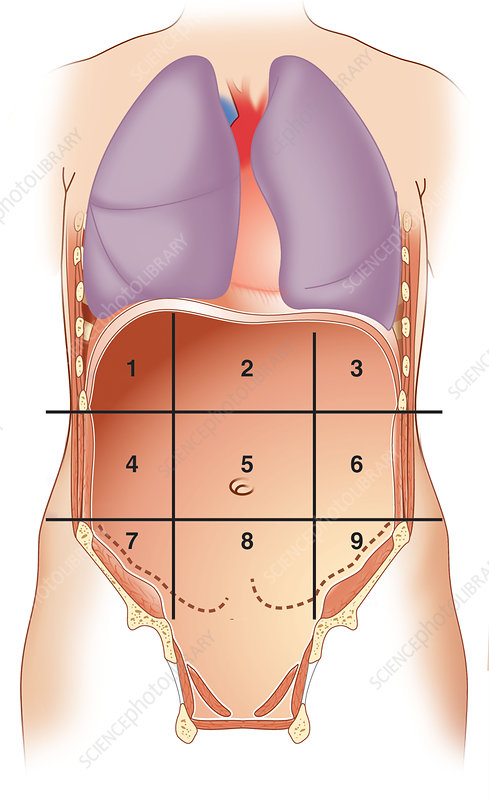
what number is right iliac region
7
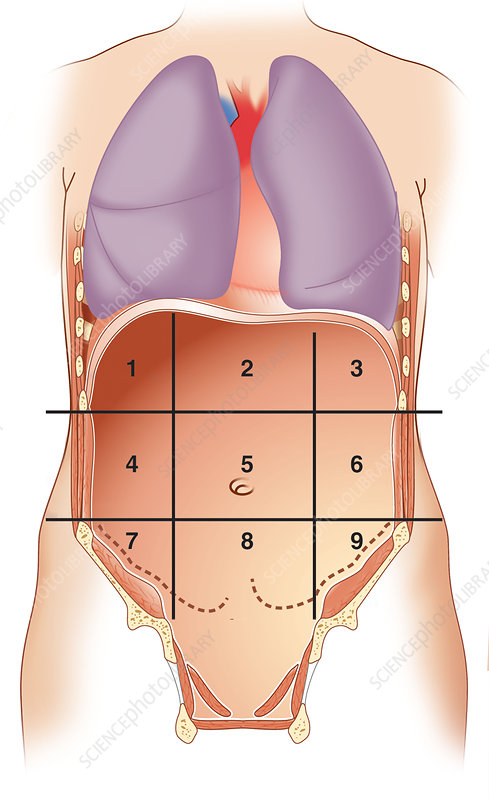
what number is hypogastric region
8
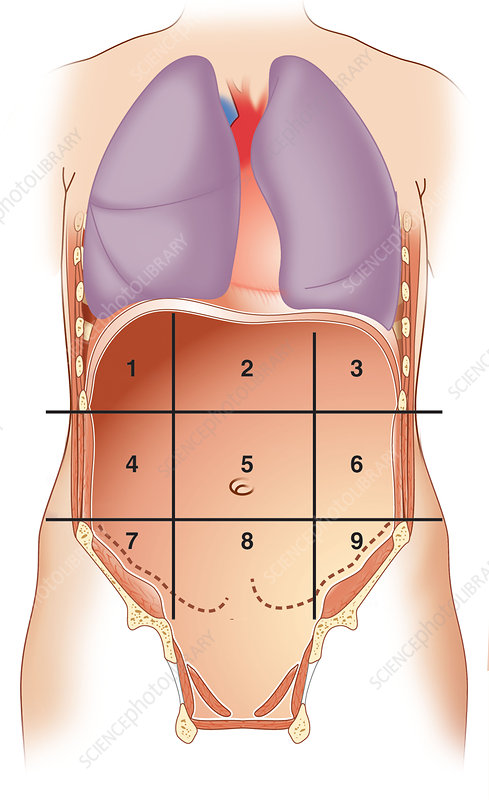
what number is left iliac region
9
histology
the study of tissue structure and function
nervous tissue
internal communication
brain
spinal cord
nerves
muscle tissue
contracts to cause movement
muscles attached to the bone
muscles of the heart
muscle walls of hollow organs
epithelial tissue
sheets of cells that covers a body surface or lines a body cavity
lining of digestive system
glans
skin surface
connective tissue
supports protects bind to other tissues
bones
tendons
fat and other padding tissue

apical surface
–Not attached to surrounding tissue
–Exposed to the external environment or cavity of internal organ
