Cell Respiration Diagram | Quizlet
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
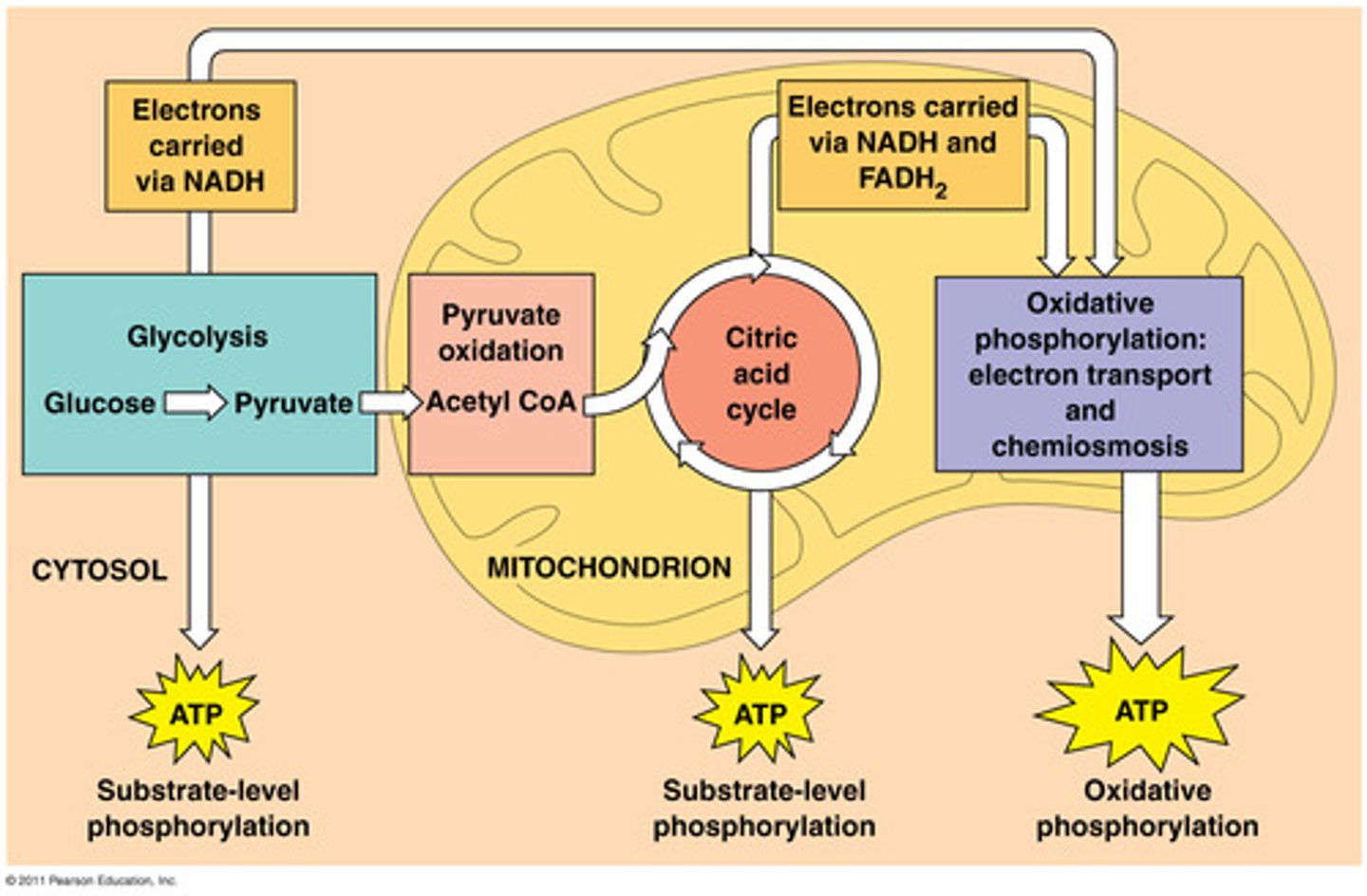
Aerobic Respiration
Requires oxygen for cellular respiration. Glucose (C6H12O6) + Oxygen 6(O2) → Carbon-dioxide 6(CO2) + Water 6 (H2O) + Energy (ATP), makes about 36 -38 ATP ( more than anaerobic)
Anaerobic Respiration
Doesn't require oxygen, makes 2 ATP. Goes through glycolysis and regenerates NAD+ to keep glycolysis going.
TERM
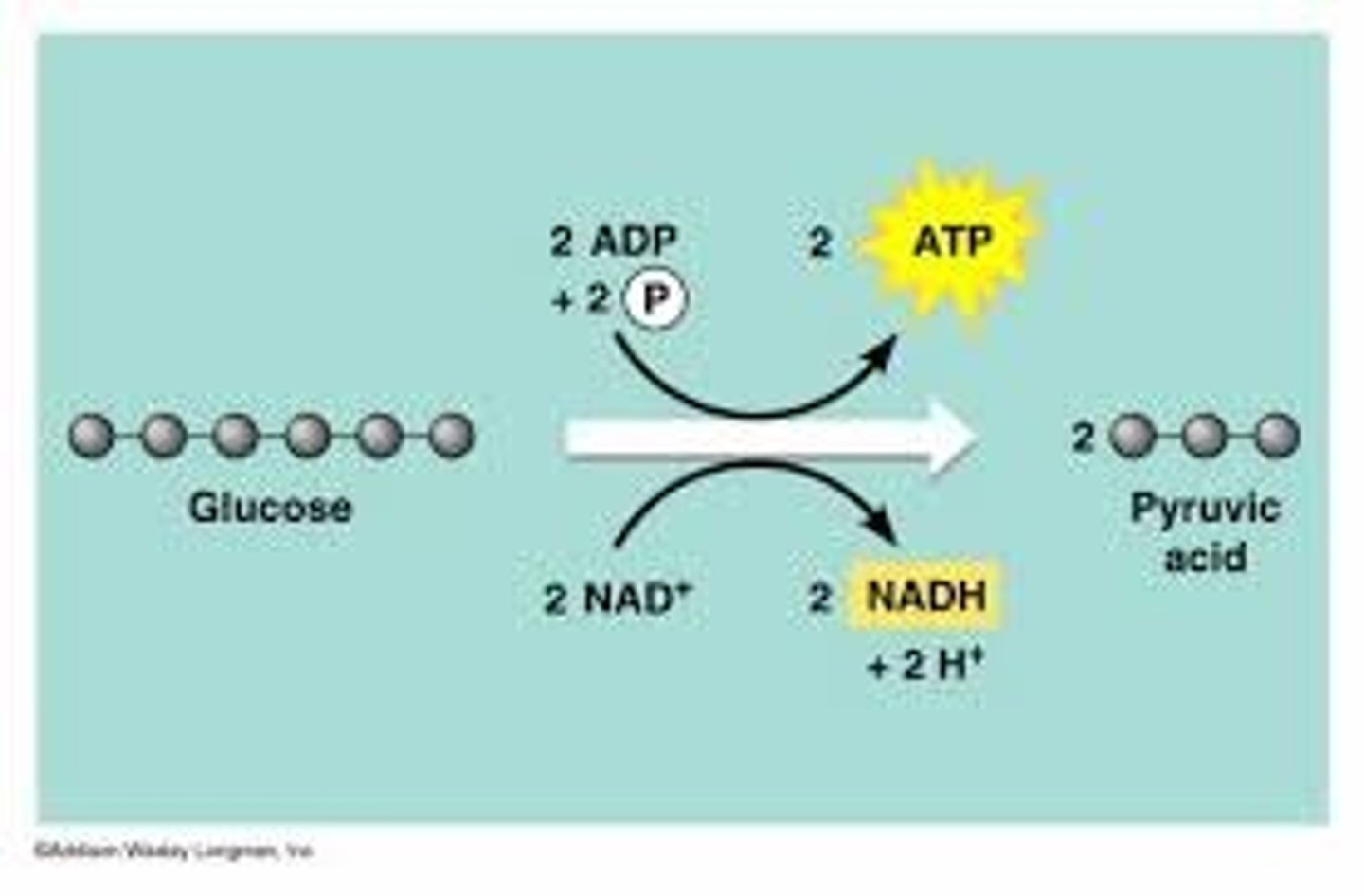
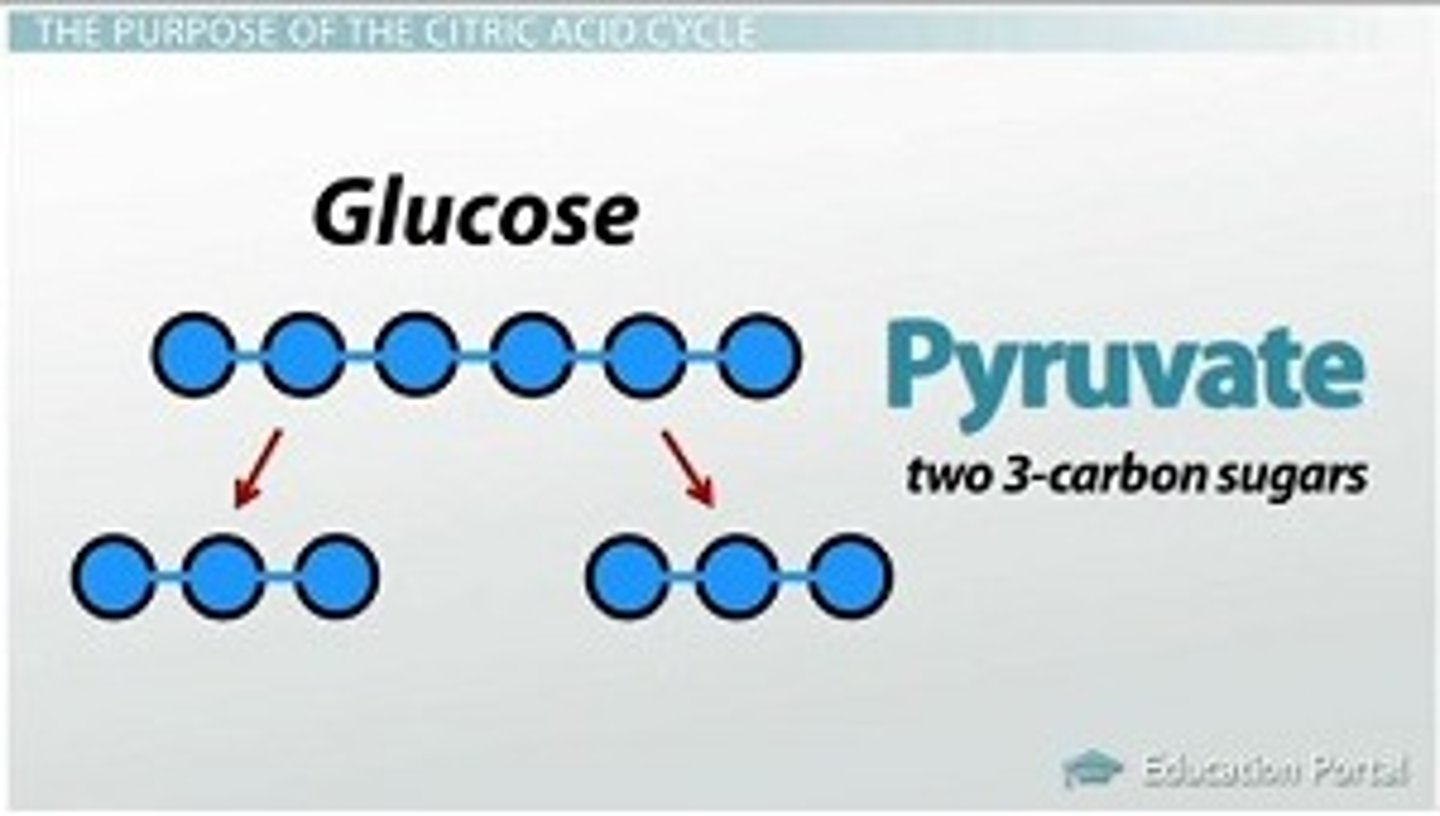
Glycolysis
DEFINITION
