BIS104 Final
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
Which face of the Golgi complex faces the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
A. Trans face
B. Cis face
C. Lateral face
D. Medial face
B
What determines the sequence of incorporation of sugars into oligosaccharides in the Golgi?
A. Ribosomes
B. Glycosyltransferases
C. Lipid transferases
D. ATPases
B
Which enzyme cleaves mannose residues during glycosylation of N-linked oligosaccharides?
A. alpha-Mannosidase I/II
B. GlcNAc Transferase I/II
C. Galactosyl-transferase
D. Sialyltransferase
A
Which enzyme adds NAG residues during glycosylation of N-linked oligosaccharides?
A. alpha-Mannosidase I/II
B. GlcNAc Transferase I/II
C. Galactosyl-transferase
D. Sialyltransferase
B
According to the vesicular transport model, how is cargo transported through the Golgi complex?
A. Cargo is shuttled in vesicles from the CGN to the TGN, but each golgi cistern remains static
B. Each cistern matures as it moves from the cis face to the trans face
C. Cargo moves through the cytoplasm independently
D. Cargo is transported by microtubules
A
Which model suggested that each cistern of the Golgi complex matures as it moves from the cis to the trans face?
A. Vesicular transport model
B. Cisternal maturation model
C. Anterograde transport model
D. Endocytosis model
B
What is a key feature of the current model of Golgi transport?
A. It only involves vesicle transport
B. It combines the cisternal maturation model with vesicle retrograde transport
C. It disregards vesicle transport
D. It focuses solely on anterograde transport
B
In the current model, what serves as the primary anterograde carriers?
A. Vesicles
B. Golgi cisternae
C. Microtubules
D. Ribosomes
B
Which of the following accurately describes the pathway of proteins destined for the lysosome?
A. Rough ER → trans Golgi cisternae → cis Golgi network → plasma membrane
B. Rough ER → cis Golgi cisternae → trans Golgi network → clathrin vesicles → lysosome
C. Rough ER → trans Golgi network → cis Golgi network → lysosome
D. Rough ER → cis Golgi cisternae → trans Golgi network → clathrin coated vesicles → endosome → lysosome
D
What marker is added (in the cis golgi) to proteins destined for the lysosome?
A. Ubiquitin
B. Phosphate
C. Mannose-6-phosphate (M6P)
D. Sulfate
C
What properties directs a protein to the lysosome?
A. Presence of a signal sequence (SS)
B. High hydrophobicity
C. Presence of an acid patch
D. A and C
E. All of the Above
D
Which enzyme adds two phosphates from UDP to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) during M6P creation in the cis Golgi?
A. GlcNAc phosphotransferase
B. Phosphodiester glycosidase
C. Mannosidase
D. Kinase
A
What are the byproducts of the phosphate addition to GlcNAc by GlcNAc phosphotransferase?
A. 2 ATP
B. 2 UDP
C. 2 UMP
D. 2 GDP
C
What enzyme is responsible for removing the N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) from the phosphates attached to it and freeing M6P from the active site?
A. GlcNAc phosphotransferase
B. Phosphodiester glycosidase
C. Phosphatase
D. Glycosyltransferase
B
Which receptors recognize and bind to Mannose-6-Phosphate (M6P) in the trans Golgi?
A. Arf1
B. GGA adaptor protein
C. Clathrin proteins
D. Mannose protein receptors (MPR)
D
What role does Arf1 play in the process of M6P recognition and binding?
A. It recognizes M6P and binds directly to it.
B. It recruits GGA adaptor protein to the MPR-M6P complex.
C. It forms clathrin vesicles.
D. It mediates the fusion of the clathrin vesicle with the endosome
B
What is recruited by Arf1 and MPRs to form a complex in the Golgi membrane?
A. Clathrin proteins
B. GGA adaptor protein
C. Phosphatase
D. Kinase
B
What does the GGA adaptor protein recruit to the MPR-M6P complex in the Golgi membrane?
