*****5555 Knee and Lower Leg!
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
distal end of femur: blue
lateral supracondylar line
distal end of femur: green
medial supracondylar line
distal end of femur:
popliteal fossa
distal end of femur: red
intracondylar fossa
distal end of femur: purple
medial epicondyle (doesn’t articulate with the tibia)
distal end of femur: pink
lateral epicondyle (doesn’t articulate with the tibia)
distal end of femur: yellow
lateral condyle (smooth parts that articulates with the tibia)
distal end of femur: black
medial condyle (smooth parts that articulates with the tibia)
distal end of femur: light green
adductor tubercle (on medial side)
distal end of femur: orange
patellar surface
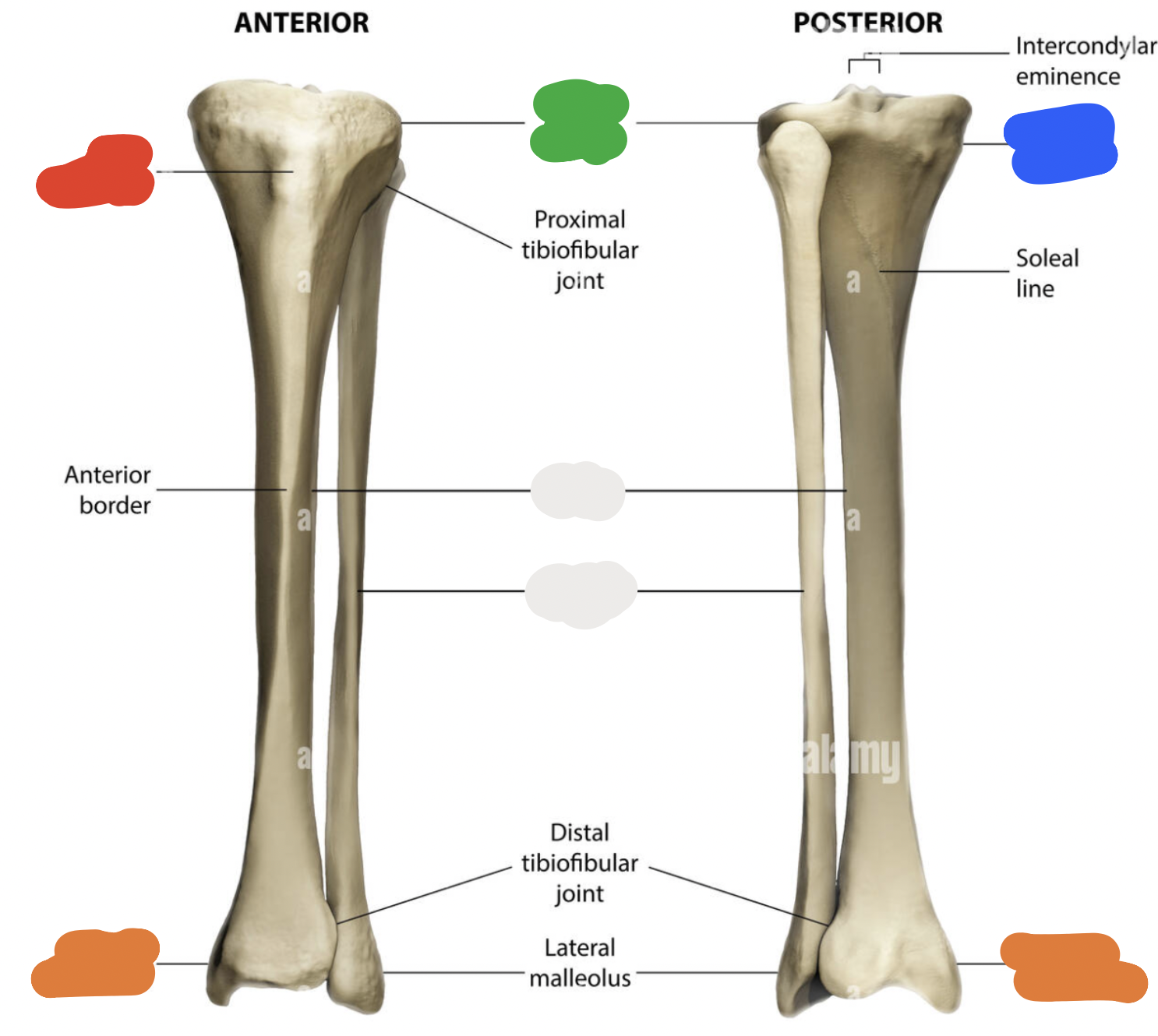
proximal end of tibia: blue
medial condyle (articulates with condyles of the femur)
proximal end of tibia: green
lateral condyle (articulates with condyles of the femur)
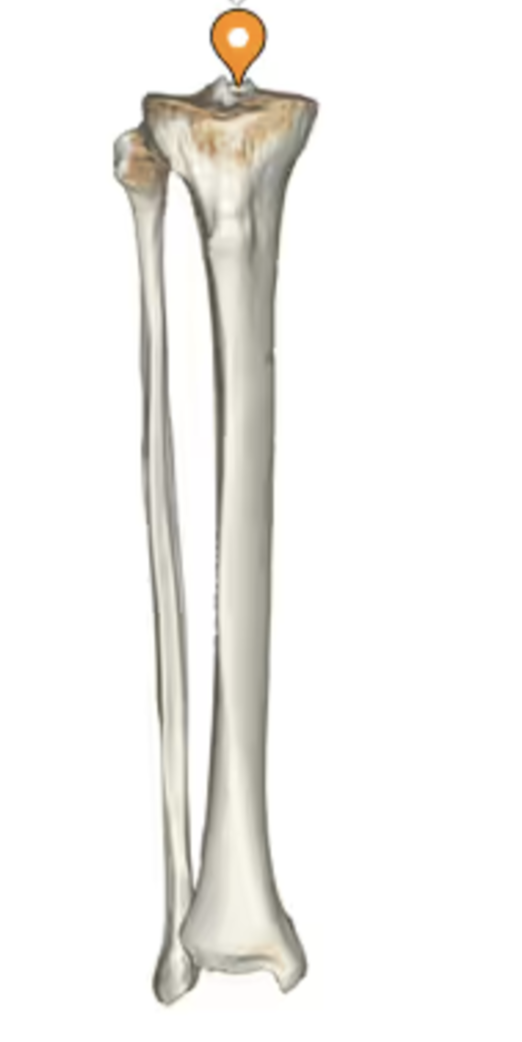
proximal end of tibia:
tibial intercondylar eminence
