Heart Practice Worksheet
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
The heart is a cone-shaped muscular organ located within the:
Mediastinum
The hearts apex rests on the:
Diaphragm
The coronary arteries that nourish the myocardium arise from the:
Aorta
The coronary sinus empties into the:
Right atrium
Relative to roles of the heart chambers the ________ are receiving chambers.
Atria
Relative to roles of the heart chambers the ________ are discharging chambers.
Ventricles
The membrane that lines the heart and also forms the valve flaps is called the:
Endocardium
The ________ is made of cardiac muscle.
Myocardium
The myocardium is thicker on on the ________ side of the heart.
Left
The flow of blood through the heart:
From the right atrium through the ________ valve to the right ________.
Tricuspid, ventricle
The flow of blood through the heart:
From the right ventricle through the ________ (semilunar) valve to the pulmonary trunk to the right and left pulmonary ________.
Pulmonary, arteries
The flow of blood through the heart:
From the right and left pulmonary arteries to the capillary beds of the ________.
lungs
The flow of blood through the heart:
From the lungs to the right and left ________ ________ to the left ________.
Pulmonary veins, atrium
The flow of blood through the heart:
From the left atrium through the ________/________ valve to the left ________.
Bicuspid/mitral, ventricle
The flow of blood through the heart:
From the left ventricle through the _________ (semilunar) valve and into the ________ to enter systemic circulation.
Aortic, aorta
The cardiac cycle:
The contraction of the ventricles is referred to as:
Systole
The cardiac cycle:
The period of ventricular relaxation is called:
Diastole
The cardiac cycle:
The two heart sounds are referred to as ________ and ________.
Lub, dub
The cardiac cycle:
The first sound is a result of closure of the ________ valves; the second heart sound is caused by closure of the ________ valves.
Cuspid, semilunar
The cardiac cycle:
The heart chambers that have just been filled when you hear the first heart sound are the ________, and the chambers that have just emptied are the ________.
Ventricles, atria
The cardiac cycle:
