Lecture 13: Fluid Mosaic Model, Membrane Proteins
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Morris: Chapter 5 sections 5.1-5.2 and figure 5.8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Cell membranes
cells are defined by membranes
lipids are the main component of cell membranes
E-book - BIOL*1090 F24 - Macmillan Learning Achieve
https://courselink.uoguelph.ca/d2l/le/content/896731/viewContent/3842265/View
Function of biological membranes
define cell boundary (organelles; mitochondria, Golgi, etc)
define enclose compartments
control movement of material into and out of cell
allow response to external stimuli
enable interactions between cells
provide scaffold for biochemical activities
energy transduction; mitochondria/chloroplast provides scaffolding for biochemical activities producing energy
Plasma membrane
PM: plasma membrane
SR: sarcoplasmic reticulum
endoplasmic reticulum equivalent, movement of cations into muscle cells causing contractions
Red blood cells are used to study PM b/c they don’t have nuclei or internal membrane
Trilaminar structure made of a phospholipid bilayer
Trilaminar structure
made of phospholipid bilayer
~6nm thick
made up of phospholipids (phosphate head, hydrophobic tail, polar hear - inner layer)
micelle: formation of phospholipids into sphere shape (no lumen)
liposome: double phospholipid membrane layer with a lumen inside
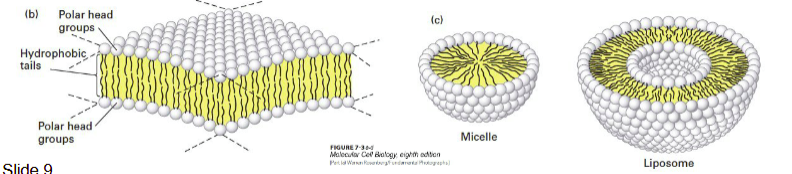
Phospholipids forming the plasma membrane
lipid molecules spontaneously aggregate to bury their hydrophobic tails in the interior and expose their hydrophilic heads to water
micelles are formed by fatty acids with only one hydrophobic tail
amphipathic: hydrophobic (non-polar) and hydrophilic (polar) regions
Phospholipid structure
two fatty acid chains
esterified (ester bonds)
stereospecific (left to right) numbering sn-1 and sn-2 of the glycerol, sn-3 has head group linked by phosphate residue
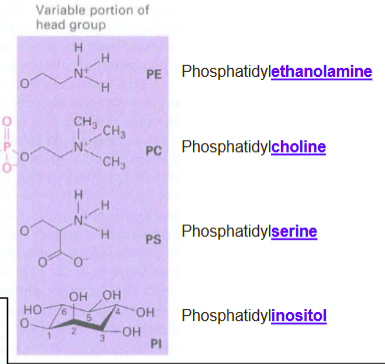
What attaches to the glycerol portion of phospholipid?
phosphatidyl-:
ethanolamine
choline
serine
inositol
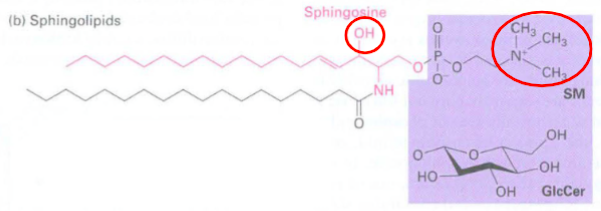
Other type of phospholipid:
sphingolipid: mimics the shape of glycerol — has hydroxyl instead of ester
class of lipids containing backbone of sphingoid bases instead of glycerol which are a set of aliphatic amino alcohols
groups bonded to terminal oxygen:
phosphocholine forms sphingomyelin/SM (nervous system)
hydroxyl group forms a ceramide
glucose forms glucosesphingolipid
important in signal transduction and cell recognition
Phospholipid synthesis basics
occurs at the interface of the cytosol and outer ER (which has all the enzymes for synthesis and distribution)
multistep process
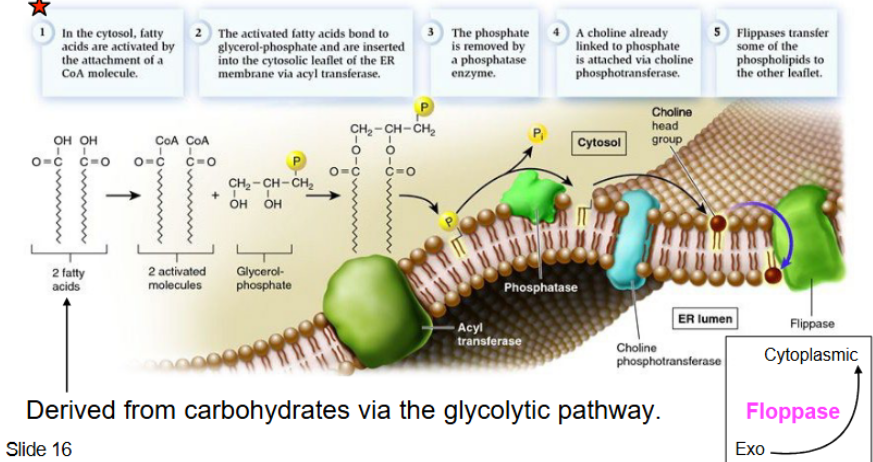
Phospholipid synthesis steps pt 1
cytosol: fatty acids (FA) activated by attachment of CoA molecule → activated FA bonds to glycerol phosphate into ER membrane → phosphate removed by phosphate enzyme → choline is attached via choline phosphotransferase → flippases transfer phospholipid to leaflet
flippases → phospholipid to inner leaflet membrane
floppases → phospholipids to outer leaflet membrane
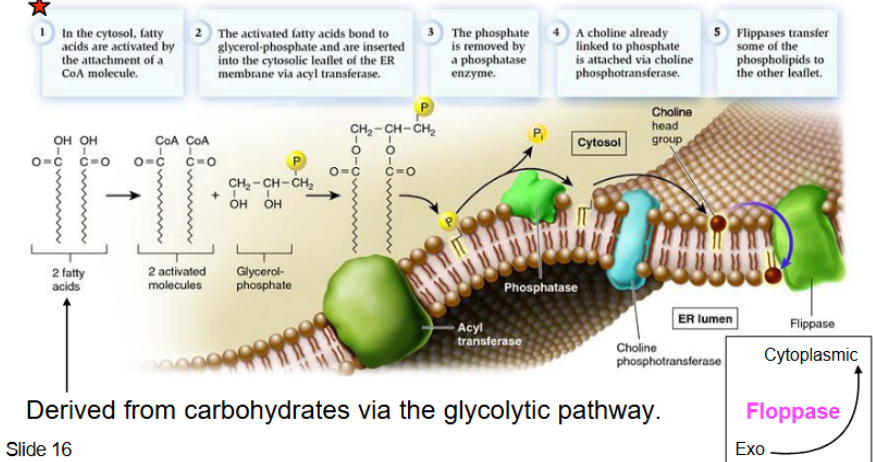
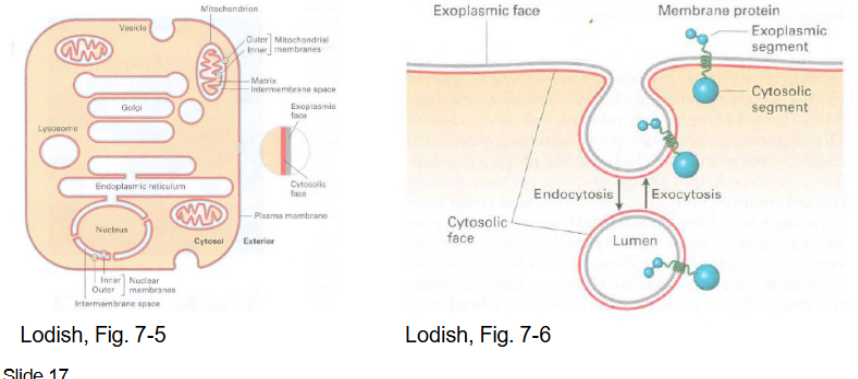
Phospholipid synthesis steps pt 2
vesicle containing phospholipids) leaves the ER for the cytoplasmic cellular membrane on the exterior leaflet (exocytosis via the 2 inner and outer membranes)
different cells have different cell membranes (integral, peripheral, chloroplast, glycoprotein, glycolipid)
Fluid Mosaic Model
fluid: individual lipids move
mosaic: diverse ‘particles’ like proteins, carbohydrates, and cholestorol penetrate the lipid layer
proposed by Seymour Jonathan Singer and Garth Nicolson in 1972
2-dimensional liquid restricting the diffusion of membrane components
proteins embedded in layer, are mobile, and can interact
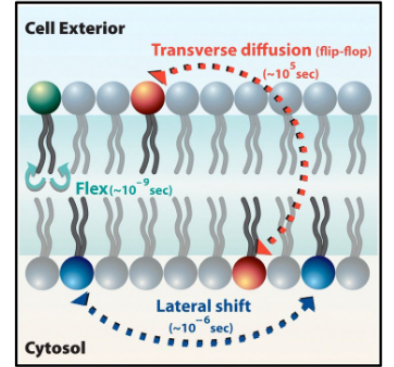
Dynamic of plasma membrane - Lipids
Lipids:
move easily, laterally, within leaflet
movement to other leaflets is slow
Dynamic of plasma membrane - Membrane Proteins
diffuses within the bilayer
movement is restricted
rapid movement is spatially limited (small area it can move fast)
long range diffusion is slow
biochemical modification can alter protein mobility → important for signal transduction
