Botany Exam 3
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
In respiration, the majority of the energy in the original glucose molecule is....
released as heat
When glucose is respired, which stage of cellular respiration produces most of the ATP?
electron transport chain (ETC)
Thermogenic plants produce heat during aerobic respiration......
by decreasing ATP yield
In cellular respiration, electrons (along with H+) are extracted from glucose and ultimately accepted by....
oxygen
In most cases when plants are respiring aerobically, the energy in one molecule of glucose will be captured in _____ molecules of ATP.
30-38
In glycolysis...
glucose is oxidized to pyruvic acid
The Krebs cycle...
can occur in cells where photosynthesis is also taking place.
Who is respiring?
You right now, plants in the dark, plants in the light.
Plants generate carbon intermediates during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. Why are these intermediates important for plants?
Intermediates are important for plants because they can allow plants to start making amino acids, N-bases, fatty acids, chlorophyll, anthocyanins, hormones, alkaloids, essential oils, and other sugars for cell wall and nucleic acids.
Which of the following is not a criterion for an element to be considered essential for plant growth?
found in a commercial fertilizer
Which of the following essential elements is not obtained by plants as a soil mineral?
Carbon (C)
Which of the following elements is an essential micronutrient for plants?
iron (Fe)
A bag of fertilizer is labeled 15-10-5. These three numbers mean that....
The bag contains 15% nitrogen (N), 10% phosphorus (P) as super phosphate, and 5% potassium (K) as potash by weight
Match the essential elements with their functions.
calcium (Ca) - increases gelling of the pectin in the middle lamella
nitrogen (N) - component of amino acids, nucleic acids, chlorophyll
phosphorus (P) - component of nucleic acid, phospholipids, and ATP
potassium (K) - involved in opening and closing of stomata
sulfur (S) - component of some amino acids
A saprobe obtains energy from
dead organic matter
All of the following are characteristics of the cyanobacteria except...
eukaryotic cells
The decomposition of organic sources of nitrogen to release ammonia is called....
ammonification
Nitrogen fixing bacteria can be found living in association with....
legumes, cycads, and water fern
In the process of nitrogen fixation, bacteria
convert nitrogen gas (N2) to ammonium (NH4+)
In the nitrogen (N) cycle, the conversion of ammonium (NH4+) to nitrate (NO3-) is performed by....
chemosynthetic bacteria
Mycorrhizae are important because they.....
enhance uptake of minerals, especially phosphate, in poor soils
A symbiosis in which two organisms live together tot he advantage of one and the disadvantage of the other is a ......
parasitism
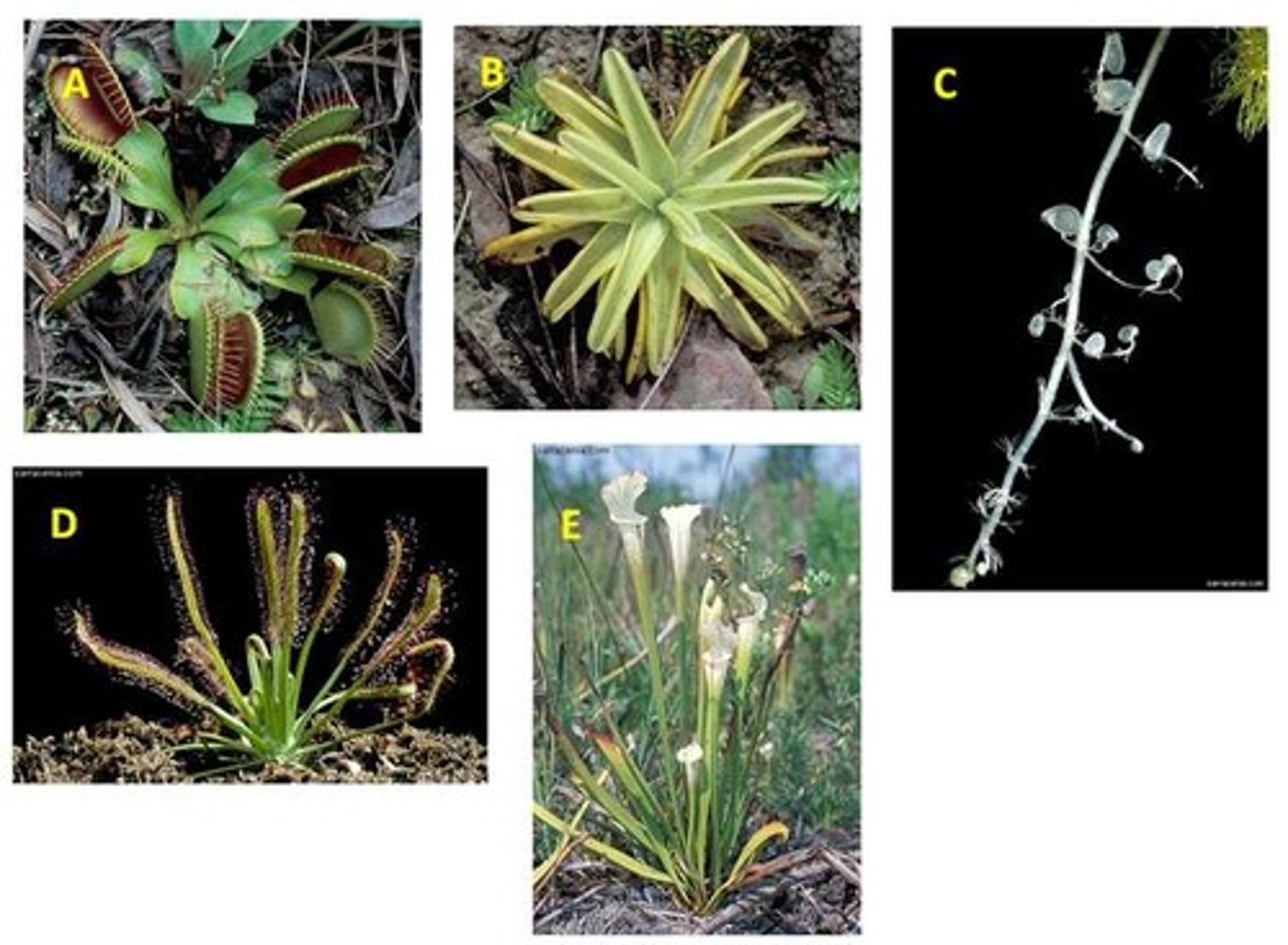
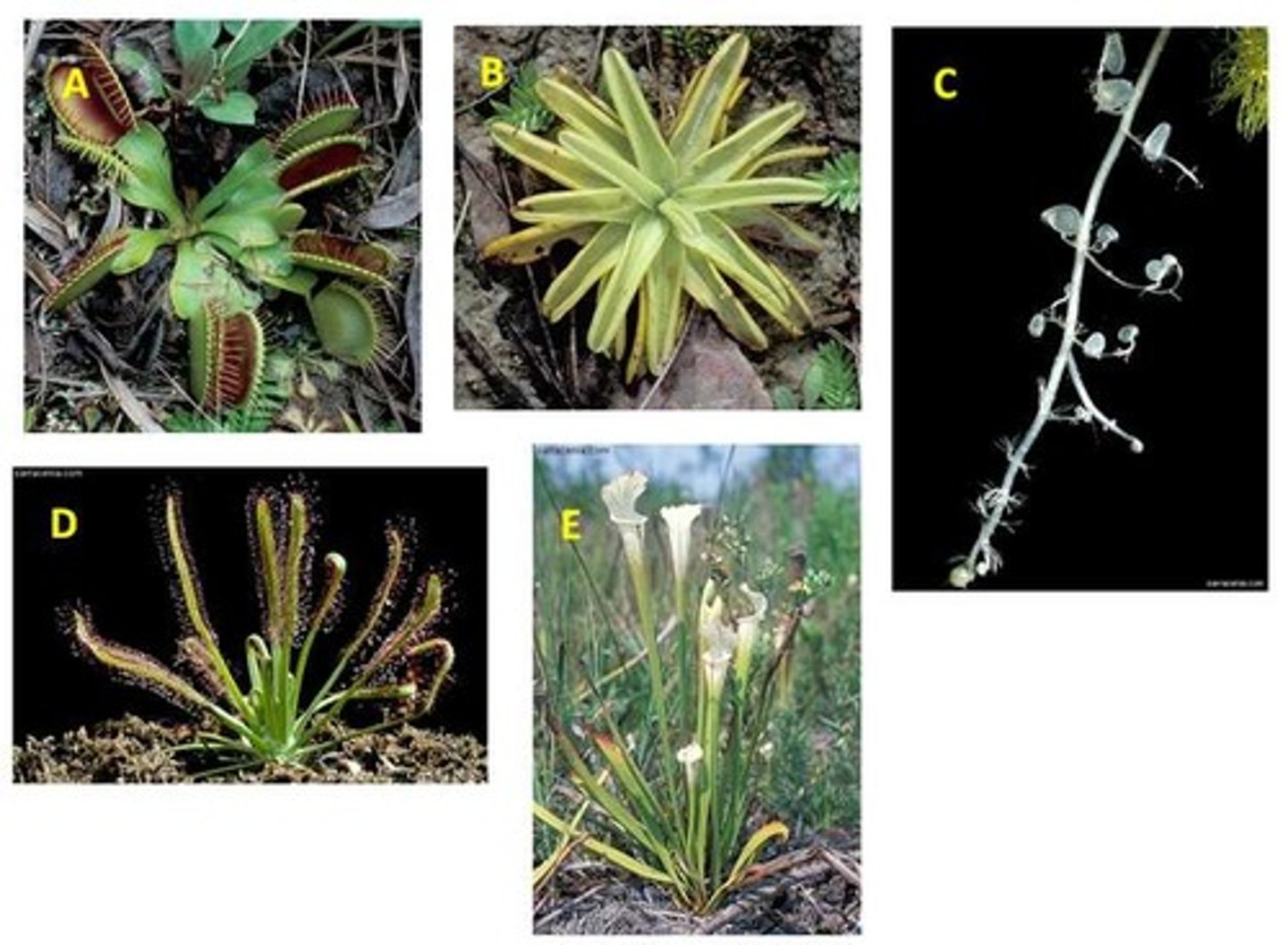
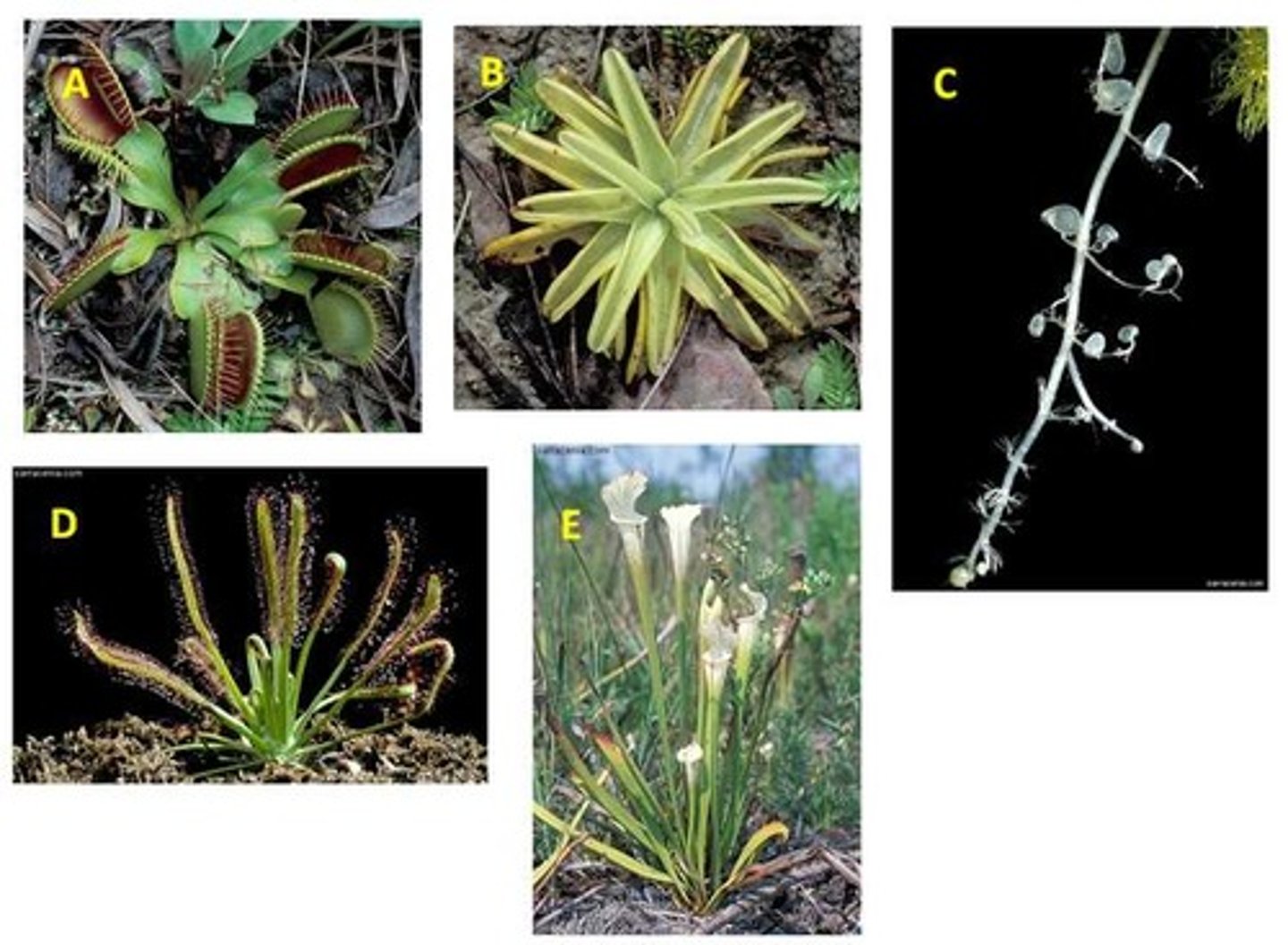
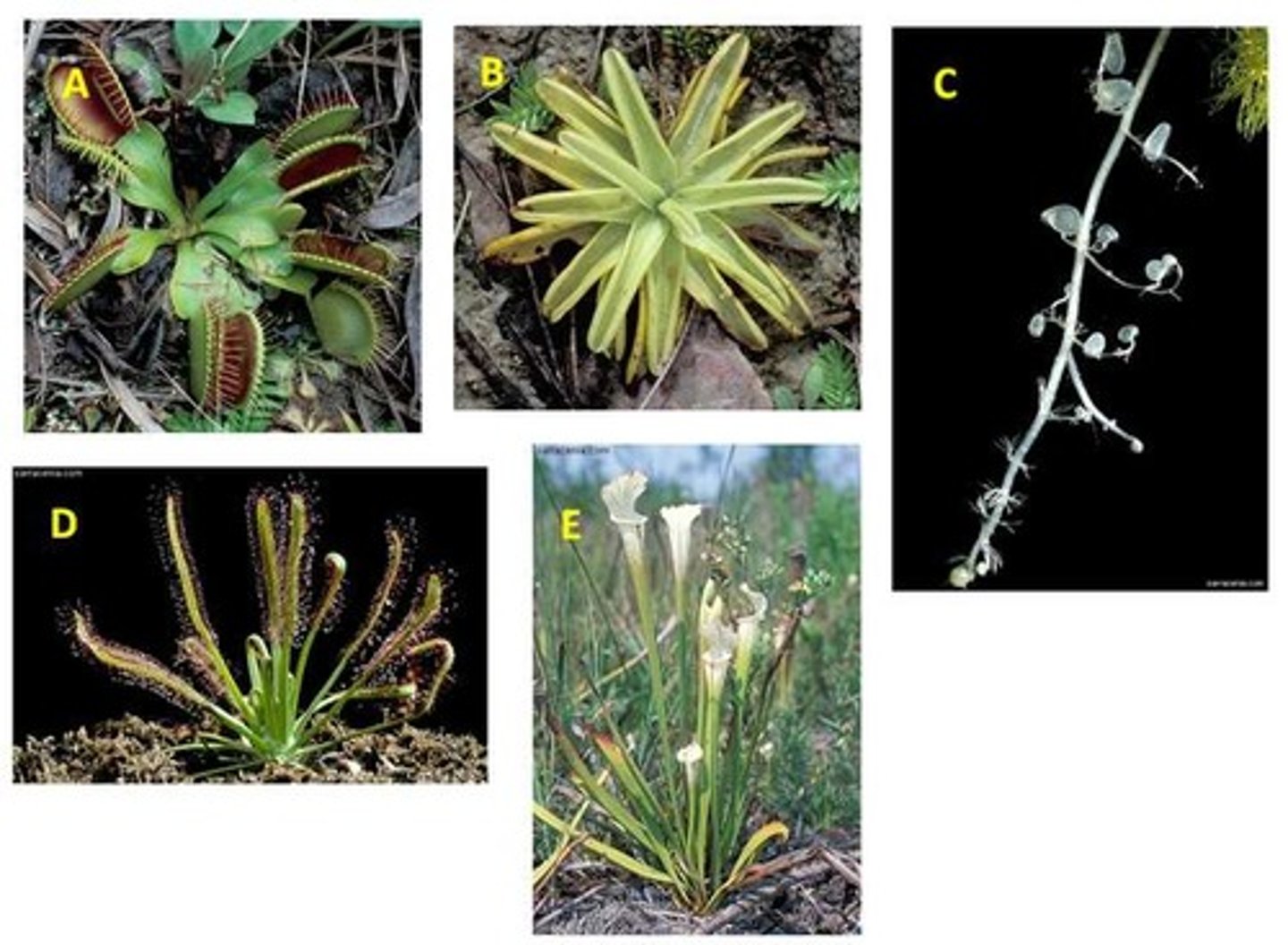
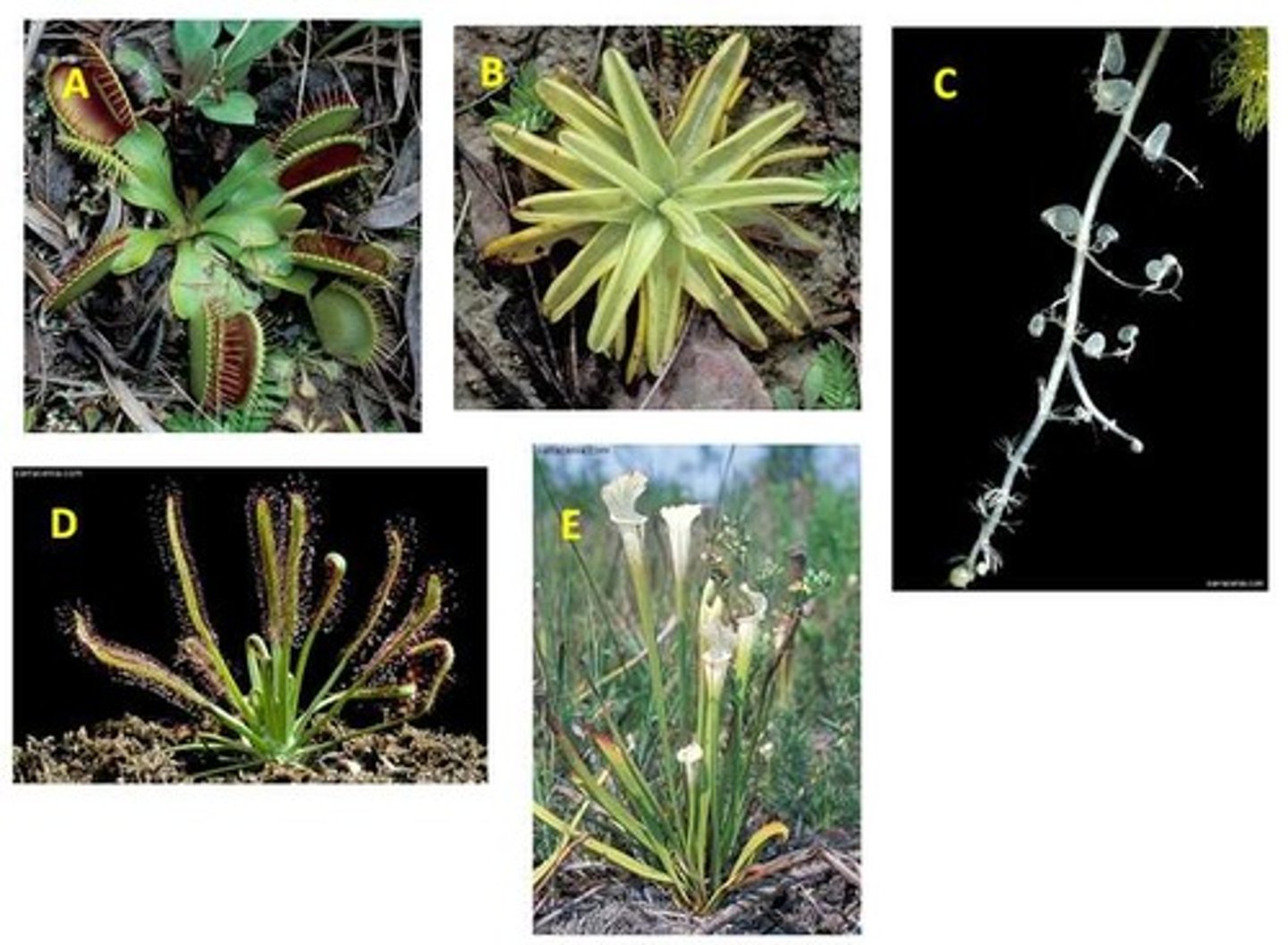
Carnivorous plants....
possess a collection of adaptations found in a wide variety of plants.
Carnivorous plants feed on small animals, such as insects, because they (the plants).....
grow in soils which are low in minerals.
Venus Flytrap
A

