chemical analysis
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
pure substance
-only pure substances melt and boil at specific temps

diff between physical and chemical test
physical= testing physical propeprties
chemical= reacting with other chemicals
impure substances
melt and boil at diff temps
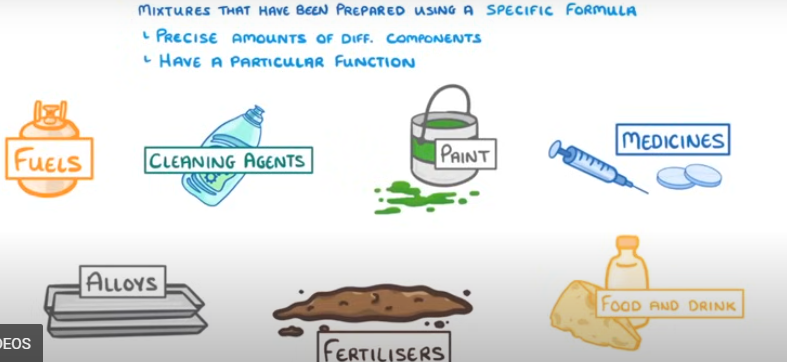
what are formulations
chromotography

paper chromotography

paper chromotography in 6 steps
1 draw a line with a pencil near the bottom of filter paper- BASELINE
2 add sample of ink to the pencil line
3 fill beaker with shallow amount of solvent (water/ethanol)
4 place filter paper into the solvent
5 wait for solvent to seep up the paper
6 once solvent reaches top take the paper out and leave it to dry (results are called- CHROMOTOGRAPH
what can u do to improve accuracy of paper chromotography
use pencil instead of ink as ink would dissolve and move up
make sure pencil line and spot of ink dont submerge (that is the reason why the water in the beaker is shallow)
place a lid on top of the beaker to stop the solvent from evaporating
analysis of dyes in paper chromotography
if any chemicals arent soluble = stays on baseline
diff dyes will travel at diff rates = seperates= meaning each one is a diff substance
mobile phase
substance molecules can move in (liquid/gas)- in this case solvent in the beaker
stationary phase
materials molecules cant move in (solid/thick liquid)- paper used
how does mobile and stationary phases work during paper chromatography
diff chemicals will constantly change between mobile and stationary
dissolves in solvent→ moves a bit → binds to paper → repeat
=how much they spend in each phase determines how fast they move up the paper
more/less soluble ink=
more= longer time in mobile phase =faster
less= longer in stationary= slower
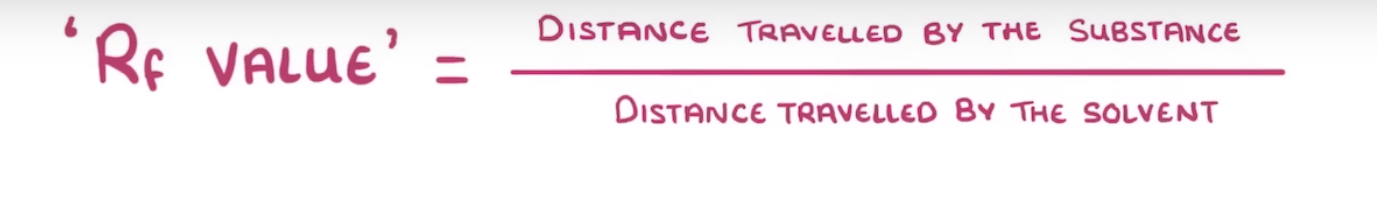
what is Rf and why is it that way
ratio of how far the compound travels
NOT DISTANCE bcs how long the paper has waited in the solvent can also determine the distance
how far each substance travels depends on
its properties
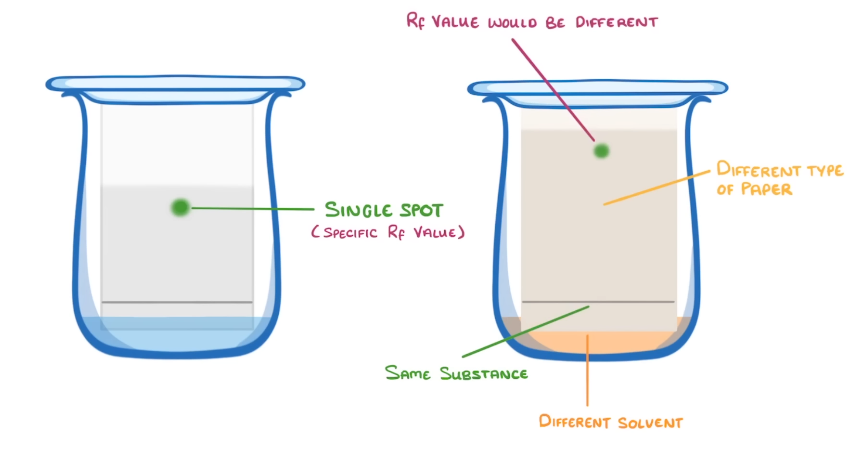
what happens to paper chromotography with a pure substance
wont seperate out and stay as a single spot =has a specific Rf value
HOWEVER id the solvent/ paper type of different the chromatogram will be different= diff Rf vlaue
how to test for chlorine
put a damp litmus paper inside the test tube with gas sample
if present: BLUE→ WHITE
-poisinous: mask or fume cupboard
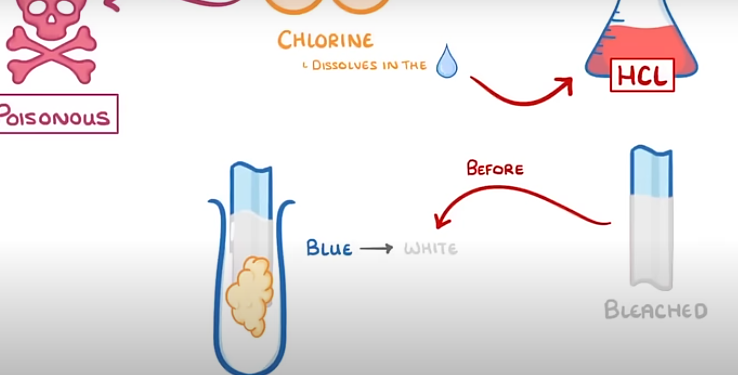
during test for chlorine why might the litmus paper turn red before bleaching white
bcs chlorine dissolves in water which forms hydrochloric acid.
acidic=red
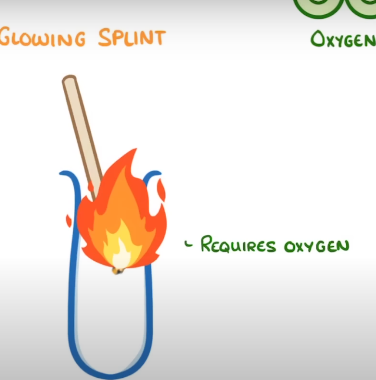
how to test for oxygen
place glowing splint into the test tube with sample gas
if oxygen is present, it will relight the splint.
this is bcs burning requires oxygen
how to test for hydrogen
put a lit splint inside the test tube with the gas sample.
if present: squeaky pop
bcs heat energy causes hydrogen to burn with oxygen = forms water

how to test for carbon dioxide
bubble gas sample through limewater
if present: limewater will go cloudy
bcs Calcium carbonate formed is a solid= makes it appear cloudy