–May possess cilia or microvilli

basal surface
–Attached to the basement membrane
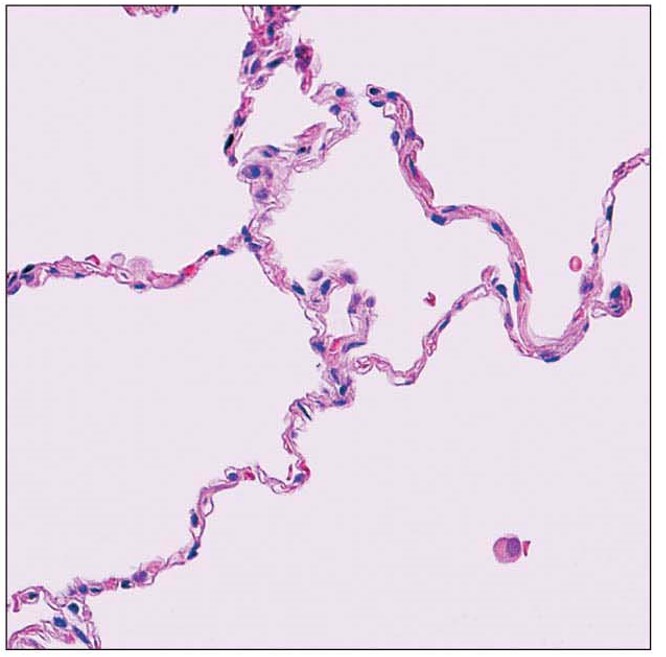
Simple squamous epithelia description
one layer of squamous cells; the thinnest
Simple squamous epithelia key location
alveoli
lining of blood vessels
glomeruli (Kidneys)
serosa of the ventral body cavity
Simple squamous epithelia main functions
supports rapid diffusion
filtration
secretion
Simple squamous epithelia picture
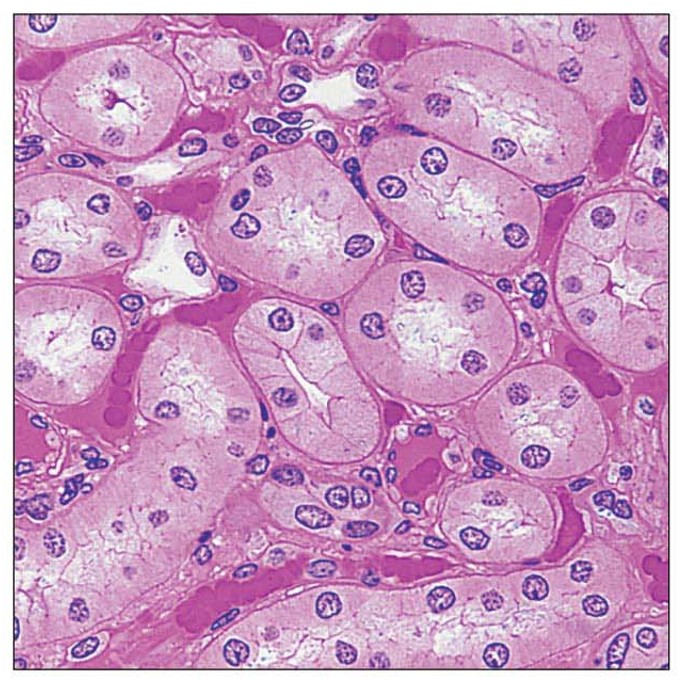
Simple cuboidal epithelia description
one layer of cuboidal cells
Simple cuboidal epithelia key locations
kidney tubes
Simple cuboidal epithelia main functions
absorption and secretion
Simple cuboidal epithelia picture
Simple columnar epithelia description
one layer of columnar cells
may have cilia or microvilli
