Week 9i Microbio Exam 3
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
sepsis
refers to bacterial contamination
asepsis
is the absence of significant contamination
-aseptic surgery echniques
aseptic surgery techniques
prevent the microbial contamination of wounds
sterilization
removing and destroying all microbial life
commercial sterilization
killing Clostridium botulinum endospores in canned goods
disinfection
destroying harmful microorganisms on inanimate surfaces or environments
antisepsis
destroying harmful microorganisms from living tissue
degerming
the mechanical removal of microbes from a limited area
sanitization
lowering microbial counts on eating utensils to safe levels
biocide (germicide)
treatments that kill microbes
bacteriostasis
inhibiting, NOT KILLIN, microbes
selection of disinfectant
1) must be fast-acting in the presence of organic materials
2) must be effective against all microorganisms without destroying tissue or acting as a toxin if ingested
3)easily penetrate the material to be disinfected without discoloration or damage
4) easy to prepare and stabile in the environment where it is to be used
5) inexpensive and easy to use
6) not have an unpleasant odor
is there a perfect disinfectant?
there is no perfect disinfectant that meets all criteria
patterns of microbial death are caused by
microbial control agents
example of microbial death
exponential death rate
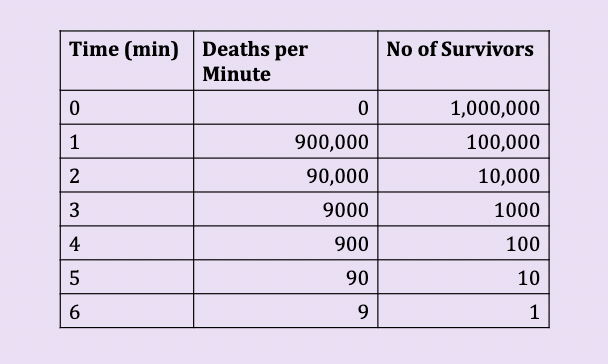
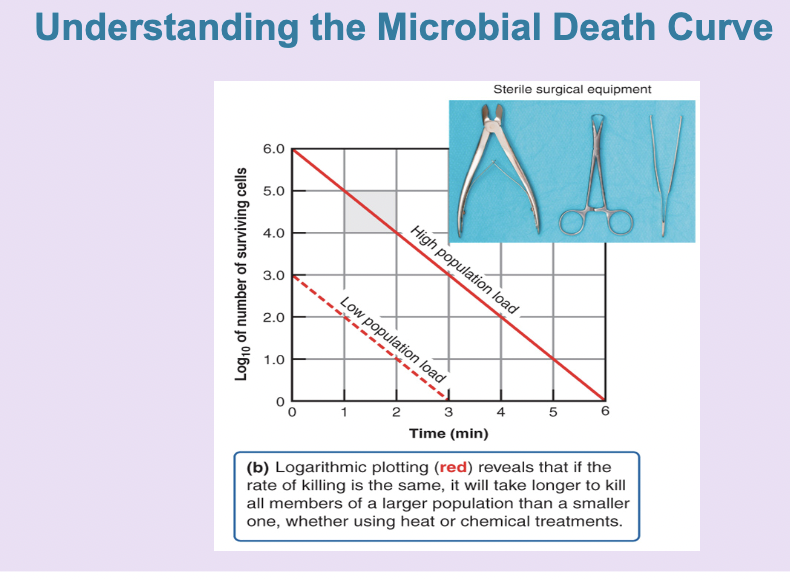
microbial death curve
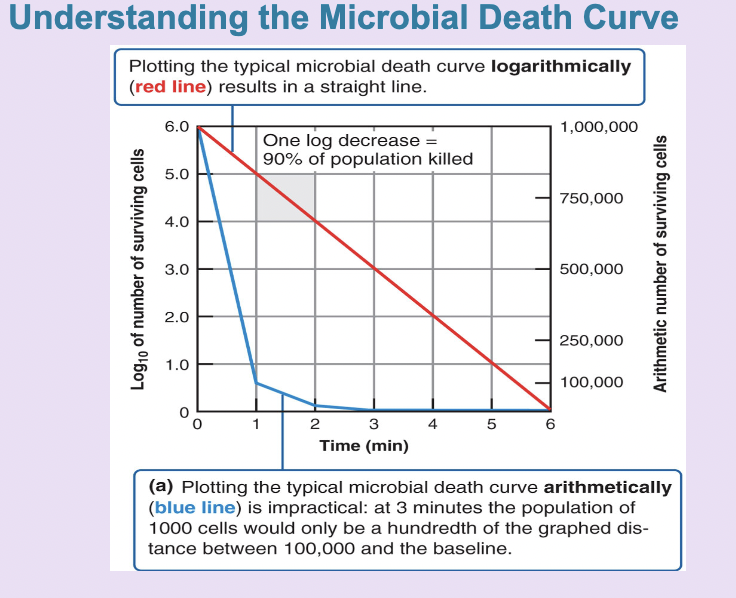
effectiveness of treatment for the rate of microbial death depends on
-number of microbes
-environment (organic matter, temperature, biofilms)
-time of exposure
-microbial characteristics (endospores, cell wall)
action of microbial control agents
