chapter 5 structure and function of large biological molecules
1/127
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
what are the 4 main classes of large molecules of organisms?
carbohydrates
lipid
protein
nucleic acid
how many amino acids are there?
20
hormone
steroid, signal that travels through the body
what are the 2 functions of polysaccharides?
strengthens plant and fungal cell walls and exoskeletons
stores glucose for energy
steroid backbone
picture
triacyglycerol
fat, oil, glycerol, 3 fatty acids, energy source
steroidd
4 fused rings with attached chemical groups, component of
where is chitin found?
animals and fungi
what are the 3 classes of macromolecules?
carbohydrate
protein
nucleic acid
macromolecule
large molecule of covalently bonded atoms
polymer
long and large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
monomers
small and similar building blocks that make up polymers
what reaction connects monomers?
dehydration synthesis
what occurs in dehydration reaction, condensation reaction, dehydration synthesis?
2 monomers are bonded together through the loss of a water molecule
what type of reaction converts polymers to monomers?
hydrolysis
hydro
water
lysis
break
what type of reaction is C6H12O6 + C6H12O6→C12H22O11 + H2O?
dehydration reaction
glucose (C6H12O6)
monomer, monosaccharide
what happens when 2 monomers are joined?
water molecule is removed
carbohydrate
sugar, starch, fuel, building material
hydrolysis
reaction that is the reverse of dehydration synthesis
monosaccharide
monomer of carbohydrates, fuel, C source that can be converted to other molecules or combines into polymers
ribose
5-C pentose sugar with the formula C5H10O5
penta
5
hexose (C6H12O6)
sugar
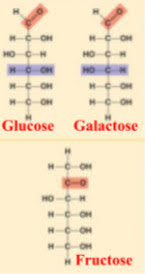
what are the 3 hexose sugars?
glucose
galactose
fructose
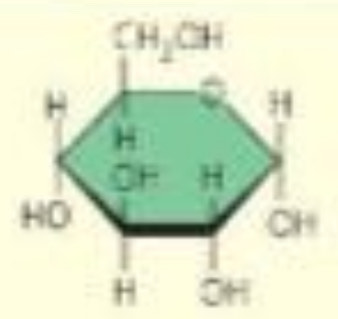
what are the 2 functional groups that hexose sugars have?
carbonyl
hydroxyl
what is the difference between aldehyde sugar and ketone sugar?
the location of the carbonyl group
where are the carbons in a ring structure?
at the corners or numbers
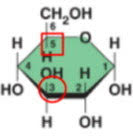
what is happening in this reaction: C6H12O6 + C6H12O6→C12H22O11 + H2O?
2 monomers are joined to make a polymer
disaccharide
two monosaccharides joined together through dehydration synthesis
what are the 3 disaccharide with the formula C12H22O11?
maltose, malt sugar
sucrose, table sugar
lactose
what 2 monosaccharides make maltose, malt sugar?
glucose
what 2 monosaccharides make sucrose, table sugar?
glucose and fructose
what 2 monosaccharides make lactose?
glucose and galactose
where is maltose, malt sugar found?
beer
where is sucrose, table sugar found?
plants
where is lactose found?
milk
what do all sugars end in?
ose
glycosidic linkage
covalent bond between 2 monosaccharides
what does a 1 - 4 glycosidic linkage mean?
a number 1 C of one monosaccharide is joined to a number 4 C of another monosaccharide
what are the 2 types of polysaccharides?
storage
structural
storage polysaccharide ex
plants store starch
structural polysaccharide ex
cellulose makes up plant cells
why can cellulose not be digested by humans?
they do not have the enzymes
what 3 organisms can digest cellulose?
cow
termite
fungi
what carbohydrate has 1 - 4 B glucose linkages?
starch
glycogen
storage polysaccharide produced by vertebrates that is in the liver of animals
chitin
structural polysaccharide that gives cockroaches their crunch
lipid
fat, wax, oil, phospholipid, steroid, diverse group of molecules
what characteristic do all lipids have?
hydrophobic
what are the 2 building blocks of fats?
glycerol
fatty acid
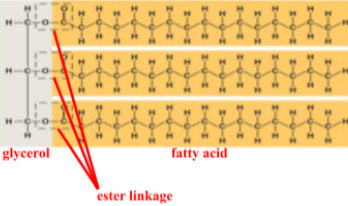
a fat had 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol molecule. how many water molecules will be removed to form it?
