8.7 pH & pKa & 8.8 Properties of Buffer & 8.9 Henderson - Hasselbalch Equation
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
8.10 Buffer Capacity
Last updated 12:17 PM on 4/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
1
New cards
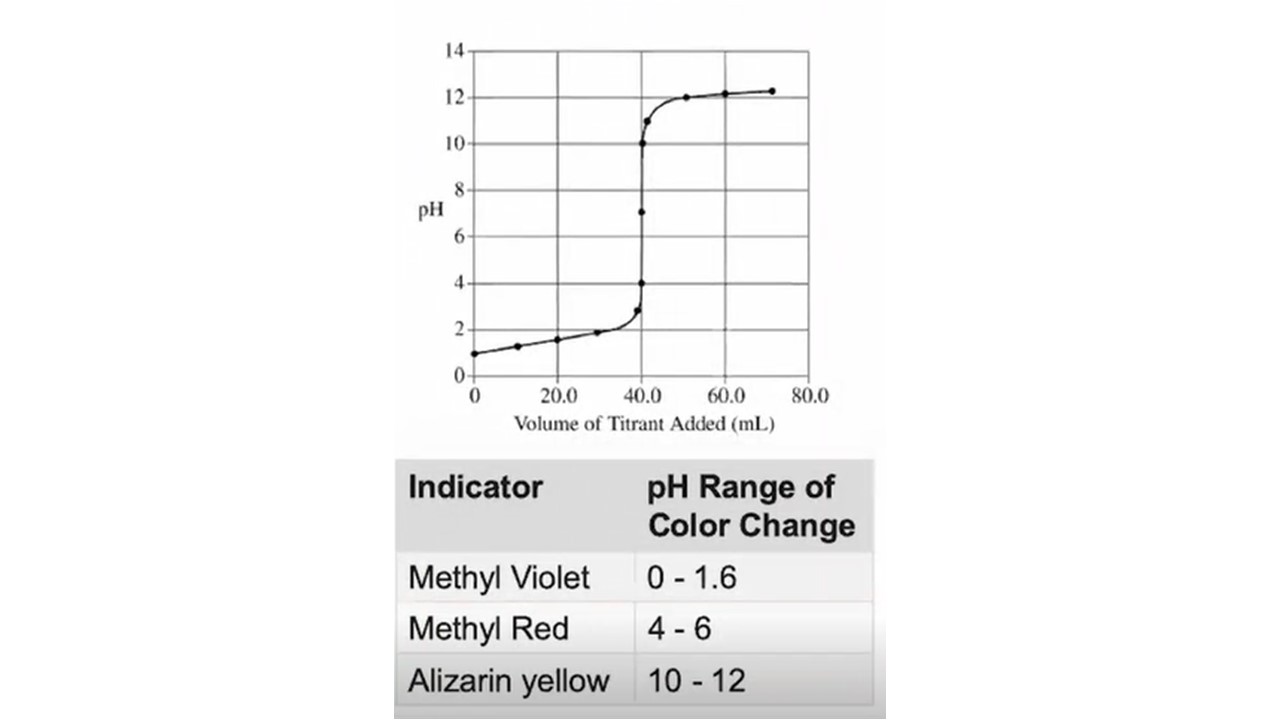
Which one is the best indicator for the titration?
It always needs to be in the range of the equivalence point.
In this case it’s strong acid +strong base = equi. p.t. pH =7
Methyl Red
In other cases it’s
weak acid + strong base = equi. p.t. above 7
weak base + strong acid = equi. p.t. below 7
In this case it’s strong acid +strong base = equi. p.t. pH =7
Methyl Red
In other cases it’s
weak acid + strong base = equi. p.t. above 7
weak base + strong acid = equi. p.t. below 7
2
New cards
Diff btw equivalence p.t. and end point of a titrant.