proximal end of tibia:
Gerdy’s tubercle (is lateral)
proximal end of tibia: red
tibial tuberosity (right above where tibia and fibula articulate)
proximal end of tibia:
shaft
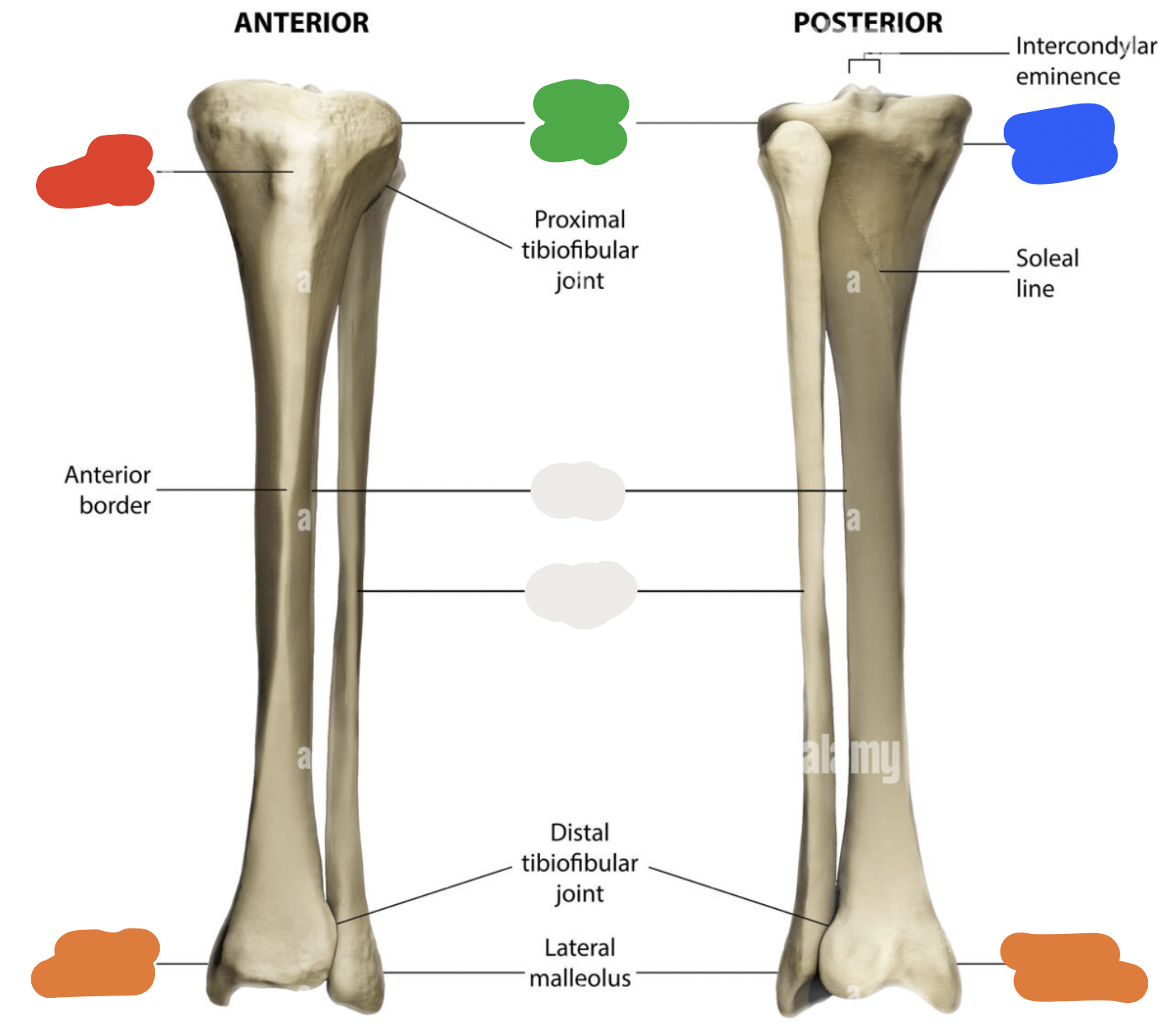
proximal end of tibia: orange
medial malleolus (because tibia will always be lateral to the fibula!)
fibula: blue
head
fibula: green
shaft
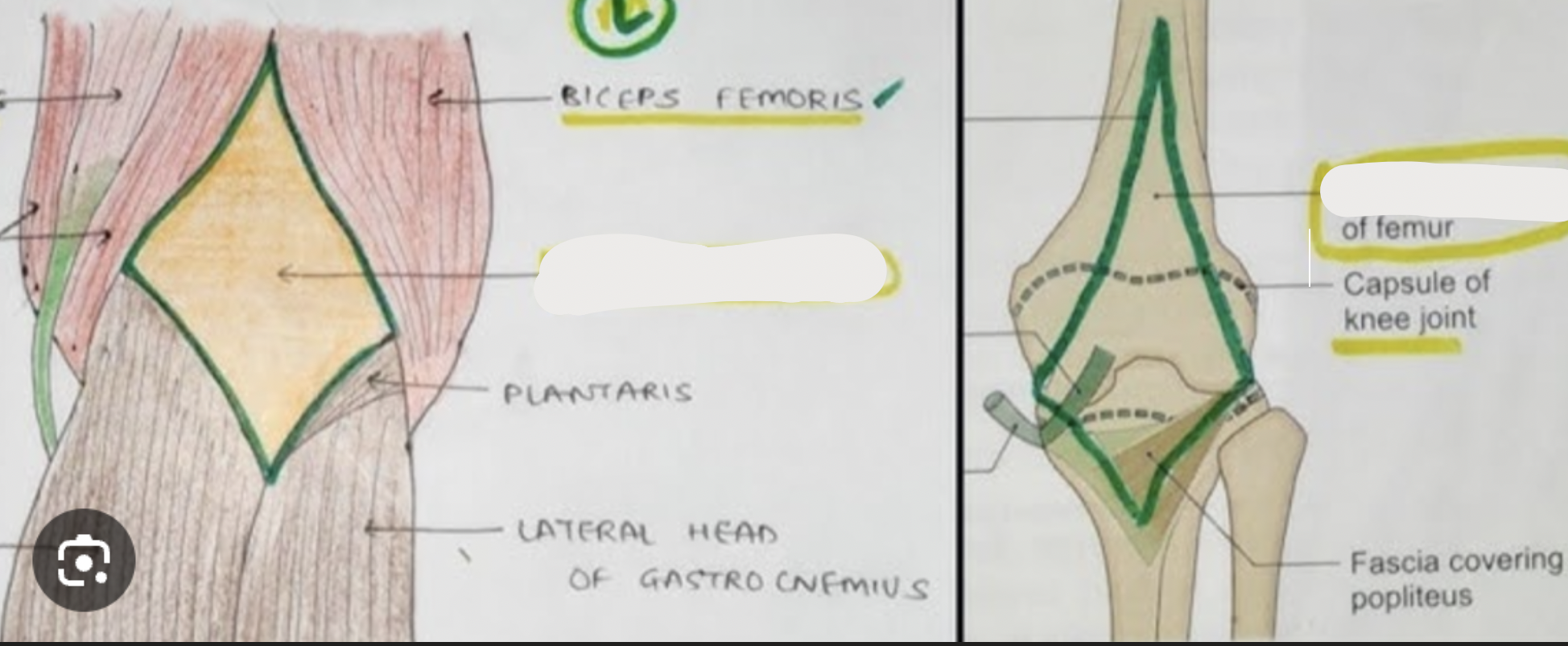
contents of popliteal fossa
popliteal artery
popliteal vein
tibial nerve
common fibular nerve
borders of popliteal fossa
supralaterally: biceps femoris
supramedially: semimembranosus
infralaterally: lateral head of gastrocnemius
inframedially: medial head of gastrocnemius
review of knee joint
femorotibial joints (lateral and medial): between the lateral and medial condyles of the femur and tibia
femoropatella joint: between the patella and femur
fibula is positioned slightly __ and __ to the tibia
posterior; lateral
joint capsule and ligaments
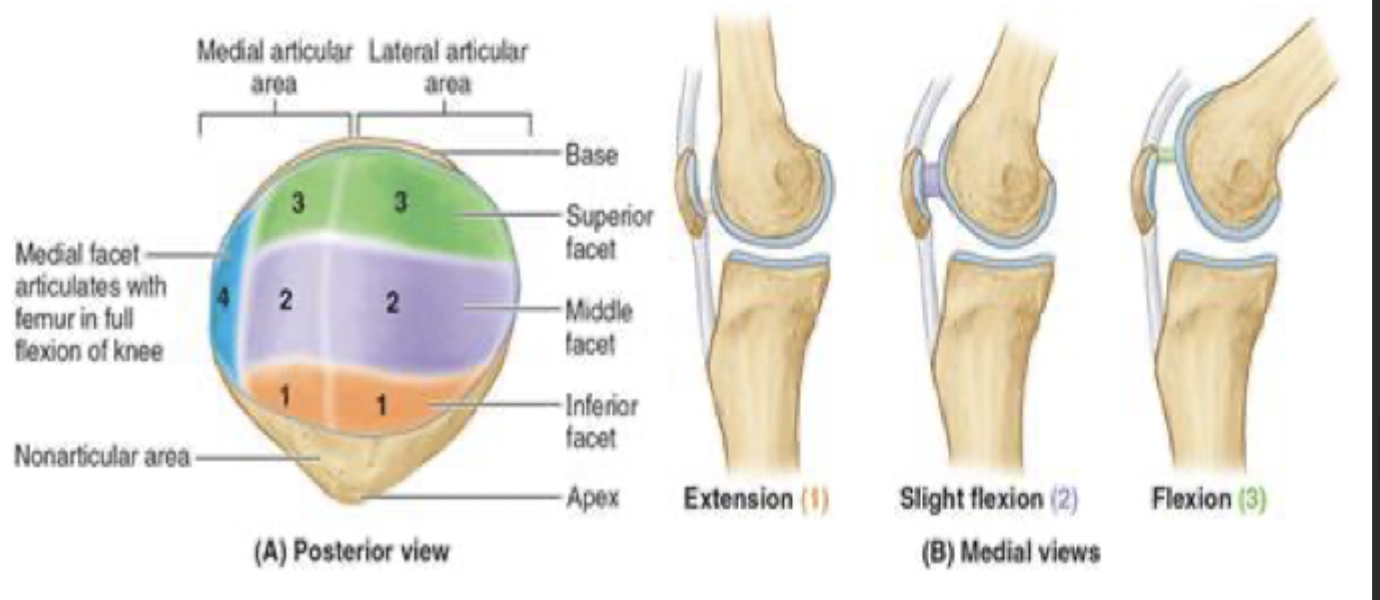
menisci: fibrocartilage plates located on the articular surface of the tibia