A. Arf1
B. Clathrin proteins
C. M6P
D. UDP-GlcNAc
B
What structure is formed when clathrin proteins are recruited to the MPR-M6P complex?
A. Golgi complex
B. ER membrane
C. Clathrin vesicle
D. Lysosome
C
After leaving the trans Golgi, where does the clathrin vesicle move towards?
A. Nucleus
B. Endoplasmic reticulum
C. Golgi complex
D. Periphery (plasma membrane)
D
What event disrupts the interaction between Mannose-6-Phosphate (M6P) and its receptors (MPR) in the endosome?
A. Fusion of the clathrin vesicle with the Golgi complex
B. Increase in pH
C. Decrease in pH
D. Binding of M6P to lysosomal enzymes
C
What happens to the Mannose-6-Phosphate (M6P) and MPR after it gets dumped out in the endosome?
A. M6P gets degraded and MPR is recycled
B. M6P is recycled back to the Golgi complex and MPR fuses to the lysosome
C. Both are exported out of the cell
D. M6P fuses to the lysosome and MPR is recycled
D
What protein interacts with the LDL receptor to initiate the process of LDL uptake?
A. AP2
B. Clathrin
C. APoB
D. NPXY
C
Which protein is recruited by the LDL receptor after APoB interaction and functions to recruit clathrin to make a complete vesicle?
A. APoB
B. AP2
C. Clathrin
D. LDL
B
What digests LDL into free cholesterol?
A. lysosome
B. endosome
C. clathrin coated vesicle
D. APoB proteins
A
What is an example of paracrine signaling?
A. Immune cell signaling
B. Hormonal signaling
C. Neurotransmitter diffusion into the synapse
D. Direct cell-to-cell communication
C
How many transmembrane domain proteins do G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) typically have?
A. 3
B. 5
C. 7
D. 10
C
In the Sutherland and Rodbell Experiment, what was found when epinephrine was added to supernatant 1 (containing GP)?
A. GP activity was observed.
B. No GP activity was observed.
C. cAMP activity was observed.
D. Membrane solubilization occurred.
B
What was the result when epinephrine was added to pellet 1 (membrane) in the Sutherland and Rodbell Experiment?
A. GP activity was observed.
B. No GP activity was observed.
C. cAMP activity was observed.
D. Membrane solubilization occurred.
B
Which combination of supernatants resulted in GP activity in the Sutherland and Rodbell Experiment?
A. Supernatant 1 (GP) + pellet 2 (membrane)
B. Supernatant 2 (cAMP)+ supernatant 1 (GP)
C. Pellet 1 (membrane) + supernatant 2 (cAMP)
D. Pellet 2 (membrane) + supernatant 1 (GP)
B
What is the initial response of the adrenergic receptor upon binding to epinephrine?
A. Activation of Adenylyl Cyclase (AC)
B. Inhibition of Adenylyl Cyclase (AC)
C. Activation of Glycogen Phosphorylase (GP)
D. Inhibition of Glycogen Phosphorylase (GP)
A
What does Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) convert during the adrenergic receptor signaling pathway?
A. ATP to cAMP
B. ATP to ADP
C. Arg to NO
D. GTP to cGMP
A
What happens when cAMP binds to the regulatory subunit of protein kinase A (PKA) in the adrenergic receptor signaling pathway?
A. It activates PKA and causes it to release its catalytic subunits
B. It inhibits PKA and causes it to bind tightly to its catalytic subunits
C. It activates Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) to convert ATP into cAMP
D. It inhibits Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) to inhibit ATP to cAMP
A
What is the role of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A (PKA) in the adrenergic receptor signaling pathway?
A. They phosphorylate Adenylyl Cyclase (AC).
B. They phosphorylate Glycogen Phosphorylase Kinase (GPK) into GPK-P
C. They cleave Glucose from glycogen
D. They degrade epinephrine
B
What happens after GP is phosphorylated by GPK (kinase) into Glycogen Phosphorylase Phosphate (GPP)?
