Canine Pelvic Limb: Osteology
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Four parts of the pelvic limb
1.) pelvic girdle
2.) thigh
3.) crus/leg
4.) pes
bone of the pelvic girdle
os coxae
bone of the thigh
femur
bones of the crus/leg
tibia and fibula
bones of the pes
tarsi, metatarsi, and phalanges
Hip joint
ball and socket joint formed by the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the hip bone
Where is the flexor surface of the hip joint?
cranial aspect
Stifle
knee joint; formed by the femur, tibia, and patella
Where is the flexor surface of the stifle?
caudal aspect
Where is the flexor surface on the tarsus?
cranial aspect
Where is the flexor surface on the digits?
plantar side
The extensor surface for each joint will be __________ of the flexor surface
opposite
*for example, the extensor surface of the hip joint will be the caudal aspect, since its flexor surface is the cranial aspect
Four main bones of the os coxae
1.) ilium
2.) ischium
3.) pubis
4.) acetabulum
ilium
largest and most superior past of the os coxae
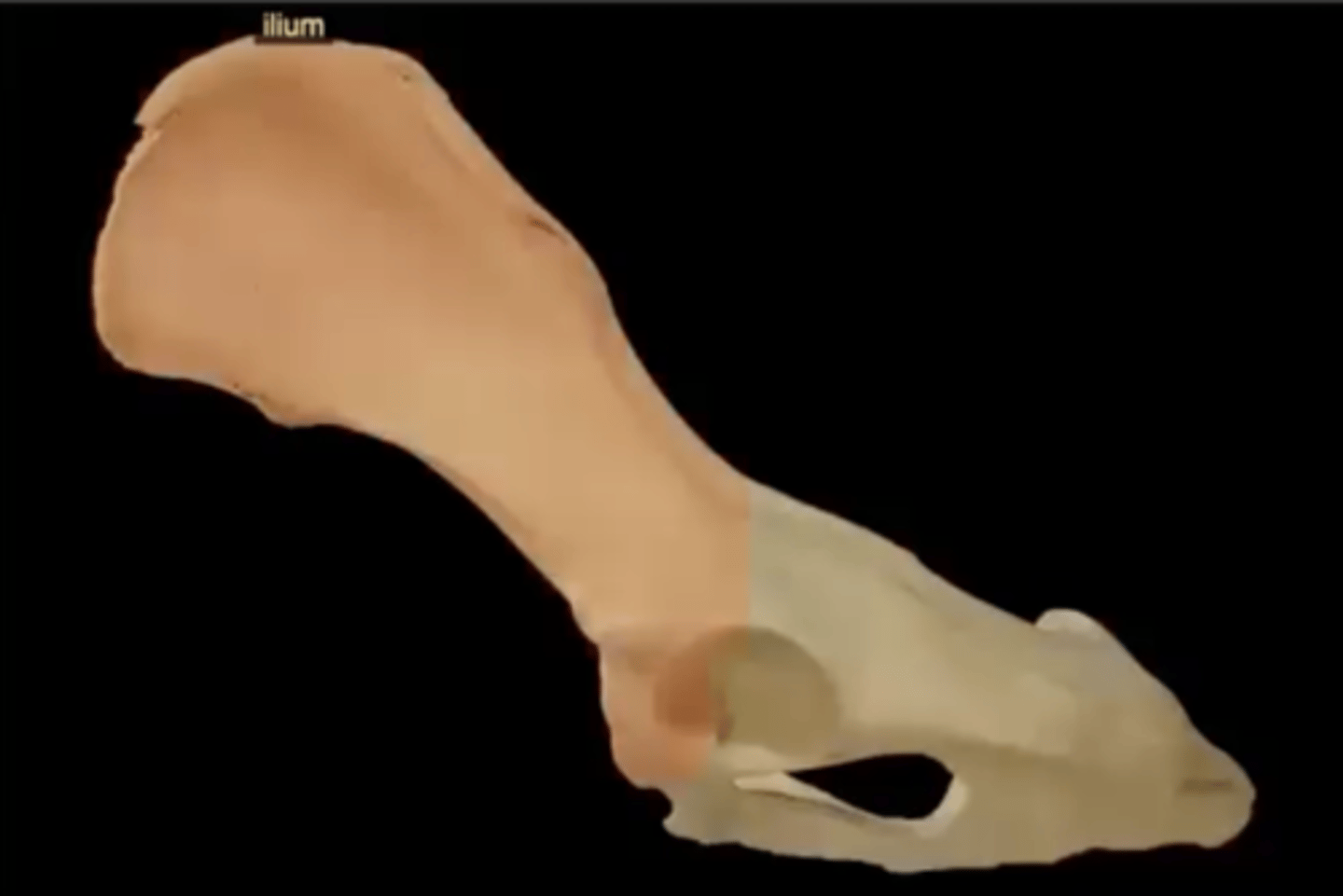
Six parts of the ilium
