Pre IB Chemistry - Matter
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Solid
form of matter with its own definite shape and volume
liquid
form of matter that flows, has its own definite shape and volume & takes shape of container
gas
flows to conform to shape of container and fills entrie volume of container
vapor
gaseous state of a substance that’s solid/liquid at room temperature
physical property
characteristic that can be observed/measured without changing the sample’s composition
extensive property
dependent of amount of substance present (mass, length, volume), property of matter
intensive property
independent of amount of substance present (density) & can be used to identify samples since they’re unchanging, property of matter
chemical property
ability or inability of a substance to combine w/ 1 or more substances
characteristics of a substance
particles, volume, shape —→ liquid, gas, solid, or plasma?
physical change
alters a substance w/o changing it’s composition
phase change
a transition of matter from one state to another
freezing water,
grinding coffee beans
chemical change
substances change into other substances
silver spoon tarnishes
rusting
usually energy is absorbed/released, color changes, gas produced, formation of a precipate, irreversibility
law of conservation of mass
mass is not created nor destroyed it’s conserved
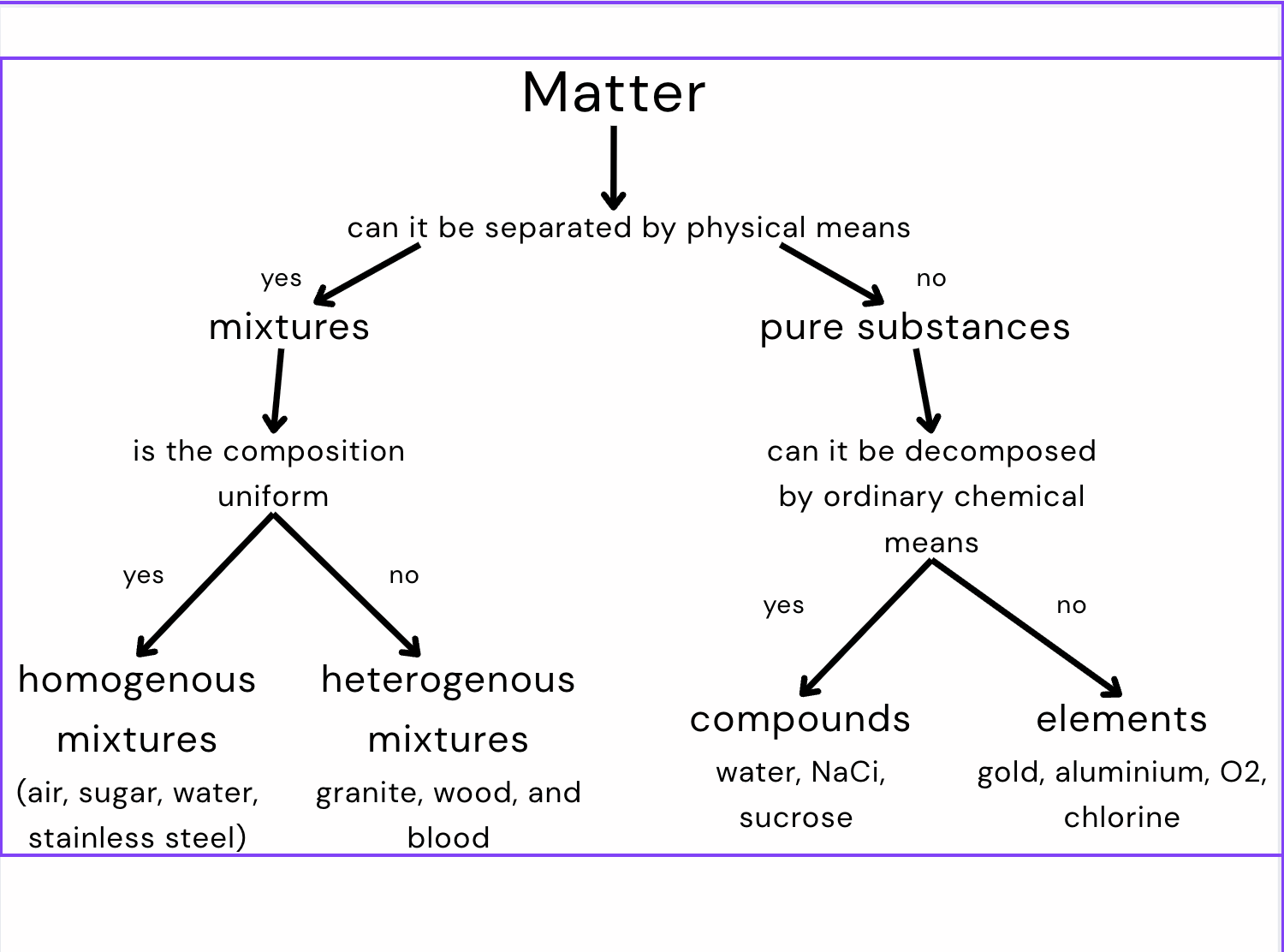
element
pure substance that can’t be separated into simpler substances
compound
made up of +2 different elements combined chemically
law of definite proportions
a compound is always composed of the same elements in the same proportion by mass
percent by mass
ratio of mass to each element to the total mass of the compound expressed as a percentag
substance
form of matter that has a uniform and unchanging composition, aka pure substance
heterogenous mixture
doesn’t blend smoothly and individual substances remain distinct
homogenous mixture
constant composition throughout; always has a single phase, ex solution
solution
can be all three states of matter
filtration
uses a porous barrier to separate a solid from a liquid
distillation
a physical separation technique that’s based on substances’ boiling points
sublimation
solid changes to vapor without melting
cromatography
separates components of a mixture dissolved in either gas or liquid based on the ability of each to travel or be drawn across the surface of a fixed substance
crystallization
a separation technique that results in the formation of pure solid particles of a substance from a solution containing the dissolved substance
alloy
homogenous mixture of metals and it helps with srength and durability in manufacturing
mixture
made of two or more substances with the individual properties maintained
plasma
is ionized gas, makes up 90% of visible universe, is a conductor
Classification of matter