A. Turns GTP into cGMP
B. It cleaves glucose from glycogen in the form of Glc1P
C. Activates AC to make ATP to cAMP
D. Releases Galpha protein from G-protein trimer
B
Which component of the G protein complex can bind GTP and also function as a GTPase?
A. Gα subunit
B. Gβ subunit
C. Gγ subunit
D. Adenylyl Cyclase
A
What was observed in the experiment when glucagon was added to liver cells without ATP?
A. Decreased cAMP production compared to baseline
B. No change in cAMP production compared to baseline
C. Increased cAMP production compared to baseline
D. Inhibition of Adenylyl Cyclase (AC)
B
GPCR starts with epinephrine binding to adrenergic receptor on the ____ side which exposes the ___ region on the other side
A. cytosolic side, GPK-P
B. extracellular side, GEF
C. cytosolic side, GEF
D. extracellular side, GPK-P
B
What is the role of the GEF (Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor) in GPCR signaling?
A. Binds to epinephrine
B. Converts GTP to GDP which binds Galpha
C. GEF binds directly to Gα
D. Converts GDP to GTP which binds to Galpha
D
What happens to Gα when it binds to GTP during GPCR signaling?
A. It dissociates from the G protein complex
B. It binds to epinephrine
C. It activates Adenylyl Cyclase (AC)
D. It binds to cAMP
A
What enzyme is bound by GTP-Galpha and converts ATP to cAMP in GPCR signaling?
A. Adenylyl Cyclase (AC)
B. Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor (GEF)
C. Glycogen Phosphorylase Kinase (GPK)
D. Glycogen Phosphorylase (GP)
A
What is the primary mechanism responsible for the fast shutoff of GPCR signaling?
A. Phosphorylation of the receptor by GRK
B. Conversion of Gα-GTP to Gα-GDP which happens spontaneously
C. Binding of cAMP to the regulatory subunit of PKA
D. Recruitment of Arrestin to the receptor
B
Which enzyme is responsible for cleaving remaining cAMP into AMP during fast shutoff of GPCR signaling?
A. Adenylyl Cyclase
B. Protein Kinase A (PKA)
C. cAMP Phosphodiesterase
D. G-Protein Receptor Kinase (GRK)
C
What is the primary mechanism responsible for the slow shutdown of GPCR signaling?
A. Conversion of Gα-GTP to Gα-GDP
B. Phosphorylation of the receptor by GRK, causing arrestin + clathrin to be recruited
C. Binding of Arrestin to the receptor
D. Degradation of cAMP
B
What effect does phosphorylation of the Y416 residue have on the Src protein?
A. It activates the kinase and turns on the pathway
B. It inhibits the kinase and turns off the pathway
C. It has no effect on the pathway
D. It degrades the protein
A
What effect does phosphorylation of the Y527 residue have on the Src protein?
A. It activates the kinase and turns on the pathway
B. It inhibits the kinase and turns off the pathway
C. It has no effect on the pathway
D. It degrades the protein
B
What happens when Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) binds to the EGFR (Tyr Kinase Receptor)?
A. Dimerization of Tyr Kinase Receptor
B. Activation of MAPK
C. Recruitment of Grb2
D. Phosphorylation of Ras
A
Which domain of Grb2 interacts with phosphorylated Tyr residues on the EGF/Tyr Kinase Receptor?
A. SH2 domain
B. SH3 domain
C. Kinase domain
D. GEF domain
A
Which domain of Grb2 recruits the SOS GEF?
A. SH2 domain
B. SH3 domain
C. Kinase domain
D. GEF domain
B
What is the function of SOS (Son of Sevenless) in the EGFR signaling pathway?
A. Phosphorylates MAPK
B. Recruits Grb2
C. Converts RasGDP to RasGTP
D. Phosphorylates EGFR
C
True or False: MAPK-phosphate phosphorylates transcription factors in the cytoplasm.
False (happens in nucleus)
What is the correct order of phosphorylation in the EGFR pathway?