1.) wing
2.) body
3.) iliac crest
4.) tuber coxae
5.) tuber sacrale
6.) greater ischiatic notch
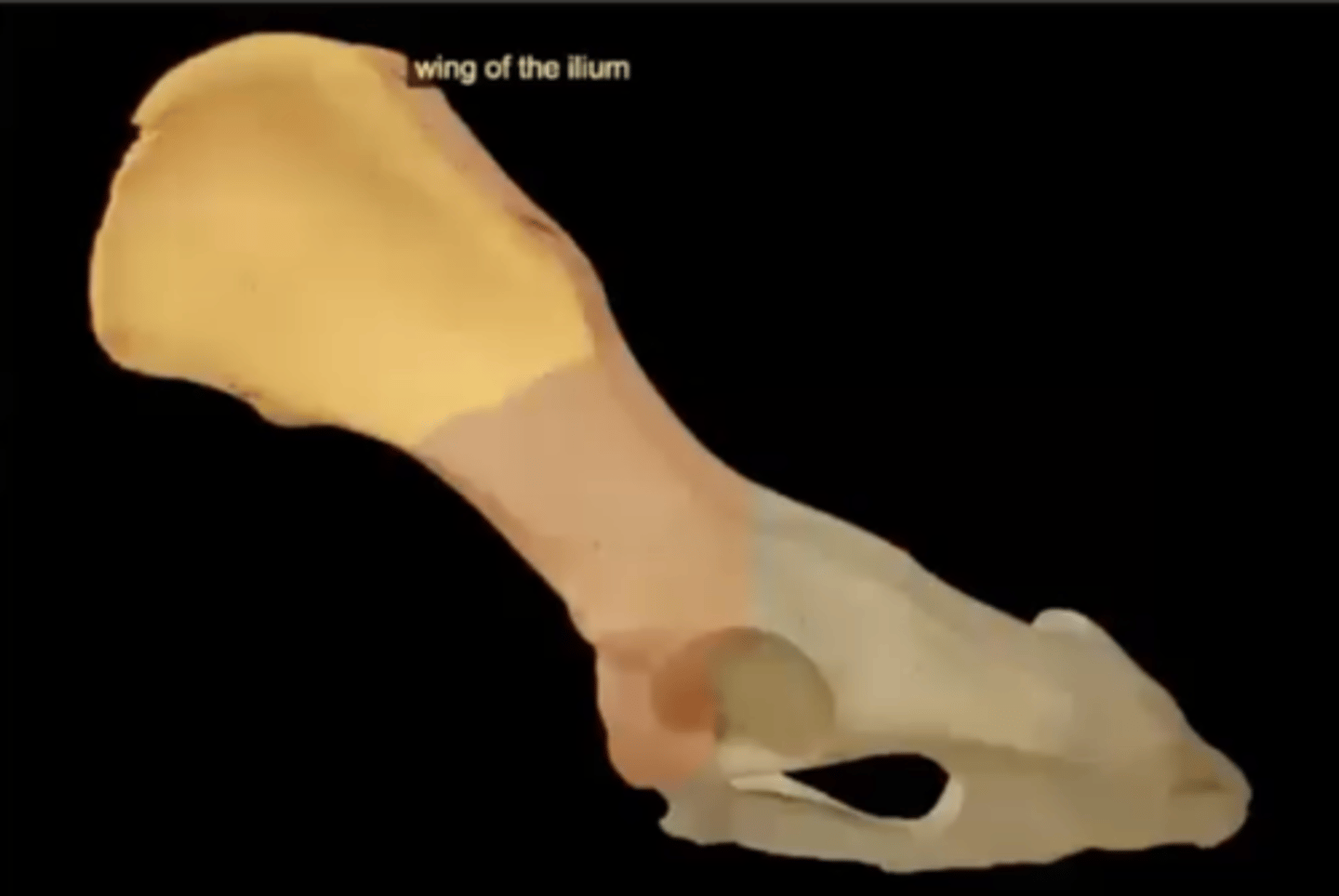
wing of the ilium
the upper flaring portion of the ilium that looks like a fan
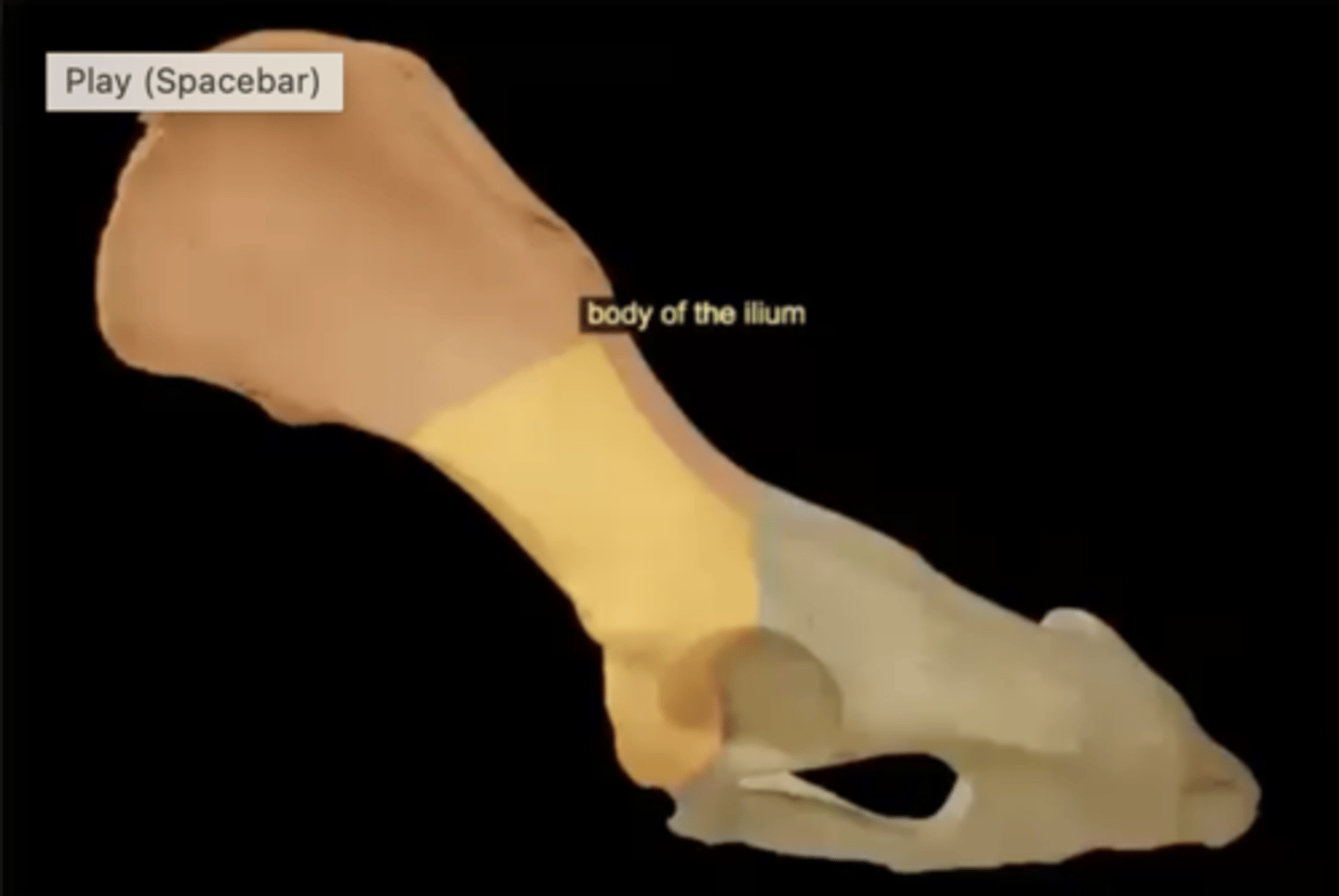
body of the ilium
handle of the fan, superior part of the acetabulum
iliac crest of the ilium
superior border of ilium

tuber coxae of the ilium
has two prominences; the cranial and caudal ventral iliac spines
tuber sacrale of the ilium
dorsomedial projection of the wing of ilium
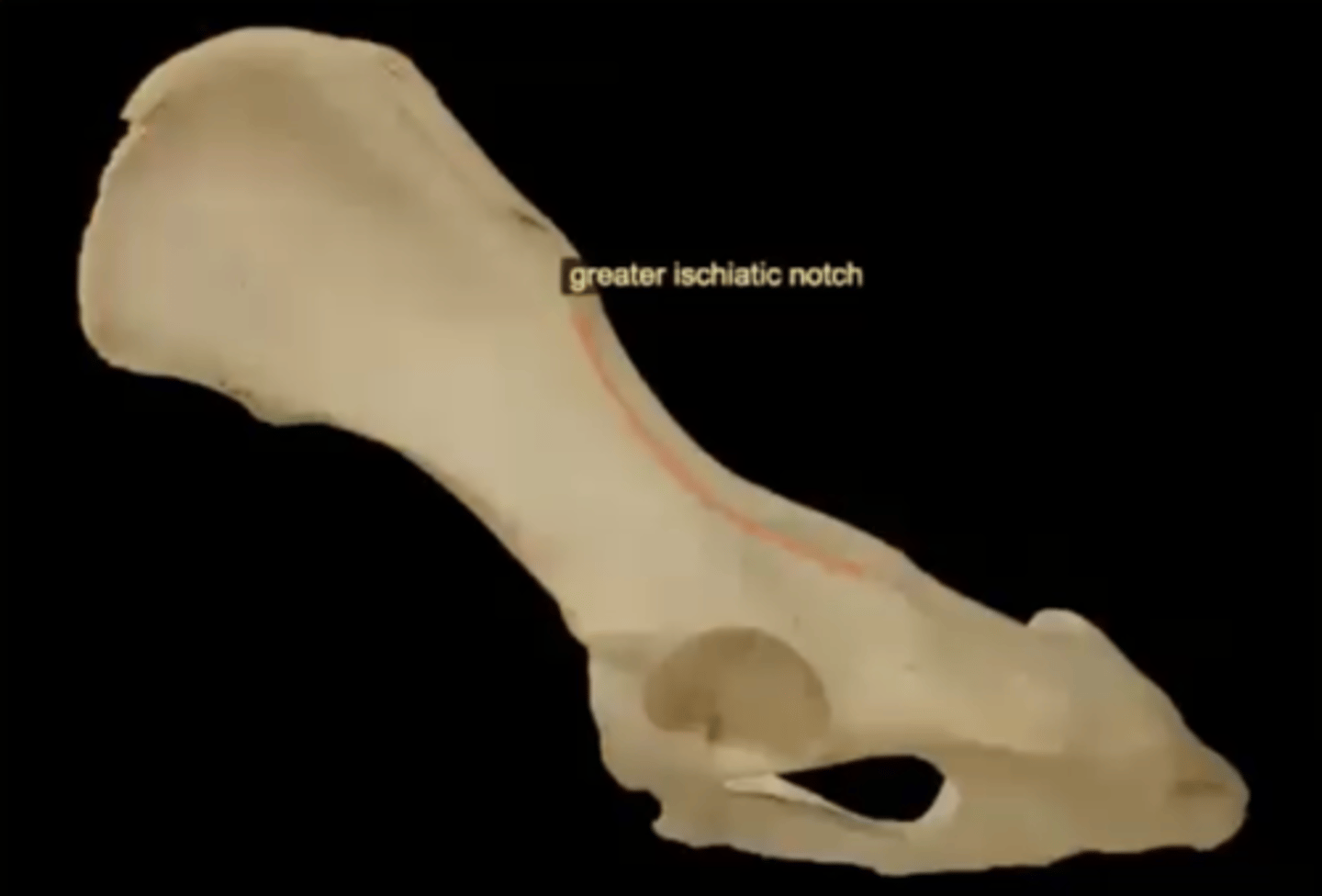
greater ischiadic notch of the ilium
long notch running along the caudal border of the ilium
ischium
the lower, posterior portions of the pelvis
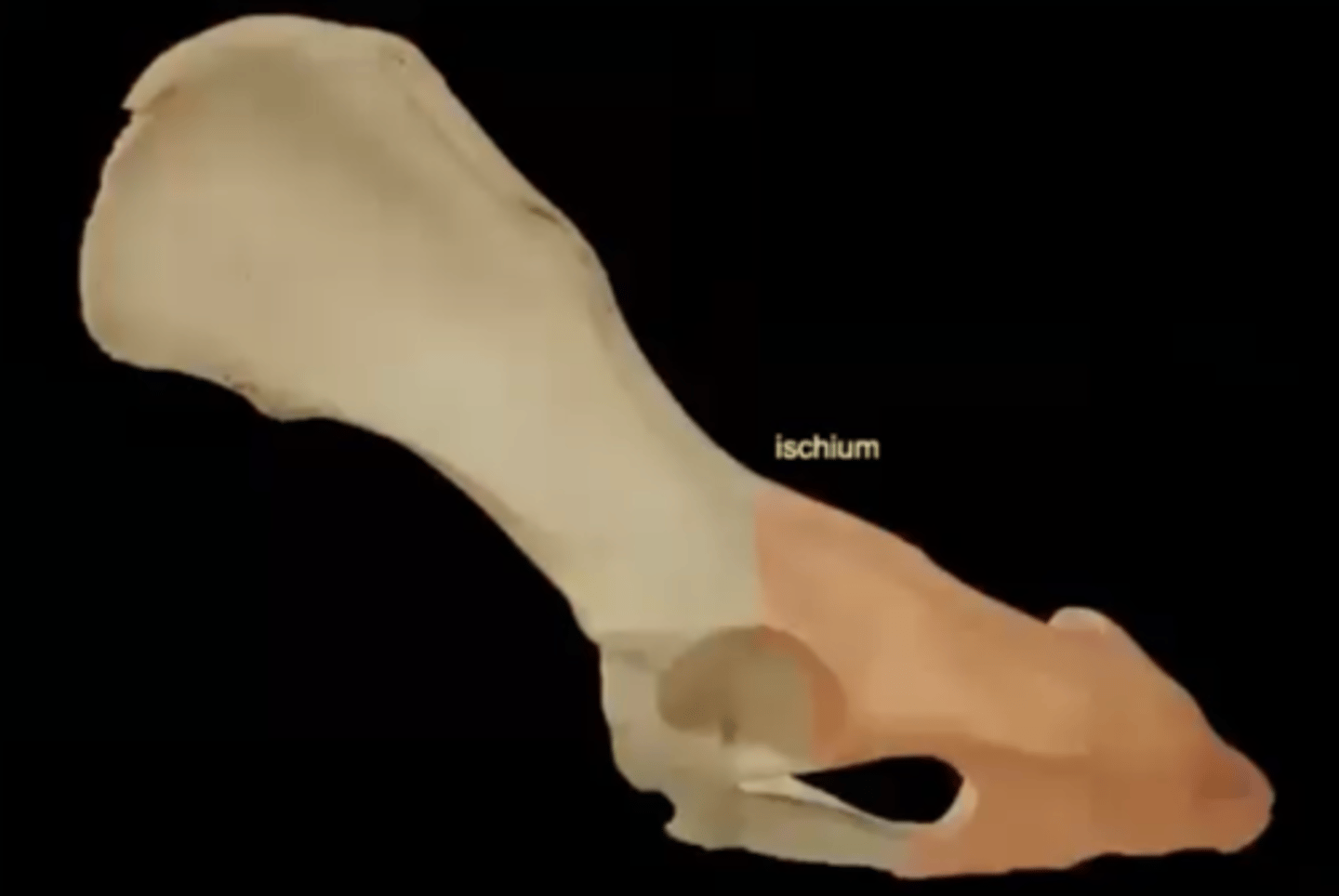
Four parts of the ischium
1.) ischiatic tuberosity
2.) ischiatic spine
3.) lesser ischiadic notch
4.) sacrotuberous ligament
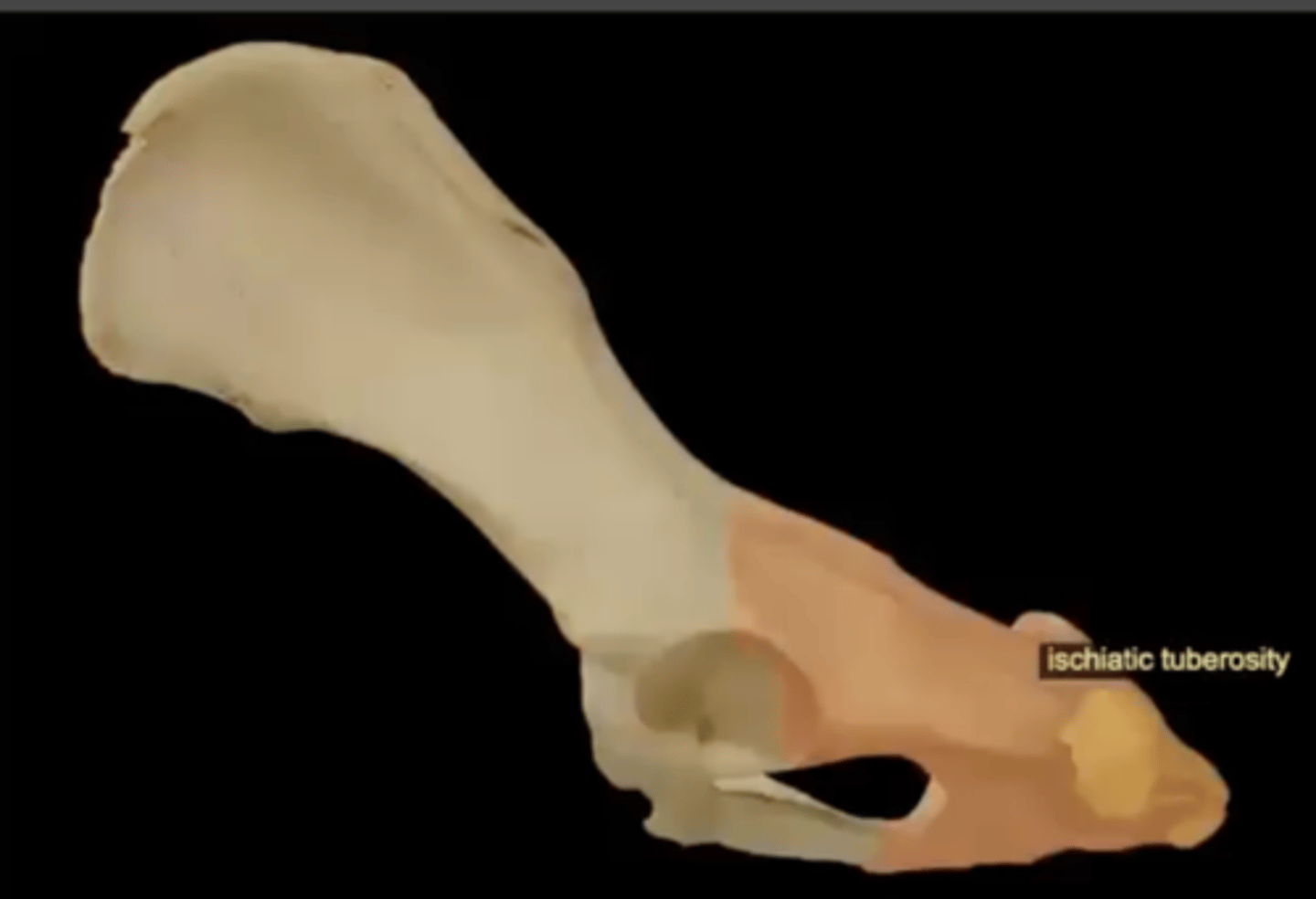
ischiatic tuberosity of the ischium
the bony protuberance at the bottom of the ischium where the hamstring muscles attach
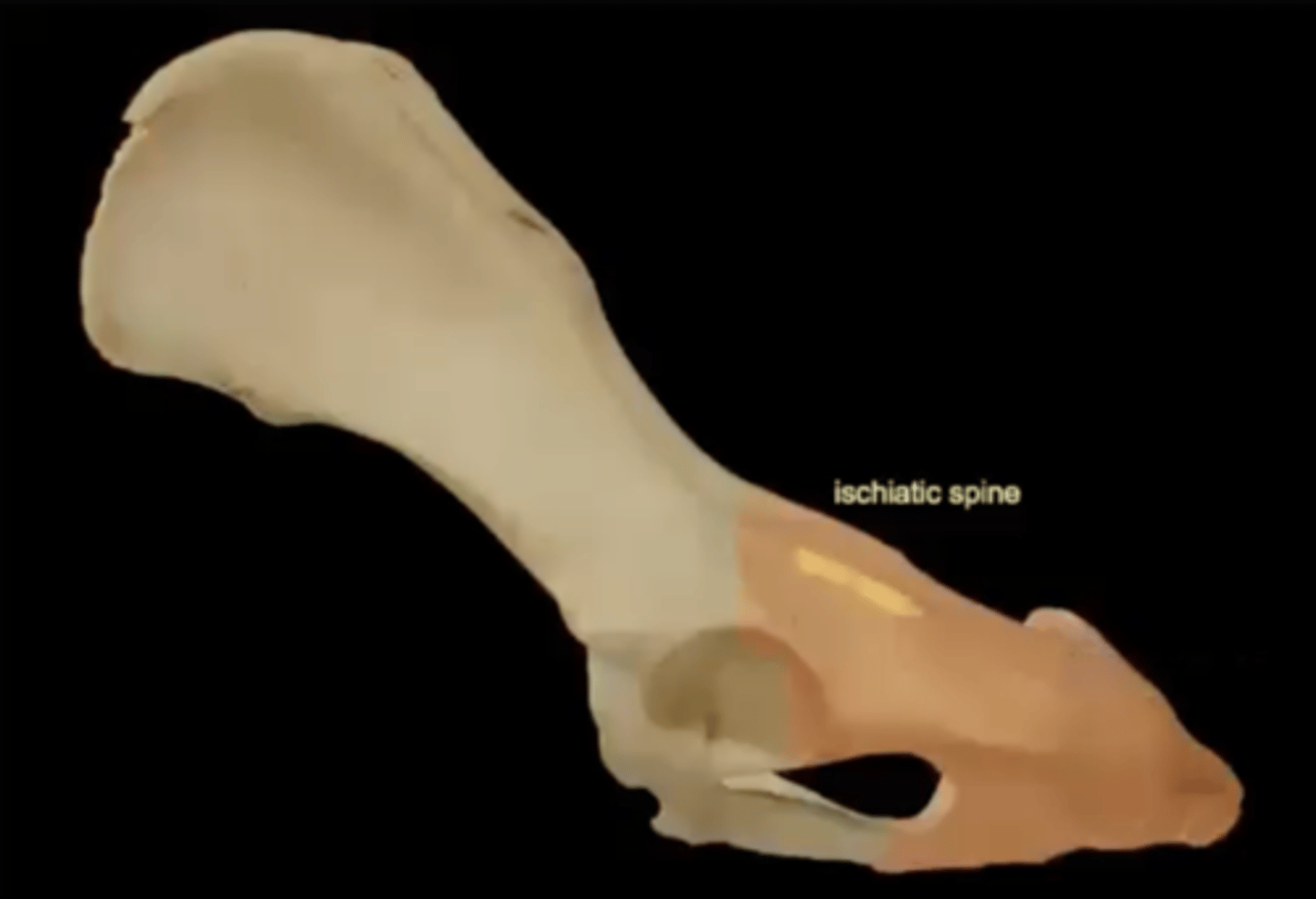
ischiatic spine of the ischium
