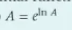Chapter 18: Rates 🏎️☁️
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
most basic rate equation:
rate = change in concentration / time
in a second order reaction, what happens?
if the concentration of the reactant is doubled, the rate is doubled (to the power of 2!)
what is the overall order?
the sum of orders with respect to each reactant
what is the usual unit of rate?

three methods of continuous monitoring:
gas collection
mass loss
colour change (colorimeter)
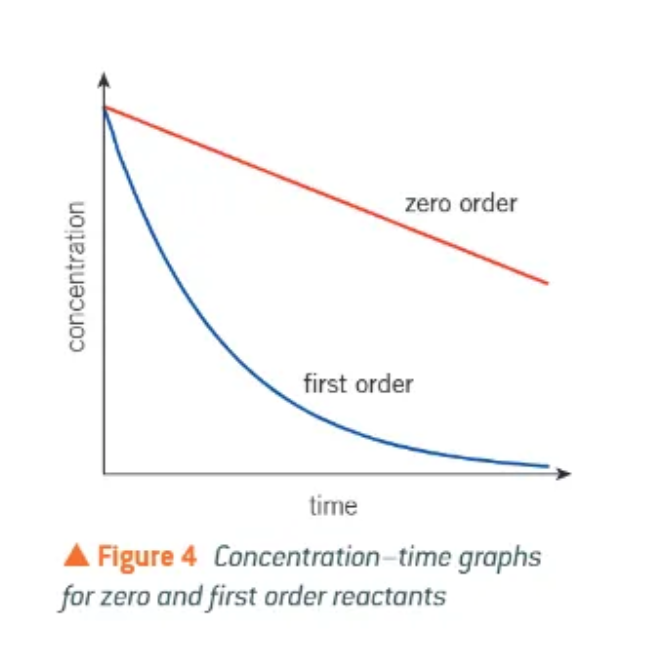
what is the gradient of a concentration-time graph?
the rate of reaction
in a conc/time graph, what do 0 and 1 order lines look like?
0 order = a straight line going downwards → reaction rate doesn’t change!
1 order = a curved line going downwards
what is a half-life?
the time taken for half of a reactant to be used up
first order reactants + half-lives:
first order reactants have constant half-lives!
the conc. halves every half life, and the half life stays the same.
what are the two ways of determining k for a first order reaction?
tangent + substitute into rate equation
using the other formula
formula for calculating k from a half-life:
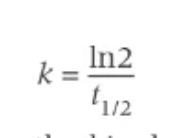
gradients of 0,1, and 2 order reactants on a rate-concentration graph:
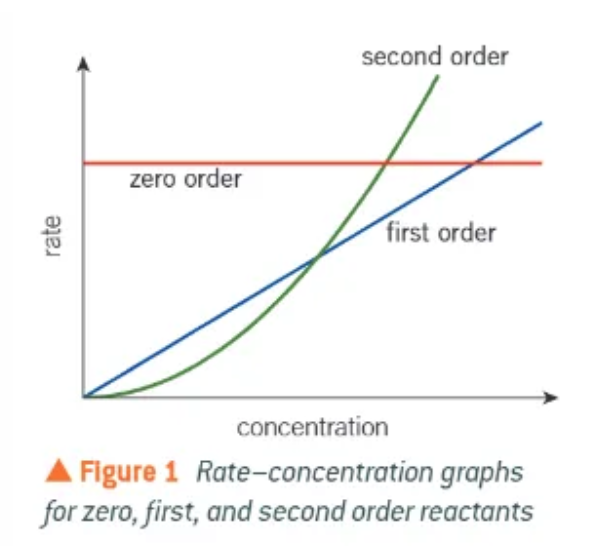
k cannot be worked out from a 2nd order reactant on a rate-concentration graph because it is a curve. what can be done so that it can be worked out?
plot another graph of rate against concentration squared. This makes a straight-line graph, with a straight line through the origin. the gradient of this line with be k.
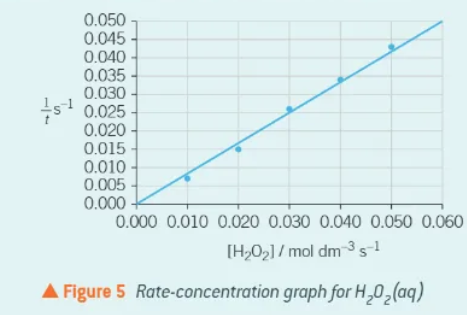
what kind of graph should be plotted from a clock experiment?