function: deepen the tibial surface and act as a shock absorber
lateral
medial
joint capsule and ligaments: collateral ligaments
collateral ligaments: during knee extension, the ligaments are taut and during knee flexion, they are loose (which allows for a little rotation)
tibial or medial collateral ligament:
fused to the joint capsule and the meniscus
function: stabilize the knee joint during knee ROM
fibular or lateral collateral ligament:
attaches into the head of the fibula
not fused to joint capsule or meniscus- so more flexibility
function: stabilize the knee joint during knee ROM
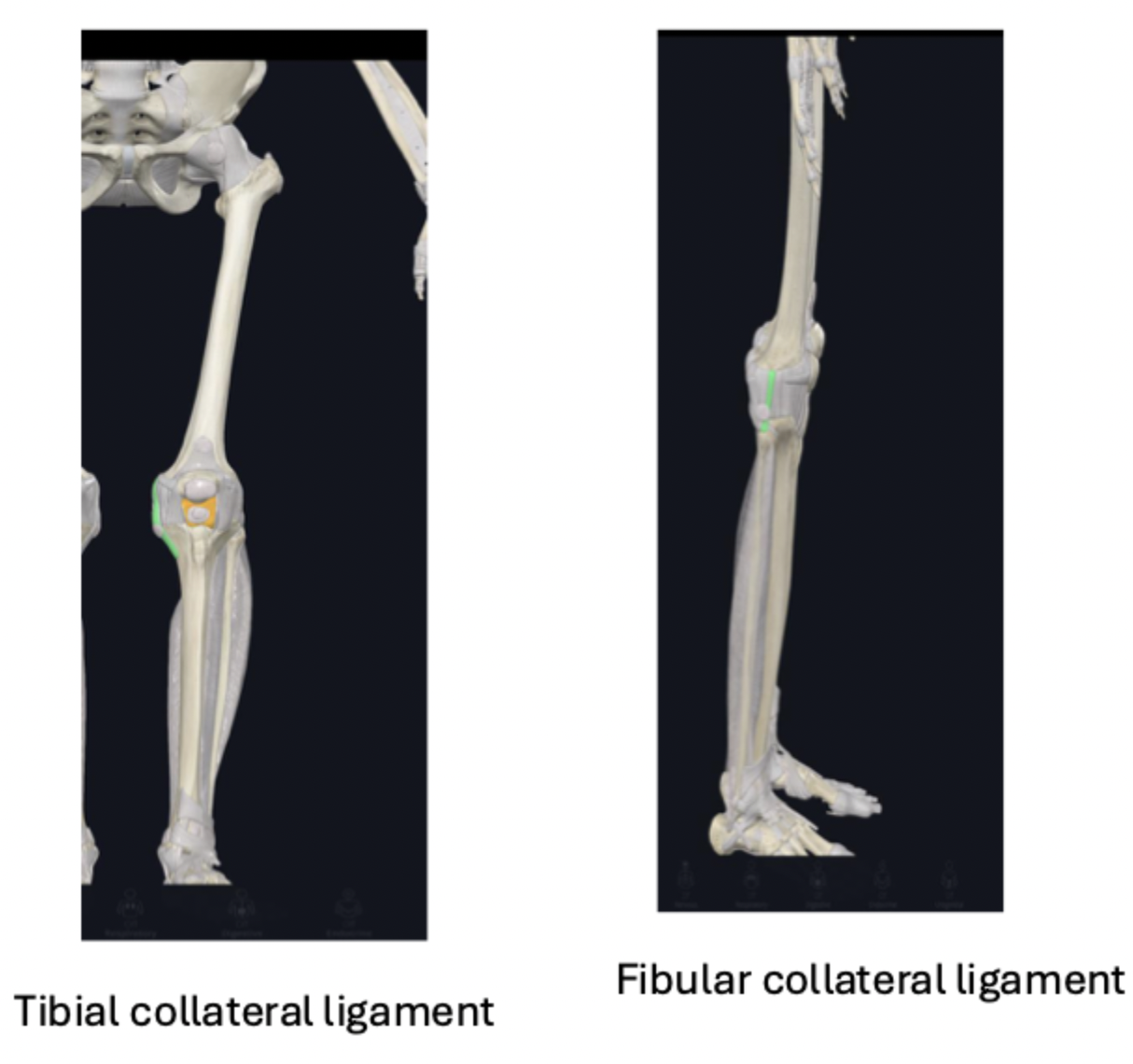
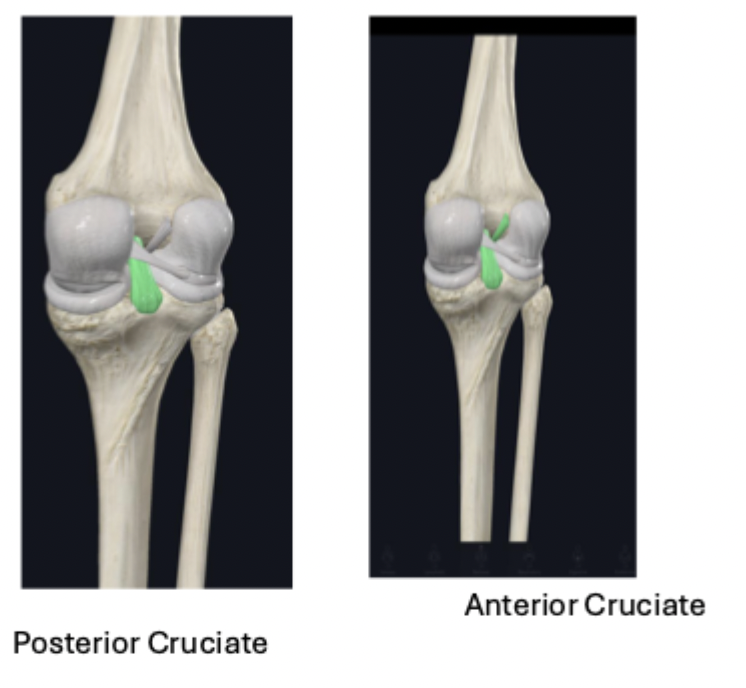
joint capsule and ligaments: cruciate ligaments
intra-articular ligaments
anterior cruciate ligament:
function: provide stability and prevent hyperextension
posterior cruciate ligament:
stronger and thicker than the anterior
function: prevent hyperextension of the knee joint and when weight bearing on a flexed knee, it helps to stabilize the femur, especially when walking down a steep hill
