Earth Materials Exam One
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Who was James Dana and Why do we care?
James Dana defined what a mineral was with a mineral classification scheme
What is the IMA
International Mineralogical Association
Mineral names and nomenclature with specific criteria that must apply for the substance to be considered a mineral
What is the definition of a mineral?
A naturally occurring, homogenous, well-defined composition, inorganic crystalline substance
What is mineral variety?
Minerals of the same chemical composition with variances in crystal shape and color
What is the difference between ruby, sapphire, and corundum?
They are different forms of the same mineral (corundum = Al2O3)
What is a biomineral? and name three most common ones
Crystalline materials produced by living organisms; teeth (apatite), clam shells (calcite), diatoms (SiO2)
Is amber a mineral?
No because it is made from tree sap which is not crystalline
Is ruby a mineral?
Yes
Is coal a mineral?
No, it is a rock
Is graphite a mineral?
Yes
Is volcanic glass a mineral?
No because it is non-crystalline
Differentiate rocks and minerals
Elements combine to form naturally occurring crystalline solid minerals, minerals combine to form rocks
What are the two major factors used for the classification of minerals?
structure and composition
What are some properties of minerals that are controlled by their structure?
crystal form, crystal habit, cleavage, streak, luster, tenacity, density, color, conductivity
Why do we care about the chemistry of a mineral?
to characterize minerals, to determine how and where a mineral forms and to learn about Earth’s conditions, to determine the economic significance of a mineral,
What aspect of the mineral chemistry is the basis for this classification?
The dominant anion or anionic group
Give examples of 4 of these major mineral classes
Oxides (O), phosphates (PO4), halides (Cl, F, Br, I), carbonates (CO3), silicates (Si and O), sulfates (SO4)
Si4+ atoms are surrounded by how many oxygens in most silicate minerals?
What is the shape of this Si-O unit?
What is the charge of this unit?
4 b/c (SiO4)^-4
tetrahedron
4-
What color is olivine?
What is the name of the gem variety of olivine?
Green
Peridote
How many of each atom are in the following mineral Olivine (Mg,Fe)2 SiO4
2 atoms of Mg or Fe or some combination of that Fe+Mg=2, 1 atoms of Si, 4 oxygen
How many of each atom are in the following mineral Marialite Na4 (AlSi3O8)3Cl
4Na, 3Al, 9Si, 24O, 1Cl
Why study minerals?
Basic building blocks of the Earth, most of all solid Earth processes relate in some way to physical or chemical properties of minerals, minerals are the fundamental key to understanding the evolution of the solid Earth, economic significance
How many of each atom are in the garnet with this formula: Garnet (Mg, Fe, Ca)3Al2Si3O12
2Al, 3Si, 12O, and Mg+Fe+Ca=3 in any combination
What is mineral cleavage?
and give an example
Mineral cleavage is a plane along which a mineral breaks and is controlled by the structure. Planes with the weakest bonds will have the most prominent cleavage.
Biotite has a “basal cleavage” b/c of the weak bonds btwn the layers
List these from softest to hardest with the Mohs hardness scale: quartz, fingernail, apatite (teeth), pocket knife
soft to hard: fingernail (2.5), apatite (5), pocket knife (5.5), quartz (7)
What mineral will fizz if you put dilute HCl (hydrochloric acid) on it?
calcite (CaCO3)
What mineral habit is displayed? and name the mineral

blocky Halite - NaCl
What mineral habit is displayed here? and name the mineral

Botryoidal (bulbous, rounded forms) Hematite - Fe2O3
What type of luster is displayed here? and name the mineral

vitreous (glassy) Calcite
What type of luster is displayed here? and name the mineral

greasy Opal
What is this type of property called? and name the mineral

“Play of colors,” and “Shiller” effect from light scattering off, Labradorite
What type of cleavage is this? and name the mineral

octahedron, fluorite
What mineral habit is displayed here? name the mineral
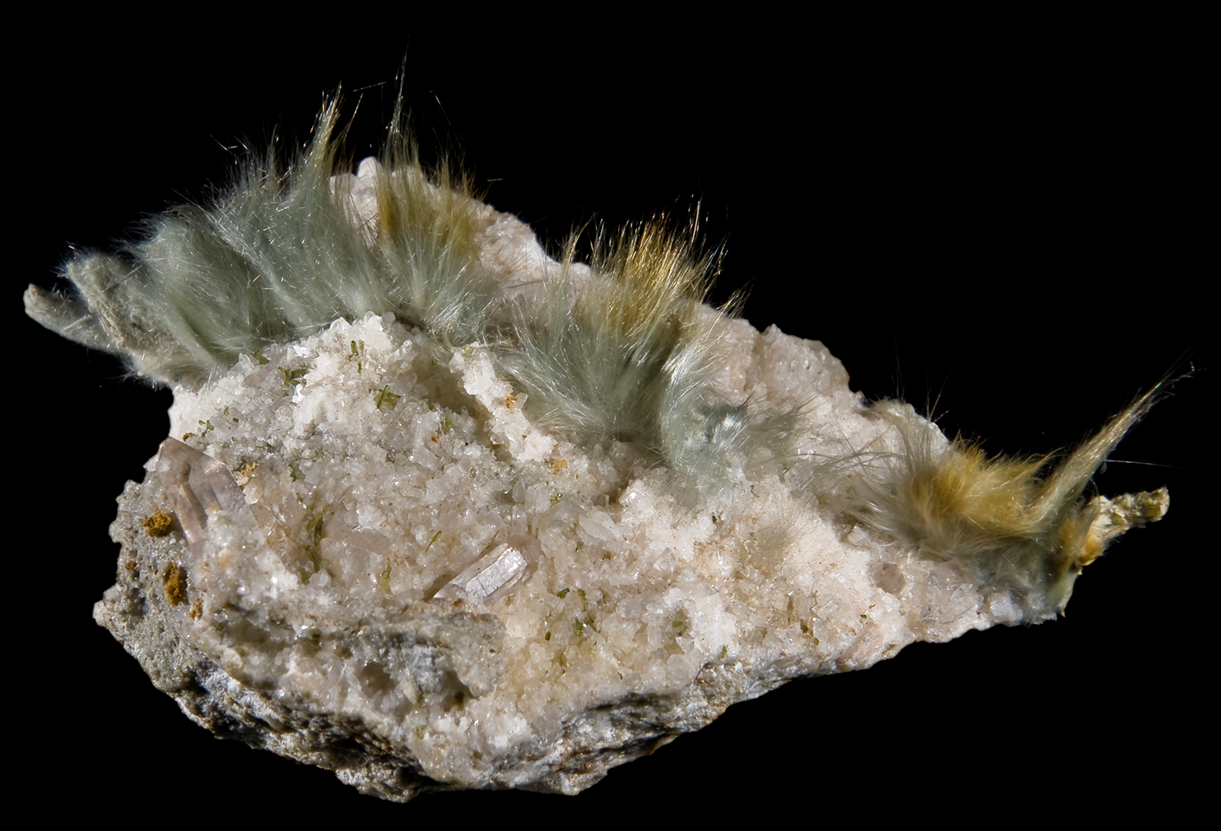

