My Classroom 9-15 + Homework 9-15
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
1
New cards
Upon impact, how fast were the objects that formed craters on the moon?
10 to 70 km/sec
2
New cards
How are craters formed?
The craters are formed due to shock waves as the impact fractures and deforms the lunar rock, it pushes downward and outward
3
New cards
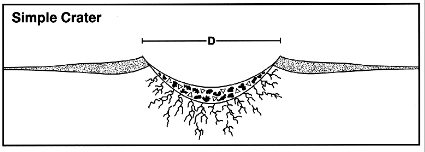
What are the attributes of simple craters?
They lack a central uplift or peak but it has peak rings and terraced walls
4
New cards
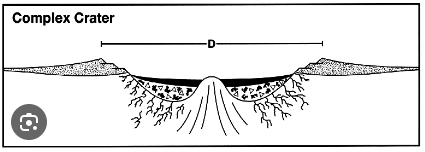
What are the attributes of complex craters?
They have uplifted centers, broad flat shallow crater floors, and terraced walls.
5
New cards
What are crater or impact basins?
They are formed by the largest impactors (greater than 300 km) and they are often deeply flooded by lava flows.
6
New cards
The size of a crater on a planet, moon, or asteroid depends on what?
The size of the impactor, the strength of gravity, and the velocity of the impactor
7
New cards
What is the capture hypothesis?
It proposed that the moon formed elsewhere in the solar system and was then captured by Earth.
8
New cards
The capture hypothesis was proposed to explain which of the following?
The moon’s lack of iron, low density, and lack of volatile elements
9
New cards
The capture hypothesis can't be right for which of the following reasons?
The moon was not torn apart by tides.
10
New cards
What is the fission hypothesis?
Suggests that the protoplanet became unstable and may have split in two pieces. One forming the moon and the other forming the Earth.
11
New cards
Why can’t the fission hypothesis be right?
Because astronomers have not been able to show why a protoplanet would break up.
12
New cards
If the moon and Earth accreted together, which of the following should be true?
They should have similar compositions.
13
New cards
What is the co-accretion hypothesis?
It was the idea that the Earth and the moon formed together in orbit around each other
14
New cards
What is the large-impact hypothesis?
It proposes that as the solar system was forming, an object about the size of Mars collided with a larger object about the size of Earth
15
New cards
According to the large-impact hypothesis, why does the moon have a low density?
The two objects had differentiated before the impact.
16
New cards
What are true statements about the moon?
\-Currently, the formation of new impact craters on the Moon is rare. Most were formed billions of years ago.
\-The side of the Moon facing Earth and the side facing away have different features.
\-The Moon does not have enough gravitational pull to retain an atmosphere.
\-The lunar surface is covered with a layer of dust.
\-The side of the Moon facing Earth and the side facing away have different features.
\-The Moon does not have enough gravitational pull to retain an atmosphere.
\-The lunar surface is covered with a layer of dust.
17
New cards
What are true statements about Mercury
\-Mercury has a weak magnetic field.
\-Like the Moon, Mercury has many impact craters.
\-Mercury contains a large proportion of dense metals.
\-Like the Moon, Mercury has many impact craters.
\-Mercury contains a large proportion of dense metals.
18
New cards
Why does the same side of the moon always face Earth?
The moon rotates in the same direction that it revolves and the moon's period of rotation is equal to its orbital period.
19
New cards
How did the moon achieve its synchronous rotation?
The Earth raises tidal bulges on the moon. As the moon rotated through these bulges, internal friction slowed the moon's rotation until it achieved tidal coupling
20
New cards
How do we find the relative ages of the moon's maria and highlands?
by counting the number of impact craters
21
New cards
Why do almost all impact craters have a circular shape?
High-speed projectiles vaporize explosively upon impact, sending out spherical shock waves.
22
New cards
What aspects about the moon are due to its small size?
The moon has no atmosphere, a magnetic field, or plate tectonics. The moon’s surface geology is dominated by impact craters.
23
New cards
Rank the stages of the moon’s history
First: differentiation, cooling, cratering, lava flooding, slow surface evolution: Last
24
New cards
What is the composition of the Moon?
The Moon is mostly composed of silicate rock
25
New cards
How does the composition of the moon compare to that of Earth or Mercury?