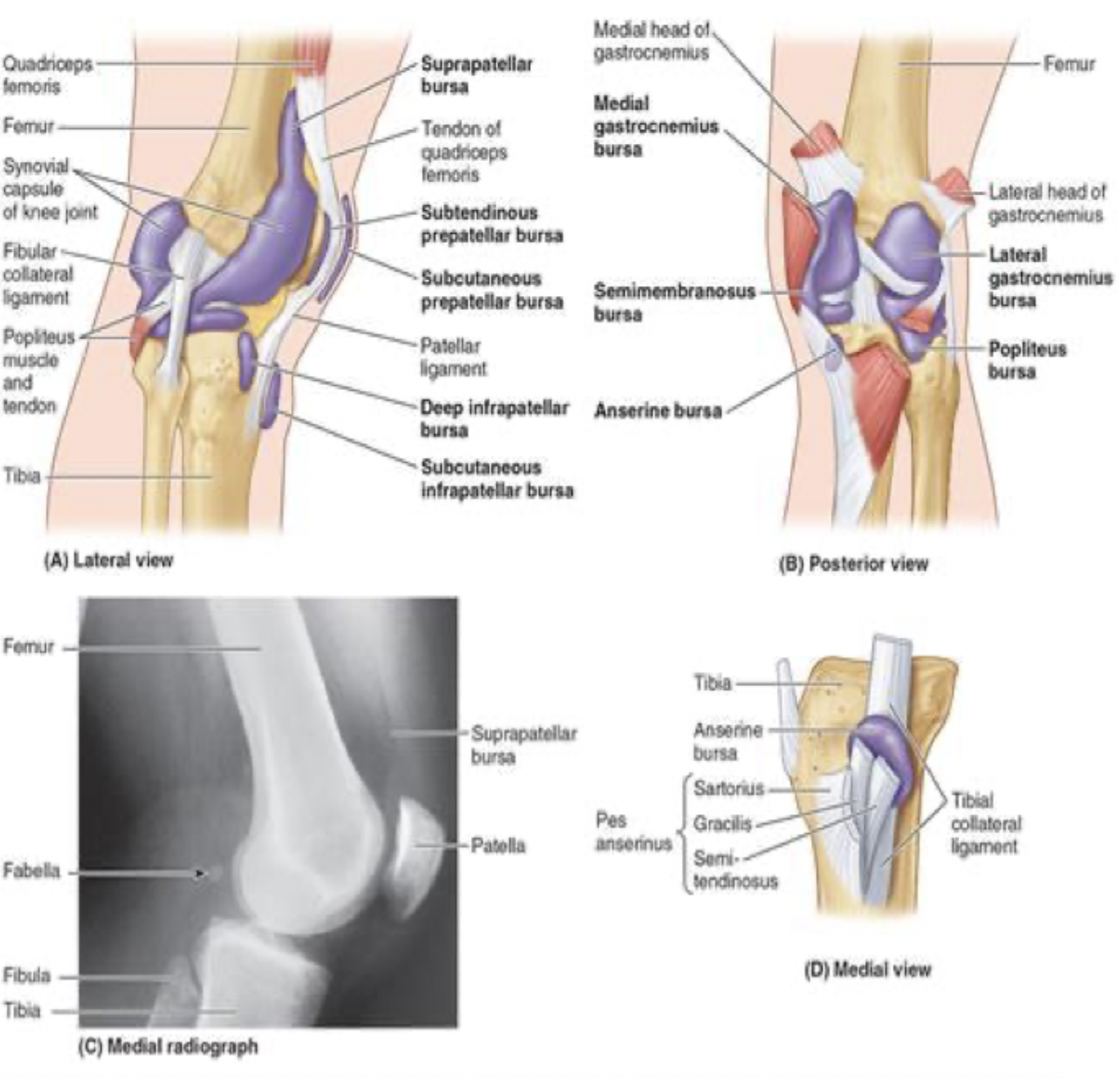
femoropatella articulation and ligament
patellar ligament: begins at the distal end of the quadriceps tendon and crosses over and attaches to the patella and then crosses over and attaches into the tibial tuberosity
additional knee joint supports
medial
pes anserinus: this is the insertions of the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinous
medial head of the gastrocnemius
lateral
iliotibial tract
biceps femoris insertion on head of fibula
lateral head of gastrocnemius
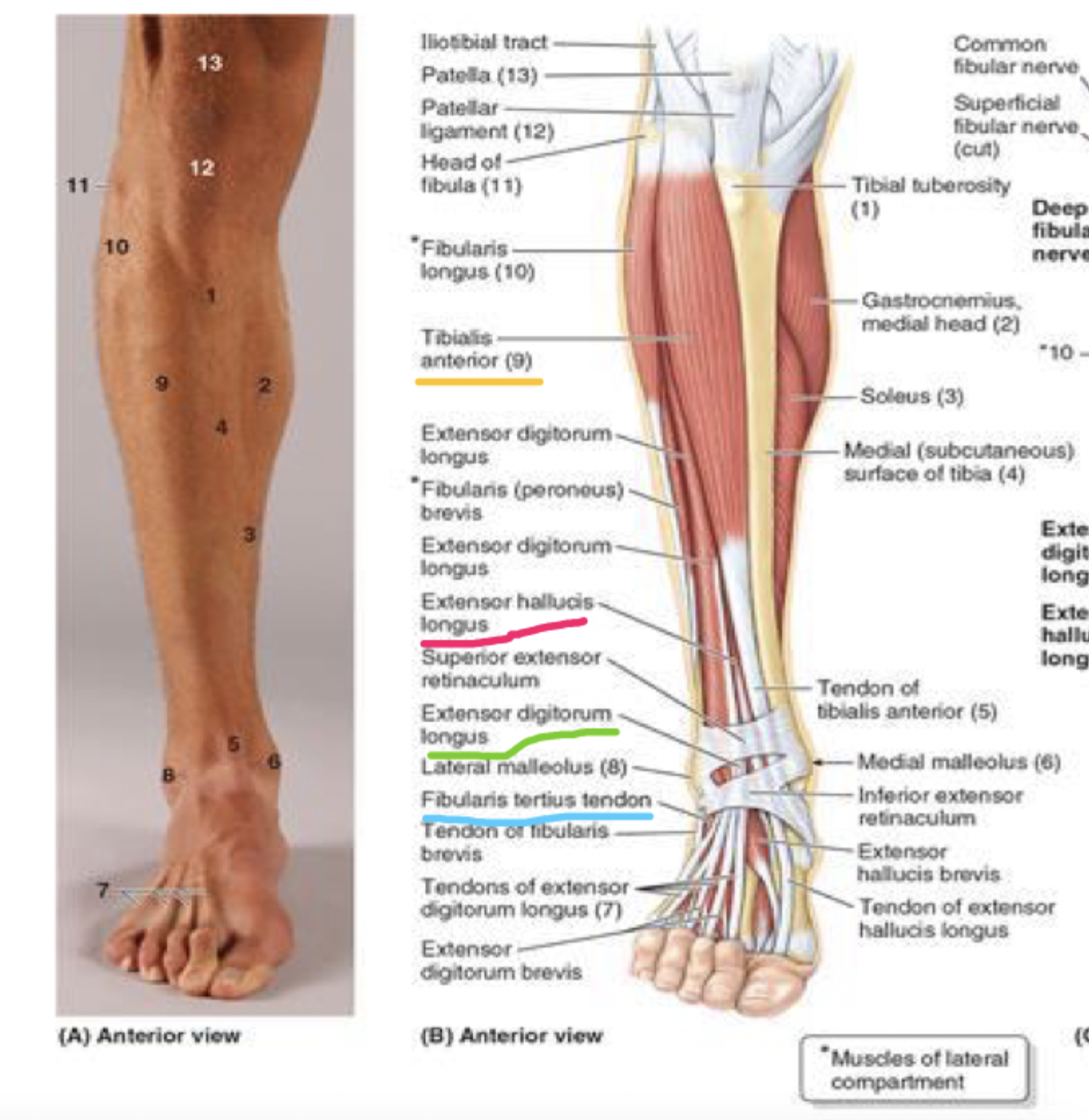
muscles of the anterior compartment
dorsiflexion
tibialis anterior (TA)
extensor hallucis longus (EHL)
extensor digitorum longus (EDL)
fibularis tertius
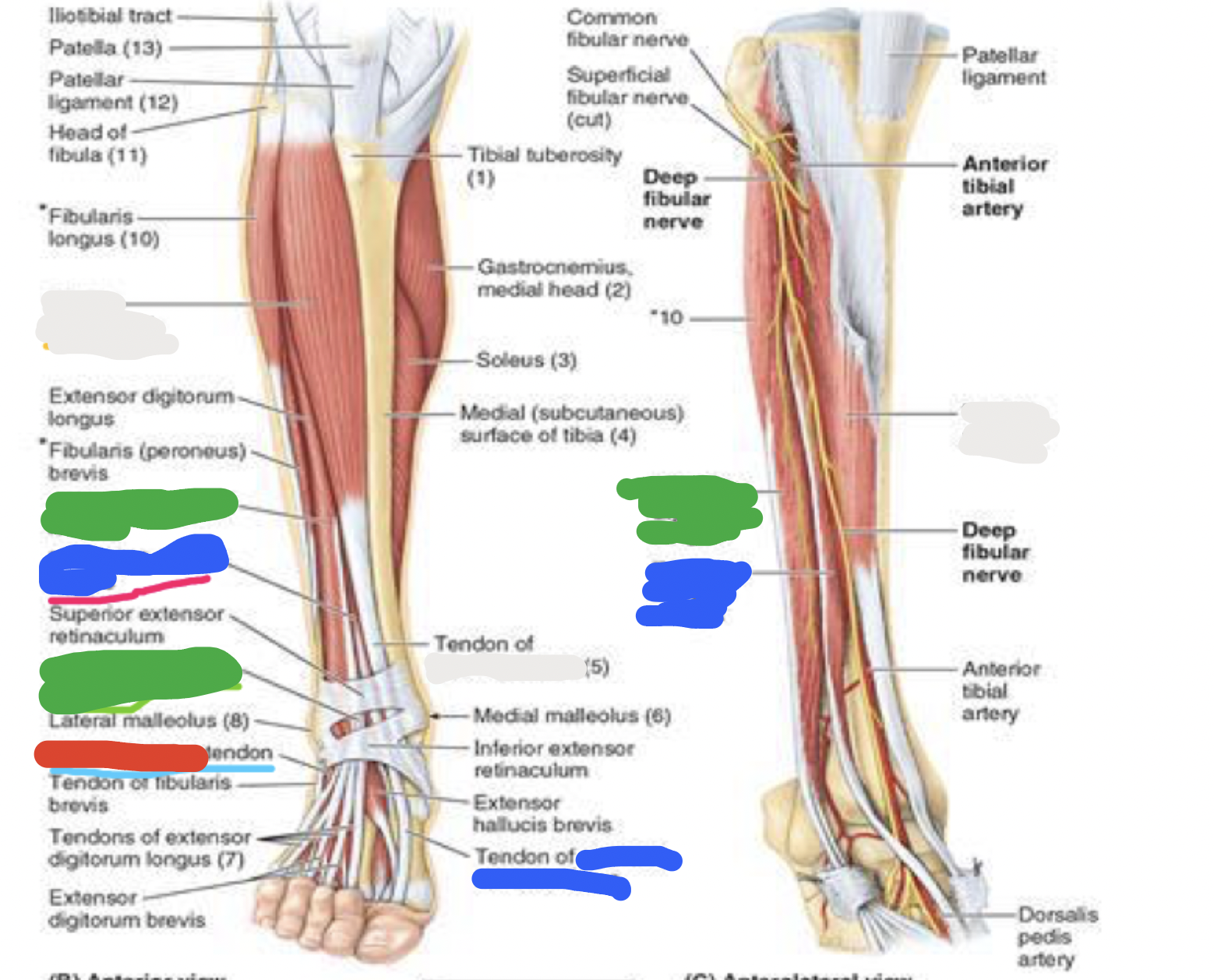
muscles of anterior compartment: white; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
tibialis anterior (TA)
proximal attachment
lateral condyle
tibia
interosseous membrane
distal attachment
