Finance 2043 - Exam 1 Review
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Primary goal of a firm is…
To maximize shareholder wealth.
Investors look at these factors when deciding to invest:
Risk, Return, Impact on share price.
Principle - Time Value of Money:
The concept that money available today is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its potential earning capacity through interest or investment.
Marginal Cost-Cost Benefit Analysis
A decision-making tool that compares the additional costs of an action to the additional benefits it provides. It helps determine if the benefits outweigh the costs and if the action should be pursued.
Marginal benefit must be greater than marginal cost to make an investment.
________ decisions focus on how a company will invest its resources.
Investment
_________ manage a firm’s cash, investing it when possible.
Treasurers
As risk of stock _______, the expected return will be ________
increases; higher.
How does bankruptcy work in a partnership?
If both partners are able to cover their debt, it is split 50/50
If one partner is unable to cover their debts, the other party is fully liable for their partner’s debt.
Taxation of Partnerships
Do not pay income tax directly
Partners are taxed one time at the personal level
Taxation of Corporations
Double taxation at the firm level and the personal level
Principal Agent Problem in a firm can incur costs such as:
Agency Costs
The costs that shareholders bear due to a manager within the firm acting in their own interest rather than the interest of the firm.
What is the role of the Board of Directors?
Approve strategic goals and plans.
B.O.D is focused on the long-term goals of the firm.
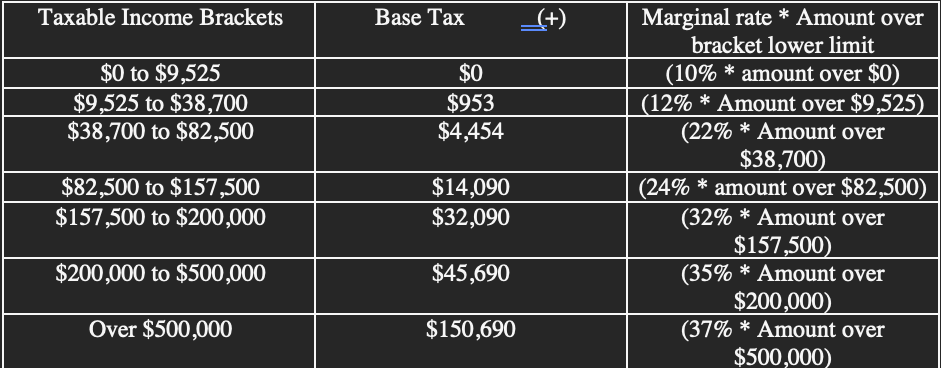
Tax Liability Chart
This chart represents the tax liability for personal income.
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
Created in 1934 when congress passed the Securities Exchange Act.
Requires ongoing disclosure by companies whose securities are traded in secondary markets (NYSE, NASDAQ)
Companies must make a 10-Q filing every quarter and a 10-K filing annually.
Commercial Banks
Traditional business model:
Taking in and paying interest on savings from depositors, and then investing or lending those funds back out at higher interest rates.
Investment Banks
Assist companies in raising capital
Advise firms on major transactions and business strategies
Engage in trading and market-making activities
Finance
Science and art of managing money.
Raising, allocating, and investing money are major financial decisions.
Managerial Finance Function
Make key decisions on:
Investment (allocating capital in assets, capital budgeting)
Financing (raising funds, capital structure among resources of funds - loans, bonds, stocks)
Working capital (short-term business operation)
Principles that guide manager’s decisions:
Time Value of Money
Tradeoff between return and risk (maximize return, minimize risk)
Cash is king (cash flow matters more than profit because firms need cash to run a business)
Competitive financial markets (keep a firm’s competitive position in the market environment)
Incentive to employees and managers
Sole Proprietorship
Income from the business “passes through” to the owner, taxed at the personal level
Unlimited liability
Partnerships
“Pass through” business, do not pay income tax directly
Unlimited liability
Corporations
Stock holders are business owners
Double taxation at the firm level and the personal level
Limited liability
Shadow-Banking System
Non-bank financial institution.
Do not accept deposits.
Not subject to the same regulations as traditional depository institutions.
Public Offering
The sale of either bonds or stocks to the general public.
Primary Market
Financial market where securities are initially issued; the only market where the issuer is directly involved in the transaction.