1st process of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, occurs in the cytoplasm
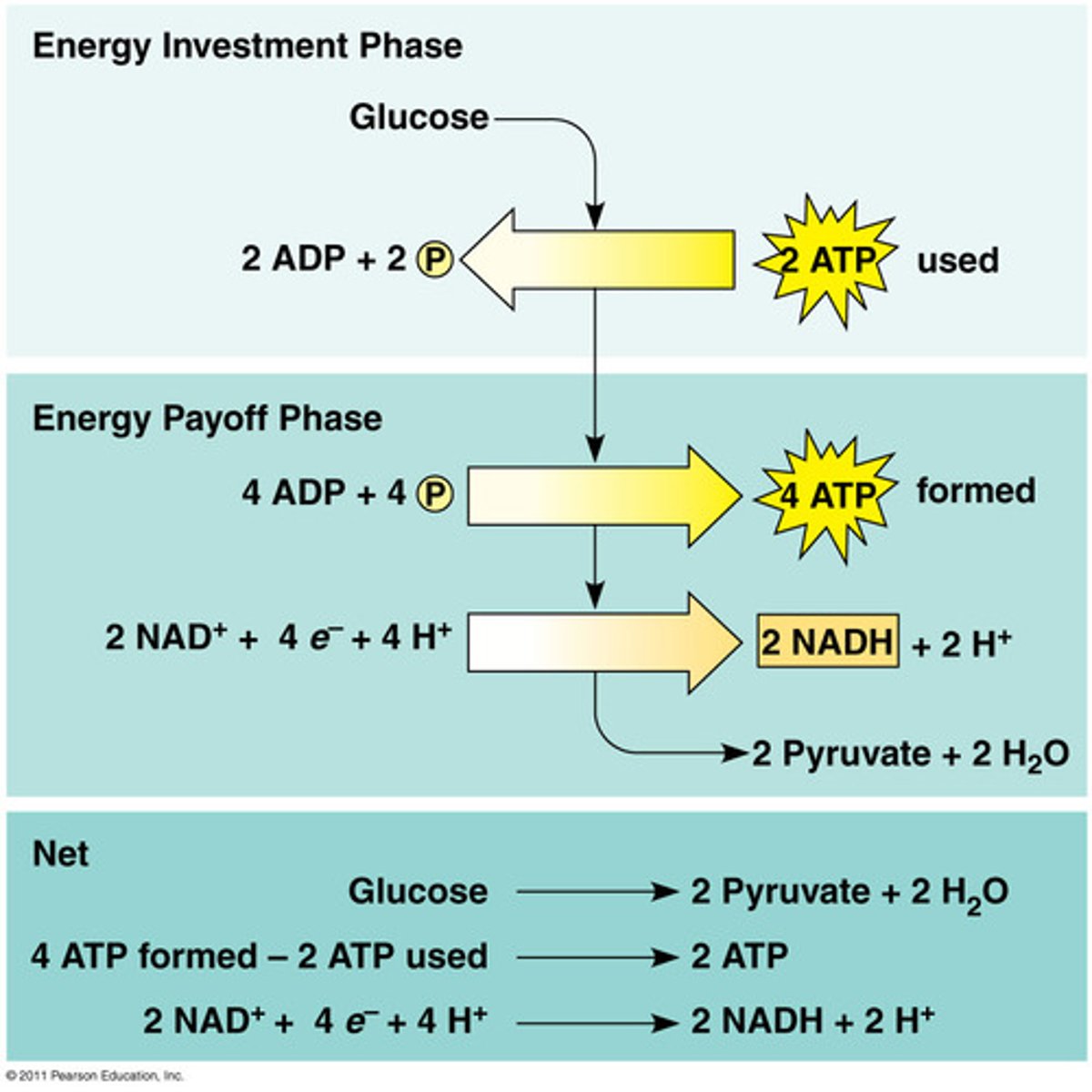
Glycolysis Process
Splits glucose into 2 pyruvate, makes 2 ATP, and 2NADH
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Completely breaks up pyruvic acid as CO2, which is exhaled or goes to the atmosphere and makes ATP, FADH2, and NADH.
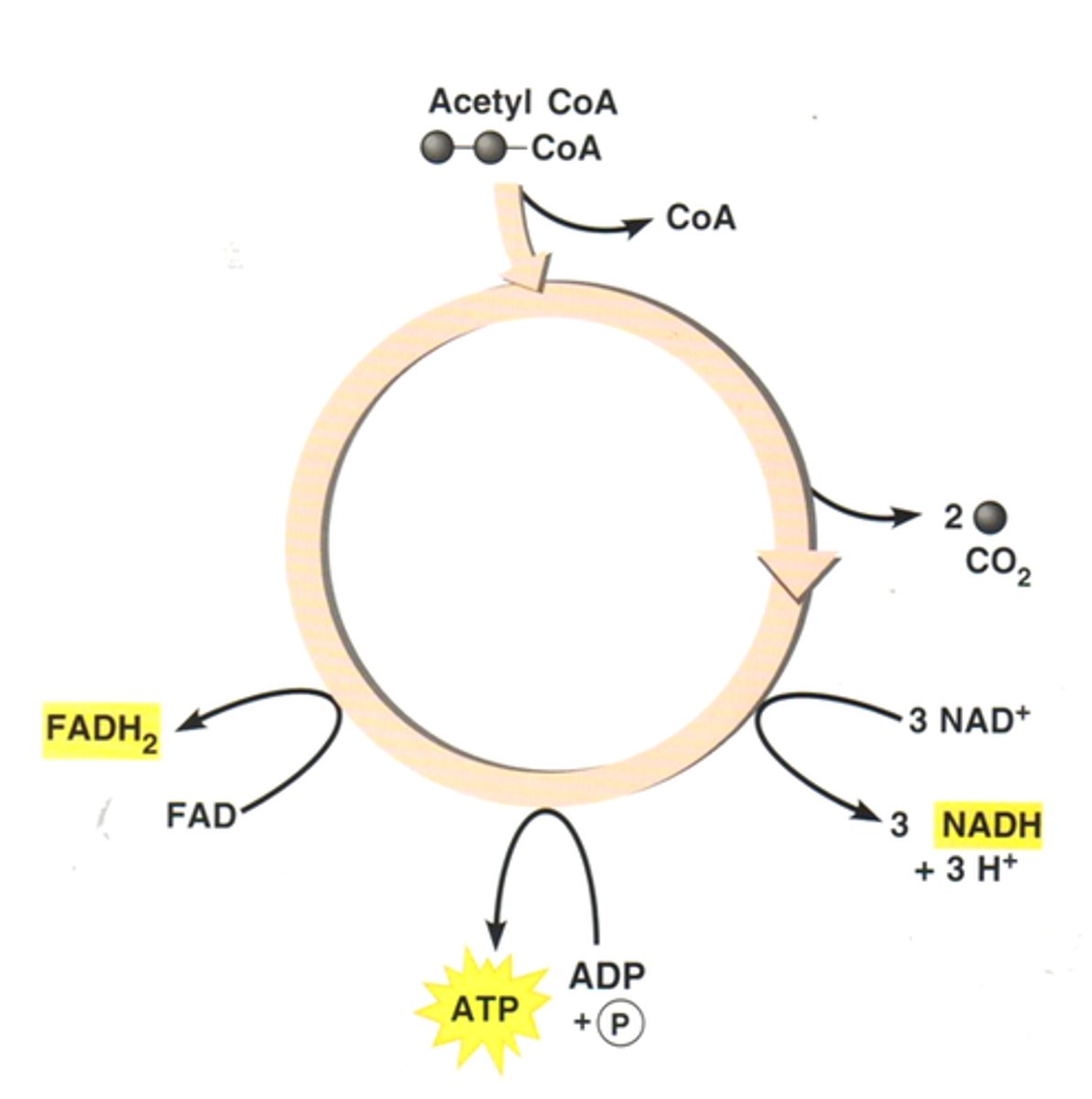
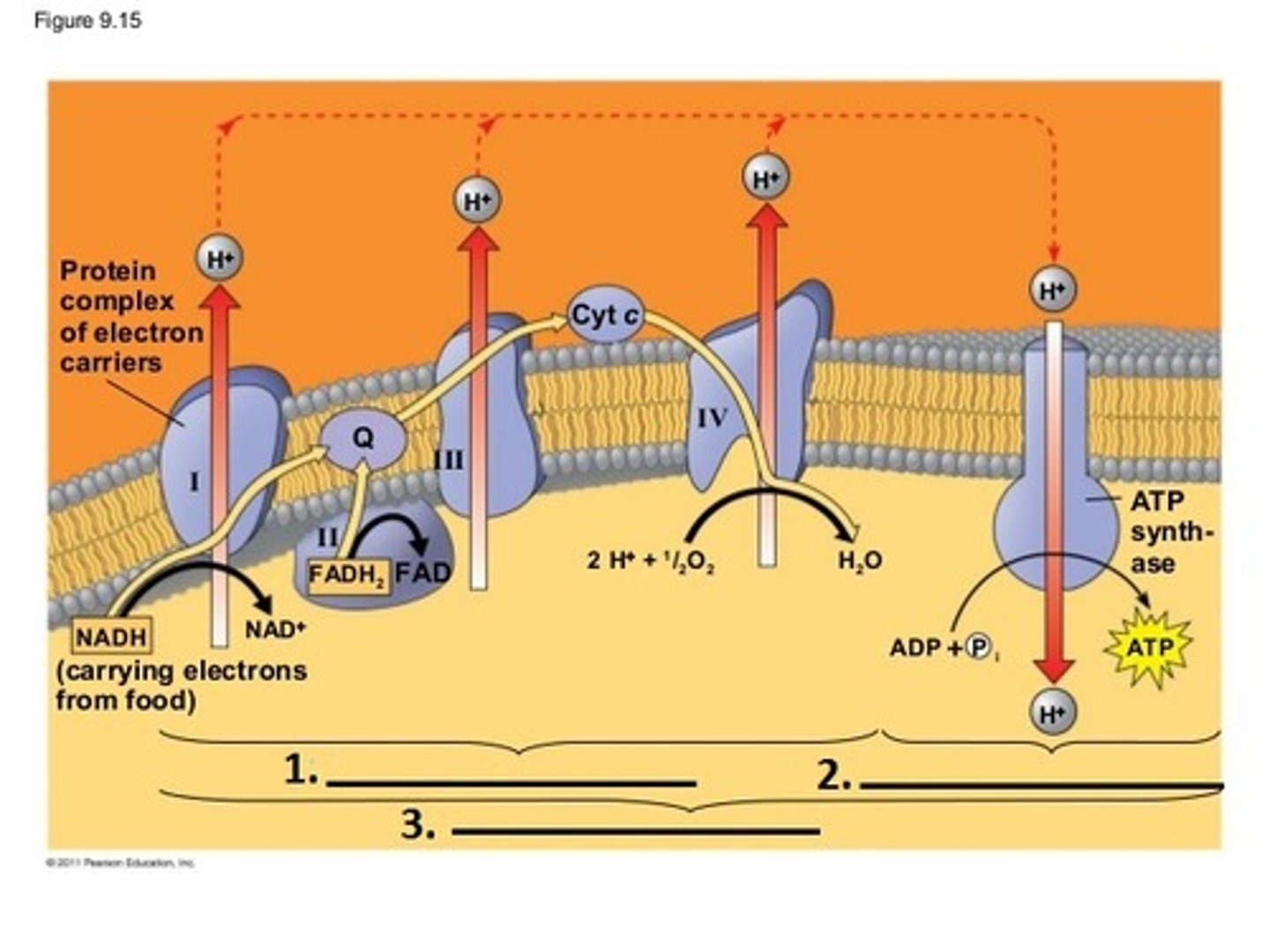
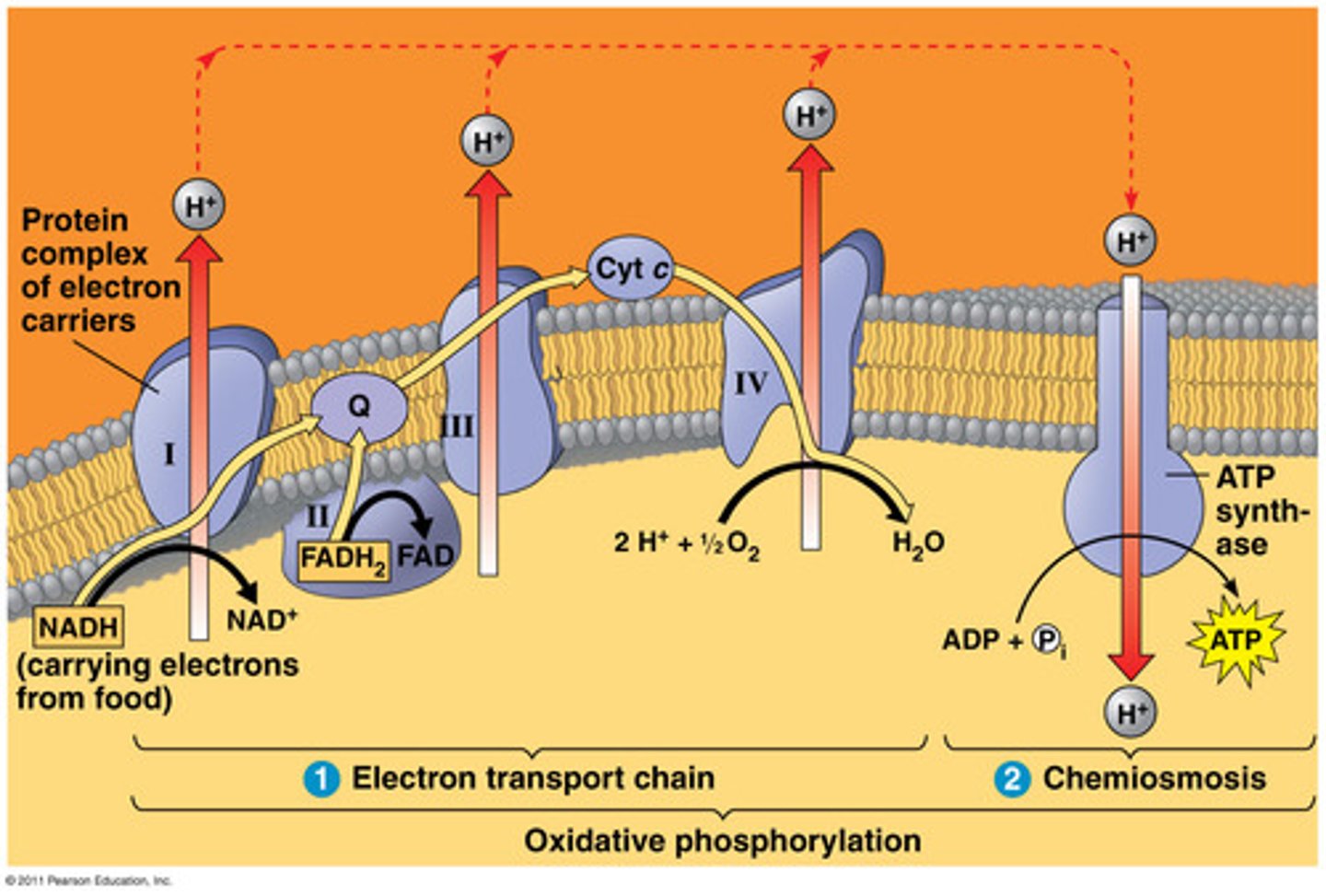
Electron Transport Chain
High energy electrons from FADH2 & NADH are passed along the ETC to pump H+ into the intermembrane space.