3
New cards


4
New cards
Acid and Base indicators

5
New cards
What’s in a buffer?
1. Weak acid or Weak base
2. It’s conj. salt
e.g. NH3 & NH4+
6
New cards
What’s a neutral solution?
created to from equimolar amounts of a strong acid and base that reaction a 1:1 ratio.
7
New cards
When water is added to a solution (not buffer), what happens? How it affect pH?
Dilution happens, where the H ions will decrease (pH - potential H) so, pH increase.
8
New cards
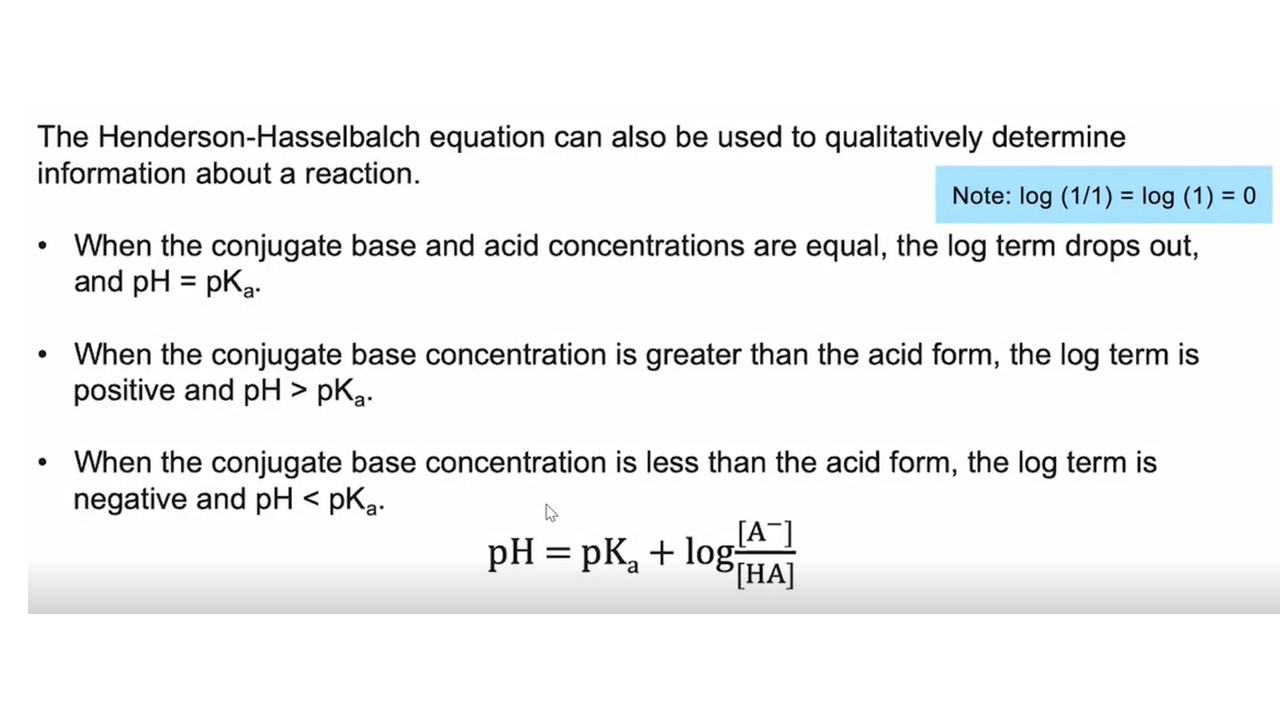
Relationship btw pH and pKa
9
New cards
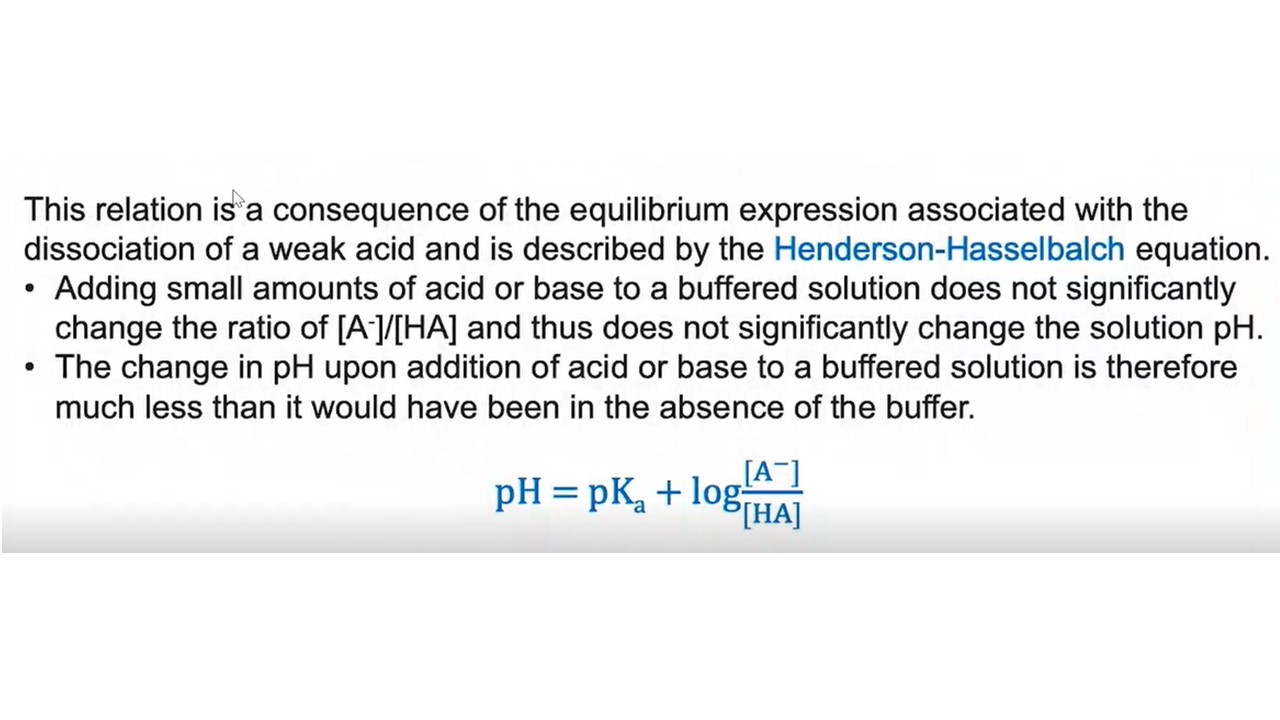
What will happen if acid or base is added but in small amounts to a buffered solution?
10
New cards
Relationship btw concentration, pH and capacity
Increasing the concentration of the buffer components (ratio constant) keeps pH of the buffer the same
But increases the capacity of the buffer to neutralize added acid or base
But increases the capacity of the buffer to neutralize added acid or base
11
New cards
When a buffer has more conj.acid than base
Greater Buffer capacity for added base than added acid
12
New cards
When a buffer has more conj.base than acid
Greater buffer capacity for added acid than added base