some goblet cells
Simple columnar epithelia key locations
GI tract (stomach to rectum)
gallbladder
fallopian tubes (cilia)
Simple columnar epithelia main functions
absorption
secretion
propel substances along apical surface
Simple columnar epithelia picture
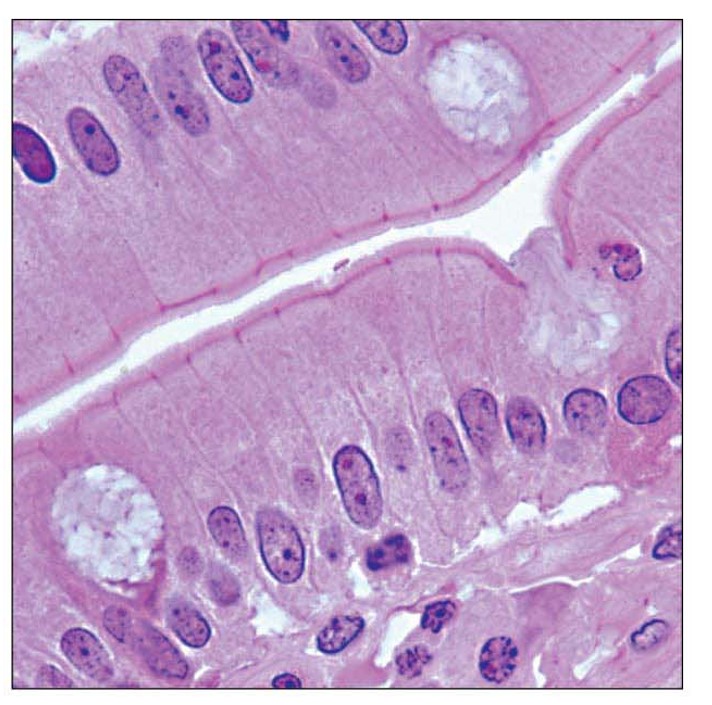
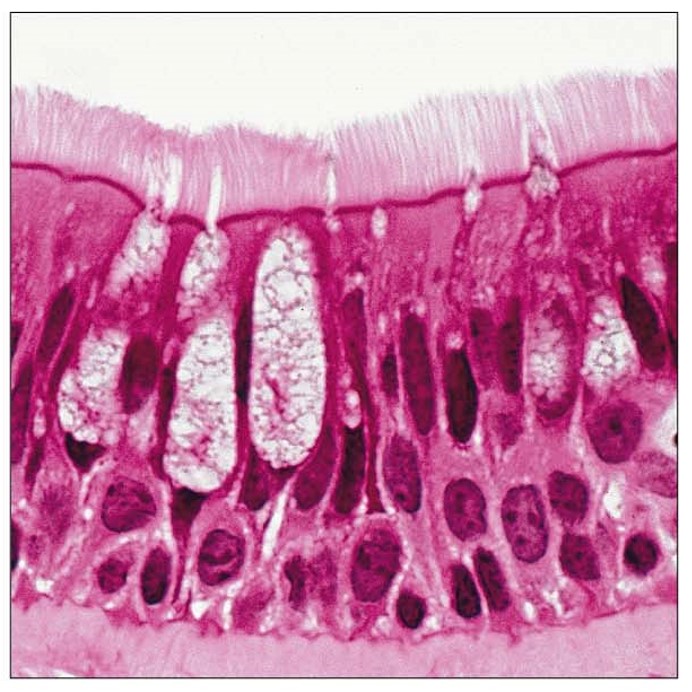
Pseudostratified columnar epithelia description
will appear to have multiple layers; but actually has one
cells have varying heights
can have cilia or goblet cells
Pseudostratified columnar epithelia key locations
nasal cavity
pharynx
larynx
trachea
Pseudostratified columnar epithelia main functions
secretion
propel mucus (cilia) towards throat
Pseudostratified columnar epithelia picture
Stratified squamous epithelia, non-keratinized picture
