unit 2 - Cell structure and function
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Nucleus
structure:
double membrane (nuclear envelope) with pores
functions:
stores genetic information (DNA)
synthesis of RNA
ribosome subunit assembly
Rough ER
structure:
studded with ribosomes attached to nuclear envelope
functions:
site of membrane-bound protein and secreted protein synthesis
cell compartmentalization
mechanical support
role in intracellular transport (transport vesicles to the golgi)
smooth ER
structure:
folded, tubelike structure (cisternae)
functions:
detoxification
calcium storage
lipid synthesis
Golgi complex
structure:
membrane-bound structure composed on flattened sacs (cisternae)
functions:
folding and chemical modification of synthesized proteins
packaging protein traffic
“mail center” — different glycoproteins on outside
ex. if trying to make lysosome it comes from Golgi, synthesize hydrolytic enzyme in rough ER → goes to Golgi —> releases it out as transport vesicle that becomes a lysosome
issue in hydrolytic enzymes = issue in rough ER or golgi
ribosomes
structure:
composed of rRNA and protein
large and small subunits
types: bound or free (cytoplasmic)
Functions:
protein synthesis
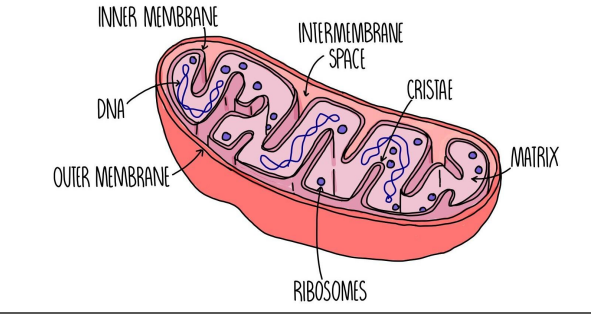
mitochondria
structure:
double membrane
outer: smooth; inner: highly folded
more fold = more ETC
Functions:
site of oxidative phosphorylation (cristae/inner membrane)
site of Krebs cycle (matrix)
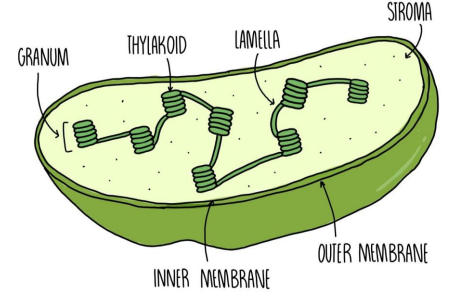
chloroplast
structure
double outer membrane (thylakoid sac stacked: grana and fluid: stroma)
function
site of photosynthesis
thylakoid: light reactions
stroma: Calvin-benson cycle
lysosome
structure:
membrane-enclosed sacs that contain hydrolytic enzymes
functions:
intracellular digestion (recycle cell organic materials + programmed cell death apoptosis)
vacuole
structure:
membrane bound sac
functions
storage and release of macromolecules and cellular waste products
central: water retention — turgor pressure
when plant is in hypotonic environment
contractile: osmoregulation (protists)
live in freshwater/hypertonic environments + pushes water out
food: phagocytosis, fuse with lysosome
cellular eating
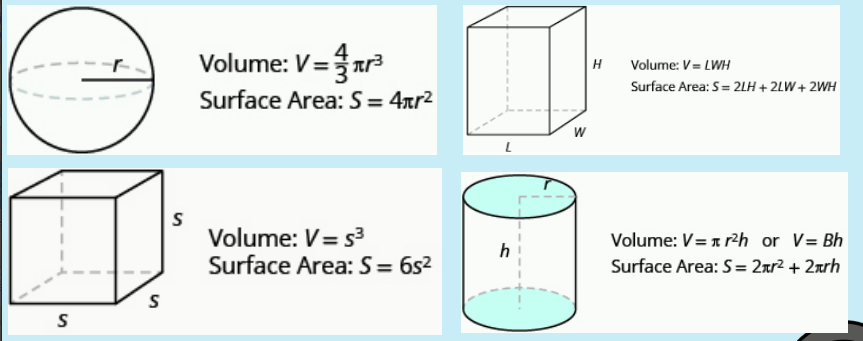
SA:V
smaller cells typically have a higher area to volume ratio and more efficient exchange of materials with the environment
large surface area + small volume!
simple diffusion
passive transport, no NRG
down concentration gradient
goes straight through w no assistance
small, nonpolar
no transport protein needed
examples: CO2, O2, N2
small amount of H2O leak through membrane
facilitated diffusion
passive transport, no NRG
down concentration gradient
small molecules
requires transport protein
channel vs. carrier protein
channel + passageway straight through, carrier = binding to pass through (changes shape)
ex. water, NA+, K+, Ca+
Active transport
requires input of NRG
against concentration gradient
requires transport protein (carrier protein)
example NA+, K+, Ca+, H+