VM 565 Midterm
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What does the first heart sound (S1) indicate?
A. Opening of semilunar valves
B. Closure of AV valves
C. Opening of AV valves
D. Closure of semilunar valves
B.
What congenital heart disease is commonly seen in Golden Retrievers?
A. Mitral dysplasia
B. Tricuspid valve dysplasia
C. Subaortic stenosis
D. Pulmonic stenosis
C.
Which heart condition is most associated with an S3 heart sound?
A. Pulmonic regurgitation
B. Mild mitral valve regurgitation
C. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
D. Mild Pulmonic stenosis
C.
What is considered a normal capillary refill time in dogs?
A. >3 seconds
B. 1–2 seconds
C. <0.5 seconds
D. 3–5 seconds
B.
Which condition is associated with jugular venous distension?
A. Left-sided heart failure
B. Systemic hypertension
C. Right-sided heart failure
D. Hypovolemia
C.
What type of murmur is typical for a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)?
A. Systolic
B. Diastolic
C. Continuous
D. Mid-systolic click
C.
Which valve is best heard at the left apex?
A. Pulmonic
B. Tricuspid
C. Aortic
D. Mitral
D.
What is a gallop rhythm?
A. Split S2
B. Presence of an S3 or S4
C. Bradyarrhythmia
D. Ejection click
B.
Pulse deficits are most commonly associated with:
A. Murmurs
B. Arrhythmias
C. Hypovolemia
D. Tachypnea
B.
What does jugular venous distension reflect?
A. Left atrial pressure
B. Aortic pressure
C. Right atrial pressure
D. Pulmonary venous pressure
C.
Which murmur is best heard on the right sternal border?
A. Flow through a left to right patent ductus arteriosus
B. Flow through a left to right ventricular Septal Defect
C. Mitral regurgitation
D. Pulmonic stenosis
B.
A split S2 heart sound may be heard in which condition?
A. Mitral regurgitation
B. Pulmonary hypertension
C. Aortic stenosis
D. Tricuspid regurgitation
B.
What finding is consistent with right-sided heart failure?
A. Pulmonary crackles
B. Ascites
C. Syncope
D. Left apical murmur
B.
Which valves or valve is auscultated at the left heart base?
A. Mitral
B. Tricuspid
C. Aortic and Pulmonic
D. Aortic and Mitral
C.
Which of the following would result in a continuous heart murmur?
A. Aortic regurgitation
B. Aortic stenosis and mitral valve regurgitation
C. Aortic regurgitation with pulmonic stenosis
D. Tricuspid valve regurgitation
C.
Which heart sound occurs just before S1 that is not commonly heard in normal small animal patients?
A. S2
B. S3
C. S4
D. Opening snap
C.
Which diagnostic tool is most reliable to detect pulmonary edema?
A. Thoracic auscultation of crackles
B. Pulse oximetry
C. Thoracic radiographs
D. Capillary refill time
C.
A left apical systolic murmur is most consistent with:
A. Mitral regurgitation
B. Tricuspid stenosis
C. Pulmonic stenosis
D. Aortic regurgitation
A.
Which murmur pattern is most typical of subaortic stenosis?
A. Continuous
B. Diastolic
C. Crescendo-decrescendo systolic
D. Holosystolic
C.
Why should you palpate pulses during auscultation?
A. Detect hypotension
B. Detect arrhythmias
C. Assess murmur intensity
D. Detect pulse deficits
D.
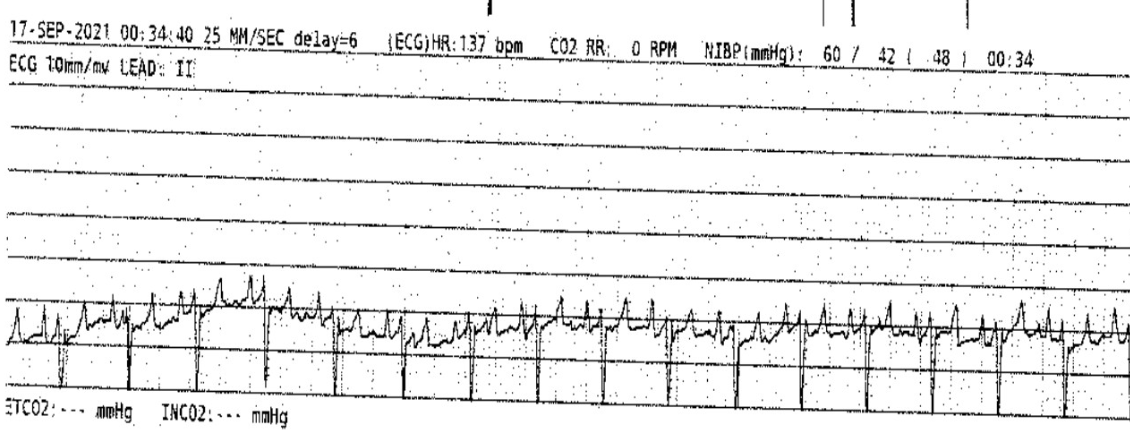
What side of the heart is affected?
