Chemical Safety and Nuclear Chemistry
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
HAZARD
defined as any source of potential harm, damage or adverse effect on someone or something.
RISK
the probability that a person or a thing is harmed or damaged when exposed to a hazard.
Physical Hazards
are factors within the environment that may cause harm on the body even without touching it and they are generally discernible and perceptible.
Physical Hazards
slippery floors, poor lighting and ventilation, and excessive noise
Chemical Hazards
refer to the chemical substances that may cause harm upon exposure to them
Chemical Hazards
gases, fumes and liquids.
Safety Hazards
are working conditions that can cause injury, illness or death.
Safety Hazards
slippery floors, unguarded moving equipment parts and disarranged chords and wires.
Ergonomic Hazards
are physical factors in the environment that may cause problems on the musculoskeletal system.
Ergonomic Hazards
poor workstation design, repetitive movements and poor workflow.
Psychological Hazards
are the aspects of the working environment that may affect the mental health of the individuals
Psychological Hazards
workload, stress and discrimination.
Biological Hazards
are biological substances that may threat the health of living organisms exposed to it.
Biological Hazards
viruses, bacteria and animals.
hazardous substance/physical or health
According to Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) of the United States of America, a __________ is any chemical that presents _____ hazard.
physical hazard
Under OSHA’s Health Communication Standard (HCS), ________ means a chemical that is a combustible liquid, a compressed gas, explosive, flammable, an organic peroxide, an oxidizer, pyrophoric, unstable (reactive) or water-reactive.
fire hazard, reactive hazard and explosion hazard.
Physical hazards are classified as
Health hazard
means a chemical that may cause acute or chronic health effects to exposed personnel. They are classified as either systematic effect or target organ effect.
Republic Act 6969
a substance is hazardous when it present either a short-term acute hazard or long-term chronic toxicity.
Toxic Substances and Hazardous and Nuclear Wastes Control Act of 1990
Republic Act 6969
Acute hazards
are those that have obvious and immediate impact while
chronic hazards
are those that have more hidden, cumulative and long-term impact.
Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals
GHS stands for
United Nations
It is an internationally agreed-upon system created by the_____that requires manufacturers, importers and downstream users and distributors of chemical substances and mixtures.
unifying the communication/replacing the specific regulations
The establishment of GHS had an objective of _________________ on hazardous products and of__________ in countries around the world.
oxidizers

flammable, self-heating

explosive

corrosive to metals

gas under pressure

acute toxicity

skin and eye irritant

target organ toxicity

corrosive to skin and eyes
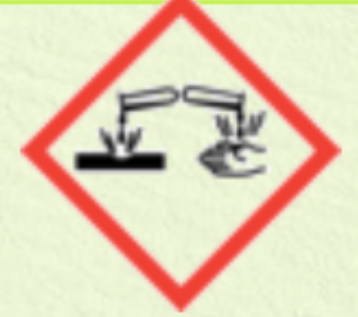
aquatic toxicity

Flash Point
the minimum temperature at which a liquid gives off vapor within a test vessel in sufficient concentration to form an ignitable mixture with the air near the surface of the liquid.
National Fire Protection Association
NFPA stands for
comprehensive information/chemical substance being handled
A GHS Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is a document that provides __________ on the __________
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
are garments and devices that serves as a barrier between the user and the hazard being exposed to.
Nuclear reactions
are reactions that involve the changes of atoms from one element, to atoms of another element
spontaneous decay or bombardment
Nuclear reactions could be achieved by either _________ of particle.
Nuclear decay or radioactivity
is a nuclear reaction in which an unstable isotope disintegrates into a more stable form.
Nuclear radiation
is the transmission of energy from a nuclear reaction, through space or even some sort of material.
Half-life
is the time at which the amount of the reactant becomes one-half of the initial amount of the reactant
Activity (R) of the sample
is defined as the rate in which a sample decays. Becquerel (Bq) is the SI unit of activity.
Coulombic repulsion and short-range attraction
Nuclear Stability Determined by the ________________
Karlsruhe Nuclide Chart
This chart of nuclides helps you predict the type of radioactive decay and stable nuclides.
valley of stability
Black dots represent the
Nuclear Binding Energy (Eb)
the smallest amount of energy required to break down a nucleus of the atom.
Nuclear binding energy per nucleon (BEN)
is the binding energy divided by the number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) of an isotope.
Nuclear transmutation
is defined as the transformation of one nuclide into another, via bombardment of particles.
Nuclear Fission
occurs when a nuclide, usually large is split into smaller nuclides and particles via decay or bombardment
Spontaneous fission
happens when nuclides decay via fission naturally
Induced fission
occurs in nuclear reaction that require a high energy to conduct usually via bombardment of particles or electromagnetic radiation.
Nuclear chain reaction
happens when the initially produced neutrons or other particles trigger new set of fission reactions.
Nuclear Fusion
happens when light nuclides are forced together, causing them to combine into one or more nuclides.
Nucleosynthesis
is the universal process of forming new atomic nuclei from pre-existing protons, neutrons, and lighter nuclei. This typically occurs in the stars of the Universe.
The CNO-I cycle or Bethe-Weizsacker cycle
is one of the important synthesis cycles that produces Helium in stars
Radiation
is a mode of energy transfer that is contactless.
Particle Radiation
happens when a particle is given off
Electromagnetic Radiation
occurs when only pure energy, without any mass whatsoever is emitted
Nuclear Radiation
the origin of radiation is the atomic nucleus
Ionizing radiation
has enough energy for bond breaking or electron removing.
Nuclear Reactors
are facilities that utilize controlled nuclear reaction as a source of energy, for example the induced fission of Uranium-235.
Nuclear meltdown
occurs when too many neutrons make the chain reaction uncontrollable.
Control rods
are made up of boron or cadmium metal. They absorb neutrons to regulate the neutron flux.
Moderators
lessen the energy of fast neutrons. Examples are water or deuterated water which function as coolants
International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale (INES)
Nuclear accidents are categorized using the
Positron Emission Topography (PET) Scans
are used for imaging physiological aspect of the body. It is primarily used in clinical diagnosis of certain diseases, especially in determining benign or malign tumors.
Radiation Therapy
involves the use of high doses of radiation to kill cancer cells and lessen the size of tumors.
Food irradiation
ionizing radiation is applied in food to extend its shelf-life and improve the food safety by eradicating the insects and microorganism that grow in the food itself.
Radioactive Dating
employs comparing abundance ratio of a radioactive isotope to estimate the age of a material. The most common is the use of Carbon-14 as basis in estimating the age of materials