Oxygen is the last electron acceptor which becomes water. 32 ATP is made by oxidadtive phosphorylation as H+ passes thru the ATP synthase.
Waste products of cell respiration
Water, carbon dioxide, heat
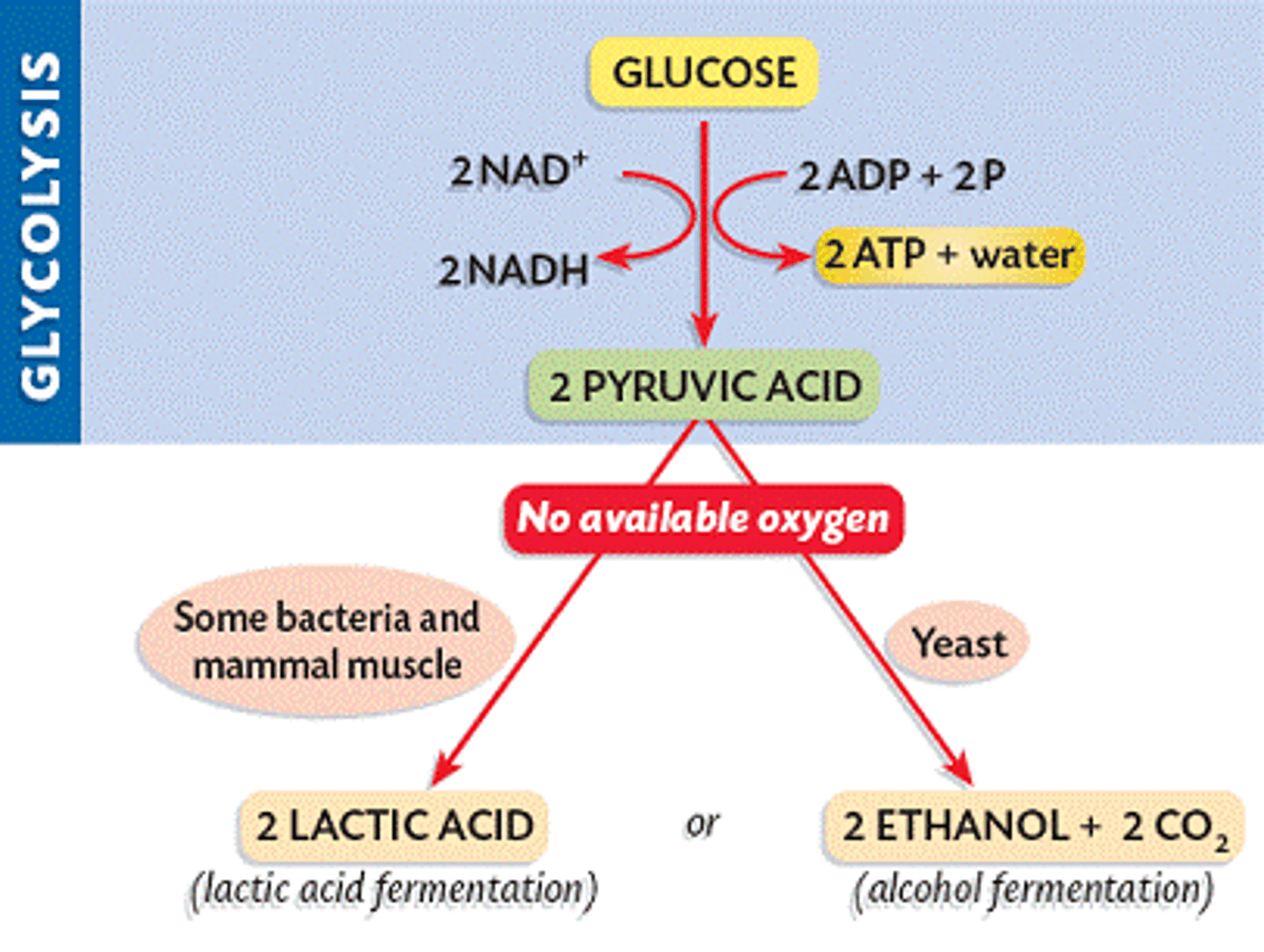
Fermentation
Result of anaerobic respiration, 2 ATP and recycles NAD+
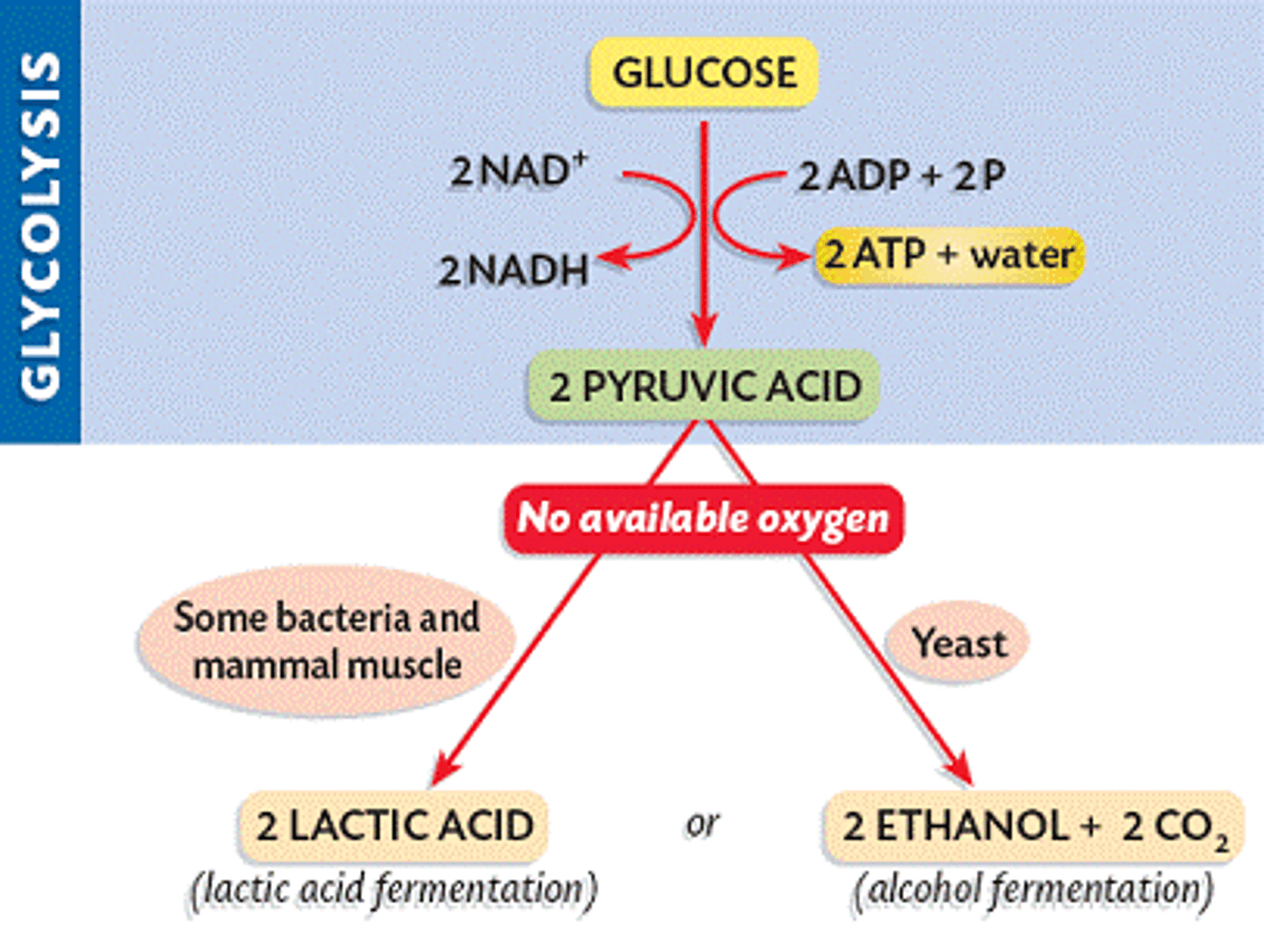
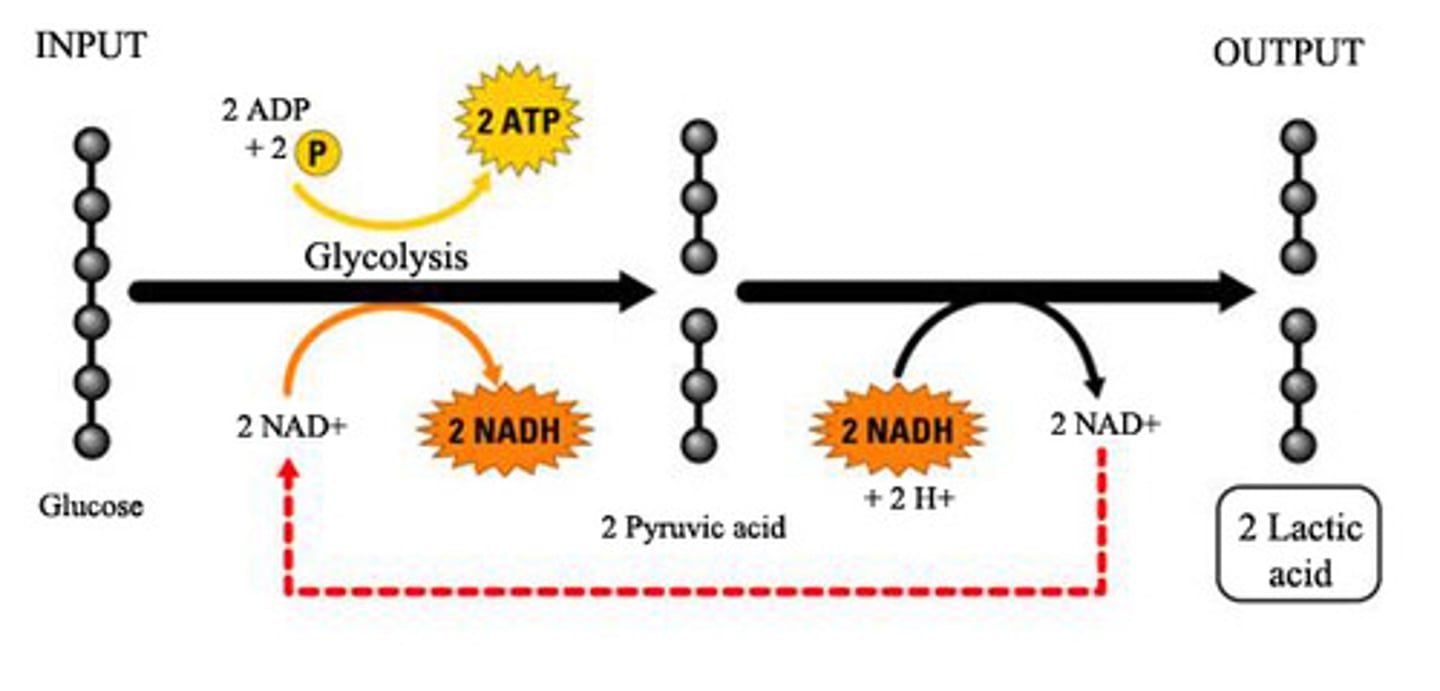
Lactic Acid fermentation
type of fermentation of animal cells during anaerobic respiration. examples of lactic acid, humans, bacteria make cheese, yogurt, sour cream , kimchi, saurkraut
Alcoholic fermentation