fibrous (whisker-like), amphibole
What mineral habit is displayed here?
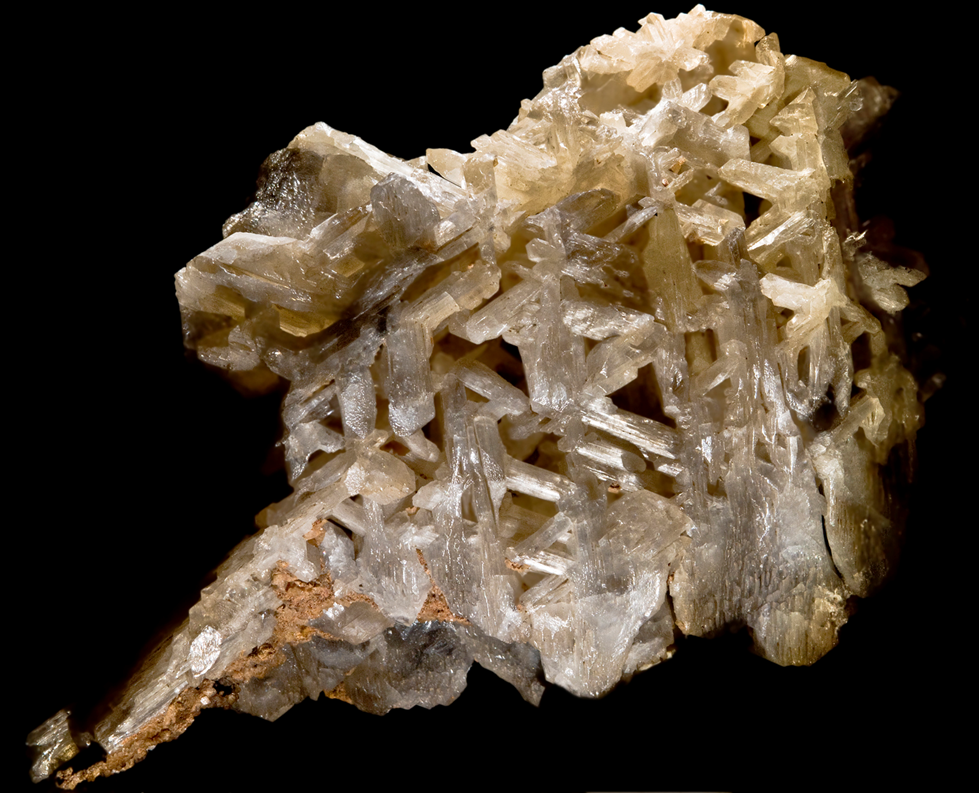
reticulated (forms a network)
what mineral habit is displayed here?
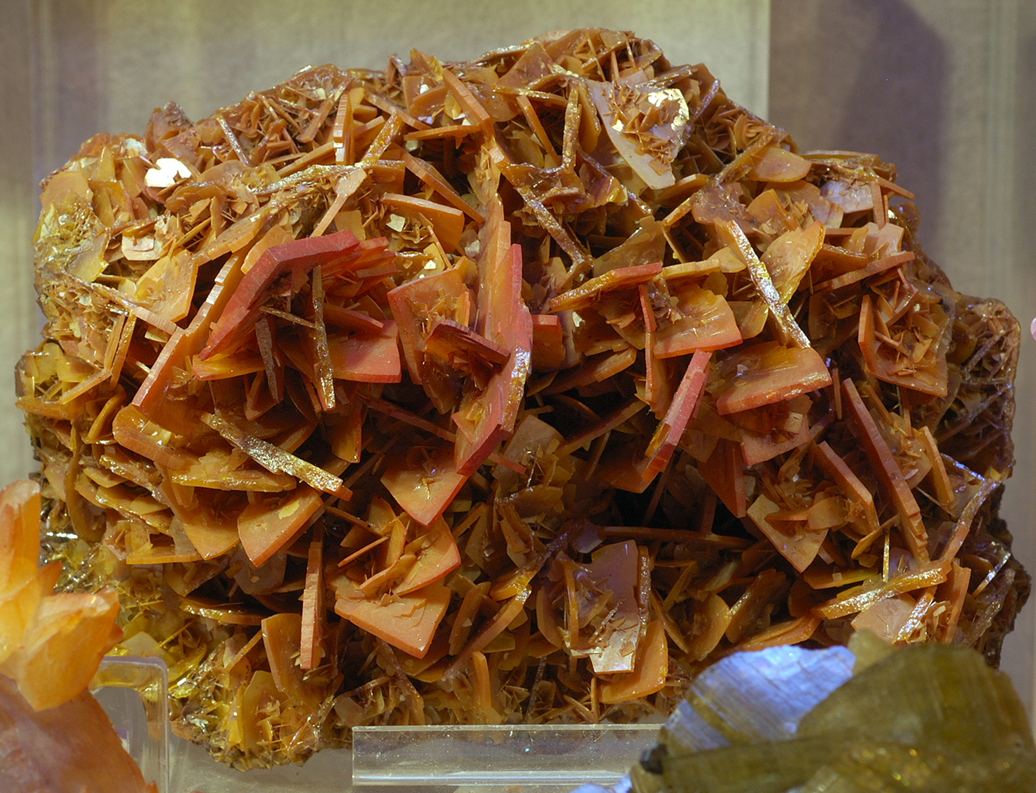

platy
what mineral habit is displayed here?
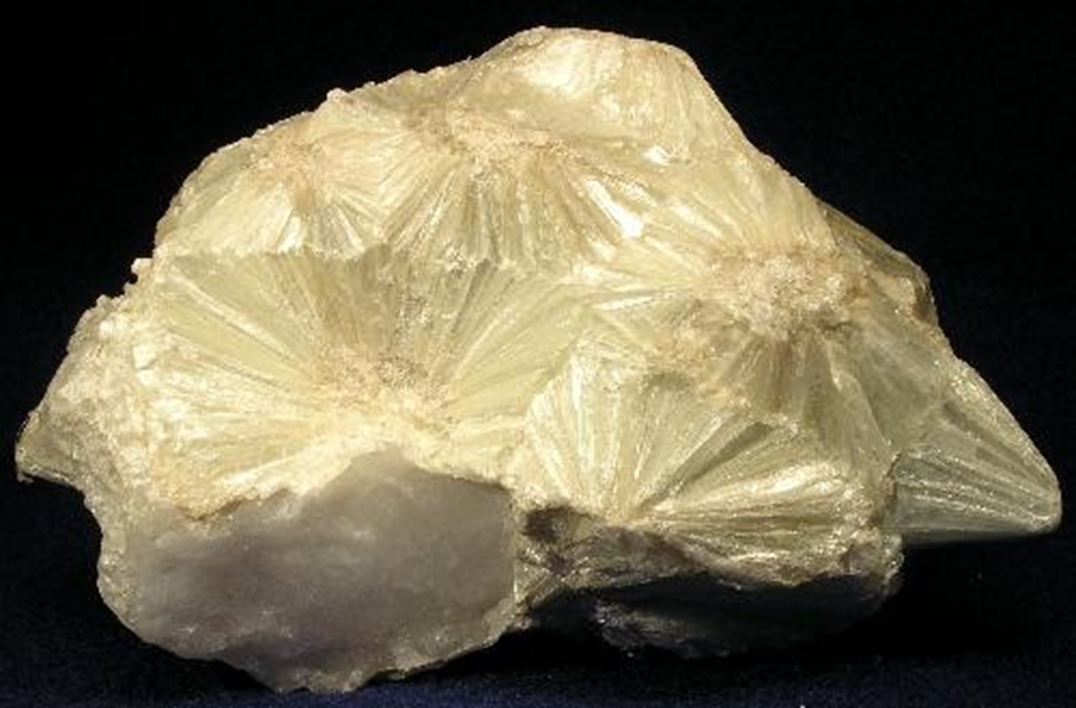

stellate (arranged in a radiating pattern like that of a star)
What mineral habit is displayed here?
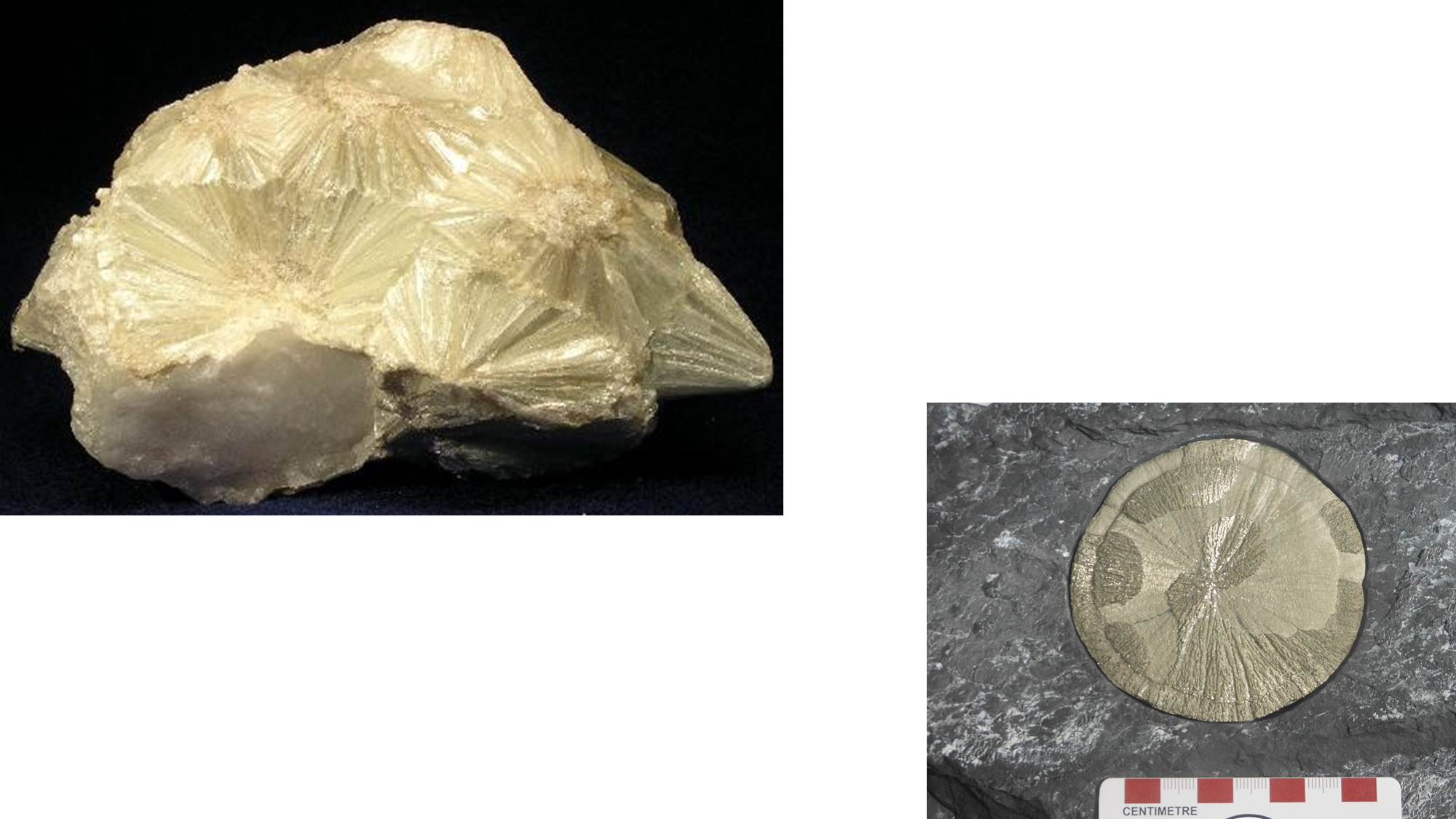

radiating pyrite
what mineral habit is displayed here? and name the mineral
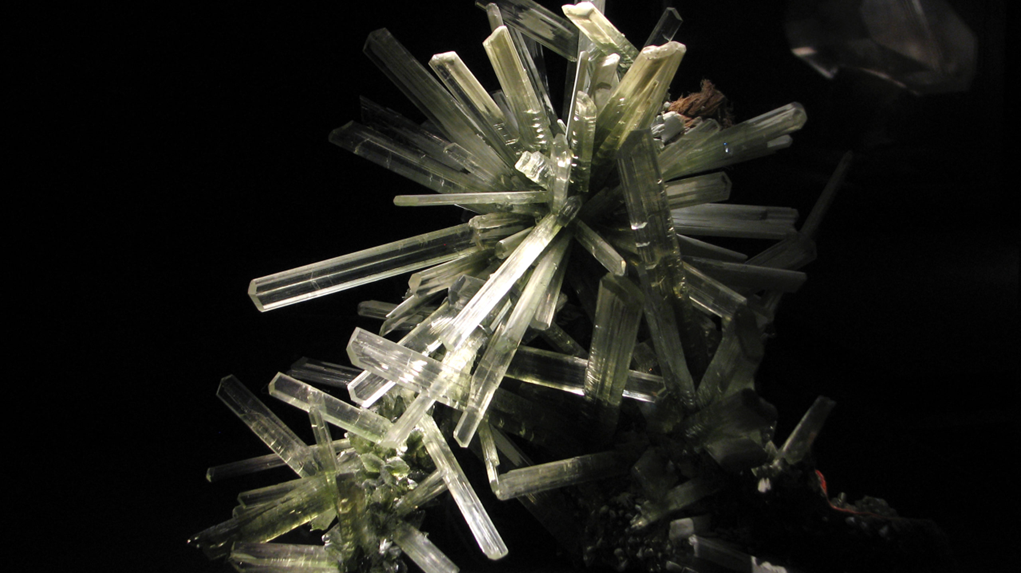

