Social Exchange Thoery & Equity Theory
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Social Exchange Theory
An economic model of relationships where people weigh rewards and costs to determine their satisfaction and commitment.
People assess whether the rewards (e.g., love, support, companionship) outweigh the costs (e.g., effort, conflict, emotional labor).
If the benefits exceed the costs, they are more likely to stay in the relationship.
people are inherently selfish
even if it is unfair, as long as they personally feel the rewards outweigh the costs.
Comparison Level (CL)
Expectation of outcomes people think they should receive in a relationship
Standard with which people determine how satisfactory a relationship is; what they feel they deserve
More satisfied when outcomes meet or exceed CL
Comparison Level for Alternatives (CLalt)
People compare their relationship to other potential partners or single life. If they believe they could have a better relationship elsewhere, they may leave.
CLalt represents the lowest level of outcomes a person will accept in a relationship based on their available alternatives.
Greater commitment: If a person believes their current relationship far exceeds their alternatives, they will stay and feel more committed.
Less commitment: If a person perceives many good alternatives, they may be less committed and more likely to leave.
People are more dependent on their relationship when they perceive few or no alternatives.
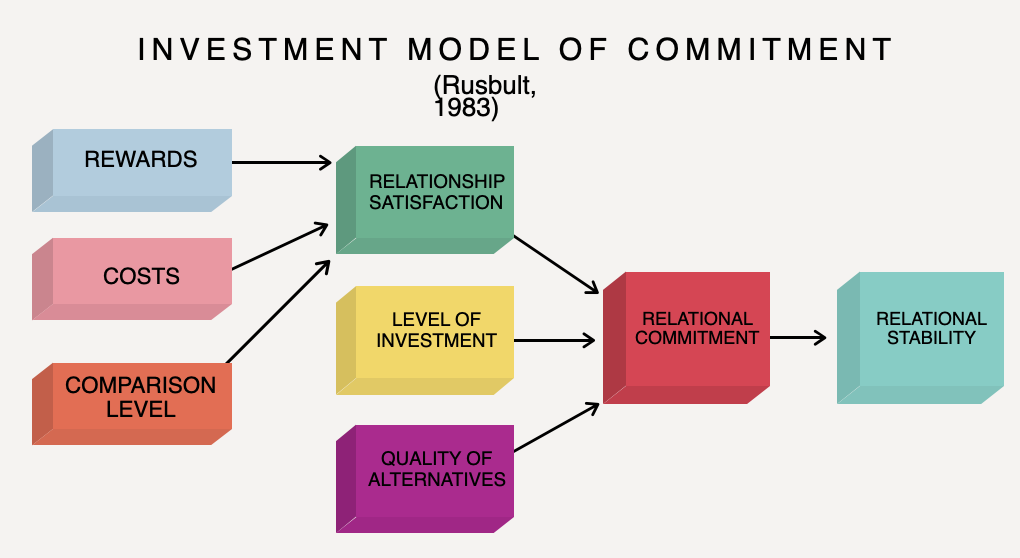
Investment Model Of Commitment
Research Examples for SET
Marriages
When rewards outweigh costs = greater happiness, less conflict & stress
Violence and Abuse
Different types of Commitment
Equity Theory
Examines whether the distribution of resources in a relationship is fair or equitable
Determined by comparing the ratio of contributions and benefits
People with equitable relationships--most satisfied
Determined by comparing the ratio of contributions and benefits
Overbenefited: more benefits and less contributions to relationship
Underbenefited: more contributions and less benefits to relationship
Equitable: each person contributes & benefits from the relationship equally
Equity Thoery argues and reality
ARGUES:
People want fair relationships and will work to create or restore equity
REALITY
Often, people attempt to maximize benefits & perceive themselves as contributing more than they actually do
Culture & Equity Thoery
These expectations of equity can be shaped by social norms, cultural values, and personal beliefs about what constitutes fairness within a marriage.
Research consistently shows that in many heterosexual marriages, there is an inequitable division of labor, with women often being underbenefited.
“second shift” to describe the phenomenon where working women come home after their day jobs to take on additional unpaid labor, such as housework and childcare.
Domain-specific equity (Sprecher)
Finding areas that each person is good at