For privately owned firms to go public.
Corporate issues stock to public investors, through an Initial Public Offering (IPO)
Secondary Market
Financial market in which pre-owned securities (not new issues) are traded.
Trade for pre-owned securities, such as government and corporate stocks and bonds.
Capital Market
Enables suppliers and demanders of long-term funds (maturities longer than 1 year) to make transactions.
What key securities are traded on the Capital Market?
Corporate bonds
Corporate stocks
US Treasury bonds (T-notes)
US Treasury notes (T-bonds)
Private Placement
The sale of a new security directly to an investor or group of investors.
What are financial markets?
Forums in which suppliers and demanders of funds can transact business directly.
What is the difference between the Primary Market and the Secondary Market?
Primary markets are for privately owned firms go to public. The corporate first time issues stock to general public investors, so-called Initial Public Offering (IPO).
Secondary markets trade for pre-owned securities, including (government and corporate) bonds and stocks.
Efficient Market Hypothesis
At any point in time securities’ prices fully reflect all information available about the firm and its securities.
Securities markets are typically in equilibrium, security prices are fully and fairly priced.
Since stocks are fully and fairly priced, investors have little chance to find either underpriced or overpriced securities, thus, to make systematic gain in securities markets
Glass-Steagall Act of 1933
Restricts commercial banks to do securities and underwriting and other high risk investment banking business.
Established the FDIC.
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
Independent agency of the US Government.
Protects depositors of insured banks located in the US against the loss of their deposits should the bank fail.
Prospectus
A portion of a security registration statement that describes the key aspects of the issue, the issuer, and its management and final position.
Underwriting
Role of investment bank in bearing the risk of reselling, at a profit, the securities purchased from an issuing corporation at an agreed on price.
Underwriting Syndicate
A group of other banks formed by the originating investment bank to share the financial risk that is associated with underwriting new securities.
Subprime Mortgages
A loan that is meant to be offered to prospective borrowers with impaired credit records.
The higher interest rate is intended to compensate the lender for accepting the greater risk in lending to such borrowers.
Played a critical role in the cause of the 2008 financial crisis.
Securitization
Process of pooling mortgages or other types of loans and then selling claims/securities against that pool in the secondary market.
What are the three components in the statement of cash flows?
Cash flow from operating activities
Cash flow from investment activities
Cash flow from financing activities
Is the cost of long-term debt higher or lower than that of short-term debt?
Long-term debt typically incurs higher interest rates; therefore, it is likely to cost more than that of a short-term debt.
Long-Term Financial Planning
Plans that lay out a company’s financial actions and the anticipated impact of those actions over periods ranging from 2-10 years.
Require input from all areas of the firm (R&D, marketing, operations, HR, accounting, finance, etc.)
Short-Term Financial Planning
Plans that specify short-term (most often cover a 0–2-year period) financial actions and the anticipated impact of those actions.
Process begins with sales forecast.
Then the development of production plans, such as cost of production, cash budget, and pro forma income statement/balance sheet.
Goals of Long-Term Financial Planning
How to build value for shareholders by creating new products/services that meet market demands.
How to generate sufficient cash flow internally or raise fund externally (debts or equity financing) to meet financial needs.
How to allocate money/capital on firm’s assets.
Depreciation
Portion of the costs of fixed assets charged against annual revenues over time.
Depreciable Value of an Asset Equation
Cost of Unit + Installation Price - Depreciable Value of an Asset
Cash Inflows (Money coming in)
Decrease in any asset
Increase in any liability
Net profits after taxes
Depreciation and other noncash charges
Sale of stock
Cash Outflows (Money going out)
Increase in any asset
Decrease in any liability
Net loss after taxes
Dividends paid to preferred and/or common stockholders
Repurchase or retirement of stock
Commodity Market
A commodity market involves buying, selling, or trading a raw product, such as oil, gold, or coffee. There are hard commodities, which are generally natural resources, and soft commodities, which are livestock or agricultural goods.
Depreciable Life of an Asset
The time over which an asset can be depreciated in a company’s accounts.
Cash is king.
Cash flow is the primary ingredient in any financial model.
Importance of Liquidity in volatile industries
Liquidity is crucial in volatile industries such as aviation or biotech, as compared to less volatile industries such as grocery.