-damage to plasma membrane (causes leakage of cellular contents & interferes with cell growth)
-damage to proteins (enzymes)
-damage to nucleic acids
damage to plasma membrane action of microbial control agents
causes leakage of cellular contents & interferes with cell growth
heat
denatures enzymes
-TDP
-TDT
-DRT
thermal death point TDP
lowest temperature at which all cells in a liquid culture are killed in 10 min
thermal death time TDT
minimal time for all bacteria in a liquid culture to be killed at a particular time
decimal reduction time (DRT)
minutes to kill 90% of a specific population of bacteria at given temperature
moist heat sterilozation
-moist heat coagulates/denatures proteins
-boiling
-free-flowing steam
autoclave
steam under pressure
-121 degrees C at 15 psi for 15 min
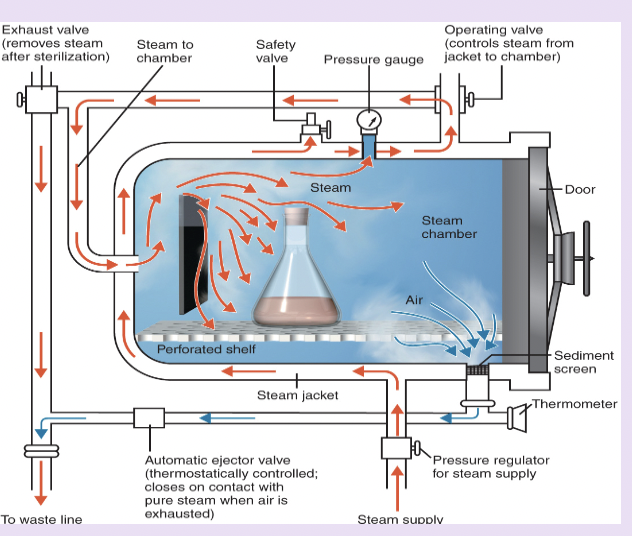
autoclave (functions)
-kills all organisms (except prions) and endospores
-steam must contact the item’s surface
-preferred method for sterilization in health care environments
moist heat autoclave
-steam to enter the steam chamber and expel air—> chamber pressure and temperature build up to the proper levels
-after the appropriate period of time, another valve opens to allow steak to escape the chamber
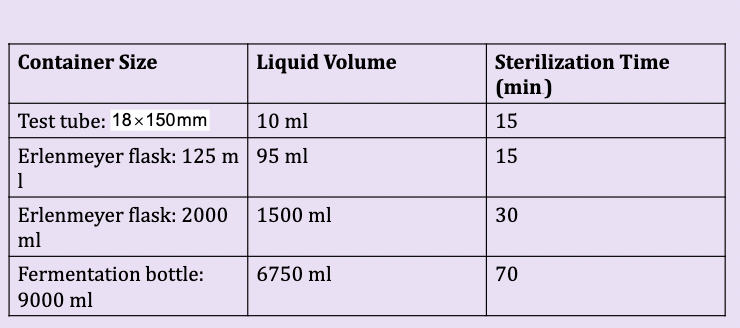
larger containers require (moist heat sterilization)
longer sterilization times
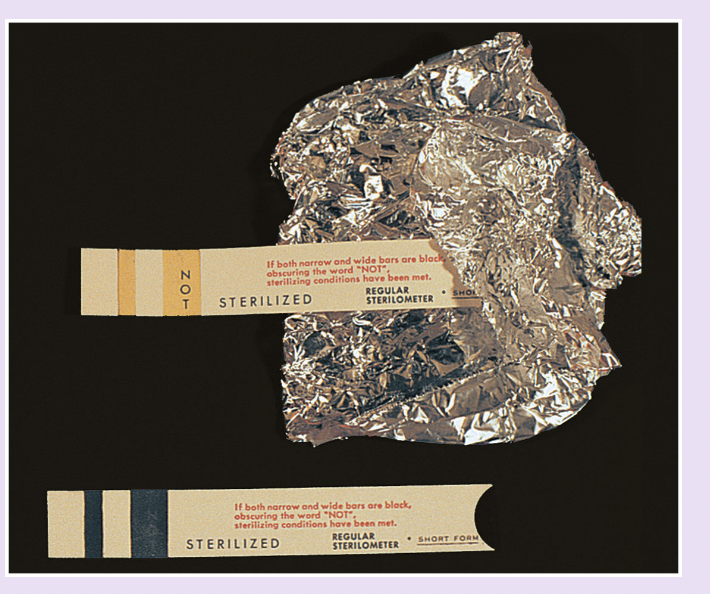
what is used to indicate sterility
test strips
the effect of container size on autoclave sterilization times for liquid solutions
*Sterilization times in the autoclave include the time for the contents of the containers to reach
sterilization temperatures. For smaller containers, this is only 5 minutes or less, but for a 9000-
milliliter bottle it might be as much as 70 minutes. Liquids in an autoclave boil vigorously, so
their containers usually are filled only up to 75% of capacity.