A. Tyr-Kinase Receptor > Ras*GDP-Rof > MAPK > MAPKKK > MAPKK
B. Tyr-Kinase Receptor >MAPKKK > MAPKK > MAPK > Ras*GDP-Rof > TFs
C. Tyr-Kinase Receptor > Ras*GDP-Rof > MAPKKK > MAPKK > MAPK > TFs in nucleus
D. Tyr-Kinase Receptor > TFs in nucleus > Ras*GDP-Rof > MAPKKK > MAPKK > MAPK
C
True or False: Phosphorylated transcription factors in the nucleus inhibit cell growth.
False (they promote cell growth)
What discovery was made in the late 1970s regarding the role of NO?
A. NO acts as a vasoconstrictor
B. NO acts as an inhibitor of guanylyl cyclase
C. NO acts as an activator of guanylyl cyclase
D. NO acts as a neurotransmitter
C
True or False: Nitroglycerin dilates blood vessels by increasing the levels of cGMP leading to smooth muscle relaxation.
True
What is the immediate effect of ACh binding to receptors on endothelial cells?
A. Activation of guanylyl cyclase
B. Release of nitric oxide (NO)
C. Increase in cytosolic calcium levels
D. Stimulation of cGMP production
C
What enzyme turns Arg into NO and is stimulated by Ca2+?
A. Guanylyl Cyclase
B. ATP Synthase
C. NO Synthase
D. cGMP phosphodiesterase
C
What does NO bind to, which gets activated and converts GTP to cGMP, promoting smooth muscle relaxation?
A. Guanylyl Cyclase
B. ATP Synthase
C. NO Synthase
D. cGMP phosphodiesterase
A
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cytoskeleton?
A. Provides structural support and maintains cell shape
B. Directs the movement of materials and organelles within the cell
C. Regulates gene expression
D. Generates forces needed for cellular locomotion
C
How are all the monomers within an actin filament oriented?
A. Randomly
B. Alternating
C. Pointed in opposite directions
D. Pointed in the same direction
D
What is the initial state of an actin monomer before it is incorporated into a filament?
A. It is bound to ADP
B. It is bound to ATP
C. It is phosphorylated
D. It is in a GTP-bound state
B
What happens when the concentration of actin falls below the critical concentration (Cc) of a given end?
A. It shrinks by depolymerizing
B. It grows by polymerizing
C. It remains unchanged
A
What happens when the concentration of actin is at the critical concentration (Cc) of a given end?
A. It shrinks by depolymerizing
B. It grows by polymerizing
C. It remains unchanged
C
What happens when the concentration of actin is above the critical concentration (Cc) of a given end?
A. It shrinks by depolymerizing
B. It grows by polymerizing
C. It remains unchanged
B
If Barbed end Cc = 0.12mM and Pointed end Cc = 0.6 mM, at what concentration range does the barbed end polymerize while the pointed end depolymerizes?
A. Above 0.6 mM
B. Between 0.12 mM and 0.6 mM
C. Below 0.12 mM
D. Once all the free actin is used up at 0 mM
B
What is equilibrium steady state for actin?
A. When the concentration of free actin reaches 0
B. When the - pointed end depolymerizes at the same rate as the + barbed end polymerizes
C. When both ends stop polymerizing/depolymerizing
D. When the free actin concentration reaches the Critical Concentration
B
What is the primary mechanism of action of Latrunculin in regulating actin dynamics?
A. Binding and capping the barbed (+) end of actin filaments
B. Binding and sequestering monomeric G-actin, lowering concentration of free monomer causing filament depolymerization
C. Preventing depolymerization by binding to the sides of actin filaments
D. Promoting filament polymerization by increasing the concentration of monomer
B
How does Cytochalasin affect actin filaments?
A. It binds to the sides of actin filaments and prevents depolymerization
B. It binds and caps the barbed (+) end of actin filaments so monomers can’t be added there
C. It promotes filament depolymerization by increasing the koff rate
D. It lowers the concentration of monomeric G-actin
B
What is the consequence of Phalloidin binding to actin filaments?
A. Filament depolymerization on both ends is inhibited
B. Monomers cannot be added at the barbed (+) end
C. Monomeric G-actin is sequestered
D. It promotes filament polymerization by increasing the koff rate
A
What is the role of cofilin in actin dynamics?