\-Earth has a large metal core, while the Moon does not.
\-Earth contains a substantial amount of liquid, while the Moon does not.
\-Mercury has a large metal core, while the Moon does not.
\-Earth contains a substantial amount of liquid, while the Moon does not.
\-Mercury has a large metal core, while the Moon does not.
26
New cards
What are the principal features of the Moon observable with the unaided eye?
\-dark mania
\-lighter highlands
\-lighter highlands
27
New cards
What is the main consequence of Mercury's orbit being so highly eccentric?
Mercury's distance from the Sun varies hugely.
28
New cards
What is the relationship between Mercury's rotational period and orbital period?
Mercury's rotational period is two thirds of its orbital period.
29
New cards
What evidence would you expect to find on the Moon if it had been subjected to plate tectonics?
\-the equivalent of mid ocean rifts and rift valleys
\-long folded mountains
\-long folded mountains
30
New cards
What evidence can you give that Mercury has a partially molten, metallic core?
Mercury has a weak magnetic field.
31
New cards
How does the large-impact hypothesis explain the moon's lack of iron?
Both planetesimals were differentiated, and the two iron cores went to Earth.
32
New cards
What is one important way in which both the Moon and Mercury are different from Earth?
they do not have an atmosphere
33
New cards
The first human being to step out onto the surface of another world was _____.
Neil Armstrong
34
New cards
Which theory of the Moon's origin do astronomers (and the evidence) favor?
the giant impact theory
35
New cards
Why does the Moon not have an atmosphere?
Because the Moon's mass is so small, its gravity cannot prevent gas molecules from quickly escaping into space.
\
\
36
New cards
Frozen water exists on the lunar surface primarily in which location?
in craters near the poles because they are permanently in the shadows so they do not receive enough sunlight to evaporate the ice and escape to space.
37
New cards
What are true statements about Venus?
\-Venus' atmosphere is much thicker than Earth's, and much hotter.
\-Due to being closer to the sun and therefore slightly hotter than Earth when it first formed, Venus' water vapor could not condense to form oceans. This lack of carbon dioxide-absorbing liquid water has caused Venus to sufferer a runaway greenhouse effect.
\- In size and mass, Venus is very similar to Earth
\-Due to being closer to the sun and therefore slightly hotter than Earth when it first formed, Venus' water vapor could not condense to form oceans. This lack of carbon dioxide-absorbing liquid water has caused Venus to sufferer a runaway greenhouse effect.
\- In size and mass, Venus is very similar to Earth
38
New cards
What are true statements about Mars and its moons?
\-Mars has polar ice caps.
\-Mars seems to have been much more Earth-like in the past.
\-Mars seems to have been much more Earth-like in the past.
\-Mars is smaller than Earth and Venus, but bigger than Earth's moon.
\-Mars seems to have been much more Earth-like in the past.
\-Mars seems to have been much more Earth-like in the past.
\-Mars is smaller than Earth and Venus, but bigger than Earth's moon.
39
New cards
Why might we expect Venus and Earth to be similar?
Both planets are about the same size, density, and have the same chemical composition.
40
New cards
Which gas is most abundant in the atmospheres of Venus and Mars?
carbon dioxide (CO2)
41
New cards
What dominates the geology of Venus?
Volcanoes
42
New cards
Measurements from orbiting spacecraft suggests that Mars had a magnetic field in its past. How could Mars lose its magnetic field?
Mars has cooled to the point that it no longer has a fluid interior.
43
New cards
What evidence do we have that Mars had much more liquid water at its surface in the past than it has today?
\-The deuterium-hydrogen ratio is 5.5 times as high as on Earth.
\-Mars rovers have found so-called "blueberries" that could only have formed in water.
\-We see large, dry outflow channels and valley networks on the surface of Mars.
\-The deuterium-hydrogen ratio is 5.5 times as high as on Earth and Mars rovers have found so-called "blueberries" that could only have formed in water.
\-Mars rovers have found so-called "blueberries" that could only have formed in water.
\-We see large, dry outflow channels and valley networks on the surface of Mars.
\-The deuterium-hydrogen ratio is 5.5 times as high as on Earth and Mars rovers have found so-called "blueberries" that could only have formed in water.