examples of sterilization indicators

heat
-pasteurization
-High-temperature short-time (HTST)
-Thermoduric
pasteurization
reduces spoilage organisms and pathogens in milk and juices
High-temperature short-time (HTST)
thermoduric
organsisms survive, (heat) but are unlikely to cause disease or to spoil refrigerated milk
ultra-high-temperature (UHT) treatments
-will sterilize milk, creamer and juice which can be stored without refrigeration
-rapidly heated to 140 degrees C for 4 seconds, then followed by rapid cooling
ultra-high-temperature (UHT) treatments process
rapidly heated to 140 degrees C for 4 seconds, then followed by rapid cooling
dry heat sterilization
kills oxidation
dry heat sterilization kills oxidation by
-flaming
-incineration
-hot-air sterilization (Oven 170 degrees C, 2 hours)
filtration
-passage of substance through a screen like material
-used for heat-sensitive materials
-high-efficiency particulate (HEPA) filters —> remove microbes > 0.3 um in diameter
-Membrane filters—> remove microbes > 0.22 um [pore sizes of as small as > 0.05um are available which can filter out viruses and large proteins]
high-efficiency particulate (HEPA) filters
remove microbes > 0.3 um in diameter
Membrane filters
remove microbes > 0.22 um [pore sizes of as small as > 0.05um are available which can filter out viruses and large proteins]
pore sizes of as small as > 0.05um
are available which can filter out viruses and large proteins
physical methods of microbial control
-low temperature
-high pressure
-desiccation
-osmotic pressure
low temperature has a (physical methods of microbial control)
bacteriostatic effect
low temperature physical methods of microbial control
-refrigeration
-deep-freezing
-lyophilization (freeze drying)
high pressure physical methods of microbial control
denatures proteins
alters carbohydrate structure
desiccation physical methods of microbial control
absence of water prevents metabolism
osmotic pressure physical methods of microbial control
uses high concentrations of salts and sugars to create hypertonic enviornment; causes plamolysis
ionizing radiation
X-rays, gamma rays, electron beams
ionizing radiation
-ionizes water to create reactive hydroxyl radicals
-damages DNA by causing lethal mutations
-Gamma rays: penetrate deeply but require hours to sterilize
-high-energy electron beams: less penetration, but fast (seconds)
-used by food industry (spices, certain meats, vegetables)
-sterilization of pharmaceuticals, disposable dental and medical supplies, mail
gamma rays ionizing radiation
penetrate deeply but require hours to sterilize
high-energy electron beams ionizing radiation
less penetration, but fast (seconds)
food industry uses ionizing radiation
spices, certain meats, vegtables
radiaiton
-ionizing radiation
-non-ionizing radiation
non ionizing radiation classification
ultraviolet, 260 nm
non ionizing radiation
-damages DNA by creating thyamine dimers
-UVC “germicidal” lamps used in hospital rooms, nurseries, operating rooms, cafeterias
-effective, but does not penetrate; good for surfaces
-must avoid contact with eyes and skin
how does nonionizing radiation damage DNA
by creating thymine dimers
where are UVC lamps
“germicidal” lamps are used in hospital rooms, nurseries, operating, cafeterias
visible blue light classification non ionizing radiation
470 nm
visible blue light non ionizing radiation
kills a wide range of bacteria due to the formation of a singlet oxygen
microwaves non ionizing radiation
kill by heat; not especiall antimicrobial
sonication
-high frequency ultrasoundwaves to disrupt cell structures
-the disruption is achieved due to the rapid changes in pressure within the intracellular liquid
how is disruption achieved in sonication
due to the rapid changes in pressure within the intracellular liquid