transcription and translation
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
DNA characterisitics
sugar: deoxyribose
double stranded
base: thymine
main single form
RNA characterisitics
sugar: ribose
single stranded
base: uracil
3 main forms: mRNA, rRNA, tRNA
What types of RNA do not encode proteins?
rRNA and tRNA
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA
Makes up ribosome – joins amino acids together by peptide bonds to make proteins
tRNA
Transfer RNA
tRNA molecules carrie amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis
One tRNA for every amino acid
mRNA
Messenger RNA
mRNAs are translated by ribosomes to make proteins
encodes proteins
transcription
when DNA unwinds and RNA polymerase binds to a promoter near the start of a gene
mRNA is synthesized in the 5’ > 3’ direction using DNA as a template
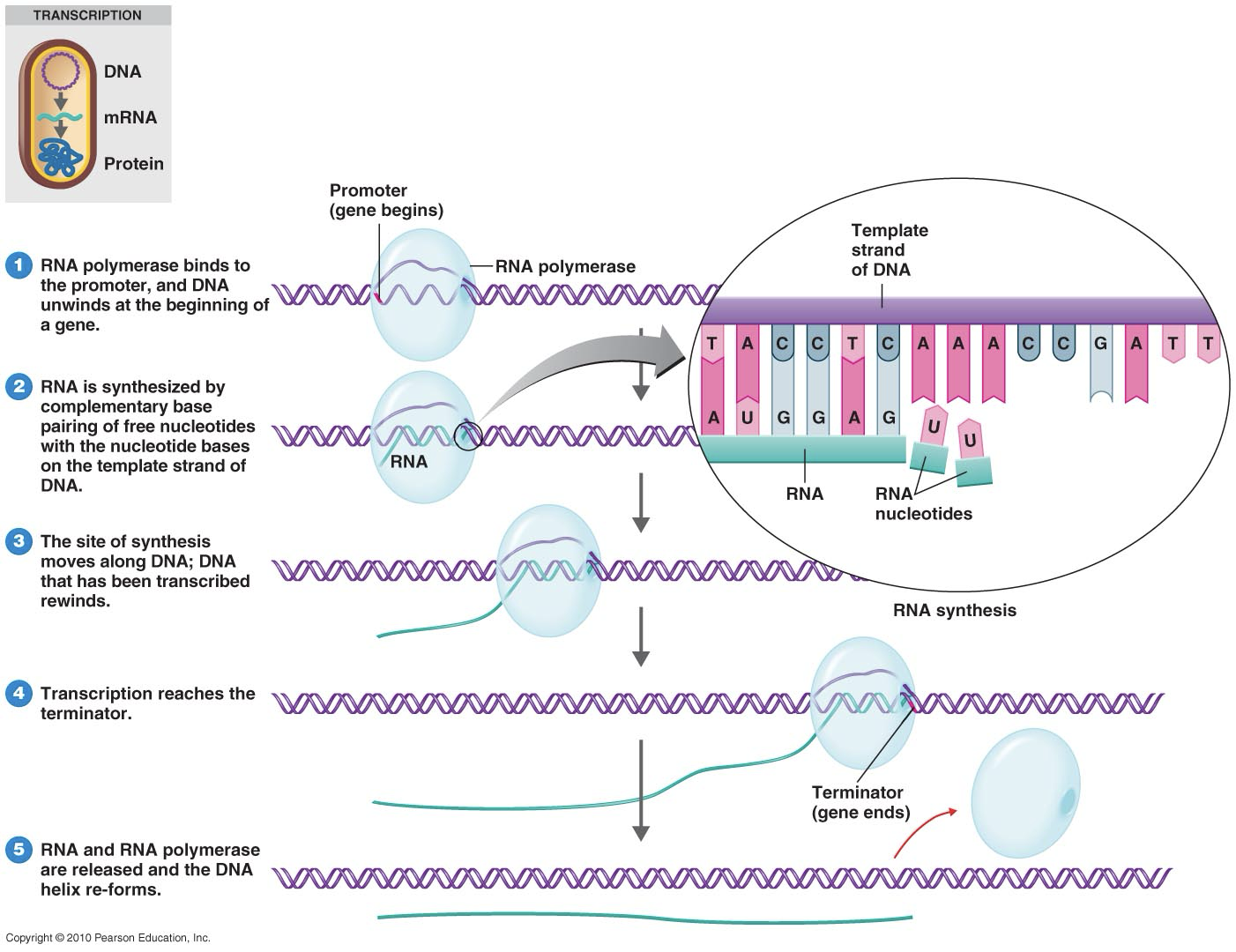
what is an antibiotic that targets transcription
rifamycin
what does rifamycin do
Inhibit synthesis of mRNA by targeting RNA polymerase
penetrates tissues
what are side effects of rifamycin
Red urine, saliva, sweat, or tears
codons
group of three nucleotides on mRNA
Start codon--AUG→formylmethionine
anticodons
Complementary sequence on the tRNA (to codon on mRNA)
for anticodons, the codon sequence determines what
which amino acid is brought to the ribosome
what “machine” carries out translation
ribosomes
translation order
Ribosome binds mRNA
mRNA codons determine which tRNA (each carry a different amino acid) “docks” in the ribosome
tRNA leaves amino acid for the forming polypeptide
process of translation step 1
components needed to begin translation come together
process of translation step 2
on the assembled ribosome a tRNA carrying the forst amino acid is paired with the start codon on the mRNA. the place where this first tRNA sits is called the P site. a tRNA carrying the second amino acid approaches
process of translation step 3
the second codon of the mRNA pairs with a tRNA carrying the second amino acid at the A site. The first amino acid joins to the second by a peptide bond. this attaches the polypeptide to the tRNA in the P site
process of translation step 4
the ribosome moves along the mRNA until the second tRNA is in the P site . the next codon to be translated is brought into the A site. The first tRNA now occupies the E site
process of translation step 5
the second amino acid joins to the third by another peptide bond, and the first tRNA is released from the E site
process of translation step 6
The ribosome continues to move along the mRNA and the new amino acids are added to the polypeptide
process of translation step 7
when the ribosomes reaches a stop codon, the polypeptide is released
process of translation step 8
the last tRNA is released and the ribosome comes apart. the released polypeptide forms a new protein
A site
attachment site for a tRNA
P site
polymerization site where peptide bonds are formed between amino acids
E site
exit site for tRNA molecules
what are Aminoglycosides effective against
gram - bacteria
what can Aminoglycosides cause damage to
auditory nerve and kidney function
examples of Aminoglycosides
streptomycin and gentamicin
what are Tetracylines used for
Broad-spectrum (gram positive and gram negative)
what is a characterisitc of Tetracylines
long retention in body and penetration
what is Tetracylines used in
animal feed – becoming more of a concern
side effects of tetracylines
Discolor teeth in children and not given to pregnant women (liver damage)
Chloramphenicol – simple structure used for
Broad–spectrum but toxicity problems
Chloramphenicol characterisitcs
Inexpensive – used in low cost situations
Ready diffusion
what can chloramphenicol cause
aplastic anemia
what is macrolides effective agaisnt
gram positive bacteria (not very effective against gram negative bacteria)
how is macrolides taken
Oral antibiotic for children
example of macrolides
erythromycin
how does the coupling of transcription and translation help prokaryotes grow quickly
Ribosomes can immediately begin the process of protein translation as mRNA molecules are by transcribed by RNA polymerase.
polyribosomes
multiple ribosomes can bind mRNAs and translate proteins simultaneously
polysomes
complex of multiple ribosomes simultaneously translating a single messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule into proteins