Right
In a patient with severe aortic regurgitation, what characteristic arterial pulse is typically felt on physical examination?
Bounding
What is the dominant factor that affects vascular resistance?
Radius of the vessel
What three starling forces would promote edema formation?
Increase in capillary hydrostatic pressure
Decrease in capillary oncotic pressure
Increase in capillary permeability
All arrhythmias are due to abnormalities in either:
Automaticity
Excitability
Conduction
What is effective stroke volume, and how does it differ from total stroke volume?
Amount of blood that is actually ejected into the arteries with each heartbeat. It differs from total stroke volume because it subtracts any blood that leaks backward due to valve regurgitation
What does the P-wave indicate?
A. Ventricular depolarization
B. Atrial depolarization
C. Ventricular repolarization
D. Atrial repolarization
B.
What does the QRS complex indicate?
A. Ventricular depolarization
B. Atrial depolarization
C. Ventricular repolarization
D. Atrial repolarization
A.
What are three characteristics of a nonpathologic (innocent) heart murmur?
Left-sided basal systolic murmur
Mild murmur < Grade 2
Resolves by 6 months of age on own
Intermittent jugular pulsations could indicate:
AV block
Ventricular arrhythmias
What is the number one differential for constant jugular pulsations?
Right-sided heart failure
What is femoral pulse pressure?
Difference between systolic and diastolic pressures
What is the primary cause of pulse deficits?
Arrhythmias
Do all cats with gallop rhythms have heart disease?
Almost always yes
Pulmonary venous enlargement is suggestive of:
left-sided CHF
What are pulmonary changes you may see with left-sided CHF?
Interstitial to alveolar infiltrates
Pei-hilar, right caudodorsal most common
T/F: Cardiac electrical activity and cardiac function are always linked
False
What types of diets should you avoid for patients with cardiovascular disease?
high salt diets
What is the goal of treatment in patients with Afib?
Slow down the heart rate
Which drug should NOT be used in patients with CHF as it can worsen cardiac output?
A. Lidocaine
B. Atenolol
C. Mexiletine
D. Diltiazem
B.
When does troponin get released into the bloodstream?
When there is myocardial damage
Which of the following findings would most support a diagnosis of infectious or inflammatory myocarditis in a dog?
A. Mildly elevated creatinine kinase (CK)
B. Elevated serum troponin I levels
C. Elevated NT-proBNP levels
D. 3/6 apical systolic heart murmur
B.
Which of the following would NOT typically be associated with elevated cardiac troponin I (cTnI) levels in dogs or cats?
A. Chagas disease
B. Leishmaniasis
C. Toxoplasmosis
D. FIP
E. Hypothyroidism
E.
What is the normal pathway of conduction through the heart?
SA node → AV node → Bundle of His → Right and Left Bundle Branches → Purkinje fibers 🫀
A cat presents to your clinic in respiratory distress. While initiating oxygen therapy and stabilizing the patient, you remember Dr. G’s lecture on BNP testing. Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding the use of the SNAP BNP test in this situation?
A. A normal SNAP BNP result confirms that the cat has congestive heart failure (CHF).
B. An abnormal SNAP BNP result rules out all non-cardiac causes of respiratory distress.
C. A normal SNAP BNP result helps rule out CHF as the cause of respiratory distress.
D. SNAP BNP is only useful after thoracic radiographs are taken
C.
The most important thing you can do for a pulseless patient is to:
Start CPR immediately
Name the shockable rhythms
Ventricular fibrillation
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia