Tablets: Excipients
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are four main methods of manufacturing tablets?
- Wet granulation.
- Dry granulation.
- Direct compression.
- Roller compaction.
What are the factors that determine the choice of manufacturing process?
- Compression properties of the therapeutic agent
- Particle size of the therapeutic agent
- Types of the excipient
- Chemical stability of the therapeutic agent
What are the general types of excipients added to tablets?
- Diluent/fillers
- Binders
- Disintegrants
- Lubricants (insoluble/soluble)
- Gildants
- Adsorbents
What are diluents/fillers?
Added to increase the mass of tablet allowing manufacture to be reliable and reproducible. Must show good compression properties and cheap.
What are examples of diluents?
- Lactose
- Starch
- Mannitol
What are binders?
Hold components together and can be added as a solution or powder.
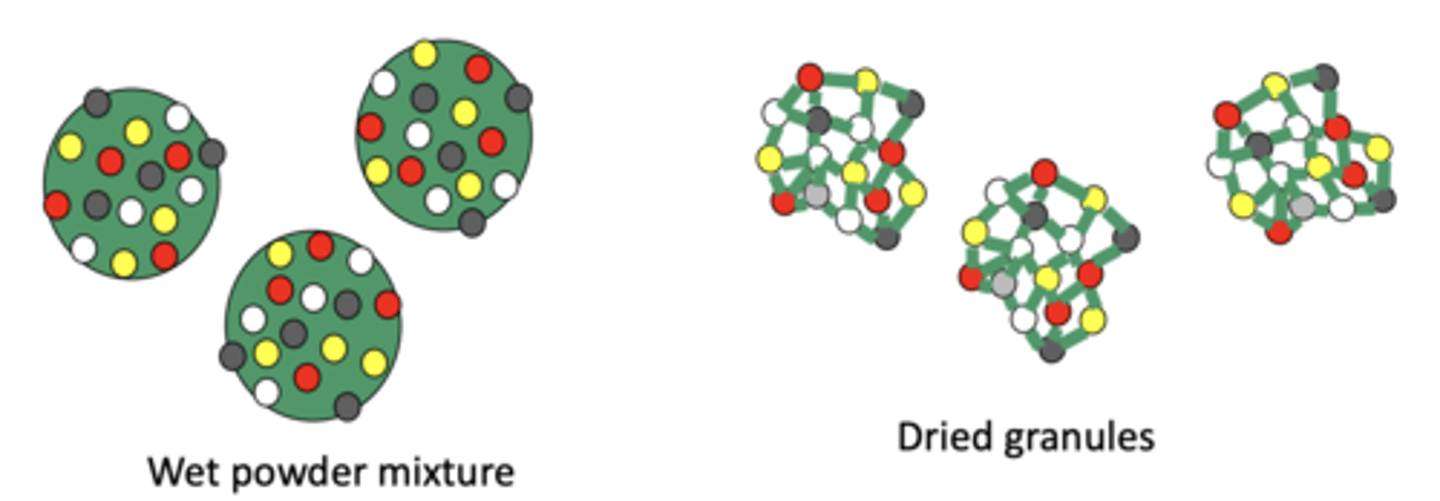
What are examples of binders?
Acacia and sucrose
What are disintegrants?
Added to facilitate the break down of the tablet upon entry to the stomach.
What are the mechanisms of disintegrants?
- Increase porosity and wettability.
- Swelling.
Describe how increasing porosity and wettability allows disintegration and give an example.
Allows gastrointestinal fluids to penetrate the bulk of the tablet and break it up. Example: starch
Describe how swelling allows disintegration and give an example.
Swelling in aqueous fluids increases the internal pressure within the tablet to break it up. Example: Sodium starch glycolate
Why are lubricants used and what are the two types?
Easy release of the compressed tablet from the mould or die. Types are soluble and insoluble.
When are insoluble lubricants added and give some examples of them?
To the final mixing stage before compression. Magnesium Stearate, Stearic Acid
What are cautions of insoluble lubricants?
- Too much lubricant may result in lower rate of disintegration.
- Mixing lubricant and disintegrant should be avoided as a film of lubricant around disintegrating agent may be formed.
Why are gildants used in tablets?
They enhance the flow properties of powders to reduce the friction between the powder and the hopper.
How do gildants work and give an example?
Gildants particles locate between the powder mixture therefore they must be fine and small. Talc
When are adsorbents used?
These are used whenever a liquid or semi-solid components are used.
What other excipient may tablets contain?
Sweetening agents - to control the taste if drug is bitter.
Colouring agent - To improve the appearance or to identify finished product.
Surface active agent - to enhance the wettability of hydrophobic tablets