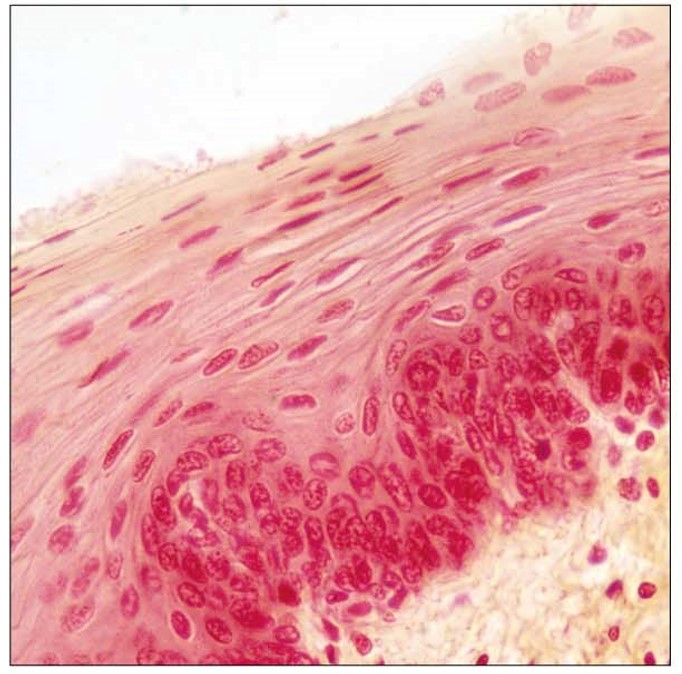
Stratified squamous epithelia, non-keratinized description
many layers of cells
cells on apical surface are squamous shaped
nuclei are found in all layers
Stratified squamous epithelia, non-keratinized key locations
oral cavity
esophagus
anus
vagina
Stratified squamous epithelia, non-keratinized main functions
protecting connective tissue from abrasive forces
Stratified squamous epithelia, keratinized picture
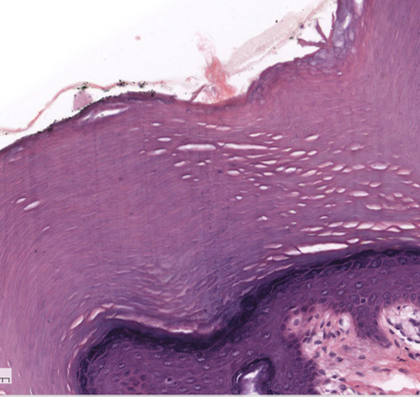
Stratified squamous epithelia, keratinized description
many layers of cells
apical layer has squamous shaped cells
no nuclei in layers near apical surface
Stratified squamous epithelia, keratinized key locations
epidermis of the skin
Stratified squamous epithelia, keratinized main functions
protecting dermis forces abrasive forces
