USU WILD 3800 Midterm
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Fall 2025, Proff. Kyra Clark-Wolf
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Ecosystem processes are governed by multiple control variables, including state factors that set the boundary for the characteristics of an ecosystems and interactive controls that operate at the ecosystem scale and both control and respond to ecosystem characteristics. Which
of the following factors are a state factor (select all that apply):
A. Climate
B. Parent material
C. Time
D. Resources
D. Resources
Climate, Parent Material, and Time (Resources are an interactive control)
Water supply is an example of which type of ecosystem service?
A. Cultural services
B. Supporting services
C. Regulating services
D. Provisioning services
B. Supporting services
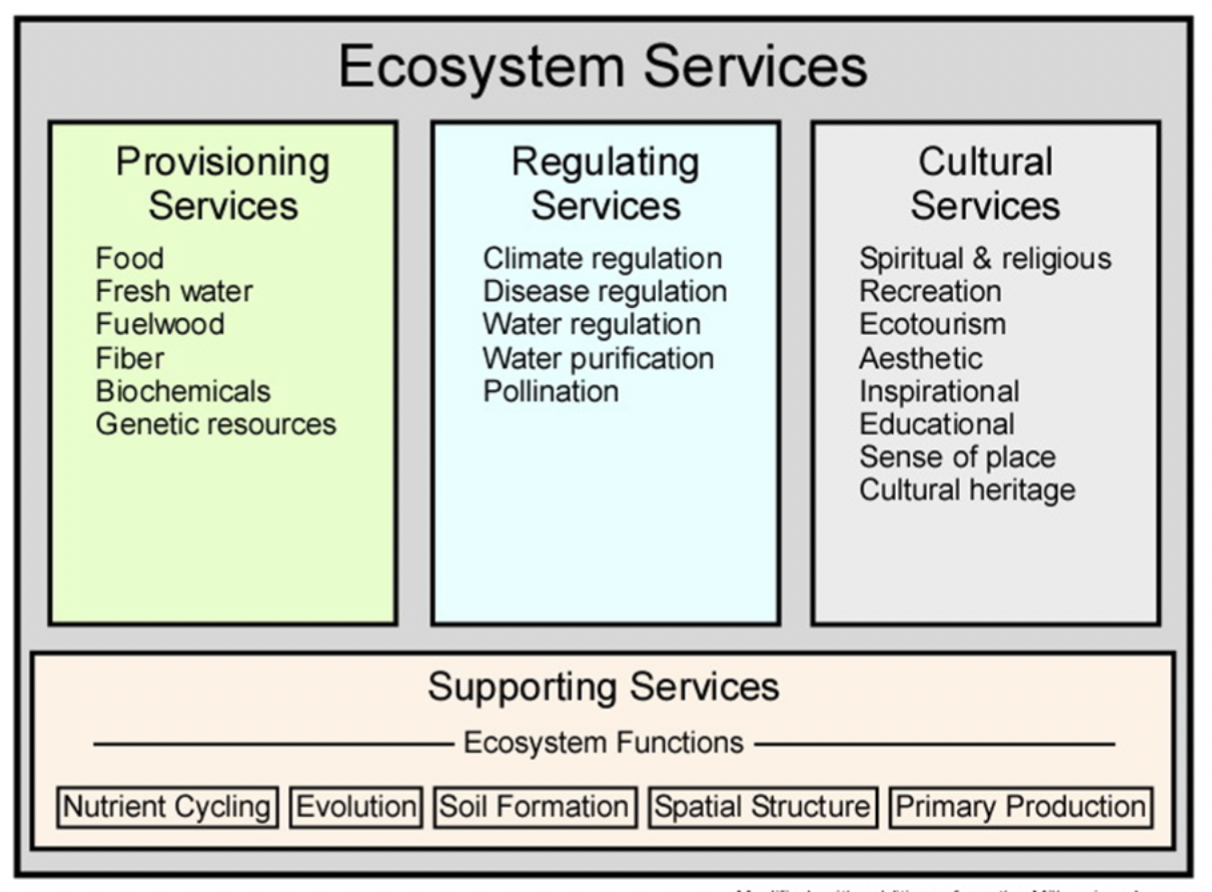
Carbon sequestration and storage is an example of which type of ecosystem service?
A. Cultural services
B. Supporting services
C. Regulating services
D. Provisioning services
B. Supporting services
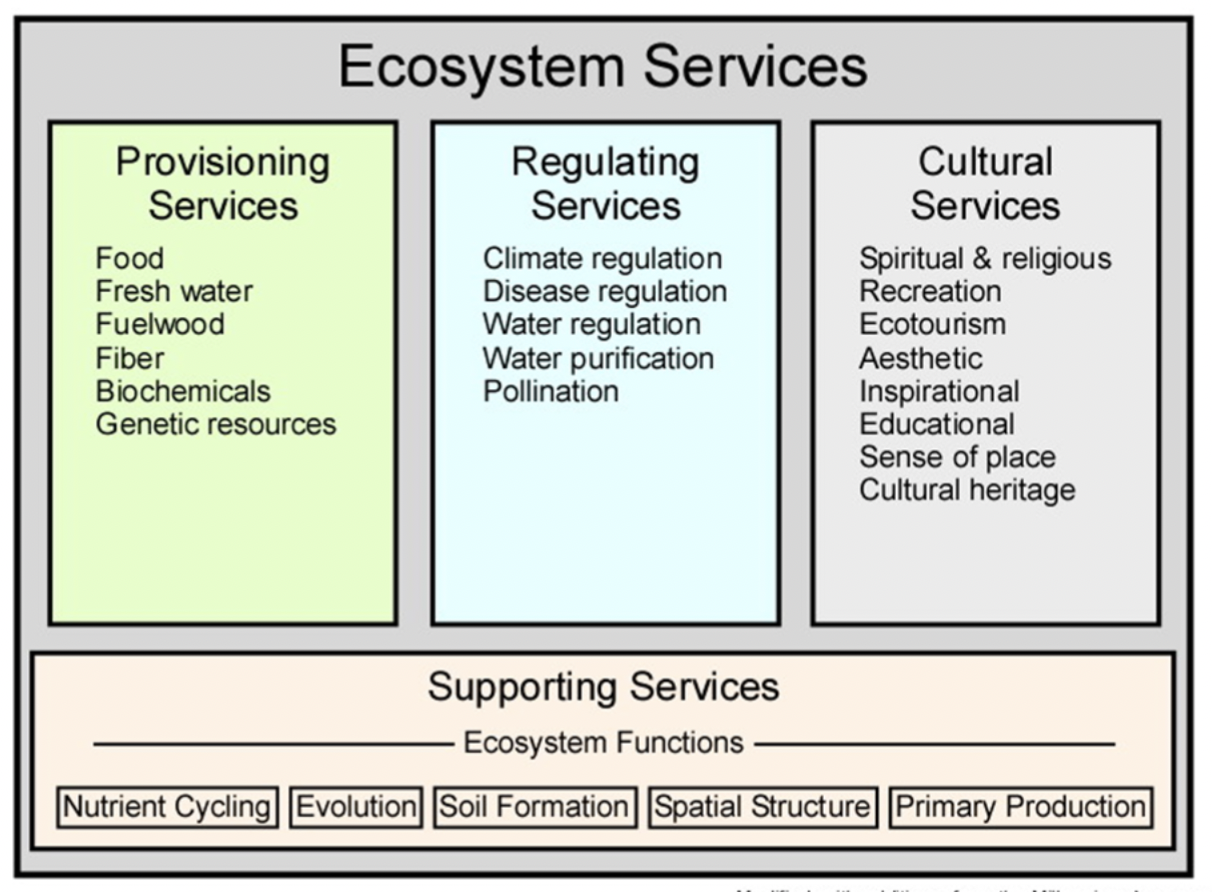
Soil formation and fertility is an example of which type of ecosystem service?
A. Cultural services
B. Supporting services
C. Regulating services
D. Provisioning services
Supporting service
Managers decide to maximize carbon sequestration in a forested watershed by halting all timber harvesting. This new management approach is likely to impact other ecosystem services. Which of the following statement is correct:
A. Halting timber harvesting leads to increased soil erosion due to lack of tree removal.
B. Halting timber harvesting can lead to the accumulation of forest fuels, potentially increasing the risk of wildfires.
C. Halting timber harvesting reduces habitat availability, leading to a decrease in forest biodiversity.
D. Halting timber harvesting decreases the amount of organic matter added to the soil, leading to reduced soil health
B. Halting timber harvesting can lead to the accumulation of forest fuels, potentially increasing the risk of wildfires.
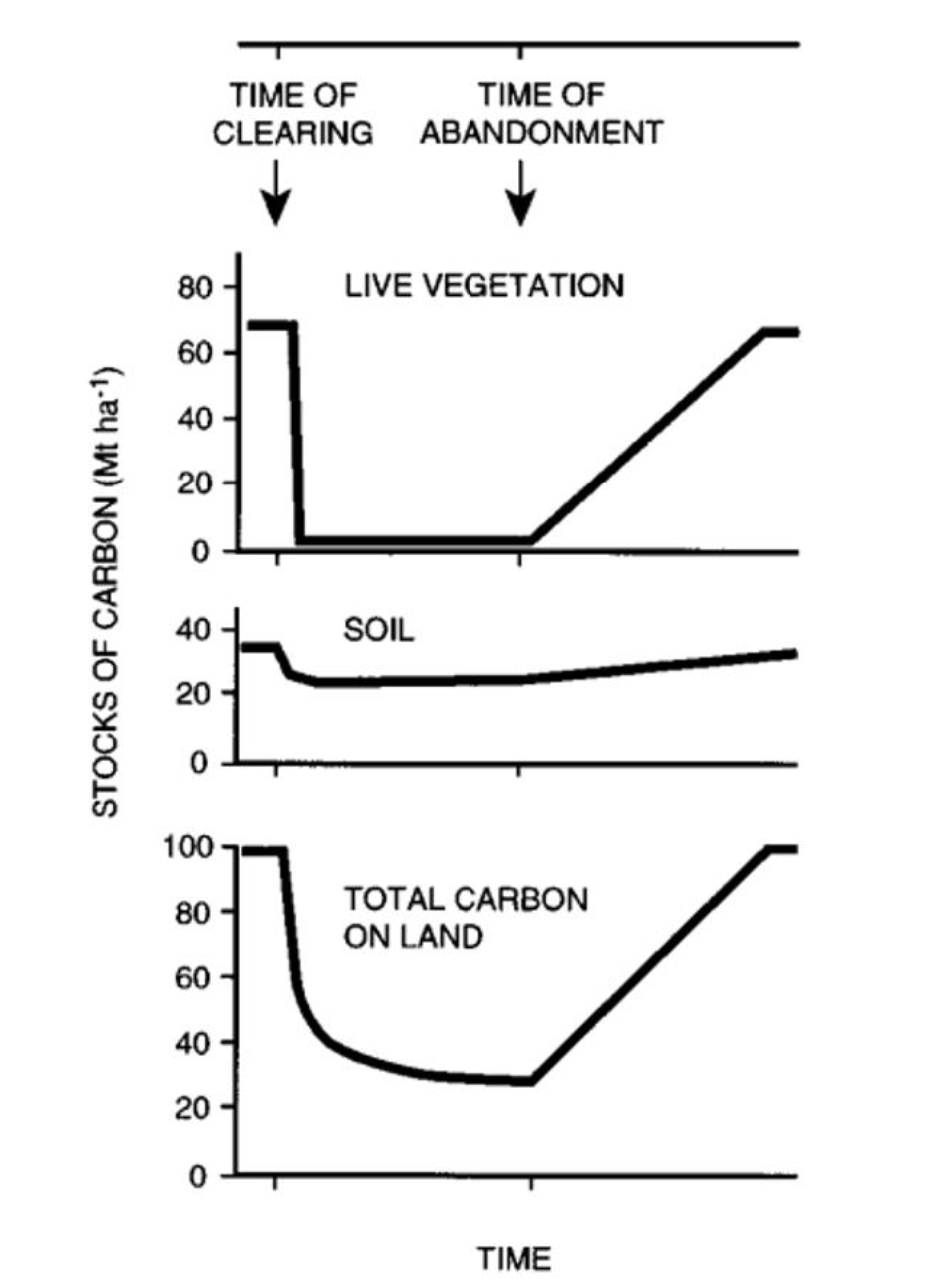
Deforestation has been shown to significantly affect tropical forest carbon dynamics. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. After deforestation, most of the carbon loss is from carbon stored in soil.
B. After deforestation, there is a short-term increase in total carbon storage in vegetation as new plants grow rapidly.
C. After deforestation, the recovery of soil carbon is generally slower than the recovery of vegetation carbon.
D. After deforestation, carbon sequestration rates increase in the long term as the cleared land becomes more productive.
C. After deforestation, the recovery of soil carbon is generally slower than the recovery of vegetation carbon.
In relation to the Earth's climate system, which of the following statements are correct? (select all that apply)
A. The balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation is crucial in determining the amount of energy available to drive Earth's climate system.
B. The fundamental cause of atmospheric circulation is due to the Earth's rotation.
C. The Earth's rotation affects the direction of surface winds and contributes to the formation of atmospheric circulation patterns.
D. The Earth's climate system is significantly affected by the presence of continents, with ocean currents playing a negligible role.
A. The balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation is crucial in determining the amount of energy available to drive Earth's climate system.
C. The Earth's rotation affects the direction of surface winds and contributes to the formation of atmospheric circulation patterns.
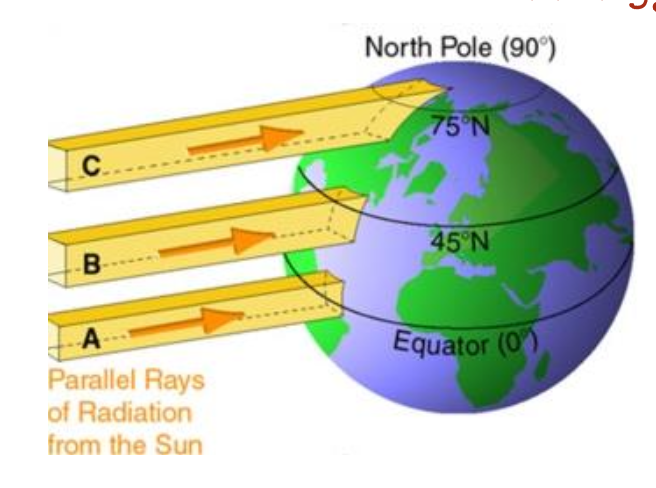
Which of the following statements about the Hadley cell is correct?