a bony projection on the ischium that is located between the greater and lesser sciatic notches
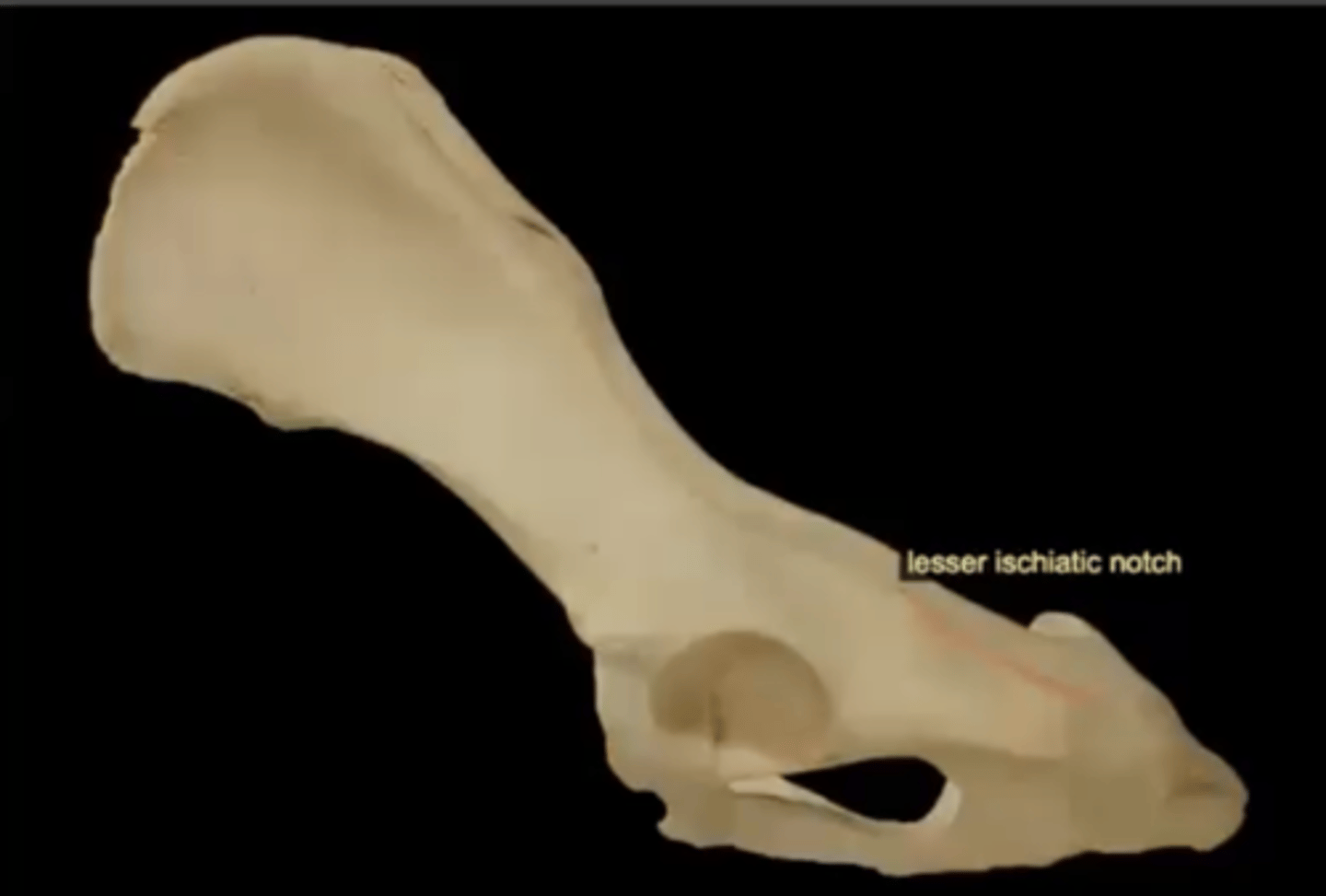
lesser ischiadic notch of the ischium
a small notch located on the dorsal (top) border of the ischium bone, between the ischial spine and the ischial tuberosity
sacrotuberous ligament of the ischium
a tough, triangular ligament that connects the sacral and caudal vertebrae to the ischial tuberosity
pubis
a bone that forms the ventral and anterior part of the pelvis, joining with the other pelvic bones (ilium and ischium)
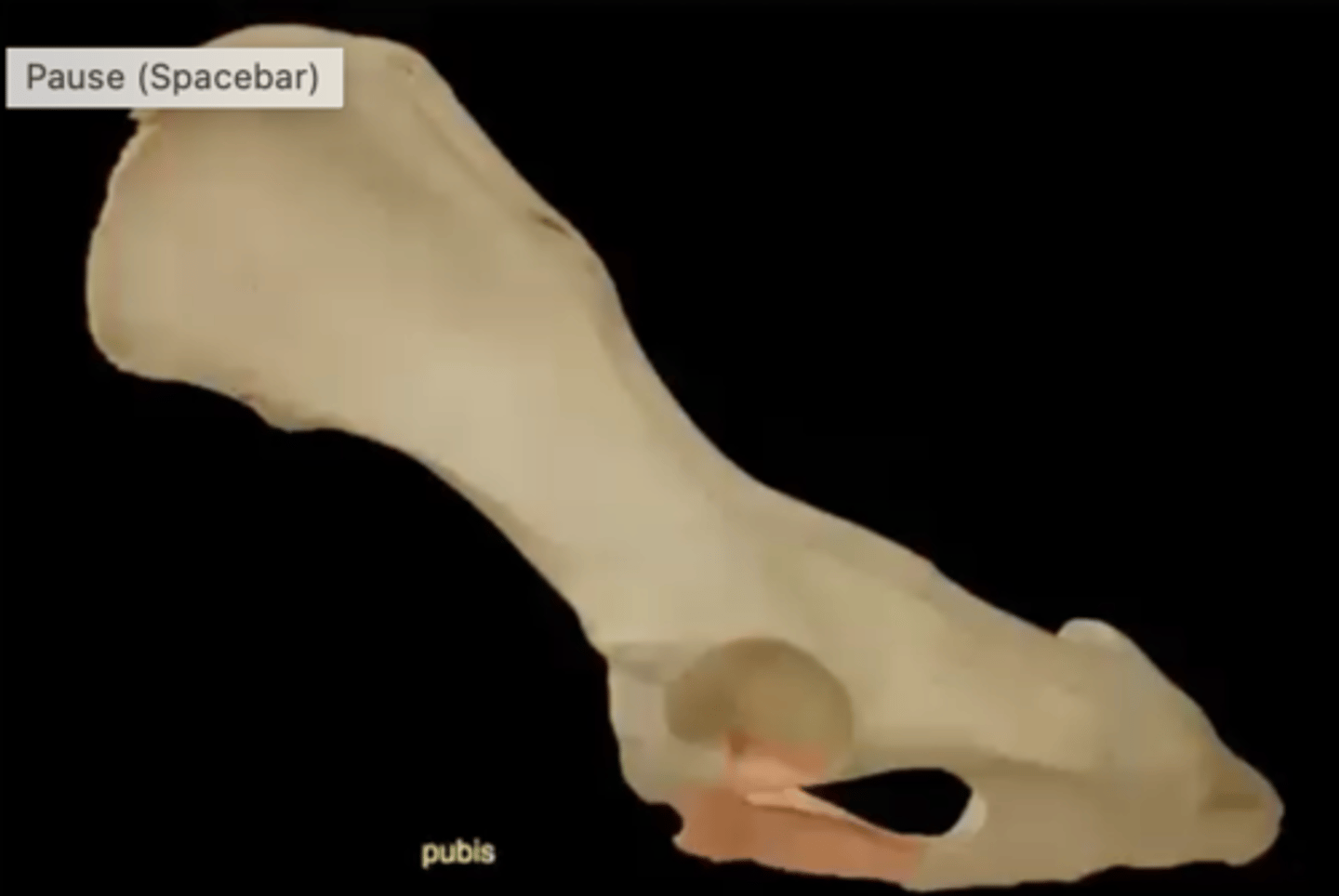
Two parts of the pubis
1.) illiopubic eminence
2.) pubic tubercle
illiopubic eminence of the pubis
bony prominence on the pelvic bone where the ilium and pubis meet
pubic tubercle of the pubis
a median bump on the underside of the pubic symphysis
acetabulum
large socket in the pelvic bone for the head of the femur
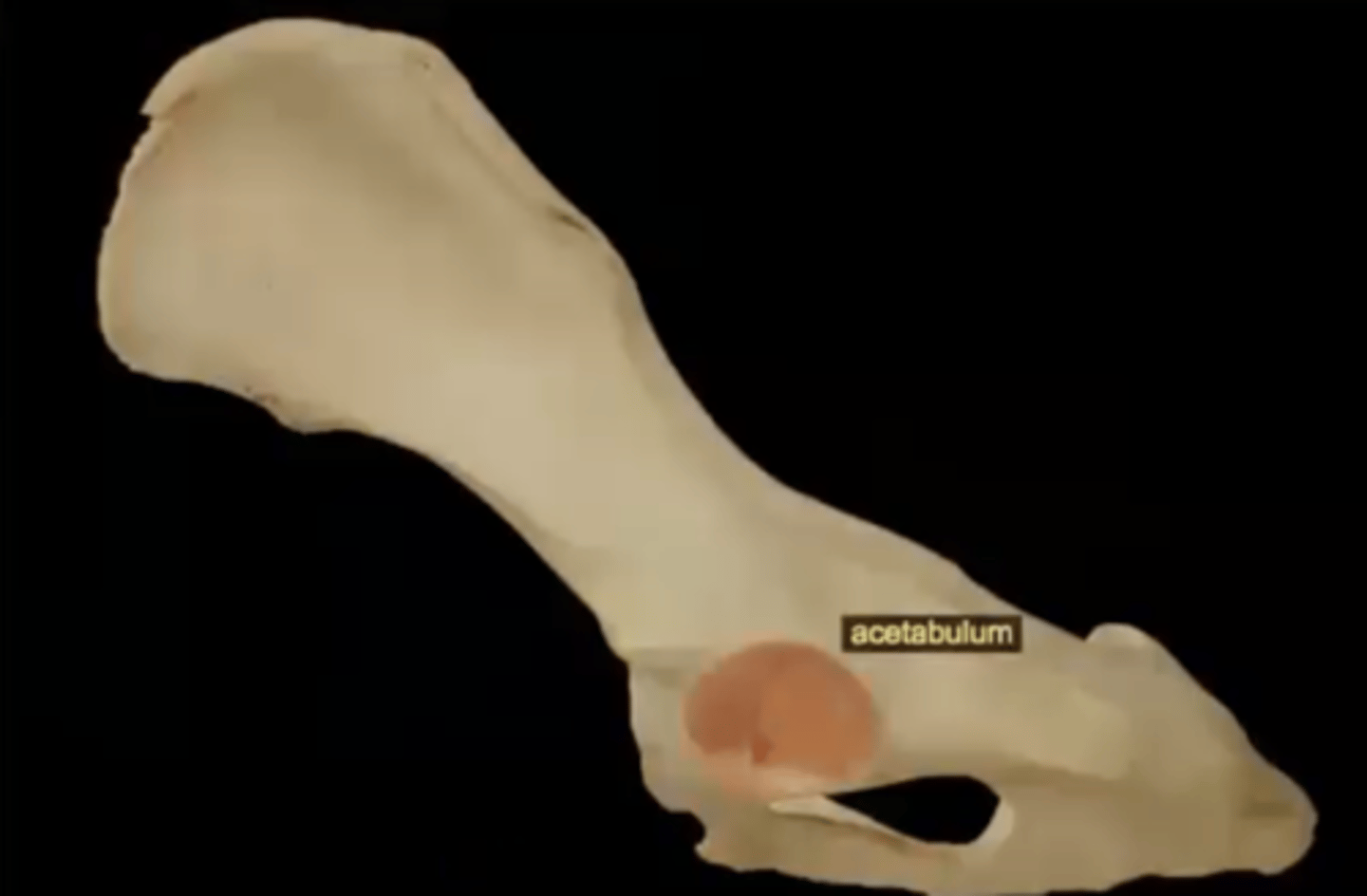
Two parts of the acetabulum
1.) acetabular fossa
2.) acetabular notch
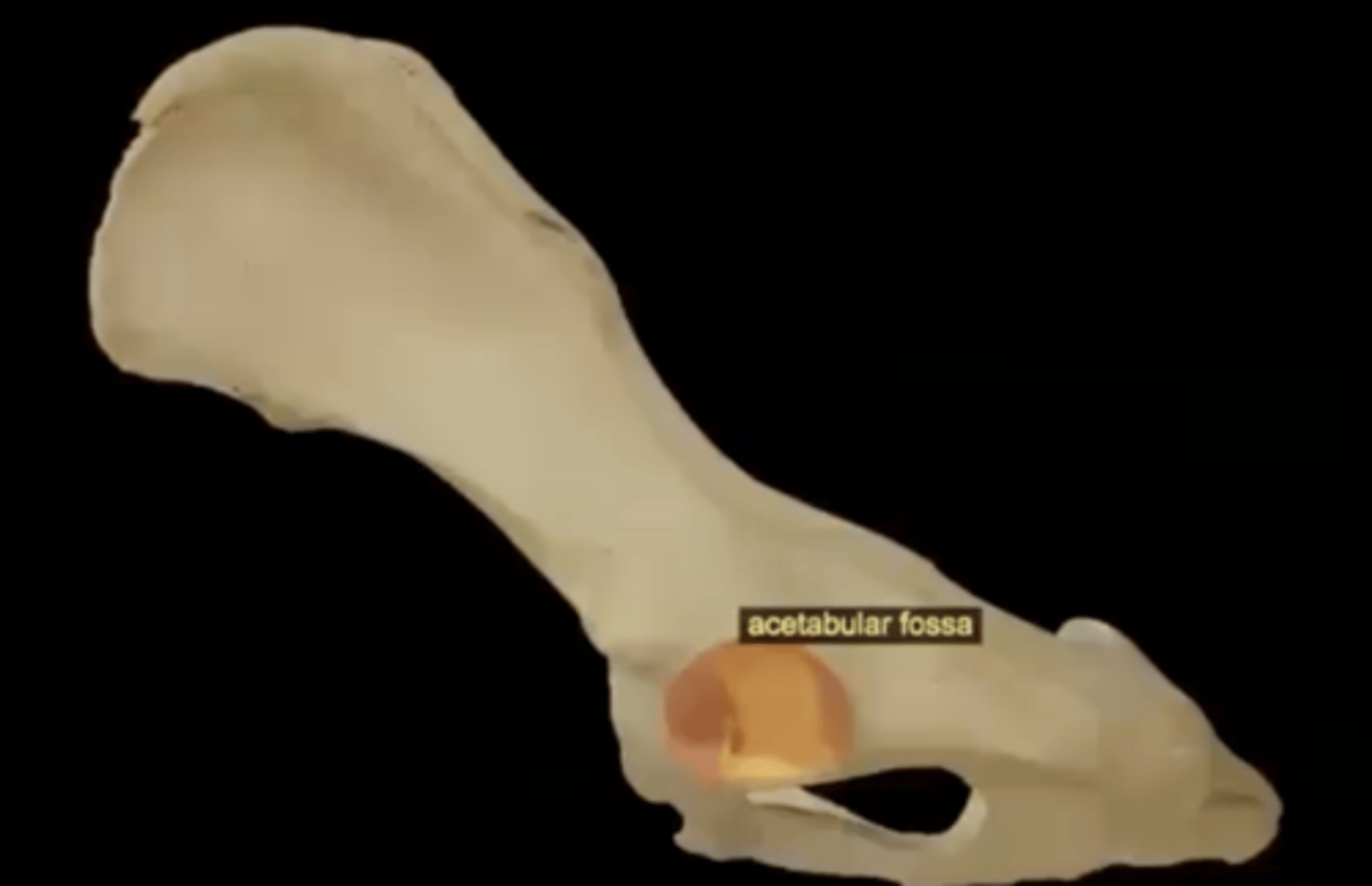
acetabular fossa