Type of fermentation in some bacteria and yeast.
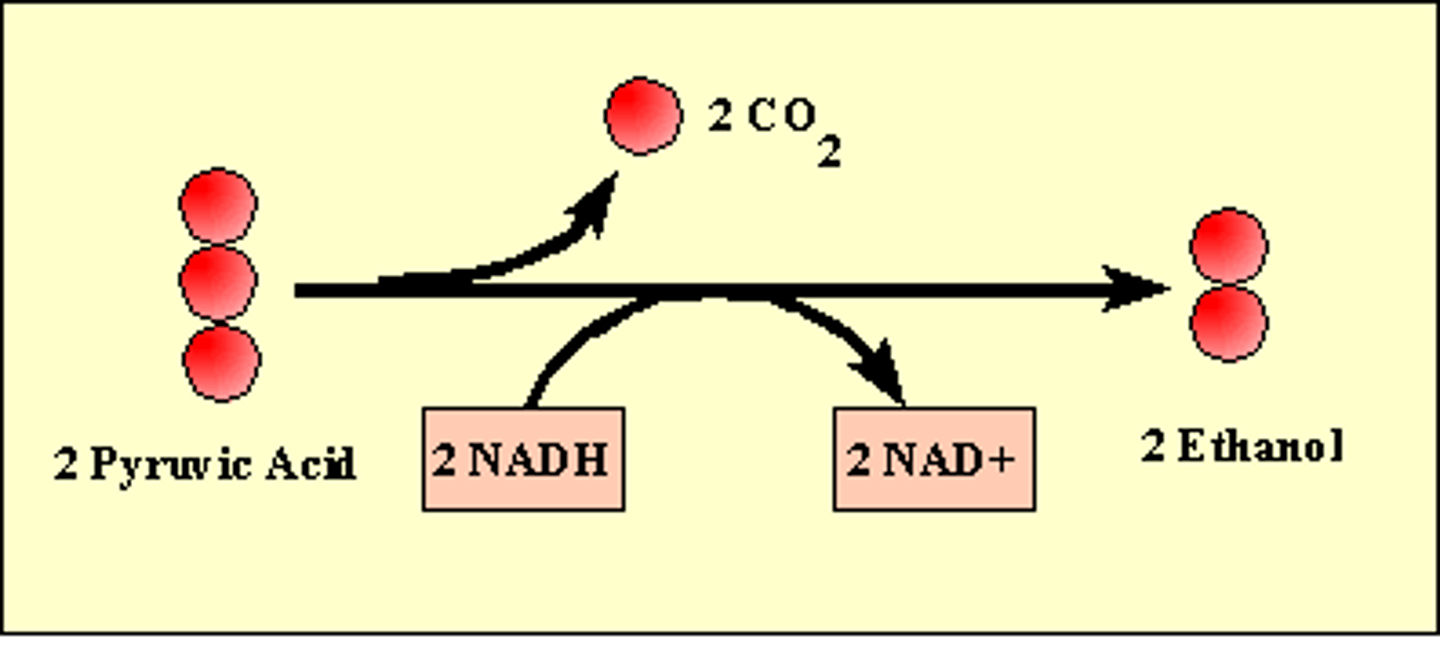
Reactants of cellular respiration
1 Glucose (C6H12O6) and 6 oxygen (O2)

Products of cellular respiration
6 Water (H2O) and 6 carbon dioxide (CO2)

Cell Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 >>>> 6H20 + 6CO2 +ATP
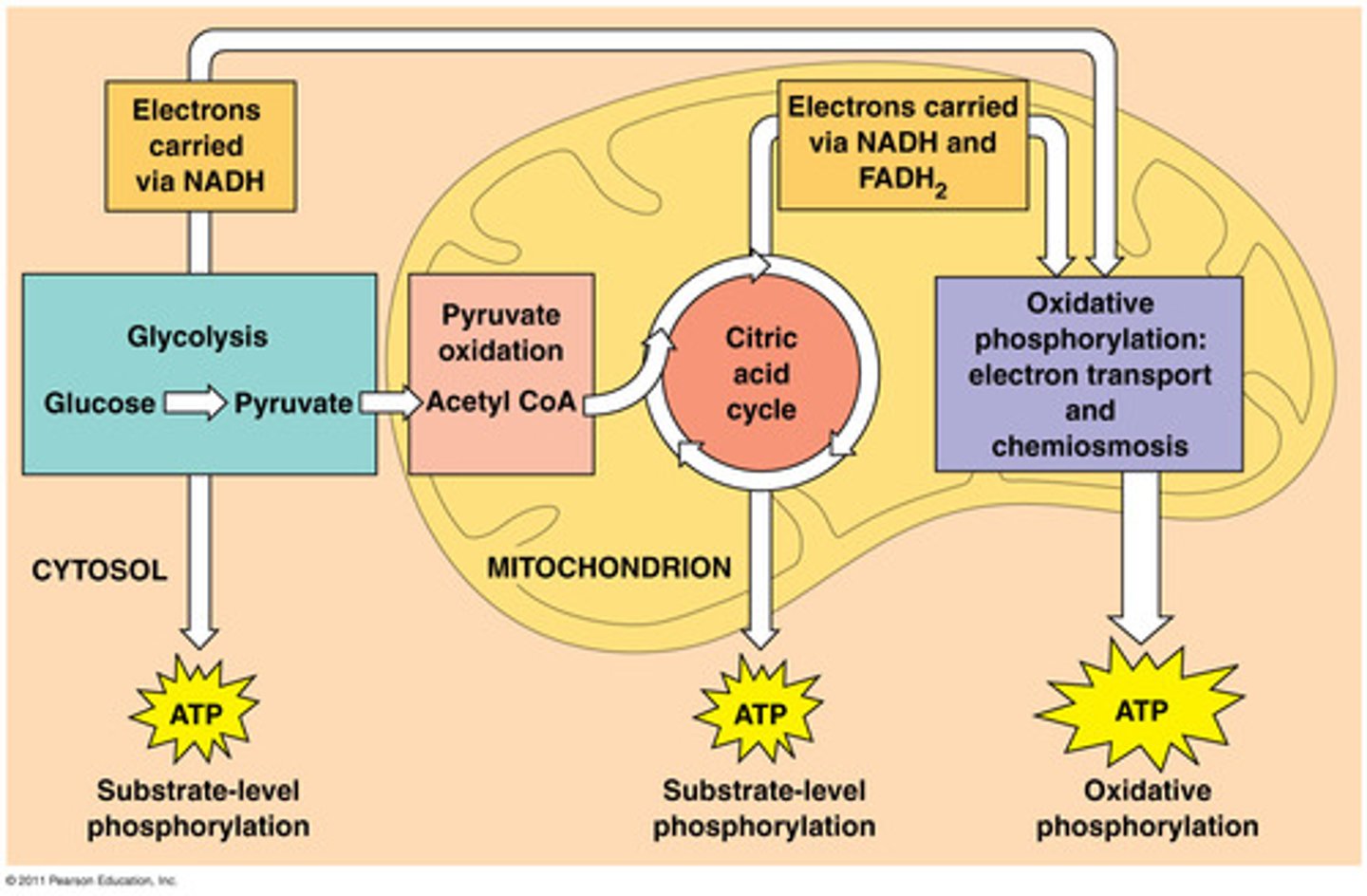
Organelle responsible for cell respiration
Mitochondria and cytoplasm
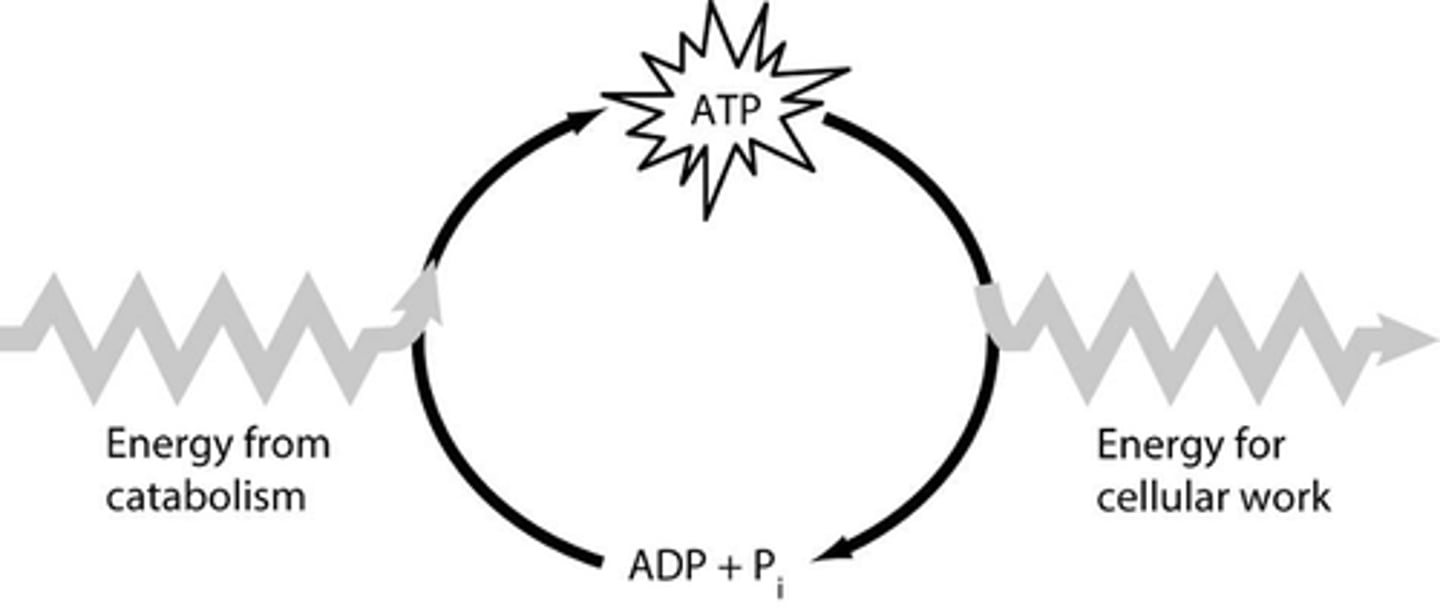
ATP -ADP cycle
Process by which cells regenerate ATP. ADP forms when a phosphate group is removed from ATP, then ATP forms again as ADP gains a phosphate group.