A. The Hadley cell is responsible for the arid climates found at around 30 degrees latitude.
B. The Hadley cell drives the major surface winds known as the westerlies.
C. The Hadley cell results in the formation of high-pressure systems at the equator.
D. The Hadley cell involves rising warm air near the equator and descending cooler air around the poles.
A. The Hadley cell is responsible for the arid climates found at around 30 degrees latitude.
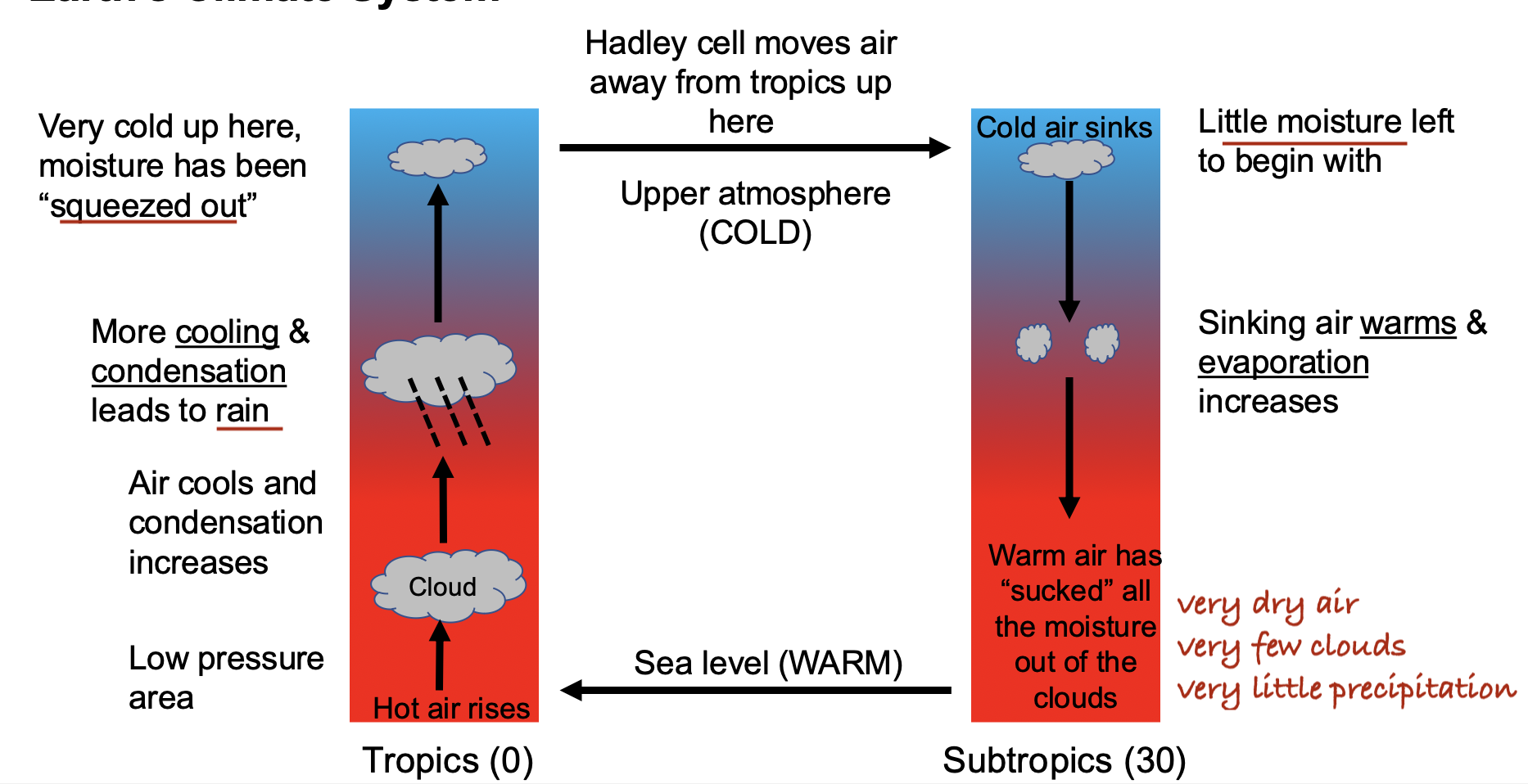
What is the major reason for Death Valley's extreme heat and arid conditions?
A. Its proximity to the Pacific Ocean
B. Its high elevation above sea level
C. Its position in a rain shadow region
D. Its proximity to volcanic activity
C. Its position in a rain shadow region
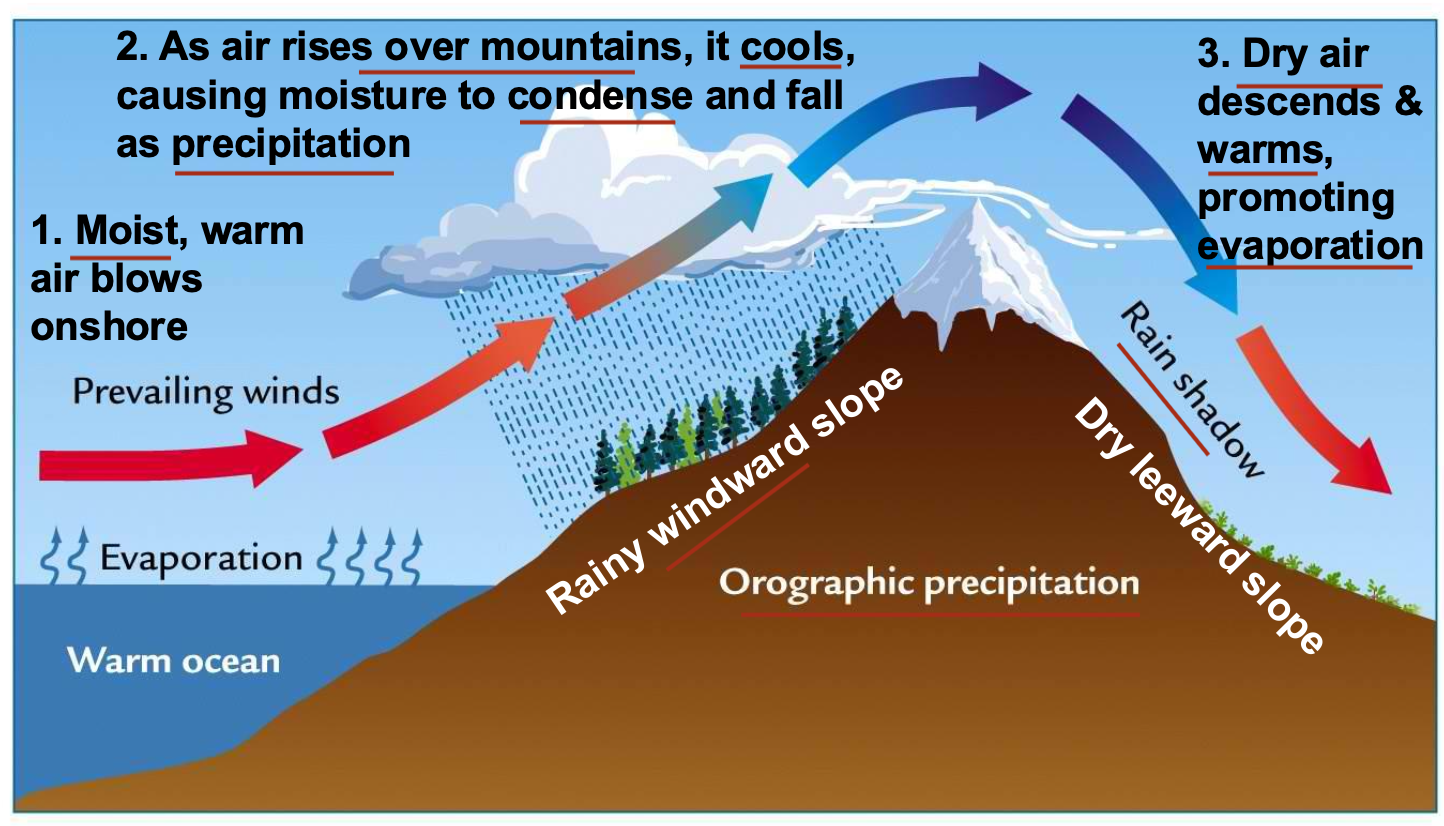
Which of the following ocean currents contributes to mild winters in Europe?
A. The North Pacific Current
B. The Gulf Stream
C. The North Equatorial Current
D. The Canary Current
B. The Gulf Stream
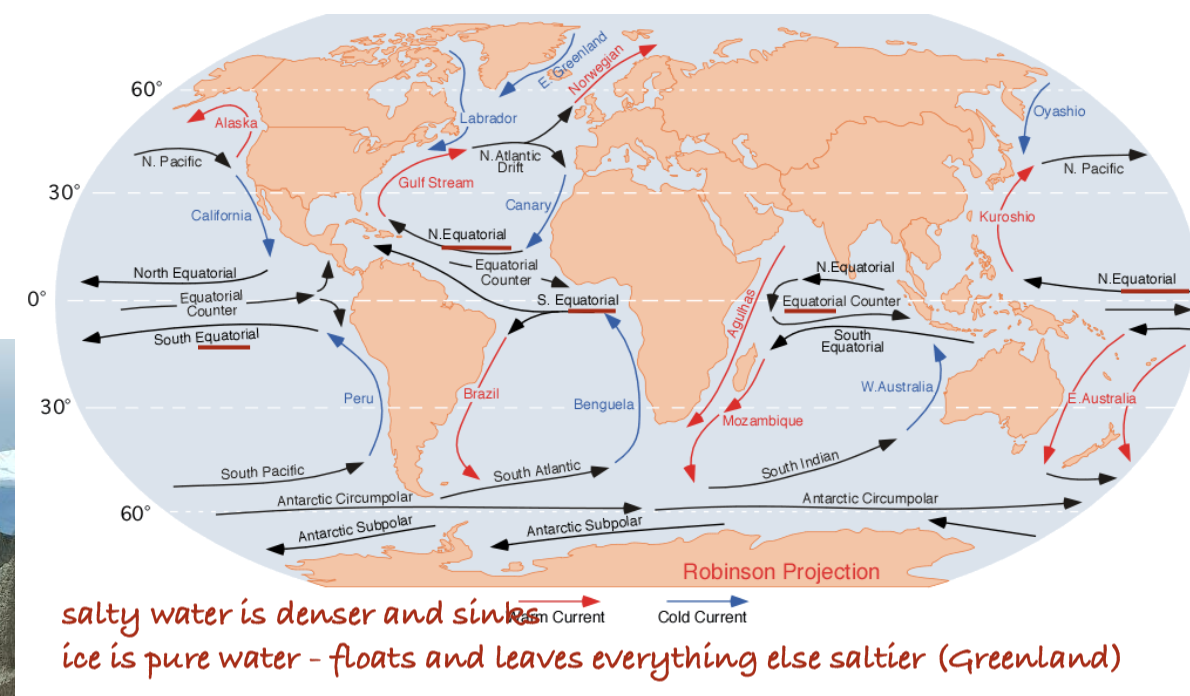
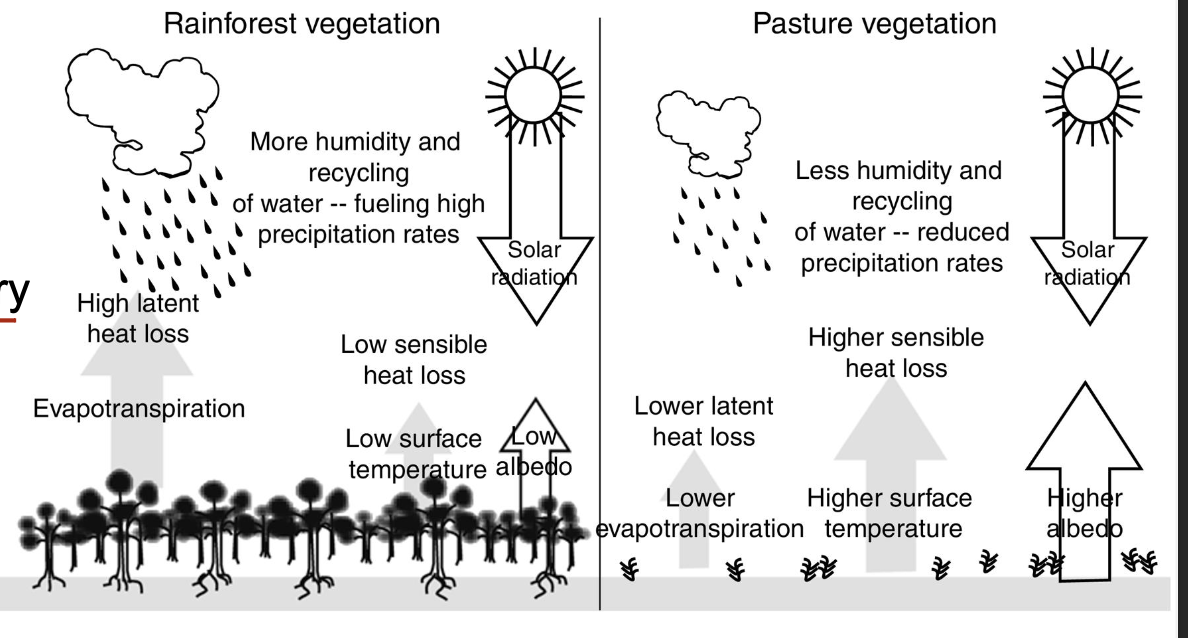
All else equal, the average air temperature in an open field is likely to be higher than a forest for what reason?
A. Forests have higher albedo (reflectance) than pasture vegetation
B. Forests transpire more water, leading to higher latent heat loss
C. Forests have higher surface temperatures, leading to higher sensible heat loss
D. Forests store more carbon out of the atmosphere
B. Forests transpire more water, leading to higher latent heat loss
(Albedo: lighter colors reflect more light and are cooler - forest have lower albedo)
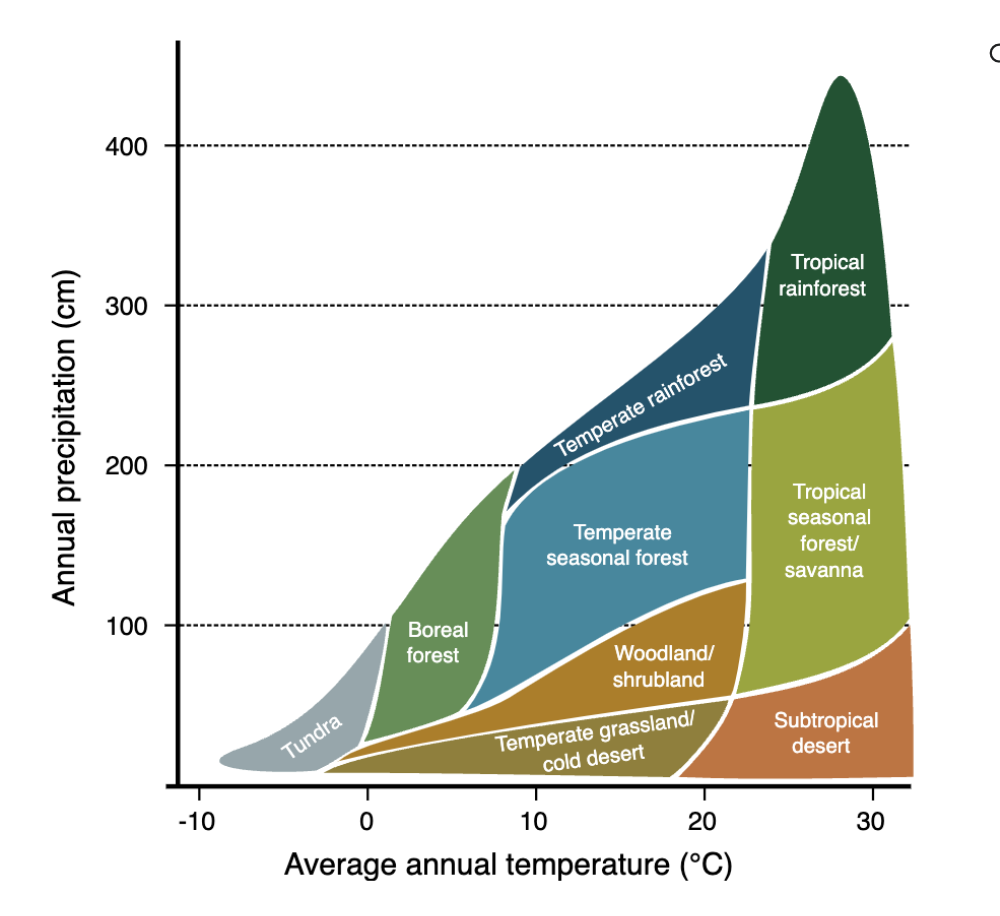
If a region receives a mean annual rainfall of 1000 mm and has a mean annual temperature of 30°C, what is the most likely biome for this region?