prismatic, gypsum
what mineral habit is displayed here?
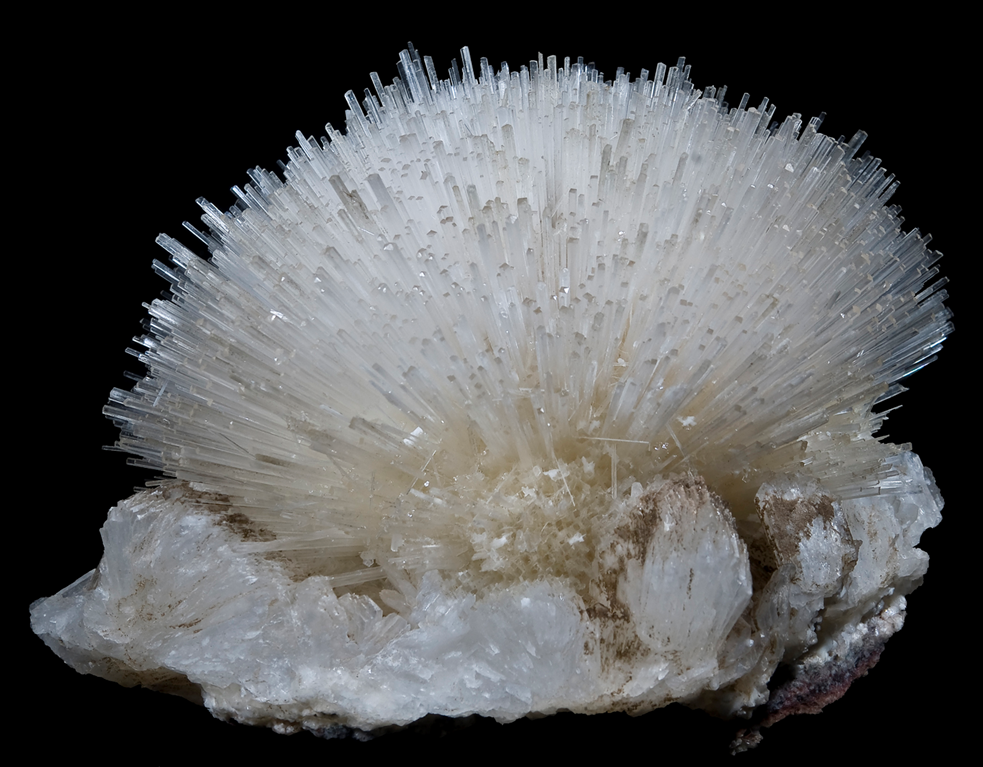

needle-like
What are the three types of luster and what are their meanings?
metallic: shiny appearance like polished metal, submetallic: not quite so shiny, nonmetallic: dull
What type of luster is displayed here?
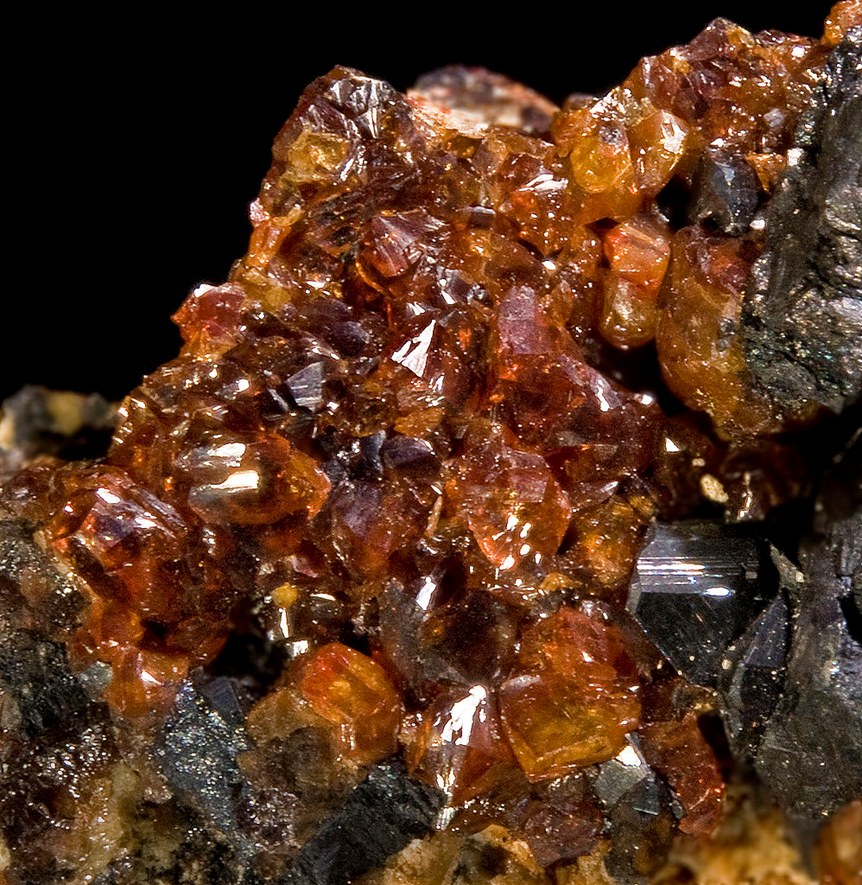
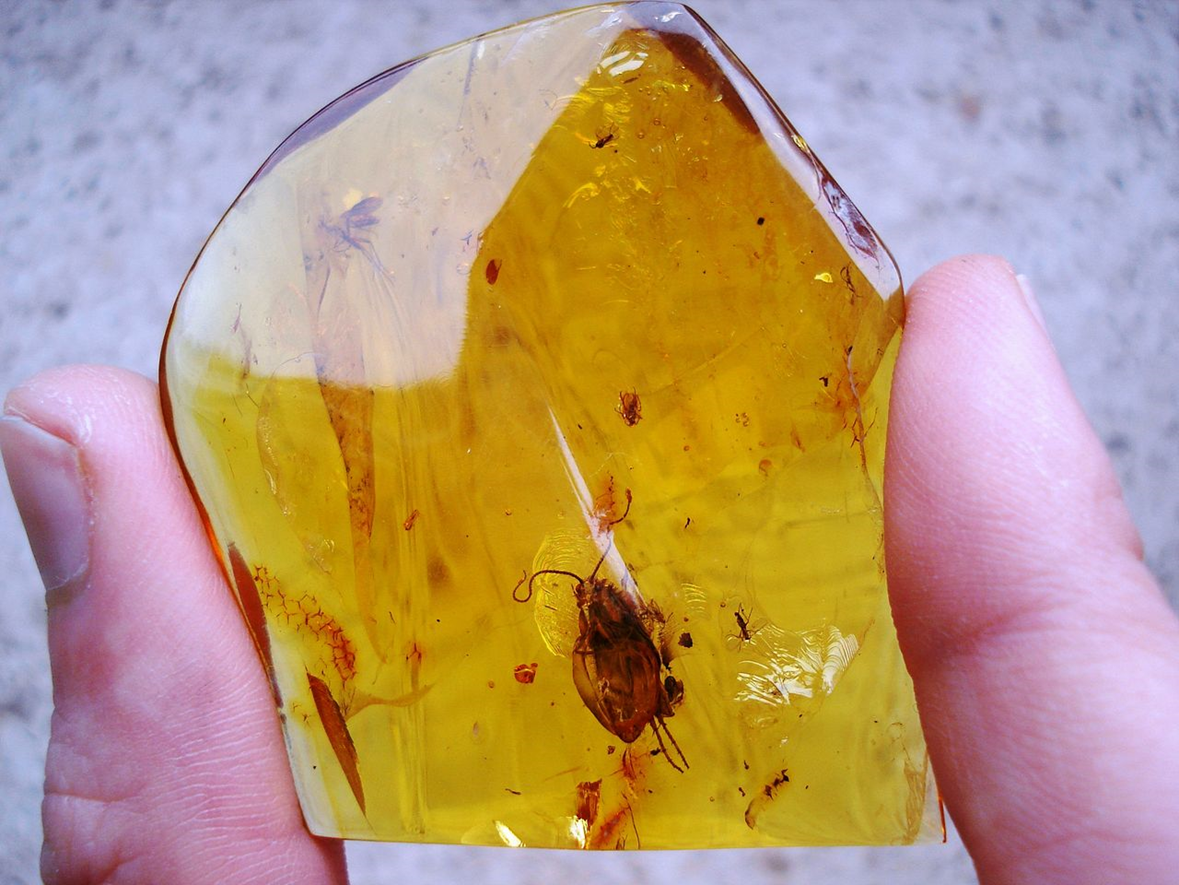