Immediately after the second heart sound the ________ are filling with blood, and the ________ are empty.
Atria, ventricles
The cardiac cycle:
Abnormal heart sounds are referred to as a ________ and usually indicate valve problems.
Murmur
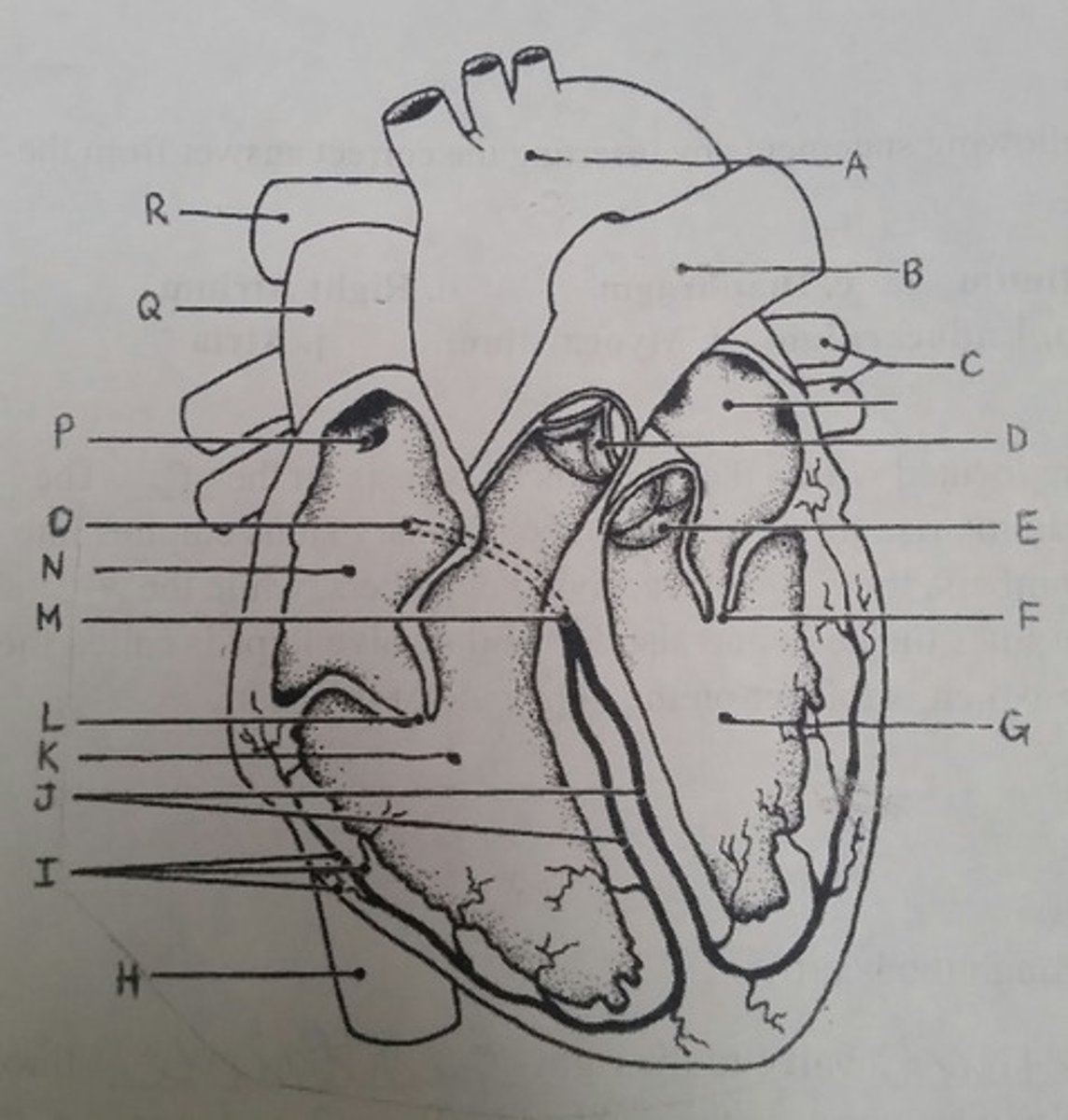
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
AV valve with 3 flaps
L (tricuspid)
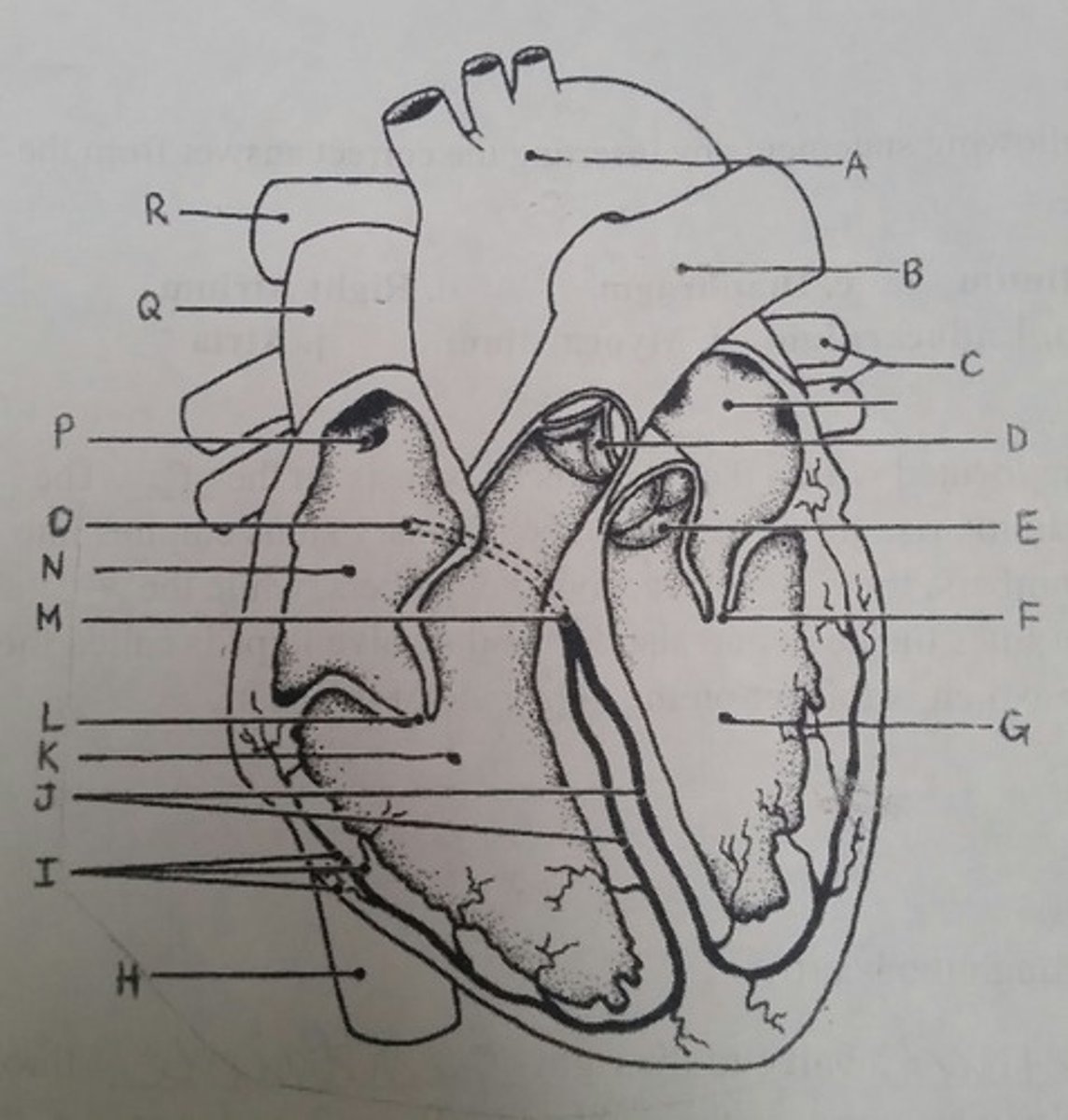
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
The pacemaker of the intrinsic conduction system
P (SA node)
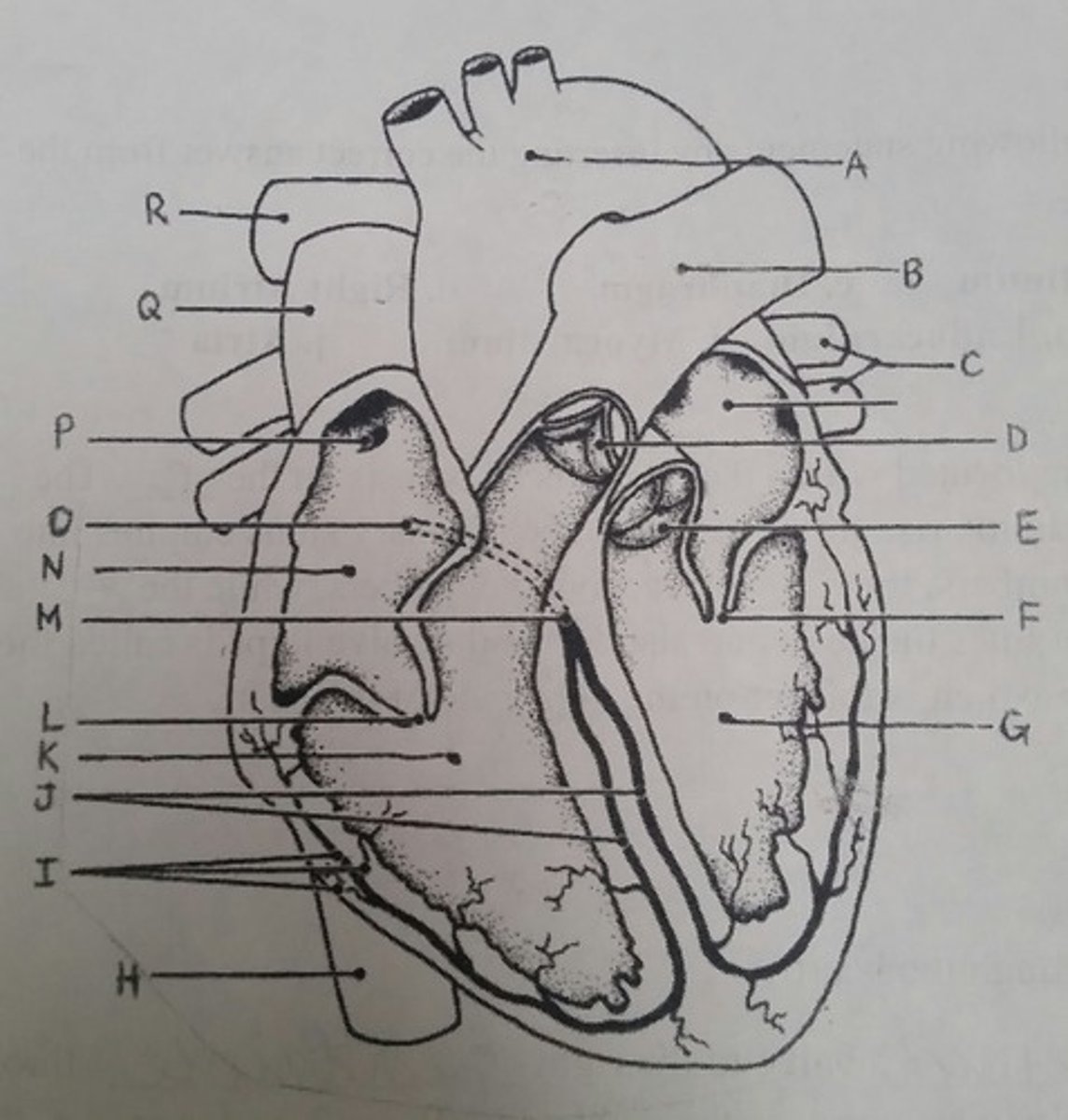
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
The point on the intrinsic conduction system where the impulse is temporarily delayed
O (AV node)
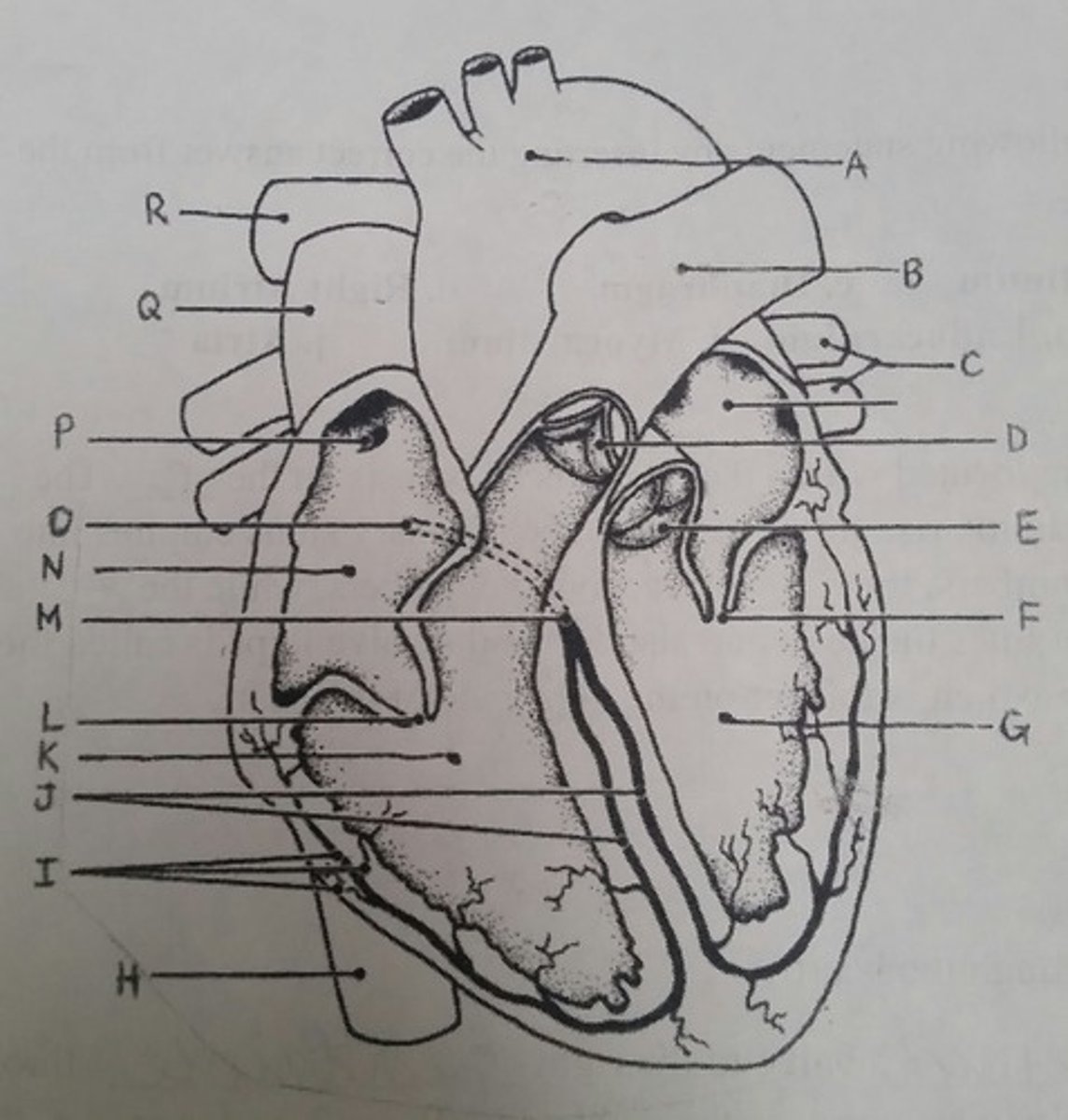