A. Tropical rainforest
B. Tropical desert
C. Temperate rainforest
D. Tropical savanna
D. Tropical savanna
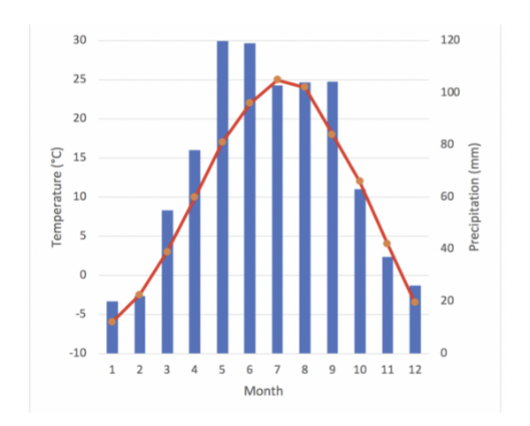
Which biome is most likely represented by this climatograph, where the red line shows temperature, and the bars represent precipitation?
A. Tropical Rainforest
B. Boreal forest
C. Tropical Savanna
D. Temperate Grassland
D. Temperate Grassland
Which of the following statements correctly describes the difference in soil texture and fertility between basalt-derived and granite-derived soils?
A. Basalt-derived soils are clay-rich and more fertile.
B. Basalt-derived soils are sandy and less fertile.
C. Granite-derived soils are clay-rich and more fertile.
D. Granite-derived soils are clay-rich and less fertile.
A. Basalt-derived soils are clay-rich and more fertile.
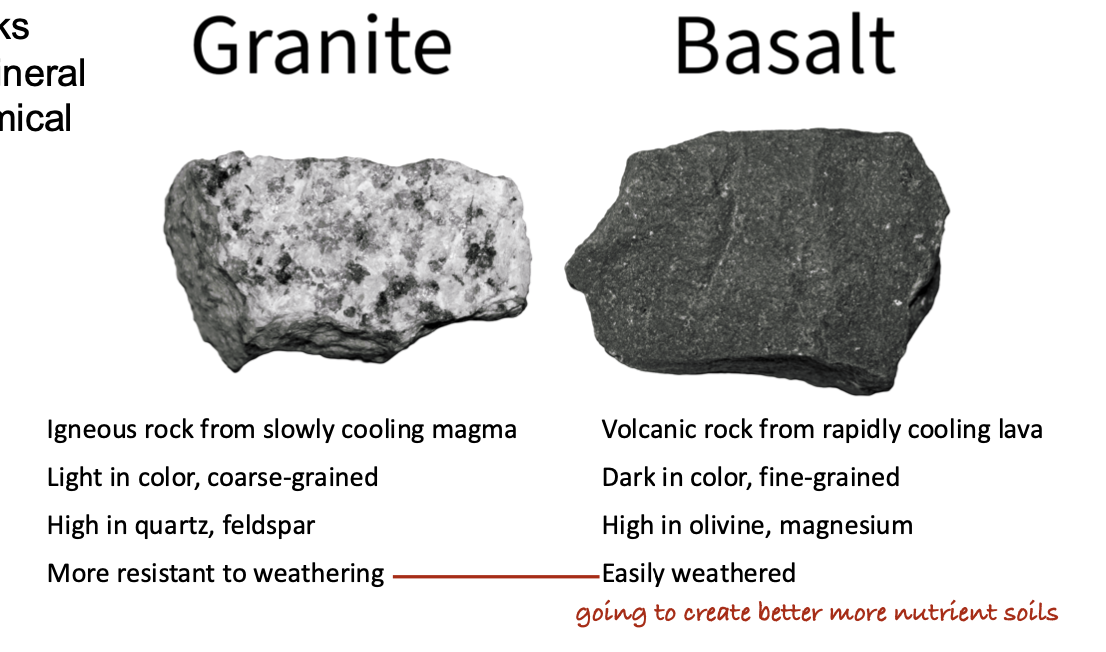
Which of the following statements about the role of parent materials in soil formation is correct?
A. Parent materials are only important in the early stages of soil formation.
B. Parent materials largely determine soil texture and mineral content.
C. Parent materials has limited influence on the accumulation of soil organic matter.
D. Parent materials are an active factor that influence soil formation
B. Parent materials largely determine soil texture and mineral content.
Which type of parent materials tends to form less fertile soils?
A. Alluvium
B. Colluvium
C. Loess
D. Lacustrine deposit
D. Lacustrine deposit
Alluvium is rivers - renewed and fertile
Colluvium is gravity - depends on rock type
Loess - wild blown, fine, and fertile
Lacusterine Deposit - Lakebottom and leached

Soils from which of the following states are more likely to have greater humus accumulation?
A. Nevada
B. Utah
C. Colorado
D. Virginia
D. Virginia
Humus is contributed to soils by plants, as well as by mycorrhizal fungi, microbes, and soil fauna. It retains water, nutrients, and stores carbon.
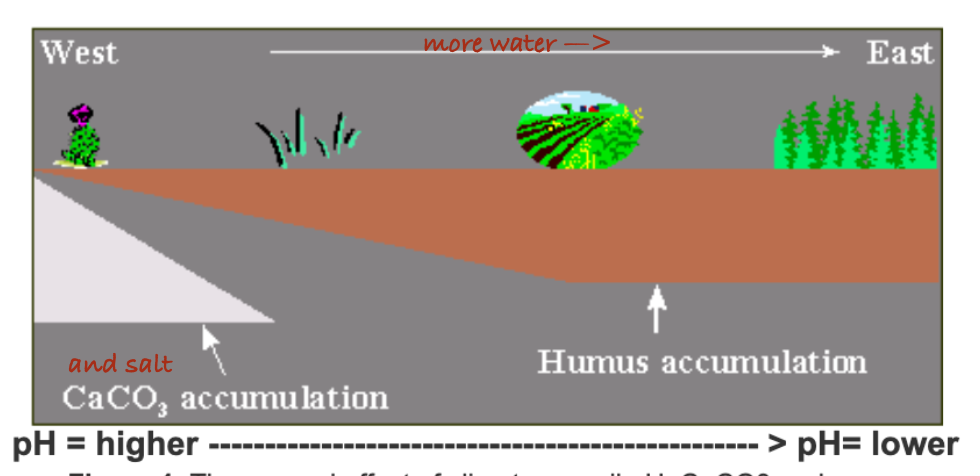
Soils in warm environments are best characterized by:
A. Strong physical weathering, slow organic matter decay.
B. Strong chemical weathering, slow organic matter decay.
C. Strong chemical weathering, rapid organic matter decay.
D. Strong physical weathering, rapid organic matter decay
C. Strong chemical weathering, rapid organic matter decay.

Soils of _______ degrees of weathering and soil development tend to be more fertile.
A. Low
B. Intermediate
C. High
D. Soil development is not related to fertility
B. Intermediate
If it was high the soils would be subjected to leaching and reduced fertility.
Based on information provided by the soil family, please identity the soil order of these four soils (in the order of Soil A, Soil B, Soil C, and Soil D)?
A. Histosol, Mollisol, Spodosol, Oxisol
B. Gelisol, Andisol, Spodosol, Ultisol
C. Histosol, Aridisol, Mollisol, Inceptisol
D. Entisol, Vertisol, Inceptisol, Oxisol
A. Histosol, Mollisol, Spodosol, Oxisol
What is the primary soil condition that contributes to the formation of a thick O-horizon in Soil A?
A. High soil clay content
B. Poorly drained soils
C. Warm soil temperature
D. High soil nutrient availability
B. Poorly drained soils
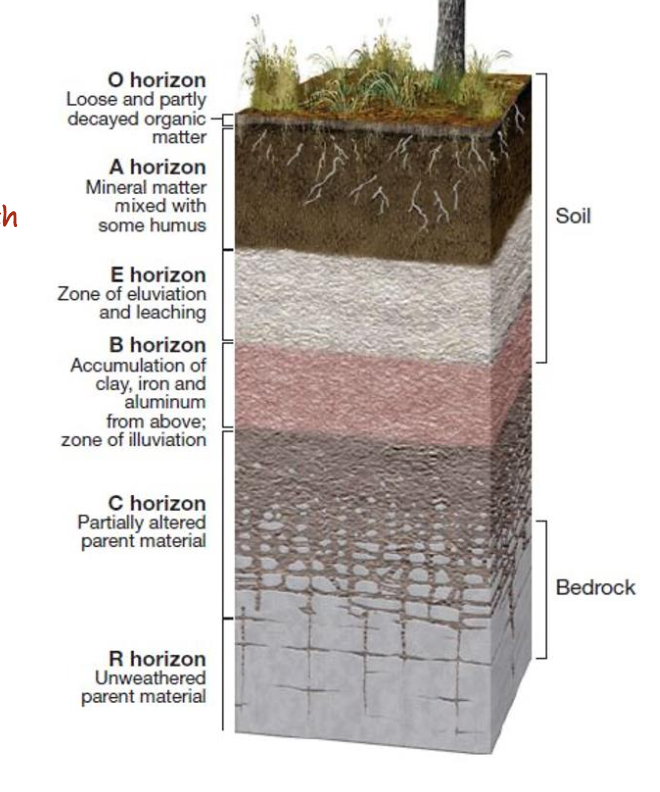
Among these four soils, three exhibit a B-horizon. What does the term 'B-horizon' signify?
A. The accumulation of organic matter
B. The accumulation of minerals mixed with organic matter
C. The leaching of silicate clay, iron, and aluminum
D. The accumulation of silicate clay, iron, and aluminum
D. The accumulation of silicate clay, iron, and aluminum
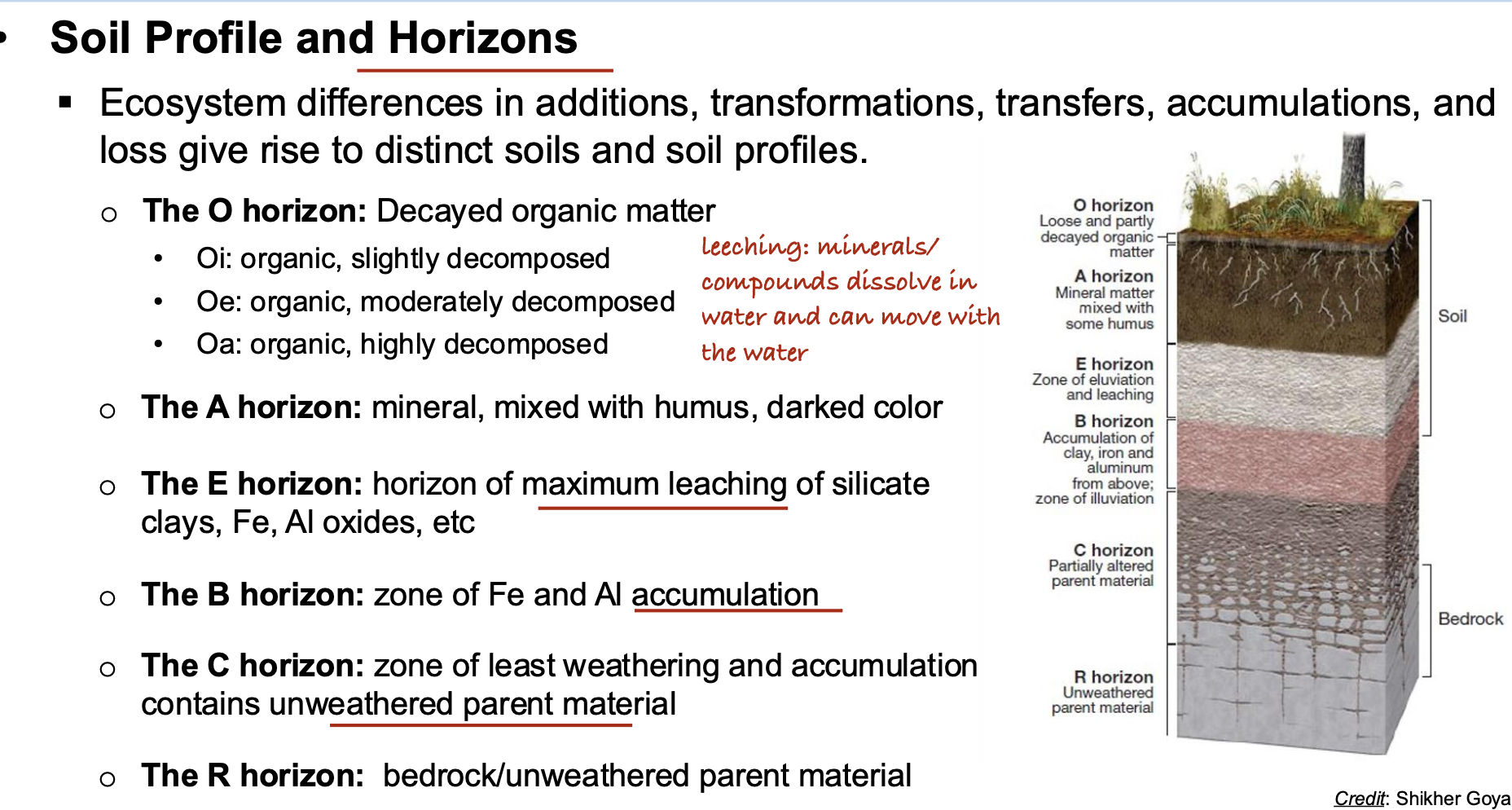
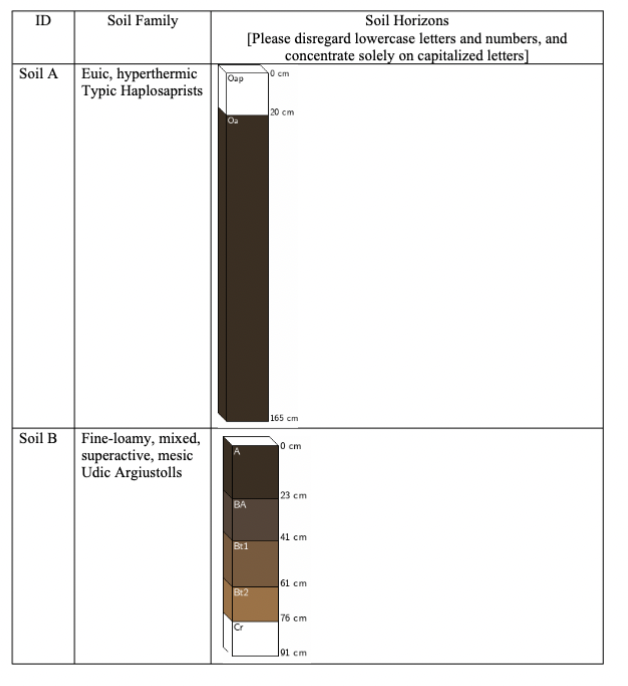
What vegetation type is most likely associated with soil B?
A. Grassland
B. Coniferous forest
C. Deciduous forest
D. Shrubland
A. Grassland ??
Its a Mollisol, which is because of the dark A Horizon full of organic material.

Which of the soils exhibited the highest degree of weathering and soil development?