circular depression located deep in the acetabulum; where the ligament for the head of femur attaches
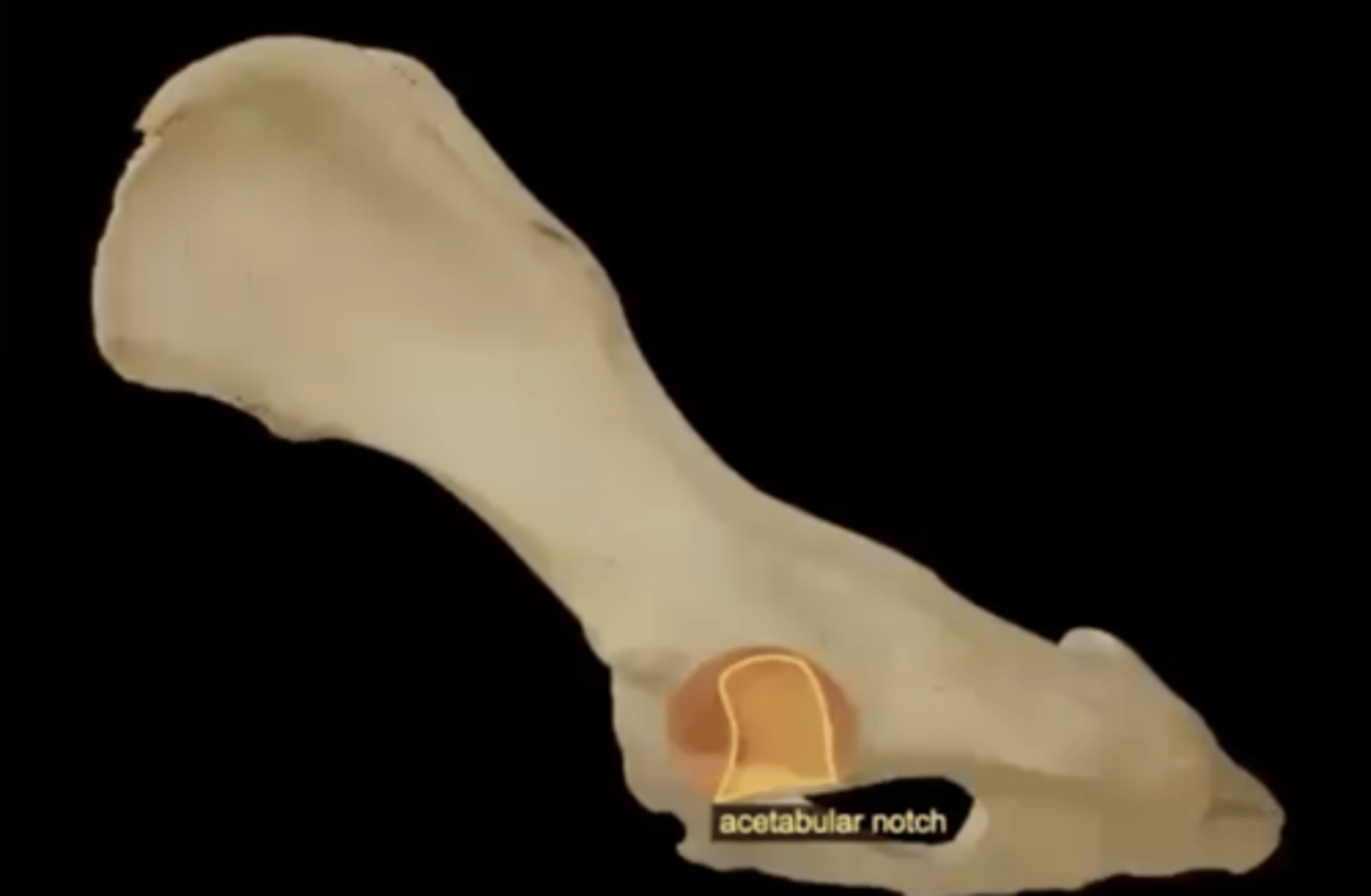
acetabular notch
incomplete wall on the inferior surface of the acetabulum
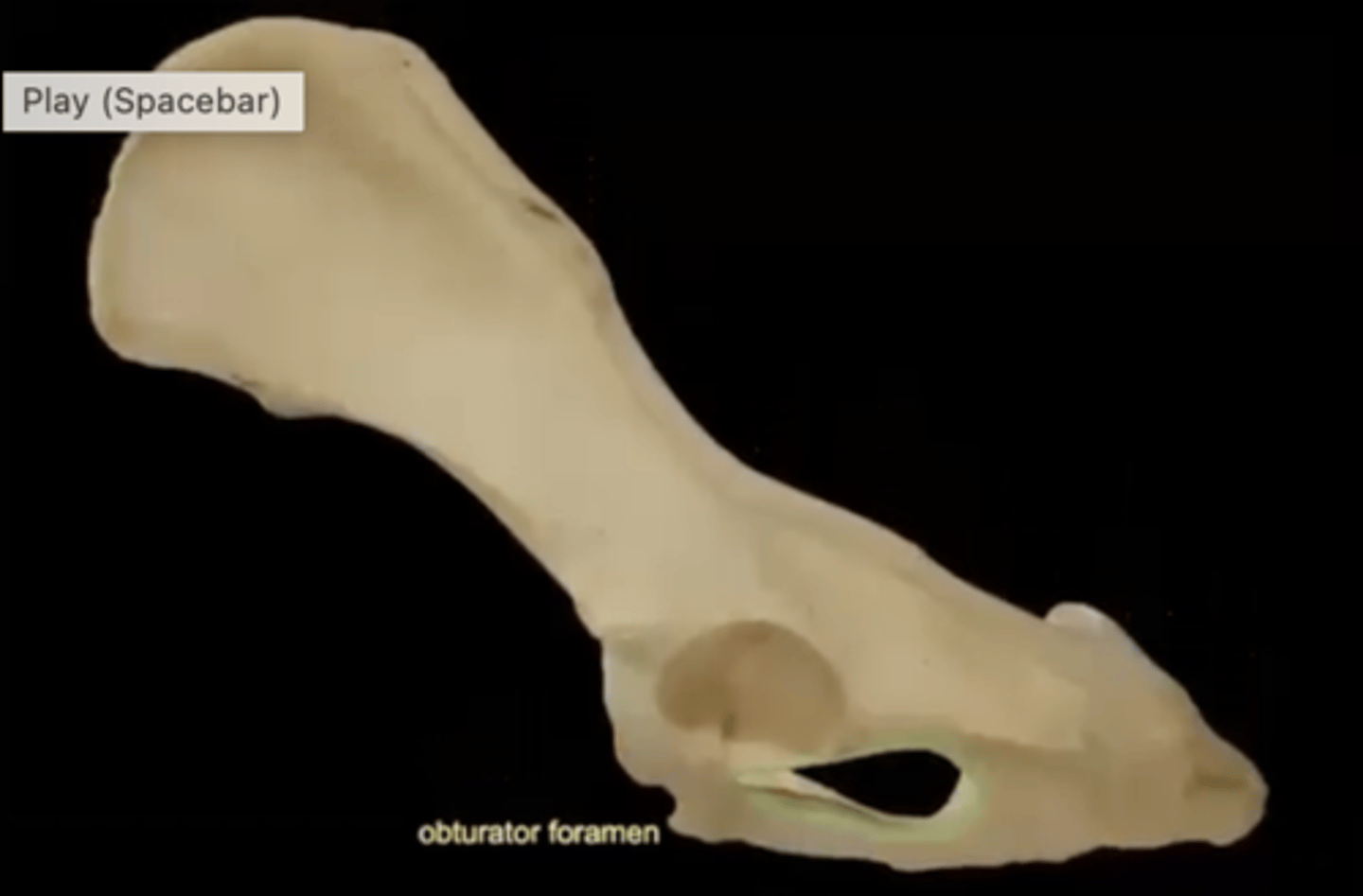
obturator foramen
opening in hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial bones
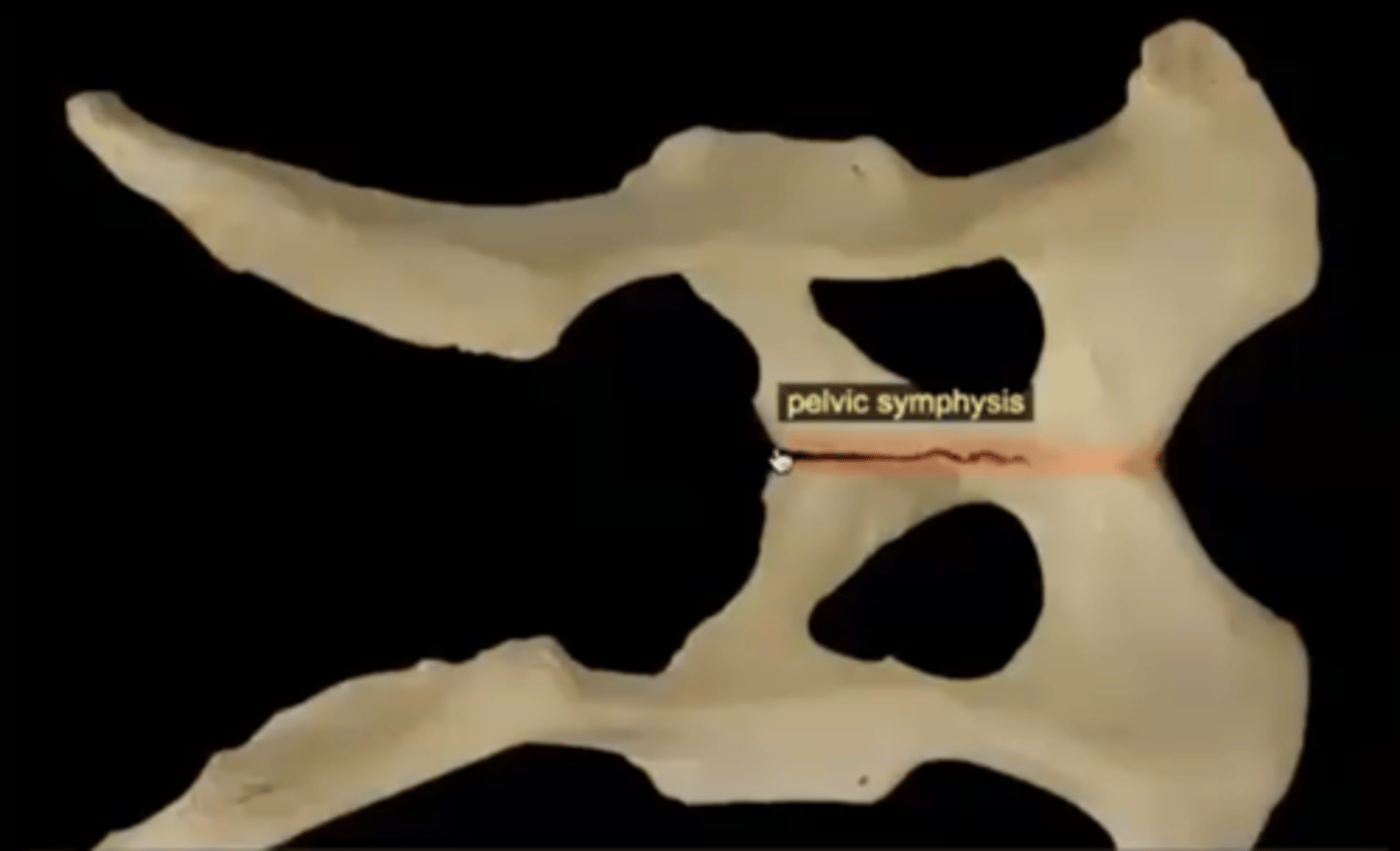
pelvic symphysis
cartilaginous joint between the two halves of the pelvis
Eight parts of the proximal femur
1.) head
2.) neck
3.) fovea capitis femoris
4.) greater trochanter
5.) lesser trochanter
6.) third trochanter
7.) trochanteric fossa
8.) intertrochanteric crest
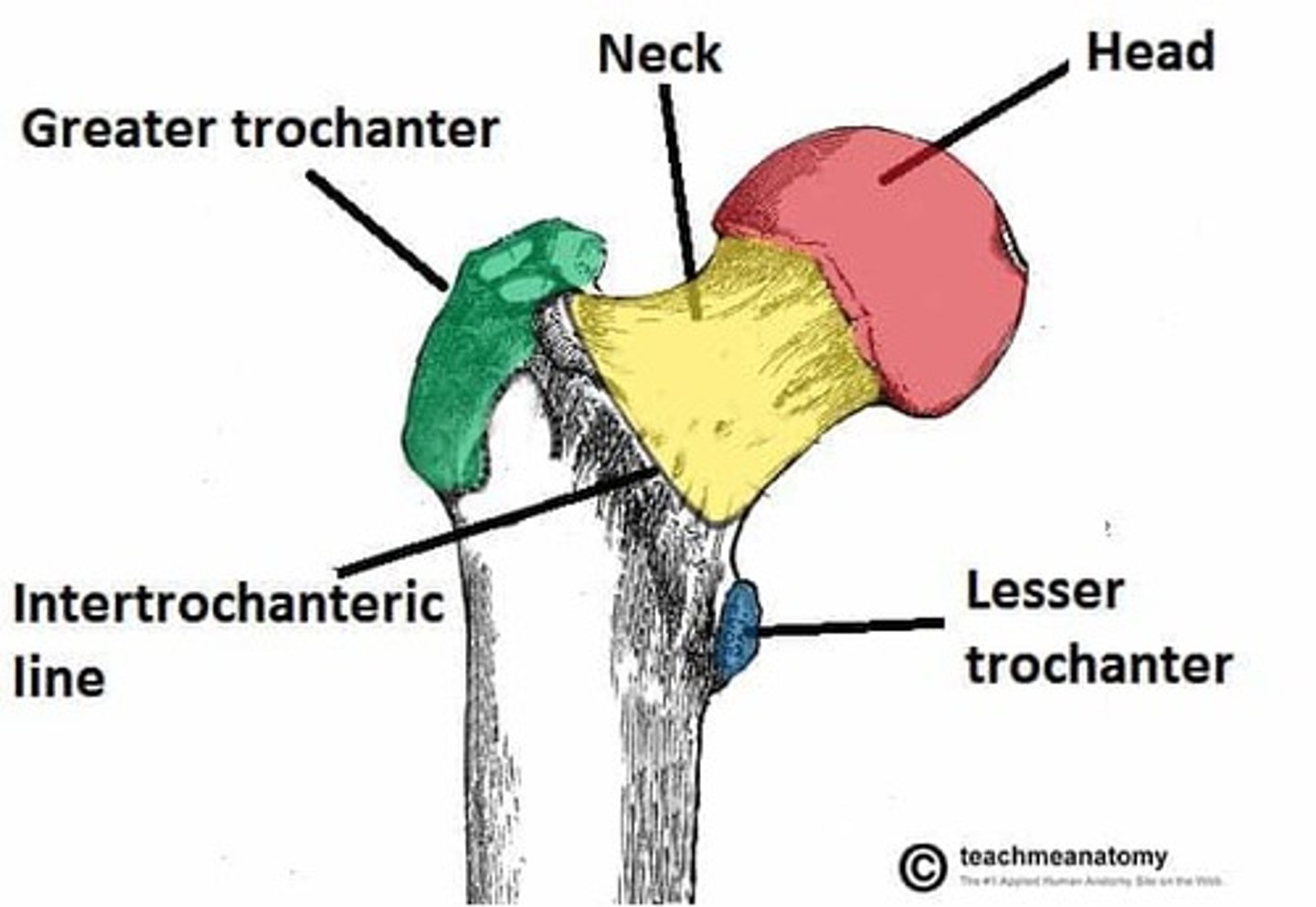
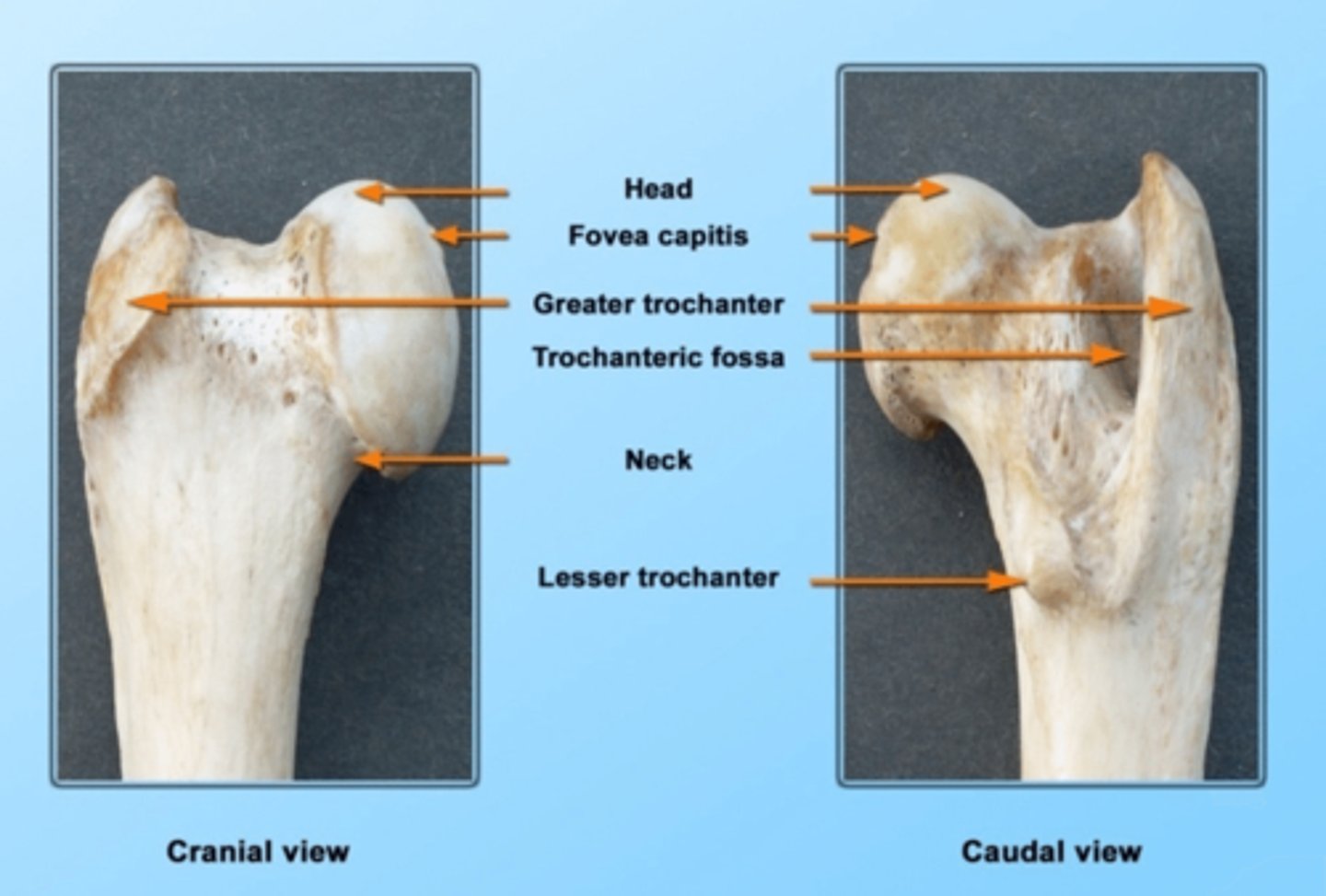
head of the femur
articulates with the acetabulum
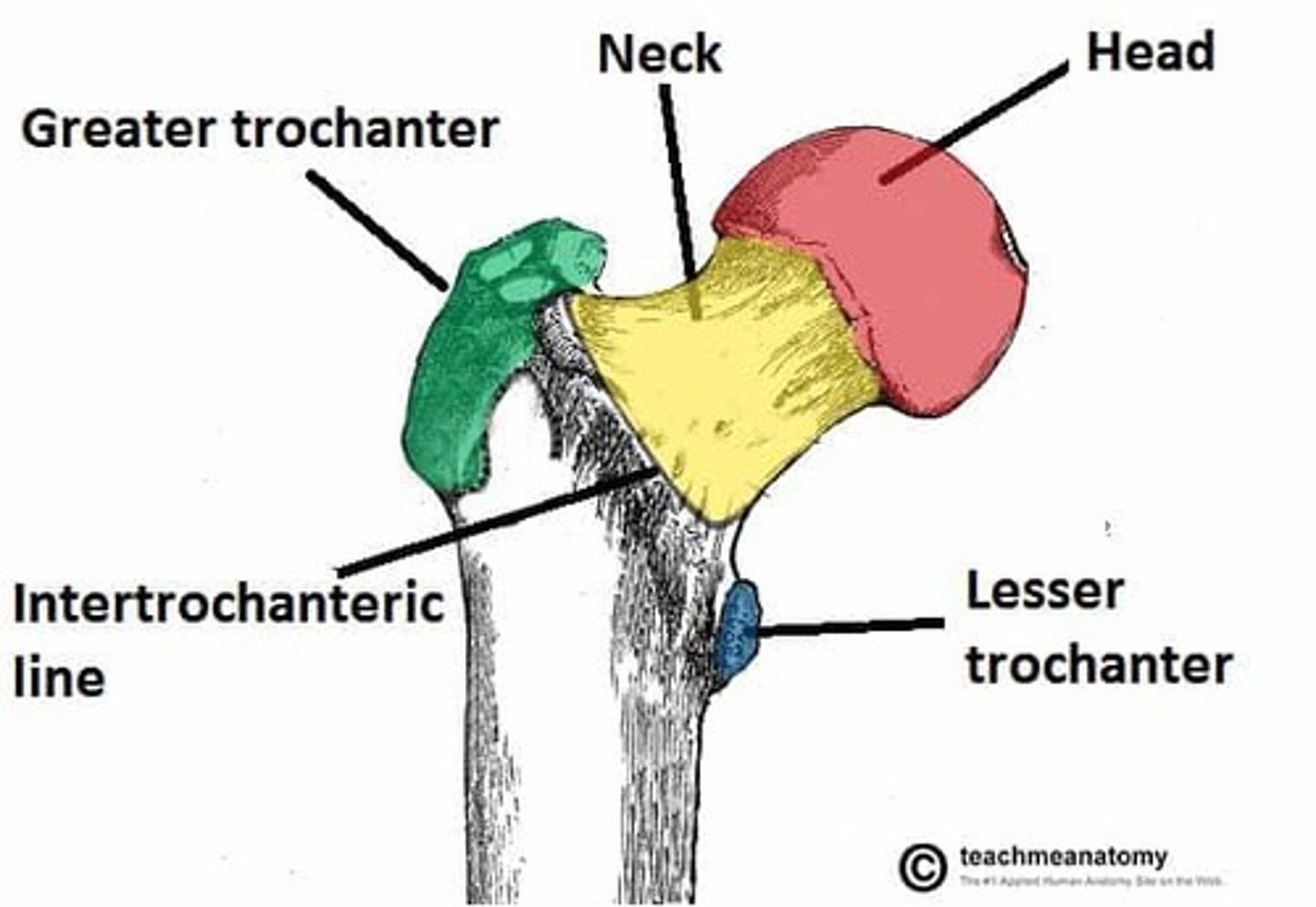
neck of the femur
connects the rounded head to the main shaft of the bone
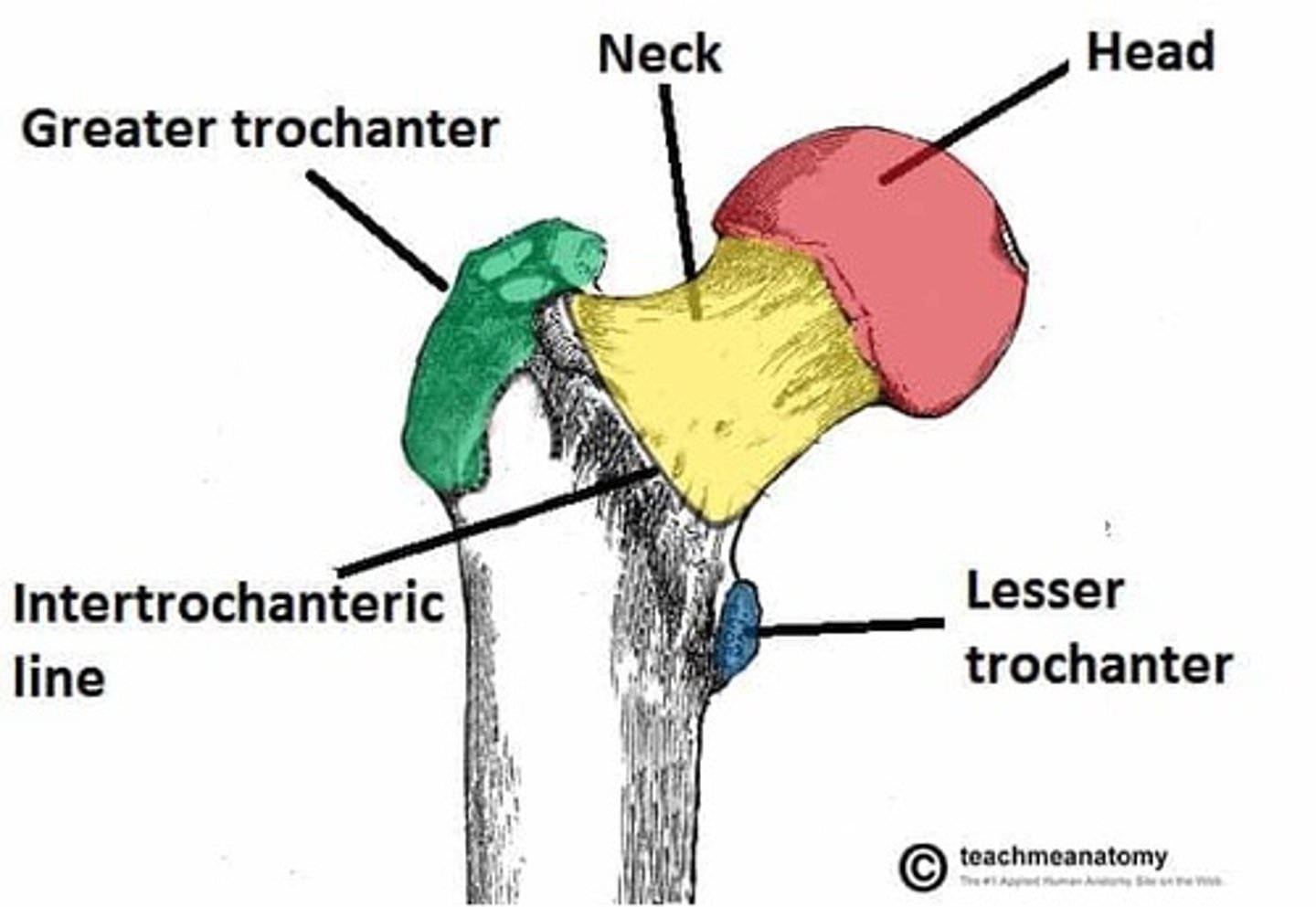
fovea capitis femoris of the femur
where the ligament of the head of the femur attaches
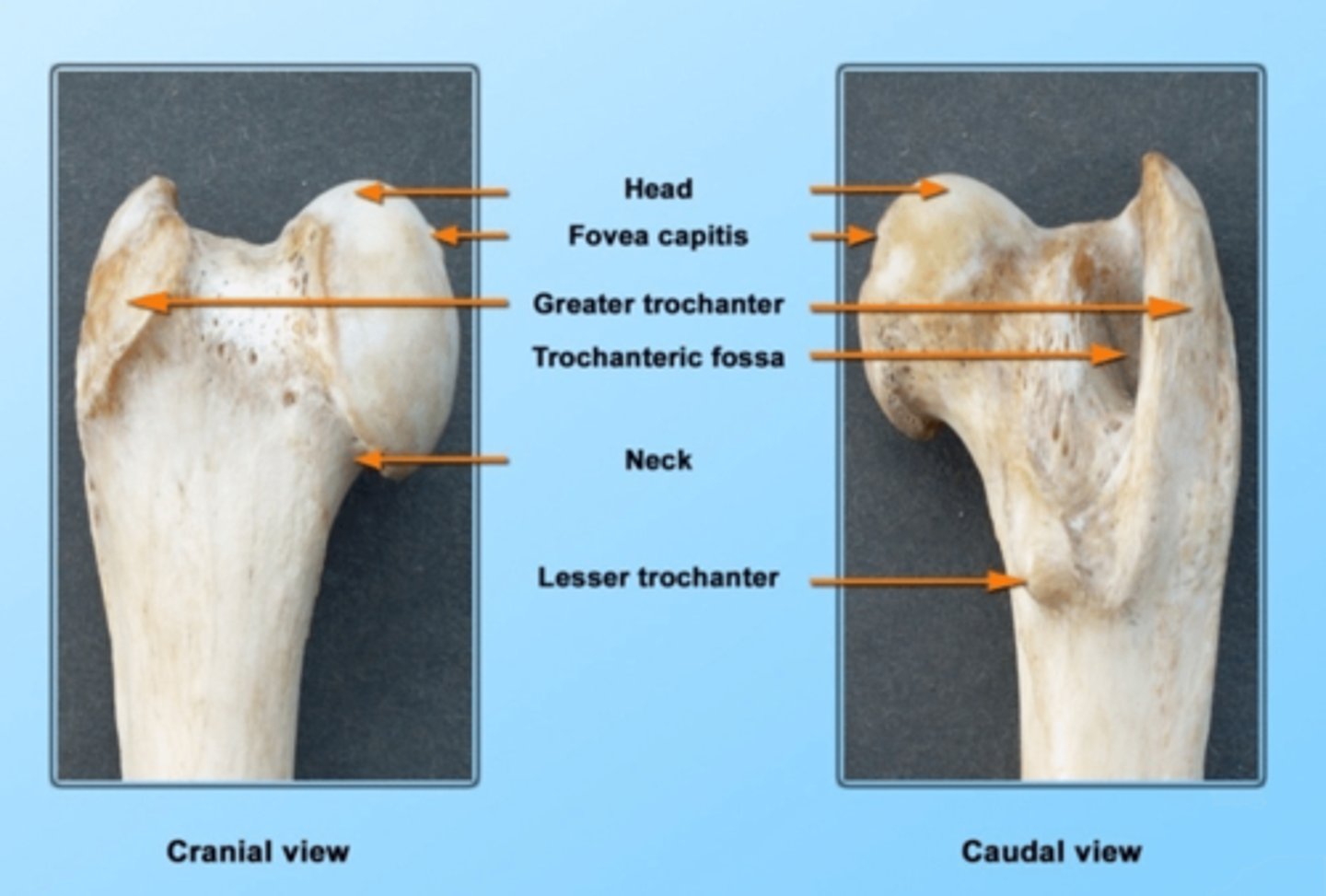
greater trochanter of the femur
large, bony prominence at the top of a dog's femur