3
what process bonds the building blocks of fats?
dehydration synthesis
fatty acid chain
picture
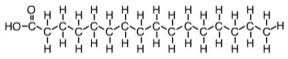
unsaturated fat
fat with one or more double bonds in its fatty acid chains
2 examples of saturated fats
butter
lard
2 examples of unsaturated fats
olive oil
cod liver oil
why are unsaturated fats liquid at room temperature?
the kinks where the cis double bonds are located prevent the molecules from packing together closely enough to solidify at room temperature
trans fat
unsaturated fat with trans double bonds formed artificially by adding H to vegetable oil
why should trans fat be limited in a diet?
it can contribute to coronary heart disease
phospholipid
phosphate group, 2 fatty acids
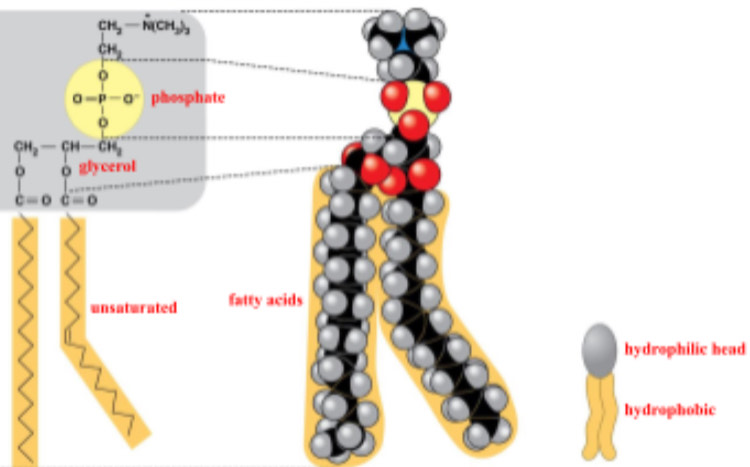
why is the tail of a phospholipid hydrophobic?
it is made up of nonpolar hydrocarbon molecules
phospholipid bilayer
structure in a plasma membrane
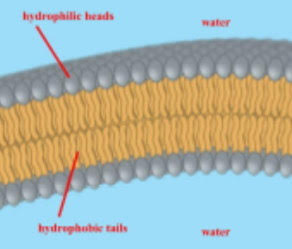