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
Returns blood to the heart from the arms, shoulders, and head
Q (superior vena cava)
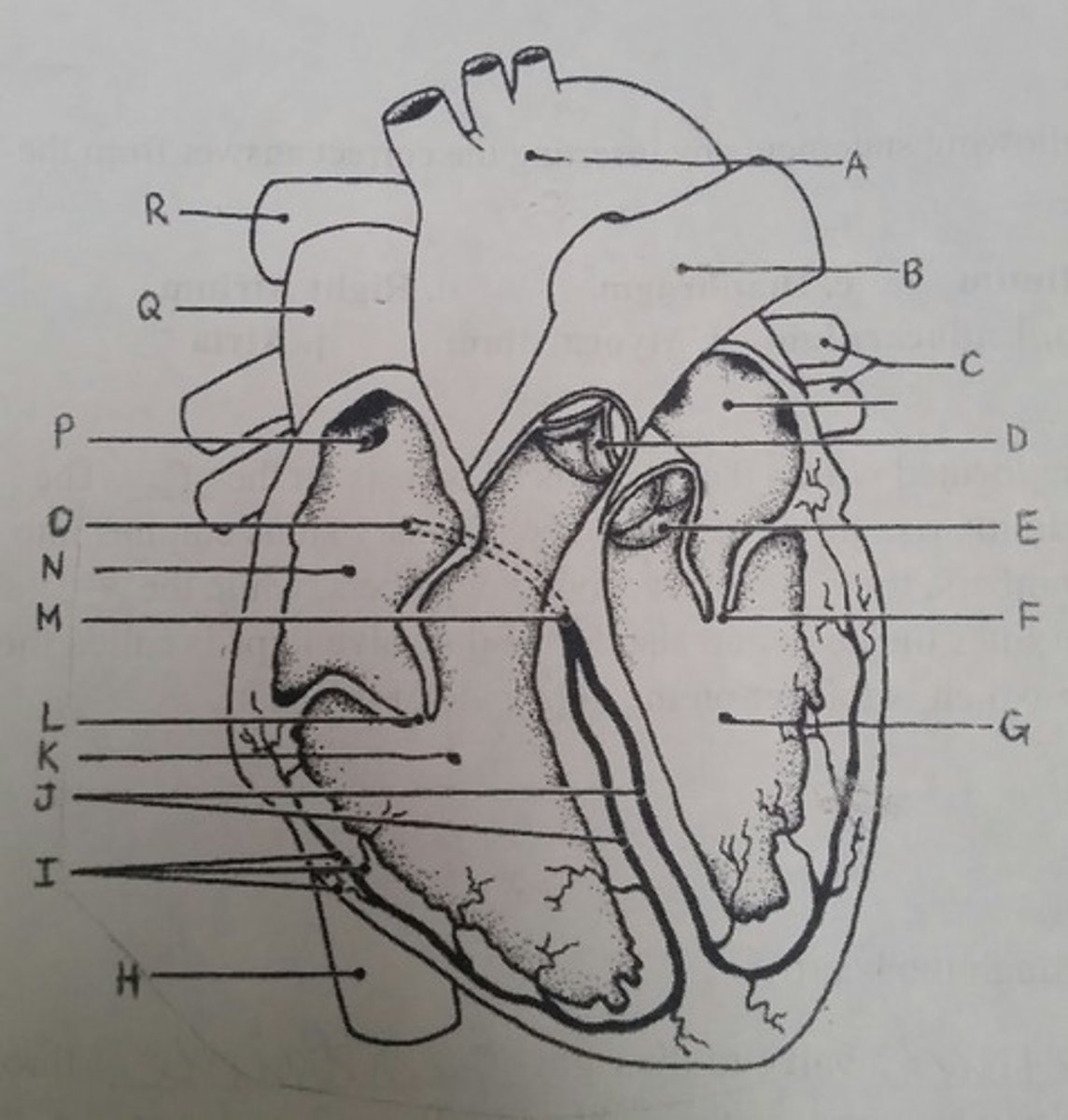
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
Prevent backflow into the ventricles when the heart is in diastole (two answers)
D, E (semilunar valves)

Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
Prevent backflow into the atria when the ventricles are in systole (two answers)
L, F (cuspid valves)
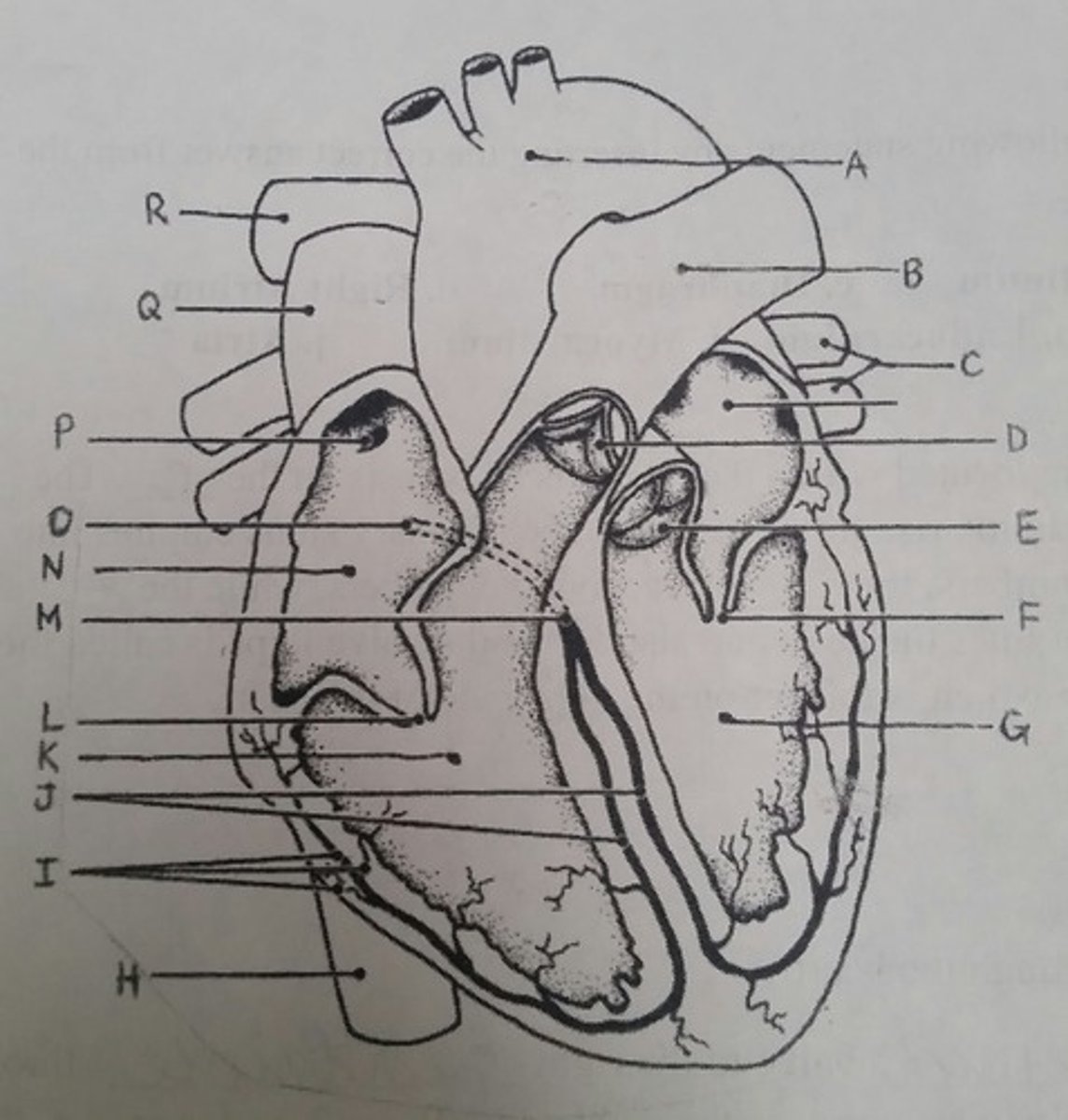
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
Supplies impulses to the papillary muscles and outer wall of the ventricles
I (purkinje fibers)
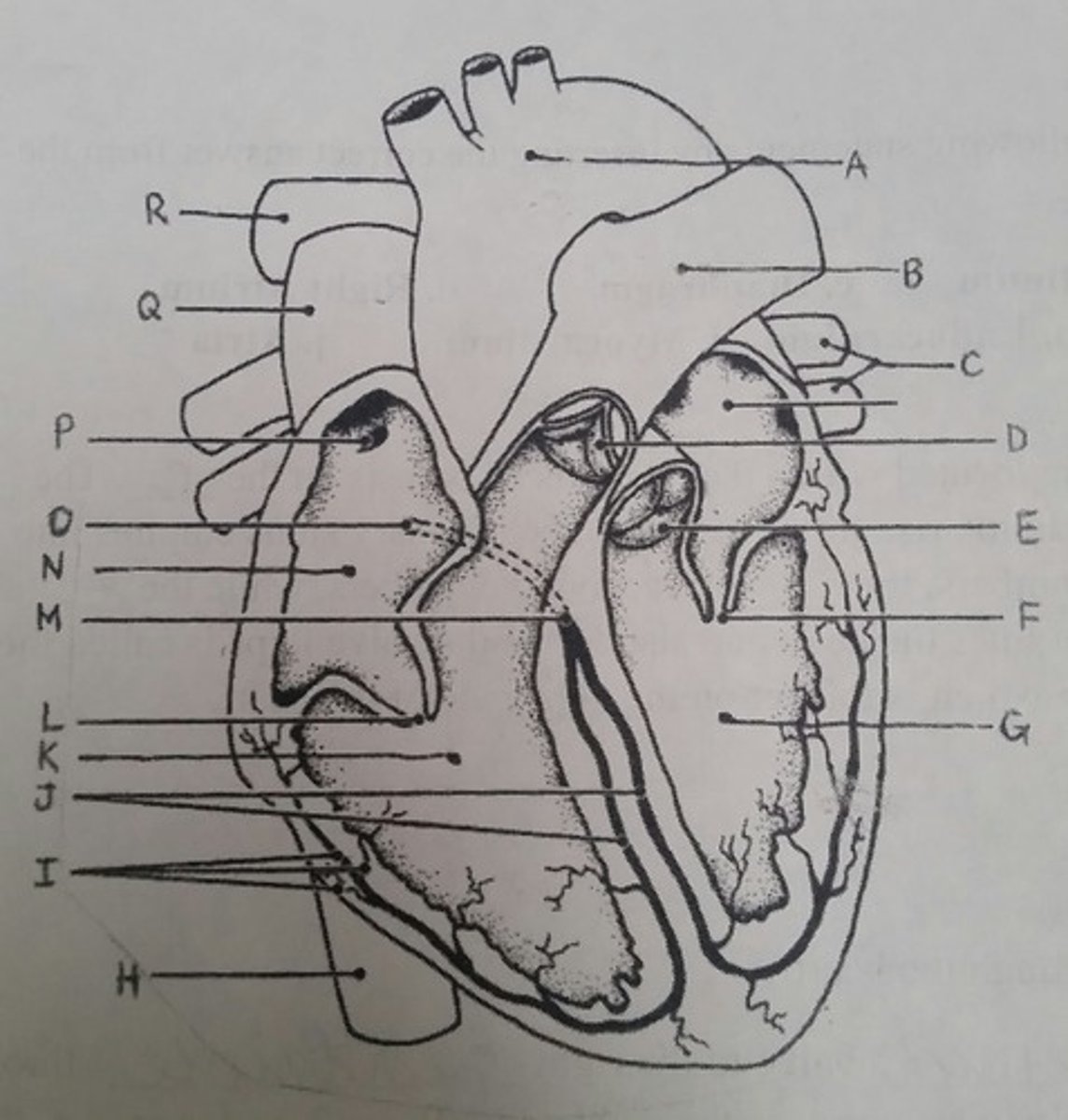
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
Depolarizes faster than any other heart region
P (SA node)
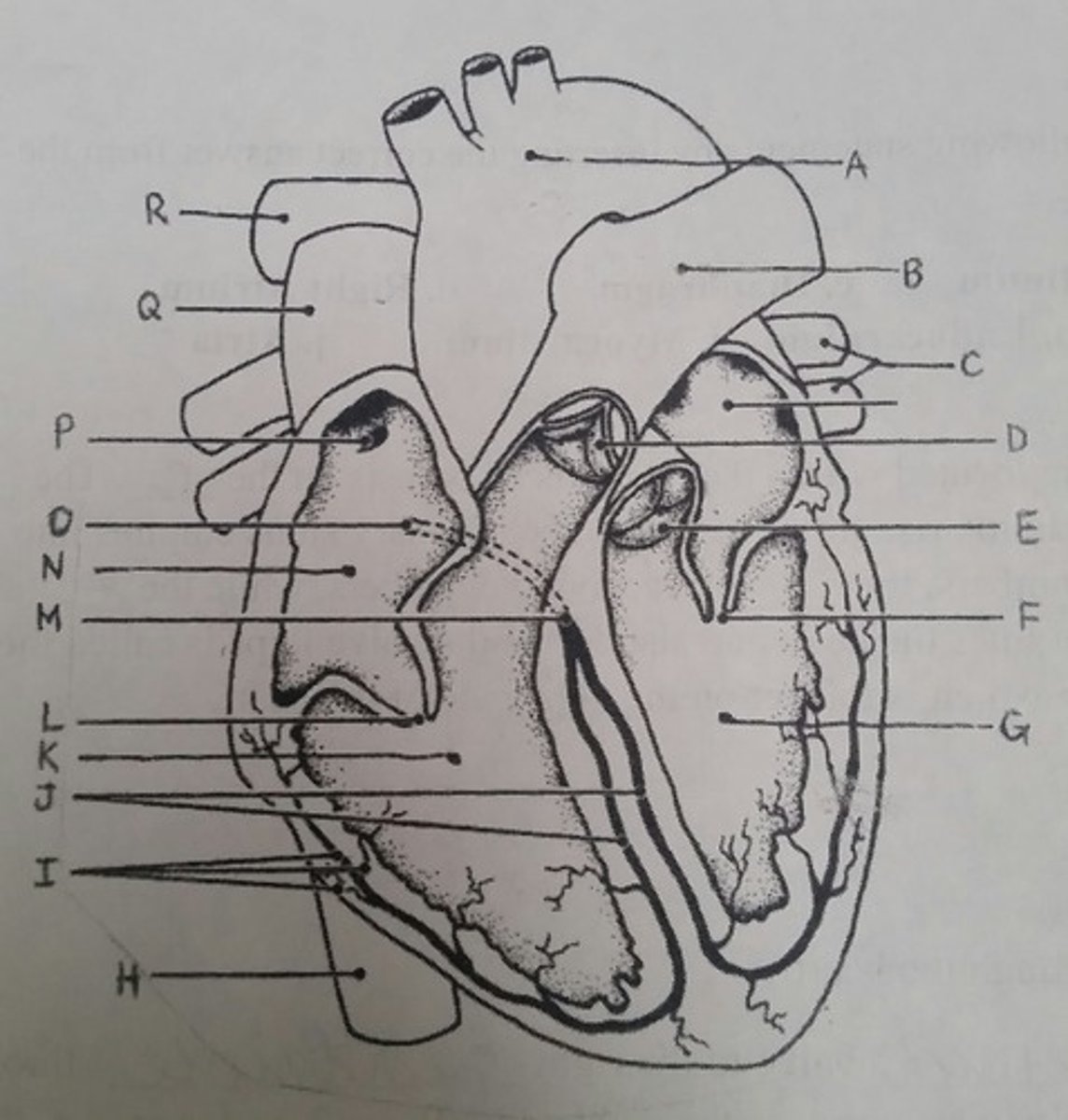
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
Returns blood to the heart from the trunk and legs
H (inferior vena cava)
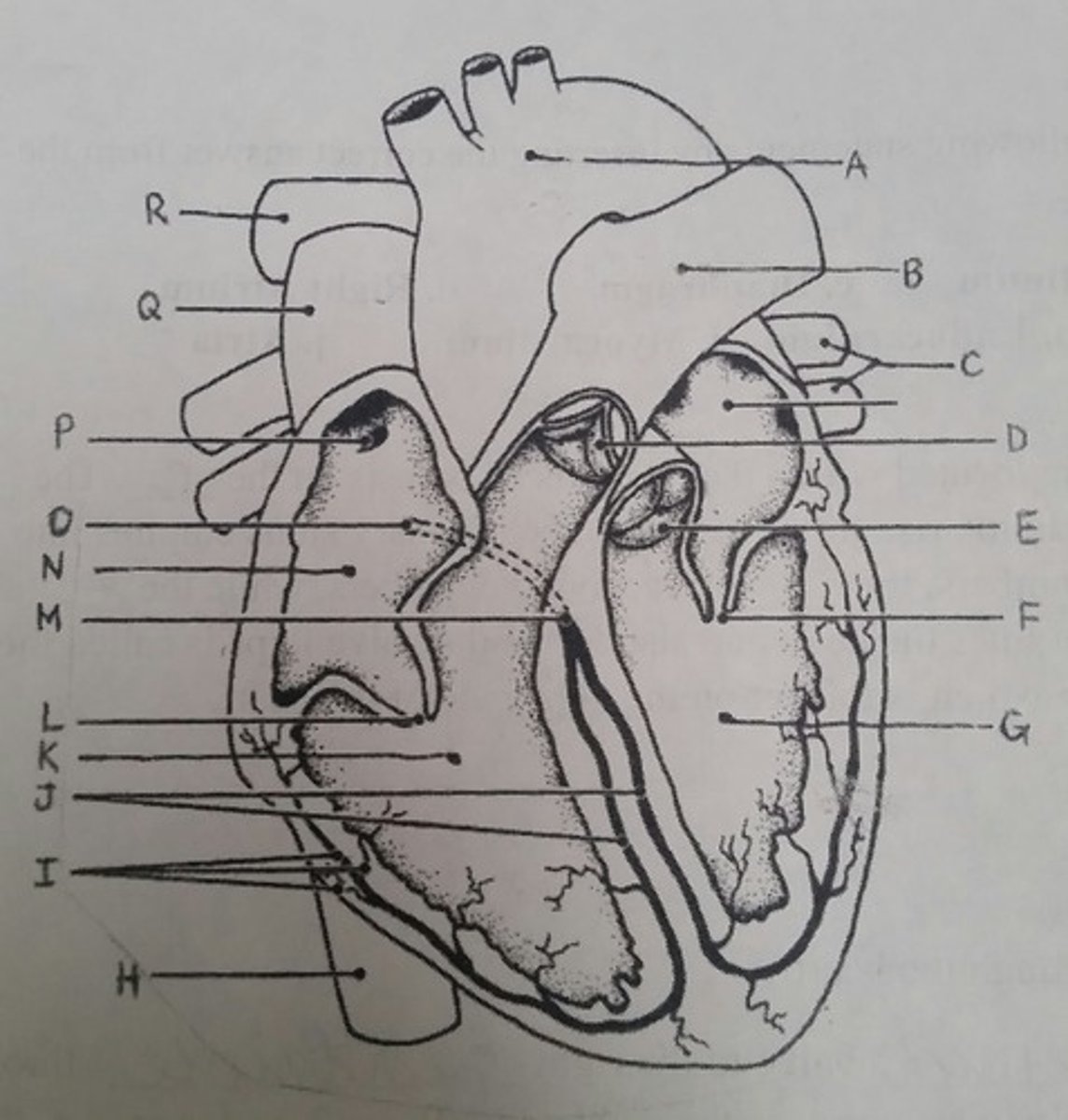
Use the letters from the diagram to identify the structure:
Returns blood to the heart from the lungs
C (pulmonary veins)
Cardiac Output:
Identify the two major factors that influence stroke volume:
Venous return and the strength of ventricular contraction
Cardiac Output:
Identify a neural factor that enhances contractility
Sympathetic activity
Cardiac Output:
Identify two hormonal factors that enhance contractility
Thyoxine and epinephrine
Cardiac Output:
Identify an ion that enhances contractility
Calcium (hypercalcemia)
Cardiac Output:
Explain how exercise increases venous return
Muscle contraction squeezes veins and increases return of blood to the heart
True or false:
Epinephrine leads to an increase in cardiac output
True (Increase stroke volume (strength of contraction) and heart rate)
True or false:
Thyroxine leads to an increase in cardiac output
True (allows the heart to be more responsive to epinephrine)
True or false:
Fear leads to an increase in cardiac output
True (Increased sympathetic stimulation increases HR and also strength of contraction to
increase SV)
True or false:
Activation of the vasomotor center leads to an increase in cardiac output
False
True or false:
Activation of the cardioinhibitory center leads to an increase in cardiac output
False
True or false:
Stimulus of low blood pressure leads to an increase in cardiac output
True (Increased sympathetic stimulates to heart to increase HR and strength of contraction to increase SV)
True or false:
Stimulus of high blood pressure leads to an increase in cardiac output
False
True or false:
Calcium channel blockers lead to an increase in cardiac output
False
True or false:
Hyperkalemia leads to an increase in cardiac output
False
True or false:
Exercise leads to an increase in cardiac output
True (Increased venous return with muscular contraction to increase SV, also increased
sympathetic stimulation to heart increases HR and strength of contraction)