medial cuneiform
base of 1st metatarsal
innervation
deep fibular nerve
main actions
dorsiflexes ankle joint
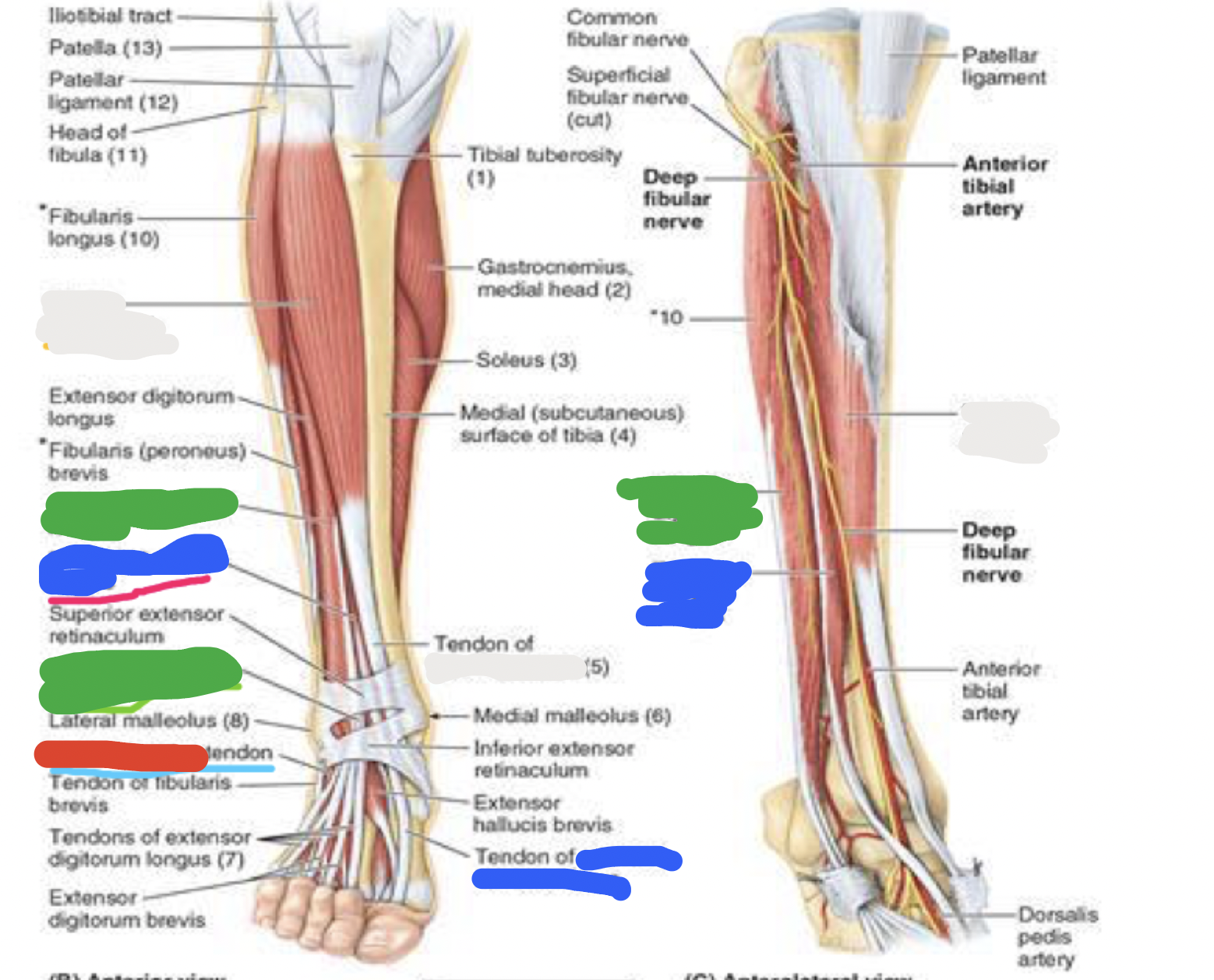
muscles of anterior compartment: blue; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
extensor hallucis longus (EHL)
proximal attachment
anterior surface of fibula
interosseous membrane
distal attachment
dorsal base of distal phalanx of great toe
innervation
deep fibular nerve
main actions
extends great toe
dorsiflexes ankle joint
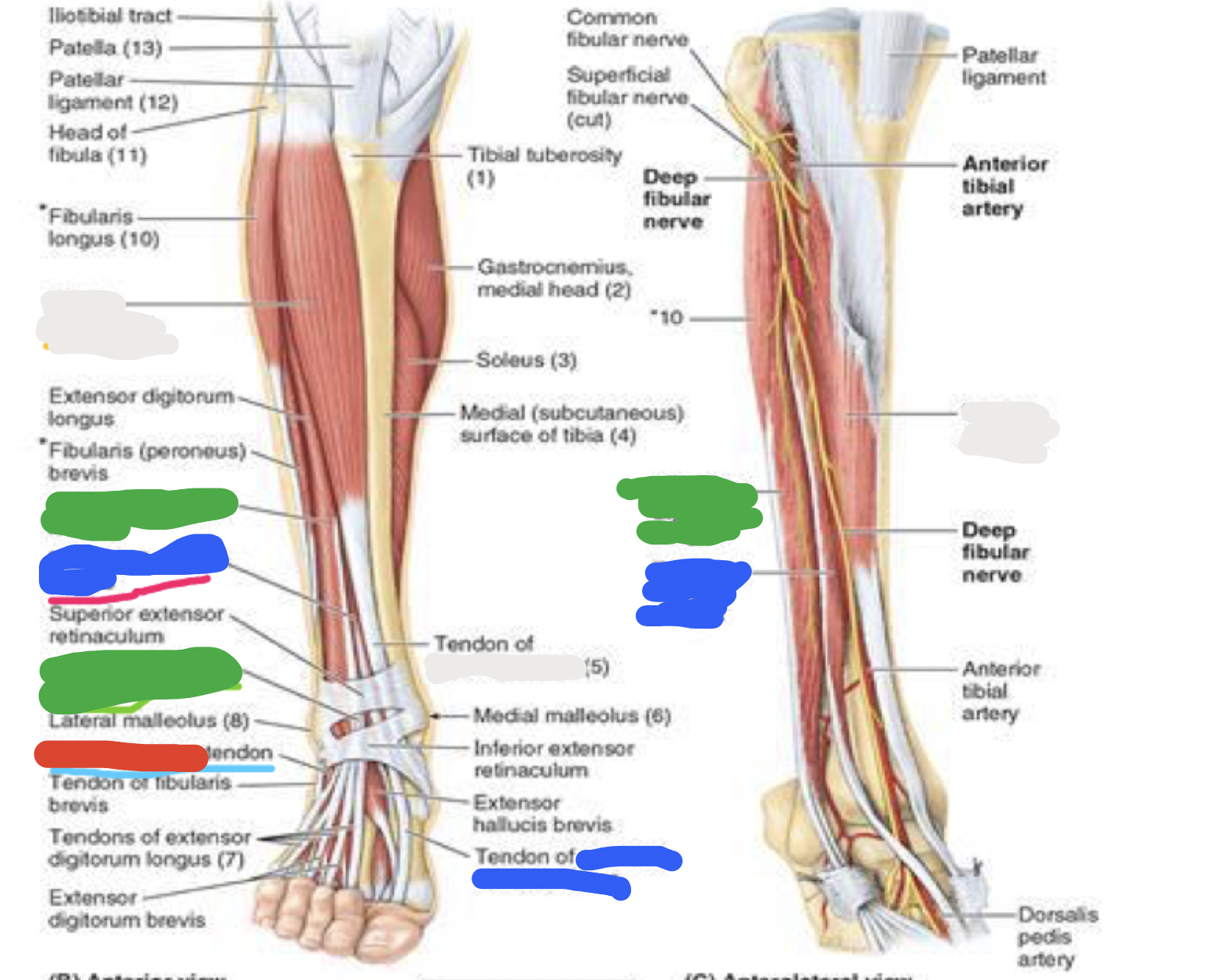
muscles of anterior compartment: green; proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
extensor digitorum longus (EDL)
proximal attachment
lateral condyle of tibia
anterior surface of fibula
interosseous membrane
distal attachment
middle and distal phalanges of lateral 4 digits
innervation
deep fibular nerve
main actions
extends lateral 4 digits
dorsiflexes ankle joint
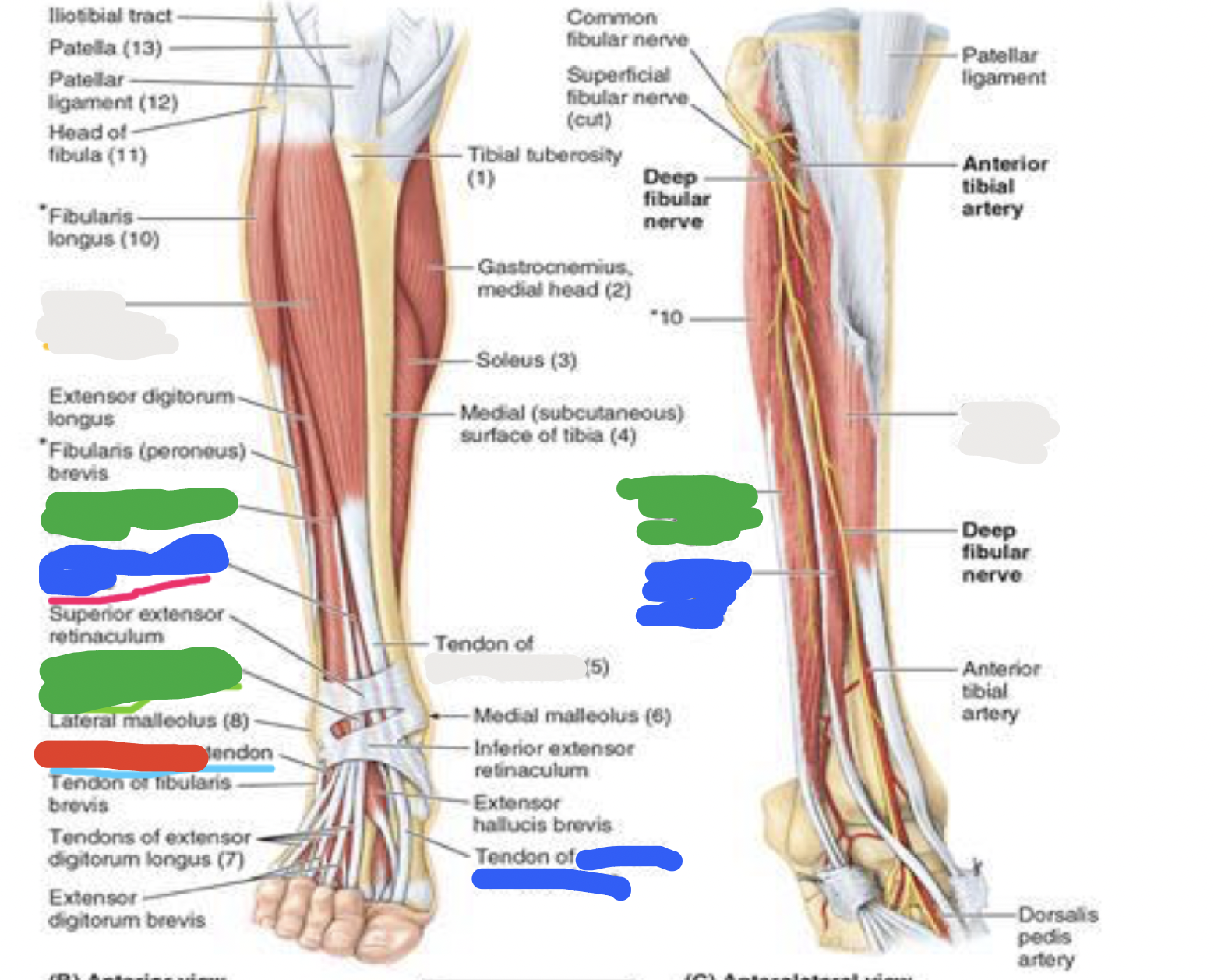
muscles of anterior compartment: red; proximal attachment, innervation, main actions