ATP Synthase
enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that adds a high-energy phosphate group to ADP to form ATP powered by H+.
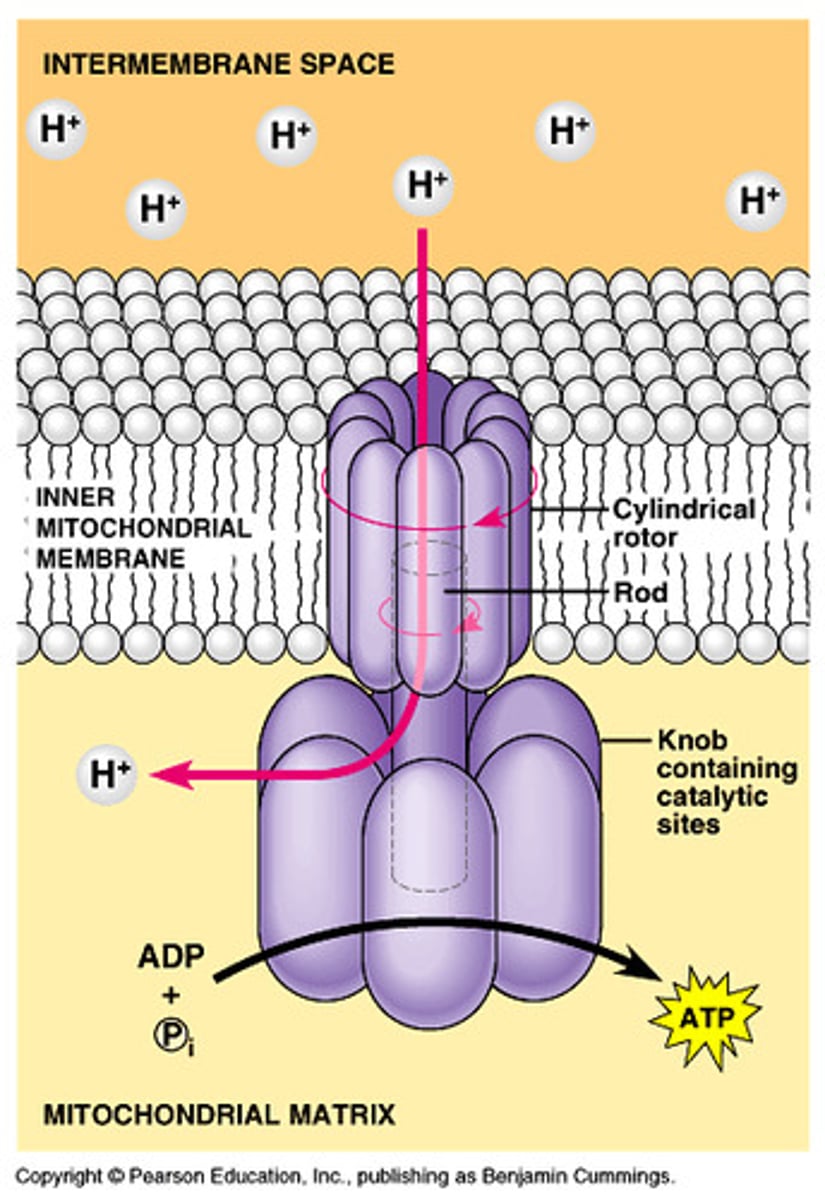
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient Hydrogen gradient established by the Electron transport chain, and the ATP synthase enzyme.
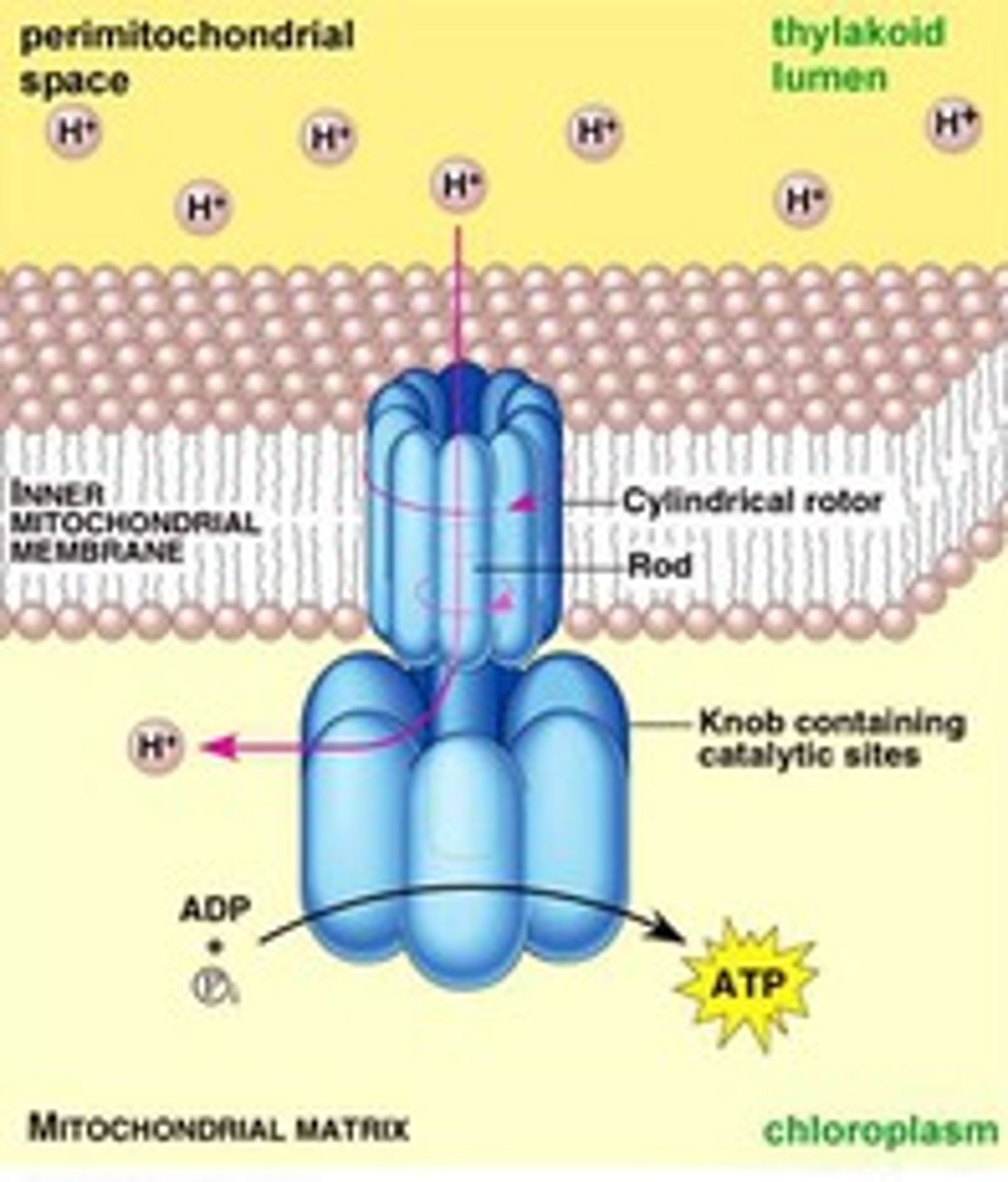
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Any set of membrane-bound protein complexes and mobile electron carriers involved in a coordinated series of redox reactions in which the potential energy of electrons is successively decreased and used to pump protons from one side of a membrane to the other.