A. Soil A
B. Soil B
C. Soil C
D. Soil D
D. Soil D
It has the smallest C Horizon, the most defined horizons, and is an Oxisol (highly weathered)
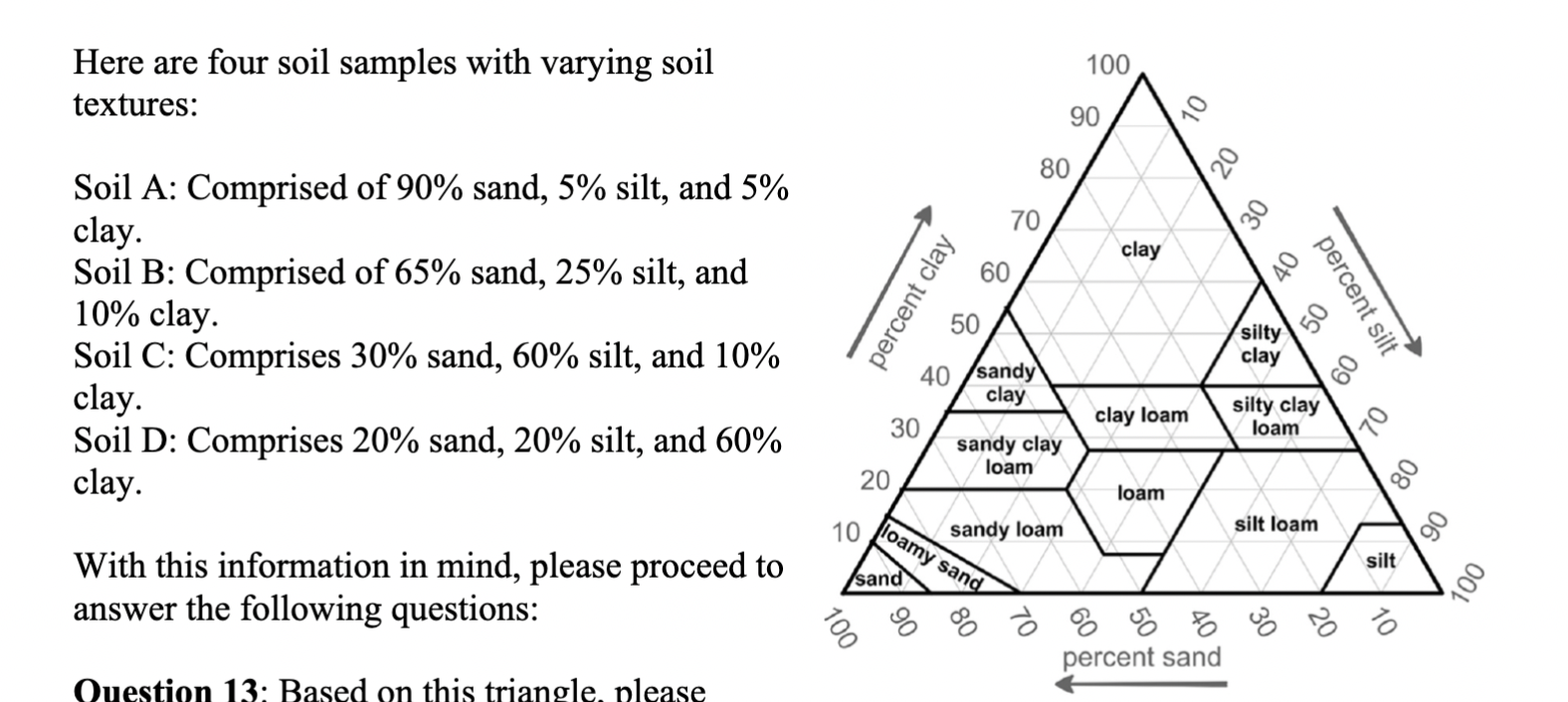
Based on this triangle, please
identify the soil types for these four soils (in the order of soil A, soil B, soil C, and soil D).
A. Sand, Loam, Silt Loam, Clay
B. Sand, Sandy Loam, Silt loam, Clay
C. Sand, Sandy clay loam, Loam, Clay
D. Loamy sand, Sandy loam, Silt Loam, Silt
B. Sand, Sandy Loam, Silt loam, Clay
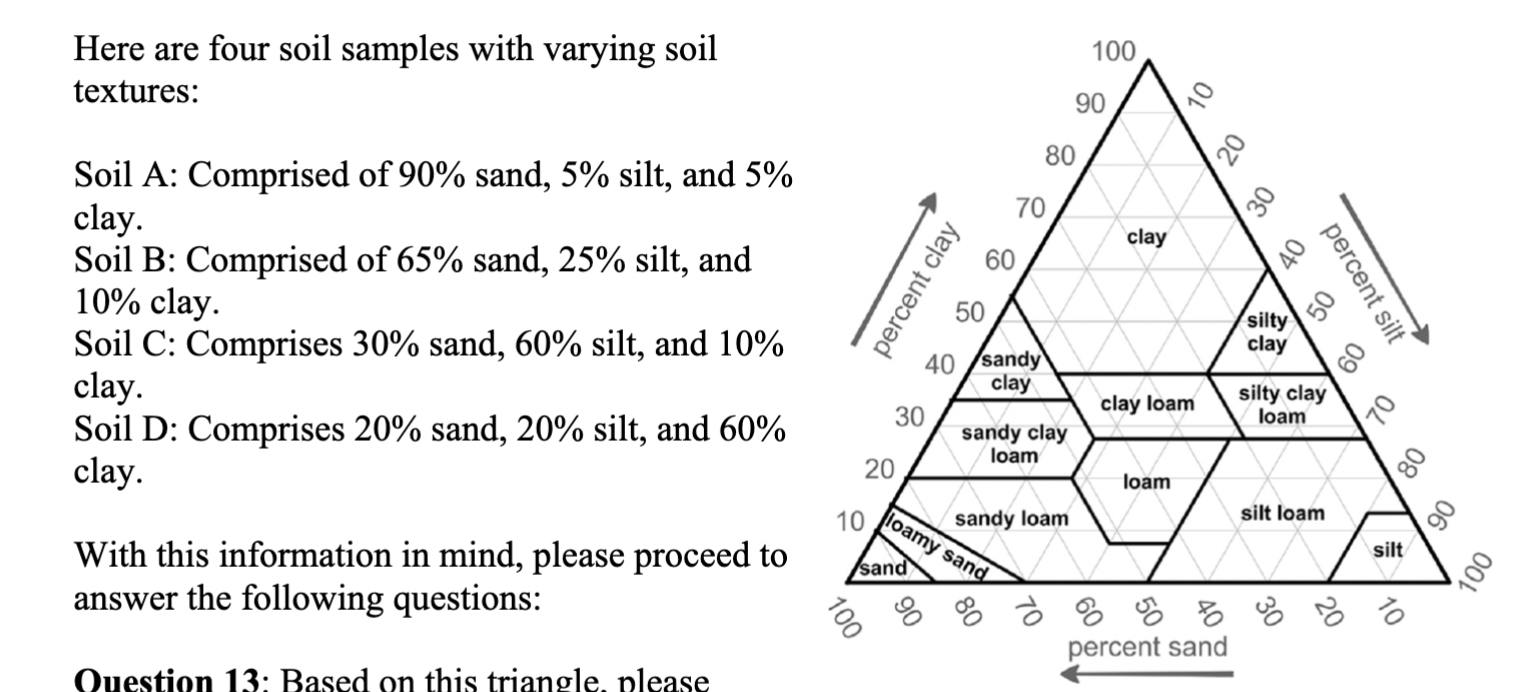
Which of these four soils has the lowest water holding capacity?
A. Soil A
B. Soil B
C. Soil C
D. Soil D
A. Soild A
Cuz its sand?
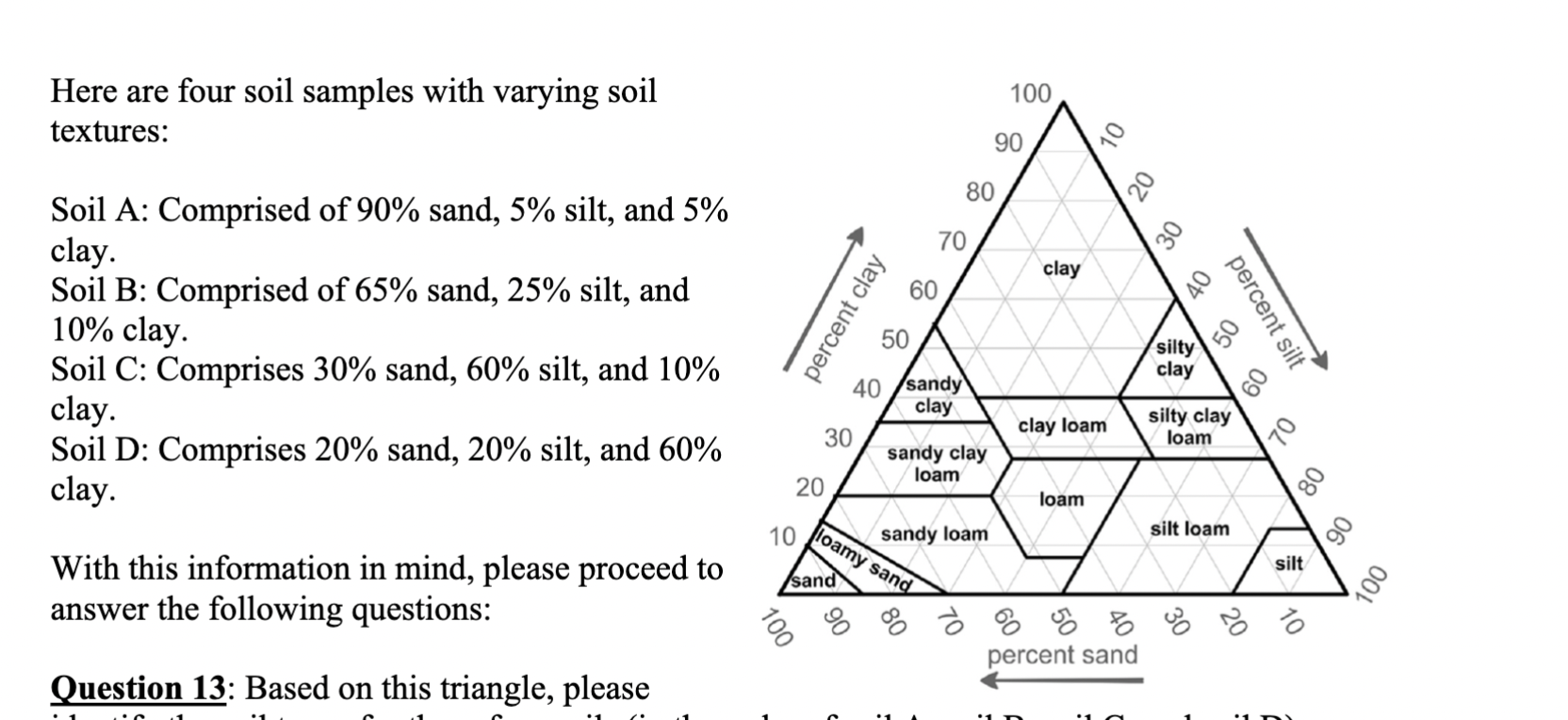
If we only consider soil texture, which of these four soils would likely exhibit the
highest cation exchange capacity?
A. Soil A
B. Soil B
C. Soil C
D. Soil D
D. Soil D
Cuz its clay?
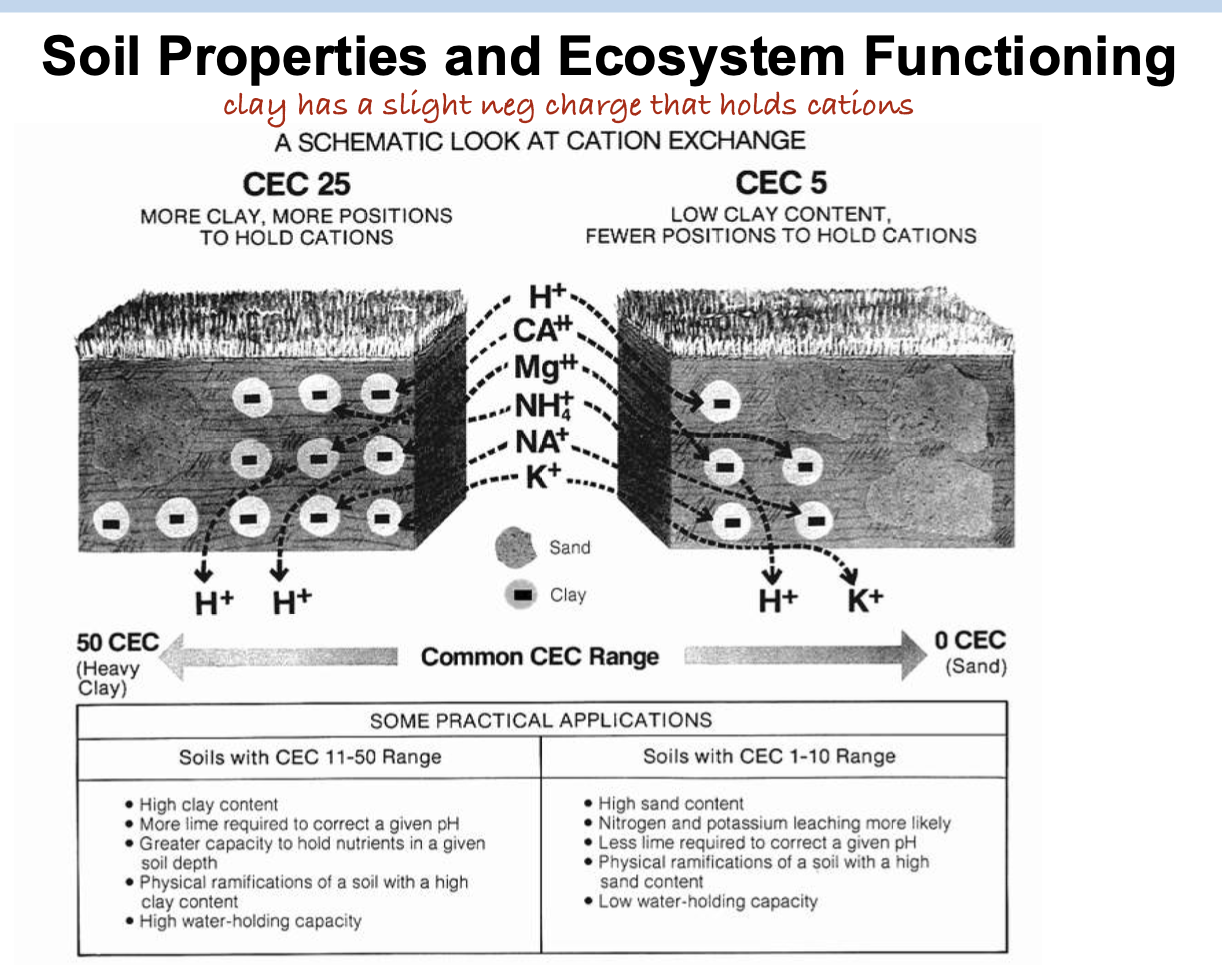
Which of the following is not an environmental or physiological factor driving the evolution of the C4 photosynthesis pathway?
A. Hot, arid, and saline environments
B. Low atmospheric CO2 environment
C. To reduce water loss during CO2 uptake
D. To facilitate photorespiration
D. To facilitate photorespiration
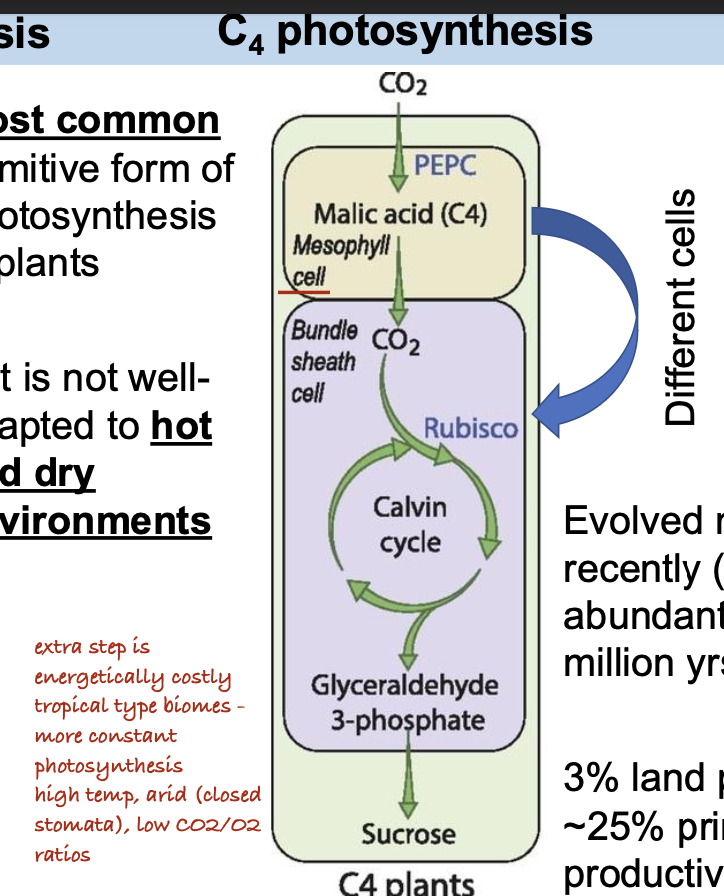
In which of the following cells do C4 plants take up CO2?