resinous
what type of luster is displayed here? and name the mineral
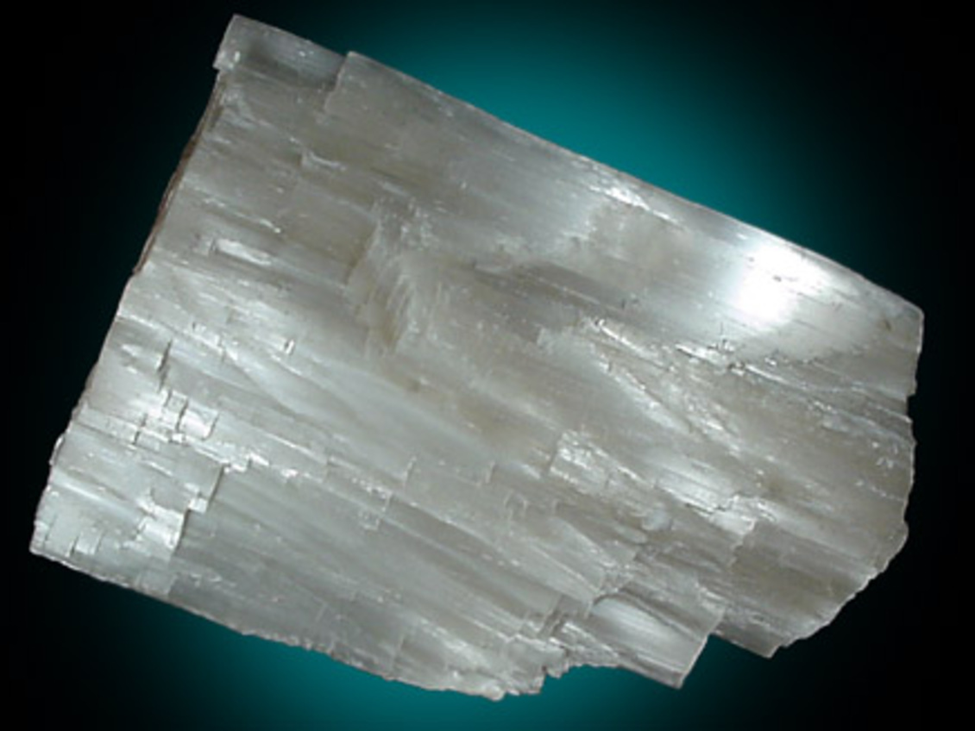

silky, gypsum
What is the term for crystals that sparkle and appear brilliant?
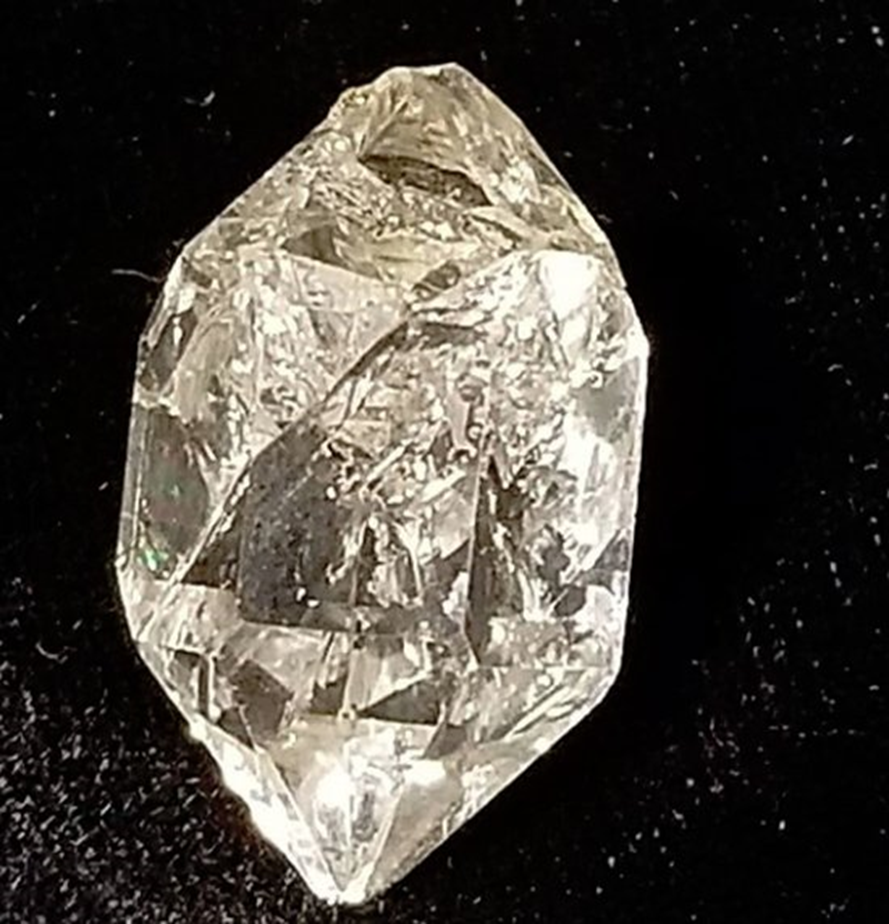