44
New cards
Layered rock and spherical concretions are evidence that water once flowed on the surface of what space body?
Mars
45
New cards
List ways that Venus, Earth and Mars are similar
\-All three are composed mostly of rock and metal.
\-All three are terrestrial planets.
\-All three have atmospheres.
\-All three have volcanic activity on their surfaces.
\-All three are terrestrial planets.
\-All three have atmospheres.
\-All three have volcanic activity on their surfaces.
46
New cards
List ways that Venus, Mars, and Earth are different
\-Only Earth has liquid water on its surface.
\-All three undergo large-scale surface changes through the different mechanisms.
\-All three undergo large-scale surface changes through the different mechanisms.
47
New cards
Compare the current atmospheres of Earth, Venus, and Mars in terms of composition.
Earth's atmosphere is composed mostly of nitrogen and oxygen, while Venus and Mars have atmospheres that are mostly carbon dioxide.
48
New cards
Compare the current atmospheres of Earth, Venus, and Mars in terms of thickness (and pressure at the surface).
Venus has the thickest atmosphere, while Mars has the thinnest.
49
New cards
Compare the current atmospheres of Earth, Venus, and Mars in terms of the greenhouse effect.
Venus has an ongoing runaway greenhouse effect, while Mars has a runaway refrigerator effect. The Earth is currently seeing an increase in the greenhouse effect.
50
New cards
Venus and Earth are nearly the same size and distance from the Sun. What are the main differences in the geology of the two planets?
\- Only Earth appears to experience plate tectonics.
\- Earth experiences significantly more erosion than Venus.
The reasons for these differences are that Venus has less erosion than Earth because there is a lack of water and ice. In addition, the wind speeds are relatively low.
\- Earth experiences significantly more erosion than Venus.
The reasons for these differences are that Venus has less erosion than Earth because there is a lack of water and ice. In addition, the wind speeds are relatively low.
51
New cards
What is the temperature of the coldest part of Earth’s atmosphere(in the mesosphere)?
about 100 K
52
New cards
Why is the surface temperature on Venus very high?
Venus has a strong greenhouse effect.
53
New cards
Why are cloud layers on Saturn less distinct than those on Jupiter for a satellite equidistant from the two planets?
Saturn is colder and cloud particles condense deeper in its atmosphere
54
New cards
Uranus has clouds of methane ice crystals. Which of the following explains why Jupiter does not have them?
Jupiter is too warm.
55
New cards
The temperature profile in a planet's atmosphere can depend on what?
The greenhouse effect, the atmosphere’s chemical composition, and the planet’s distance from the sun
56
New cards
What are true statements about the outer planets?
\-Being rich in hydrogen, the large outer planets are low in density.
\-Pluto's characteristics do not fit in with the characteristics of the outer planets
\-The outer planets are larger than Earth.
\-All Jovian planets have rings and moon systems.
\-Pluto's characteristics do not fit in with the characteristics of the outer planets
\-The outer planets are larger than Earth.
\-All Jovian planets have rings and moon systems.
57
New cards
What energy source drives the weather that we see on Jupiter?
Thermal energy escaping from Jupiter's interior that is still hot from formation.
58
New cards
The two requirements for a strong planetary magnetic field are rapid rotation and a convective interior zone composed of an electrically conductive material. Jupiter's rotational period is slightly less than 10 hours. What type of matter present within Jupiter fulfills the second requirement?
liquid metallic hydrogen
59
New cards
In which way does Saturn differ from Jupiter?
Saturn has a smaller zone of liquid metallic hydrogen
60
New cards
Why is the metallic hydrogen zone for Saturn smaller than Jupiter's metallic hydrogen zone?
Jupiter has more mass and thus greater pressure at a given depth.
61
New cards
Describe the interior heat source of Saturn
the sinking of helium into the center releases gravitational energy heating the interior
62
New cards
Which planet has the strongest magnetic field, and hence the largest magnetosphere? What is the source of it?
Jupiter
the rapidly spinning liquid-metallic hydrogen just above the core
the rapidly spinning liquid-metallic hydrogen just above the core
63
New cards
How did the giant planets grow to be so large?
Far from the Sun, light elements did not get enough energy from the Sun to escape the growing gravitational fields of the outer planets, and the planets simply kept accumulating material until none was left.