fibularis tertius
proximal attachment
anterior surface of fibula
interosseus membrane
innervation
deep fibular nerve
main actions
dorsiflexes ankle joint
eversion
muscles of the lateral compartment: fibularis longus (FL); proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
head and lateral surface of fibula
distal attachment
base of 1st metatarsal
medial cuneiform
innervation
superficial fibular nerve
main actions
***evert
muscles of the lateral compartment: fibularis brevis (FB); proximal attachment, distal attachment, innervation, main actions
proximal attachment
lateral surface of fibula
distal attachment
dorsal surface of 5th metatarsal
innervation
superficial fibular nerve
main actions
***evert
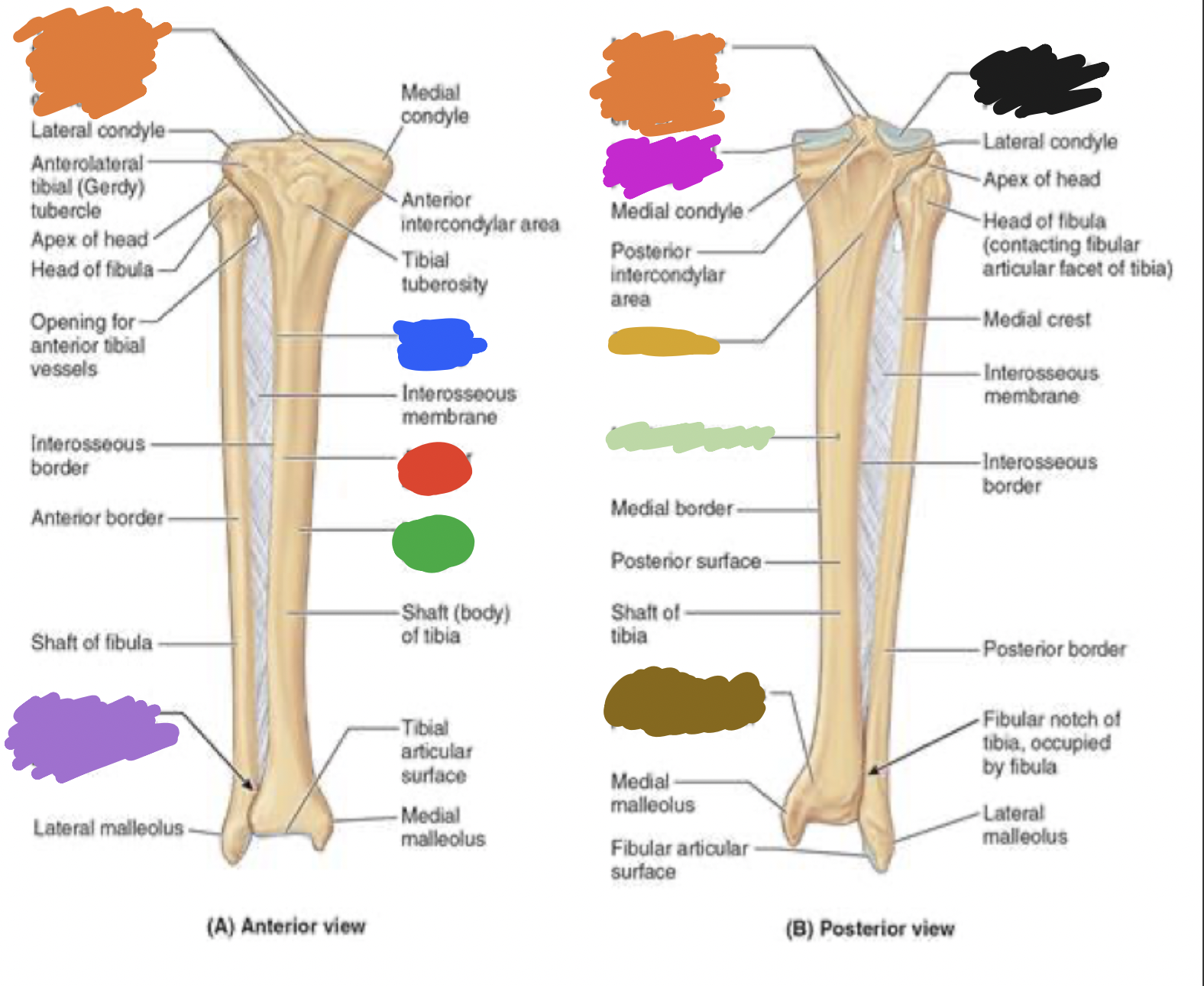
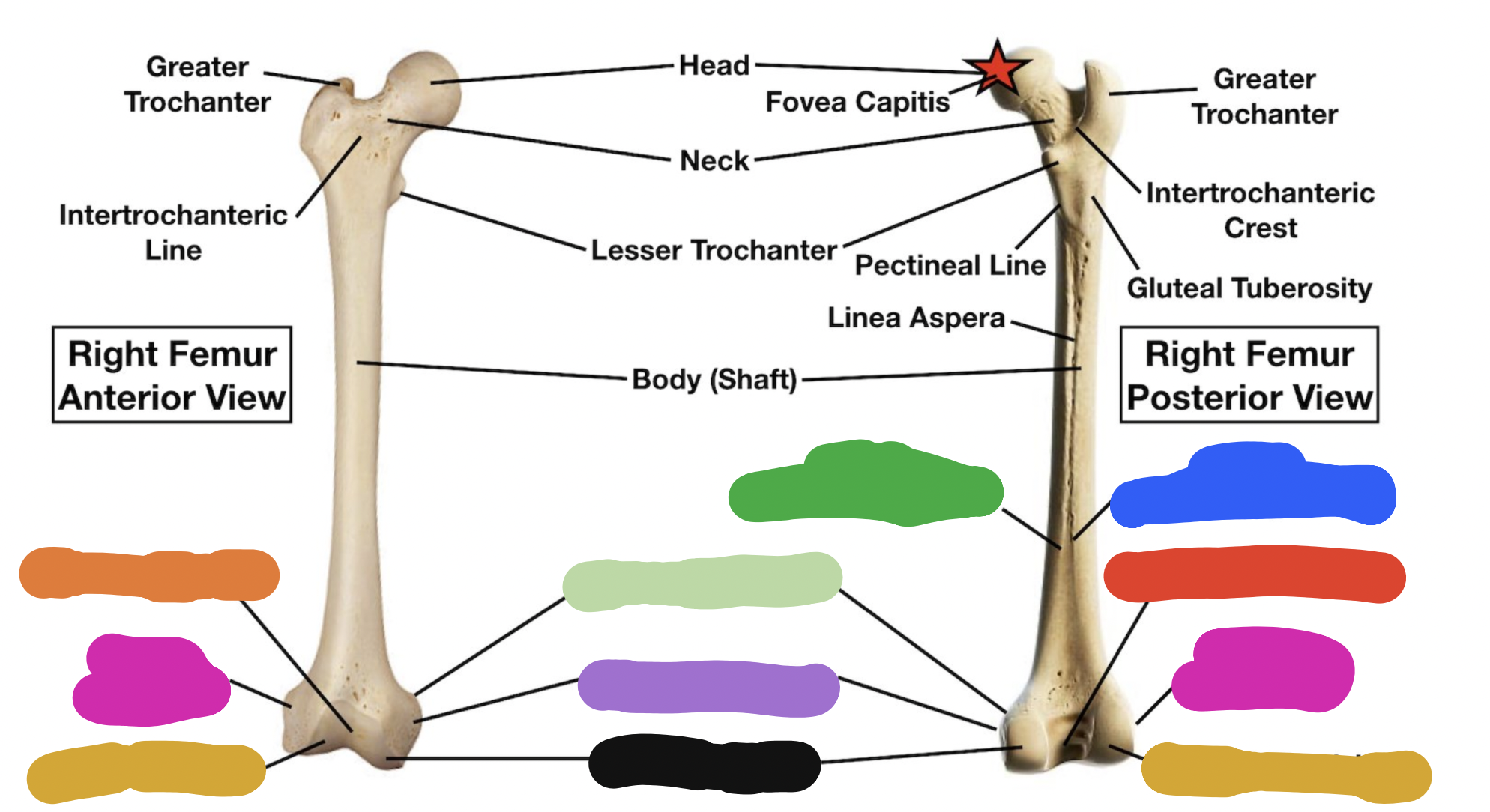
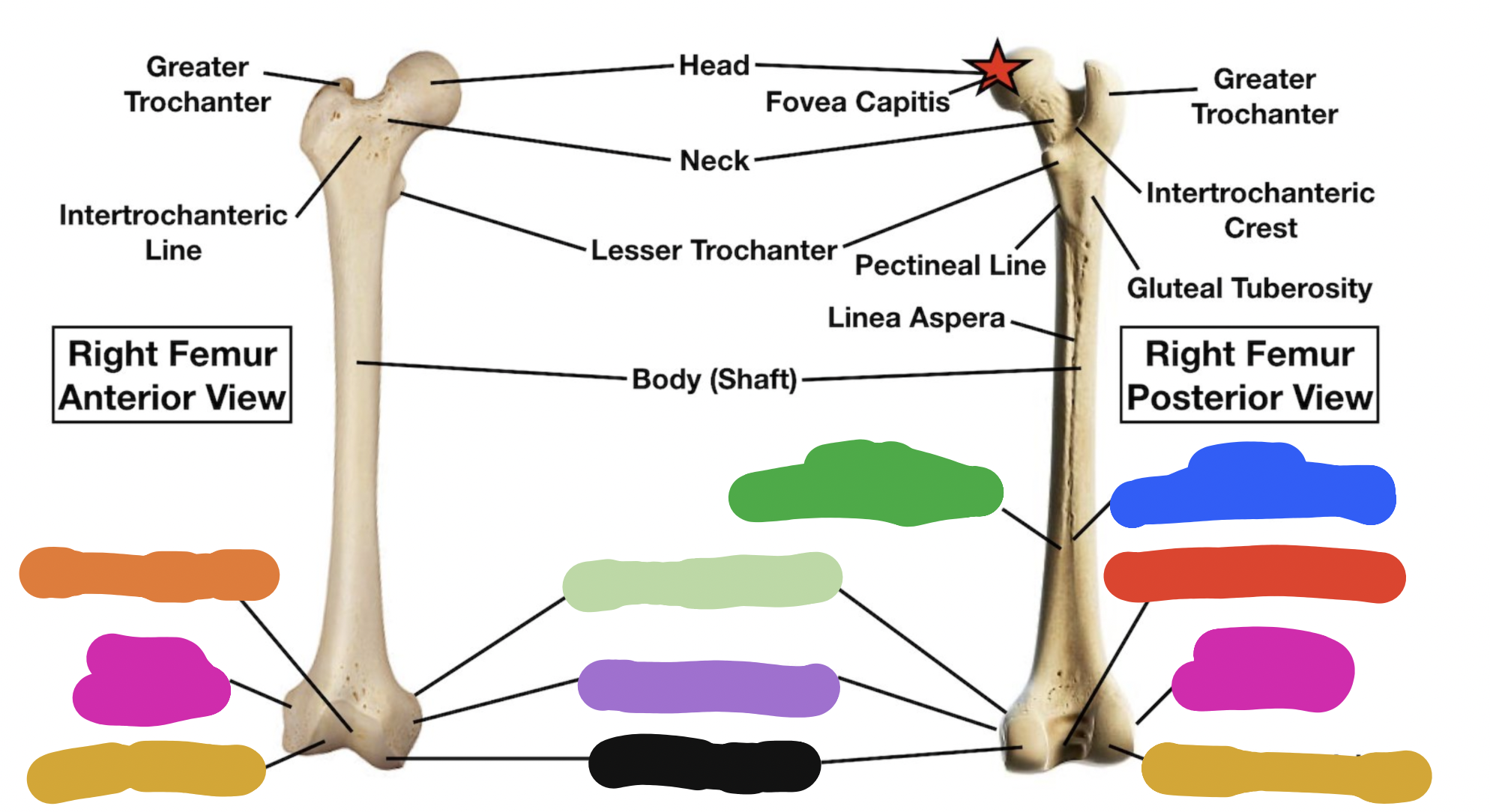
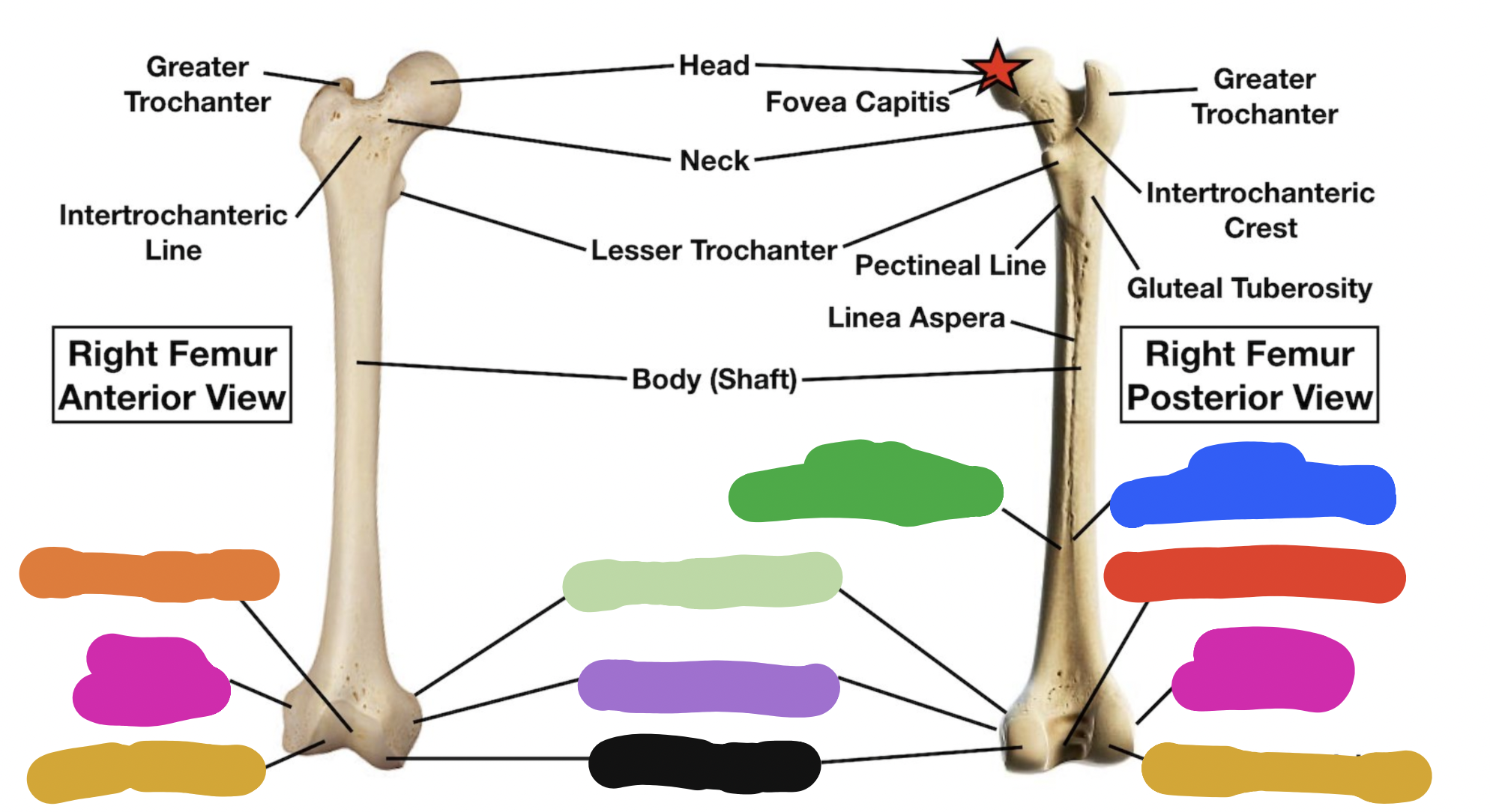
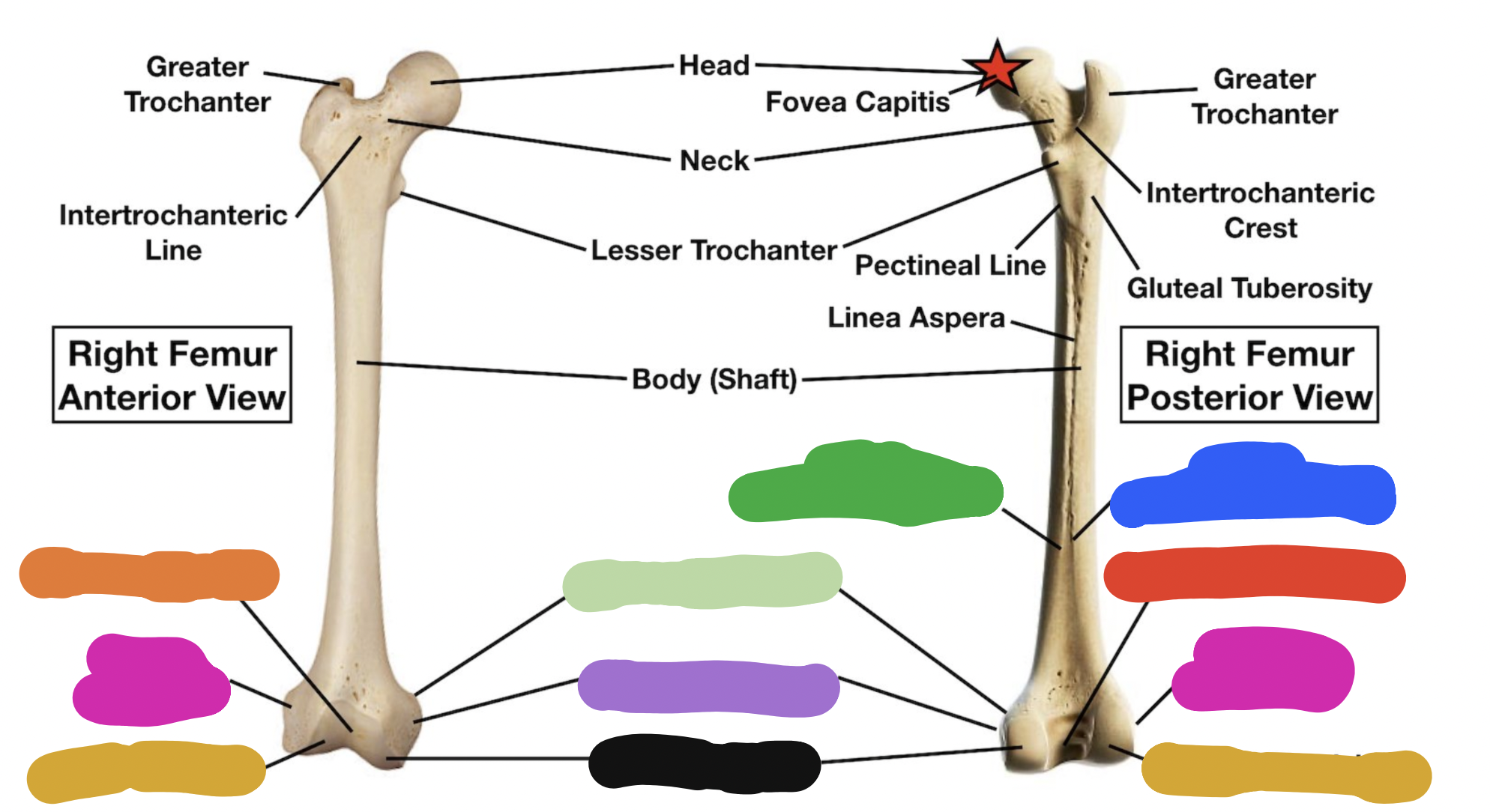
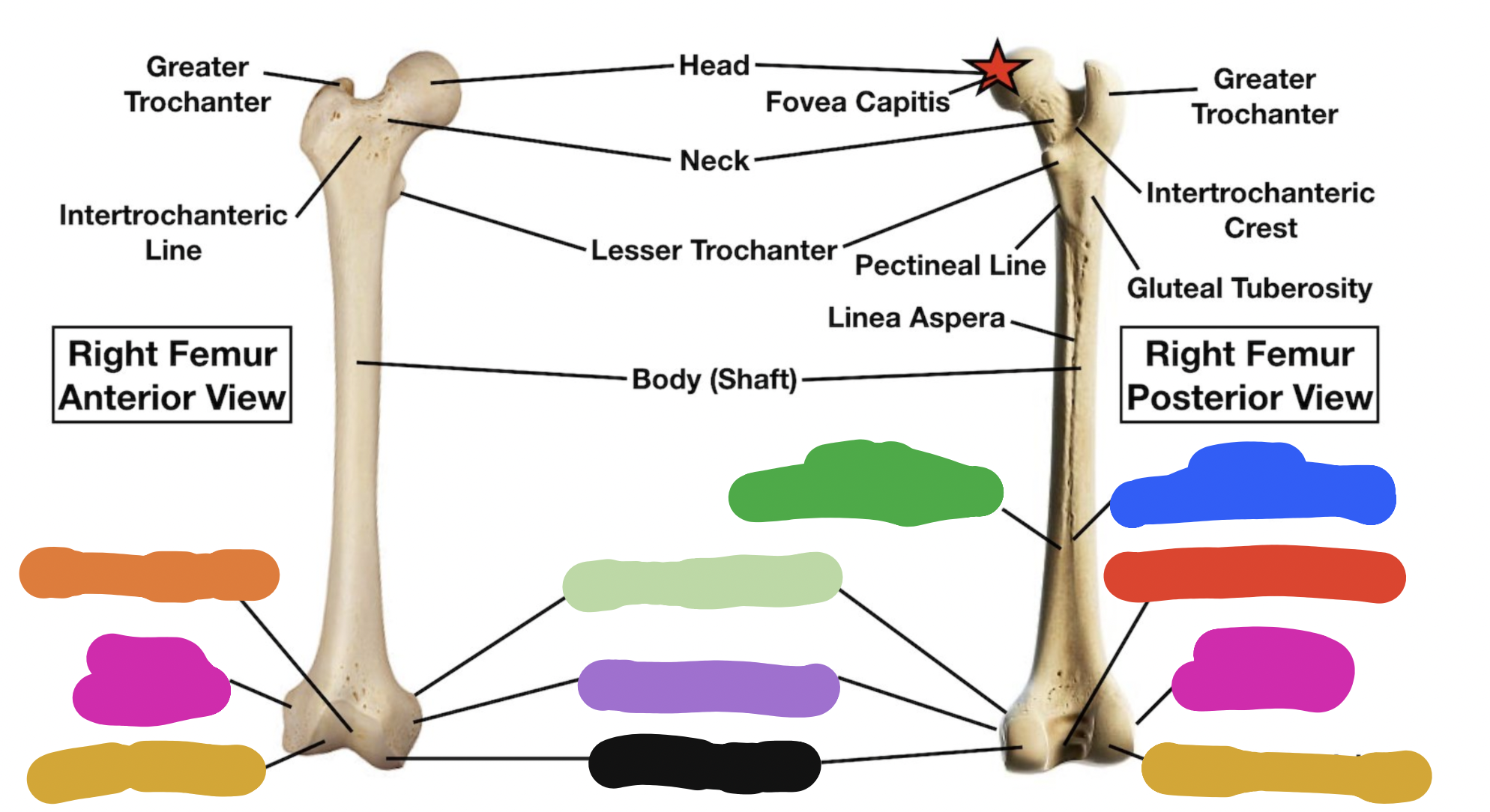
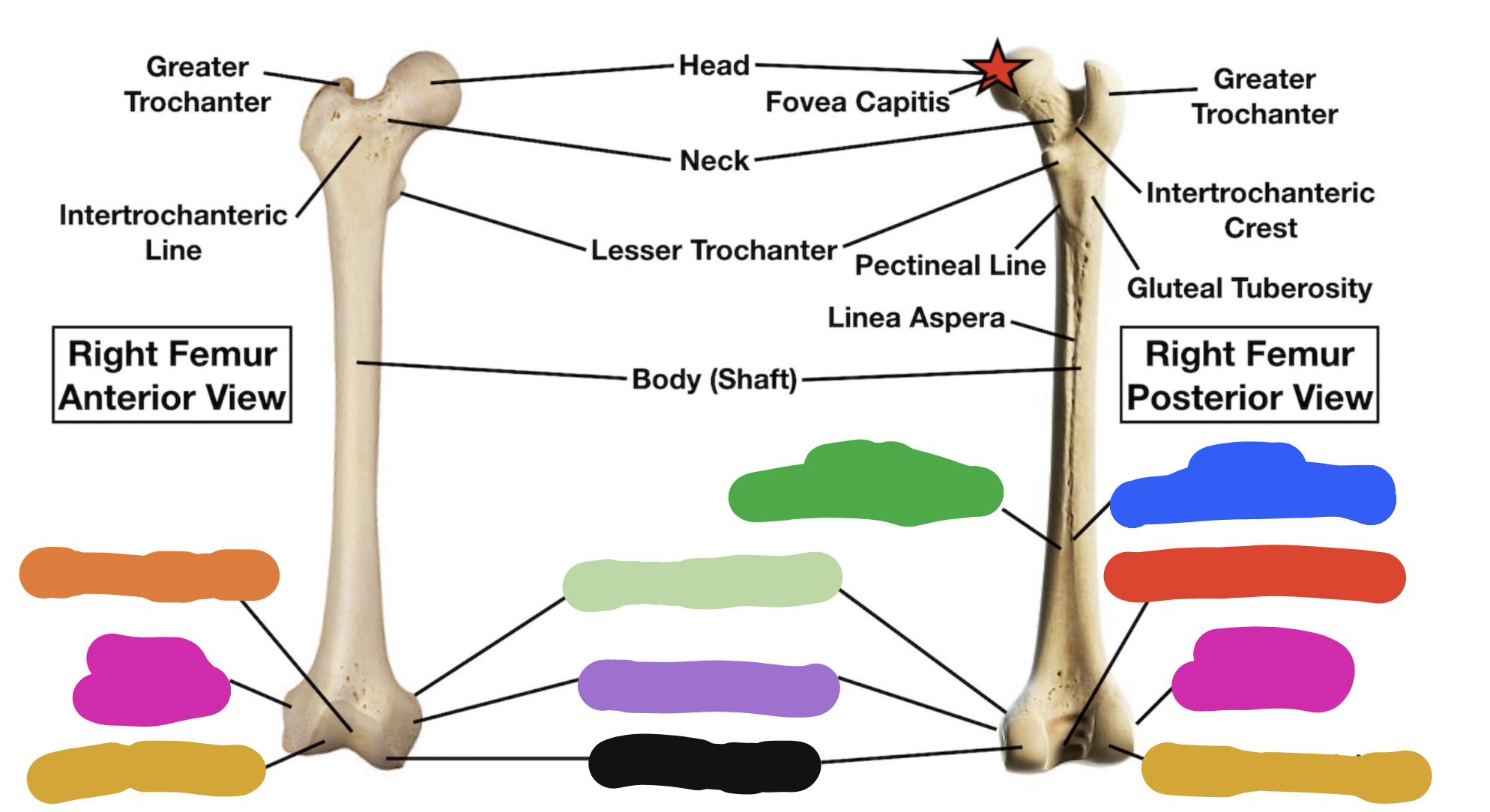