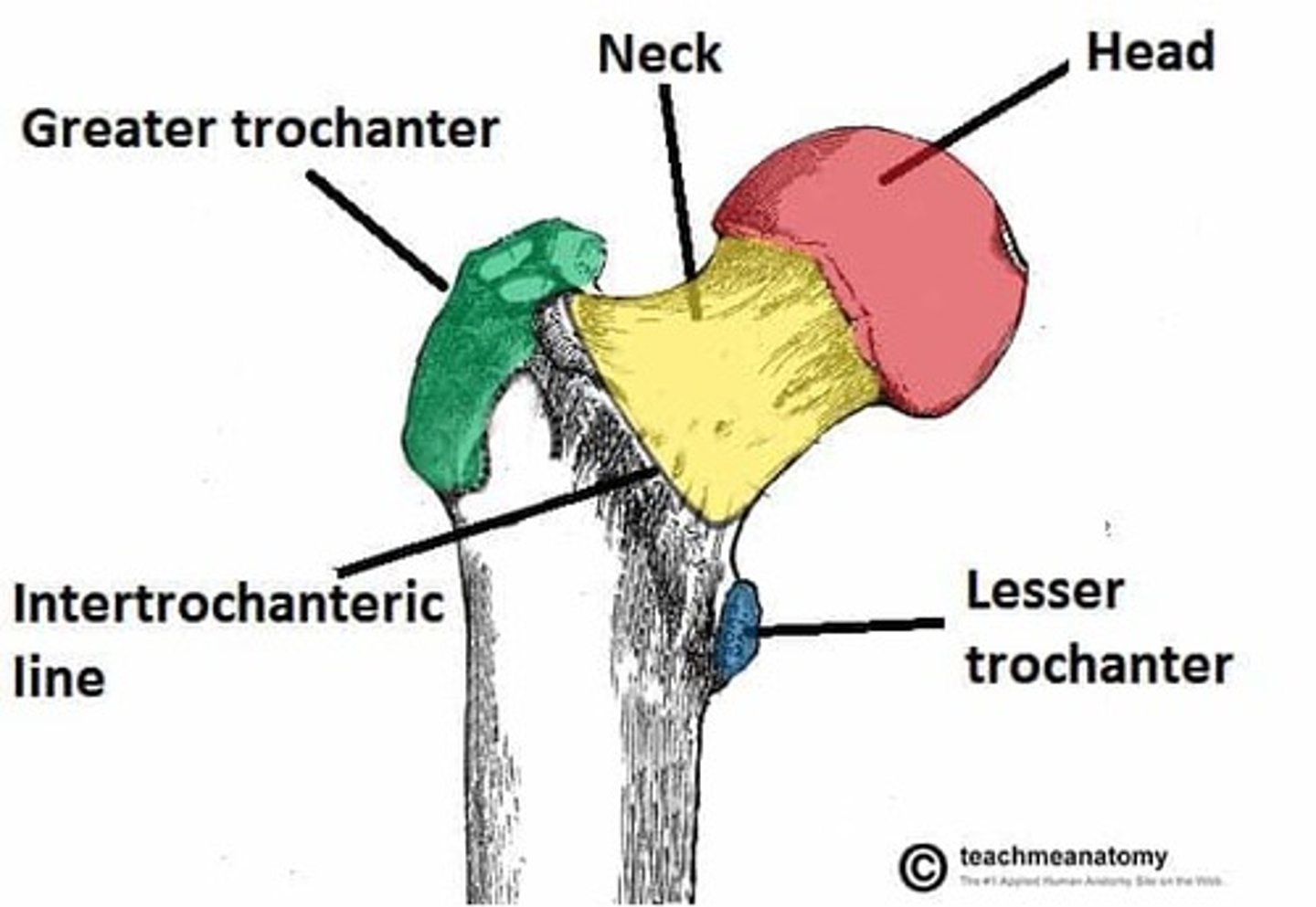
lesser trochanter of the femur
bony prominence located on the inner (medial) side of the femur
third trochanter of the femur
right below the greater trochanter
trochanteric fossa of the femur
deep notch between the root of the greater trochanter and the head of femur
intertrochanteric crest of the femur
ridge between the two trochanters on the posterior surface
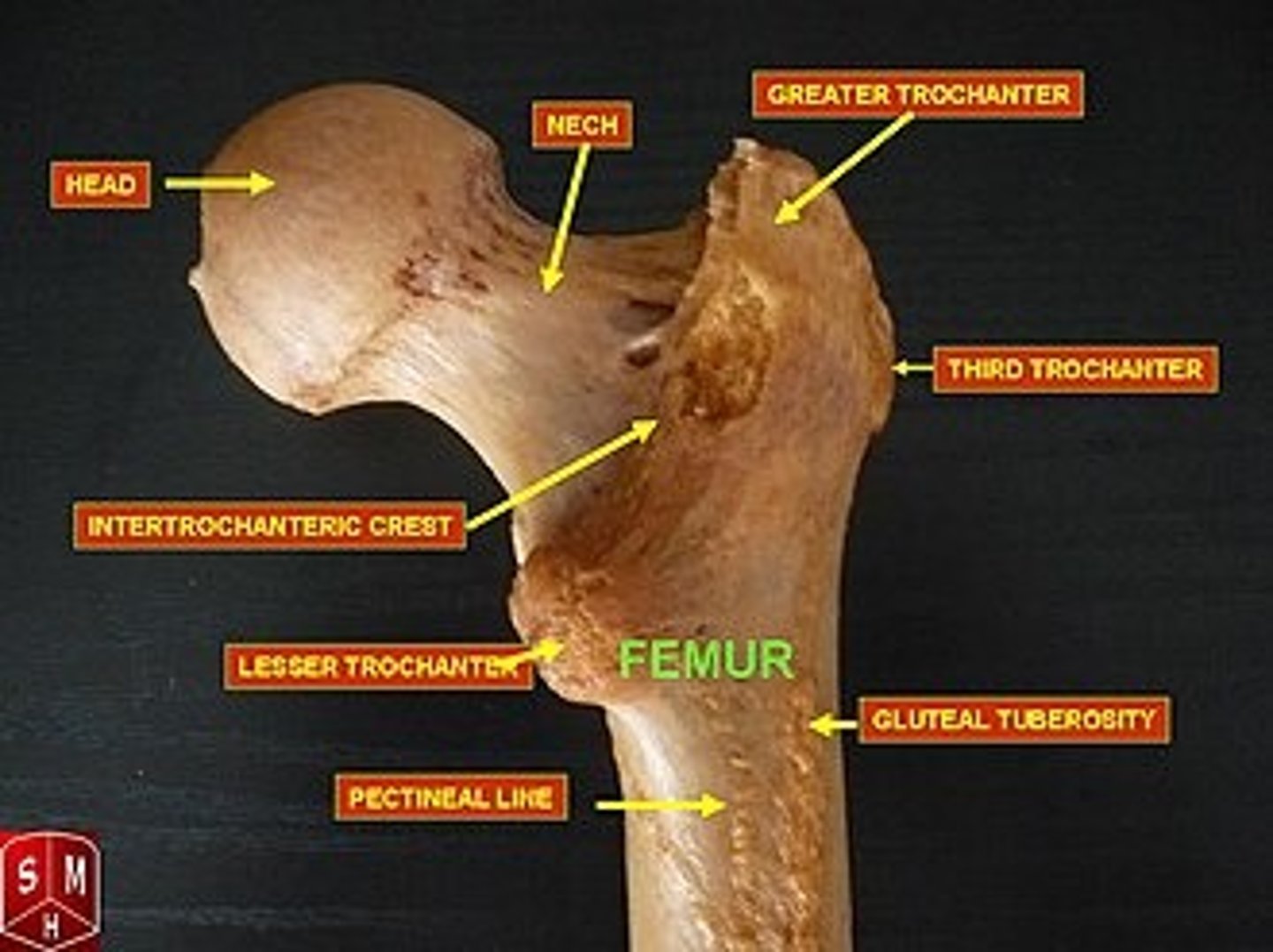
Body of the femur
The shaft of the femur; long straight middle section of bone.
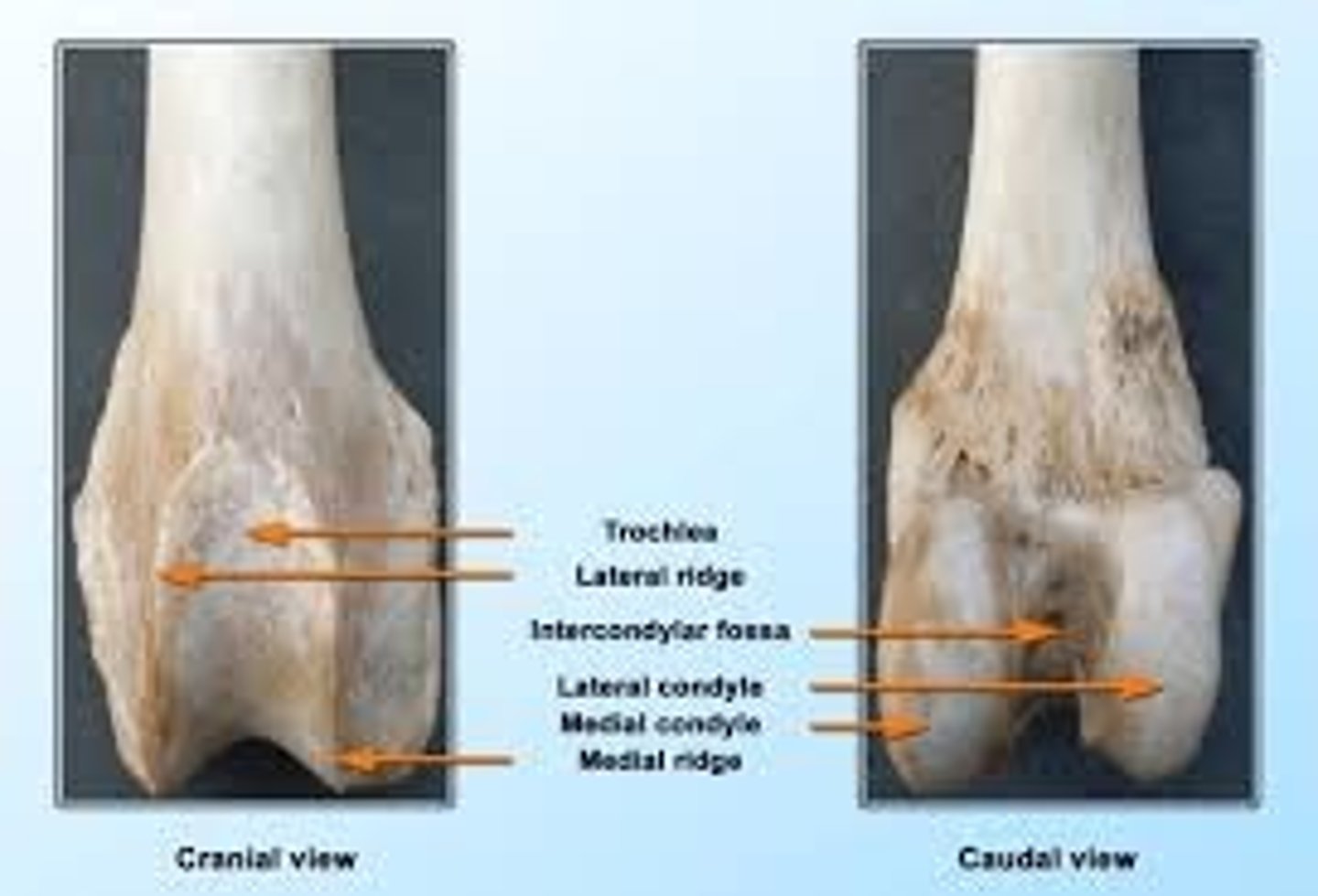
Four parts of the distal femur
1.) medial condyle
2.) lateral condyle
3.) intercondylar fossa
4.) trochlea
medial condyle of the femur
on the same side of the head of the femur; one of two rounded projections on the bottom of the femur that forms the stifle (knee) joint with the tibia
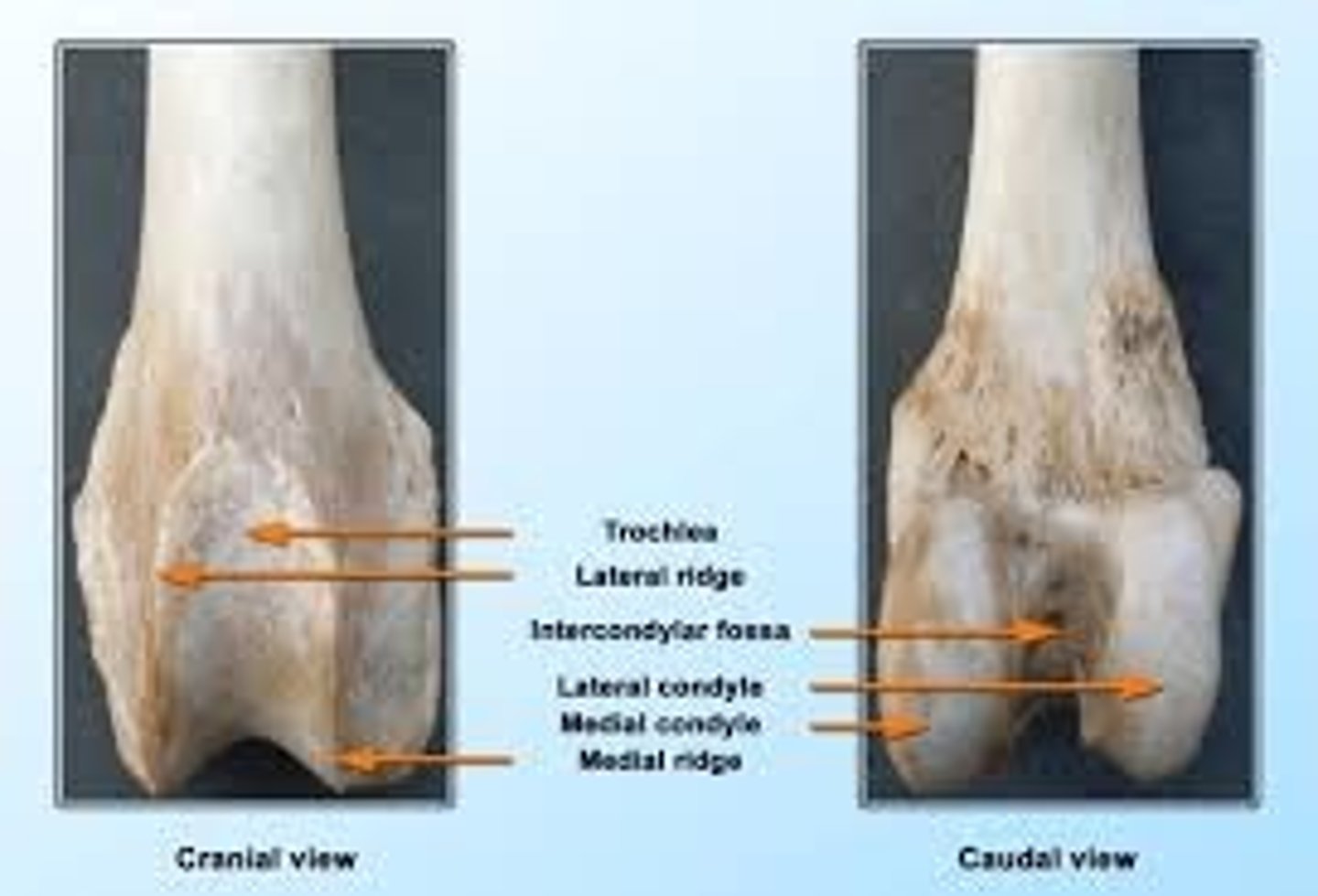
lateral condyle of the femur
outer, rounded projection at the bottom of the thigh bone that forms part of the stifle (knee) joint

intercondylar fossa of the femur
deep depression located between the condyles and beneath the popliteal surface
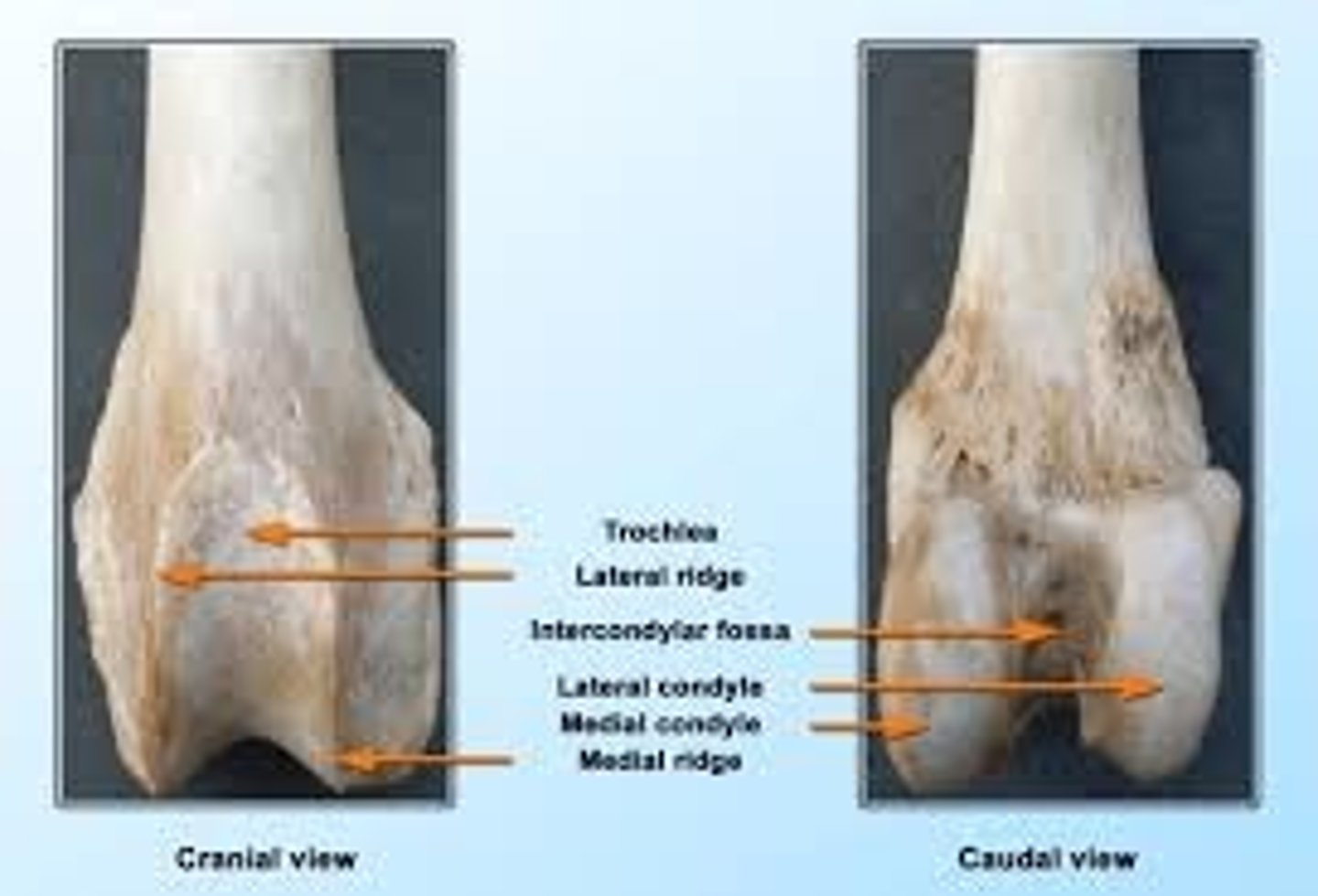
trochlea of the femur
articular groove containing the patella located cranially on the femur
Two sesamoid bones of the stifle joint:
1.) patella
2.) fabella
patella
sesamoid bone located cranially
fabella
sesamoid bones located laterally and medially
Two fabella bones
1.) gastrocnemius
2.) popliteal
The tibia and fibula are fully connected _________ and tightly connected _________
distally; proximally
The fibula is on the _________ side
lateral
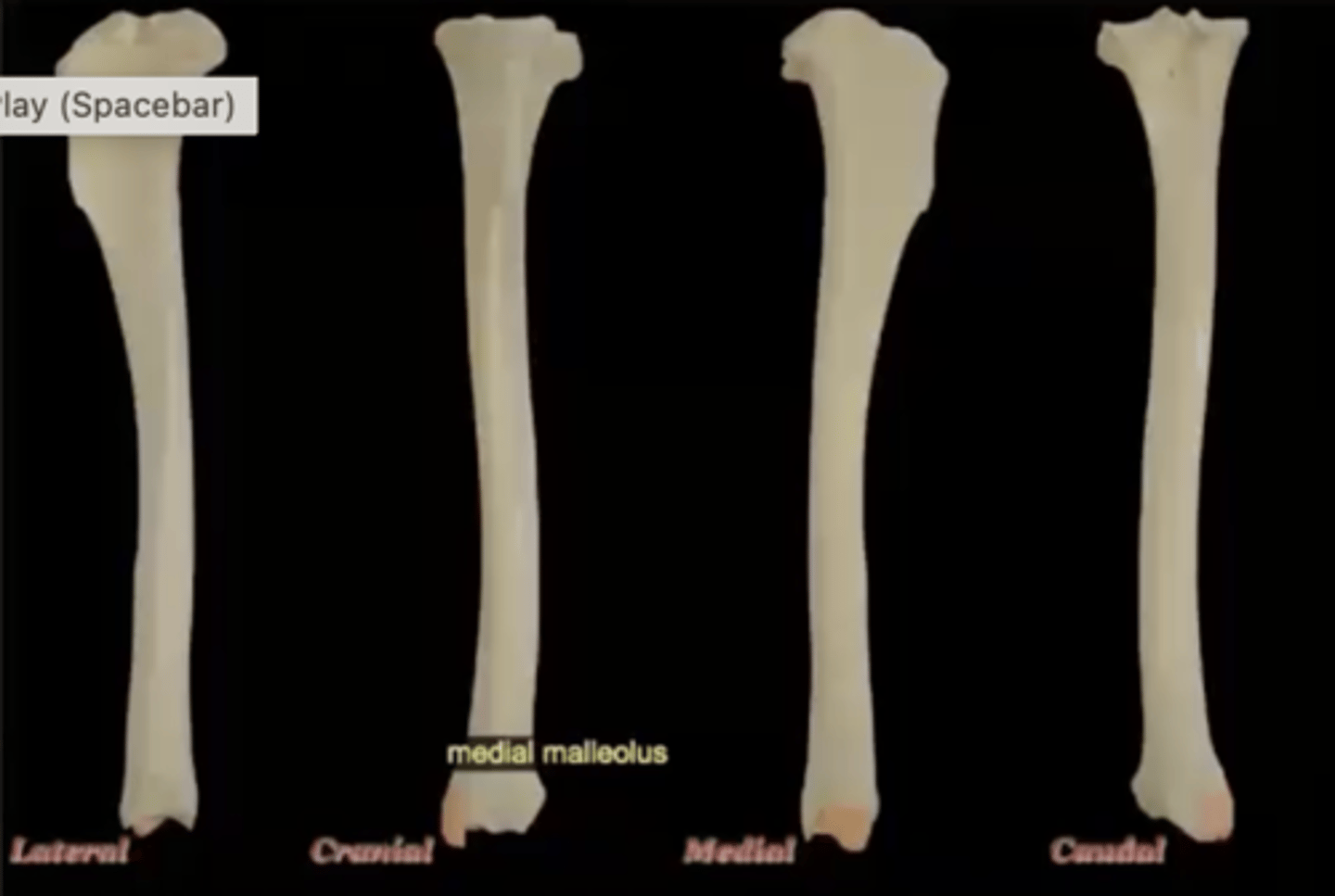
Five parts of the tibia:
1.) medial condyle
2.) lateral condyle
3.) intercondylar eminence
4.) tibial tuberosity
5.) medial malleolus
medial condyle of the tibia
medial, larger condyle of the top of the tibia
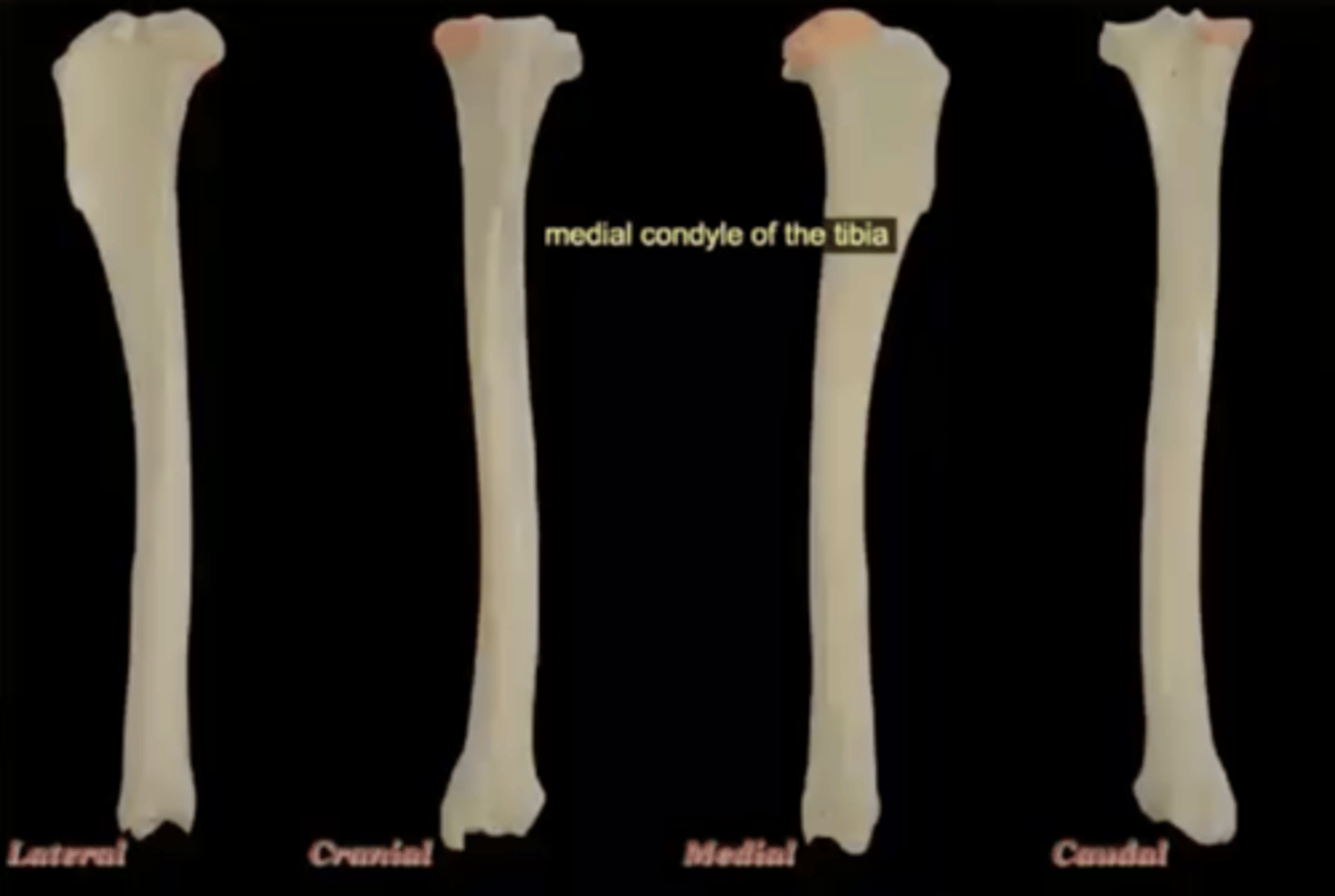
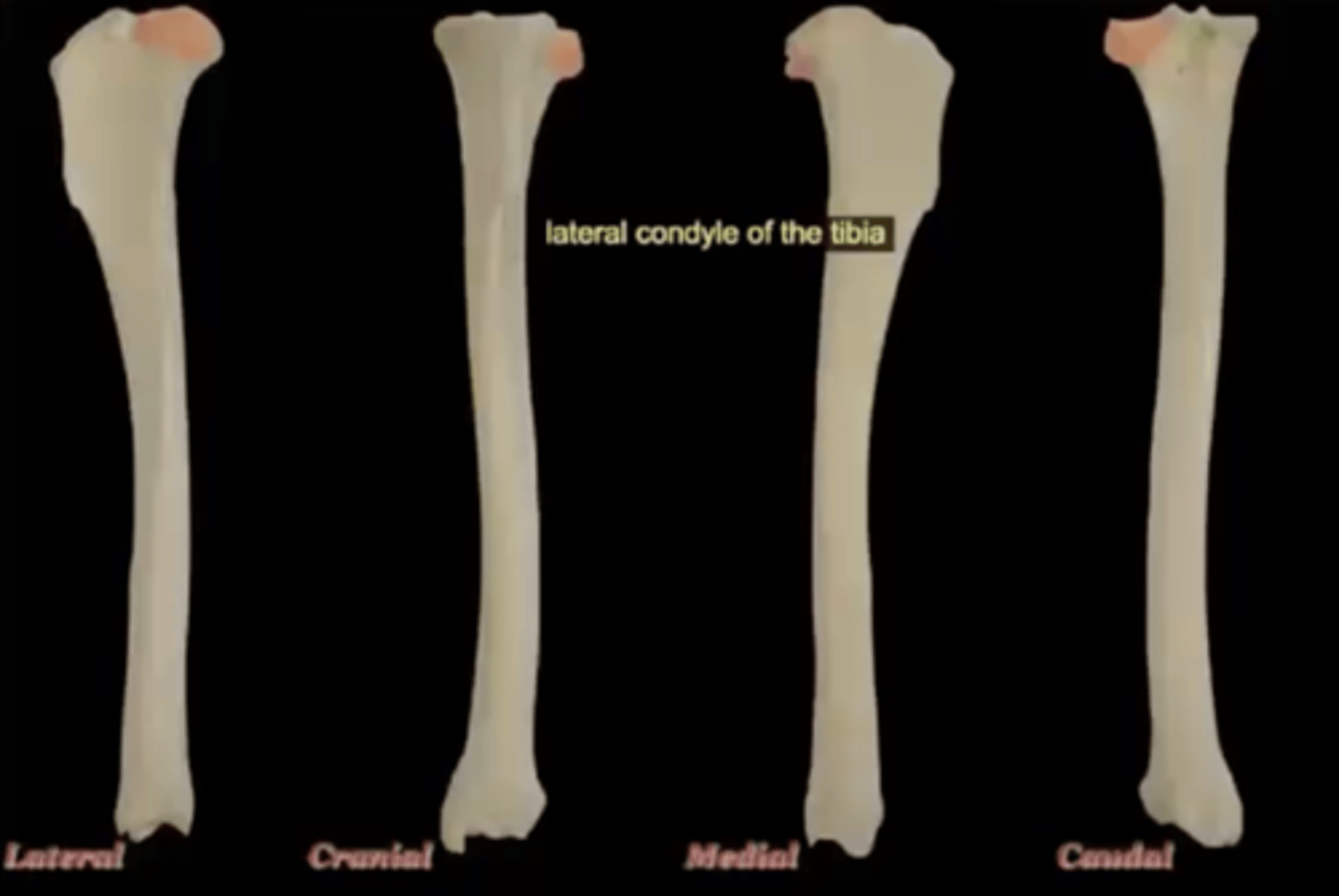
lateral condyle of the tibia
lateral, smaller condyle of the top of the tibia; on the side of fibula
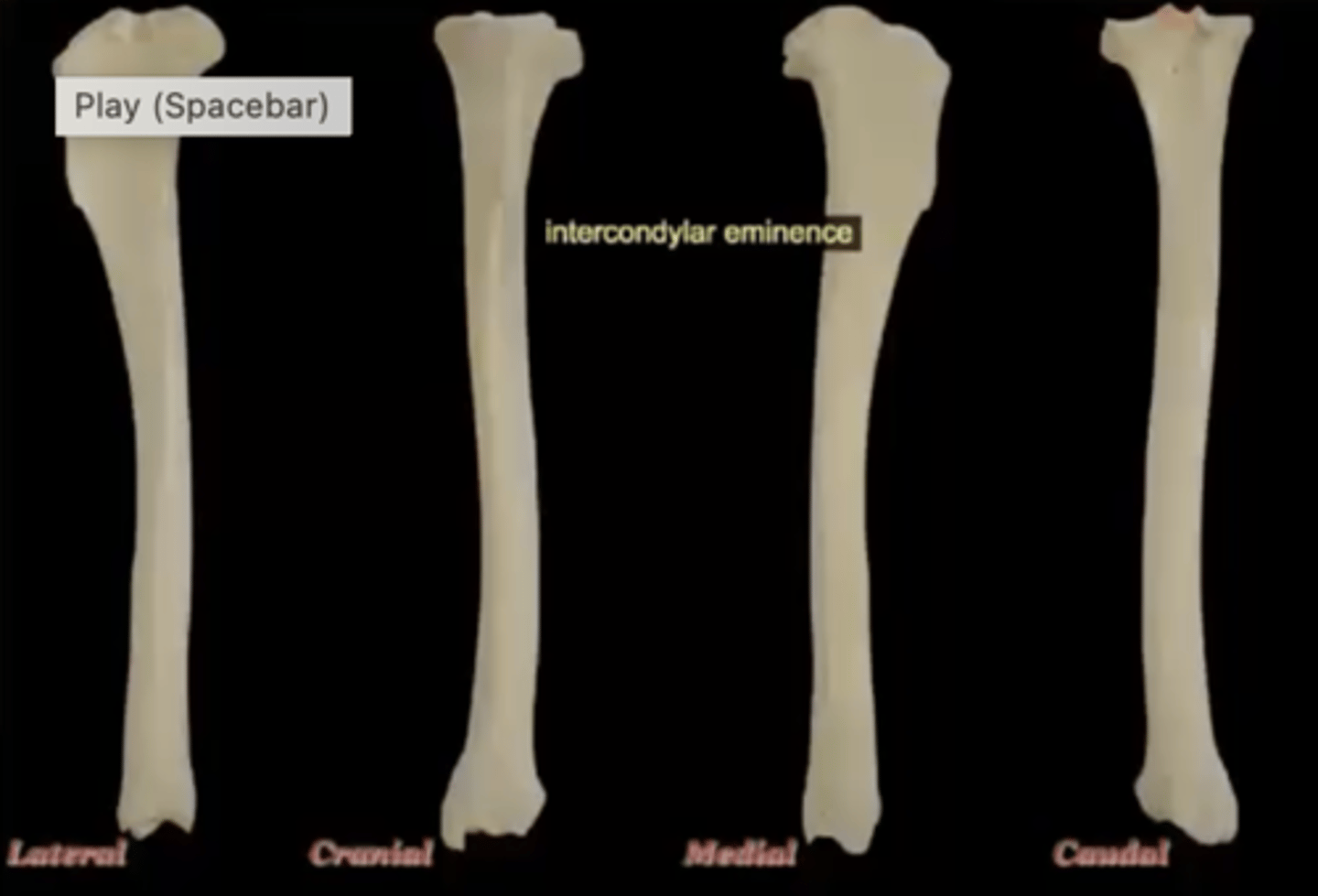
intercondylar eminence of the tibia
irregular projection located between the two condyles proximally
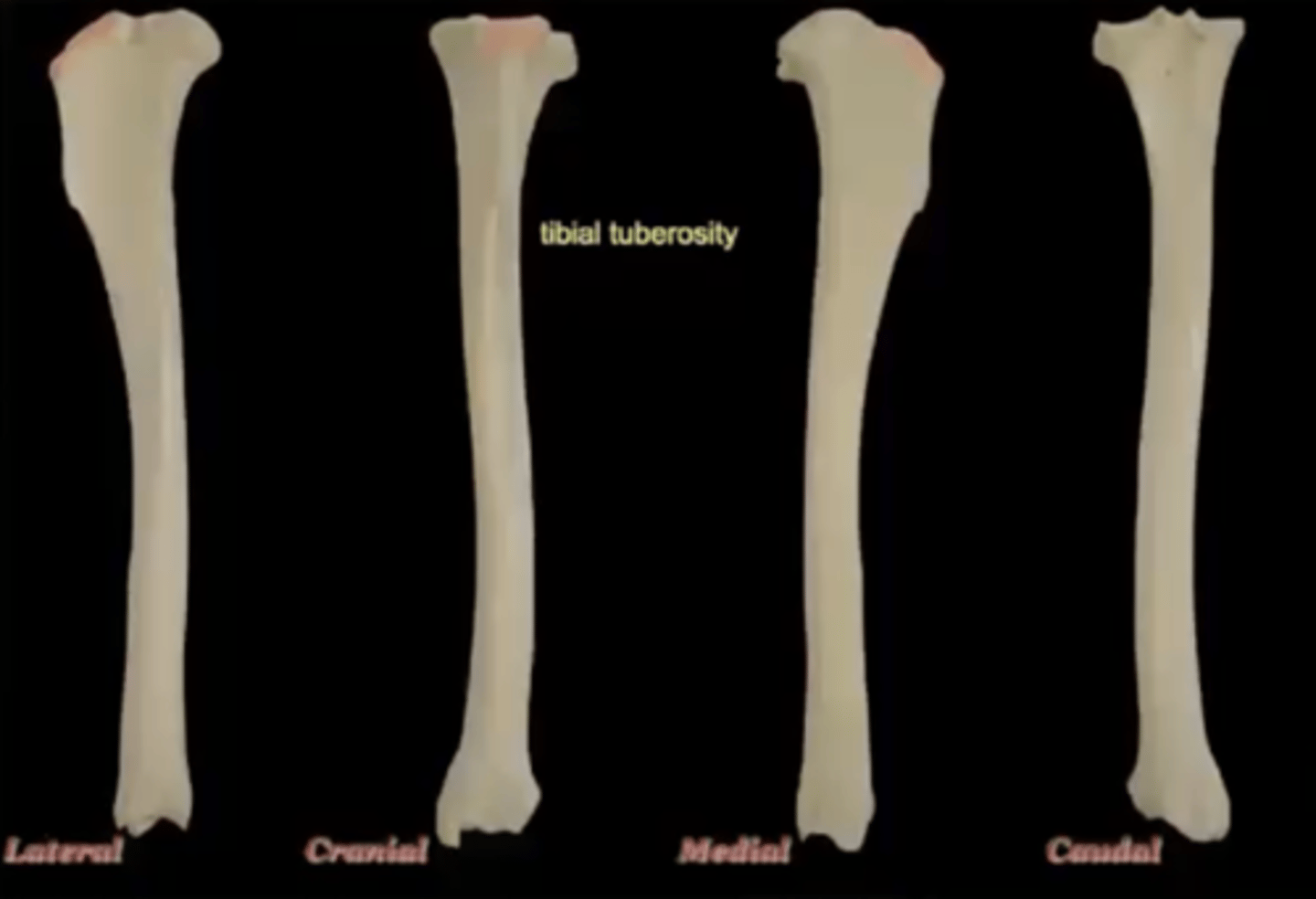