Transitional epithelia picture
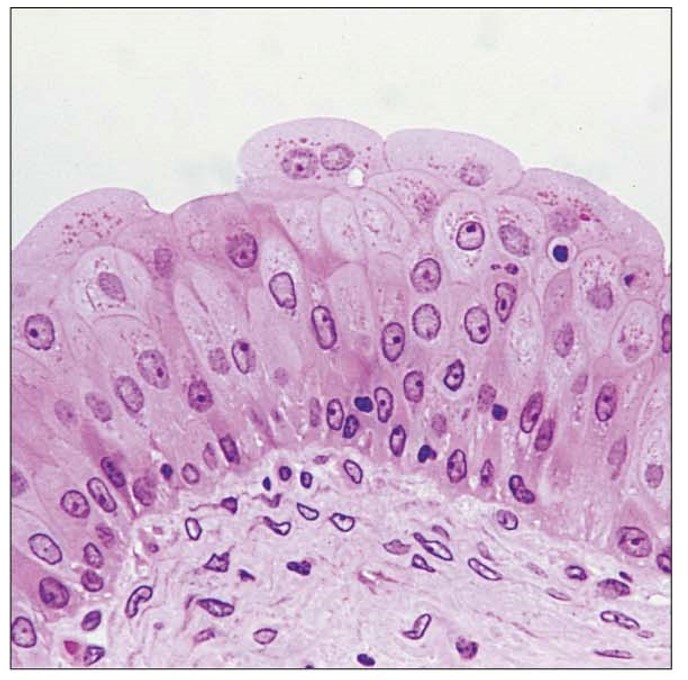
Transitional epithelia description
stratified number of layers depends on the degree of stretch
Transitional epithelia key locations
ureters
urinary bladder
urethra
Transitional epithelia main function
designed to stretch
Nervous Tissue picture
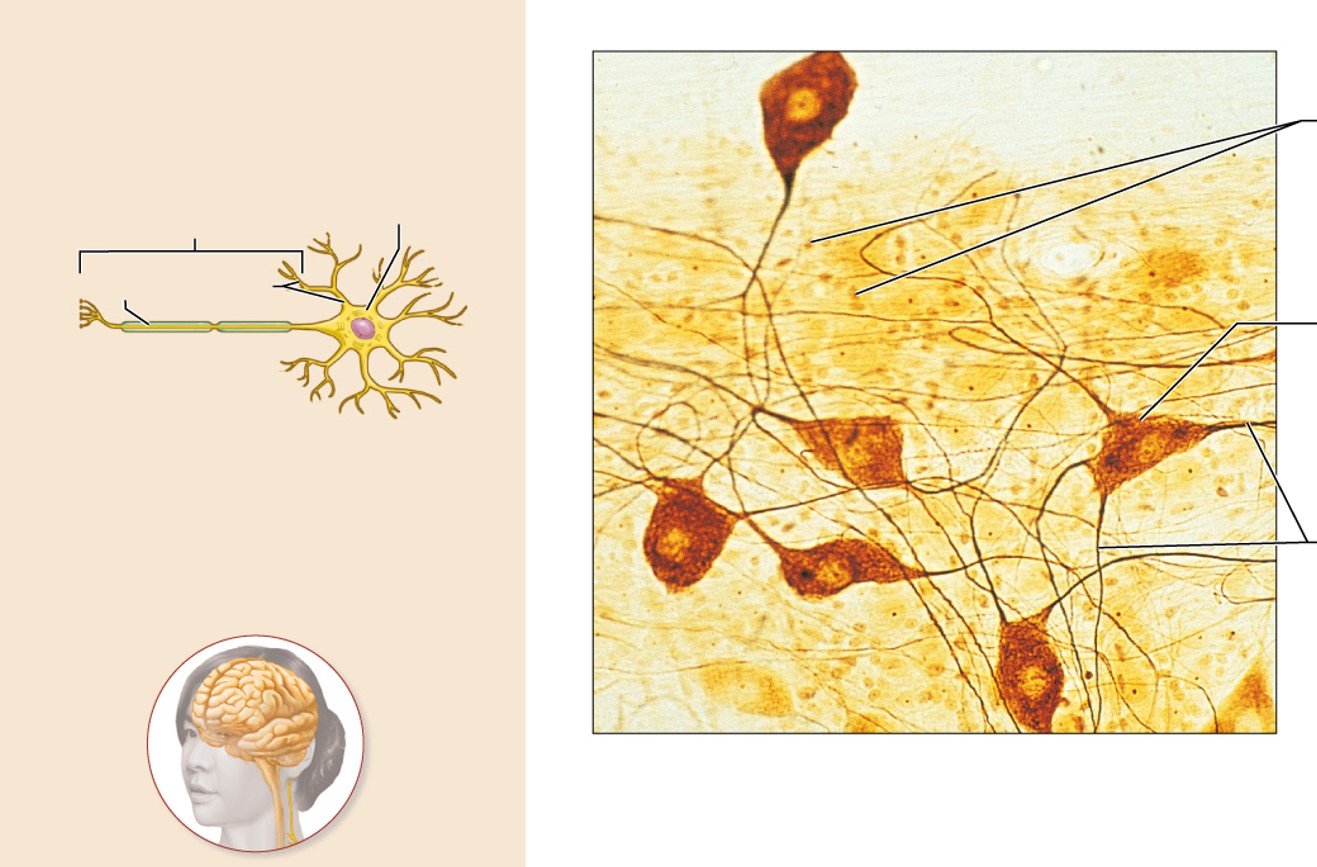
Nervous Tissue description
Neurons are branching cells; cell processes that may be quite long extend from the nucleus-containing cell body; also contributing to nervous tissue are various types of glial cells.
Nervous Tissue function
Neurons transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors (muscles and glands); glial cells support and protect neurons.
Nervous Tissue description location
brain, spinal cord, nerves