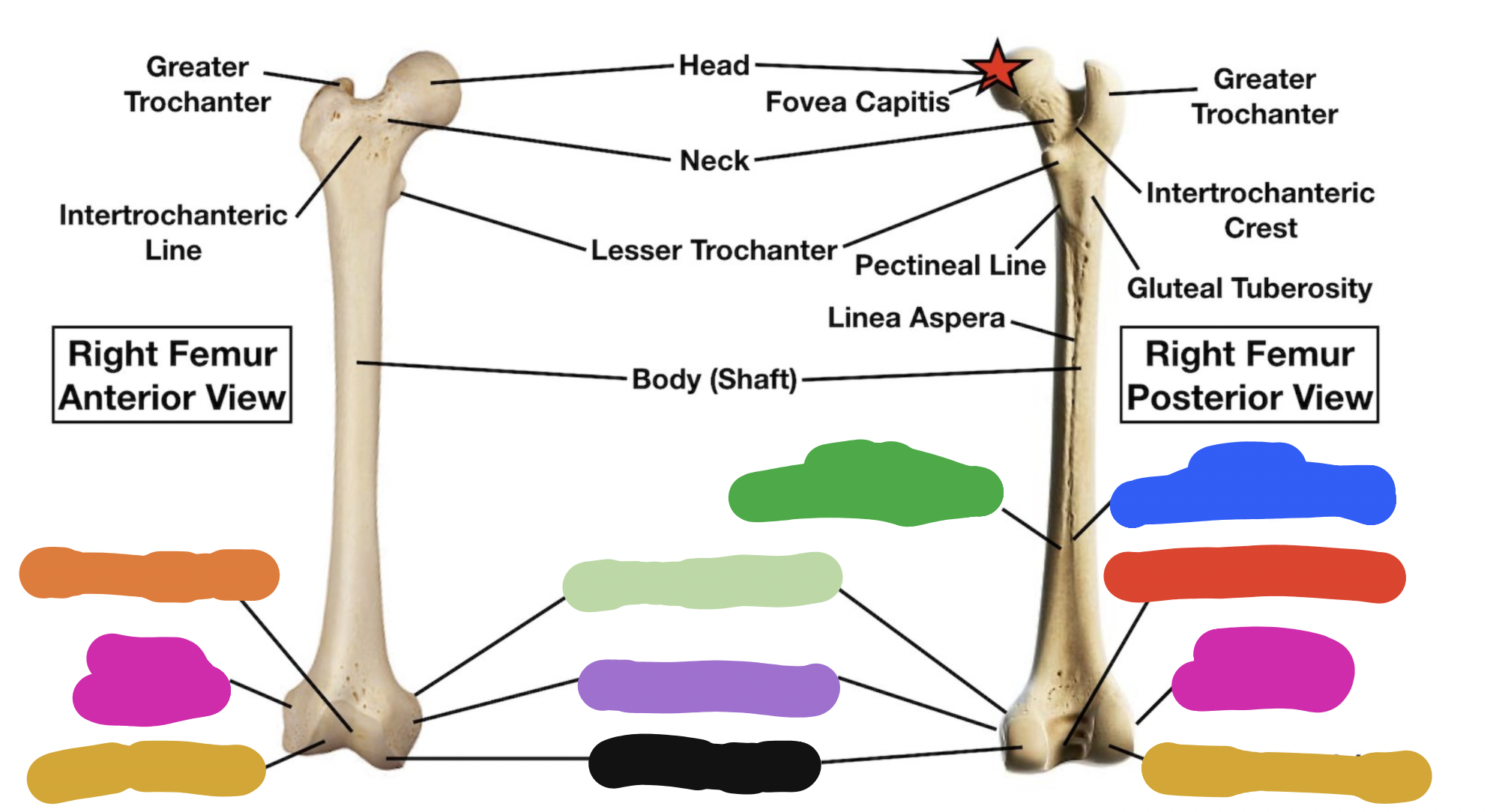
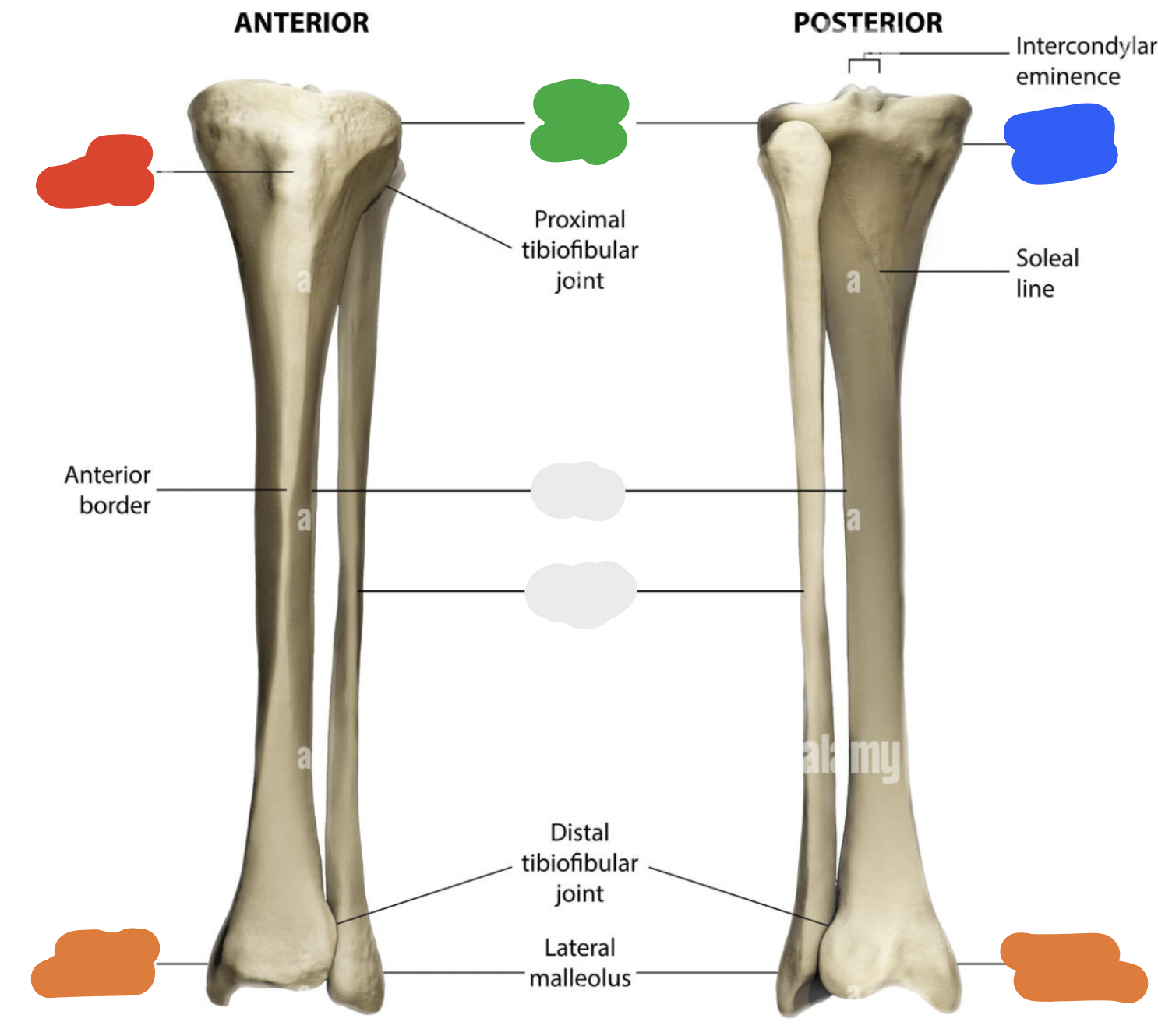
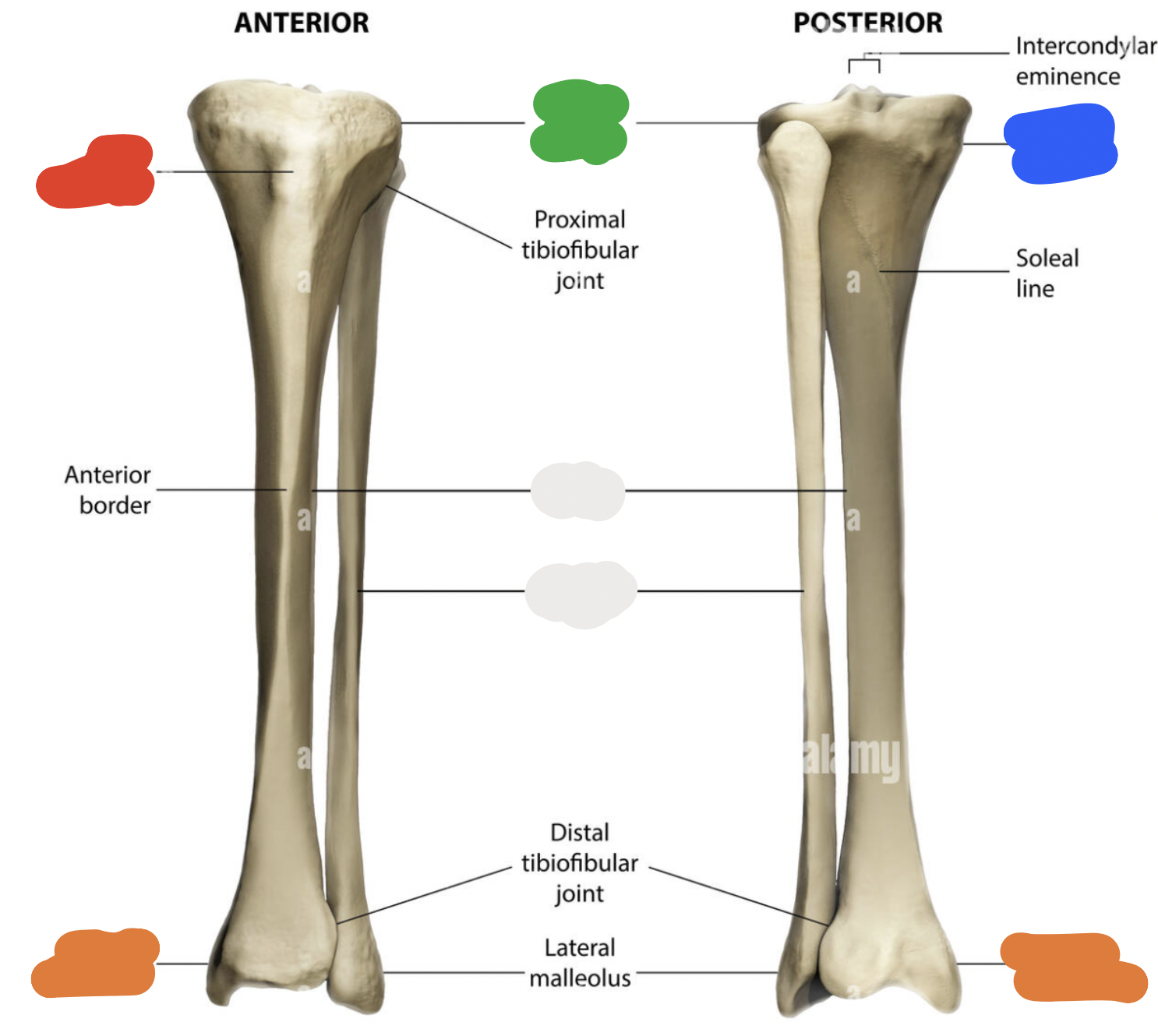
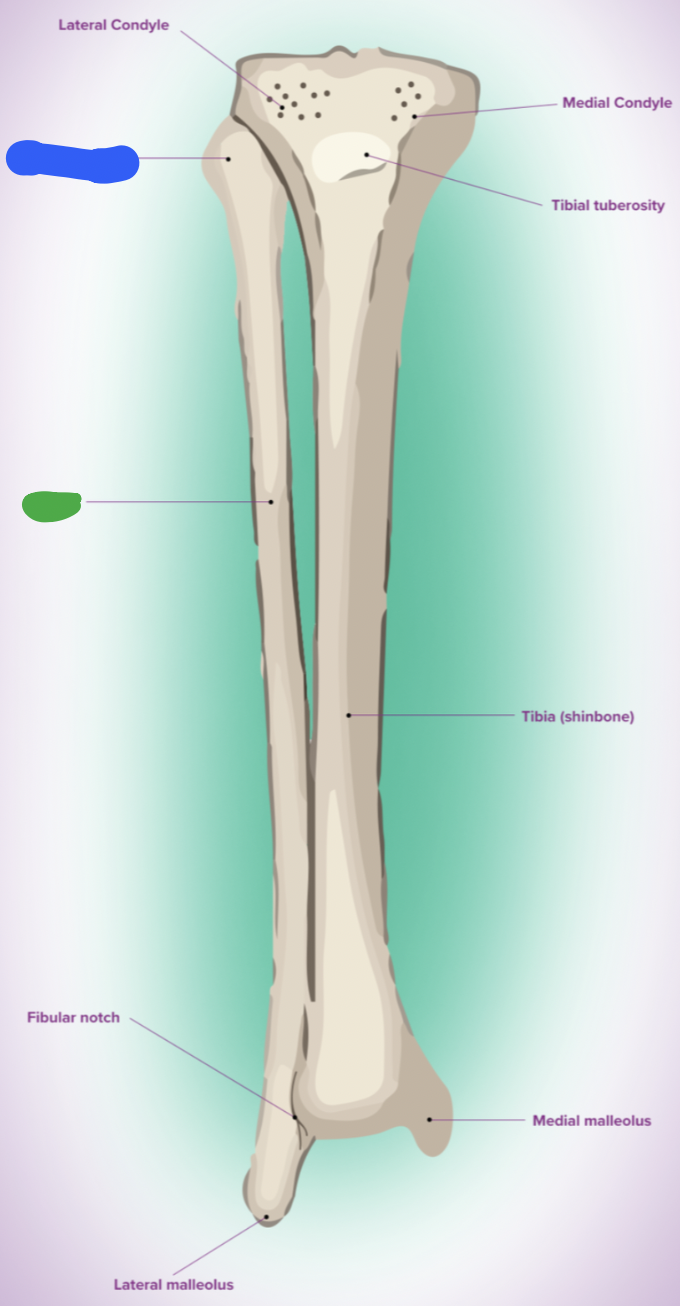
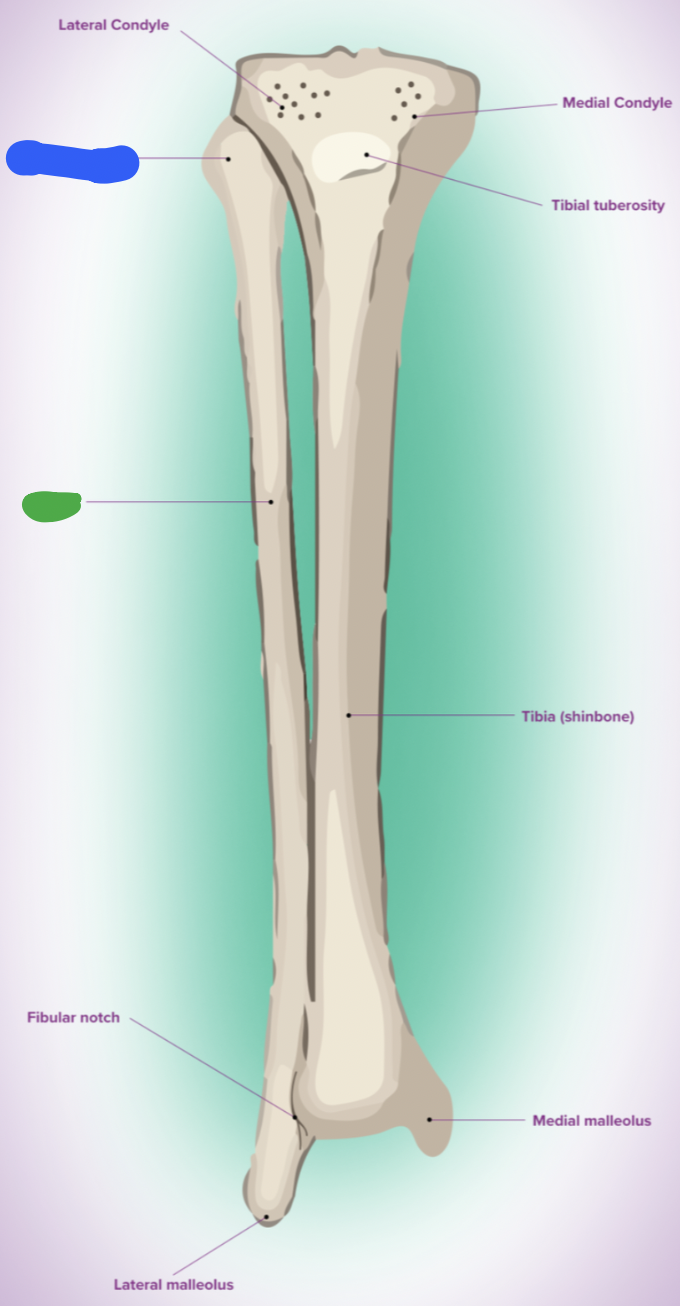
shaft of tibia: blue
lateral surface
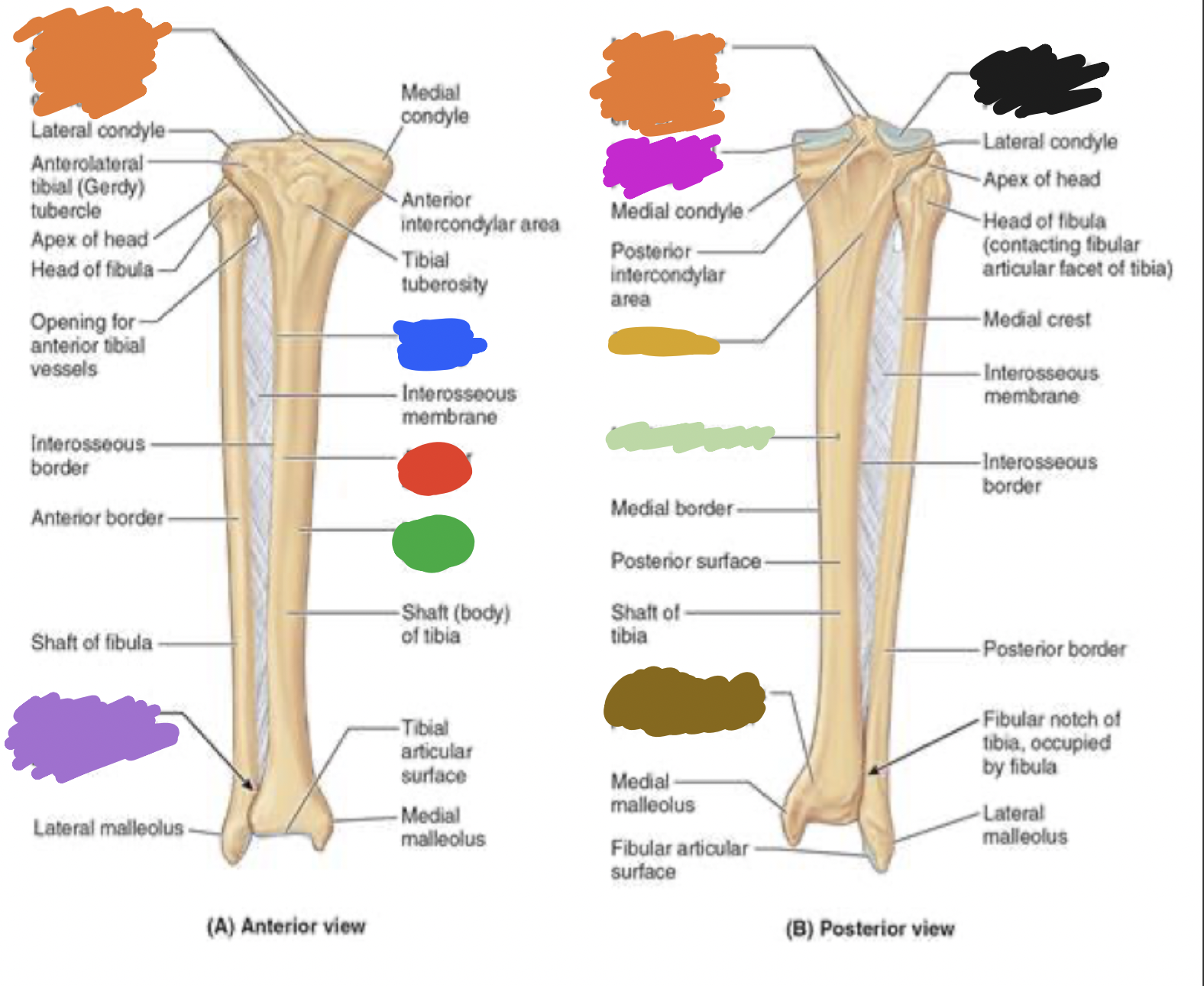
shaft of tibia: red
anterior surface
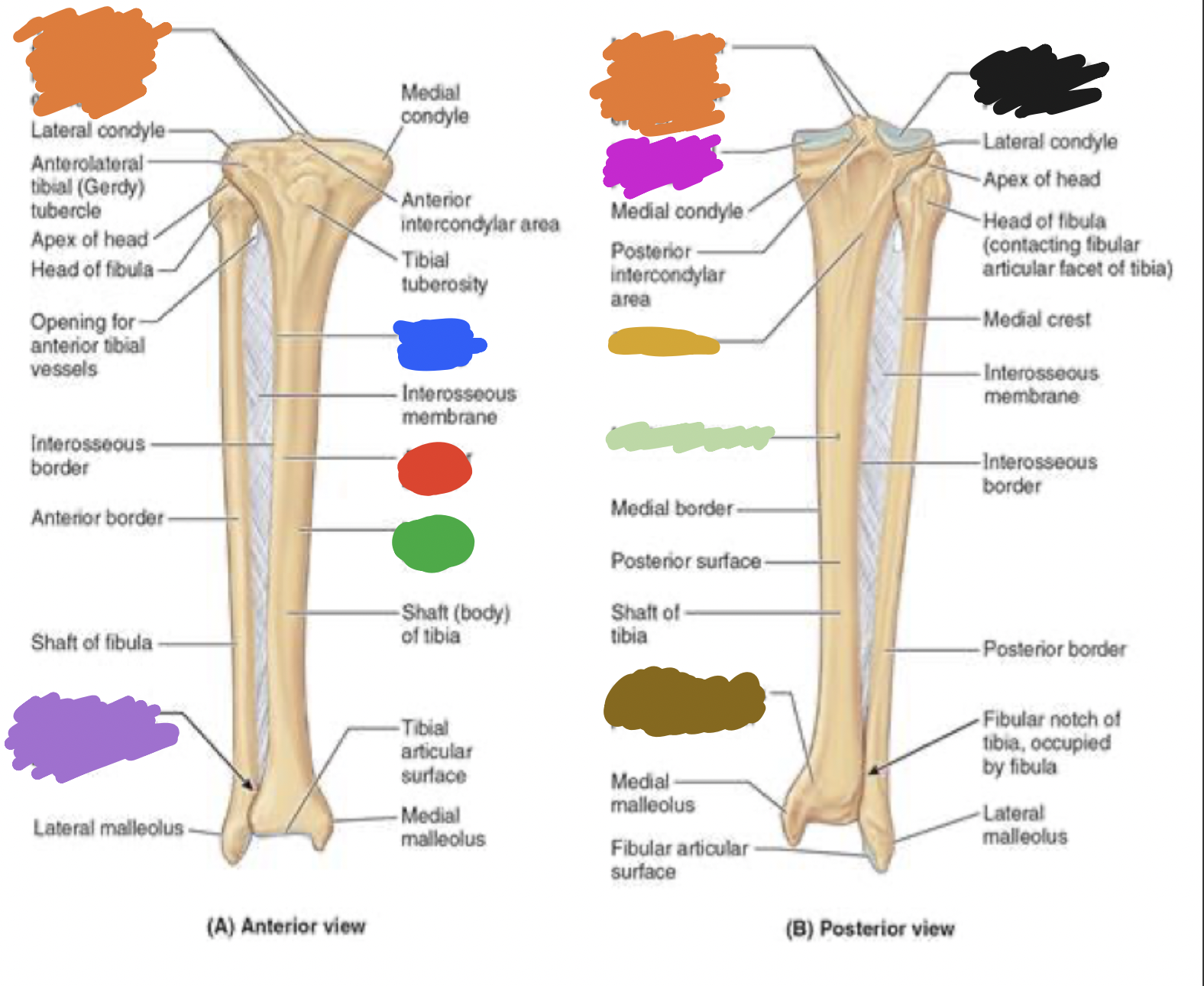
shaft of tibia: green
medial surface
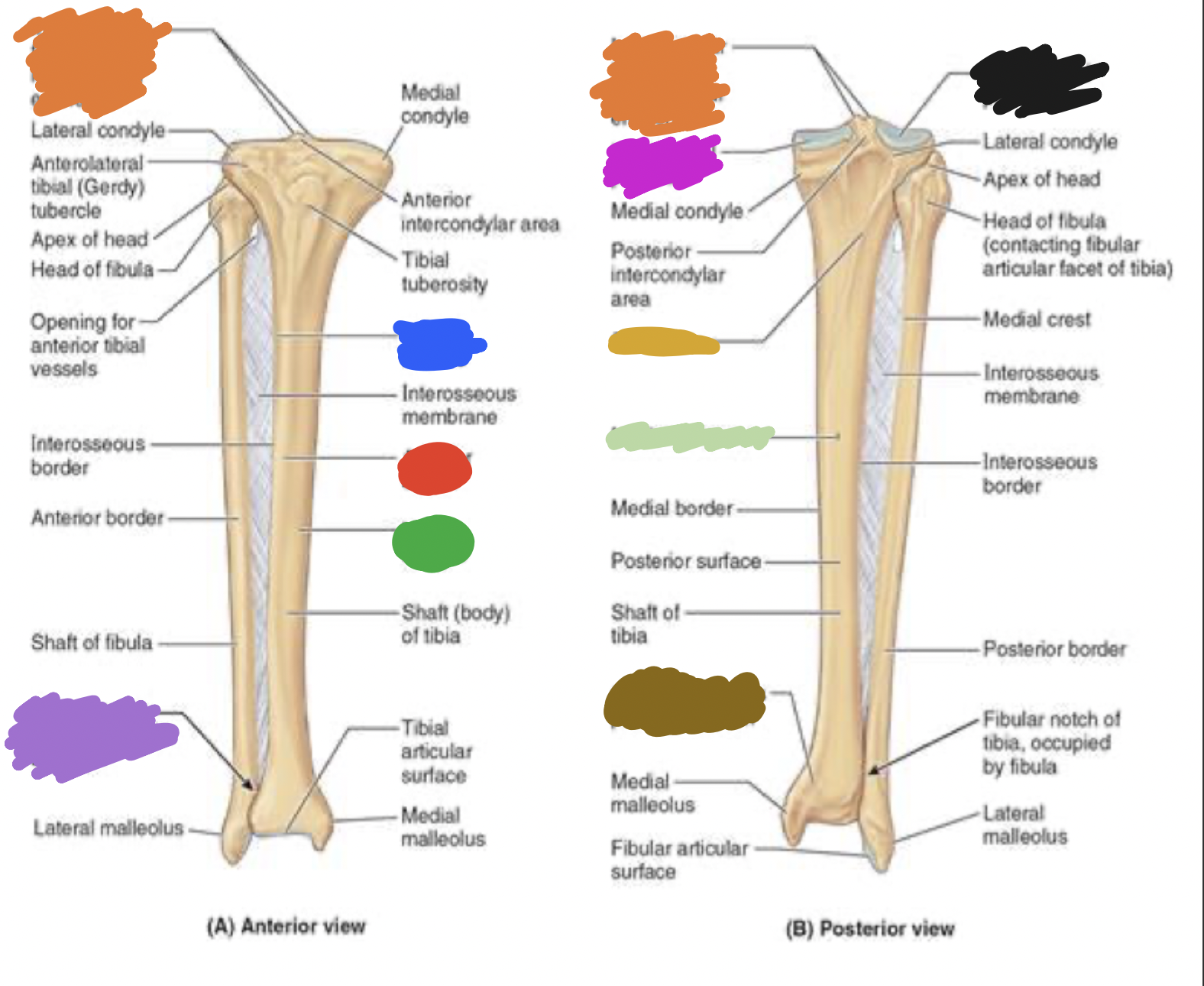
__ of the tibia: purple
fibula notch
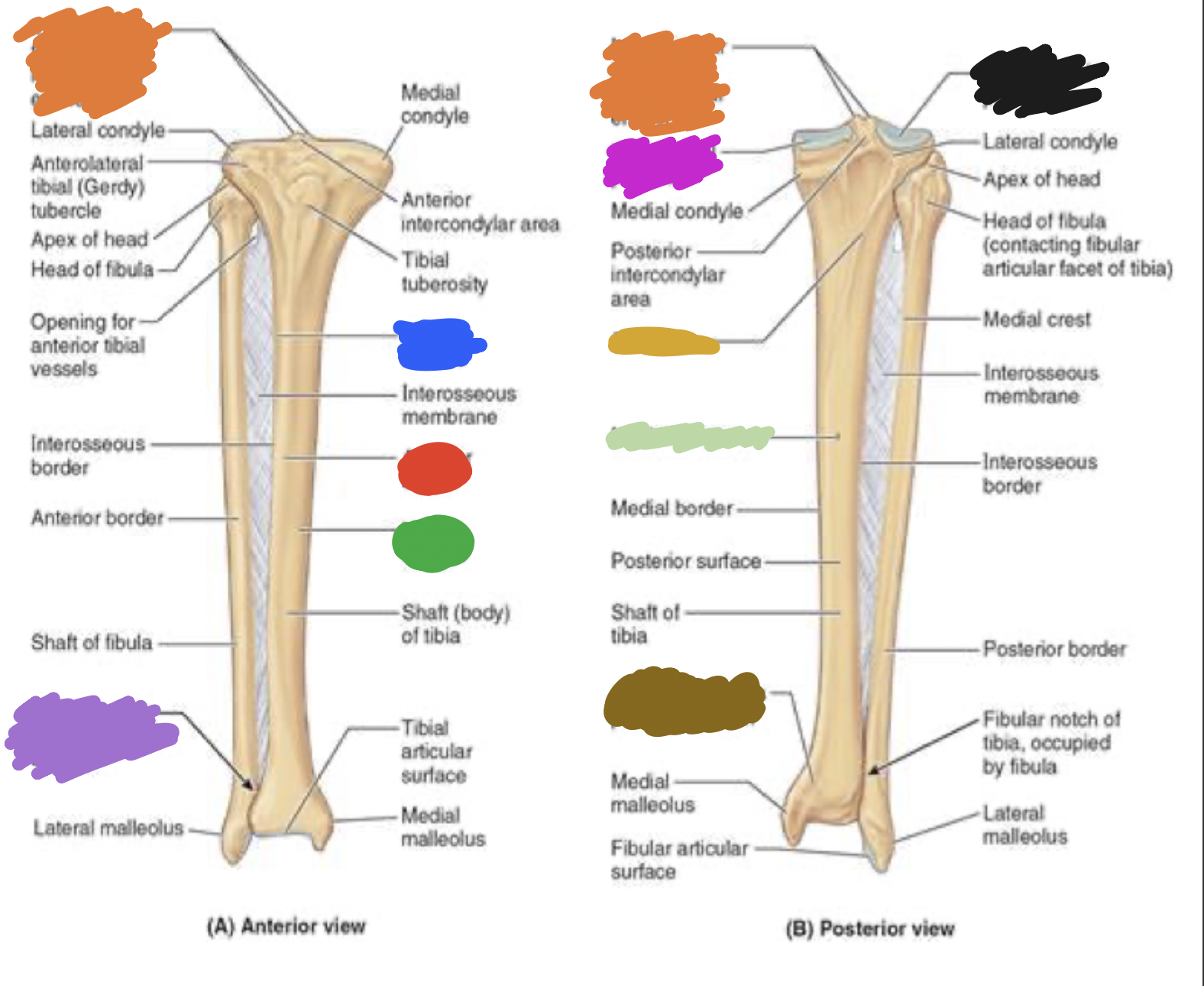
tibia: pink
medial tibia plateau
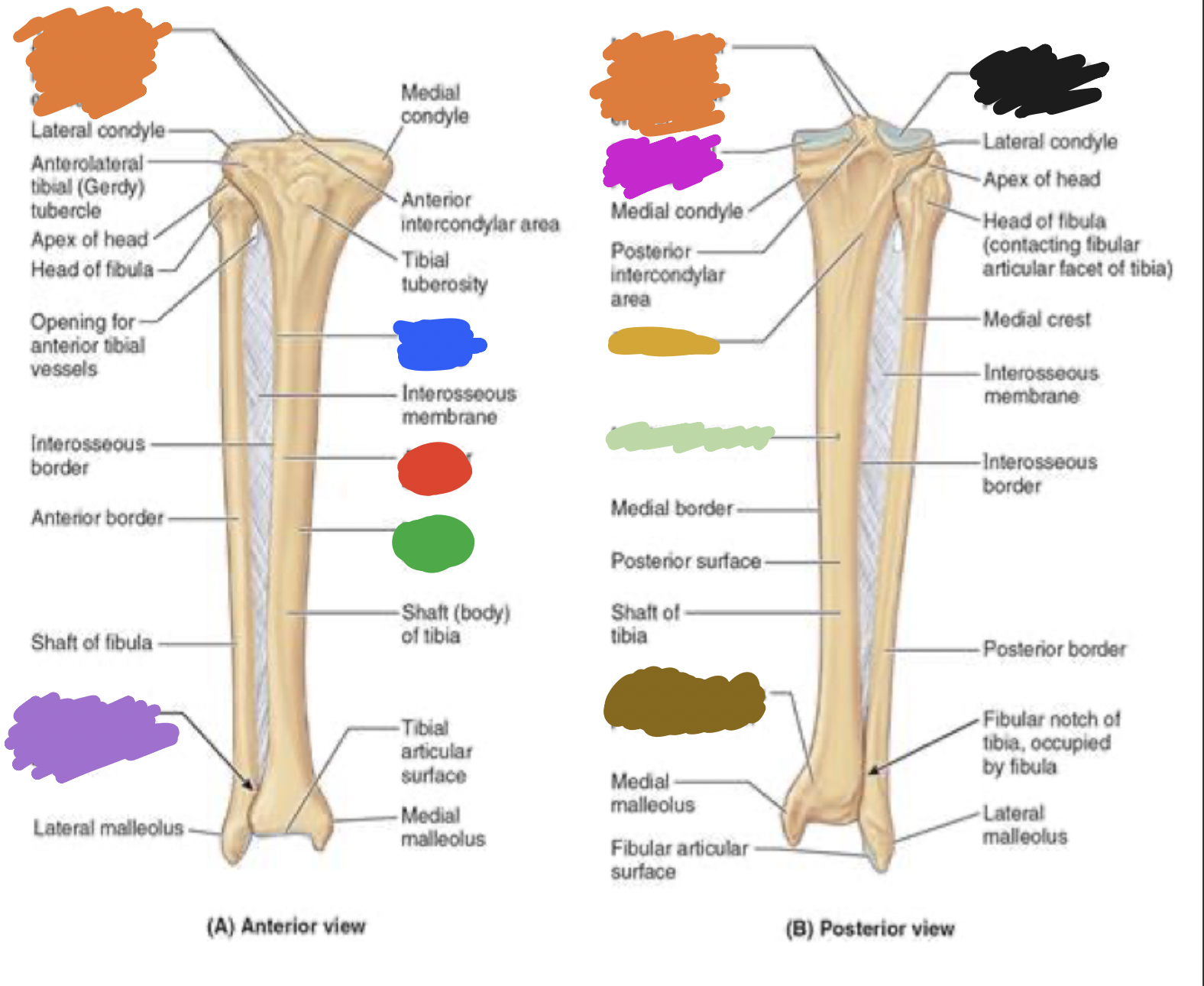
tibia: black
lateral tibia plateau
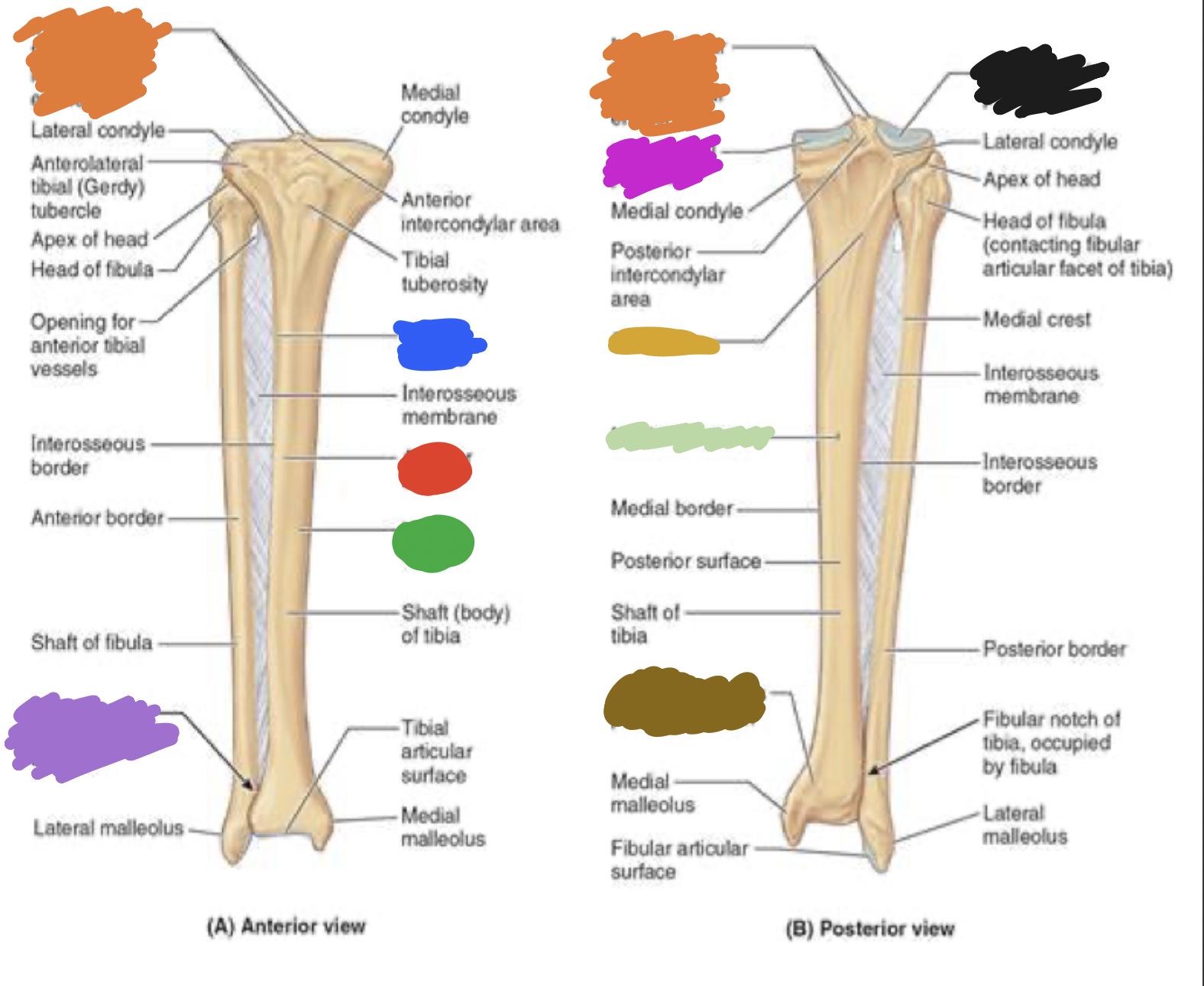
tibia: orange
intercondylar area and tubercles
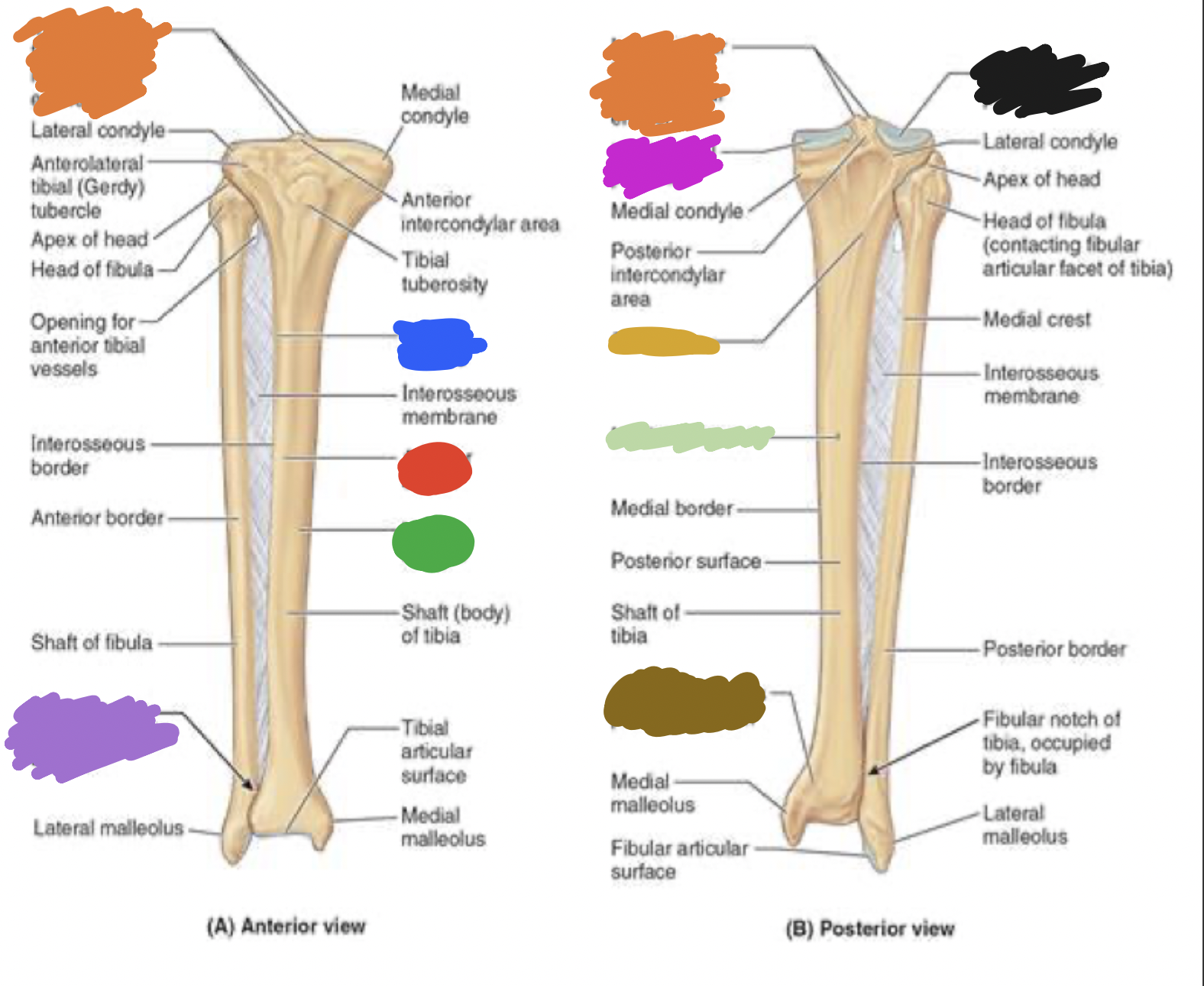
tibia: yellow
soleal line
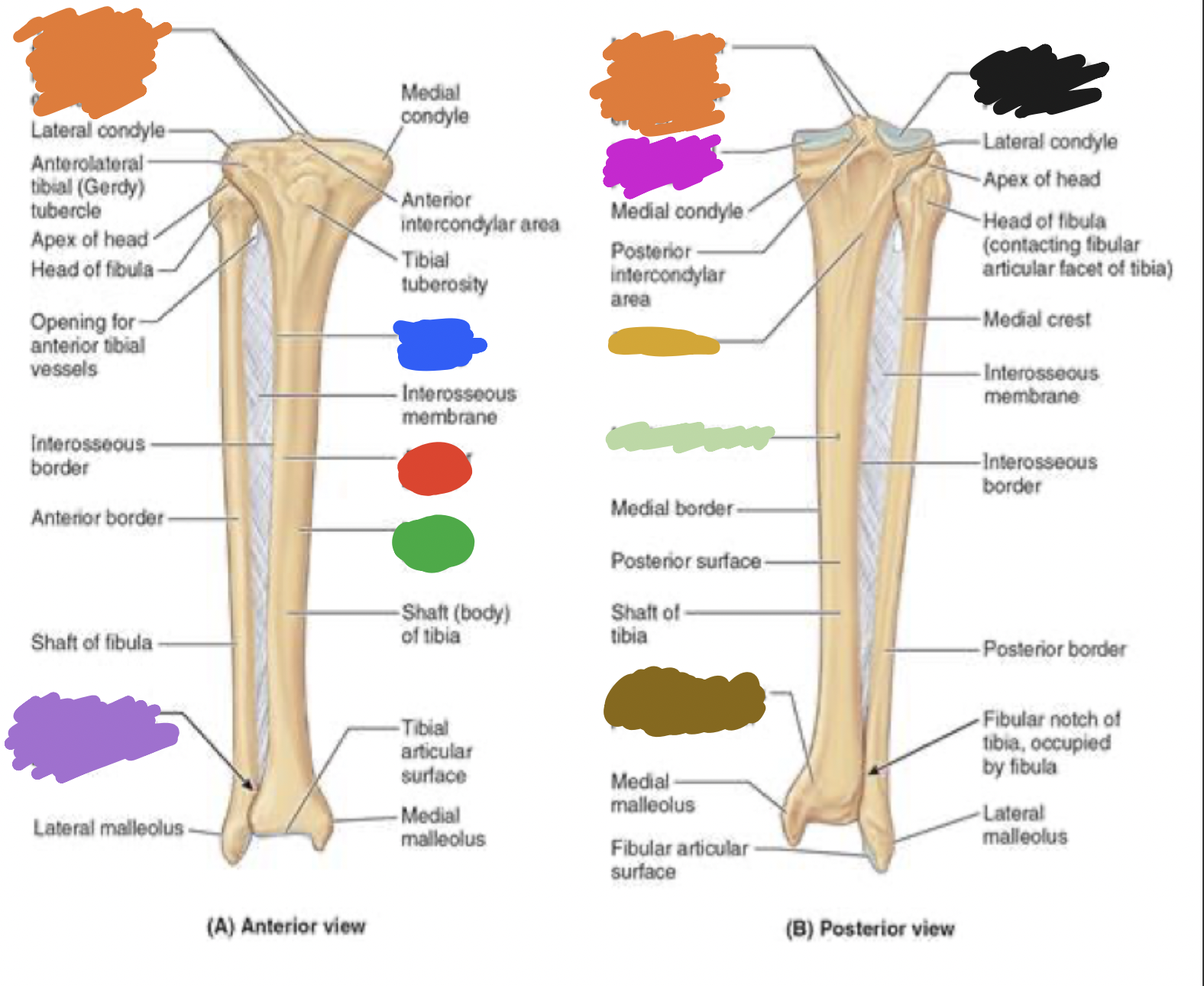
tibia: light green
nutrient foramen —> nutrient canal —> medullary —> (marrow) cavity
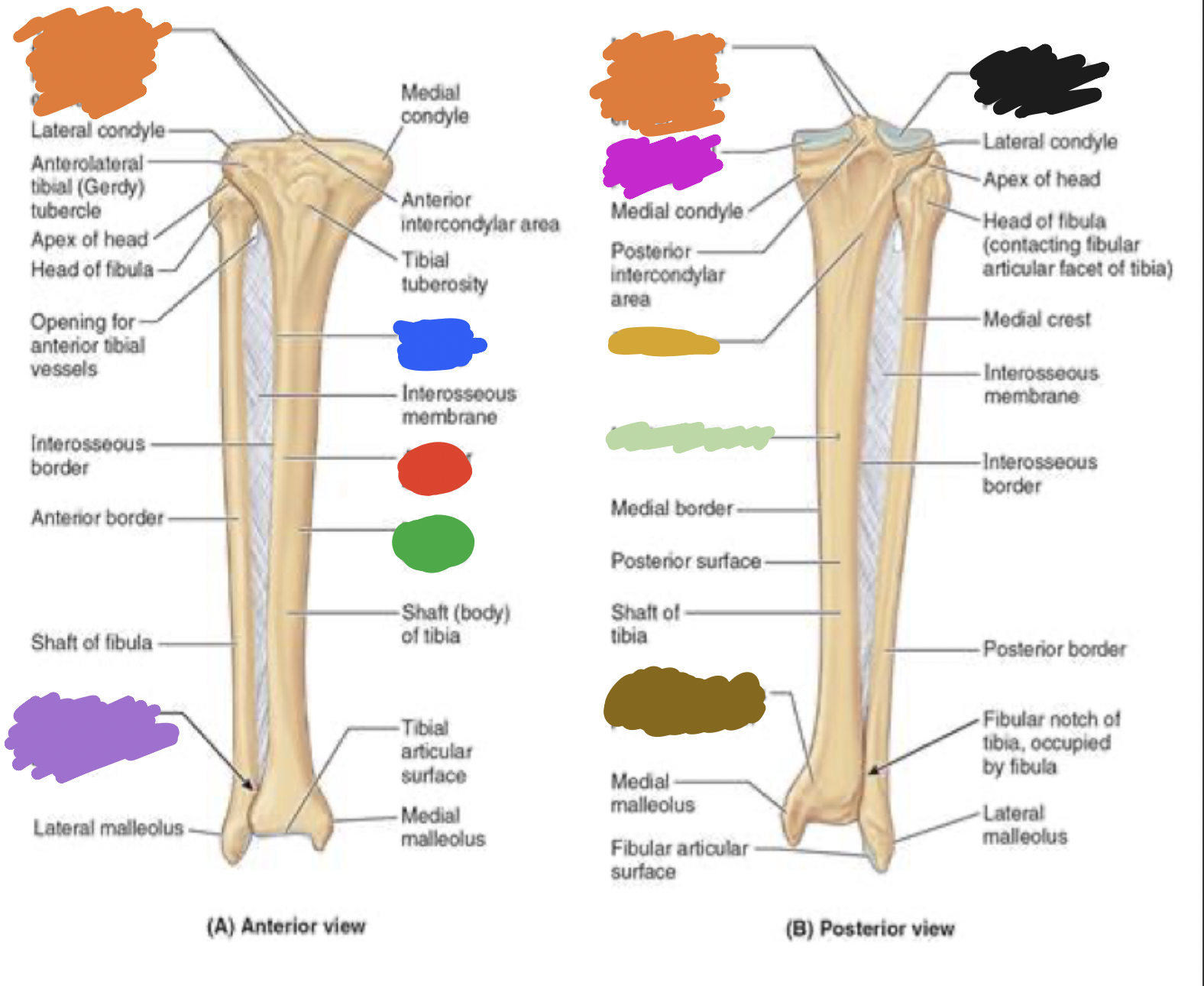
tibia: brown
groove of the tibialis posterior tendon

fibula:
neck
fibula:
lateral malleolus