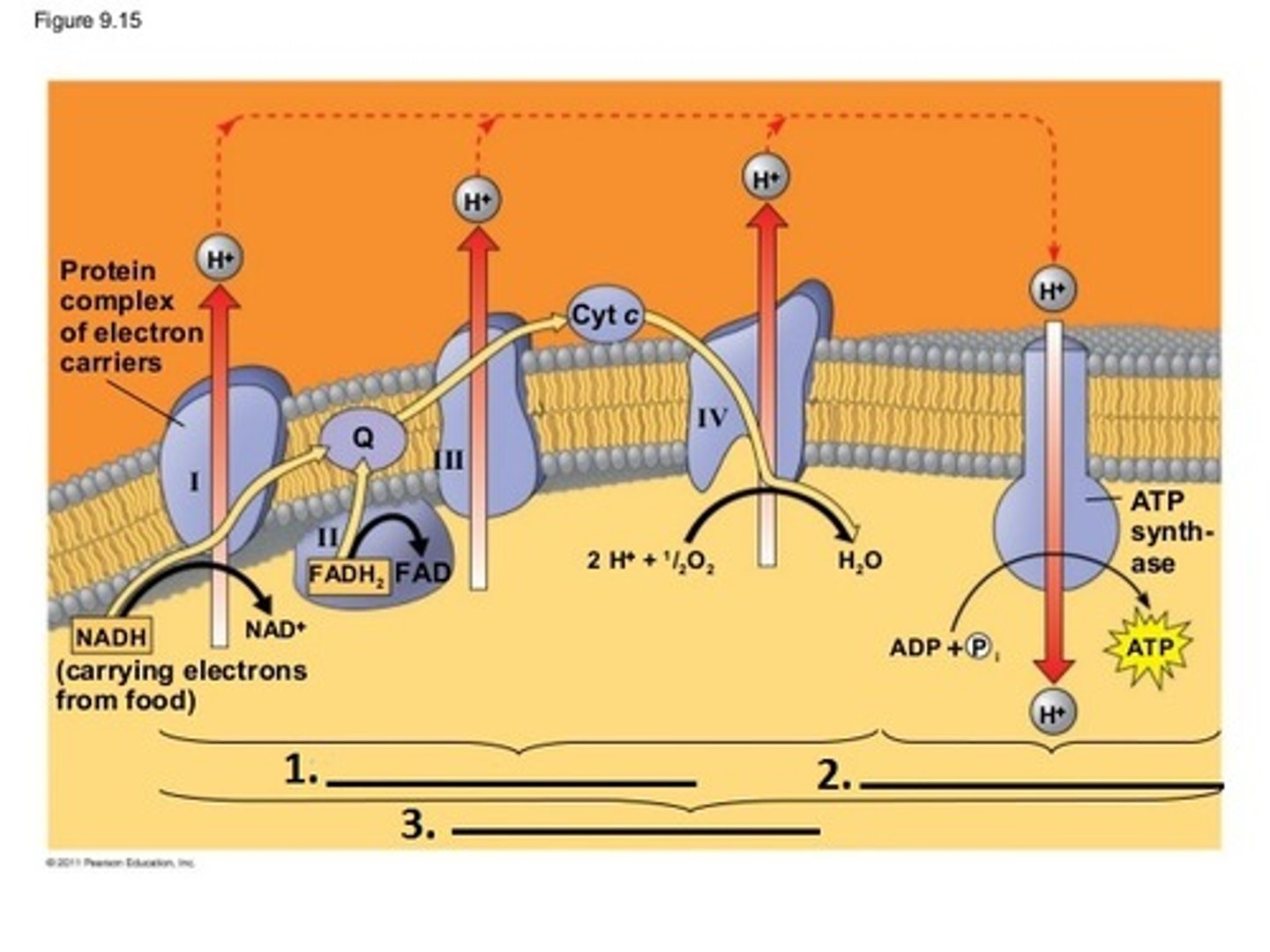
TERM
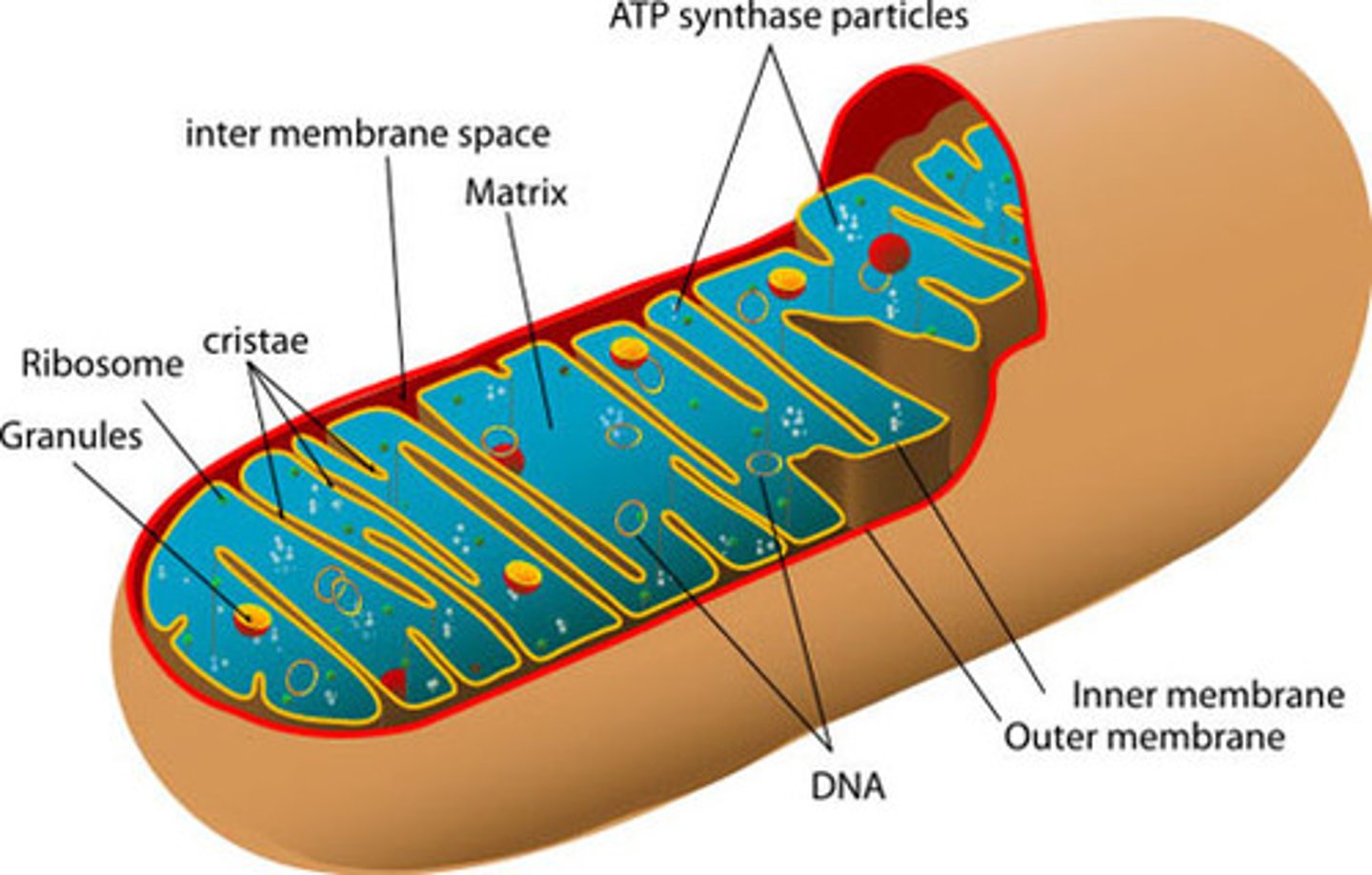
matrix of mitochondria
DEFINITION
location of krebs cycle
TERM
intermembrane space
DEFINITION
the fluid-filled space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes, this where H+ is pumped during the electron transport chain.
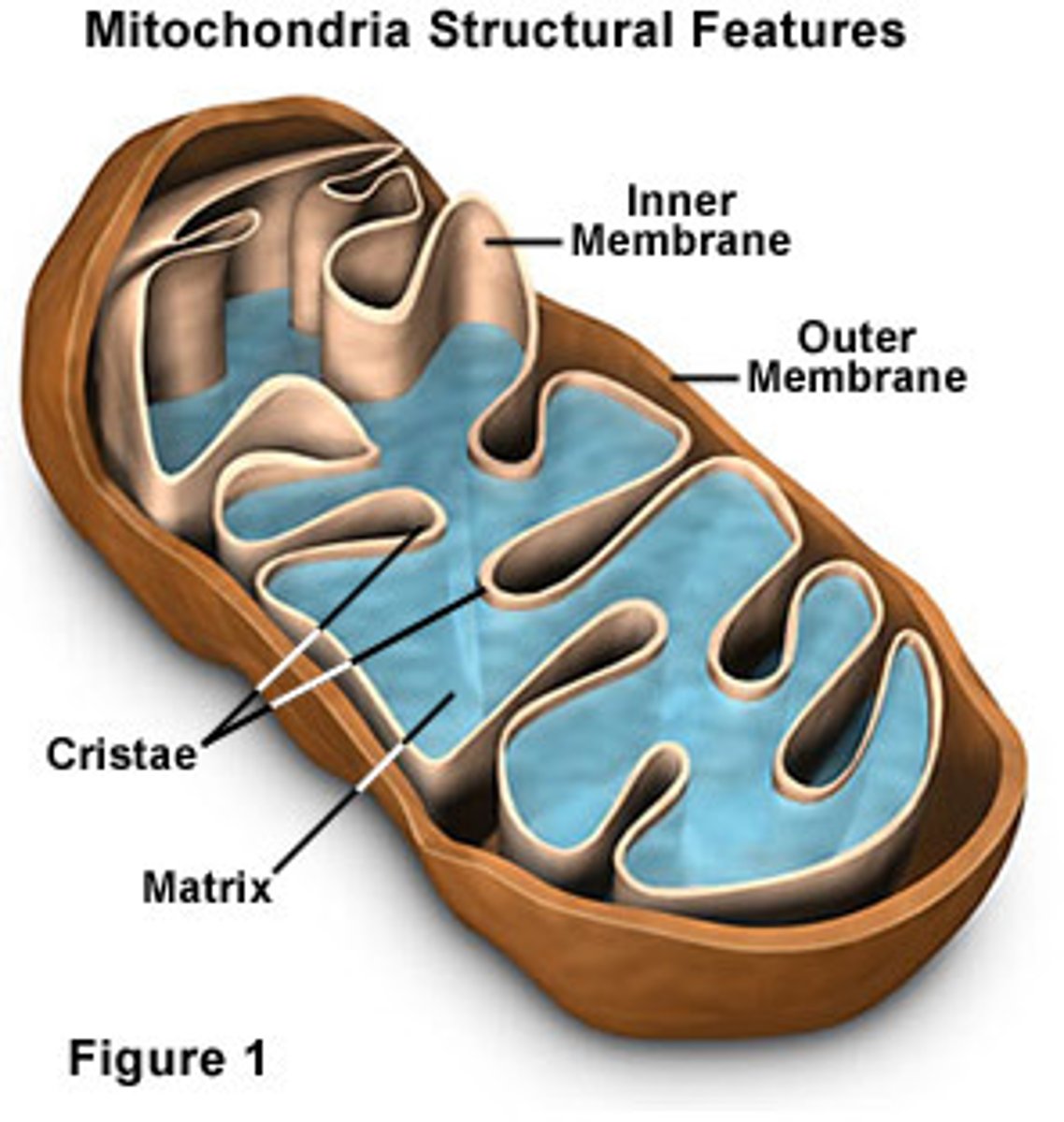
cristae of mitochondria
The carriers of the electron transport chain are located ______________.