why are the tails of the phospholipids located in the interior of a phospholipid bilayer?
to avoid the water
cholesterol
3 hexagons and a doghouse structure, steroid, component of cell membrane
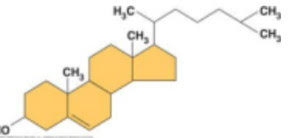
2 examples of steroids
estradiol
testosterone
enzyme
globular protein that accelerates certain chemical reactions and exhibits at least tertiary structure
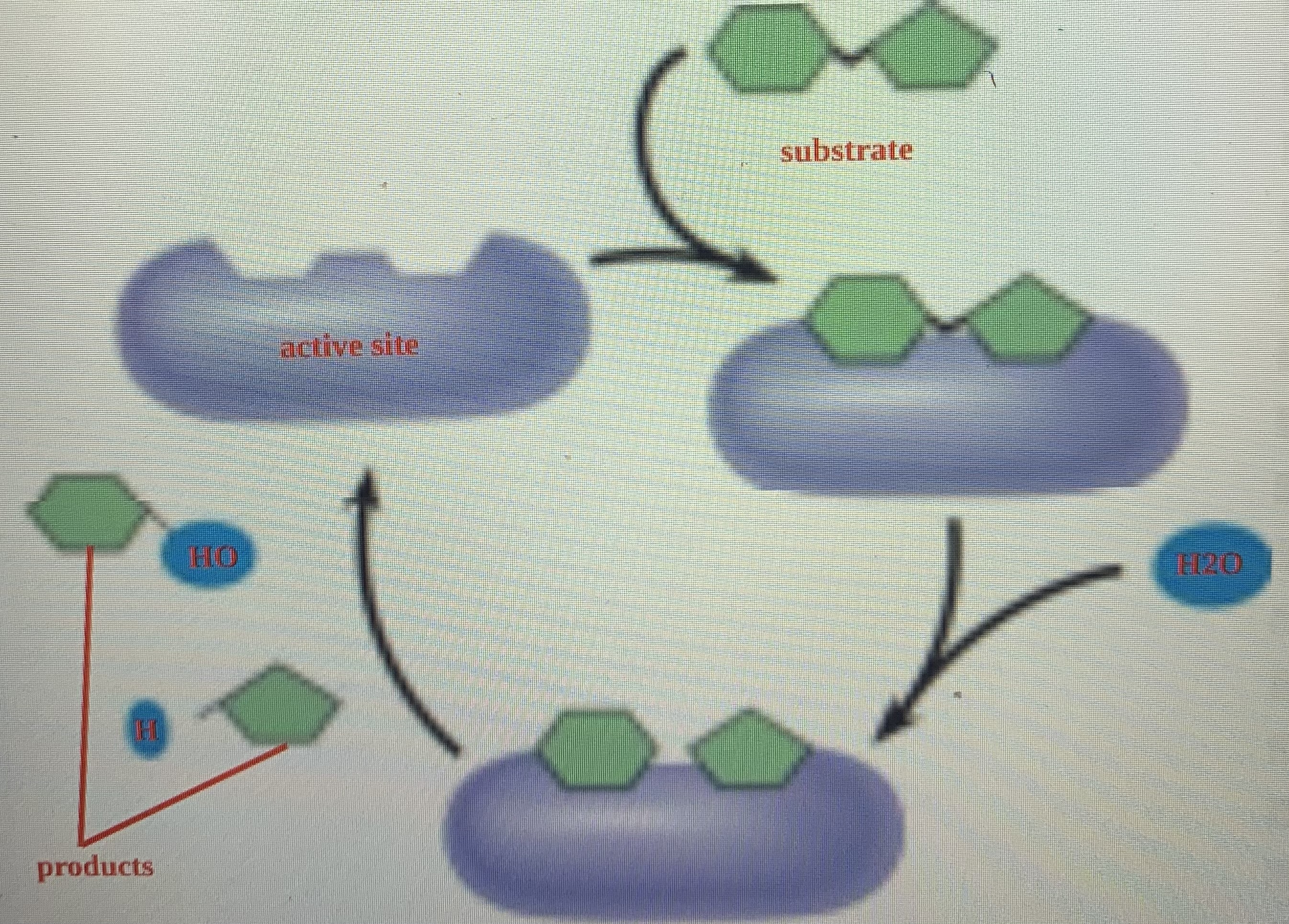
enzyme example
digestive enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of bonds in food molecules
what do storage proteins do?
stores amino acids
storage protein example
ovalbumin is used as an amino source for developing embryo
transport protein example
hemoglobin transports O from the lungs to other parts of the body
what do defensive proteins do?
protects against diseases
defensive protein example
antibodies inactivate and destroy viruses and bacteria
what do hormonal proteins do?