64
New cards
Describe the different processes that lead to substantial internal heat sources for Jupiter and Saturn.
\-gravitational contraction
\-gravitational energy from differentiating elements
\-primordial heat left over from the formation of the planets
\-gravitational energy from differentiating elements
\-primordial heat left over from the formation of the planets
65
New cards
Planetary magnetic fields are produced by what?
circulations of electrically conducting planetary interiors
66
New cards
A planet that has a dipolar magnetic field also has what?
two magnetic poles
67
New cards
It takes 84 years for Uranus to orbit the sun once, so how long does each season on Uranus last?
21 years
68
New cards
As the rotation of Uranus carries the planet's magnetic field around, what is true about the solar wind?
\-It can produce enhanced aurora and magnetic storms.
\-It can sometimes flow down into one of the magnetic poles.
\-It can drag the magnetic field out into a corkscrew pattern
\-It can sometimes flow down into one of the magnetic poles.
\-It can drag the magnetic field out into a corkscrew pattern
69
New cards
Why are planetary magnetic fields able to change and magnetic poles able to move?
changes in the circulation of the electrically conducting interior
70
New cards
From most abundant to least, what are the gases in Jupiter
Most: hydrogen, helium, ammonia, methane, and water vapor: Least
71
New cards
From most abundant to least, what are the gases in Saturn
Most: hydrogen, helium, methane, ammonia: Least
72
New cards
How do the interiors of Jupiter and Saturn differ? How does this difference affect the magnetic fields of Jupiter and Saturn?
Jupiter is denser than Saturn and Saturn has less liquid metallic hydrogen in its interior.
Jupiter’s magnetic field is stronger than Saturn’s
Jupiter’s magnetic field is stronger than Saturn’s
73
New cards
How do the seasons on Uranus differ from the seasons on Earth?
Seasons on Uranus are 84 times longer and more extreme than on Earth
74
New cards
What is our current best hypothesis as to how the whole Uranian system came to have such a large inclination?
A large impact during the latter stages of planet building tipped Uranus on its side.
75
New cards
Both Uranus and Neptune have a blue-green tint when observed through a telescope. What does this tell you about their composition?
Their atmospheres contain some methane
76
New cards
In the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn, we see ammonia, ammonia hydrosulfide, and water clouds in three distinct layers. Why don't we see these same three cloud layers in the atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune?
Because Uranus and Neptune are so cold, these three layers are likely hidden too deeply within the atmosphere to be seen.
77
New cards
We could divide the Jovian planets into two subclasses: the "gas giants" and the "ice giants." Into which group should we place the four Jovian planets?
The gas giants are Jupiter & Saturn, and the ice giants are Uranus & Neptune.
78
New cards
Rank the four Jovian planets in decreasing size
Biggest: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune: Smallest
79
New cards
Rank the four Jovian planets in increasing mass
Least: Uranus, Neptune, Saturn, Jupiter: Most
80
New cards
Rank the four Jovian planets for decreasing density
Greatest: Neptune, Jupiter, Uranus, Saturn: Least
81
New cards
Rank the four Jovian planets in increasing surface gravity
Least: Uranus, Saturn, Neptune, Jupiter: Greatest
82
New cards
What are the main atmospheric heat sources of each of the giant planets?
Jupiter: both internal energy and solar energy
Saturn: both internal energy and solar energy
Uranus: both internal energy and solar energy
Neptune: mainly solar energy
Saturn: both internal energy and solar energy
Uranus: both internal energy and solar energy
Neptune: mainly solar energy
83
New cards
Why do the upper levels of Neptune's atmosphere appear blue?
gaseous molecules in Neptune's atmosphere scatter blue light
84
New cards
Describe the differences in the chemical makeup of the inner and outer parts of the solar system. What is the relationship between what the planets are made of and the temperature where they formed?
\-Heavier elements migrated toward the inner solar system due to gravity.
\-The inner solar system has more heavy elements, while the outer planets have more light elements.
\-The hotter temperatures closer to the Sun caused lighter gases to escape from the inner planets.
\-The inner solar system has more heavy elements, while the outer planets have more light elements.
\-The hotter temperatures closer to the Sun caused lighter gases to escape from the inner planets.
