Class 10: Urinary incontinence- incontinence
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
how many adults in the us have urinary incontinence
25 million
9-12% of all adults
mostly women
urinary incontinence causes
"DRIP"
D- delirium, dehydration, depression
R- restricted mobility, rectal impaction
I - Infection, inflammation, impaction
P - polyuria, polypharmacy
bladder irritants
Nicotine
Caffeine
Alcohol
Certain acidic fruits — oranges, grapefruits, lemons and limes
All fruit juices except cranberry
Carbonated drinks
Chocolate
Artificial sweeteners
Spicy foods
risk factors for incontinence
older individuals (at highest risk)
cognitively impaired (dementia)
women are more susceptible
diabetes
immobility
pregnancy
neurologic disorders
medications
diabetes
smoking
stress incontinence
the inability to control the voiding of urine under physical stress such as running, sneezing, laughing, or coughing
stress incontinence s/s
Urine loss with exertion, coughing, lifting or sneezing
Usually involves small amounts of urine.
increased pressure on bladder during pregnancy
Stress incontinence treatment
Exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles (Kegel exercises)
surgery
Drug therapy
absorbant pads
Urge incontinence (overactive bladder)
Occurs when the bladder contracts randomly, causing a strong, sudden urge to urinate that is followed by urine leakage.
urge incontinence s/s
Abrupt and strong urge to void
difficulty holding urine
increased frequency
nocturne
urge incontinence treatment
prompted voiding, toilet q2h
pelvic flood exercise
medications
overflow incontinence
involuntary loss of urine associated with overdistention and overflow of the bladder
obstruction or lack of detrusor muscle
overflow incontinence s/s
over distended bladder
urinary retnetion
urinary obstruction
bph
overflow incontinence treatment
surgery
catheterization
absorbant pads
medication
Types of incontinence
stress, urge, overflow, reflex, functional
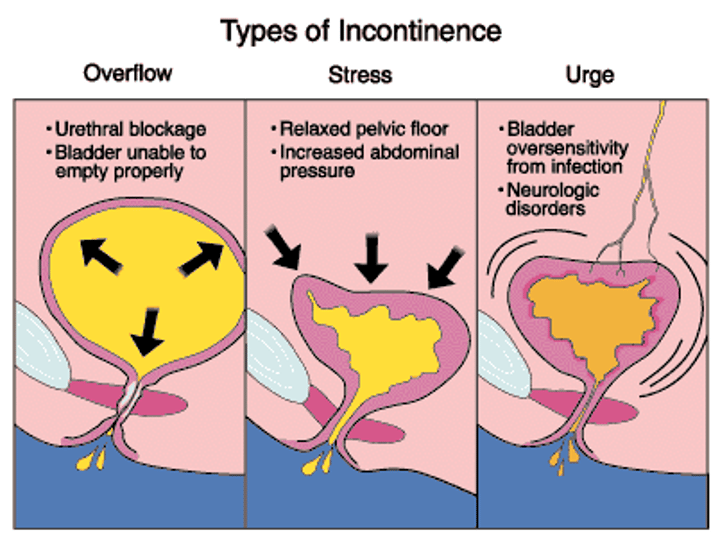
side note!!
on the test Jenna said that someone can have two types of incontinences
example: someone can have stress and urge at the same time based on s/s of the question and if its select all that apply
reflex incontinence
emptying of the bladder without the sensation of the need to void
nerve issues
example: every time the bladder is at 100ml of urine it automatically empties with no warning
reflex incontinence treatment
medication
neuromodulation
surgery
catheterization
absorbant pads
functional incontinence
the person has bladder control but cannot use the toilet in time
example: dementia, mobility issues, physical disabilities
functional incontinence s/s
not being able to reach toilet in time even though they know they have to go
functional incontinence treatment
catheterization
absorbant pads
home modifications
physical or occupational therapy
assistive devices
nonrestrictive clothing (no belts or buttons)
iatrogenic/transient incontinence
sudden urination due to outside factors like medication
due to acute illnesses, infections, and medications
once cause is removed, incontinence won't happen anymore
once incontinence is recognized, you should get
descriptions of problems
medical history/regimen
voiding history
intake and output
urinalysis and urince culture
general interventions to prevent incontinence
generous fluid intake
maintain regular void habits
maintain good hygiene
reduce consumption of bladder irritants
prevent utis
maintain skin integrity