A. It binds to G-actin and promotes filament polymerization
B. It binds to F-actin at the plus (+) end and promotes filament growth
C. It binds to F-actin at the minus (-) end and depolymerizes it
D. It binds to profilin and helps in recycling monomeric actin
C
What is the function of profilin in actin polymerization?
A. It binds to F-actin and promotes filament growth
B. It sequesters actin monomers to prevent premature polymerization
C. It binds to G-actin and helps in adding it to the plus (+) end of the actin filament
D. It binds to cofilin and inhibits its activity
C
How does thymosin-B4 contribute to actin dynamics?
A. It promotes filament depolymerization by binding to F-actin
B. It sequesters actin monomers to prevent premature polymerization
C. It binds to profilin and enhances its activity
D. It binds to cofilin and promotes F-actin stabilization
B
What activates formin, a protein involved in actin filament nucleation and elongation?
A. Binding of ATP to the FH2 domain
B. Interaction with profilin at the FH1 domain
C. Binding of RhoGTP to the Rho binding domain (RBD)
D. Interaction with cofilin at the FH2 domain
C
What is the role of profilin in the activation of formin?
A. It activates formin by phosphorylating it
B. It binds to ATP and transfers it to formin
C. It binds to the FH1 domain and passes Actin + ATP to it
D. It inhibits formin activity by sequestering ATP molecules
C
Which domain of formin directly adds Actin + ATP onto the plus (+) end of the actin filament?
A. Rho binding domain (RBD)
B. FH1 domain
C. FH2 domain
D. Profilin-binding domain
C
What is the role of Wasp in actin dynamics?
A. It binds to ATP and promotes actin polymerization
B. It recruits and binds to actin monomers, facilitating the recruitment of Arp2/3 at the C terminus
C. It severs actin filaments at the plus (+) ends
D. It binds to profilin and enhances actin polymerization
B
What is the function of Arp2/3 in actin dynamics?
A. It severs actin filaments at the minus (-) ends
B. It caps the plus (+) ends of actin filaments
C. It binds to actin monomers and promotes nucleation of side filaments
D. It binds to cofilin and promotes depolymerization of actin filaments
C
How does platelet activation lead to rapid growth of F-actin?
A. CapZ prevents actin polymerization at the plus (+) ends
B. Ca2+ activates gelsolin, which severs actin filaments at the minus (-) ends
C. CapZ releases actin monomers, allowing them to polymerize
D. Ca2+ activates gelsolin, which cuts actin at the plus (+) ends, making monomers available for polymerization
D
What does CapZ do in platelet cells in regards to actin?
A. binds to - end of actin filaments and prevents build up
B. binds to + end of actin filaments and prevents build up
C. cuts actin at + ends allowing for rapid growth of F-actin
D. recruits actin monomers
B
What protein present in listeria bacteria is released into the host cell and behaves as a nucleation center to start assembly of actin?
A. Gelsolin
B. CapZ
C. ActA
D. Arp2/3
C
What is the purpose of having two sites on the head domain of myosin?
A. one binds to the + end and one binds to the - end of actin
B. one binds actin filament and one binds and hydrolyzes ATP to drive the myosin motor
C. one binds ATP and one binds ADP
D. both bind the actin filament and promote polymerization
B
What is the primary function of Myosin Type II in muscle cells?
A. Vesicle transport
B. Cell signaling
C. Muscle contractions
D. Pigment granule transport
C
Which structure forms the single long rod-shaped tail of Myosin Type II?
A. A pair of globular heads
B. Intertwining of long alpha-helical sections of the two heavy chains
C. A single uninterrupted alpha helix
D. A pair of necks
B
True or False, Myosin Type II is found in both nonmuscle and muscle cells
A. True
B. False
A
Which type of myosin moves towards the minus (-) end of an actin filament?
A. Myosin II
B. Myosin V
C. Myosin VI
D. Myosin VII
C
What type of Myosin is used for vesicular transport?