coordinates an organism’s activities
hormonal protein example
insulin causes other tissues to take up glucose this regulating blood sugar concentration
amino acid
monomer of protein
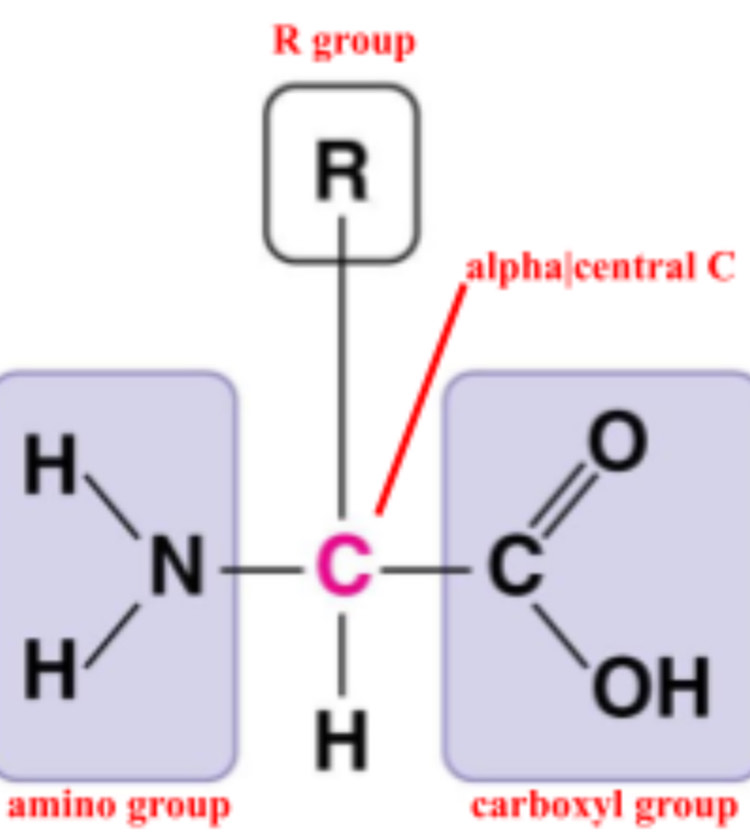
R group
side chain
how many R groups are there?
20
what makes an R group nonpolar?
hydrocarbon
what makes an R group polar?
hydroxyl, sulfhydryl, NH2
what makes an R groups acidic and electrically charged?
ionized carboxyl group
what makes an R group basic and electrically charged?
positively charged amino group
dipeptide
protein with two amino acids
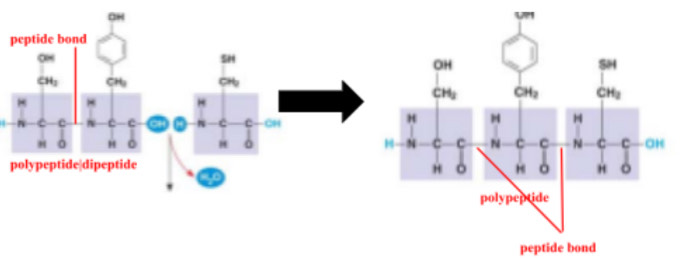
polypeptide
unbranched polymer of the same set of 20 amino acids, protein
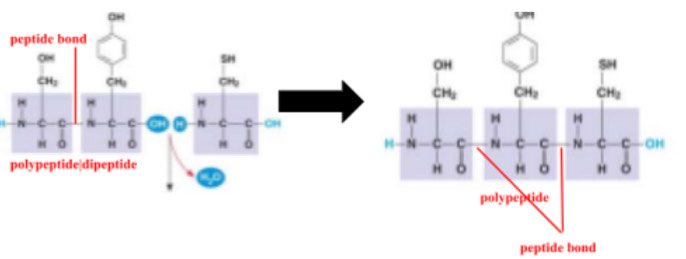
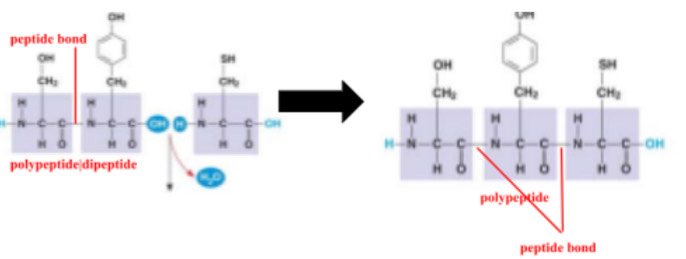
peptide bond
covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid from dehydration synthesis
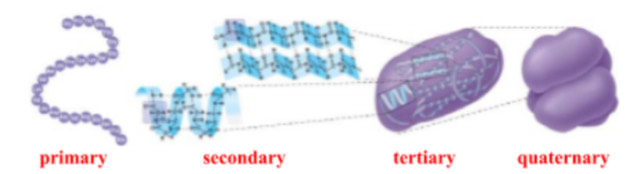
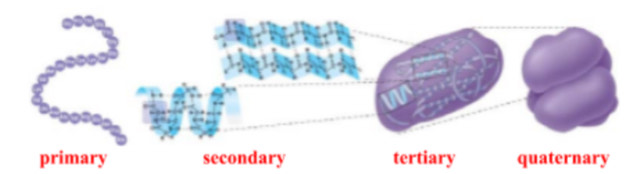
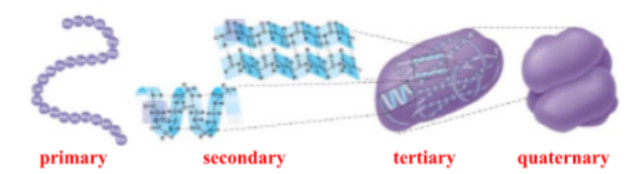
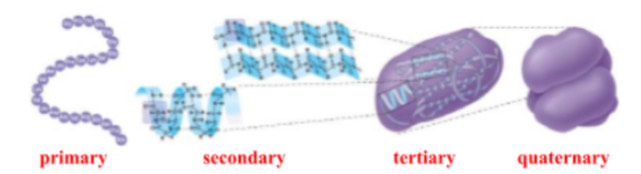
what are the 4 levels of protein stucture?
primary (Io)
secondary (IIo)
tertiary (IIIo)
quaternary (IIIIo)