A. Bundle sheath cells
B. Mesophyll cells
C. Stomatal cells
D. Xylem cells
B. Mesophyll cells
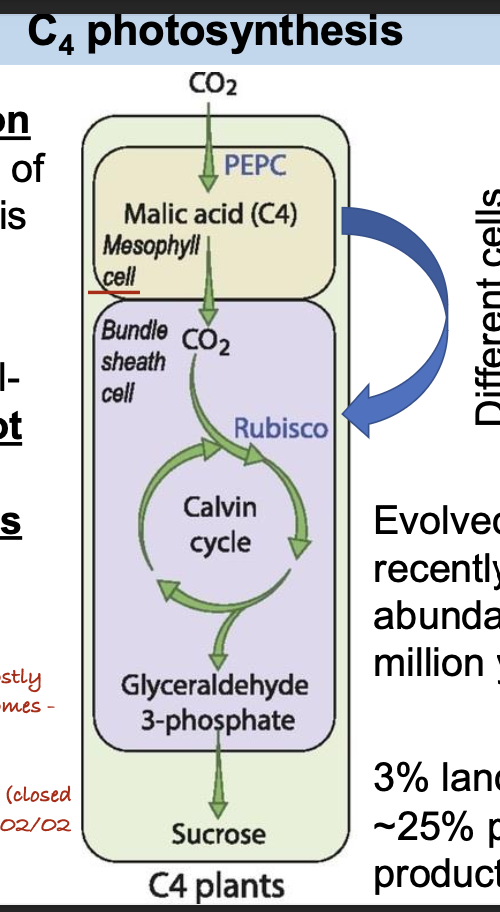
What is the term for the light level at which the amount of carbon fixed from photosynthesis is only enough to support plant respiration?
A. Light limitation
B. Light compensation
C. Light saturation
D. Photo-oxidation
B. Light compensation
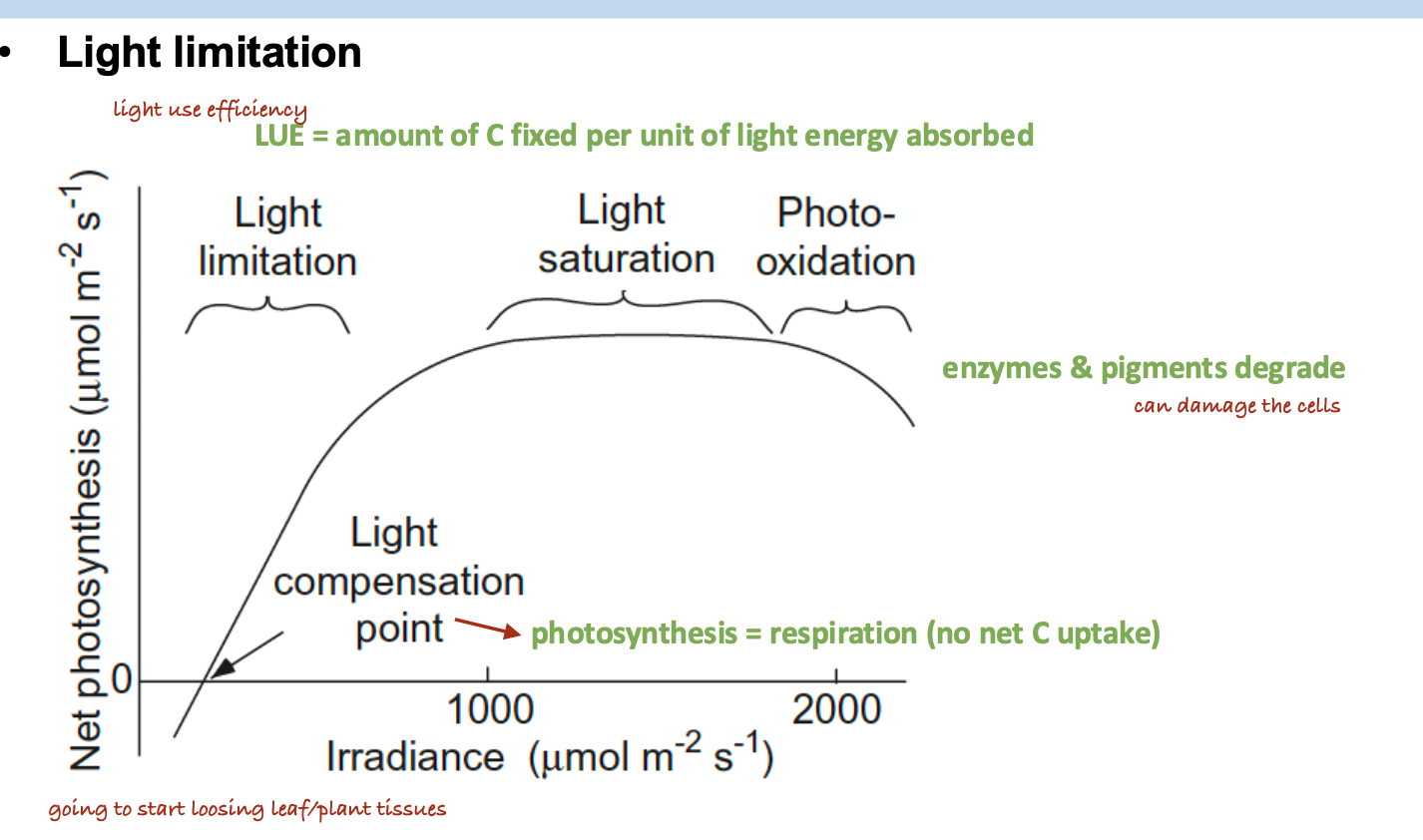
What is the primary advantage of C4 plants in hot and dry environments with limited water availability?
A. They absorb CO2 during the night and then close their stomata during the day to conserve water in hot and dry environments.
B. They have a greater ability to extract water from the soils even in hot and dry environment.
C. They have higher water use efficiency due to their ability to capture carbon dioxide efficiently while minimizing water loss.
D. They require less sunlight for photosynthesis in hot and dry environments.
C. They have higher water use efficiency due to their ability to capture carbon dioxide efficiently while minimizing water loss.
CAM has temporal separation (night/day)
Why do C3 plants benefit more from increasing atmospheric CO2 levels compared to C4 plants?
A. C3 plants have a higher rate of photorespiration, which is reduced by higher CO2 levels, leading to increased photosynthetic efficiency.
B. C3 plants use a different type of chlorophyll that becomes more efficient under higher CO2 conditions.
C. C3 plants are generally less adapted to high temperatures, and increased CO2 helps them to better withstand heat stress.
D. C3 plants can fix nitrogen more efficiently at higher CO2 concentrations, giving them a competitive edge over C4 plants
A. C3 plants have a higher rate of photorespiration, which is reduced by higher CO2 levels, leading to increased photosynthetic efficiency.
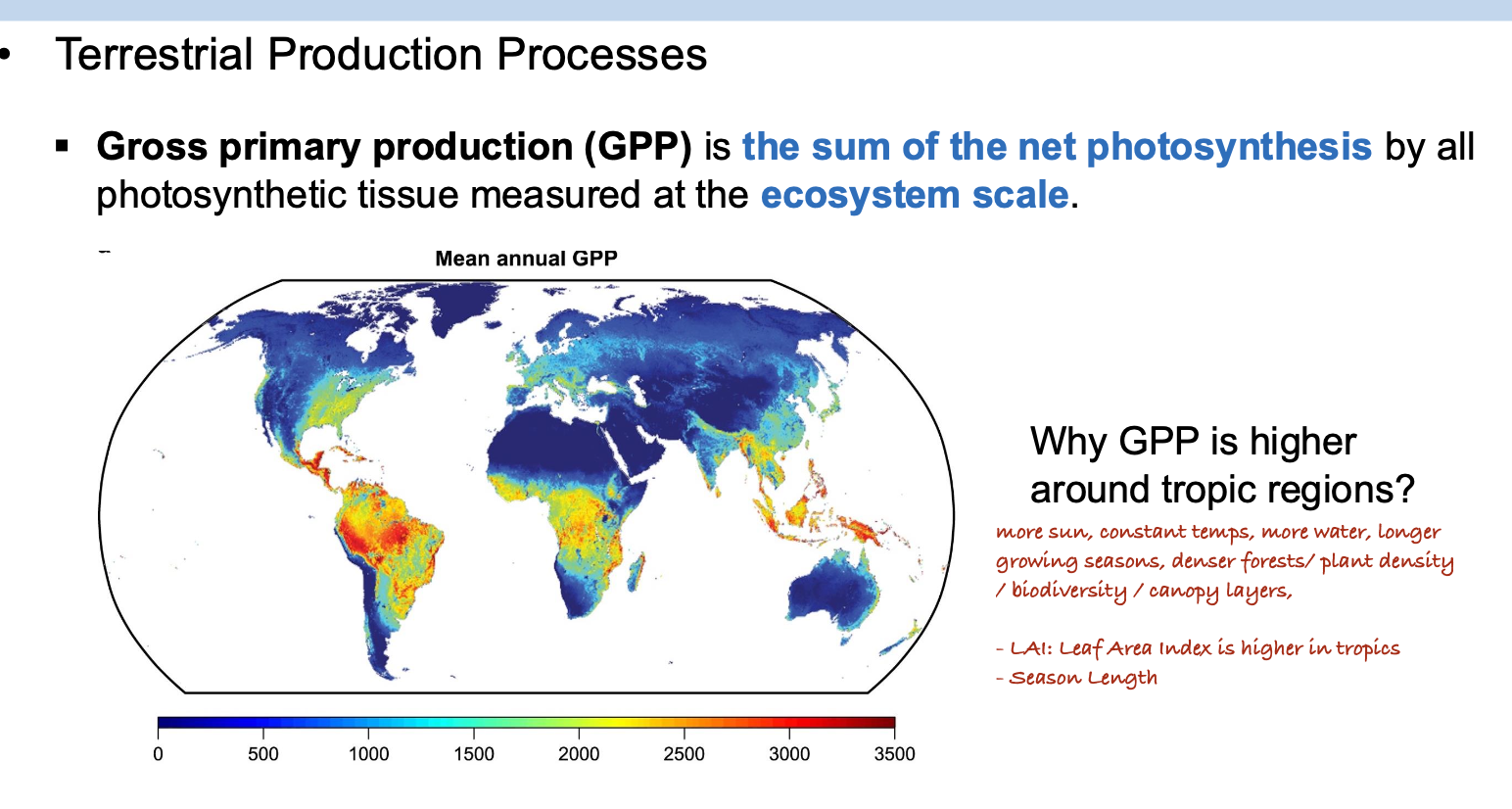
What are the primary factors determining the amount of gross primary production in a given ecosystem? In other words, why do tropical forests have higher GPP compared to other ecosystems?
A. Leaf area and season length
B. Temperature and light
C. CO2 and nutrients
D. Rainfall and light
A. Leaf area and season length
Picture an ecosystem located in the northern hemisphere. In the year 2021, the GPP of this ecosystem amounted to 2000 g C m-2 yr-1. Approximately 45% of this GPP was transformed into NPP. The resident animals within the ecosystem collectively consumed and respired a total of 315 g C m-2 yr-1, while soil microbes in the area consumed and respired 485 g C m-2 yr-1. Additionally, about 5% of the NPP was lost through leaching in the form of dissolved organic matter.
What was the net balance of carbon in 2021?
A. 45 g C m-2 yr-1
B. 55 g C m-2 yr-1
C. -45 g C m-2 yr-1
D. -55 g C m-2 yr-1
45×2000 = 900 (NPP)
NEP = 900 - (315+485+(.05×1100)) = 55 g C
B. 55 g C m-2 yr-1

Picture an ecosystem located in the northern hemisphere. In the year 2021, the GPP of this ecosystem amounted to 2000 g C m-2 yr-1. Approximately 45% of this GPP was transformed into NPP. The resident animals within the ecosystem collectively consumed and respired a total of 315 g C m-2 yr-1, while soil microbes in the area consumed and respired 485 g C m-2 yr-1. Additionally, about 5% of the NPP was lost through leaching in the form of dissolved organic matter.The ecosystem maintained consistent production processes throughout 2022. NEP was calculated to be 55 g C m^-2 yr^-1.
However, at the end of that year, a wildfire occurred within the ecosystem, resulting in the release of 100 g C m-2 yr-1 into the atmosphere. What was the net balance of carbon in 2022?
A. 45 g C m-2 yr-1
B. 55 g C m-2 yr-1
C. -45 g C m-2 yr-1
D. -55 g C m-2 yr-1
55 - 100 = -45 g C
C. -45 g C m-2 yr-1
Regarding the global carbon cycle, which of the following statements are correct?
[Select all that apply]
A. Most of the carbon on Earth is stored in pools that are not actively participating in the global carbon cycle.
B. The amount of carbon within different carbon pools remains constant over time.
C. The carbon cycle involves the movement of carbon between different pools without altering its chemical form.
D. Human activities can significantly modify the amounts of carbon residing in various carbon pools
A. Most of the carbon on Earth is stored in pools that are not actively participating in the global carbon cycle. (Ocean sediment, fossil fuels, rocks, soil)
D. Human activities can significantly modify the amounts of carbon residing in various carbon pools
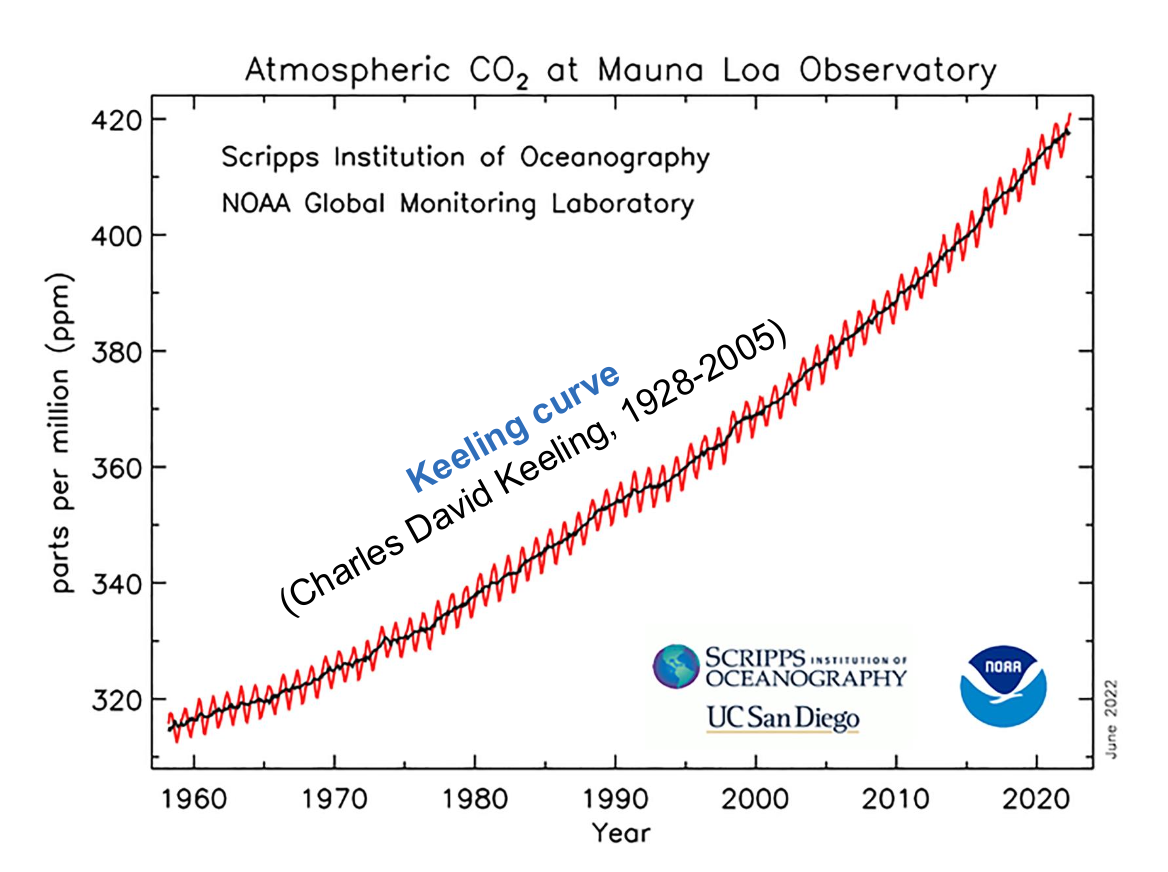
Charles David Keeling began monitoring atmospheric CO2 concentrations at the Mauna Loa Observatory in 1958, leading to the development of the Keeling Curve. What is the primary factor driving the upward trend in atmospheric CO2 concentrations?