85
New cards
The element that can act like a metal when it is under tremendous pressure and is probably responsible for Jupiter and Saturn's magnetism is _____.
hydrogen
86
New cards
The Red Spot of Jupiter is _____.
\-Long lived (observed since the 1600s)
\-variable in size
\-a high pressure storm system in the atmosphere
\-made of a reddish colored material
\-variable in size
\-a high pressure storm system in the atmosphere
\-made of a reddish colored material
87
New cards
The bluish color that makes the atmosphere of Neptune so beautiful to the human eye is caused by the interaction of sunlight with what gas?
methane
88
New cards
What are true statements about Jupiter and it’s moons?
\-Volcanic activity has been observed on Io.
\-Some of Jupiter's smaller moons are probably captured asteroids.
\-Ganymede probably was geologically active in the past.
\-Some of Jupiter's smaller moons are probably captured asteroids.
\-Ganymede probably was geologically active in the past.
89
New cards
What are true statements about saturn?
\-Smaller moons "shepherd" particles in the ring system, or keep them in their rings.
\-Saturn's rings are made mostly of ice particles.
\-Although it has the most extensive one, Saturn is not the only planet with a ring system.
\-Saturn's rings are made mostly of ice particles.
\-Although it has the most extensive one, Saturn is not the only planet with a ring system.
90
New cards
What are true statements about Saturn’s moons?
\-Some of Saturn's moons may have been captured asteroids or Kuiper belt objects
\-All of Saturn's moons are a mixture of rock and ice.
\-Smaller moons of Saturn have cracks and smooth areas that suggest past geologic activity.
\-All of Saturn's moons are a mixture of rock and ice.
\-Smaller moons of Saturn have cracks and smooth areas that suggest past geologic activity.
91
New cards
What evidence do we have that the surface of Europa is young and active?
Europa has very few impact craters and the icy crust of Europa is highly reflective.
92
New cards
Why are Europa and Ganymede necessary for the continued heating of Io?
These moons periodically tug on Io and keep its orbit elliptical.
93
New cards
Rank the Galilean satellites of Jupiter in order of decreasing size.
Largest: Ganymede, Callisto, Io, Europa: Smallest
94
New cards
Rank the Galilean satellites of Jupiter in order of increasing density.
Least dense: Callisto, Ganymede, Europa, Io: Most dense
95
New cards
Rank the Galilean satellites of Jupiter in order of decreasing distance from Jupiter.
Farthest: Callisto, Ganymede, Europa, Io: Closest
96
New cards
What are the moons of the outer planets made of, and how is their composition different from that of our Moon?
The moons of the outer planets consist of a mixture of ice and rock, whereas our Moon is just rock.
97
New cards
What is the evidence for a liquid water ocean on Europa? Why is this interesting to scientists searching for extraterrestrial life?
\-A weak magnetic field implies the existence of a liquid layer below the surface.
\-Long straight cracks in the icy crust are likely to happen over a liquid subsurface.
\-Europa has jagged blocks of ice that seem to have rotated and collided with each other which cannot happen on a solid moon.
It is interesting because life, as we know it, needs liquid water and life can be found in most places on Earth where liquid water is present.
\-Long straight cracks in the icy crust are likely to happen over a liquid subsurface.
\-Europa has jagged blocks of ice that seem to have rotated and collided with each other which cannot happen on a solid moon.
It is interesting because life, as we know it, needs liquid water and life can be found in most places on Earth where liquid water is present.
98
New cards
Explain the energy source that powers the volcanoes of Io.
Io's proximity to Jupiter is such that it experiences tidal heating which is enough to power volcanoes.
99
New cards
Why do you think the outer planets have such extensive systems of rings and moons, while the inner planets do not?
\-The outer plants have more space between them which allows them to accrete more material from the solar nebula to create rings.
\-The outer planets are larger and more massive.
\-The temperature is much cooler in the outer solar system which allows ice particles to form and rings are partly composed of these.
\-The outer planets are larger and more massive.
\-The temperature is much cooler in the outer solar system which allows ice particles to form and rings are partly composed of these.
100
New cards
Would you expect to find more impact craters on Io or Callisto? Why?
There are many more impact craters on Callisto because the impact craters on Io are removed (perhaps covered over) relatively rapidly by surface deposits from volcanic activity.