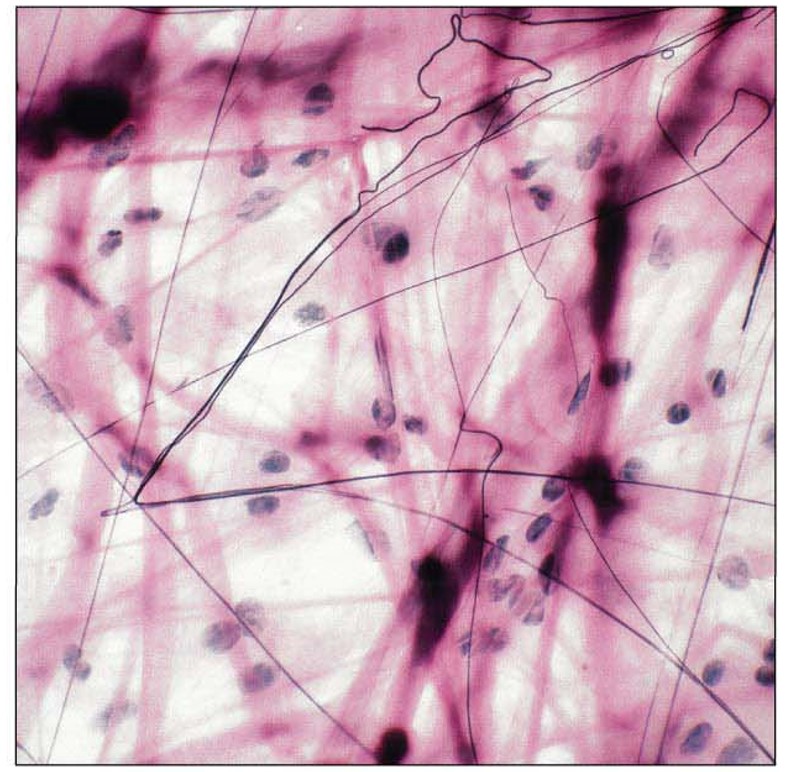
Areolar Connective Tissue structural features
RC- fibroblast
OC- Immune Cells
ECM - Abundant ground substance; all 3 fibers
Areolar Connective Tissue key functions
anchors epithelial tissue
wrap around organs to form a cushion
fight infection
Areolar Connective Tissue main location
deep to epithelial tissue
surrounding organs
Areolar Connective Tissue picture
Adipose Tissue picture
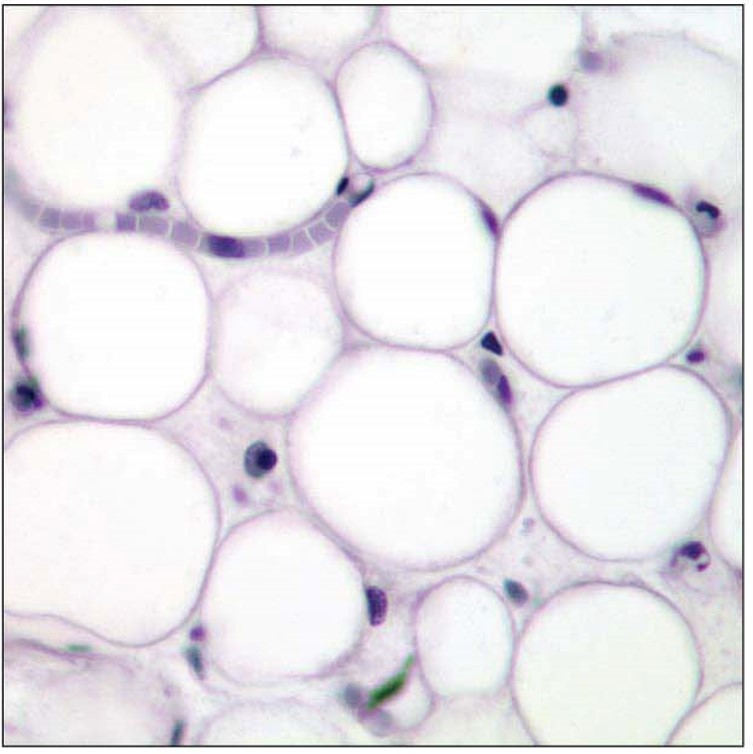
Adipose Tissue structural features
rc- fibroblast
oc- adipose cell (most abundant)
ecm- sparce; same comp as areolar
Adipose Tissue key functions
stores fat
insulates
cushions
Adipose Tissue main locations
subcutaneous tissue
wall of abdominopelvic cavity
eyes, kidneys, breasts
Reticular Connective Tissue picture
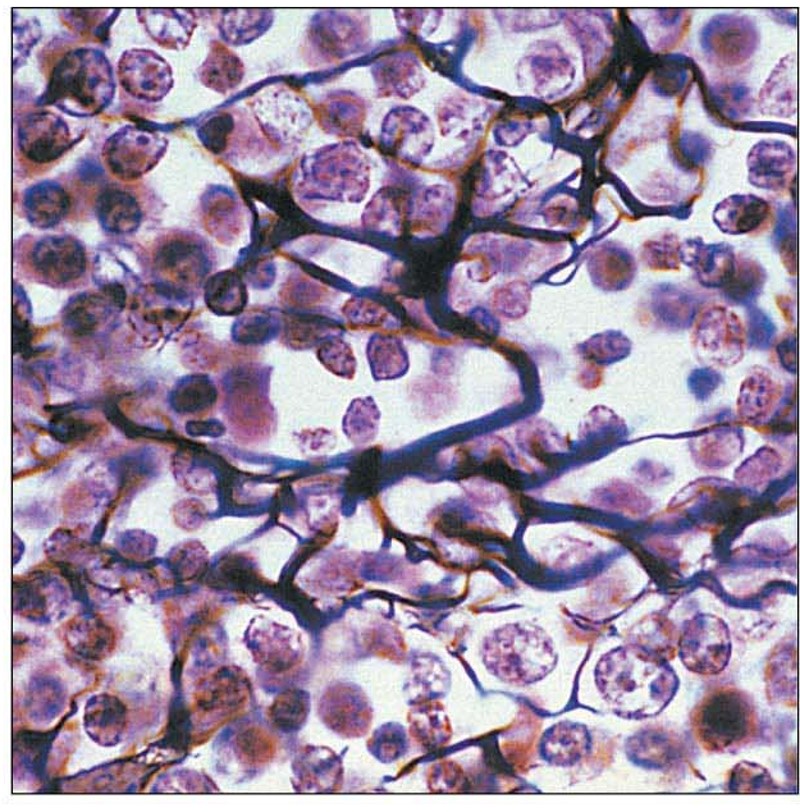