Butterwart
B

Bladderwart
C

Sundew
D

Pitcher Plant
E

What is apomixis?
Apomixis is when a seed is produced without fertilization. It is seed without sexual reproduction and is not vegetative.
Give three advantages to using micropropagation rather than conventional vegetative propagation.
Three advantages are:
1. It is faster than vegetative propagation
2. The plants are disease free and pest free
3. Many plants can be made from a small available amount of starting material.
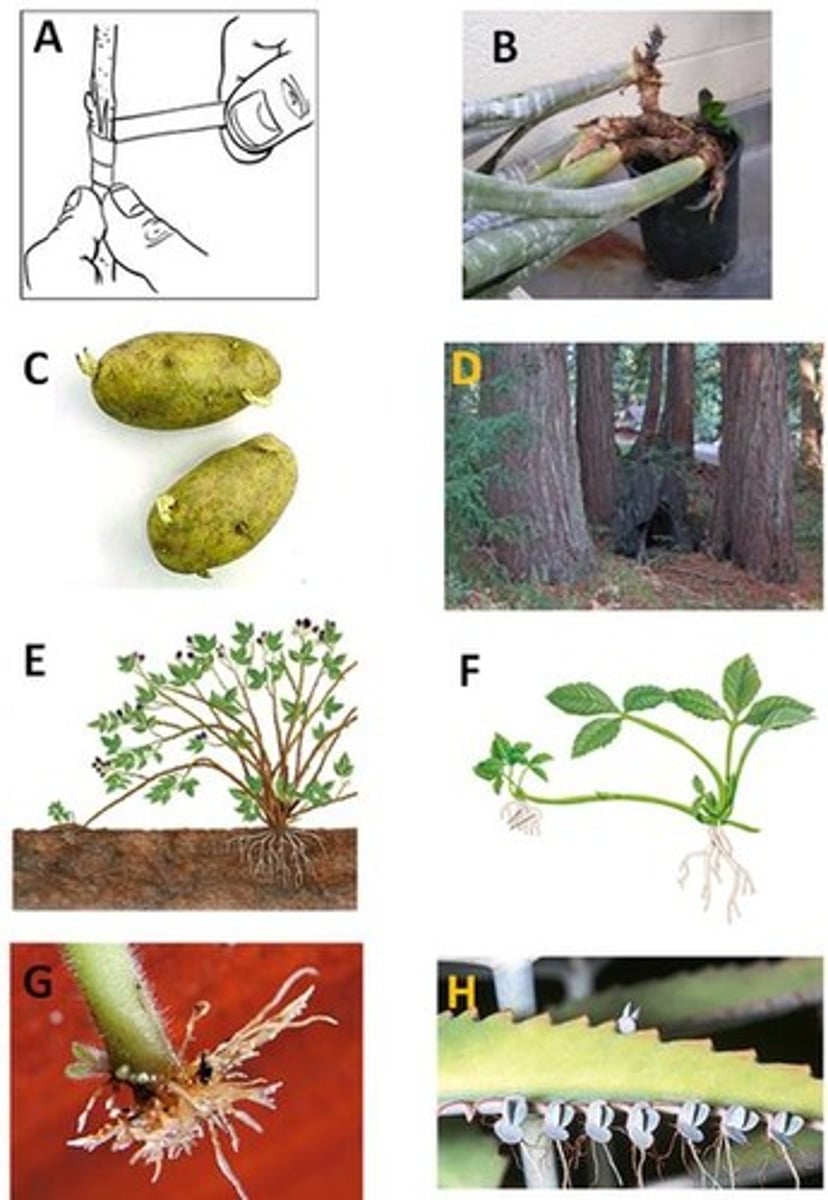
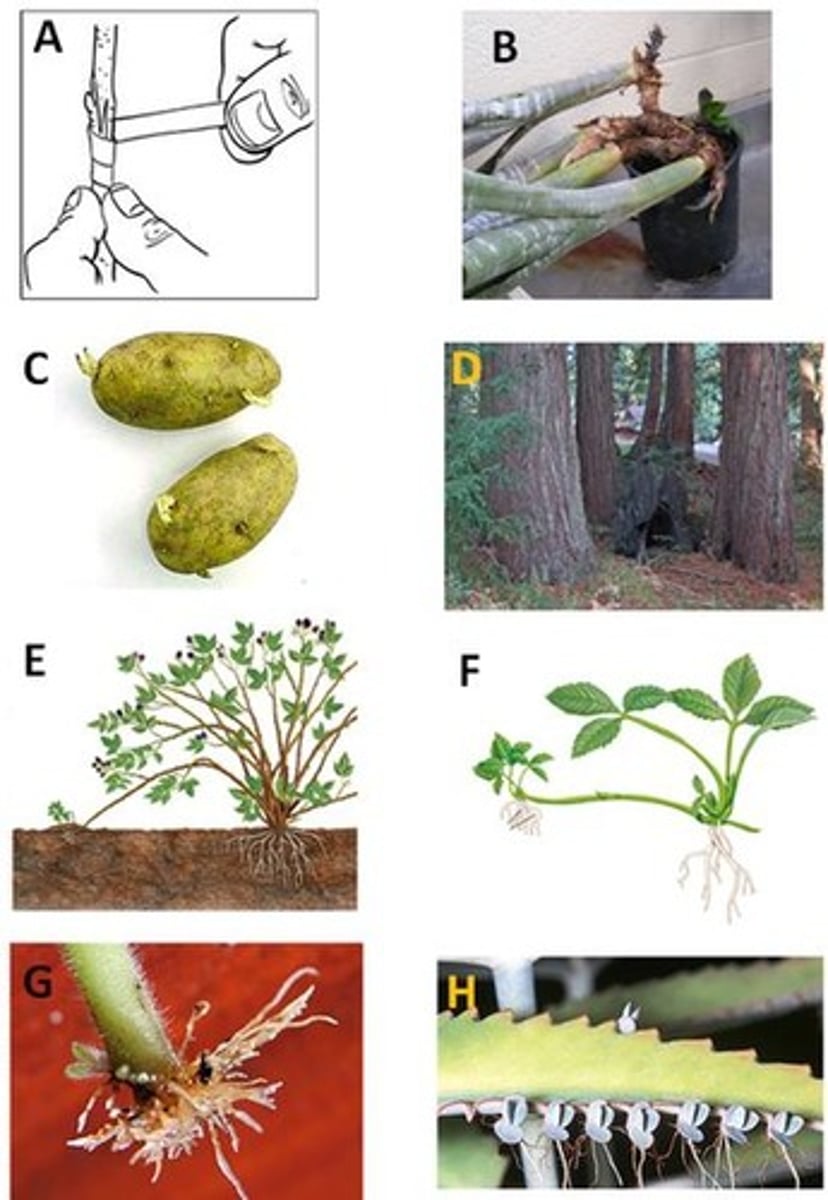
Grafting
A. Picture looks like binding of two pieces of a plant together.
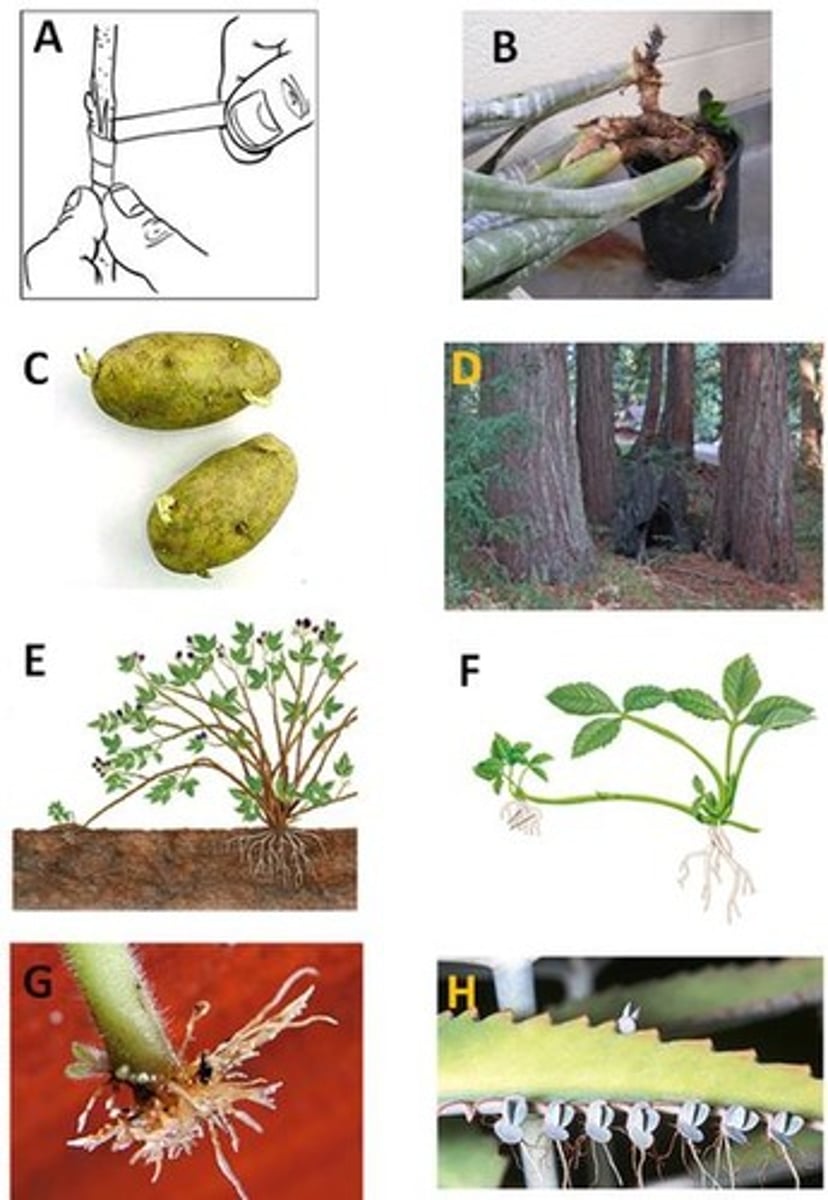
Rhizome
B. Picture looks like large green onion in a pot
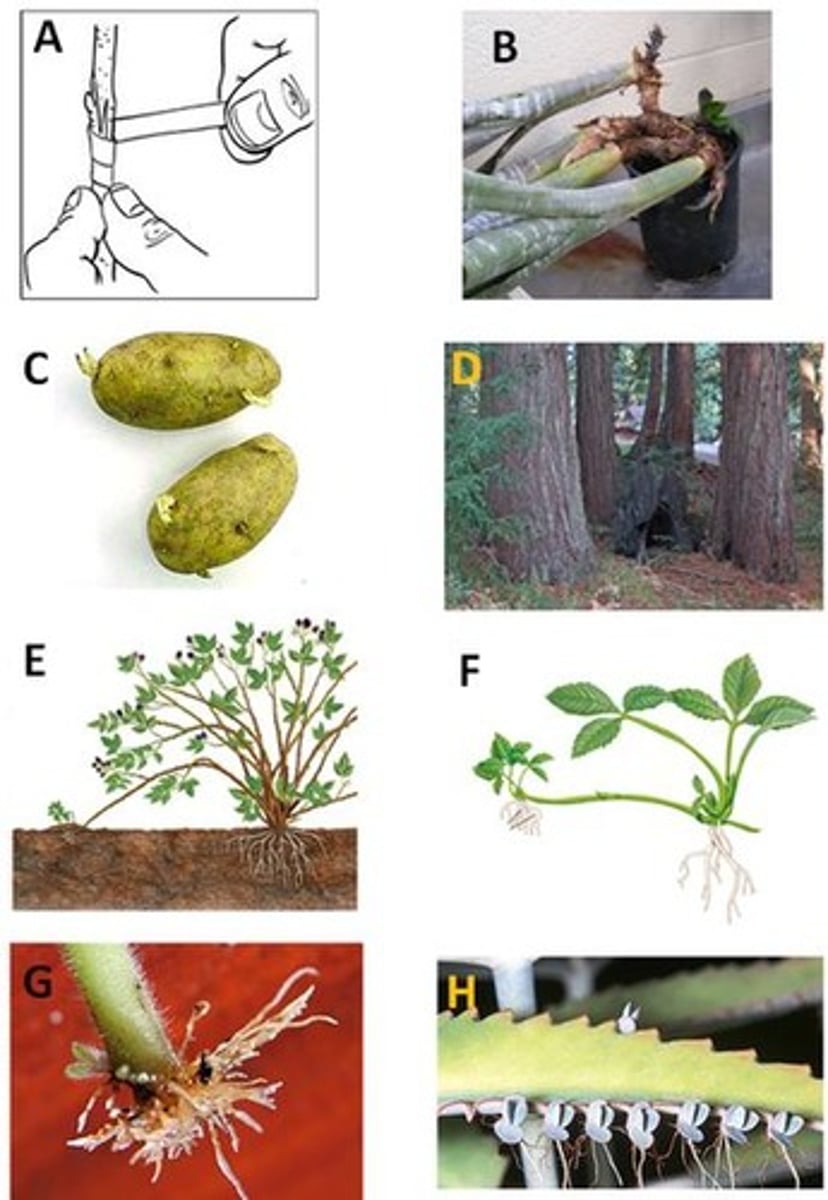
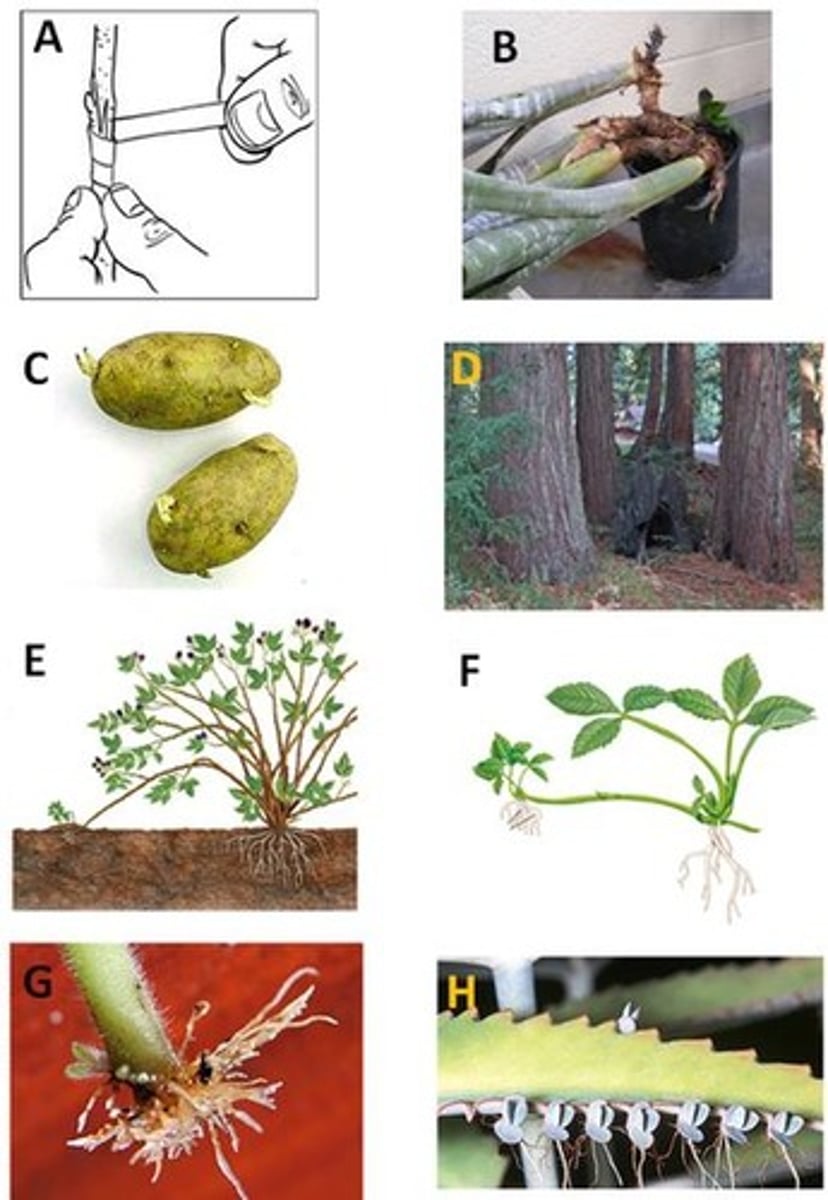
Tuber
C. Looks like potatoes
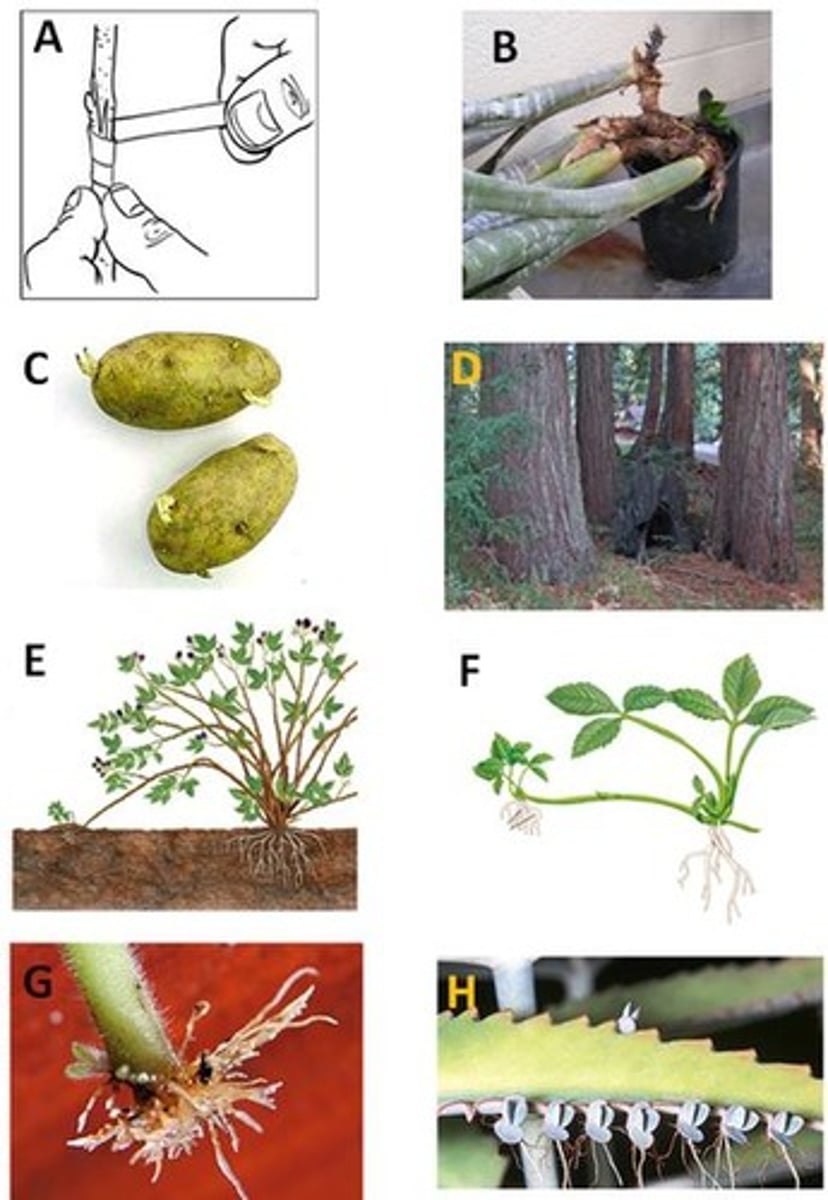
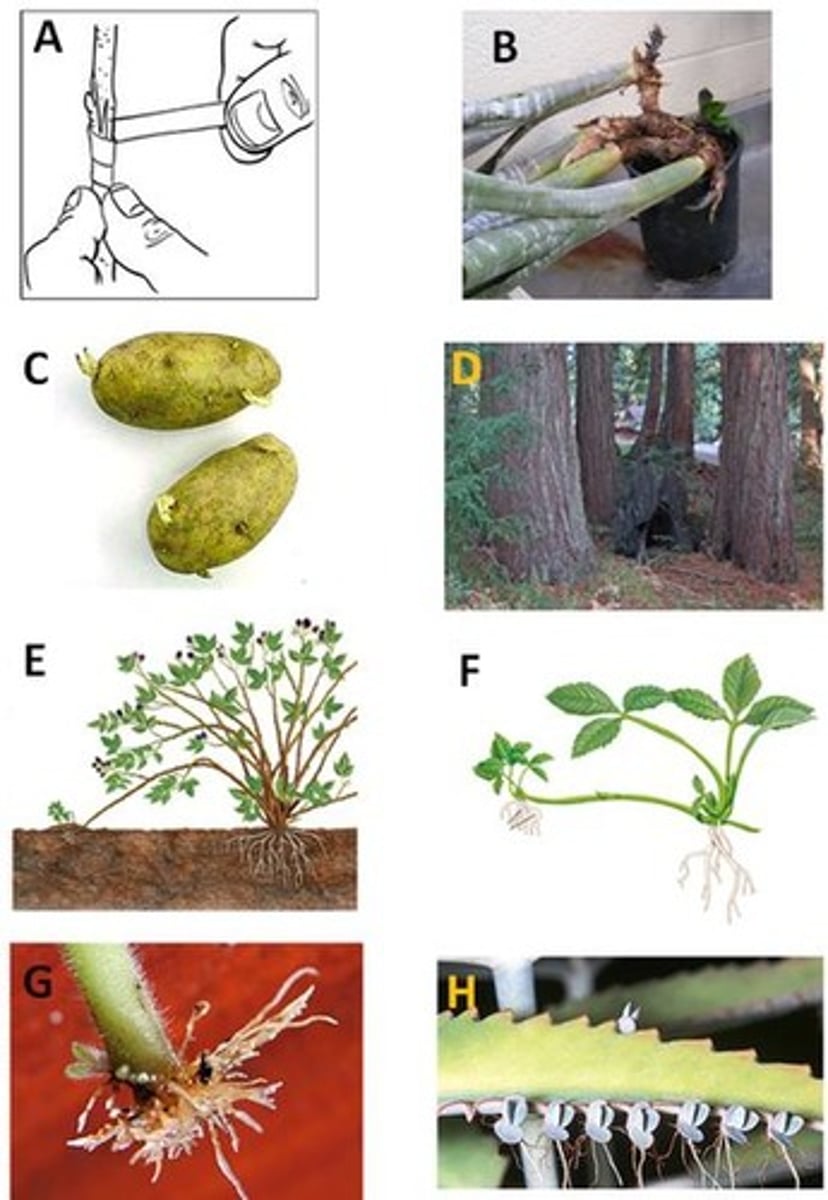
Root Sprout
D.
Layering
E.
Stolon
F.
Cutting
G
Plantlet Formation
F
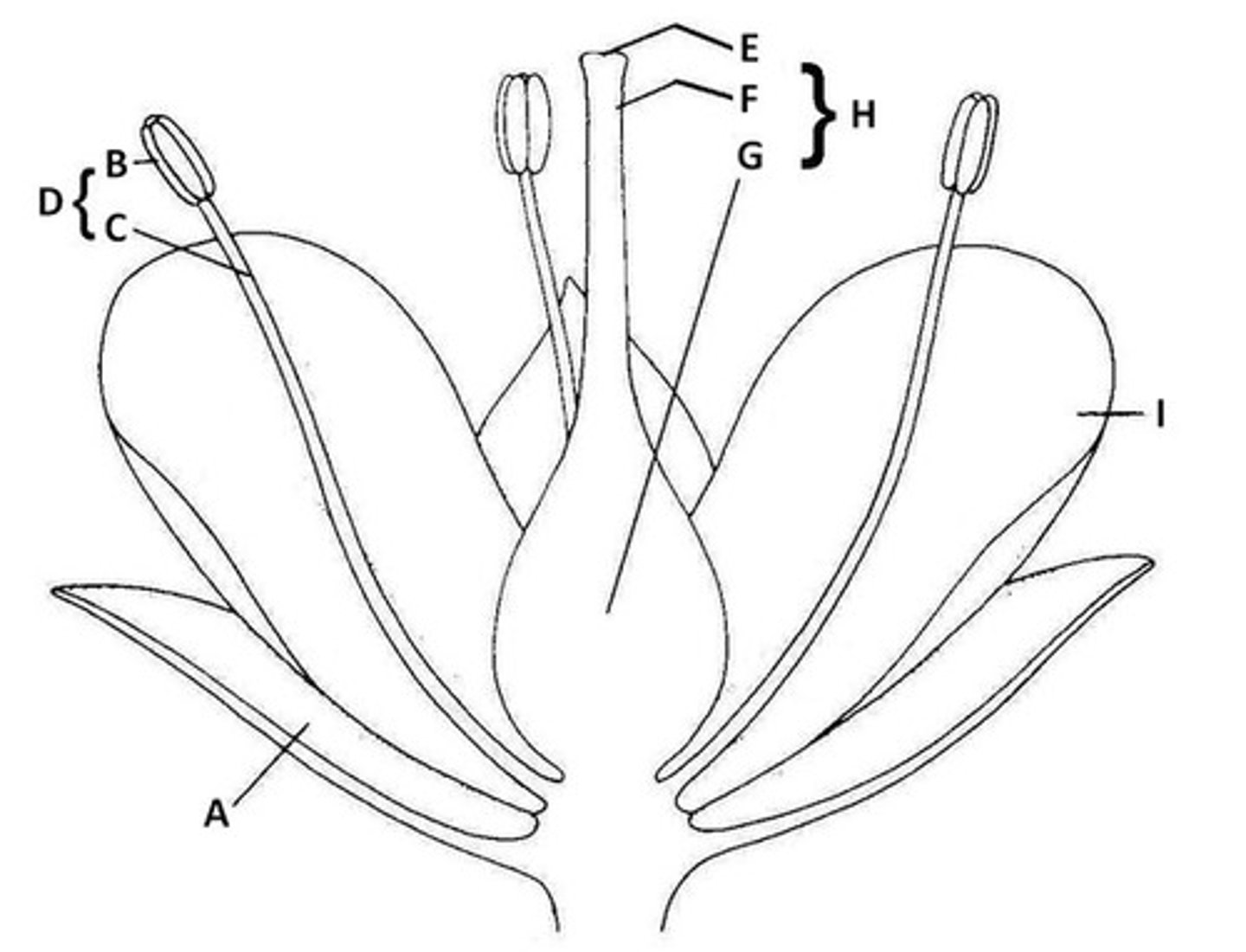
The part of the flower that frequently functions in protecting unopened flower buds is called the....
calyx/sepals
Does the drawing show a flower with a superior ovary or an inferior ovary?
Inferior Ovary
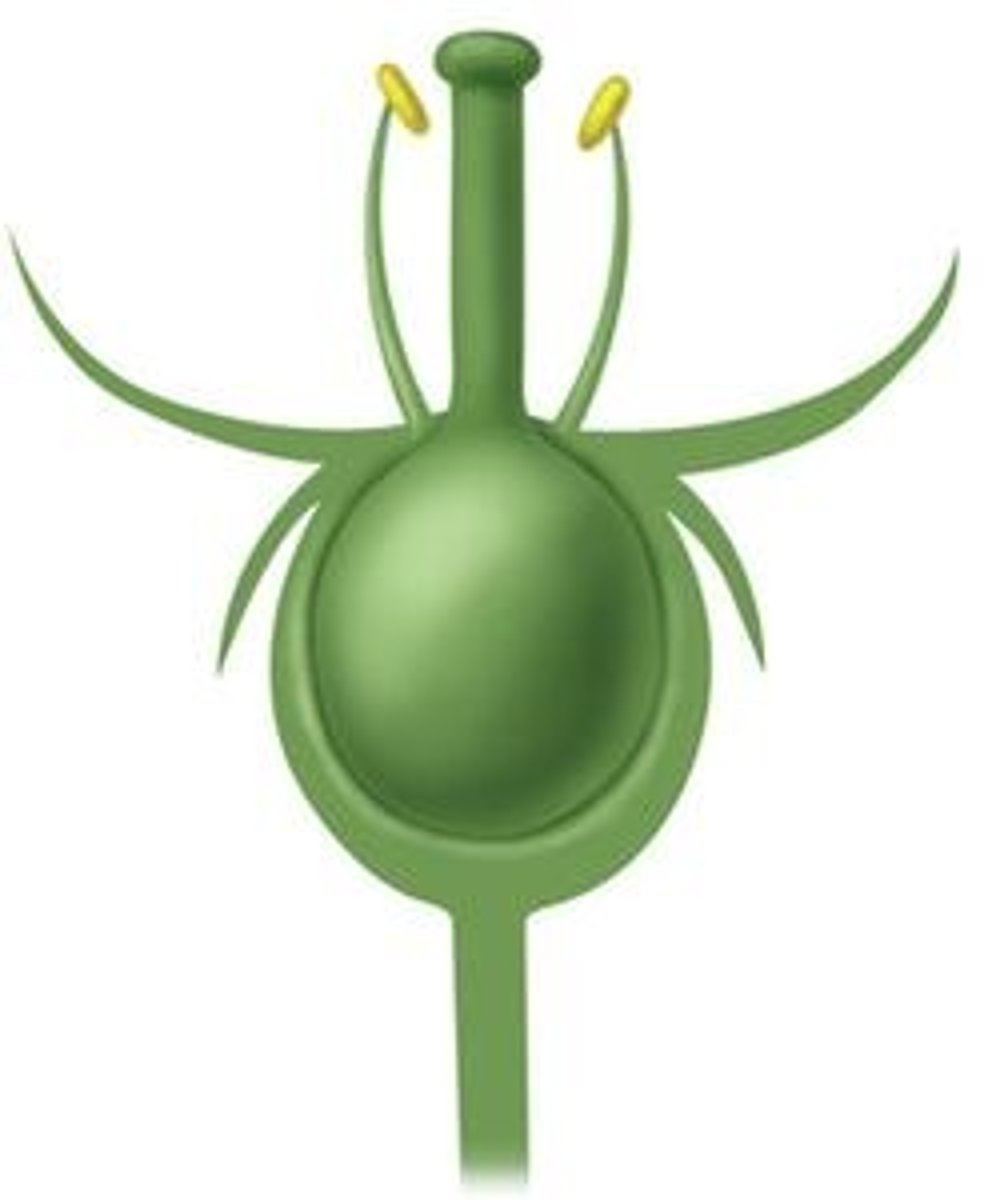
The flower in the photograph is regular or irregular?
regular (dogwood looking flower)