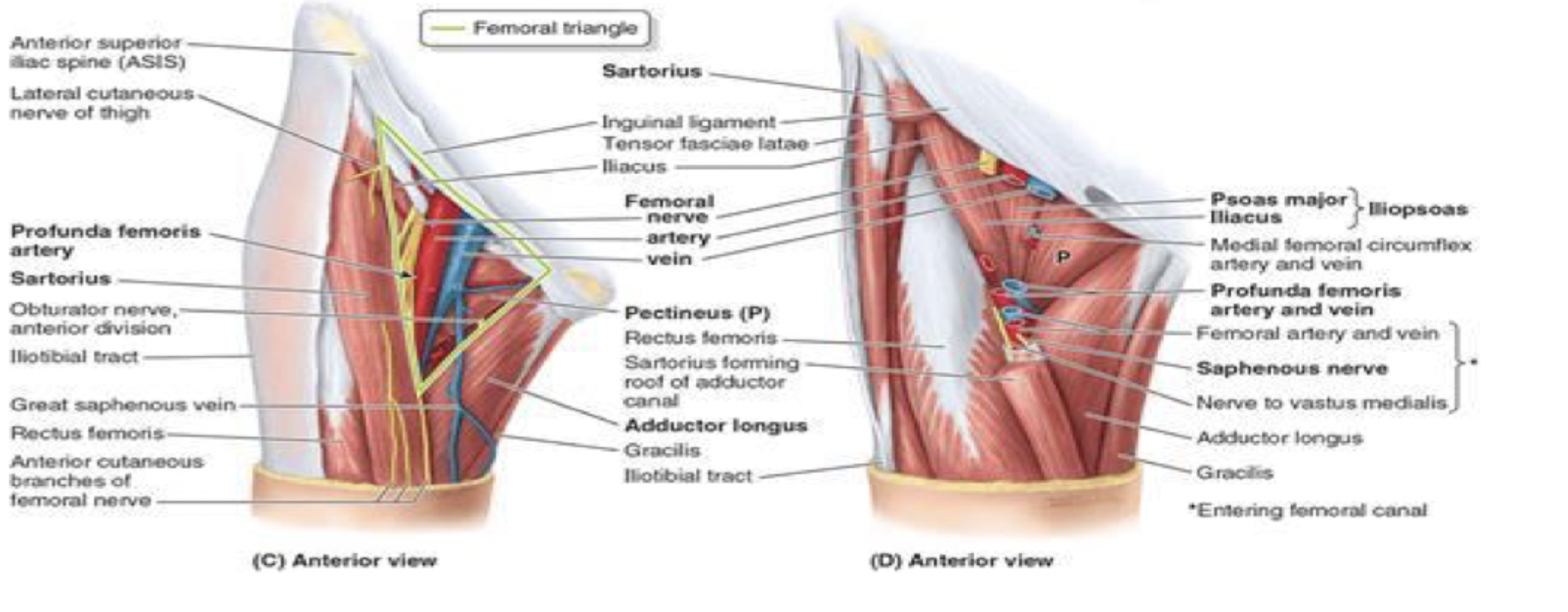
borders of the femoral triangle
superior boder: inguinal ligament
lateral border: sartorius
medial border: adductor longus
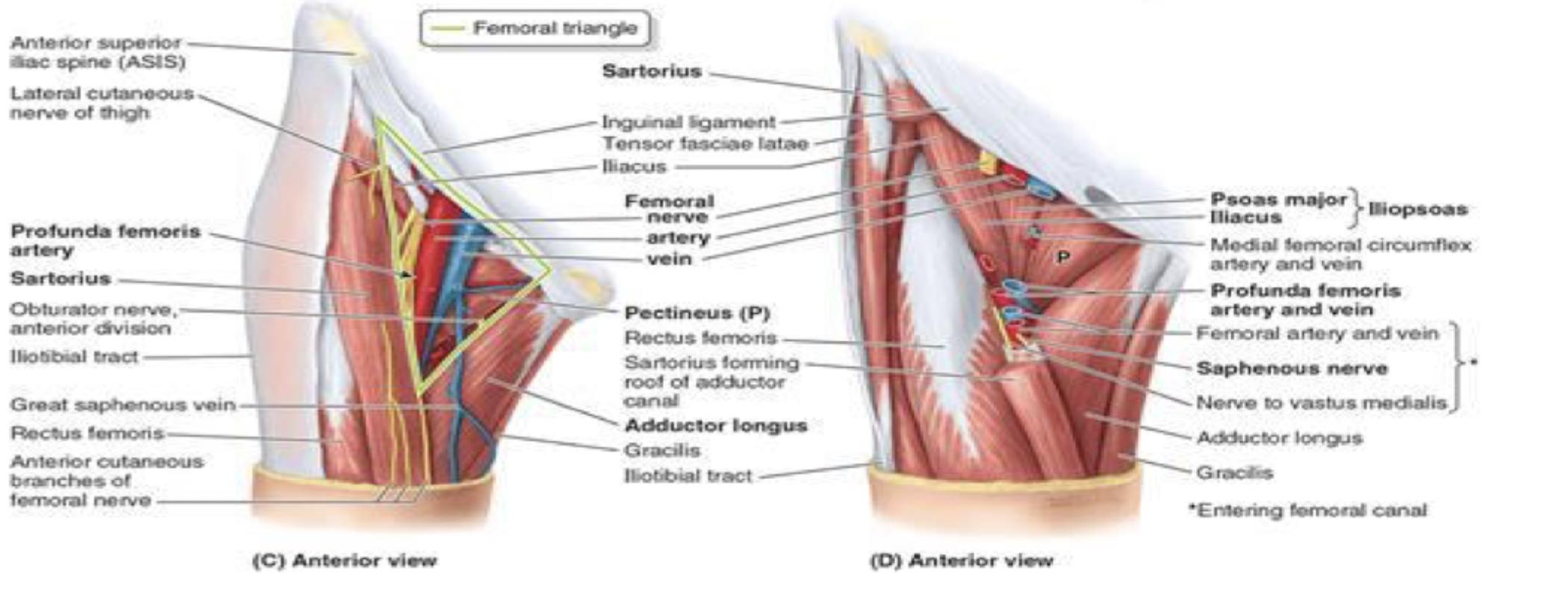
contents of the femoral triangle (lateral to medial)
NAV AL
femoral nerve
femoral artery
femoral vein
(adductor longus border)
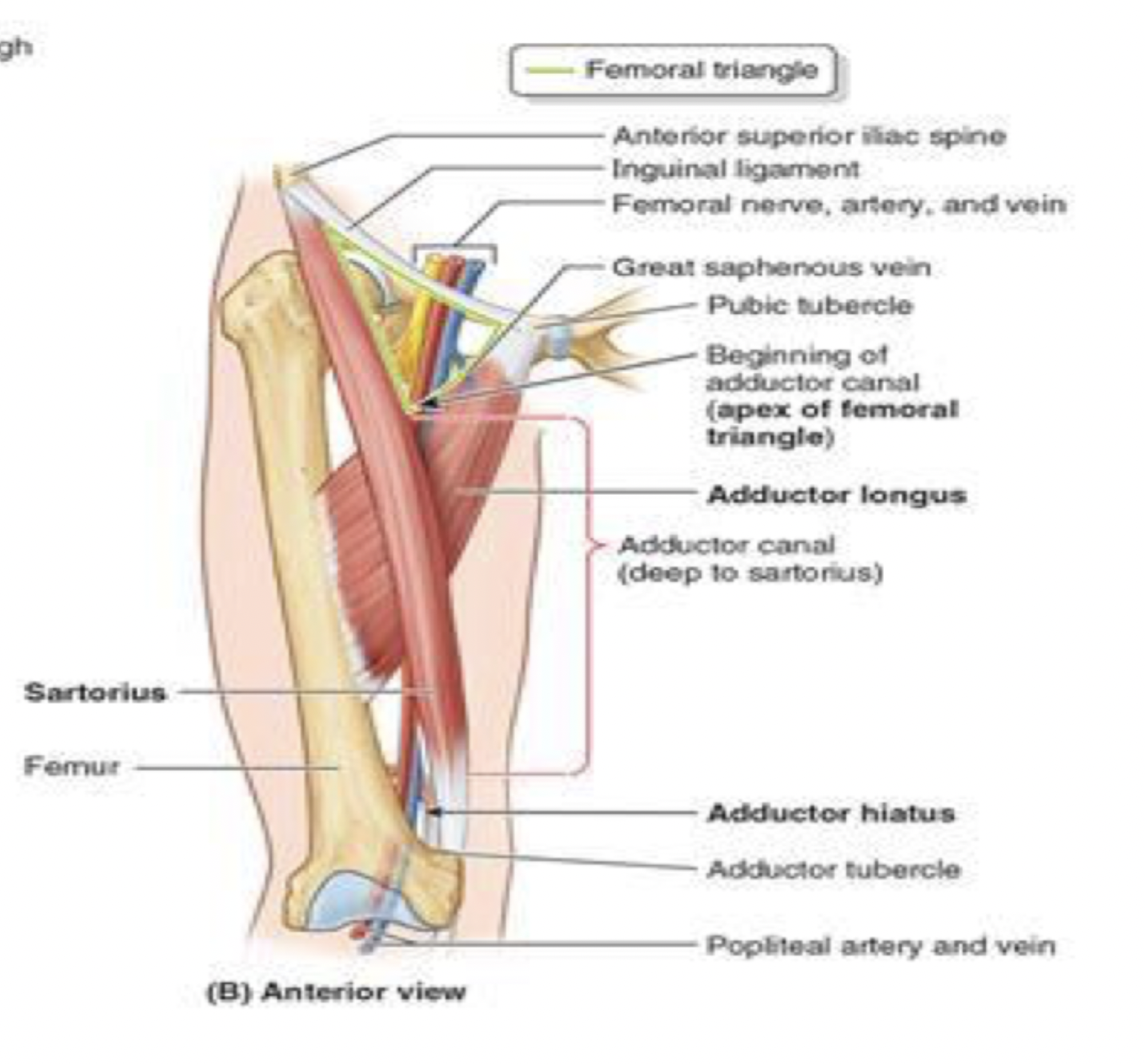
adductor canal
passageway for femoral artery and vein to be delivered down to the popliteal fossa
start anterior —> ends up going posterior
starts at the apex of femoral triangle
where they are the femoral artery and vein
roof is sartorius
goes underneath down to adductor hiatus
where they become the popliteal artery and vein
bounded posteriorly by the adductor magnus
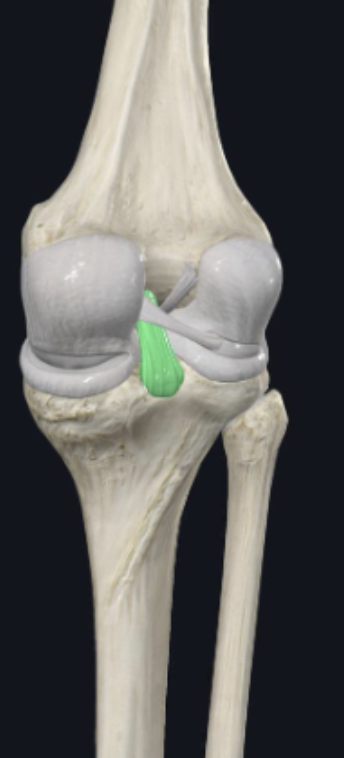
__ ligament
posterior cruciate ligament
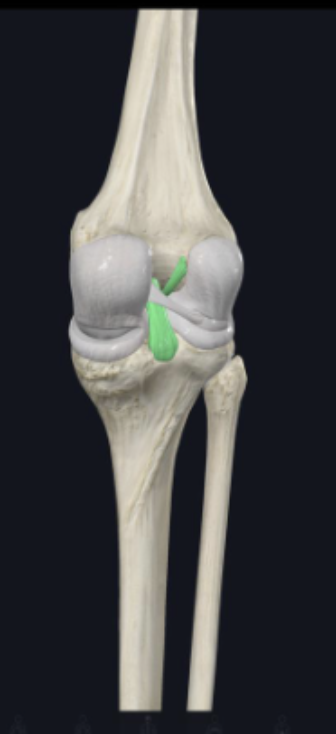
__ ligament
anterior cruciate ligament
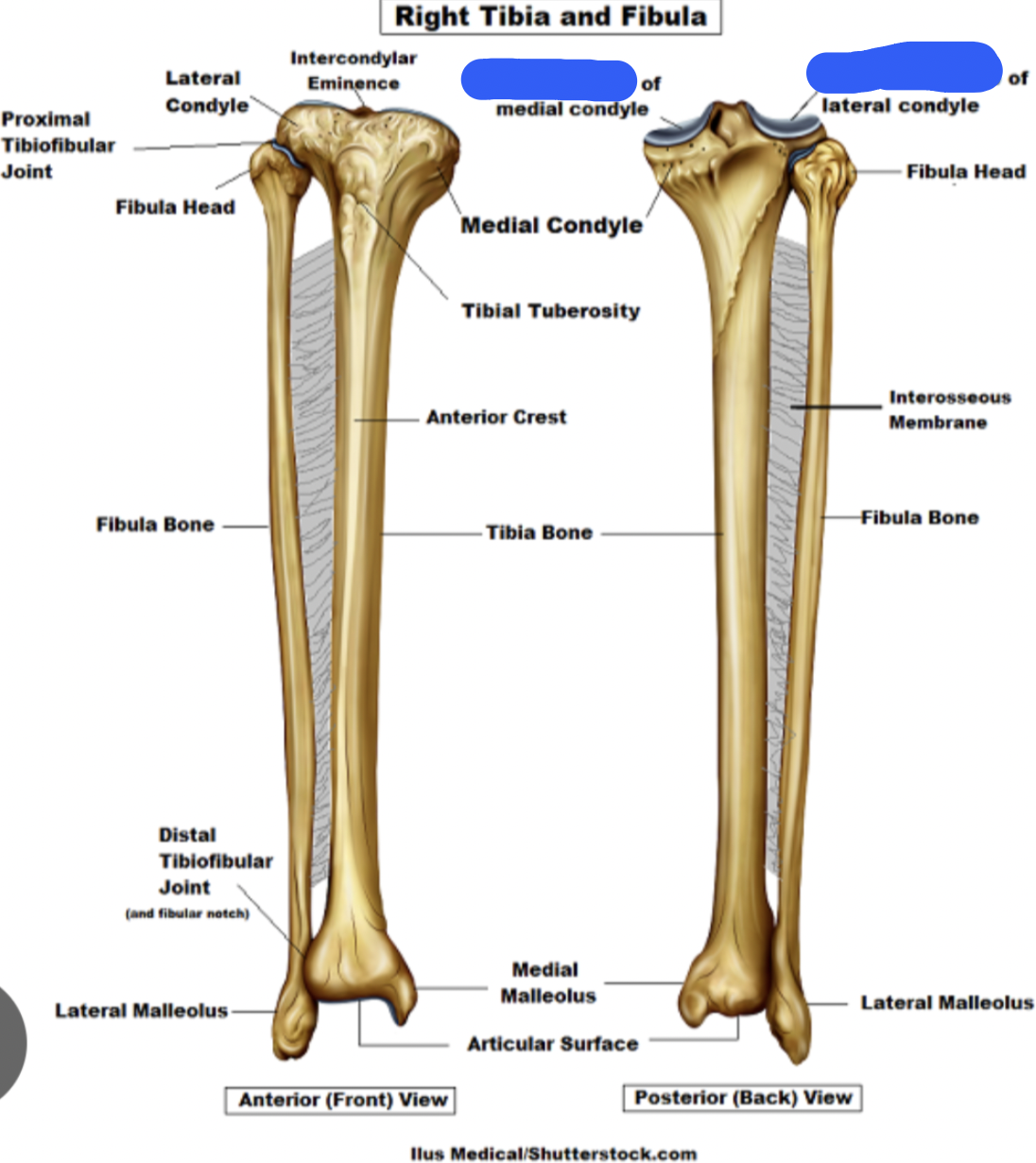
tibia:
articular surface
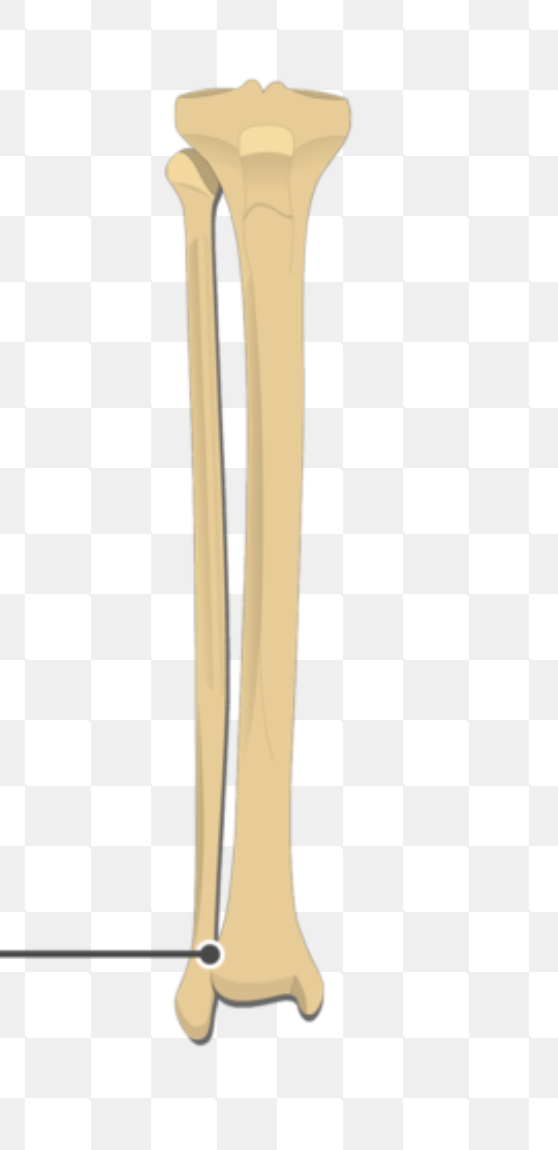

tibia:
fibular notch