tibial tuberosity of the tibia
attachment of patellar ligament; large bump on the cranial aspect
medial malleolus of the tibia
medial process on distal end, forms medial bump of ankle
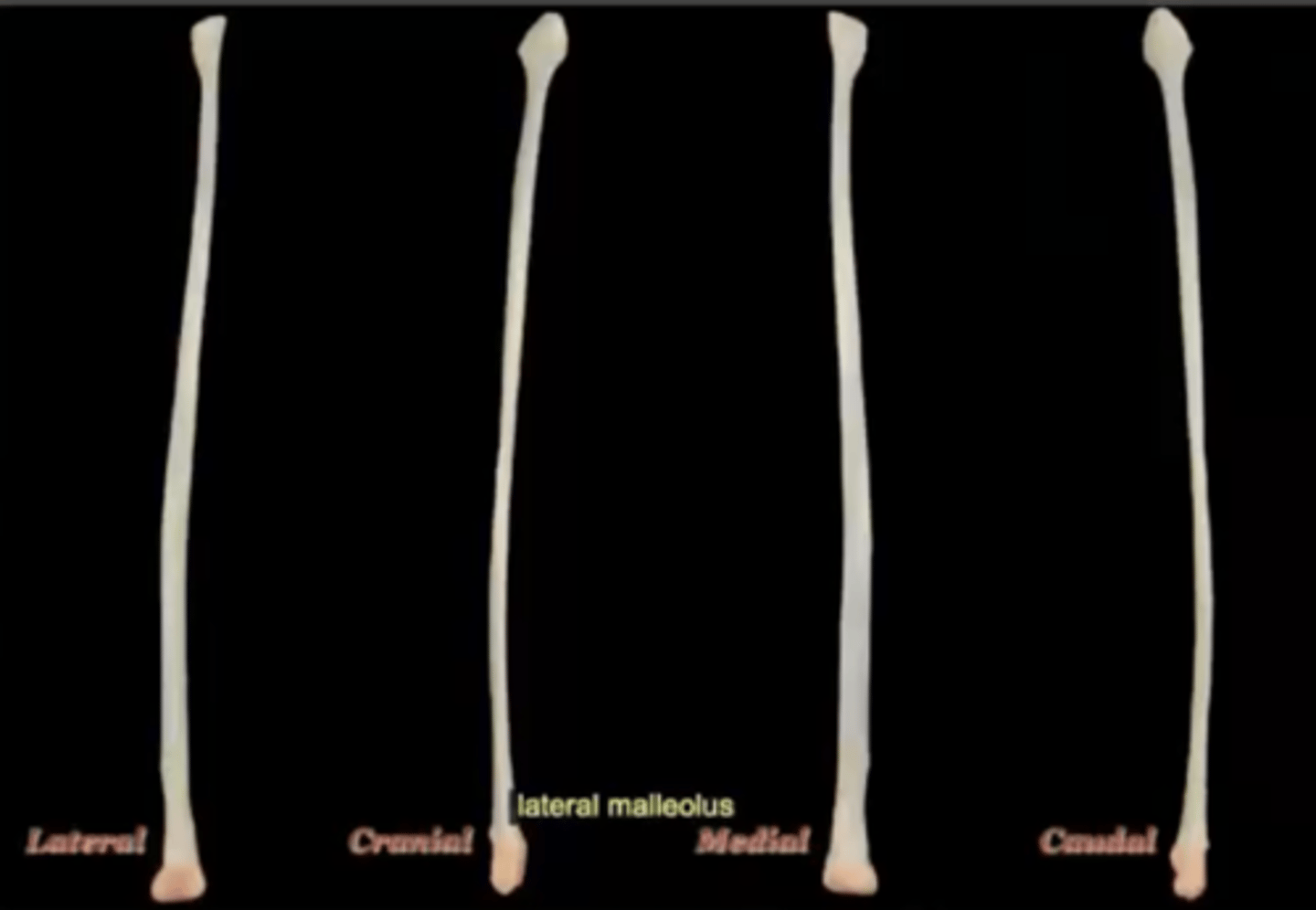
Lateral malleolus of the fibula
distal end of the fibula bone and forms a prominent knob on the outside of the ankle joint (hock)
The tarsal bones have three parts:
1.) proximal row
2.) central tarsal bone
3.) distal row
Two parts of the proximal row of tarsal bones
1.) calcaneus
2.) talus
calcaneus
large heel bone
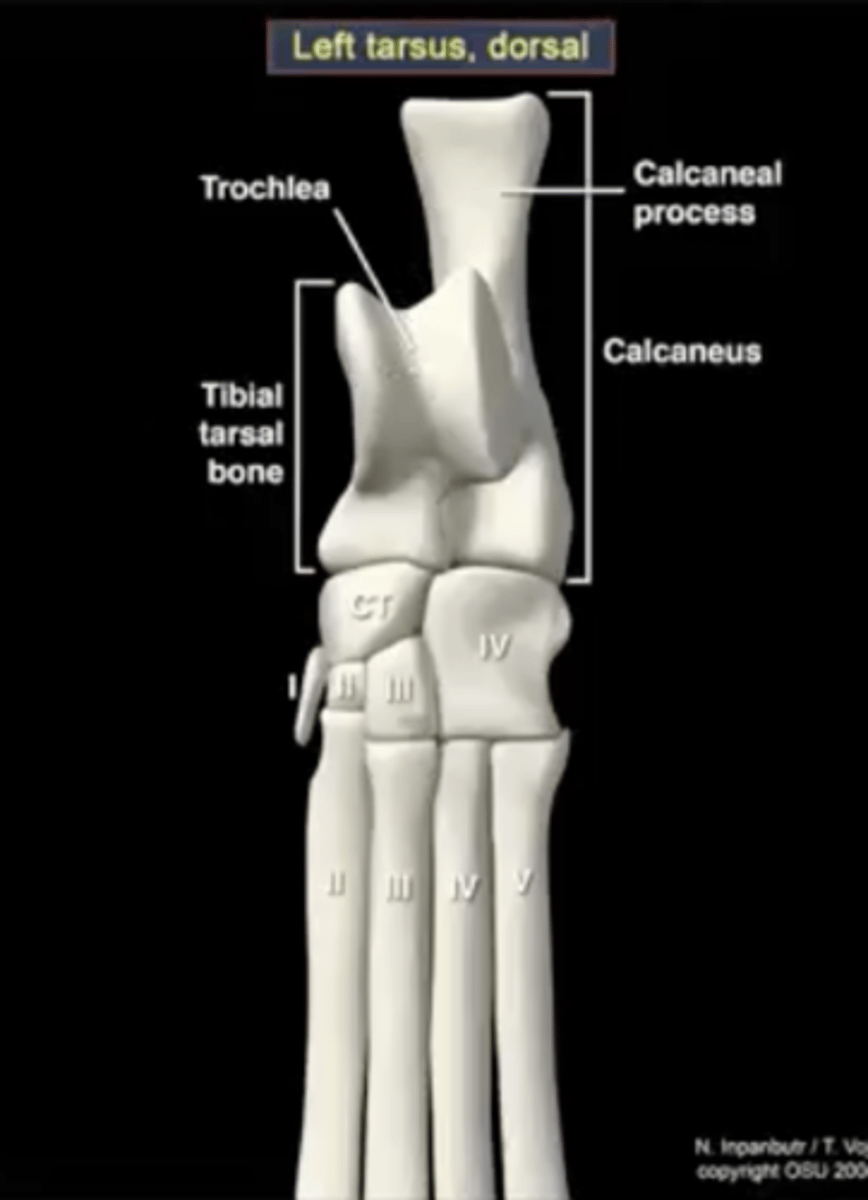
tuber calcenei of the calcaneus
calcaneal process; large process located proximally on the calcaneus
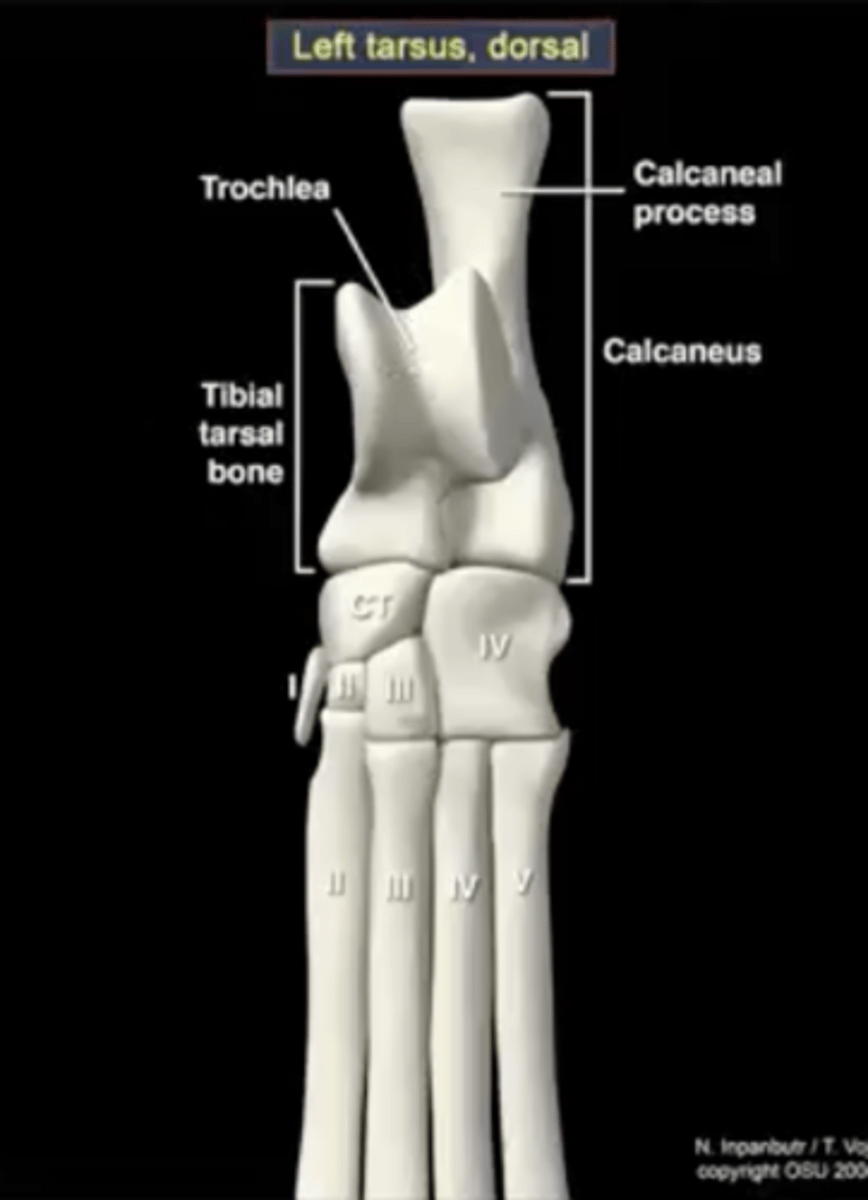
talus
ankle bone
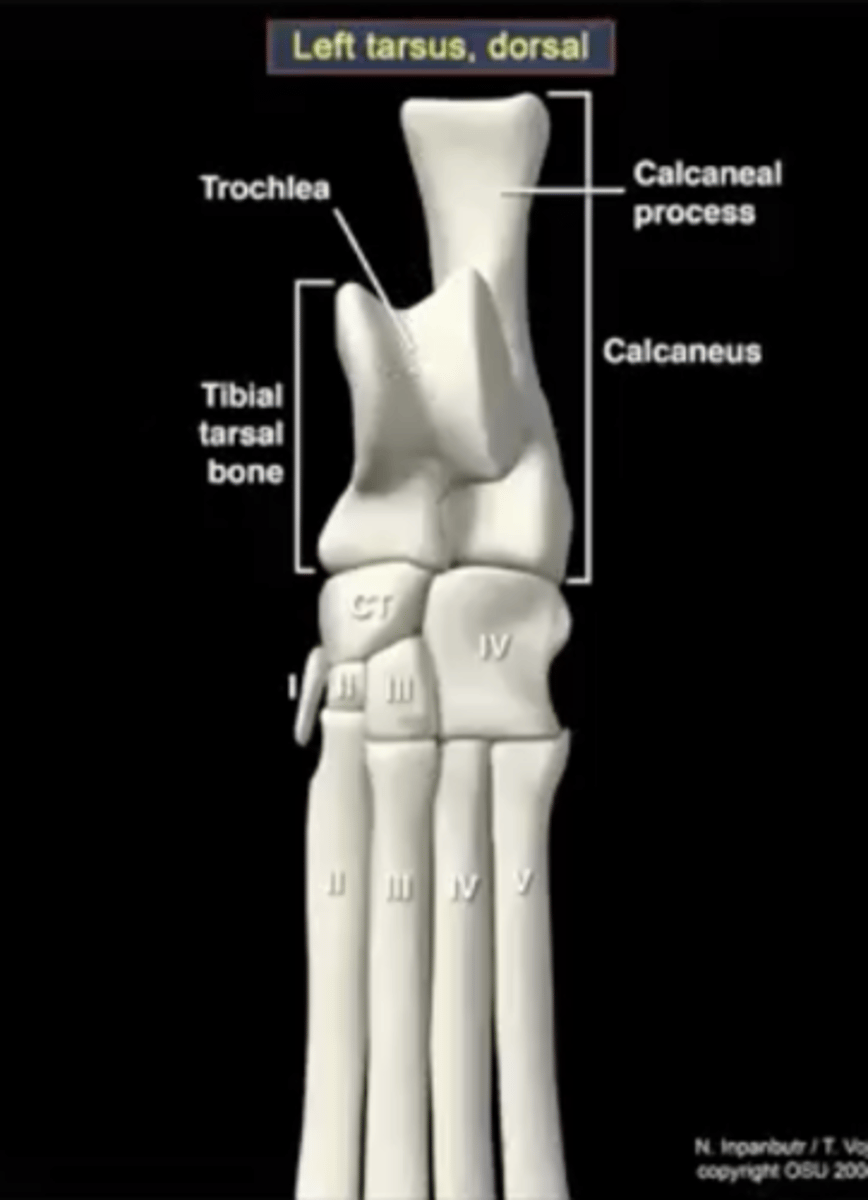
trochlea of the talus
site of articulation with the tibia
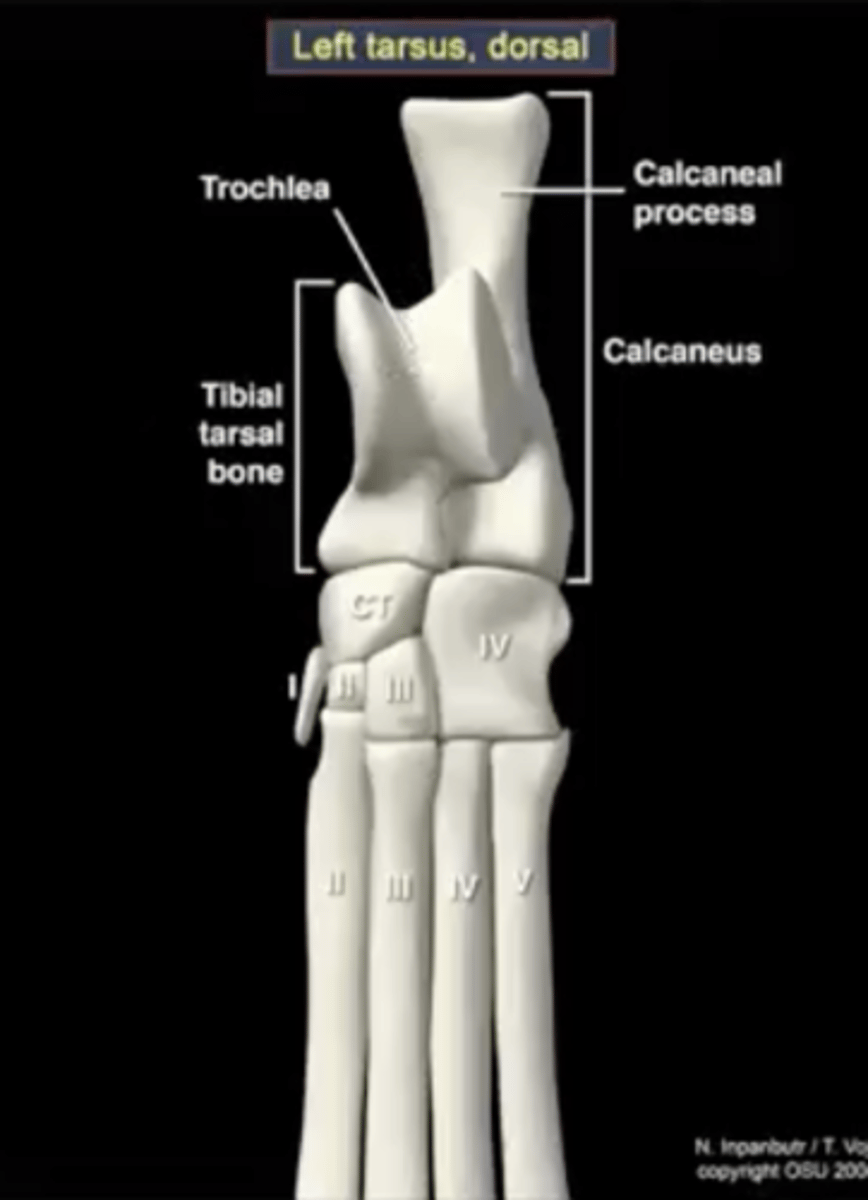
central tarsal bone
articulates with the talus
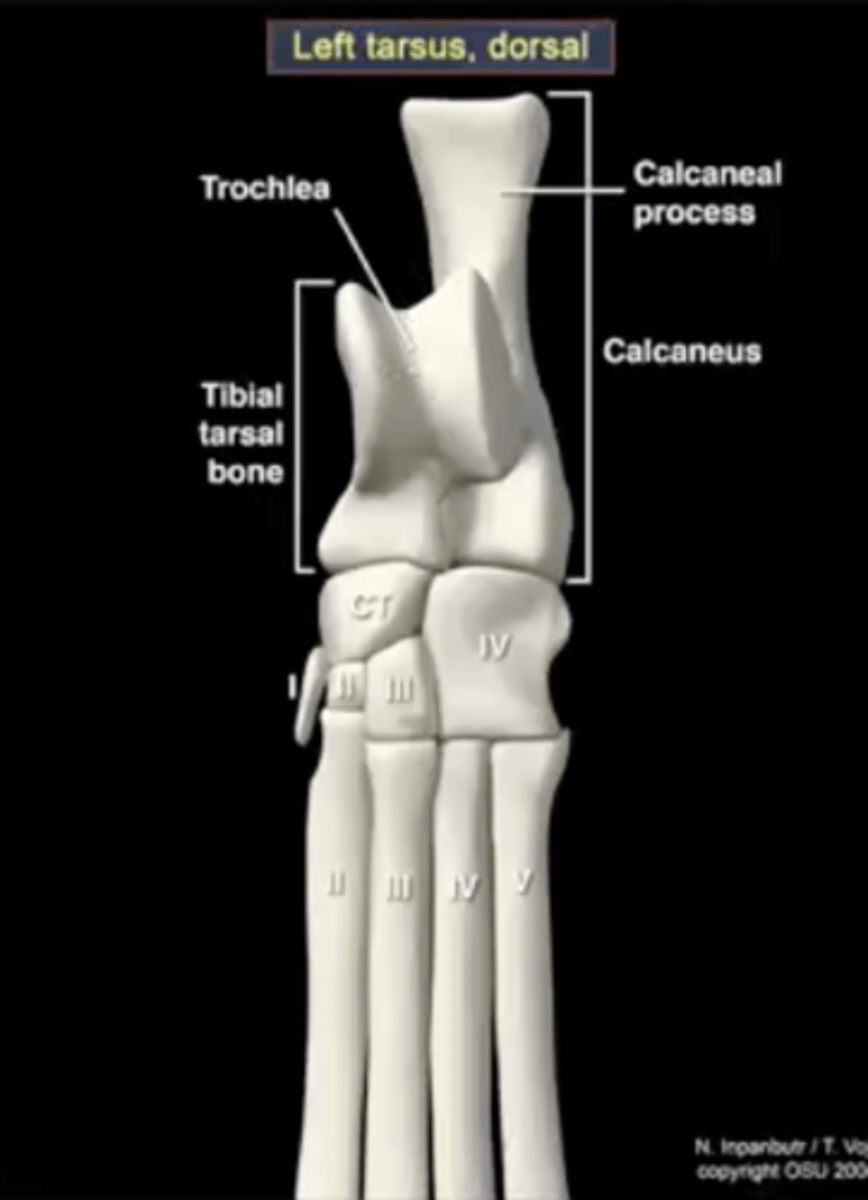
Four parts of the distal row of tarsal bones
1.) first tarsal bone
2.) second tarsal bone
3.) third tarsal bone
4.) fourth tarsal bone