A. Fossil fuel combustion
B. Deforestation
C. Agricultural expansion
D. Urbanization and mining
A. Fossil fuel combustion
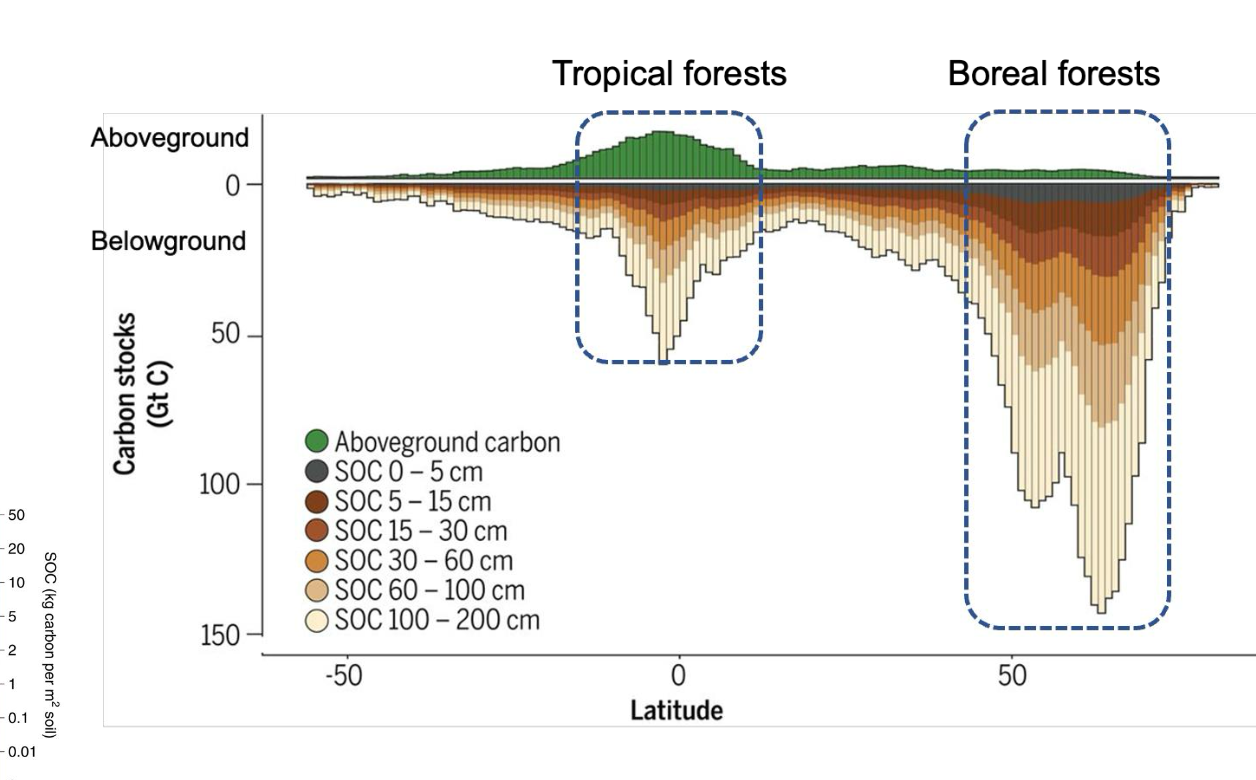
Boreal forests contribute the most to the global terrestrial carbon sink. Which of the following statements about the carbon cycle of boreal forests are correct? [Select all that apply]
A. Boreal forests have incredibly high net primary productivity, which leads to the accumulation of carbon in plant biomass.
B. Boreal forests are extensively distributed in environments with low temperatures, which reduce the decomposition of plant litter and facilitate the accumulation of carbon in soils.
C. Boreal forests generally produce high-quality litter that facilitates decomposition by microbes and the formation of relatively high proportions of mineral-associated organic matter throughout the soil profile.
D. Boreal forests generally produce low-quality litter with slow decomposition rates, resulting in the accumulation of a thick layer of organic matter composed mainly of particulate organic matter
B. Boreal forests are extensively distributed in environments with low temperatures, which reduce the decomposition of plant litter and facilitate the accumulation of carbon in soils.
D. Boreal forests generally produce low-quality litter with slow decomposition rates, resulting in the accumulation of a thick layer of organic matter composed mainly of particulate organic matter
Dryland ecosystems contribute the most to the interannual variation in global terrestrial carbon sink. What are the primary factors driving this variation? [Select all that apply]
A. The gross primary productivity of dryland ecosystems is highly dependent on rainfall, which fluctuates significantly from year to year.
B. Dryland ecosystems have dense vegetation and relatively high gross primary productivity, which are sensitive to changes in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
C. Dryland ecosystems experience significant temperature variation, which influences the rate of heterotrophic respiration of these ecosystems.
D. Carbon stored in dryland ecosystems, particularly aboveground carbon, is vulnerable to disturbances such as fires
A. The gross primary productivity of dryland ecosystems is highly dependent on rainfall, which fluctuates significantly from year to year.
D. Carbon stored in dryland ecosystems, particularly aboveground carbon, is vulnerable to disturbances such as fires
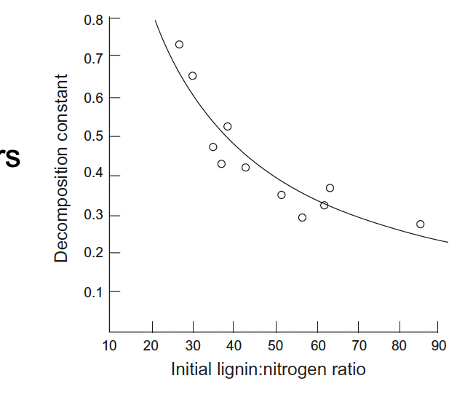
Which of the following types of litter is most likely to decompose quickly?
A. Litter C: N ratio of 10, litter lignin: N ratio of 30
B. Litter C: N ratio of 10, litter lignin: N ratio of 40
C. Litter C: N ratio of 20, litter lignin: N ratio of 30
D. Litter C: N ratio of 20, litter lignin: N ratio of 40
A. Litter C: N ratio of 10, litter lignin: N ratio of 30
Lignin is the complex substance that makes up cell walls and provides plants with stiff structure (like wood and bark). It is really easy for fungi to decompose while bacteria better decompose simpler sugars.
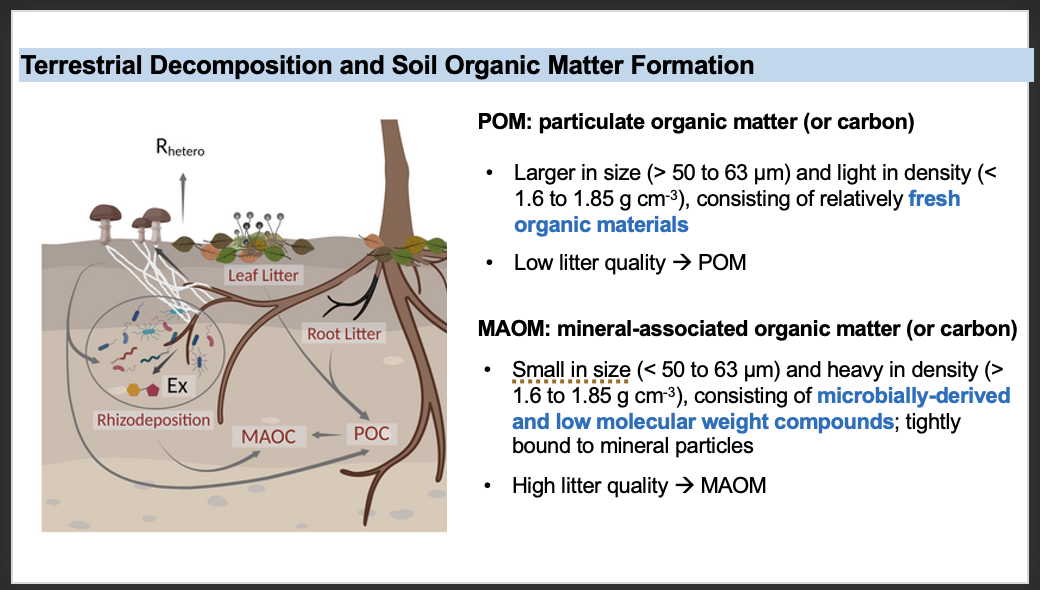
Compared to particulate organic matter, mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOM) has a higher potential for long-term carbon storage. What is the primary factor for this?
A. MAOM primarily comprises recalcitrant and undecomposed plant materials that can be stored for the long term.
B. MAOM is generally large in size and not easily broken down by soil microbes, which contributes to its long-term storage.
C. MAOM primarily consists of microbially derived carbon that is tightly bound to mineral particles, protecting it from further decomposition and enabling long-term storage.
D. MAOM is generally low in density, which facilitates its storage in soils and enhances its long-term carbon sequestration potential.
C. MAOM primarily consists of microbially derived carbon that is tightly bound to mineral particles, protecting it from further decomposition and enabling long-term storage.
A rancher wants to determine the amount of carbon stored in an 8-hectare rangeland. The rancher hired a scientist who made the following measurements:
• Aboveground biomass: 20 Mg C/ha
• Aboveground litter: 5 Mg C/ha
• Belowground biomass: 30 Mg C/ha
• Soil carbon storage (0-100 cm): 70 Mg C/ha
Based on these measurements, what is the total carbon storage of this rangeland? Note: Mg refer to megagram, 1 Mg = 1 ton (metric)
A. 1200 Mg C
B. 1000 Mg C
C. 800 Mg C
D. 600 Mg C
B. 1000 Mg C
(20 + 5 + 30 + 70) Mg C/ha x 8 hectare = 1000 Mg C
Regarding biological nitrogen fixation, which of the following statement is correct?
A. Biological nitrogen fixation rate is generally limited by the availability of dinitrogen gas as the substrate.
B. Symbiotic microorganisms that carry out biological nitrogen fixation obtain the required energy from decomposing organic matter.
C. The rate of biological nitrogen fixation is generally higher in alkaline soils compared to slightly acidic soils.
D. The synthesis and functioning of the nitrogenase enzyme generally require metal cofactors such as iron and molybdenum
D. The synthesis and functioning of the nitrogenase enzyme generally require metal cofactors such as iron and molybdenum

Which of the following groups of living organisms plays a significant role in the nitrogen mineralization process?
A. Rhizobium bacteria
B. Ammonia-oxidizing archaea
C. Pseudomonas bacteria
D. Blue green algae
C. Pseudomonas bacteria
(Mineralization is taking inorganic N2 into organic Nitrate - Rhizobium Bacteria are responsible for N Fixation)
Which of the following nitrogen cycling processes requires a strictly anaerobic environment?
A. Ammonification
B. Nitrification
C. Assimilation
D. Denitrification
D. Denitrification
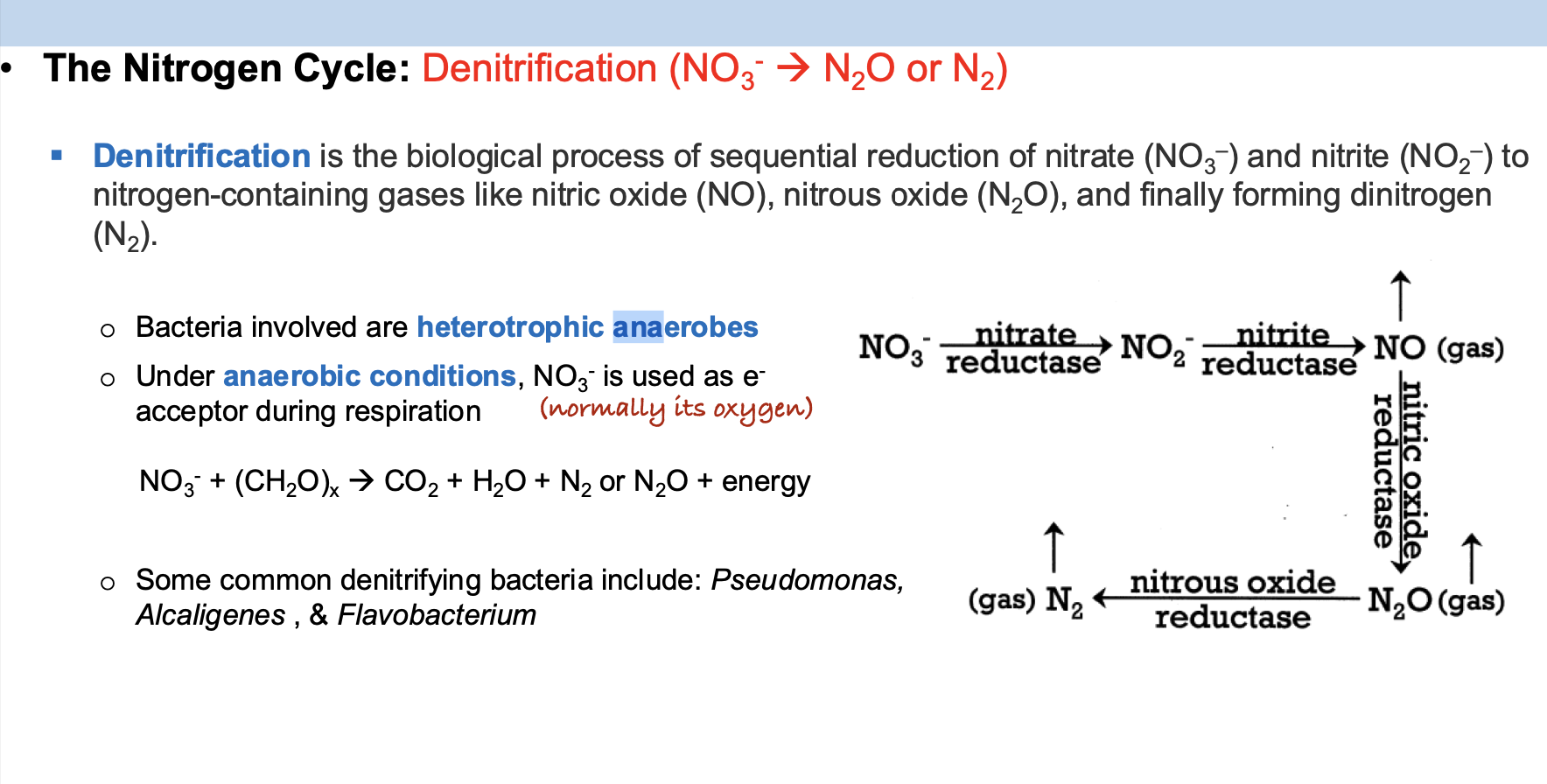
Bacteria involved in the denitrification process use which of the following as the electron acceptor during respiration?