adamantine minerals
What type of luster is displayed here?
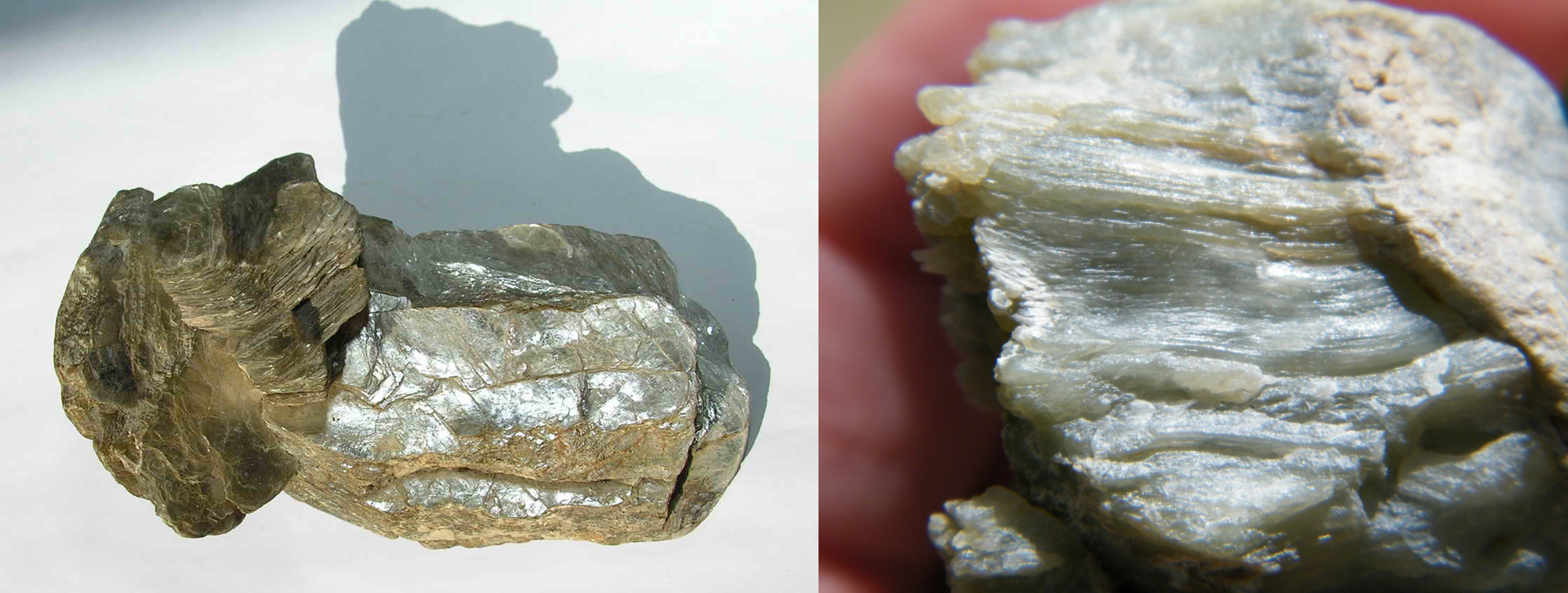

pearly
what type of luster is displayed here?
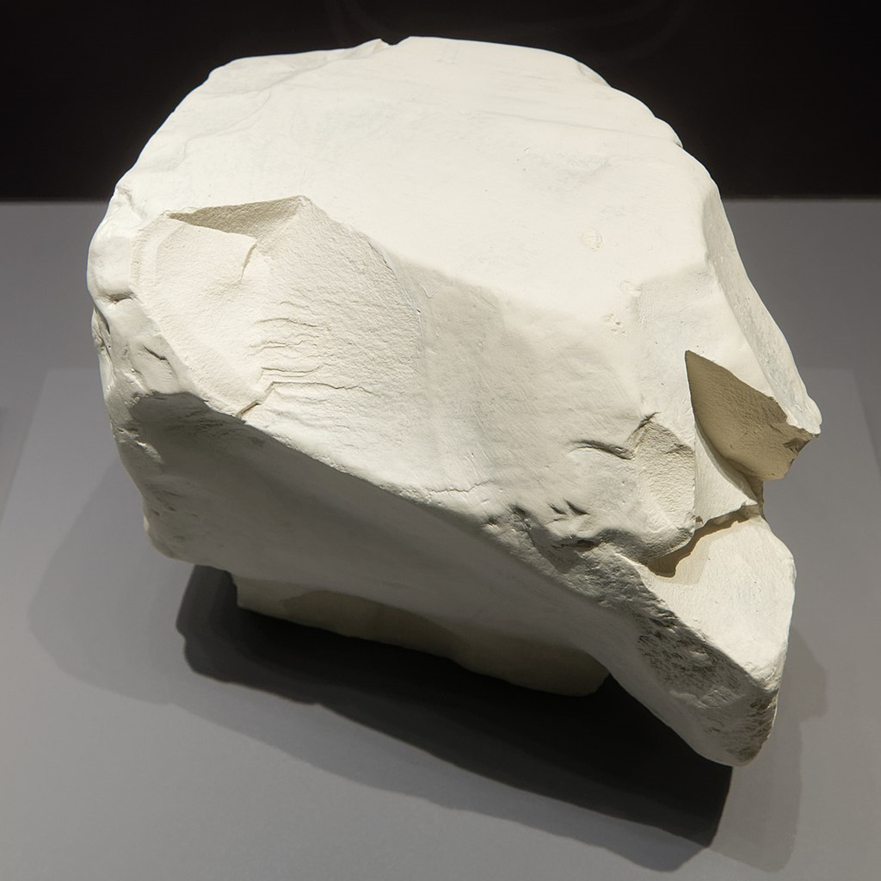

dull
What is the term for “ability to transmit light”
diaphaneity
Name the differences between transparent, translucent, and opaque
transparent is clear, translucent transmits light but not clearly, opaque does not transmit light
Name some reasons for color in minerals
metal ions, intervalence charge transfer, ionizing radiation, physical effects, band gaps
what is the streak of a mineral
the color the mineral has as a fine powder
what is luminescence
emit light when activated by energy other than visible light
What play of color is this mineral displaying?
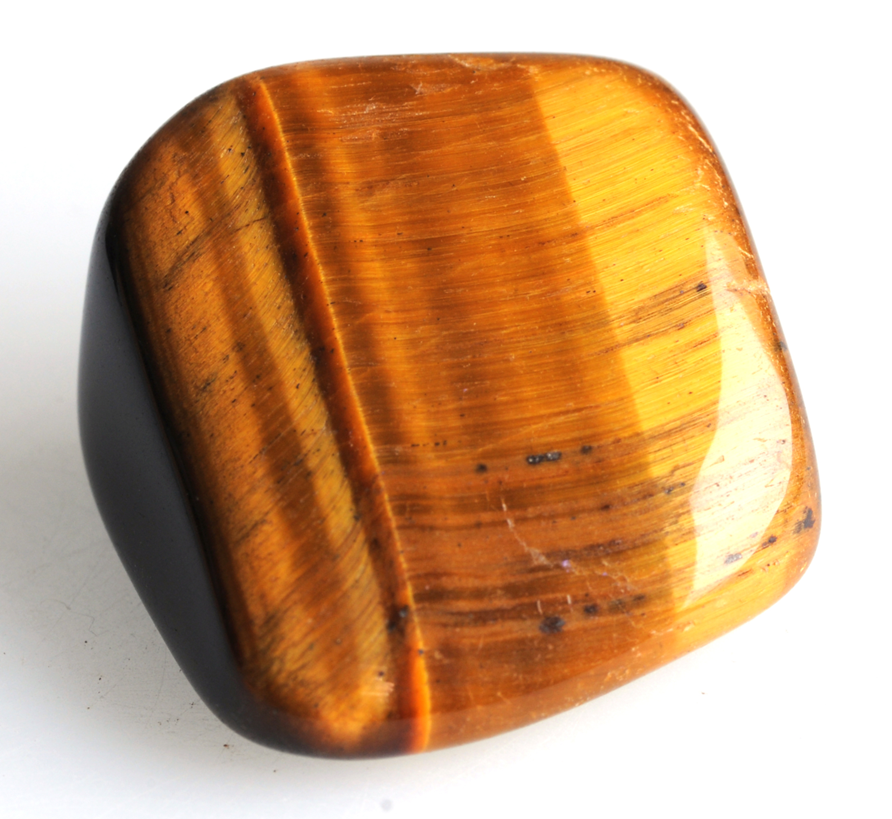