Reticular Connective Tissue structural features
rc- fibroblast
oc- immune cells
ecm- abundant reticular fibers
Reticular Connective Tissue key functions
form soft skeleton of lymphoid organs
support the development of blood; immune cells
Reticular Connective Tissue main locations
bone marrow
spleen
lymph nodes
Dense Regular Connective Tissue picture
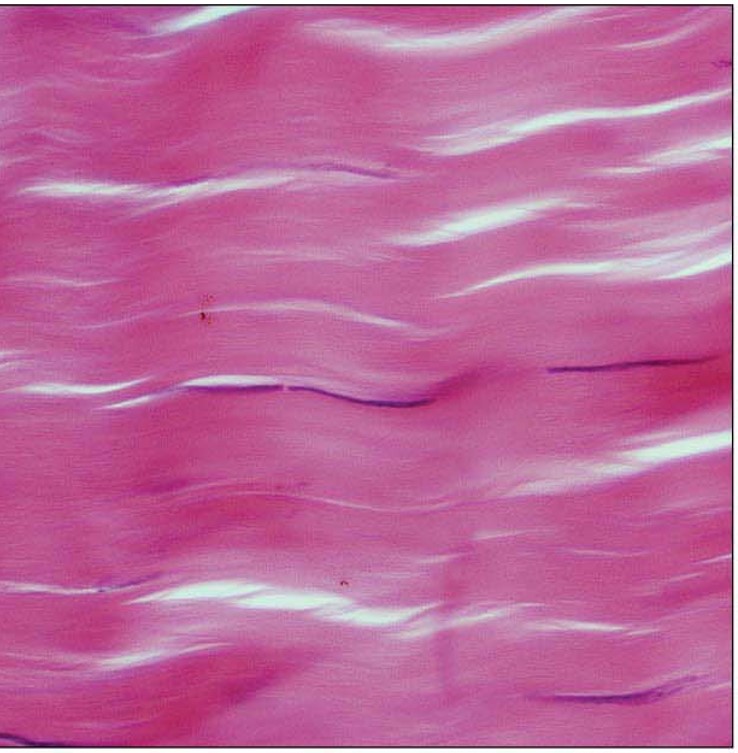
Dense Regular Connective Tissue structural features
rc- fibroblast
ecm- filled with collagen fibers arranged in parallel
Dense Regular Connective Tissue key functions
forms attachments
→ bone to bone
→ muscle to bone
Dense Regular Connective Tissue main locations
bone to bone → ligaments
muscle to bone → tendons
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue picture