what are the 2 types of secondary (IIo) protein structures?
alpha helix
beta pleated sheet
primary (Io) protein structure
sequence of amino acids, order of letters in a long word determined by inherited genetic info
secondary (IIo) protein structure
coils and folds of a polypeptide chain found in most proteins formed from H bonds between repeating parts of the polypeptide backbone
alpha helix
delicate coil held together by H bonding between every 4th amino acid, coil, single strand, ~
beta pleated sheet
2 or more segments of a polypeptide chain lying side by side connected by H bonds in a folded structure, =
tertiary (IIIo) protein structure
interaction among side chains
quaternary (IIIIo) protein structure
multiple polypeptide chains that forms one macromolecule
what 5 interactions are in tertiary protein structures?
H
ionic
hydrophobic interaction
van der Waals interaction
disulfide bridge
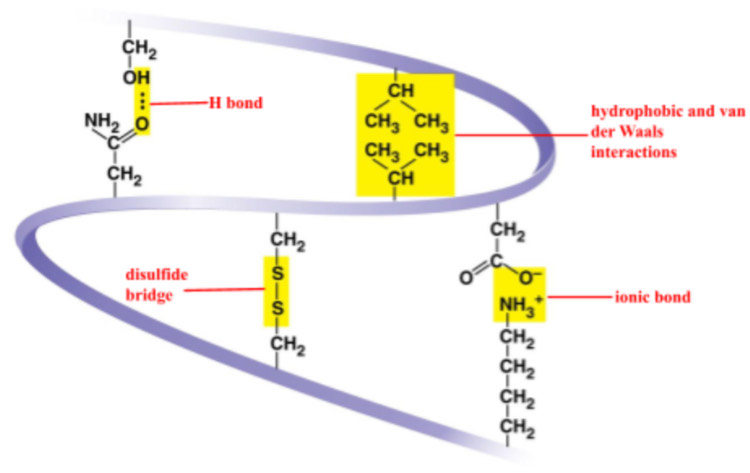
disulfide bridge
strong covalent bond that may reinforce the protein’s structure
primary (Io) protein structure example
transthyretin is made up of 4 identical polypeptide chains each composed of 127 amino acids