Sepal
A. Butter leaf-like protection of bud
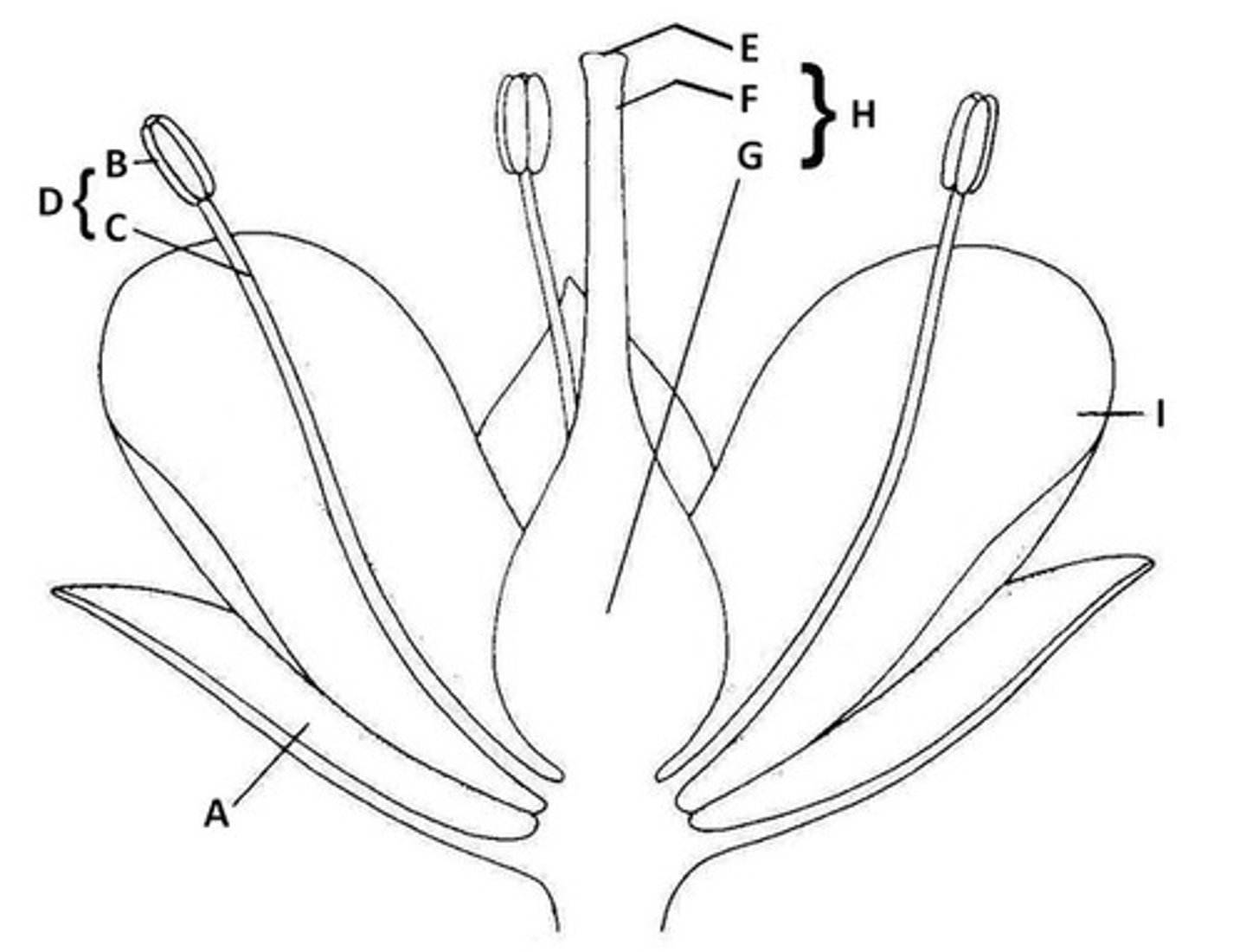
Anther
B. the very tip of parts of flowers that hold pollen
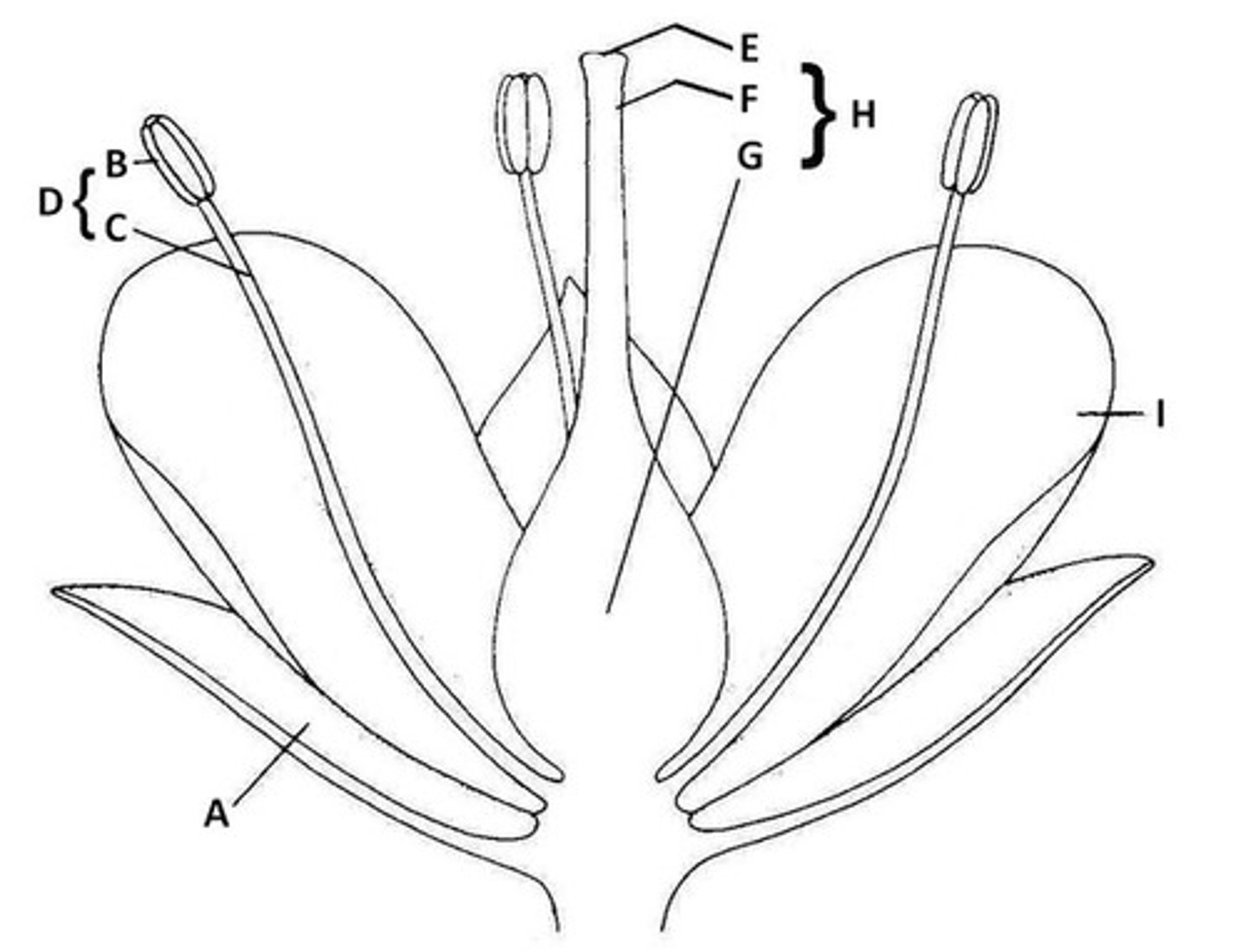
Filament
C. The shoot of the part of the flower that holds pollen
Stamen
D. Anther and Filament together
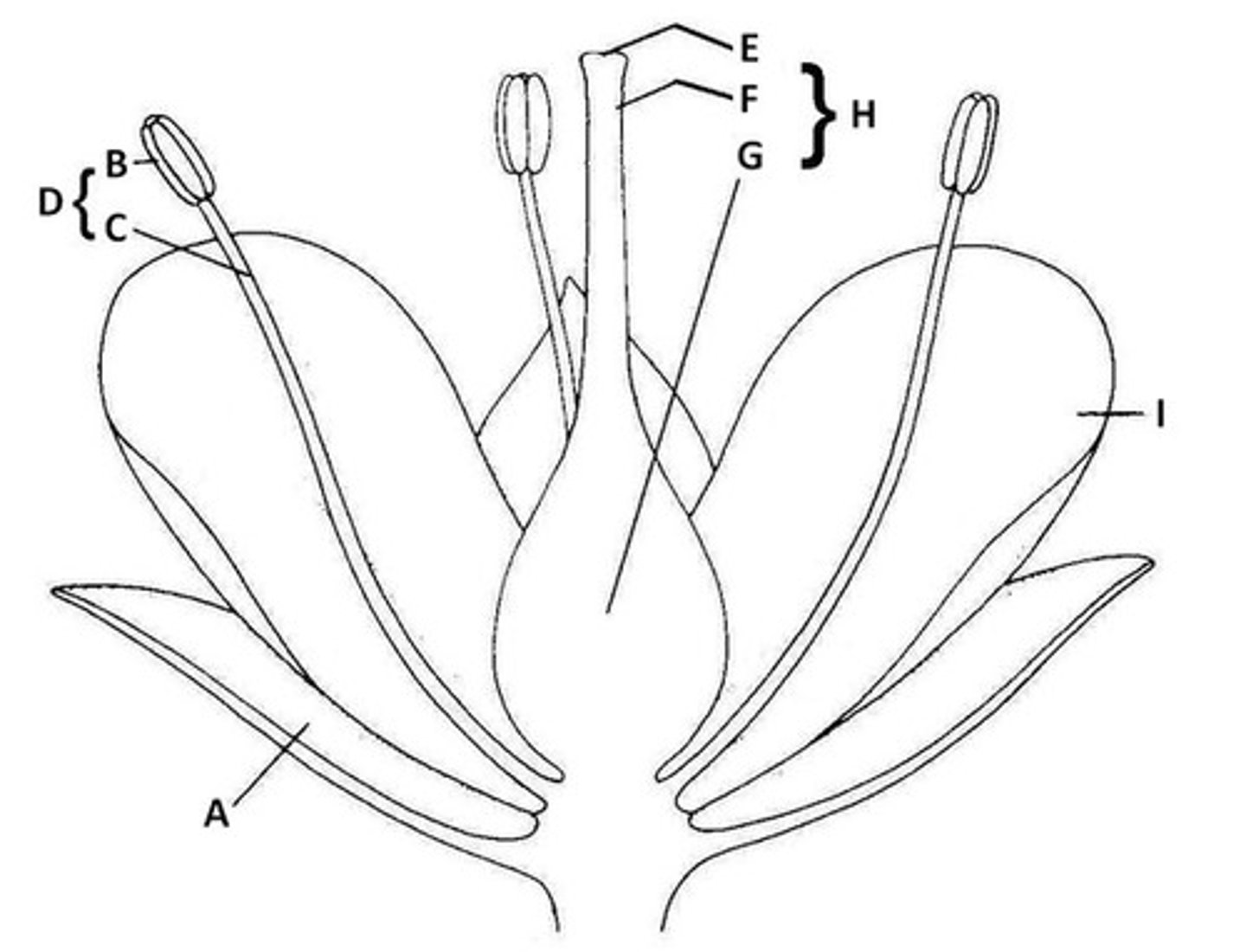
Stigma
E. The very tip of the pistil
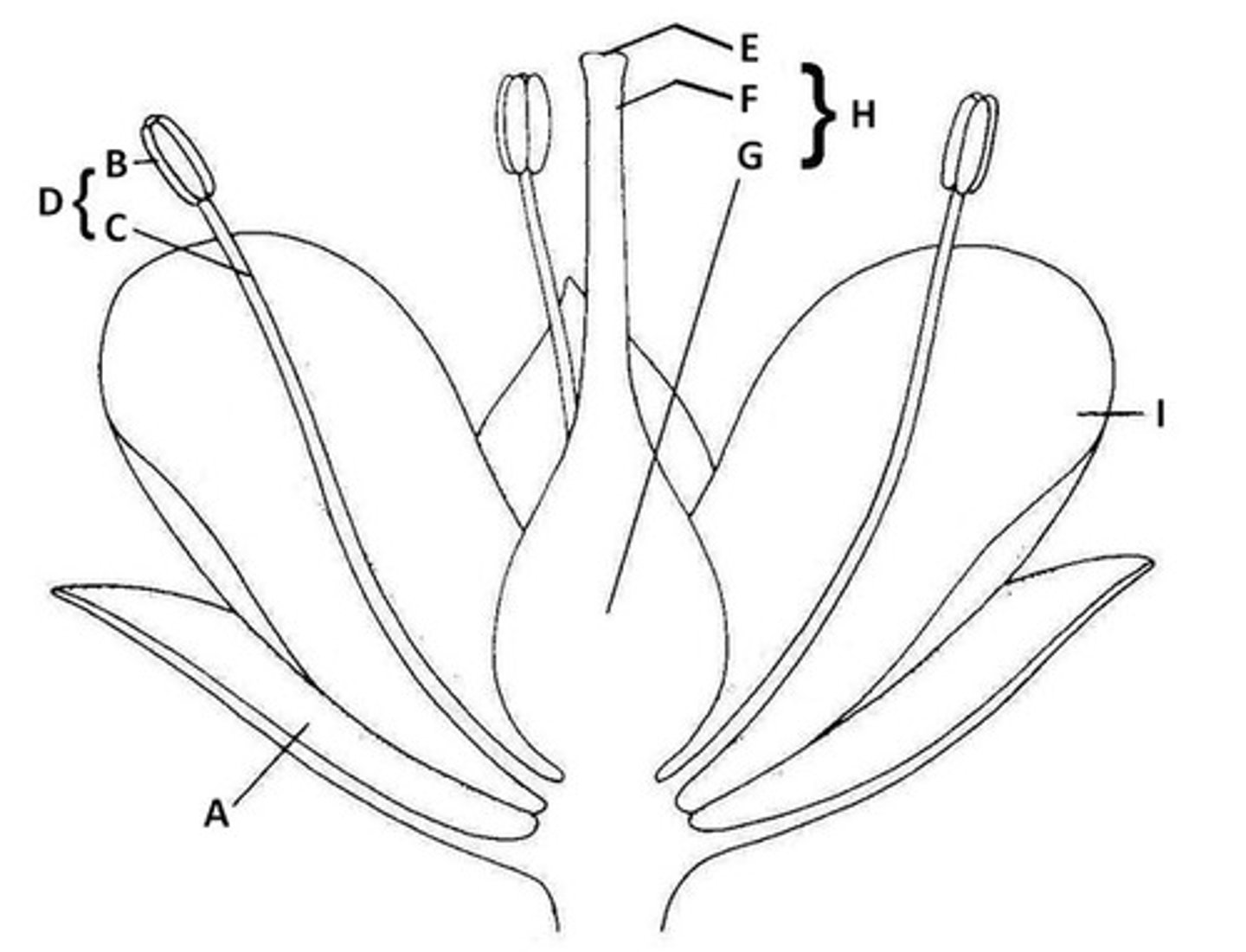
Style
F. The middle part of the pistil