Frye-Edidin Experiment (1970)
inspired Singer and Nicolson’s Mosaic
fused mouse and human cells → discover surface proteins diffuse around the unified membrane
Different biological membranes
Cell plasma membranes contain combinations of glycosphingolipids, cholesterols, and protein receptors which are organized into microdomains called lipid rafts
microdomains can compartmentalize cellular processes by organizing centers of the assembly of signaling models -> allowing closer interactions between protein receptors and effectors to promote kinetically favorable interactions that are necessary for signal trandcution
Example of differences in biological membranes
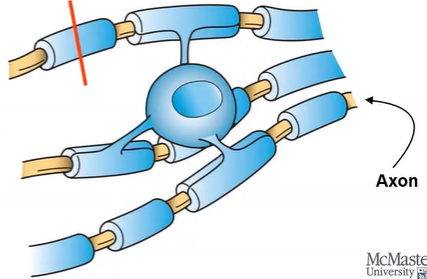
oligodendrocytes are types of neurons surrounded by myelin sheath:
myelin sheath have very few types of transmembrane protein
consists of layers of plasma membrane wrapping an axon
increases speed of electrical signals
the inner membrane of the mitochondria has a very high concentration of protein necessary for ETC and ATP synthesis
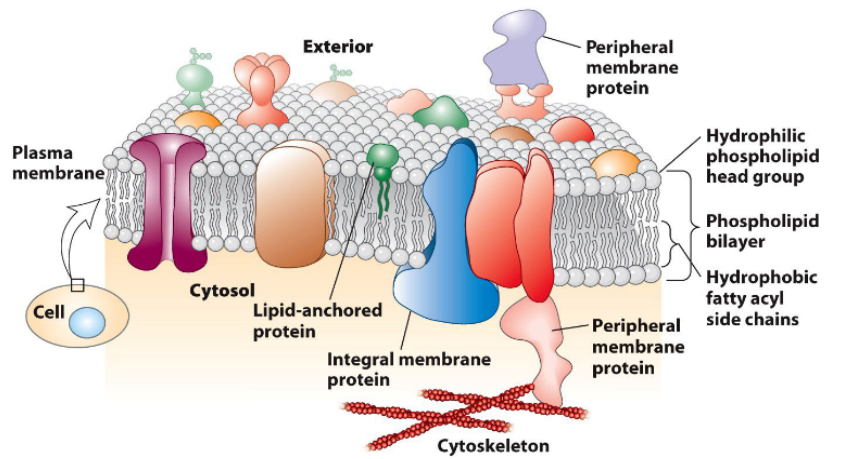
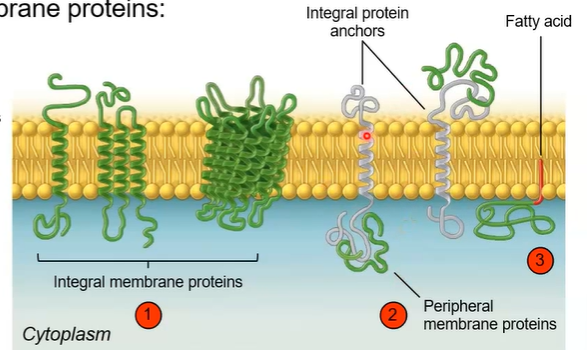
Three classes of membrane proteins
integral membrane proteins spans across the lipid bilayer
transport nutrients/ions, cell-cell communication, attachment
peripheral membrane proteins associate with the surface of the bilayer
lipid-anchored proteins are attached to a lipid in the bilayer
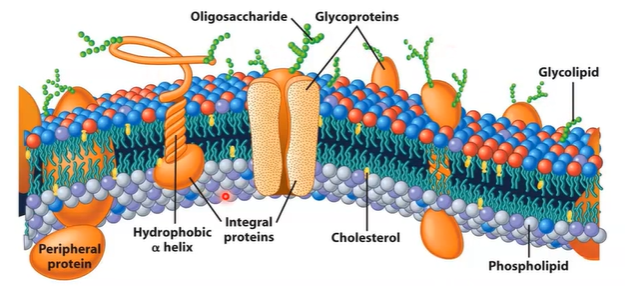
Symmetry of biological membranes
asymmetrical
two leaflets have distinct lipid composition in many plasma membranes
outer contains glycolipids and glycoproteins
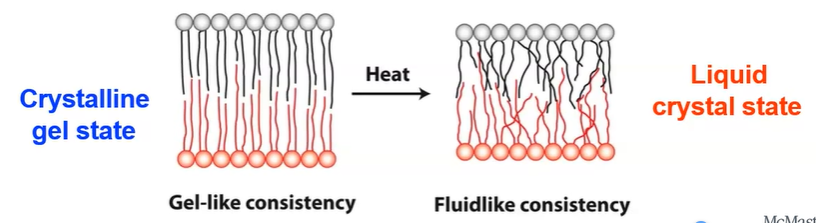
What changes fluidity
warmer and unsaturated lipids increase fluidity → liquid crystal
cooling and saturated lipids decrease fluidity → crystalline gel
How cholesterol modulates membrane fluidity
bidirectional regulator that either stabilizes/raises melting point vs intercalates the membranes
added to liquid crystal = fluidity decrease
added to crystalline gel = fluidity increase
Countering temperature changing fluidity
desaturation of lipids
exchange of lipid chains