A. Myosin II
B. Myosin I
C. Myosin V
D. None of the above
C
What condition results from a defect in myosin Va or Rab27A in humans?
A. Muscular dystrophy
B. Griscelli syndrome (partial albinism)
C. Sickle cell anemia
D. Cystic fibrosis
B
Which type of myosin moves towards the barbed (+) end of an actin filament?
A. Myosin I
B. Myosin II
C. Myosin V
D. A and B
E. All of the Above
D
What initiates the detachment of the myosin head from the actin filament?
A. Hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi
B. Binding of ATP to the myosin head
C. Release of ADP from the myosin head
D. Release of Pi from the myosin head
B
What happens immediately after ATP binds to the myosin head during rigor mortis?
A. The myosin head remains attached to the myosin head
B. The myosin head gets released and ATP hydrolyzes into ADP and Pi
C. It leaves the cell
D. The power stroke occurs
B
What happens when ADP + Pi on the myosin head bind to the myosin filament?
A. Pi gets released, inducing a power stroke
B. it turns back into ATP
C. Both stay tightly bound
D. Both get released
A
In the absence of ATP, what happens to the myosin heads?
A. They detach from actin filaments
B. They cannot bind to actin filaments
C. They remain tightly bound to actin filaments
D. They perform continuous power strokes
C
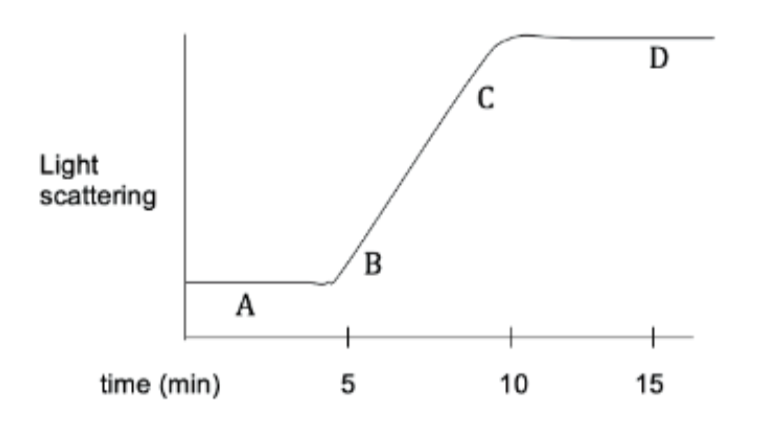
The addition of formin at one of the time points (A, B, C, D) will shorten the phase. Which time point would you add formin to speed up growth?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
A
You are studying actin dynamics and the effect of phalloidin. You add G-actin and ATP to a test tube and allow the reaction to come to steady state. This produces the light scattering plot shown below. At this point, if you add phalloidin and G-actin, what will happen to the line?
A. Stay level
B. Go up continuously
C. Go up to a new equilibrium and stay there
D. Go down to zero
E. Go down to a new equilibrium above zero and stay there
C
What is the structural unit of a microtubule?
A. Alpha-tubulin alone
B. Beta-tubulin alone
C. Alpha-beta tubulin dimer
D. Gamma-tubulin ring complex
C
Which of the following accurately describes the subunits of tubulin?
A. Alpha = GTPase, B = GTP
B. Alpha = GTP , B = GTPase
C. Alpha = ATP, B = ATPase
D. Alpha = ATPase, B = ATP
B
How many protofilaments make up a single microtubule?
A. 10
B. 13
C. 15
D. 20
B
Which tubulin subunit is in the front and associates with the + end?
A. Alpha Subunit
B. Beta Subunit
B
Which protein complex mediates the nucleation step in microtubule assembly?
A. Alpha-tubulin ring complex
B. Beta-tubulin ring complex
C. Gamma-tubulin ring complex (gamma-TuRC)
D. Delta-tubulin ring complex
C
What end does gamma-tubulin ring complex (gamma-TuRC) attach to on the microtubule?
A. Positive End (+)
B. Minus End (-)
B