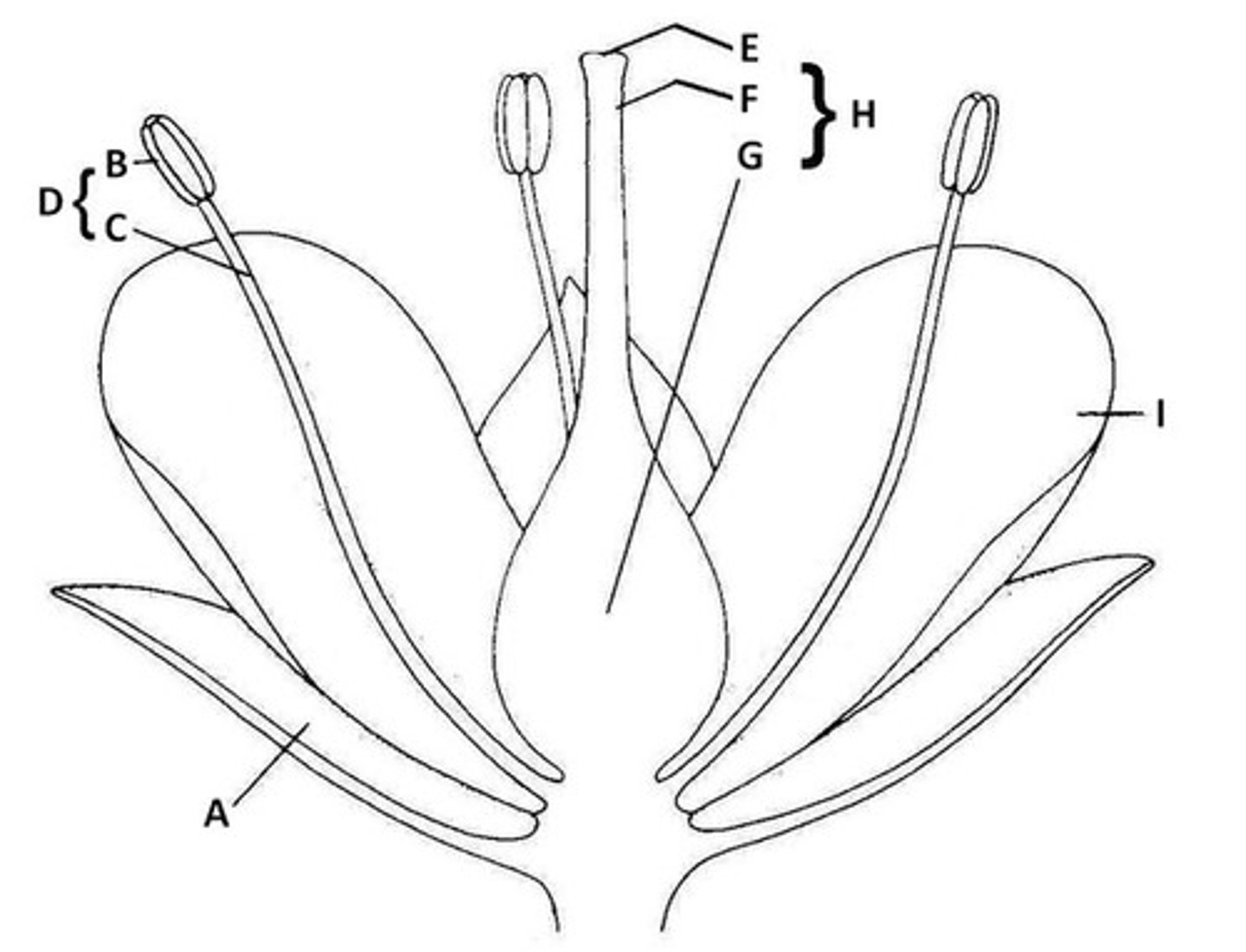
Ovary
G. The base of the pistil
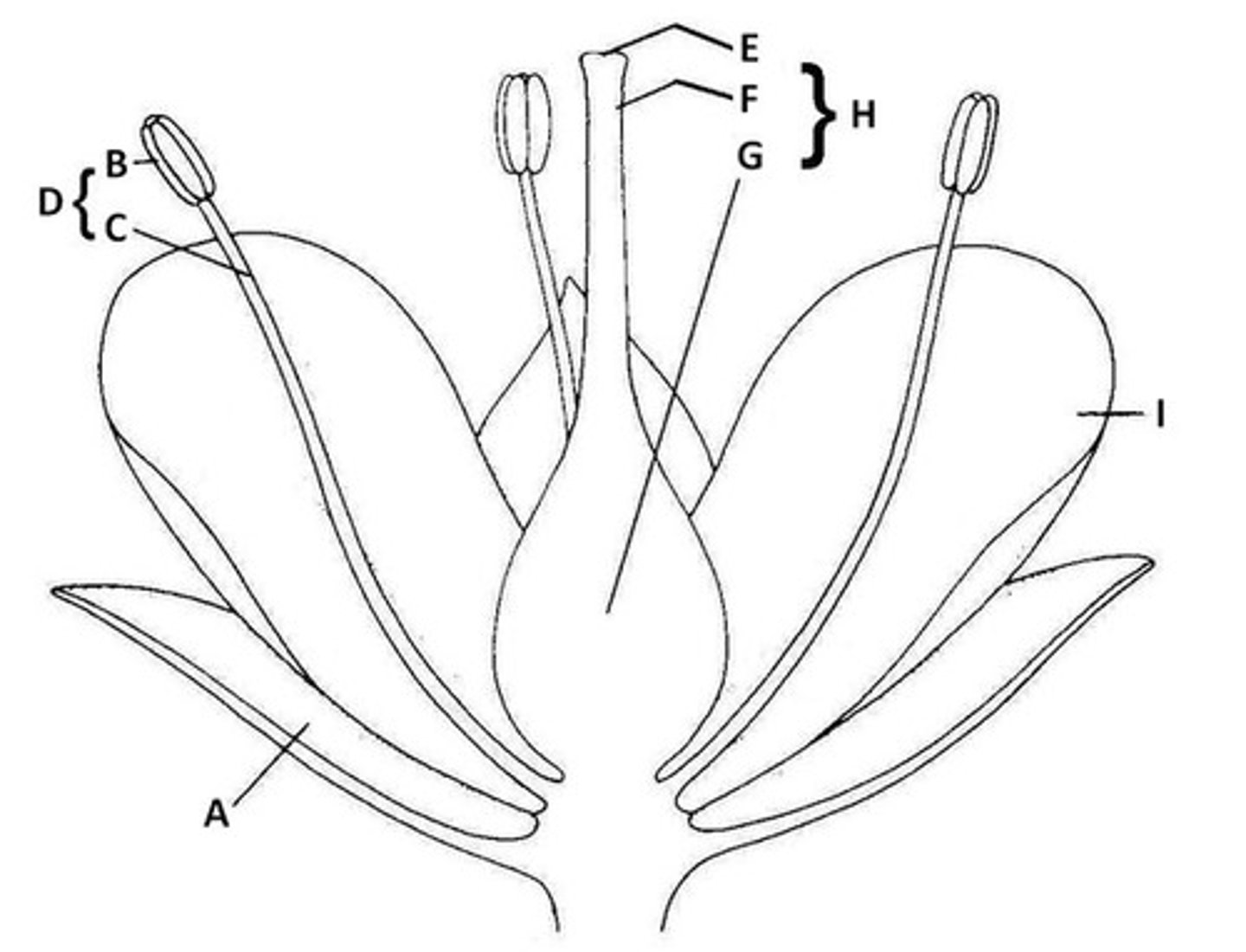
Pistil
H. The middle of the flower - stigma, style, and ovary all together.
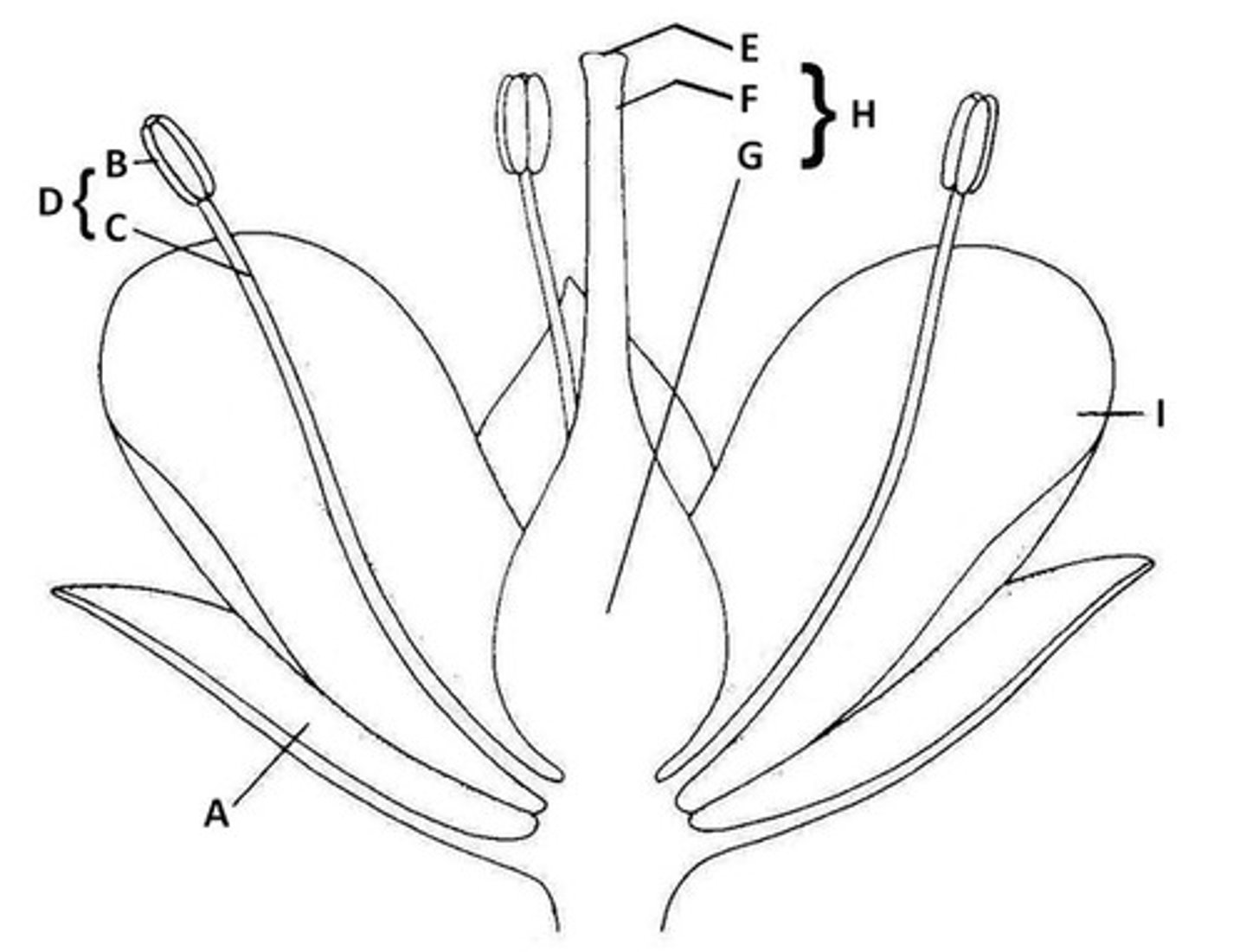
Petal
I. Colorful part of the flower
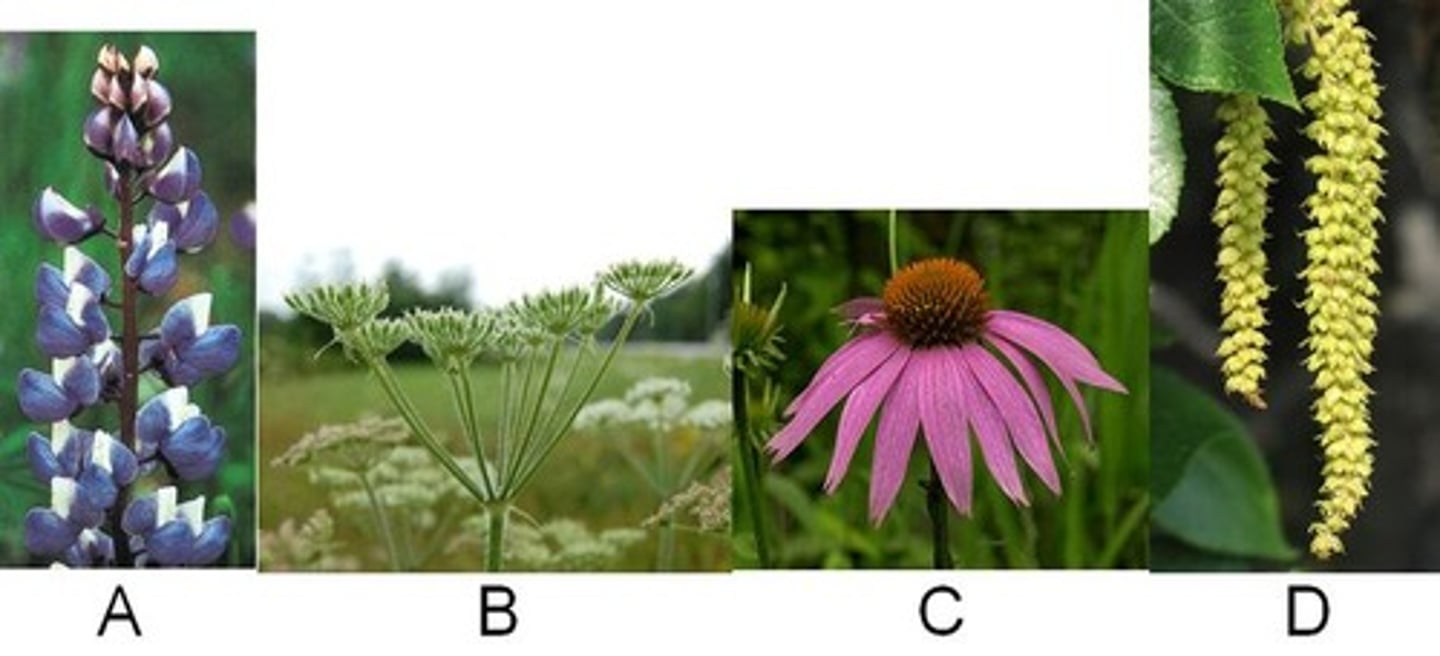
Raceme
A. Looks like tall blue flowers. Individual small flowers on its own stem connected to a tall stem.
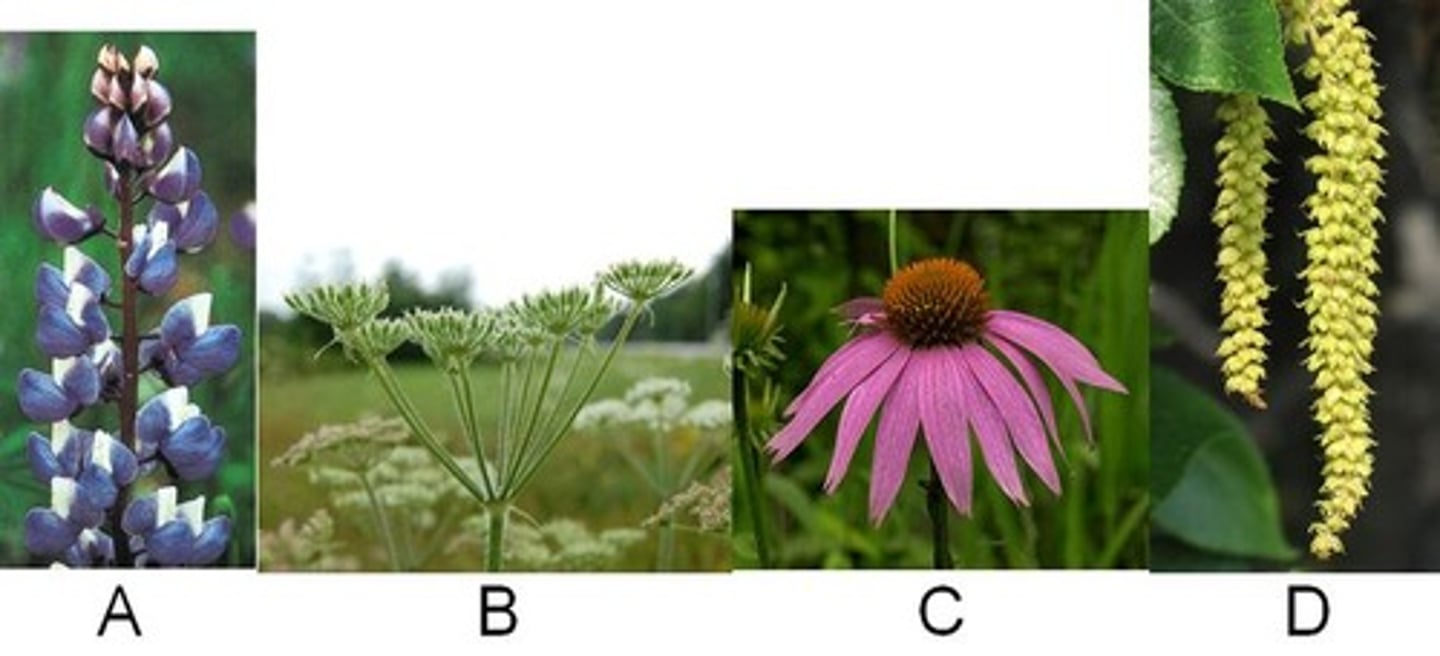