A. NO3-
B. NH4+
C. N2
D. N2O
A. NO3-
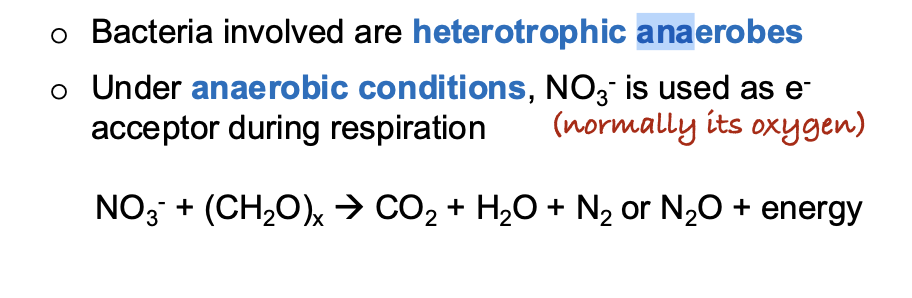
Which of the following nitrogen cycling processes is responsible for the production
of nitrous oxide (N₂O), a potent greenhouse gas?
A. Ammonification
B. Nitrification
C. Assimilation
D. Denitrification
D. Denitrification
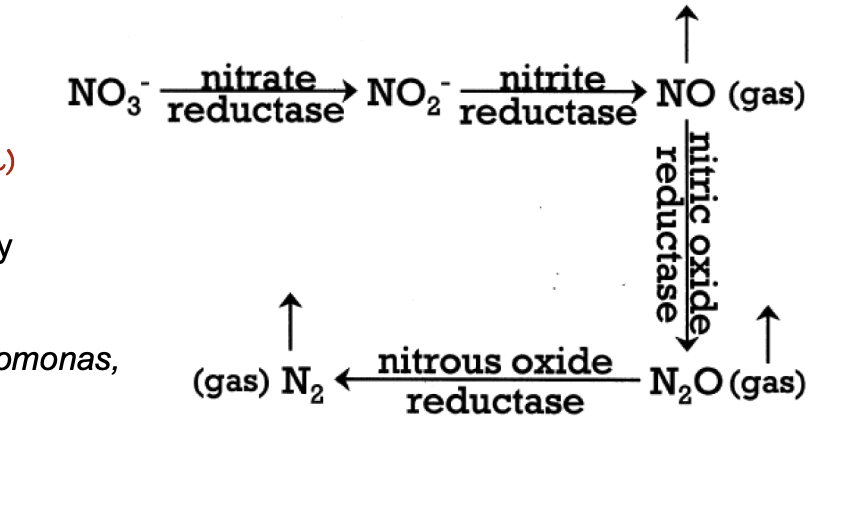
What is the primary source of nitrogen absorbed by plants?
A. Fixation
B. Deposition
C. Weathering
D. Recycling
D. Recycling
Ex: Decomposition, nitrification, things that keep N available (?)
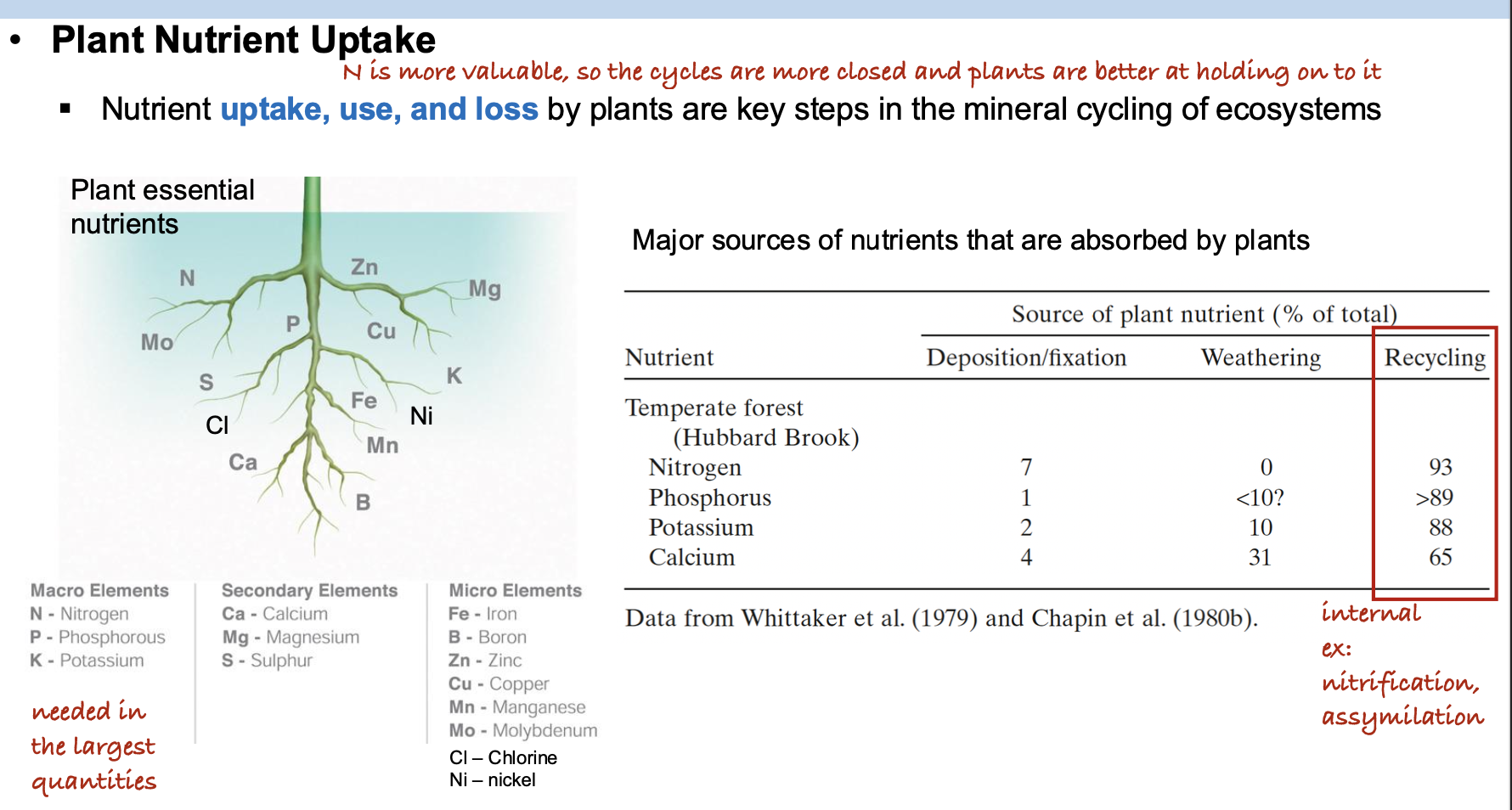
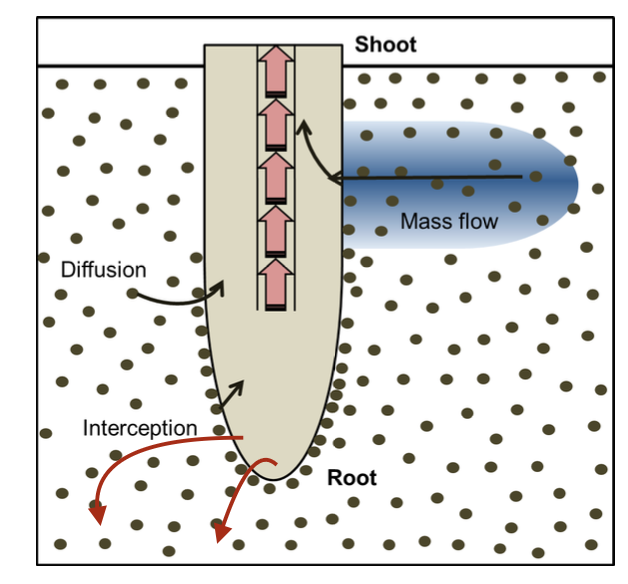
In a natural ecosystem, what is the primary mechanism by which calcium moves to
the root surface?
A. Diffusion
B. Mass flow
C. Root interception
D. Transpiration
B. Mass flow

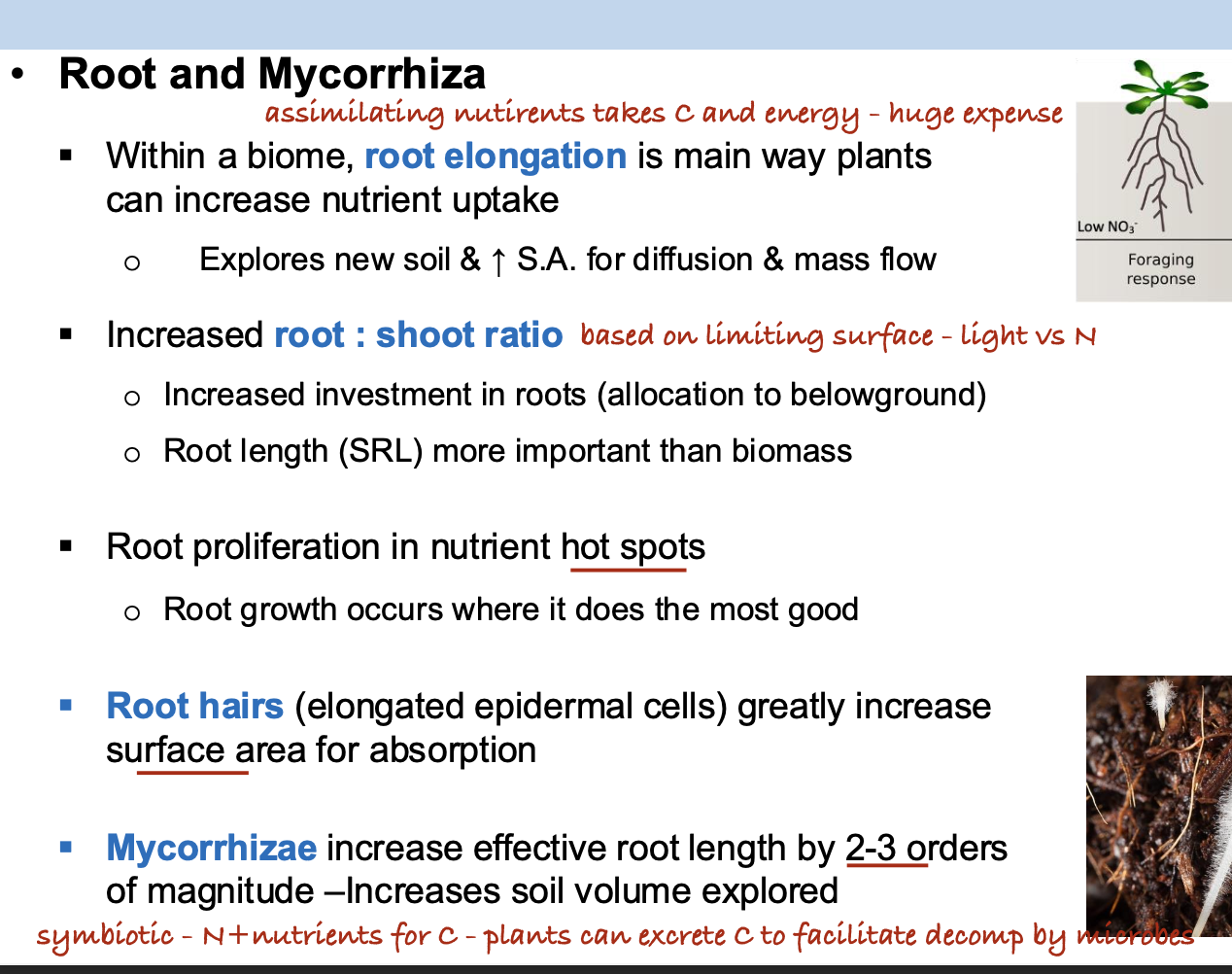
Which of the following statements regarding the role of roots in nutrient uptake are correct? [Select all that apply]
A. Root elongation is a primary method through which plants can enhance nutrient uptake.
B. In nutrient-limited environments, plants tend to exhibit a lower root-to-shoot ratio compared to nutrient-rich environments.
C. Plant tends to grow more root biomass in nutrient-rich hotspots within the soil profile.
D. Both root hairs and root mycorrhizal associations can effectively increase the root surface area for nutrient absorption.
A. Root elongation is a primary method through which plants can enhance nutrient uptake.
C. Plant tends to grow more root biomass in nutrient-rich hotspots within the soil profile.
D. Both root hairs and root mycorrhizal associations can effectively increase the root surface area for nutrient absorption.
The invasion of cheatgrass into a sagebrush ecosystem has the potential to enhance nitrogen cycling processes and establish positive plant-soil feedback that facilitates its invasion. Which of the following statements are correct regarding this process? [Select all that apply]
A. Soils under cheatgrass have been shown to exhibit a higher net nitrogen mineralization rate compared to soils under sagebrush, releasing more available nitrogen for cheatgrass uptake.
B. Under the same conditions of nitrogen availability, cheatgrass has been shown to take up more nitrogen compared to perennials, particularly for nitrate (NO3-)
C. Cheatgrass has been shown to release more nitrogen from its root exudates, which facilitates nitrogen mineralization and the availability of nitrogen.
D. Cheatgrass has been shown to be associated with a higher abundance of denitrifying bacteria, facilitating the denitrification process and promoting nitrogen availability.
I feel like and found examples of all of them in the slides.
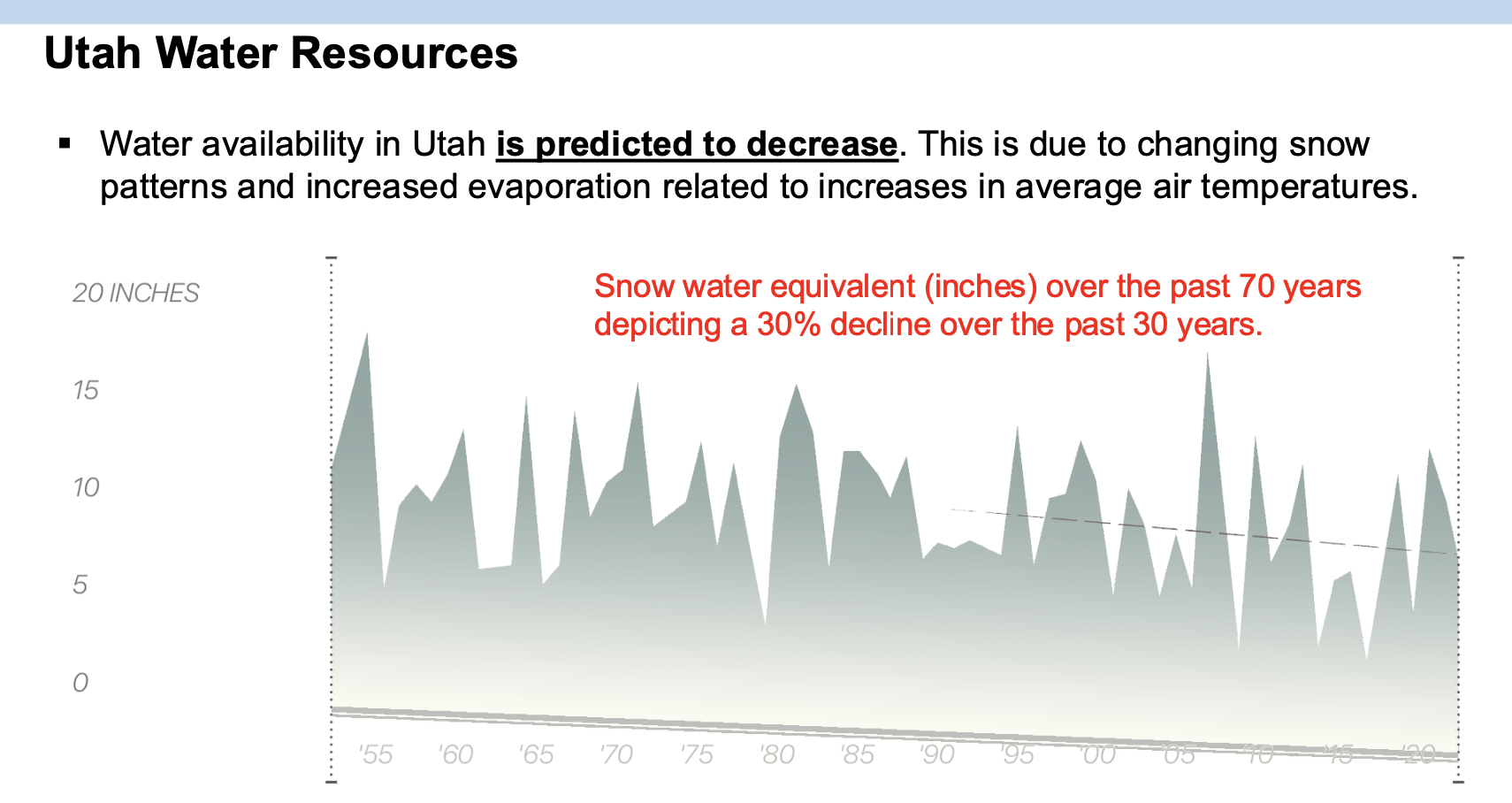
Which of the following factors is most likely to have contributed to the shrinking of the Great Salt Lake in recent years?
