SCIENCE REVIEWER
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
democritus
proposed that matter is composed of indivisible particles
john dalton
billiard ball model - atom is a uniform, solid sphere
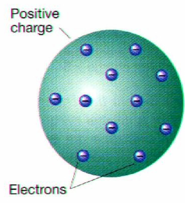
j.j. thompson
discovered electrons, made the plum pudding model
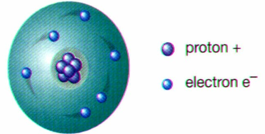
ernest rutherford
conducted gold foil experiment, discovered that protons circulate around the electron
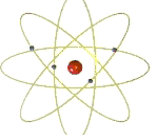
niels bohr
made the planetary model where electrons move in circular orbits within specific energy levels
erwin schrodinger
made the electron cloud model

james chadwick
discovered neutrons
dmitri mendeleev
made the periodic table
periodic table
shows all knowns elements, organized by chemical properties
electron configuration
the way electrons are distributed in the different orbitals around the nucleus of an atom
aufbau principle
electrons occupy orbitals in order of increasing energy
pauli’s exclusion principle
only two electrons can fit into a single orbital and must be an opposite spin
orbital diagrams
pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom
hund’s rule
electrons go into different orbitals in the same sub-level before pairing up inside
quantum number
used when describing the energy levels available to atoms
principal quantum number (n)
the size of the orbital
angular quantum number (l)
the shape of the orbital
magnetic quantum number (ml)
the orientation in space of a particular orbital
electron spin quantum number (ms)
the direction of the spin of an electron
possible values of principal
1,2,3,4,5,6,7
values of angular
s = 0, p=1, d=2, f=3
values of magnetic
s=0, p=-1,0,+1, d=-2,-1,0,+1+2 f=-3,-2,-1,0,+1,+2,+3
values of spin
+1/2, -1/2
ionic bond
metal+nonmetal, “transfer” of electron
covalent bond
nonmetal+metal, “share” of electron
metallic bond
metal+metal
ions
atoms that carry positive or negative charge.
cations
positive charge, lose lectrons
anions
negative charge, gain electrons
NaCl
rock salt crystals
SiO2
amethyst
HgS
cinnabar
greater than or equal to 0.4
nonpolar
0.5 - 1.9
polar
greater than 2.0
ionic