Umbel
B. Looks like horse tales or brooms
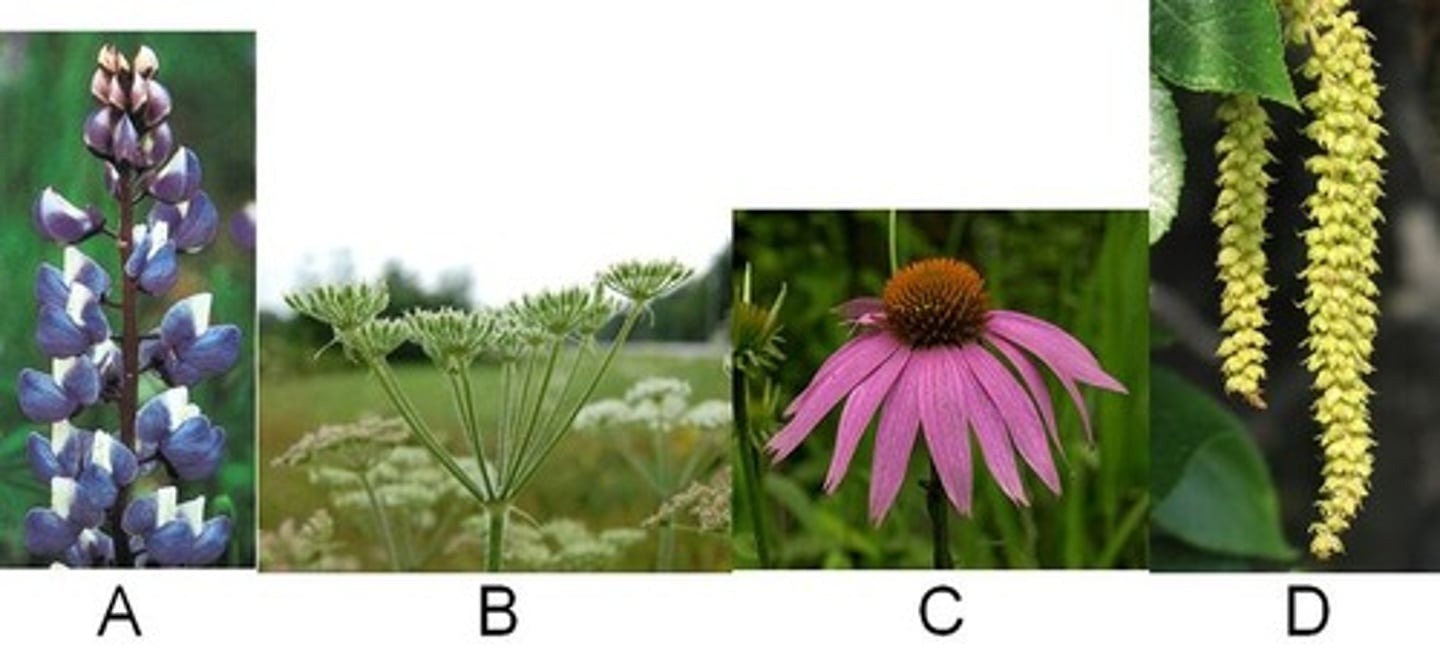