pyruvate or pyruvic acid
the end product of glycolysis, which is converted into acetyl coA that enters the Krebs cycle when there is sufficient oxygen available
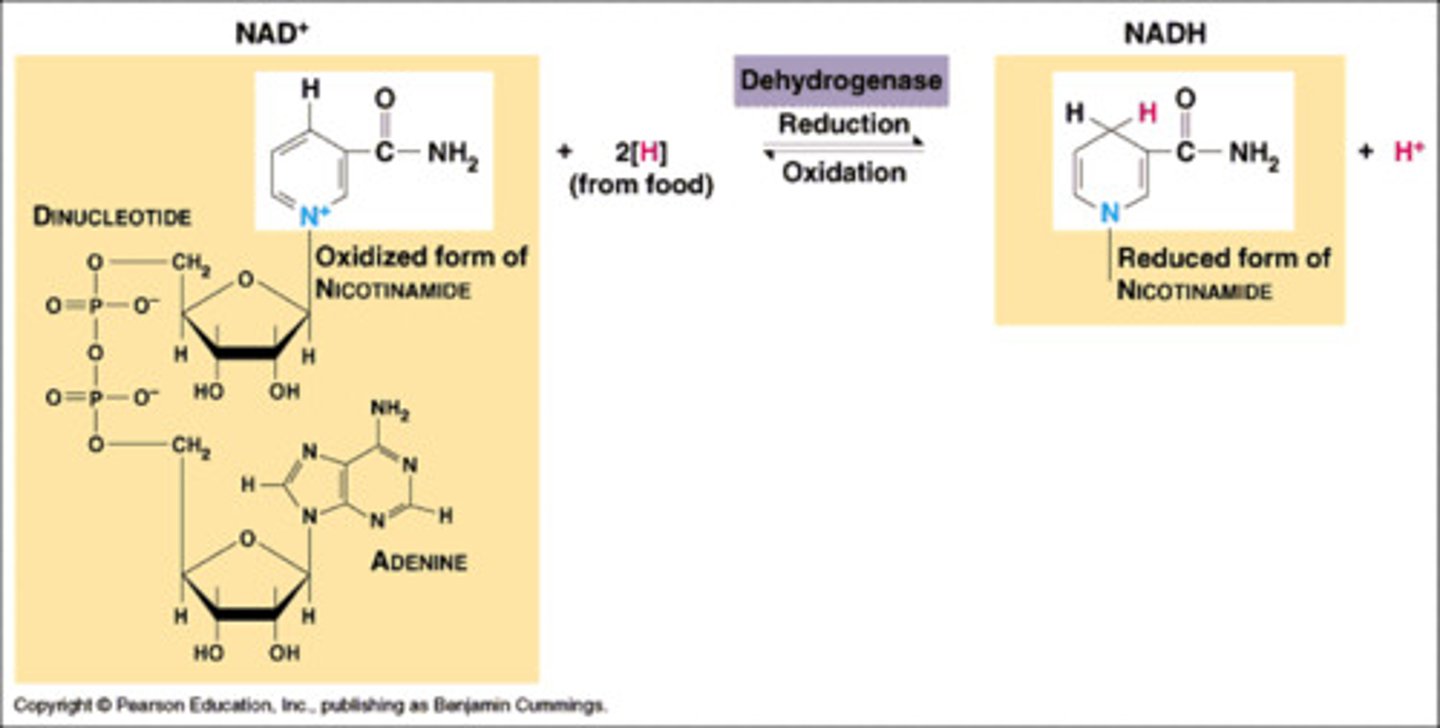
NAD+
(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) electron carrier involved in cellular respiration.
NAD+ becomes NADH when it gains H and electrons.
FADH2 and NADH
Electrons are donated to the electron transport chain
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
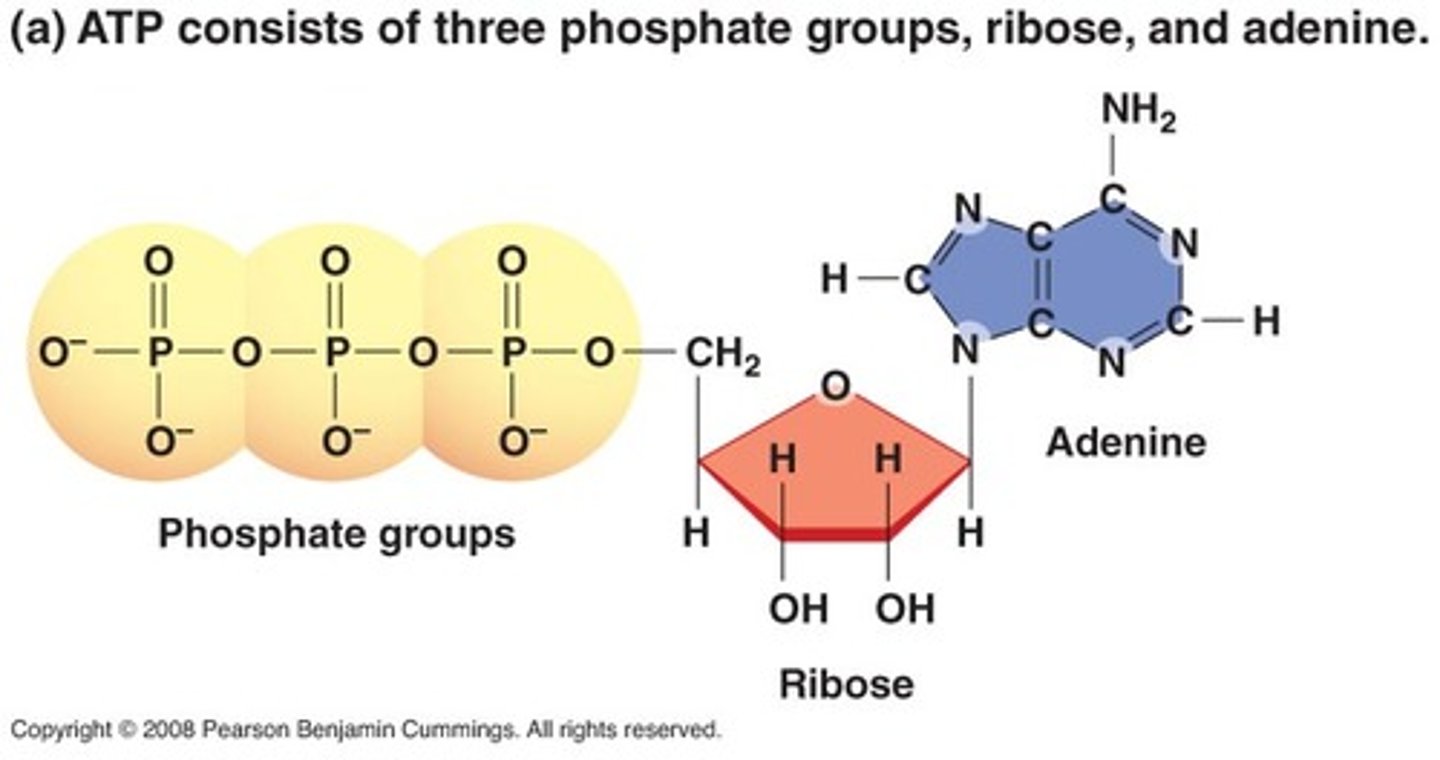
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.

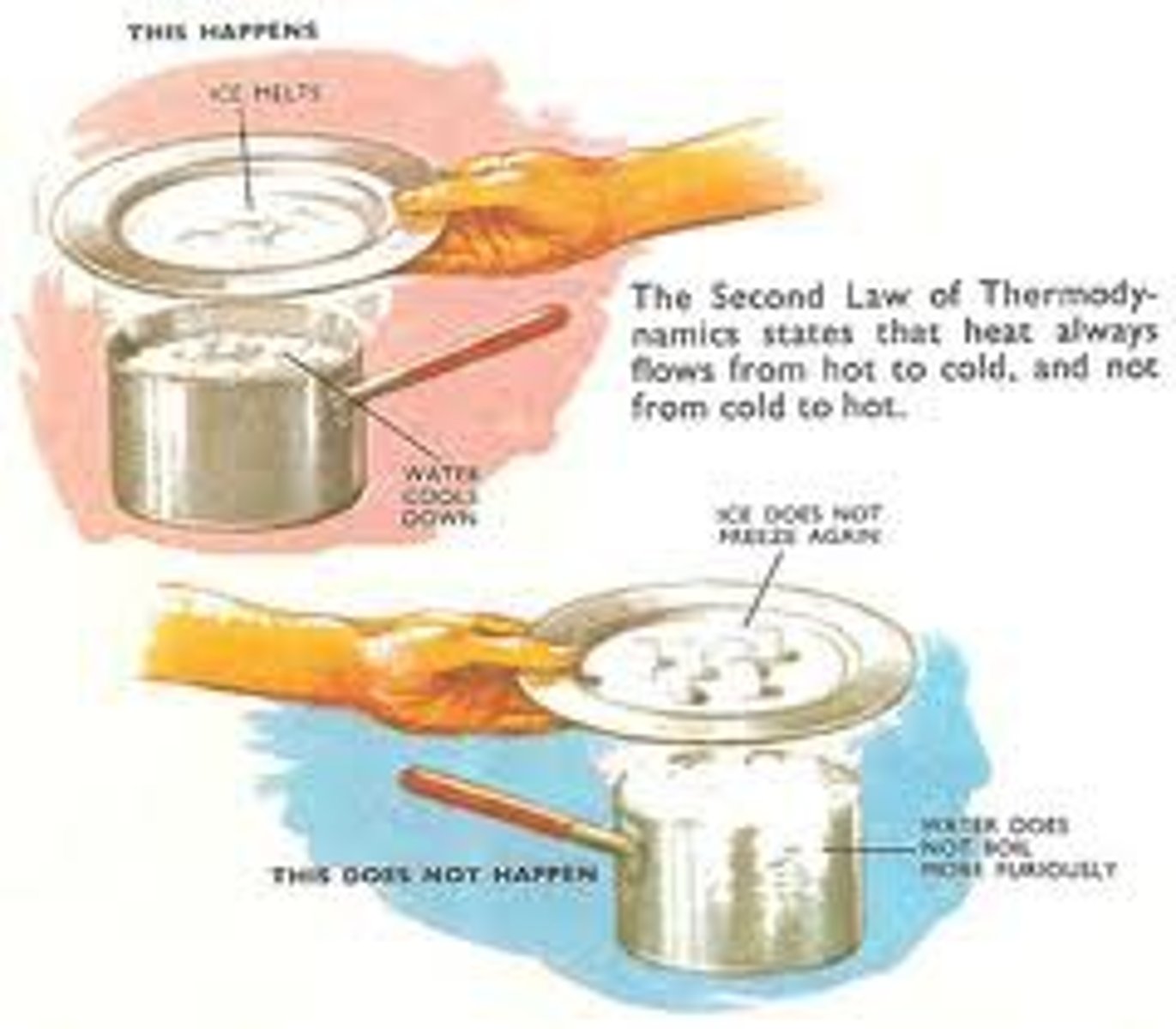
second law of thermodynamics
when energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is always degraded into lower-quality energy (usually heat)
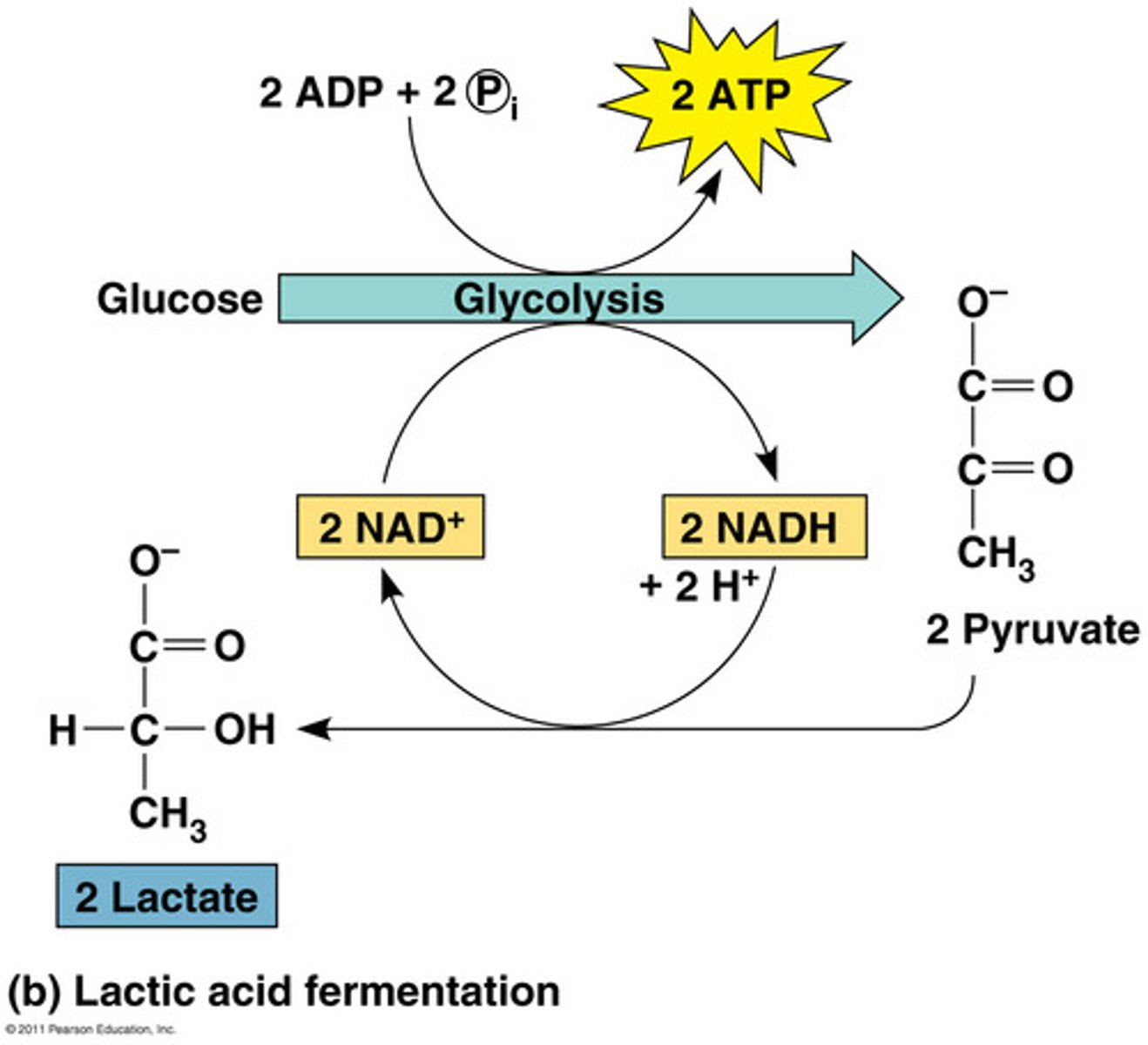
lactic acid fermentation
Process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen happens in animals and bacteria. Examples of products is yogurt, cheese, buttermilk
alcoholic fermentation
the anaerobic process by which yeasts and other microorganisms break down sugars to form carbon dioxide and ethanol
TERM
Inner Membrane
DEFINITION
Where Electron transport proteins are located
Heterotrophs are
organisms (animals) that obtain energy from the food the eat

Autrotrophs
Organisms that make their own food

Producer
An organism that can make its own food.

Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
equation for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen) ---------> 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) + energy

What is the order of steps in cell respiration?
1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs cycle
3. Electron transport chain
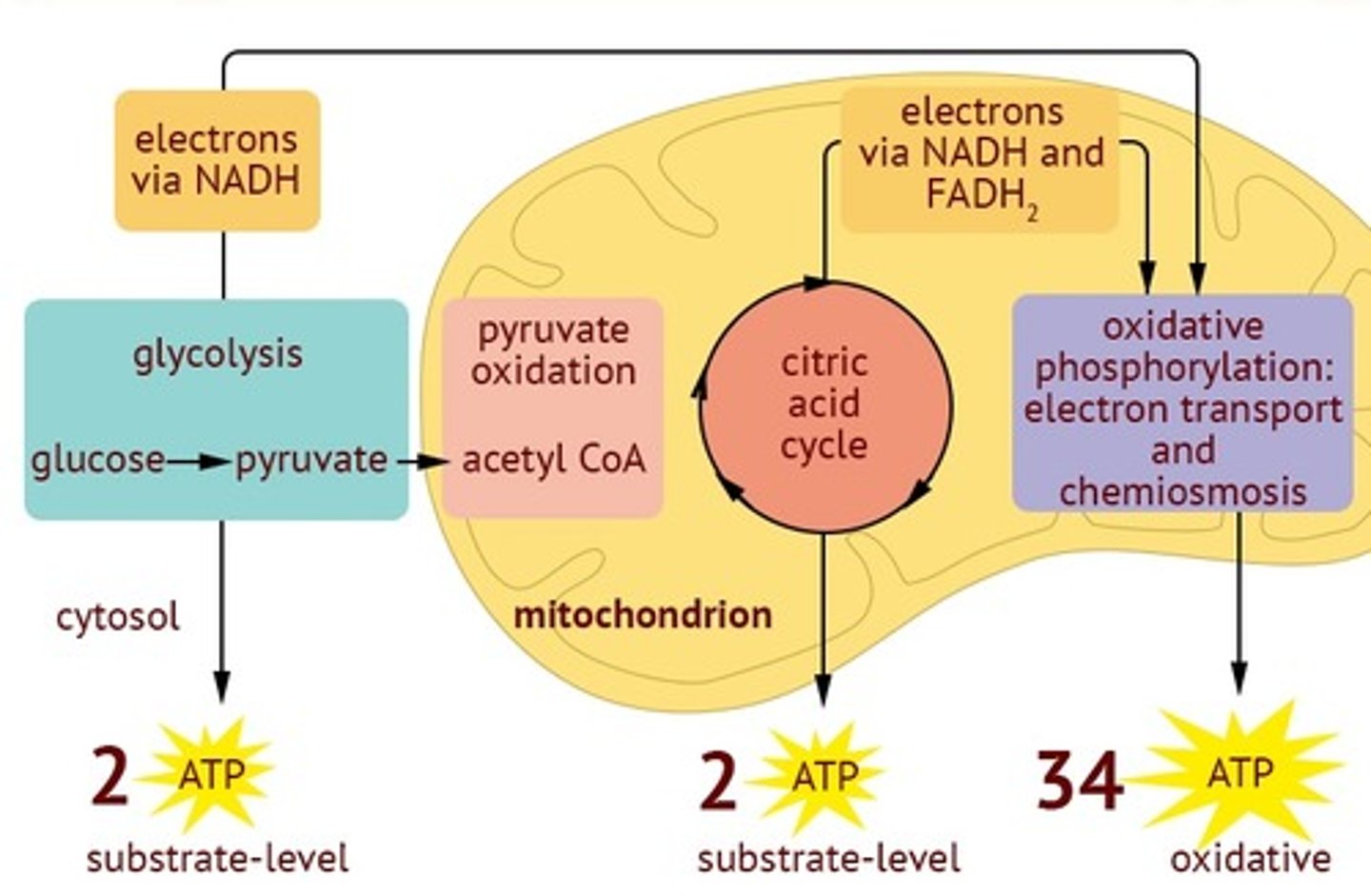
What's the role of oxygen in cellular respiration?
it's the final electron acceptor for the electron transport chain and it becomes water after accepting electrons
What step of cellular respiration produces the most ATP?
Electron transport chain
What step in cellular respiration do all organism conduct
Glycolysis
Which form of ATP has the most potential energy?
ATP, ADP has less potential energy. Energy is between the phosphate bonds.
Glycolysis
_____________ is the process of splitting a glucose molecule into 2 pyruvic acid molecules
Cytoplasm
Tell where glycolysis happens.
Tell where Krebs cycle happens.
IN THE MATRIX
Name three phases of cellular respiration
GLYCOLYSIS, KREBS CYCLE, ELECTRON TRANSPORT
A process does not require oxygen
anaerobic
aerobic
cell respiration with oxygen
Electron carriers in cellular respiration
NADH (NAD positive) and FADH2 (FAD)
Oxgyen
Needed for aerobic cell respiration
What gas is produced during alcoholic fermentation
carbon dioxide
Name the type of fermentation that occurs in human muscle cells
lactic acid
Name the type of fermentation that makes bread dough rise
alcoholic
type of fermentation used by human muscles in low oxygen conditions and microorganisms to make yogurt, cheese, pickles, sauerkraut and kimchi
lactic acid
Where do H+ ions build up as electrons are passed down the electron transport chain
intermembrane space of the mitochondrion
ATP synthase
enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that adds a high-energy phosphate group to ADP to form ATP as H ions pass through it
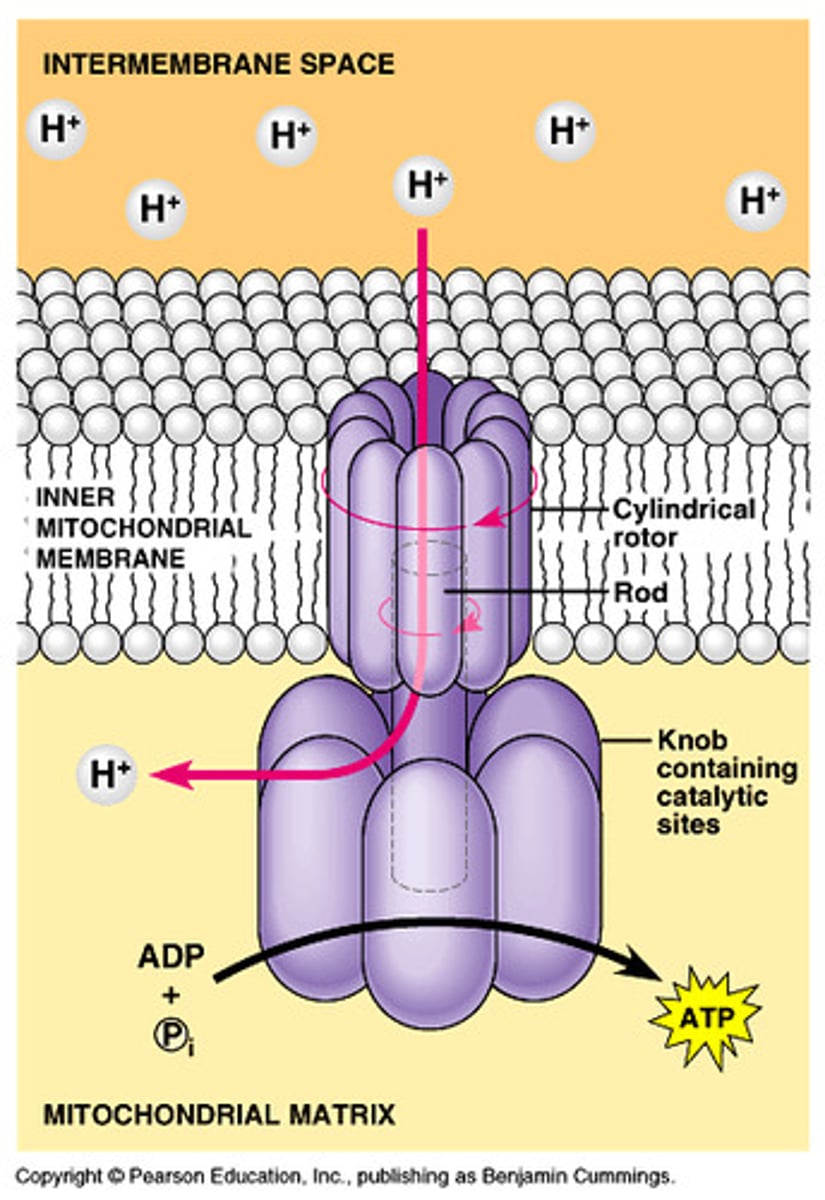
Where do NADH and FADH2 produced during the krebs cycle
Electron transport chain in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
Which phase in the cellular respiration is the most ATP made
Electron transport chain
In which phase of cellular respiration is water made?
Electron transport chain
What part of ATP is broken to release energy for use in chemical reactions?
between the phosphate groups
What is the equation for alcoholic fermentation
pyruvic acid + NADH → alcohol + CO2 + NAD+
what is the equation for lactic acid fermentation
pyruvic acid + NADH → lactic acid + NAD+
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2.
What is the equation for cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP energy
Name the ion channel through which H+ ions pass that adds Phosphate onto ADP
ATP synthase