fourth tarsal bone
articulates with the calcaneus; articulates with the fourth and fifth metatarsals
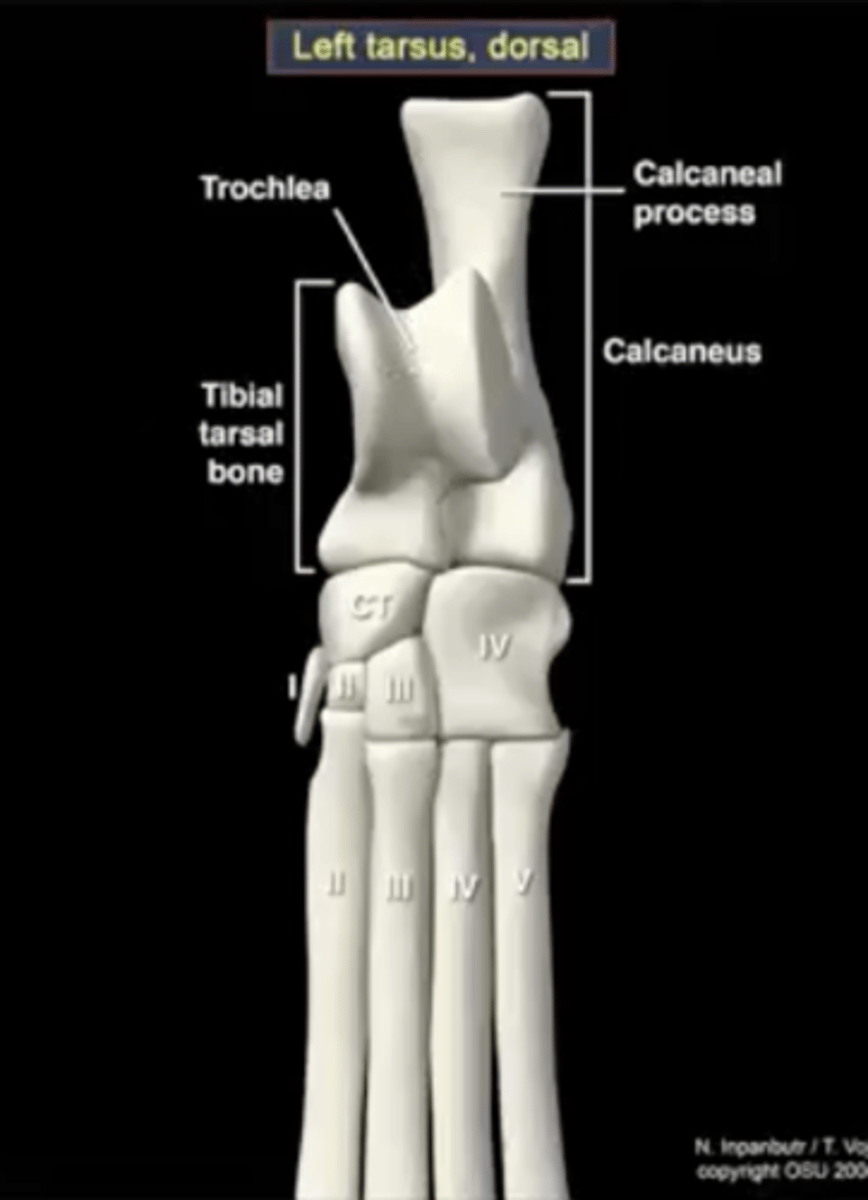
third tarsal bone
articulates with metatarsal three

second tarsal bone
articulates with metatarsal two
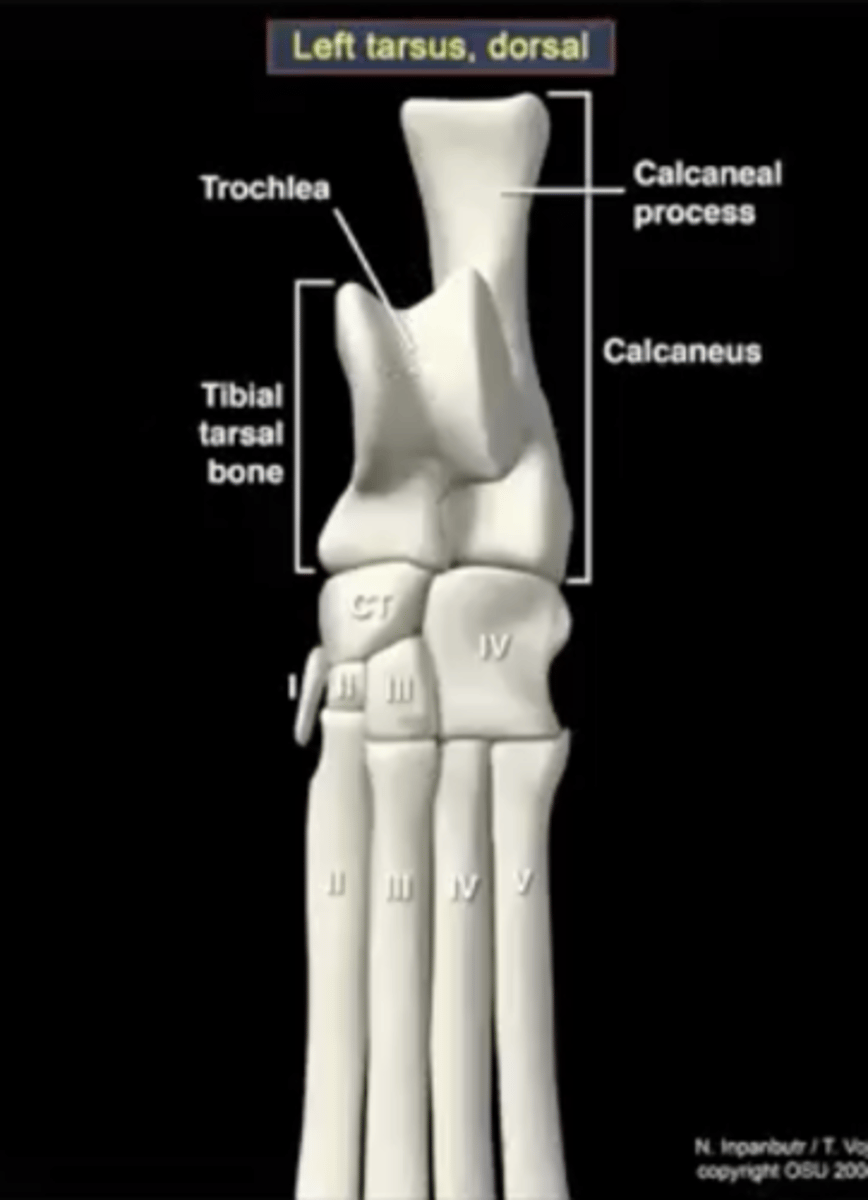
first tarsal bone
sometimes present, sometimes not
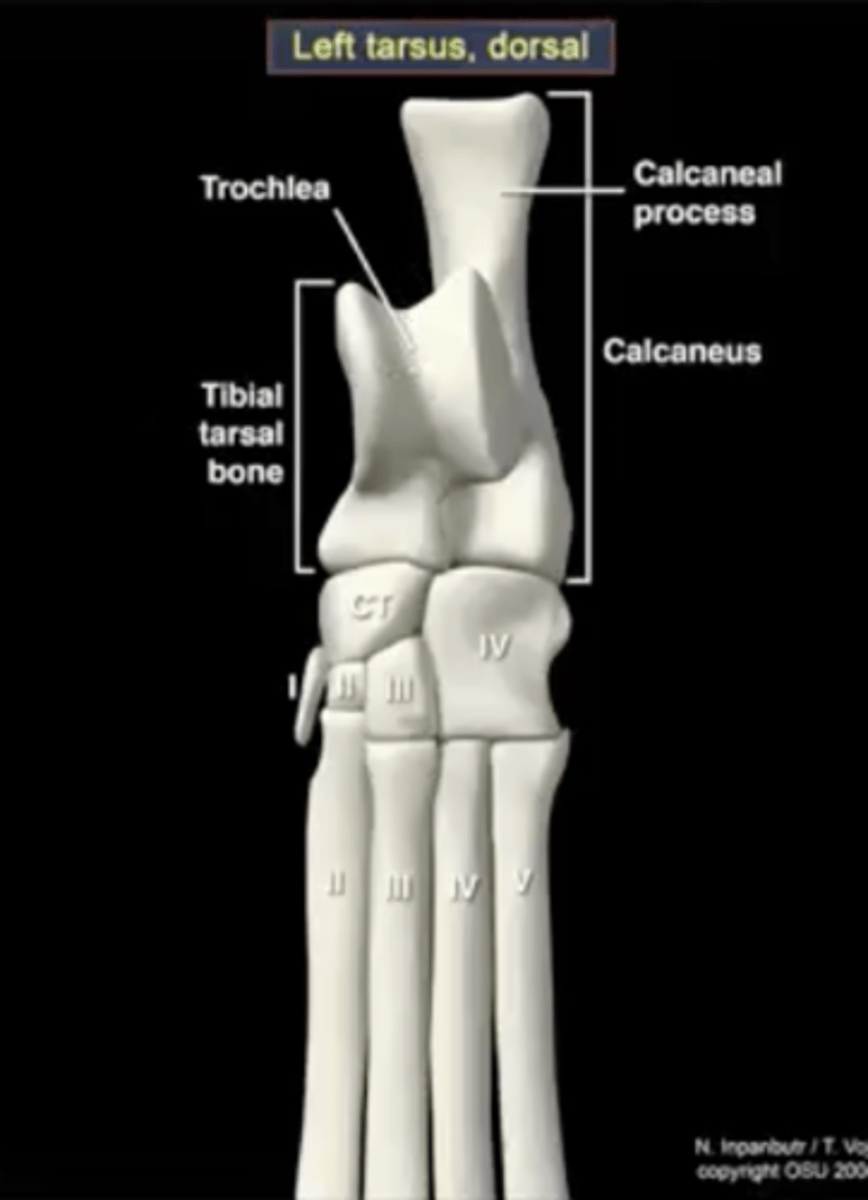
Joint between the proximal row of talus bones and the other tarsal bones
proximal inter tarsal joint
How many metatarsal bones are there?
five (II-V are always present, I may or may not be present)
Each metatarsal bone has three parts:
1.) base
2.) body
3.) head
base of metatarsal bone
articulates with tarsals
head of metatarsal bone
articulates with the phalanges
proximal sesamoid bones
located where the metatarsals meet with the phalanges
How many sets of phalanges are there?
four
Proximal phalanges
phalanges closest to the metatarsals
Middle phalanges
largest part of the phalange
Distal phalanges
the nail
Two parts of distal phalanges
1.) ungual crest
2.) ungual process
ungual crest
where the nail attaches
ungual process
inside the nail