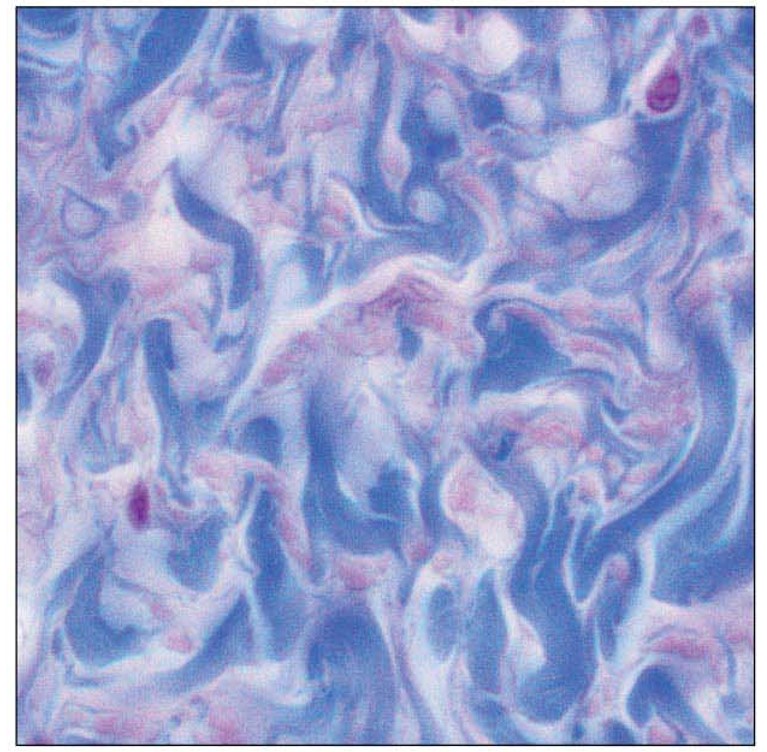
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue structural features
rc- fibroblast
ecm- abundant collagen fibers; not in parallel; some elastic fibers
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue key functions
provide great tensile strength with some flexibility
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue main locations
dermis
joint capsules
Elastic Connective Tissue picture
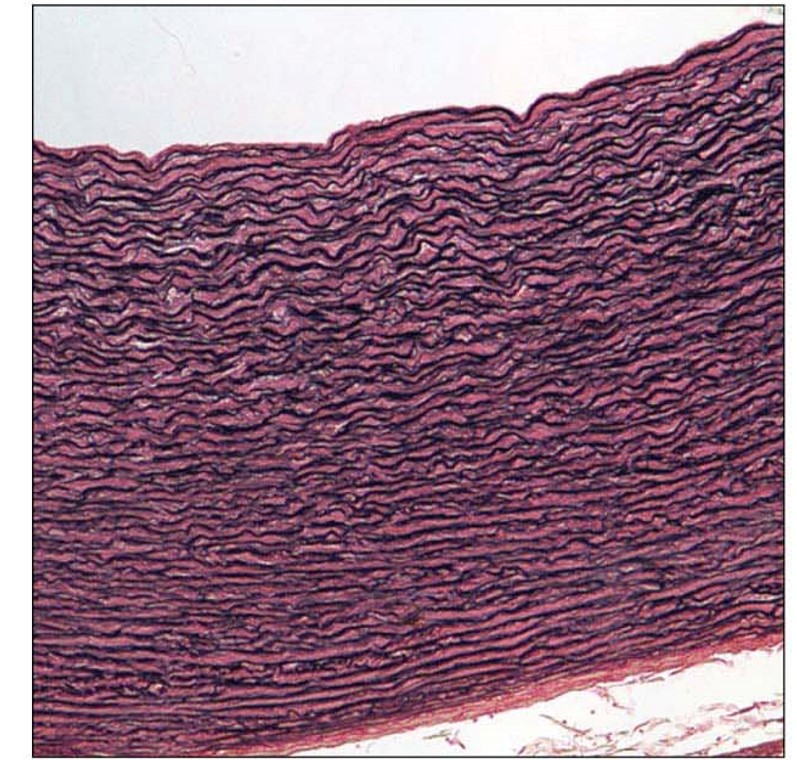
Elastic Connective Tissue structural features
rc- fibroblast
ecm- abundant elastic fibers in parallel
Elastic Connective Tissue key functions
help maintain blood
helps expire air
Elastic Connective Tissue main locations
walls of large arteries (aorta)
walls of lungs
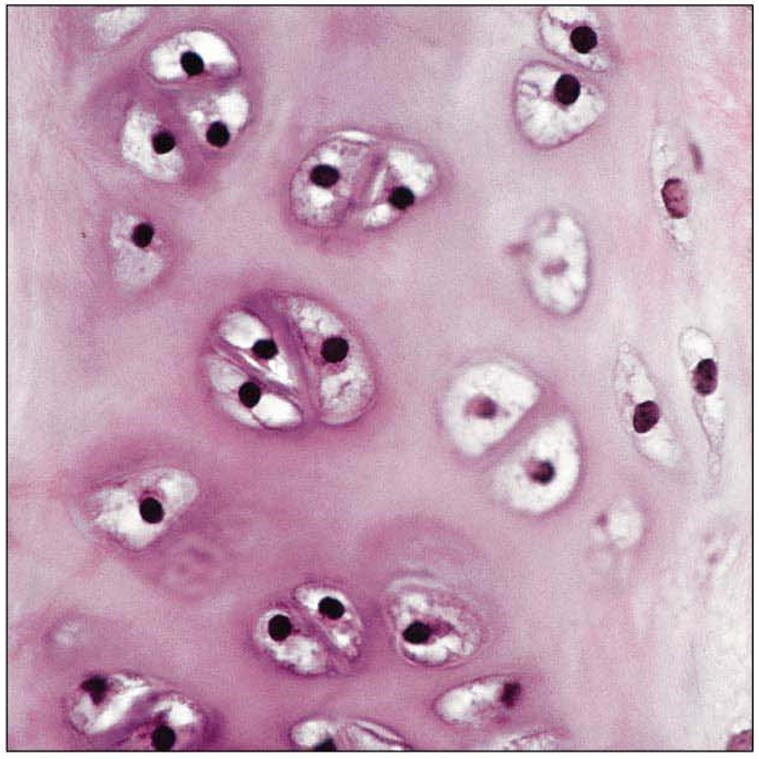
Hyaline Cartilage picture