Tiger’s Eye
What are these plays of color displaying and name the mineral
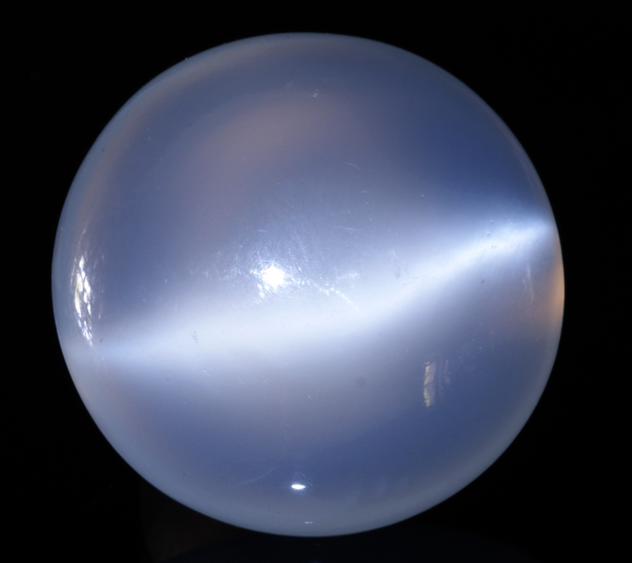


Moonstone - K feldspar, Chatoyancy (band of light), Asterism
What is cleavage of a mineral?
Breaking along smooth planar surfaces oriented along planes of weakness in the lattice
What is fracture of a mineral?
breaking in orientations unrelated to the lattice structure
What type of cleavage does biotite (mica) have?
Basal cleavage
What type of cleavage does Pyroxene have?
90 degrees btwn planes
What type of cleavage does Amphibole have?
60 degrees and 120 degrees btwn planes
What is hardness?
a mineral’s resistance to abrasion or scratching
Minerals with this element typically have magnetic properties
Fe (iron)
What are the three categories of magnetism and their meanings?
ferromagnetic are strongly attracted to magnets, diamagnetic are weakly opposed (repelled) by strong magnets, paramagnetic is weakly attracted to strong magnets
What native element has a high conductivity?
copper
List the names of the 7 crystal classes
Give the relative axial lengths for each crystal class
Give the relative axial angles for each crystal class
Cubic/isometric, a=b=c, A=B=C=90
Tetragonal, a=bcc, A=B=C=90
Orthorhombic, a≠b≠c, A=B=C=90
Rhombohedral, a=b=c, A=B=C≠90
Monoclinic, a≠b≠c, A=C=90, B≠90
Triclinic, a≠b≠c, A≠B≠C≠90
Hexagonal, a=b≠c, A=B=90, C=120
What are the 3 primary symmetry operations used to describe mineral symmetry?
rotation, reflection (mirror), rotoinversion
What fold rotation axis is represented by each of these symbols? oval, triangle, square, hexagon
2, 3, 4, 6
What are the Miller Indices of this plane?
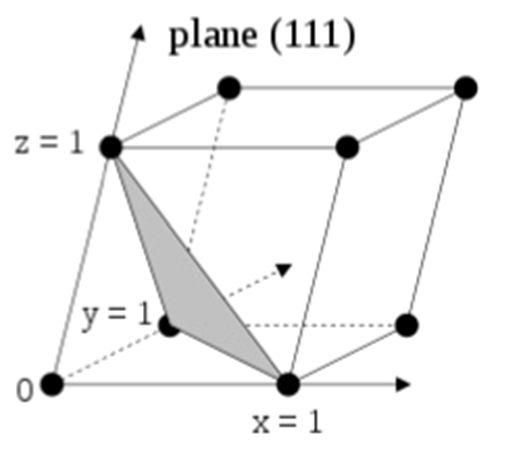

(111)
What symmetry operations are indicated by these stereonets?


2-fold rotation axis with no mirror, 4-fold rotation axis with no mirror,
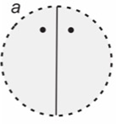
What is the fold axis of this crystal? What is the orientation of the rotation axis? What does the steronet look like?
2-fold axis, oriented vertically, oval in the middle with 2 dots inside a dashed circle
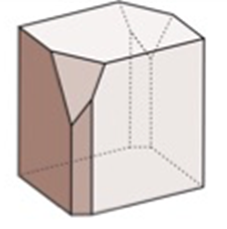
How many mirror planes are in this crystal? Where is/are the mirror plane(s) oriented? What does the steronet look like?
one mirror, oriented vertically splitting the 2 bevels
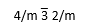
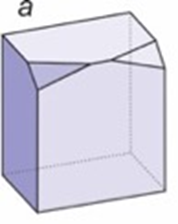
A cube has the highest symmetry of (picture). what does each of these mean
4/m = 4-fold rotation axis with a mirror plane perpendicular
3-bar = 3-fold rotoinversion axis
2/m = 2-fold rotation axis with a mirror plane perpendicular
What are the 5 unit cell types?
primitive, body centered, face centered, side centered, rhombohedral
What is the difference between a dipyramid and an octahedron?
Octahedron is cubic/isometric with a=b=c with all angles = 90 degrees while tetragonal dipyramid is tetragonal with a=b≠c with all angles = 90 degrees
Name this twin and the mineral

penetration twin, staurolite
Name the twin and the mineral

Penetration twin, pyrite
Name the twin and the mineral

Contact twin, gypsum
Name the twin and the mineral

polysynthetic twin, albite
What is the crystal system represented by the form?
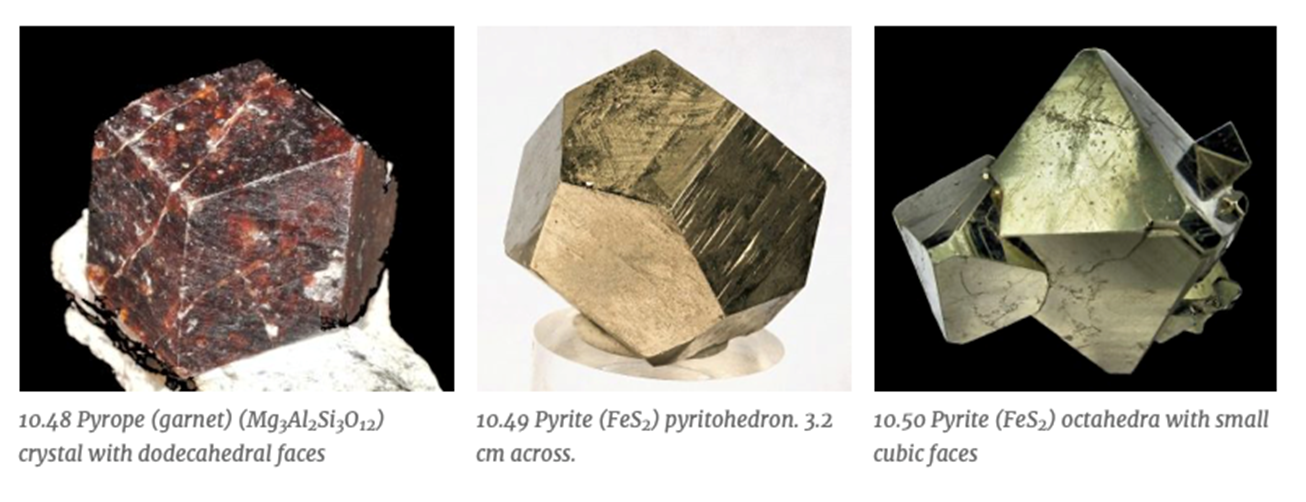

Isometric
What is the crystal system represented by the form?
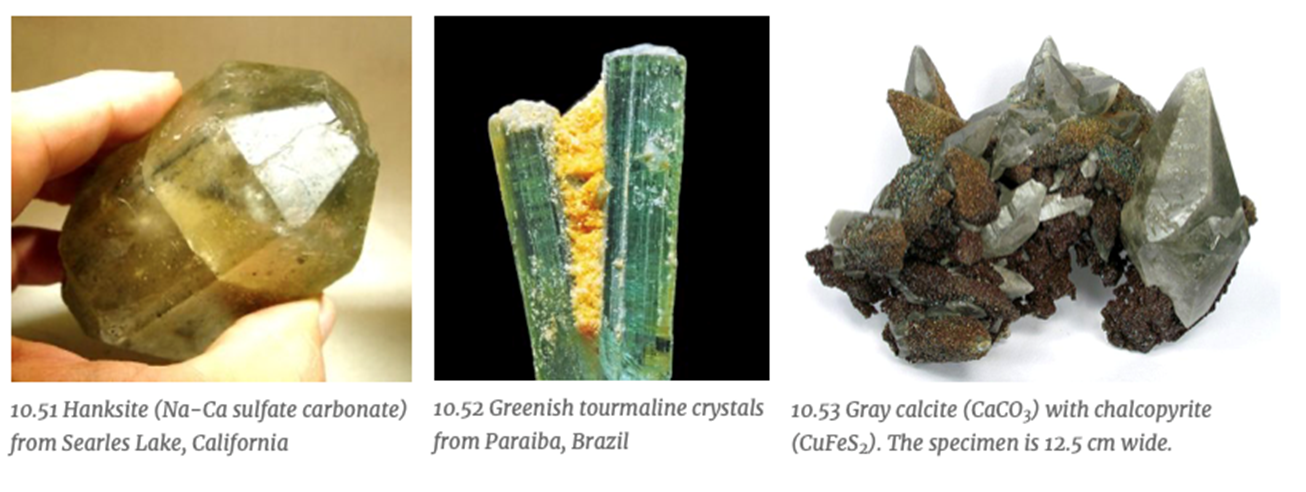

Hexagonal and Trigonal
What is the crystal system represented by the form?

Tetragonal
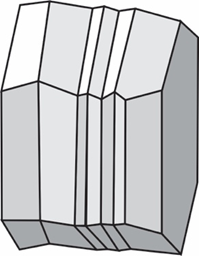
What is the crystal system represented by the form?
Orthorhombic
What is the crystal system represented by the form?
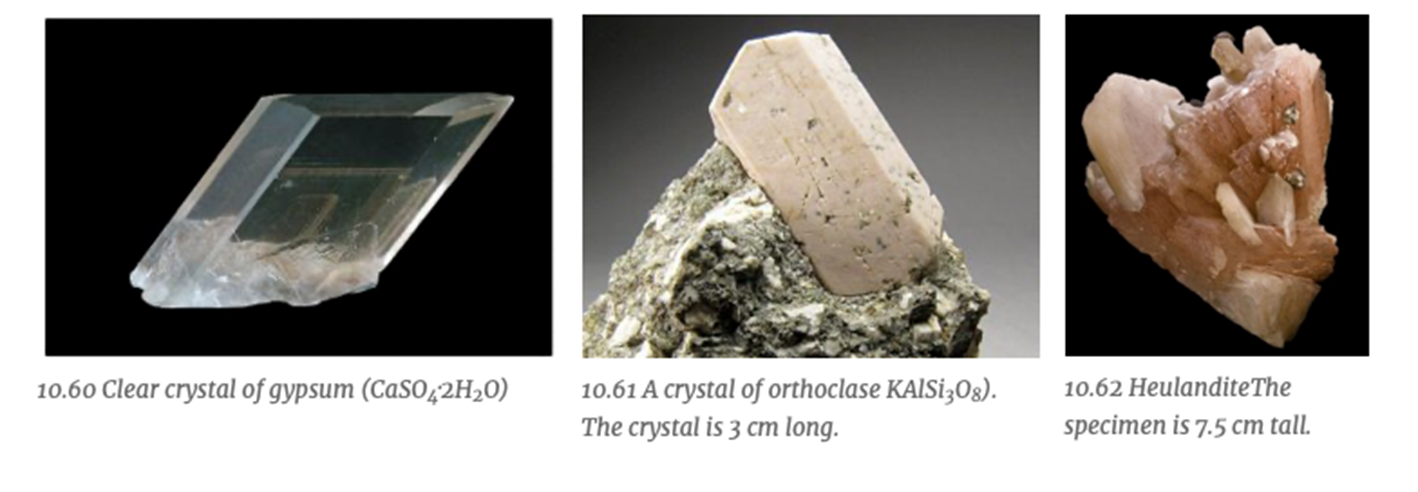

Monoclinic
What is the crystal system represented by the form?

Triclinic
What type of twin is shown?
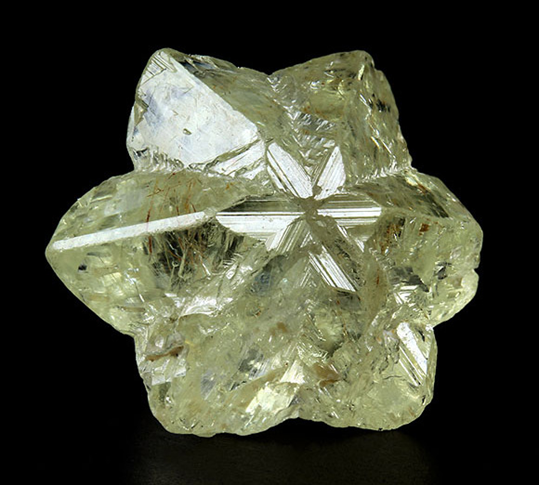

cyclic
What twin is displayed? of what mineral?

Japan Law, quartz