Head
C. Looks like a black eyed susan type flower
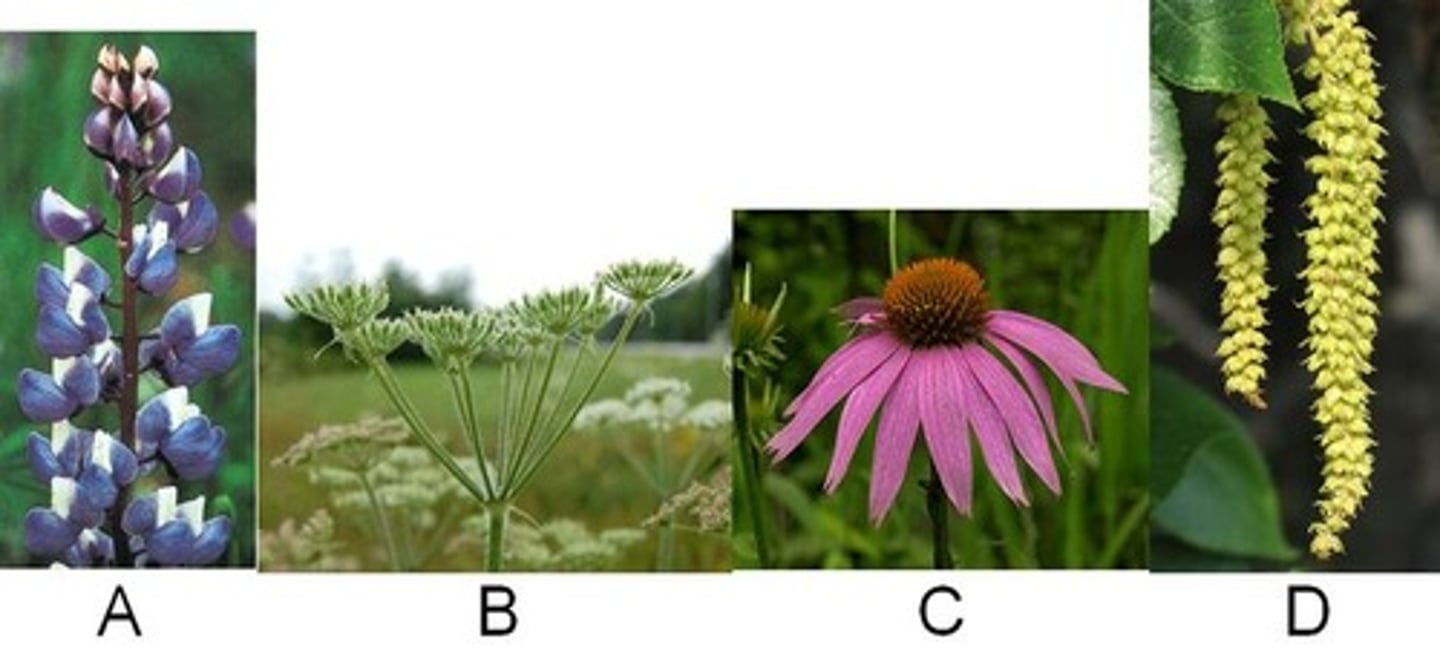

Catkin
D. Hanging long collection of individual buds.....

Squash is monoecious. This means that squash has...
male flowers and female flowers on one plant
Pollination is.....
the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma
The phenomenon of double fertilization involves the fusion between....
the egg an one sperm and the central muclei (polar nuclei) and a second sperm.
What structure is developed into a seed?
Ovule
A flower without nectar, scent, or petals that produce copious lightweight pollen uses a pollination vector of...?
Wind
A red, robust flower without a detectable scent uses a pollination vector of...?
Bird
A large white flower with strong odors and large amounts of nectar uses a pollination vector of...?
Bat
A blue or yellow flower with nectar, heavy and sticky pollen, and a sweet, pleasant smell uses a pollination vector of...?
Bees
Describe two examples of mimicry in the context of pollination of flowering plants.
Two examples of mimicry in the context of pollination of flowering plants are: Sexual mimicry, which is when some orchid type flowers mimic female bees and when the male bees try and mate they end up transferring pollen. When flowers mimic flowers, pollinators transfer pollen to the impersonator thinking that its the flower with the reward, and then find out too late that it only resembles the original flower. Since they don't run into the imposter often enough to discourage it from visiting that type of flower, it enables the mimic flowers to continue to successfully use this method of pollination.
Describe two mechanisms found in plants that increase out-crossing.
Two mechanisms that increase out-breeding in plants are: being dioecious and being monoecious. Dioecious plants are plants where the male flowers are on one plant and the female flower are on another, and they must cross-pollinate and cross-fertilize to reproduce. Monoecious plants have male and female flowers on the same plant and pollen just has to get from one flower to another.
Which of the following structures does not serve as a food reserve for seeds?
Coleoptile
The fruits produced by melons and squashes are examples of.....
pepos
A fruit that forms from the pistils of several flowers in an inflorescence is a....
multiple fruit
All of the following are dry, indehiscent fruits except....
capsule
Which of the following groups of fruits would be classified botanically as berries?
Tomatoes, grapes
Most of the flesh of an apple or pear comes from.....
the receptacle
The skin of most fruits is technically the...
exocarp
When a fruit forms without fertilization taking place, that fruit is called....
parthenocarpic
Silique
A. long dry looking pods with small black seeds
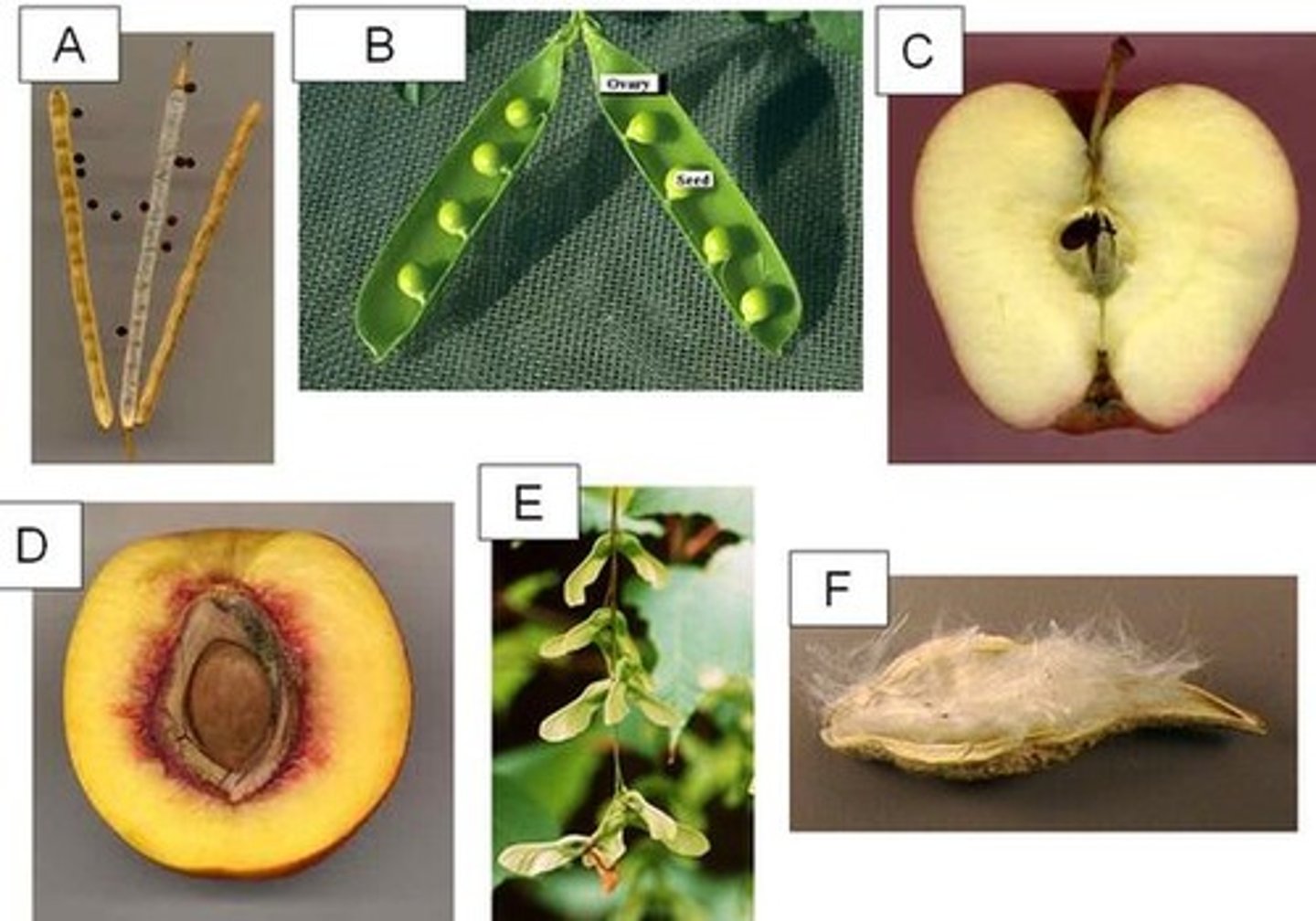

Legume
B. beans/peas
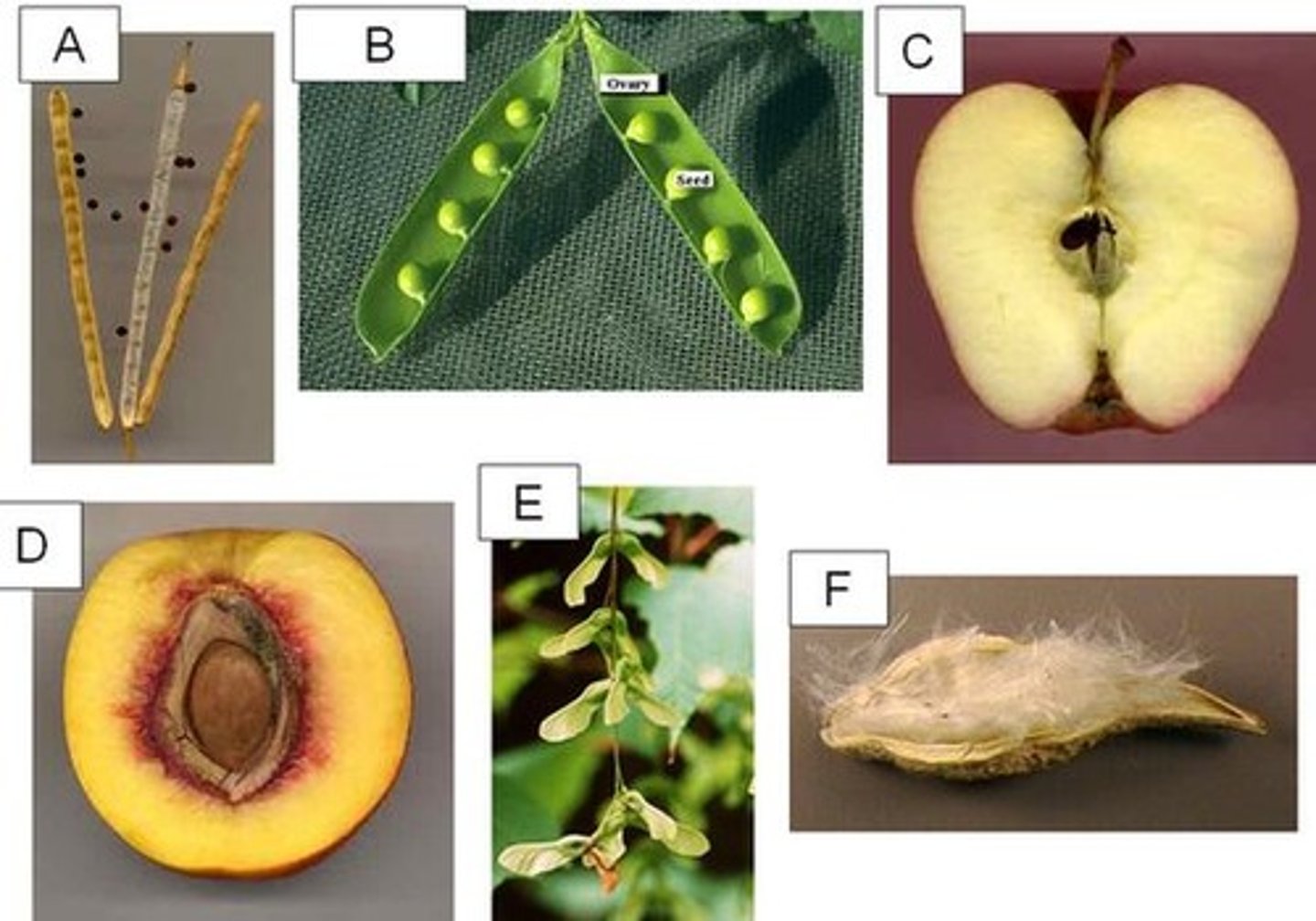

Pome
C. apple
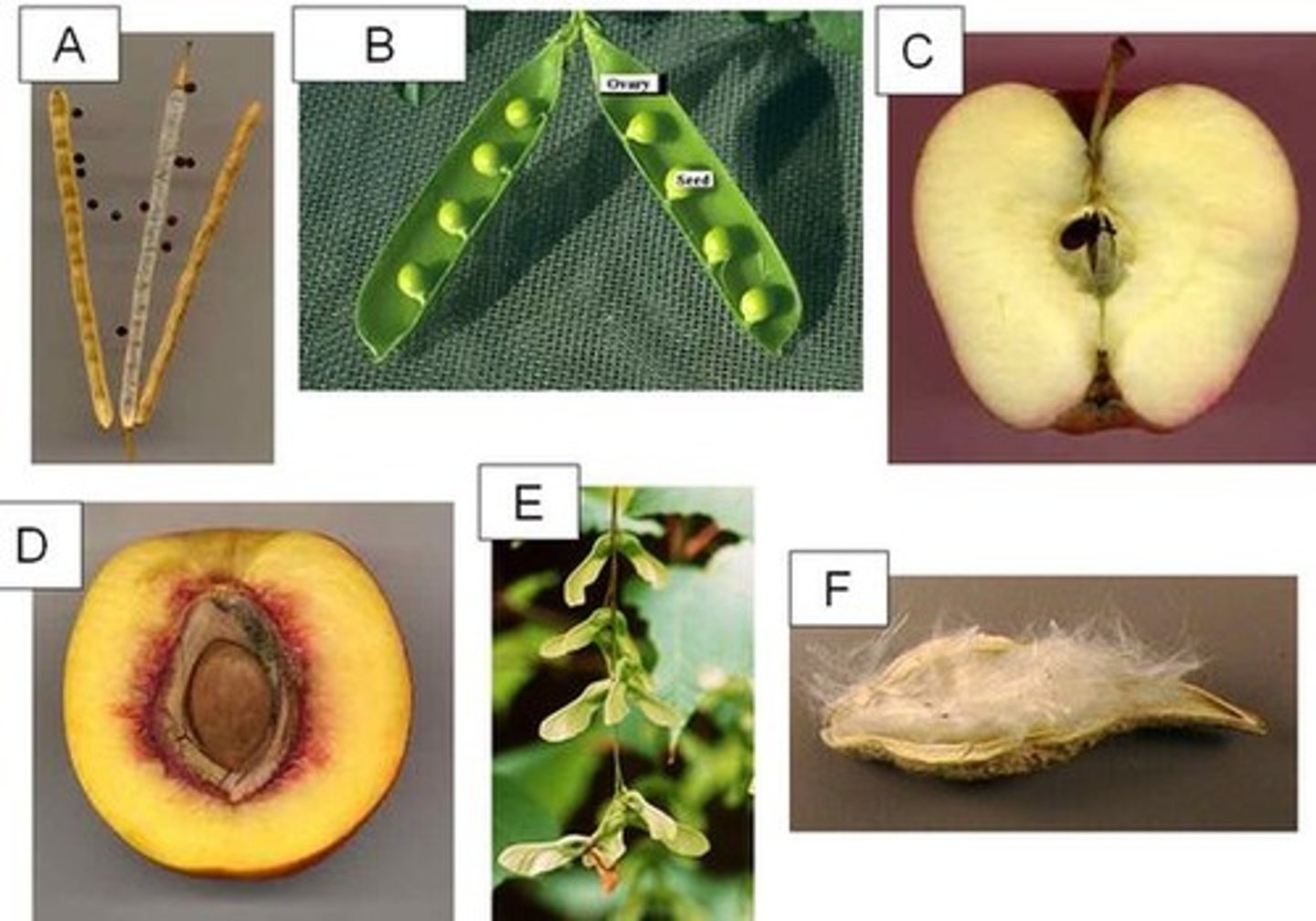

Drupe
D. peach
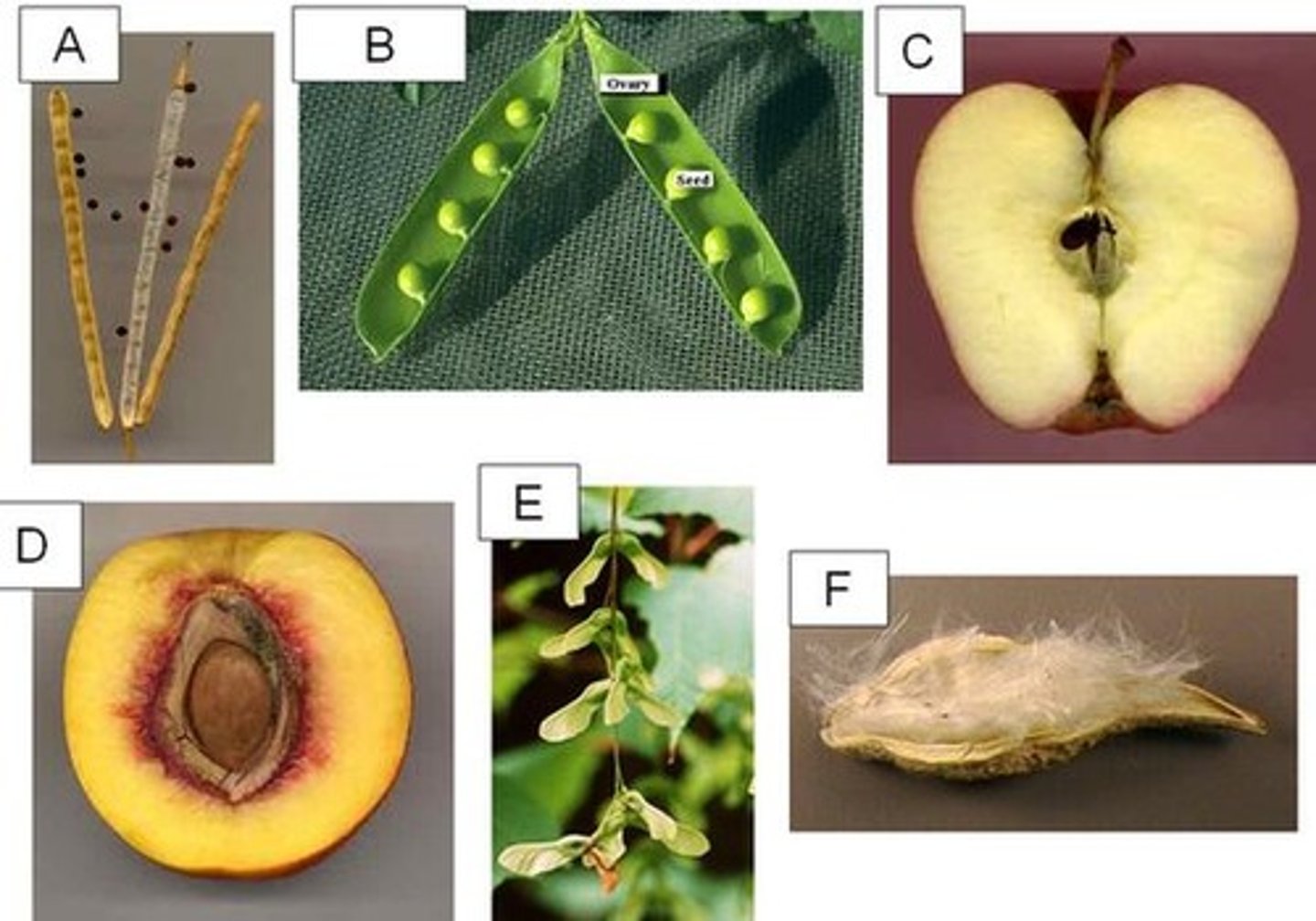

Samara
E. helicopters
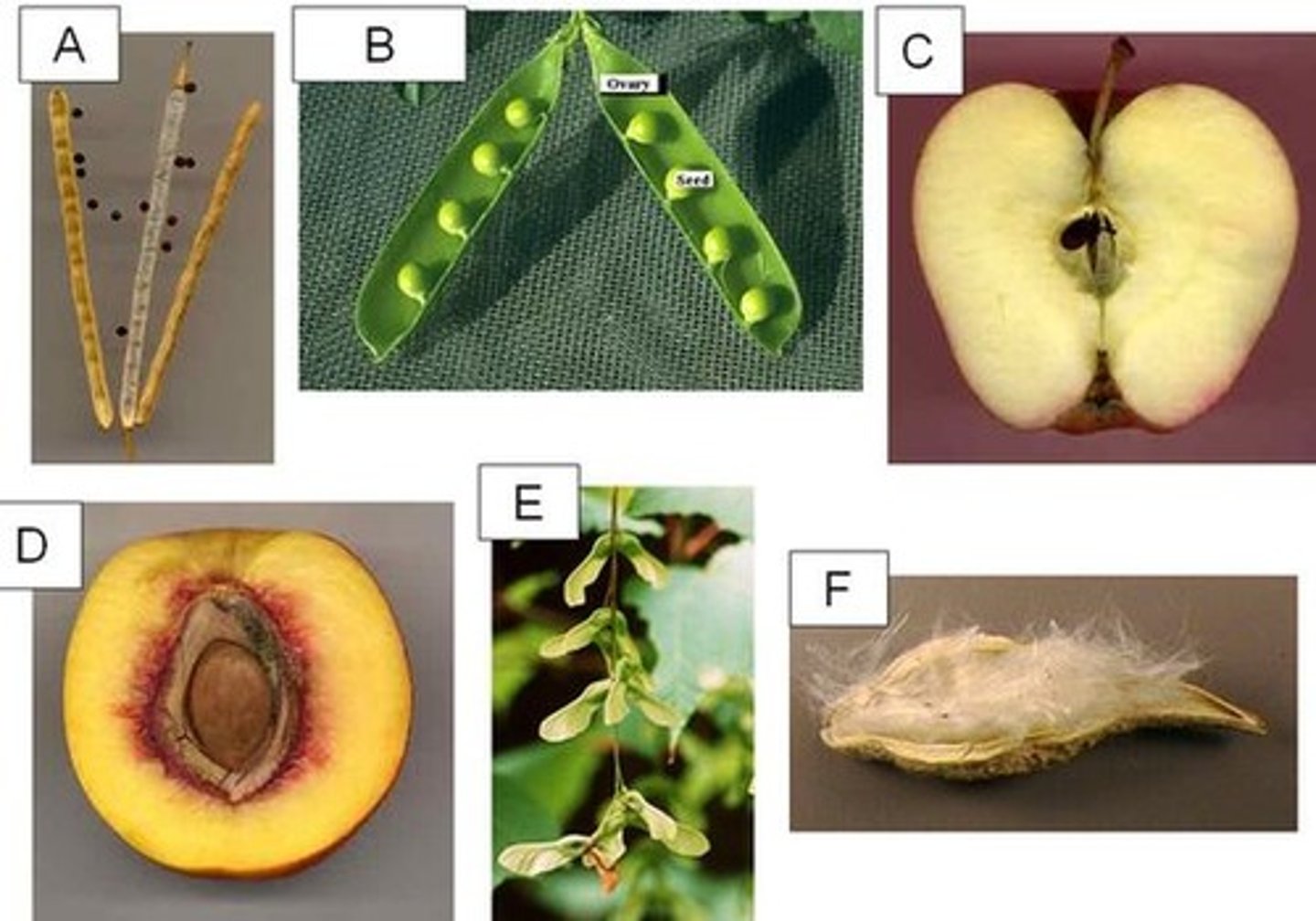

Follicle
F. milk weed
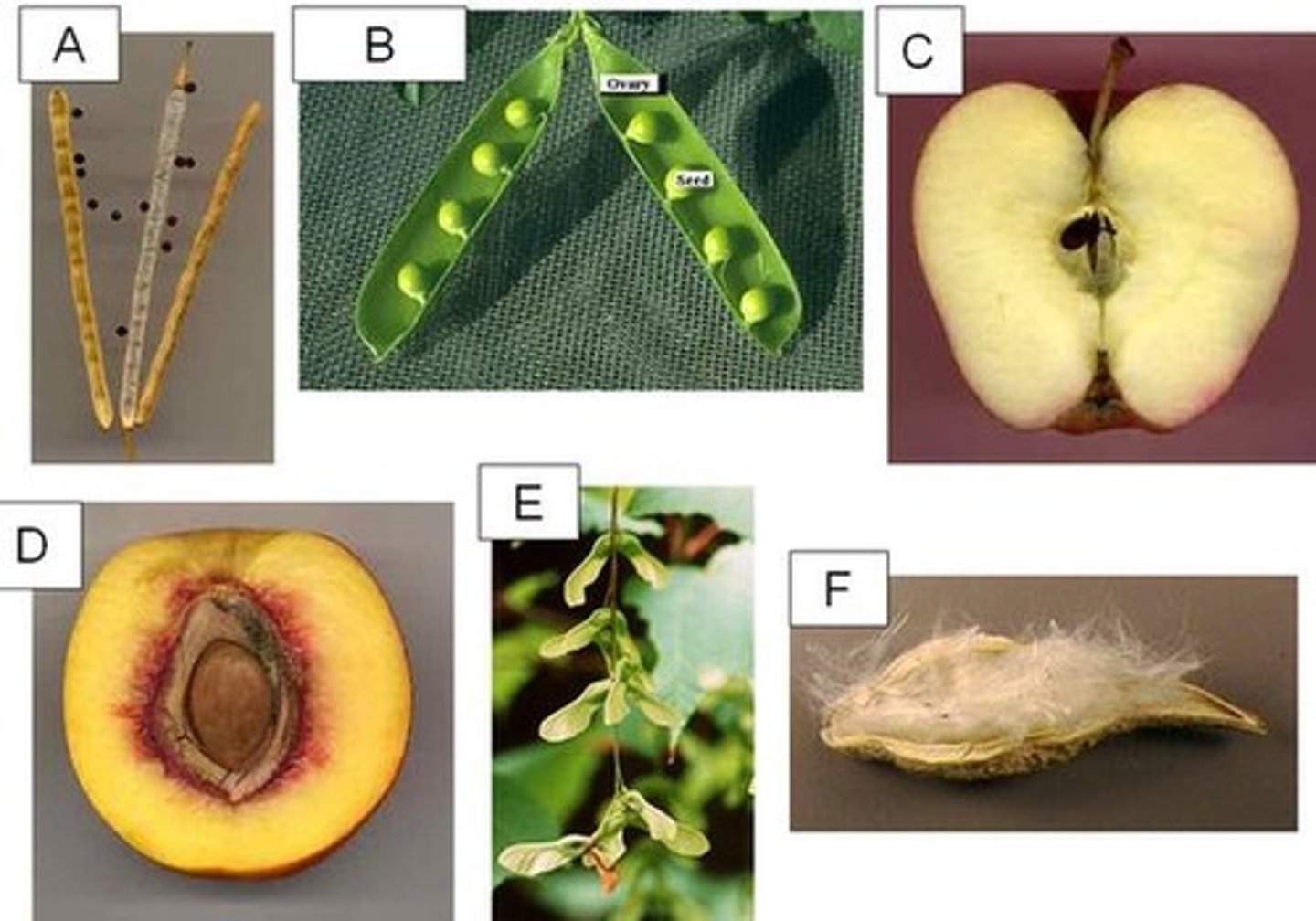

Plumule
A. the lung looking part of a bean seed
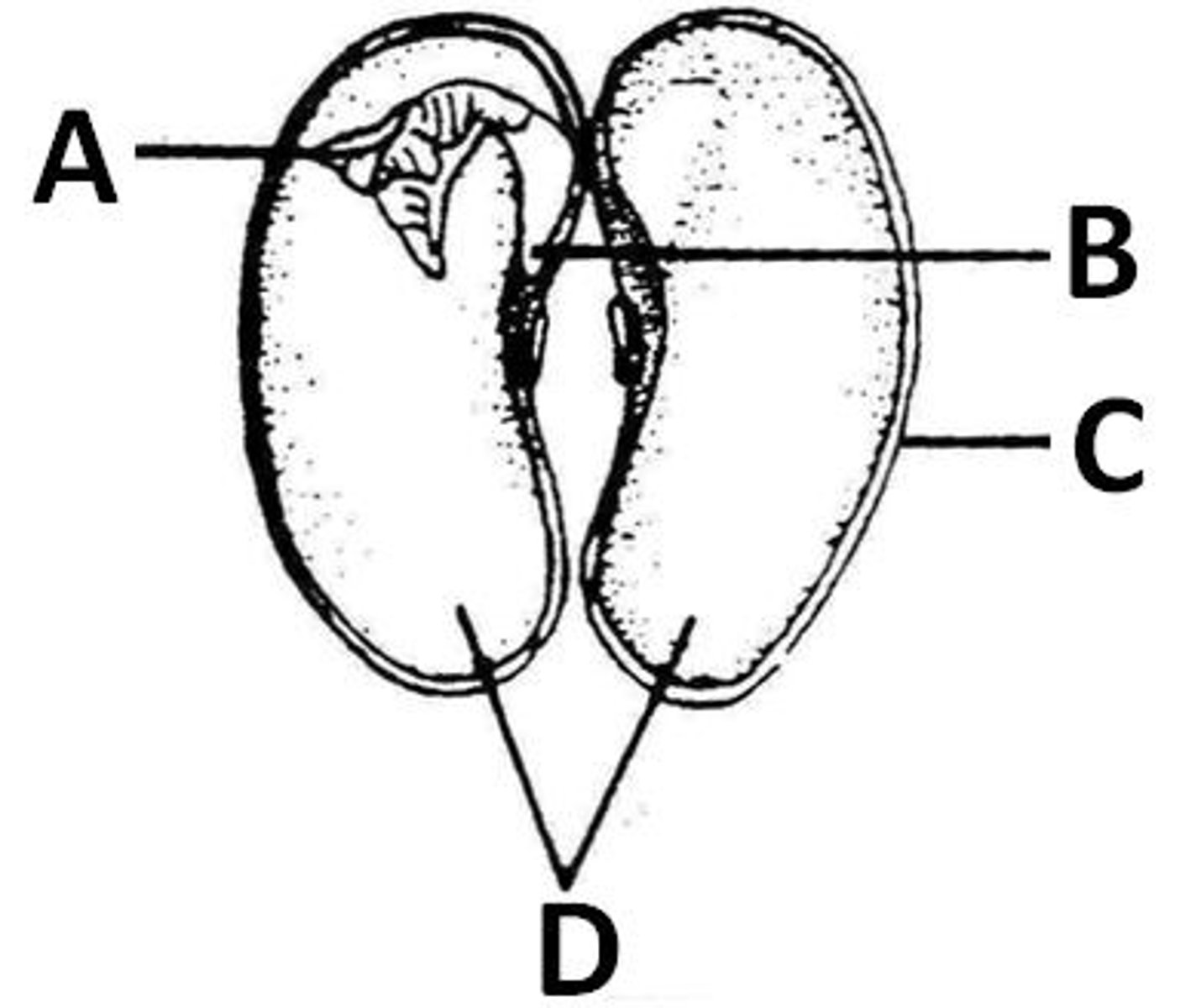
Radicle
B. where the lung part connects to the bean
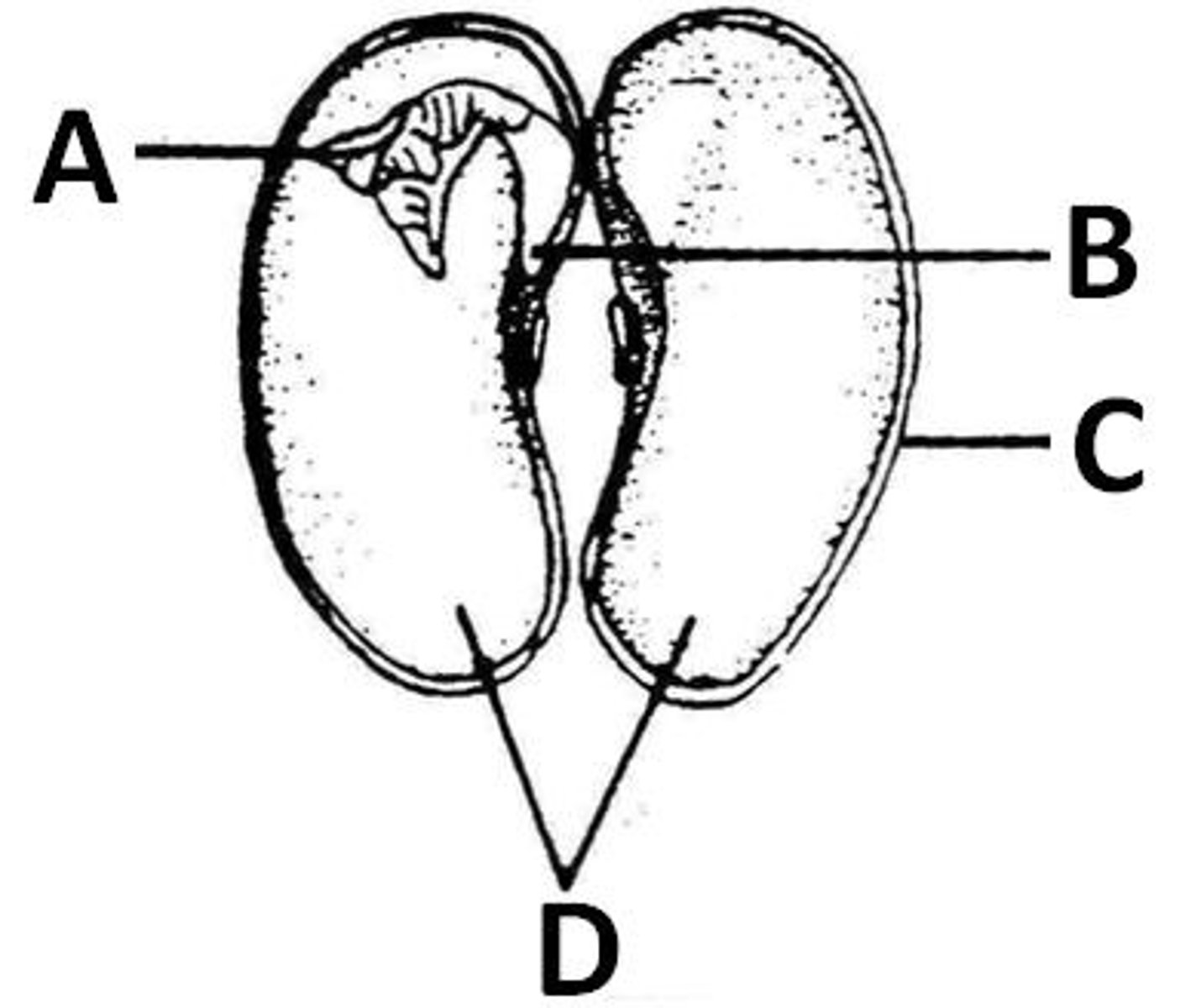
testa
C. the membrane of the bean seed
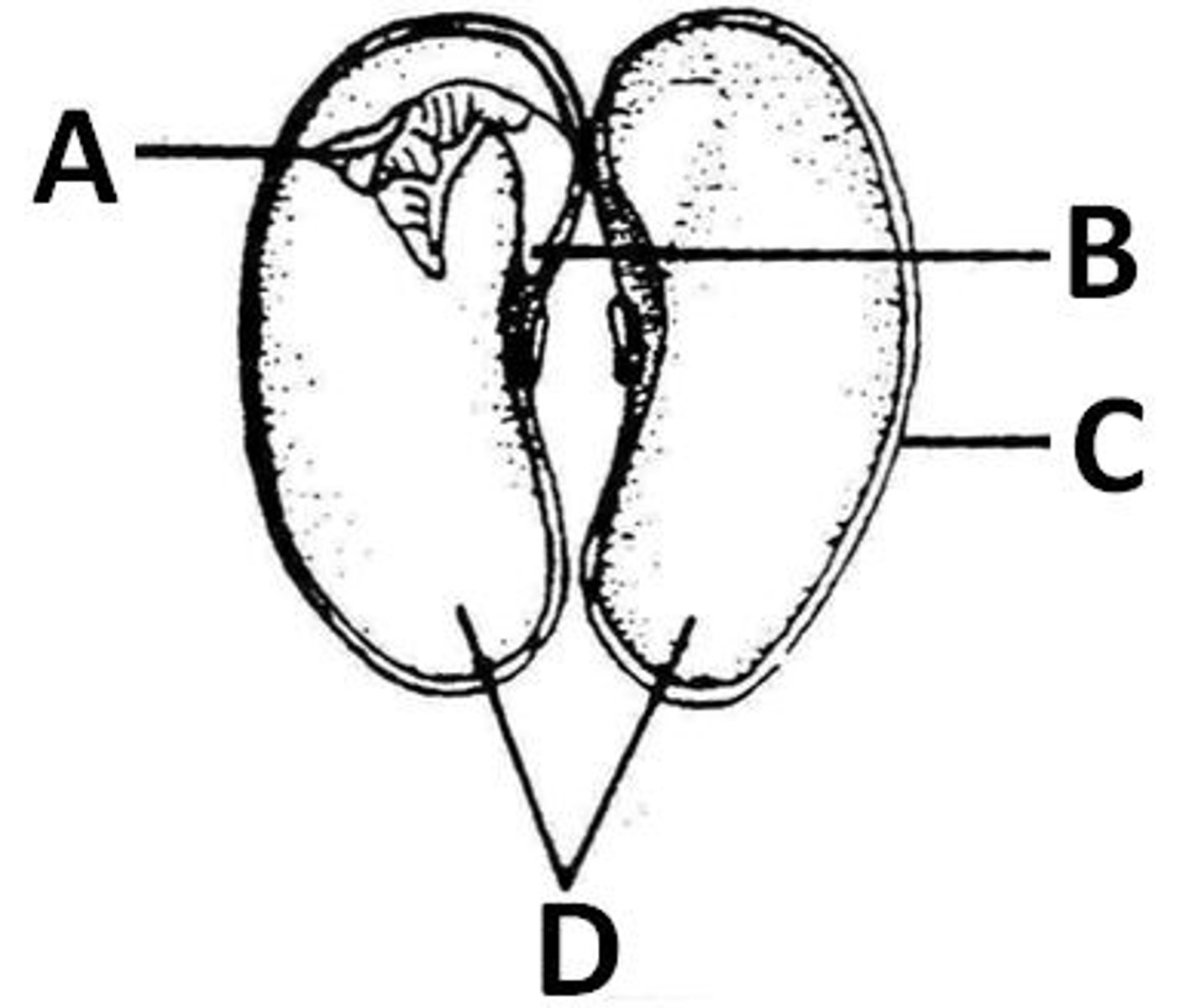
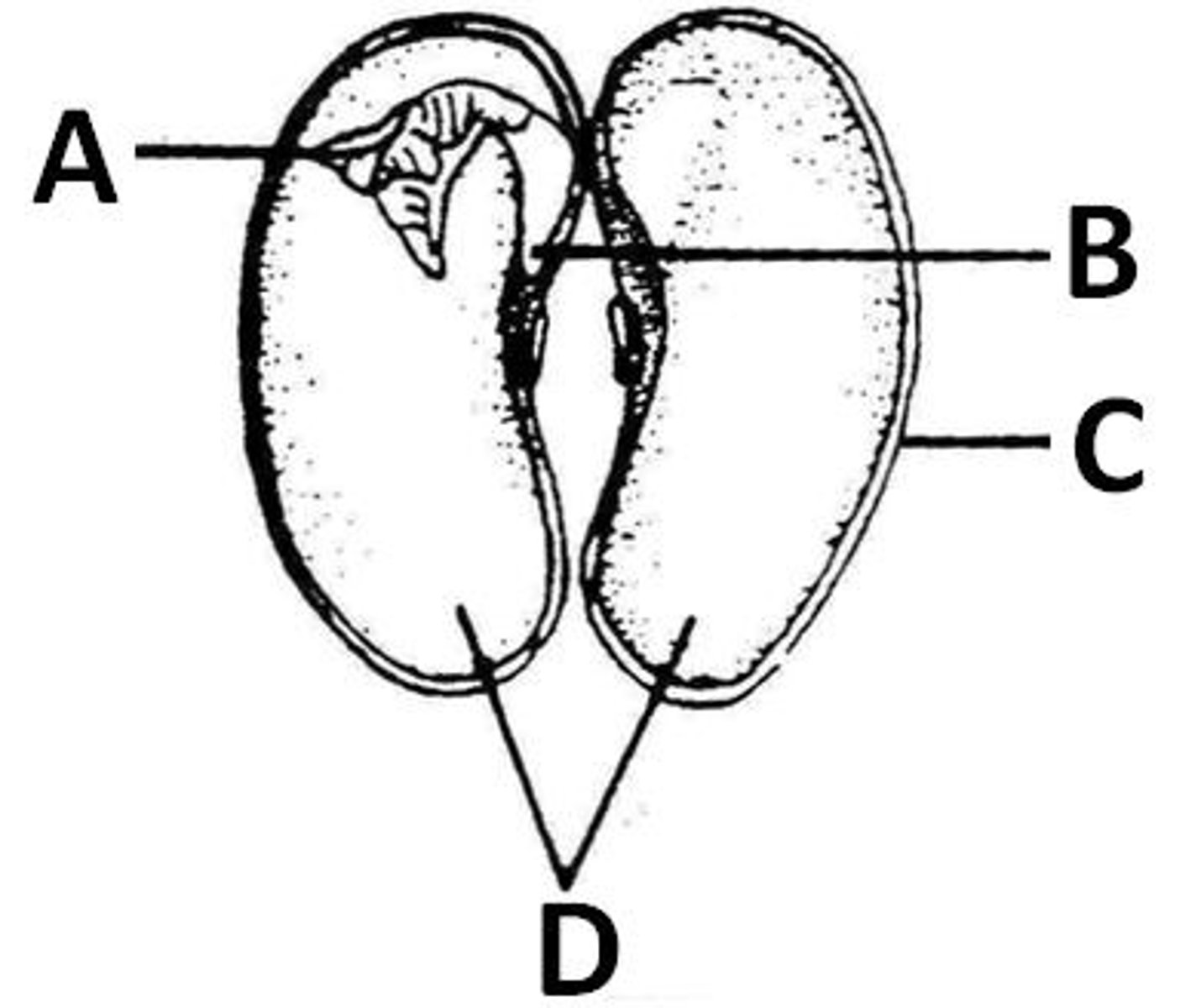
cotyledon
D. the meat of the bean seed
Some seeds are dormant until stratification takes place. What is stratification? Why is stratification an important dormancy mechanism for the plants that use it?
Stratification is when seeds are artificially exposed to cold temperatures and wet conditions to encourage germination in the spring. It is an important dormancy mechanism for plants to use because it prevents them from germinating in the fall or winter where it would only freeze and not have a chance to grow.
Explain the botany behind the saying "one bad apple can spoil the whole barrel"
Usually when referring to a bad apple, its meaning that the apple is bruised and squashed. This causes the apple to release ethylene. If, like in the saying, the apple is packed into a barrel with other apples, they are all exposed to the ethylene. The exposure causes all of the other apples to start to go bad more quickly.
Describe two ways that seeds can be wind dispersed
Two ways that seeds can be wind dispersed are: light weight seeds can be blown like dust, and some seeds have wings that can carry them along with the wind.
Morel
Ascomycetes
Corn Smut
Basidiomycetes
Has flagellated cells.....
chytrids
Ergot
Ascomycetes
Puff balls
Basidiomycetes
Chestnut blight
Ascomycetes
Black bread mold
Zygomycetes
fungal partner of most lichens
Ascomycetes
Black wart of potato
Chytrids
Make a loop in hyphae to catch nematodes....
Deuteromycetes
Saprophytic fungi and parasitic fungi differ in that....
the saprobes consume dead material and parasites consume living material
All phyla in the Fungi Kingdom are characterized by the presence of cell walls made of....
chitin
All phyla in the fungi kingdom are characterized by.....
zygotic life cycle
Wood rot fungi are of industrial interest because of their ability to....
degrade lignin