1/t ⬆ and concentration➡
this straight line through the origin indicates that the Hydrogen Peroxide is a first order reactant.
why is it unlikely for reactions with more than 2 molecules reacting to happen in one step?
it would need at least 3 molecules to collide simultaneously.
how do we know if a reaction mechanism is correct?
the rate equation only involves species that are involved in the rate-determining step.
the orders in the rate equation match the number of species involved in the rate-determining step.
hydrolysis of haloalkanes:
hydrolysed by hot, aqueous alkali:
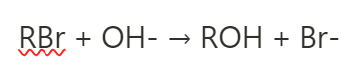
as temperature increases, so does rate. what else increases?
k, the rate constant.
generally speaking, a 10 degree rise in temperature does what do the rate of reaction?
doubles the rate of reaction
when temperature increases, the rate (+ rate constant) increase for 2 reasons:
shifts the Boltzmann distribution ➡➡ to the right → the proportion of particles that exceed the activation energy.
particles move faster, colliding more frequently.
to react, particles much have the…
correct orientation
the increase in rate with the increase in temperature is mainly down to what?
the move in the Boltzmann distribution graph (to the right!)
what is the Arrhenius equation?
the exponential relationship between the rate constant, k, and temperature, T.
🧠 think Kae-Eart (like kae 🧍♀ ear 👂t ☕)
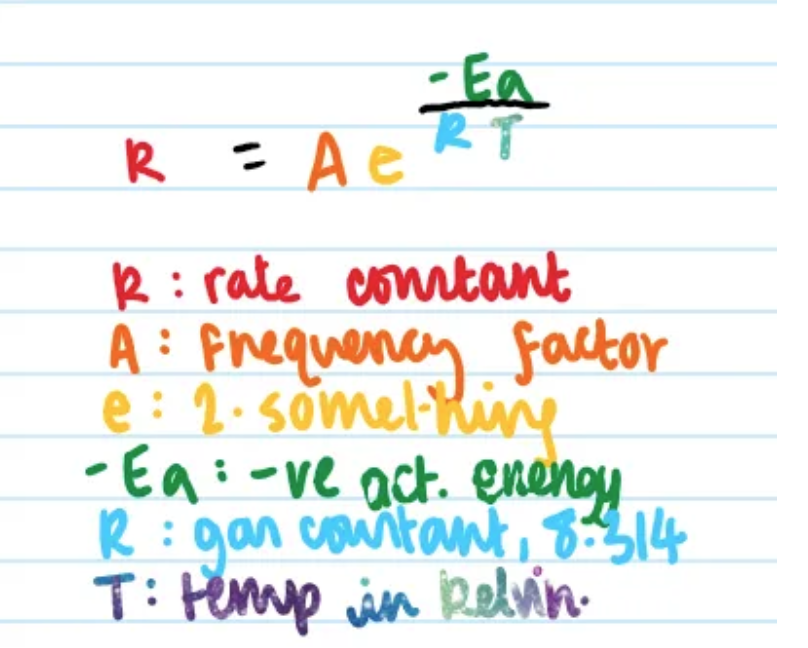
what does the exponential factor of the Arrhenius equation represent?
the proportion of molecules that exceed the activation energy (the proportion of molecules that can actually react!)
logarithmic form of Arrhenius
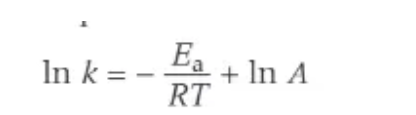
Arrhenius with y = mx + c
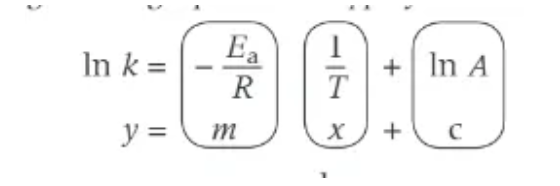
what should be plotted to use the logarithmic Arrhenius?
ln k ⬆
1/t ➡
once you find ln A, the y-intercept, how do we get A from that?