A. Increased water consumption for agriculture and urban use
B. Increased climate fluctuations and reduced precipitation
C. Increased diversion of water from rivers feeding the lake
D. Increased evapotranspiration from forest ecosystems
B. Increased climate fluctuations and reduced precipitation
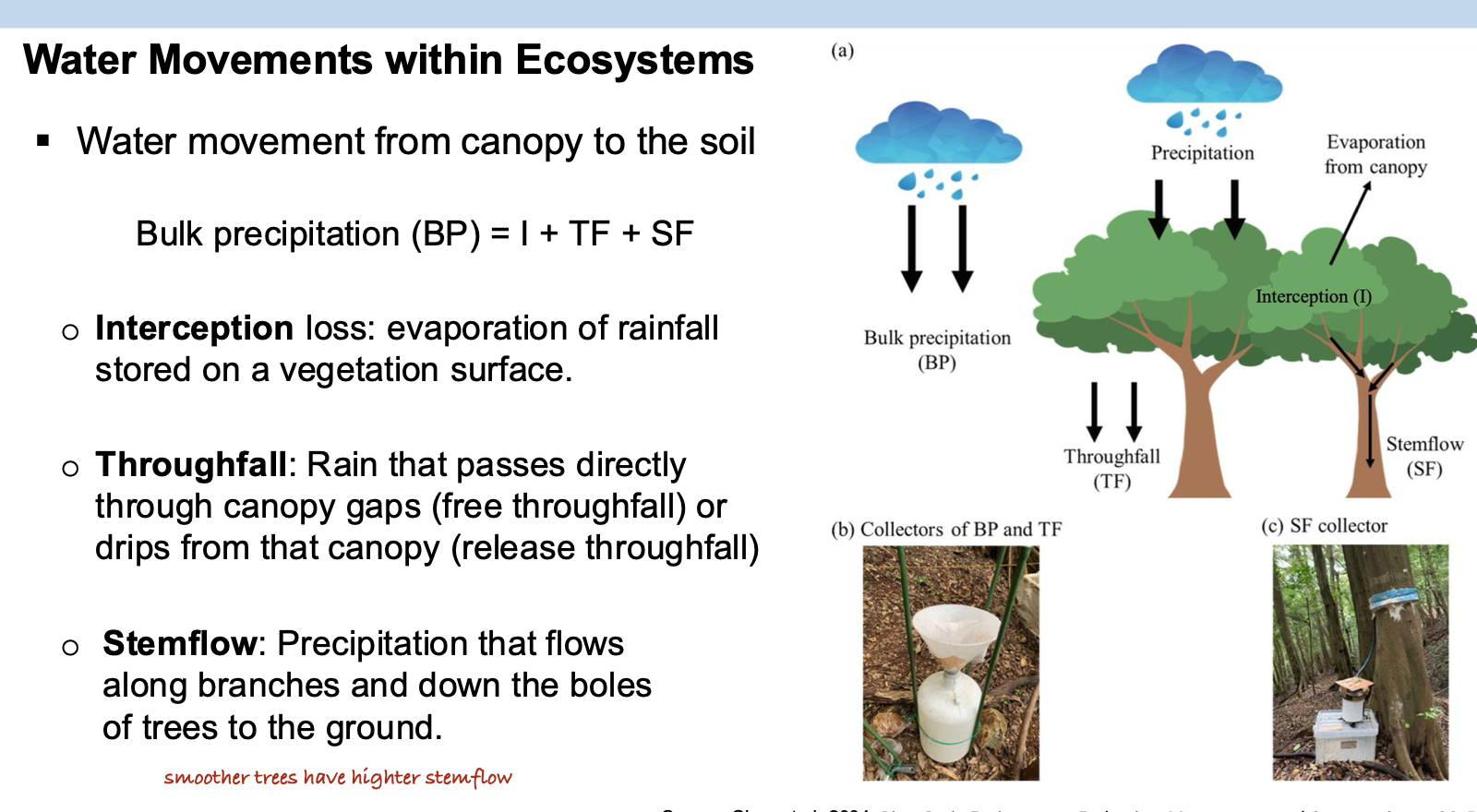
During a rainfall event in a temperate forest, the forest received a total of 30 mm of rainfall. Of this, 4 mm was intercepted by the forest canopy, 18 mm passed through as throughfall, and 8 mm was collected as stemflow.
What’s the amount of rainfall that reaches the forest floor?
A. 8 mm
B. 14 mm
C. 18 mm
D. 26 mm
D. 26 mm
8 mm + 18 mm = 26 that reaches the ground
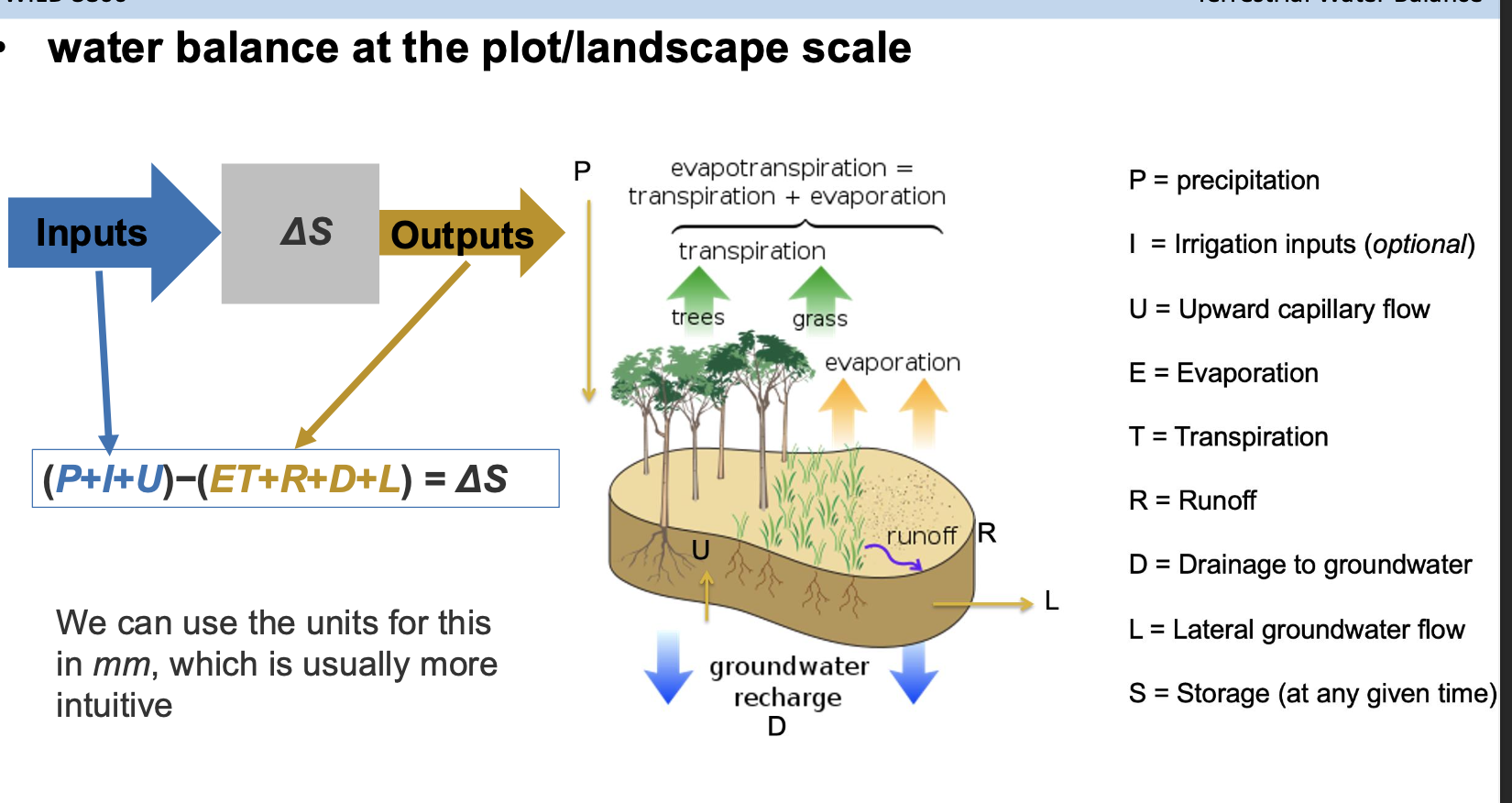
After 26 mm of rainfall reaches the forest floor, 40% of it infiltrated the
soil, transforming unsaturated soil into saturated conditions. Once the soils became saturated, an
additional 20% percolated into the groundwater. Concurrently, during this rainfall event, 4.4 mm
were lost through evapotranspiration. Assume no other water inputs apart from this rainfall, with
the remaining water being lost as runoff.
Please determine the amount of water lost as runoff.
A. 4 mm
B. 6 mm
C. 8 mm
D. 10 mm
B. 6 mm
26 - (26x.4) - (26x.2) - 4.4 = 6 mm
Which of the following correctly describes the process of water movement through plants?
A. The water potential of unsaturated air outside leaves is lower than that of saturated air inside leaves, which drives transpiration and water movement through the plant.
B. The vapor-pressure gradient between the root and the soil is the primary driving force for water movement through plants.
C. Water movement through plants is primarily driven by xylem pressure, which pushes water from the root to the leaves.
D. Water is transported from the roots to the leaves due to the pressure created by soil moisture, which is then balanced by water potential gradients.
A. The water potential of unsaturated air outside leaves is lower than that of saturated air inside leaves, which drives transpiration and water movement through the plant.

What is the term for the maximum amount of water that soil can retain against the force of gravity?
A. Wilting point
B. Permeability
C. Field capacity
D. Saturation point
C. Field capacity
Saturation point is driven by gravity. Available water capacity = field capacity - wilting point
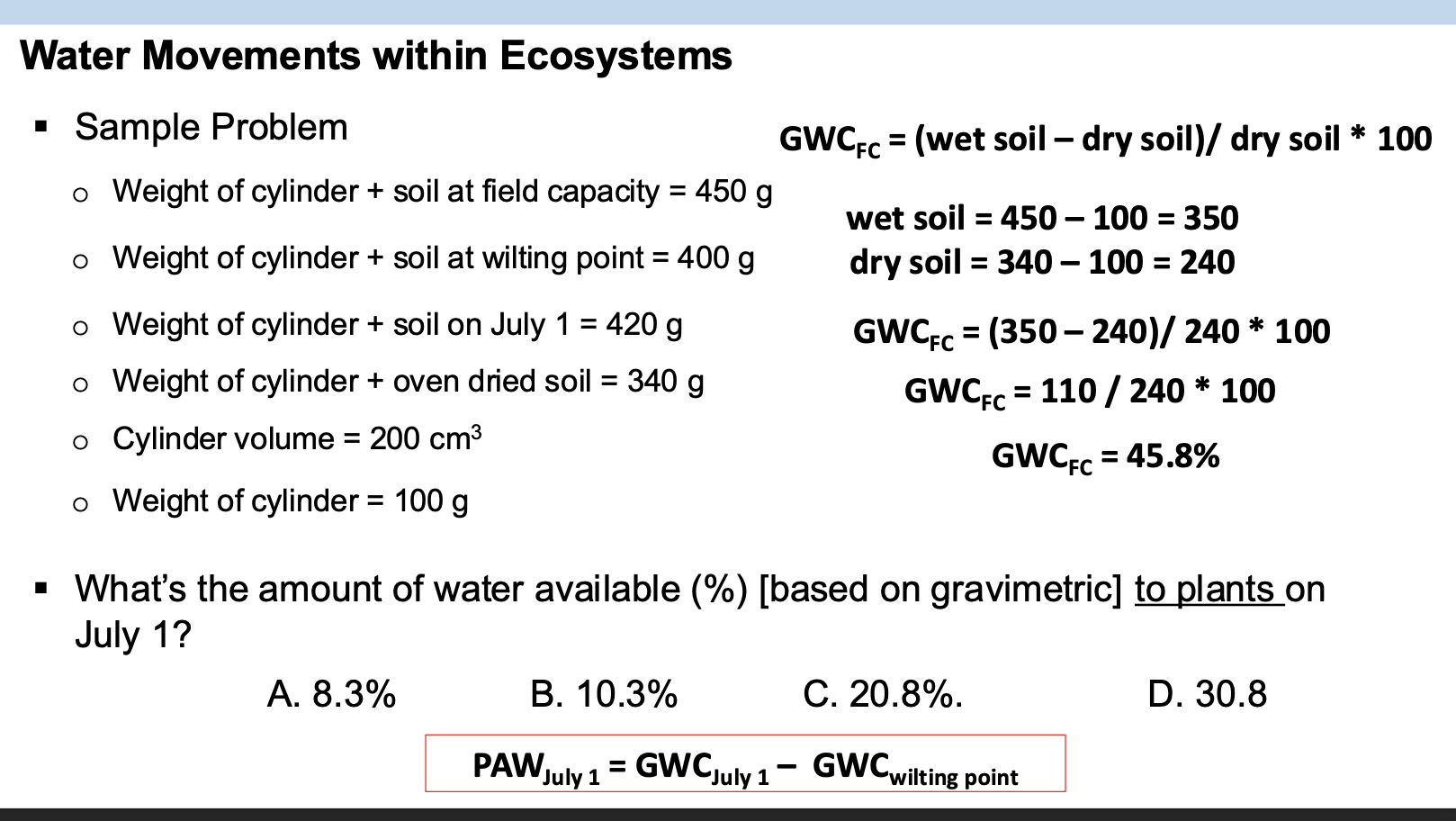
Sam conducted an experiment to determine the available water to plants for a soil near Cache
Valley. Sam first sampled soils and brought these soils into the lab and used the retention curve
method and determined the permanent wilting point for this soil was 12% water content [based
on gravimetric]. Then Sam conducted a gravimetric method and determined the field water
holding capacity was 35% water content [based on gravimetric].
On September 23rd, Sam conducted soil resampling at the same location using a cylinder. In the
laboratory, Sam measured the total weight of the cylinder and the wet soil, which was 320 g.
Subsequently, Sam placed the cylinder and the wet soil in an oven, where they were dried at
105 °C for 48 hours. After drying, the combined weight of the cylinder and the dried soil was
280 g. The weight of the cylinder alone was 120 g. Based on this information, please address the
following questions:
Part A: what is the soil water content (based on gravimetric) on September 23rd?
A. 12%
B. 23%
C. 25%
D. 35%
Part B: what is the amount of water available to plant on September 23?
A. 12%
B. 13%
C. 23%
D. 35%
Part A: C. 25%
320 g - 120 g = 200 g wet soil
280 g - 120 g = 160 g dry soil
(200-160) / 160 = .25 or 25%
Part B: B. 13%
AWC = 25 - 12 = 13%
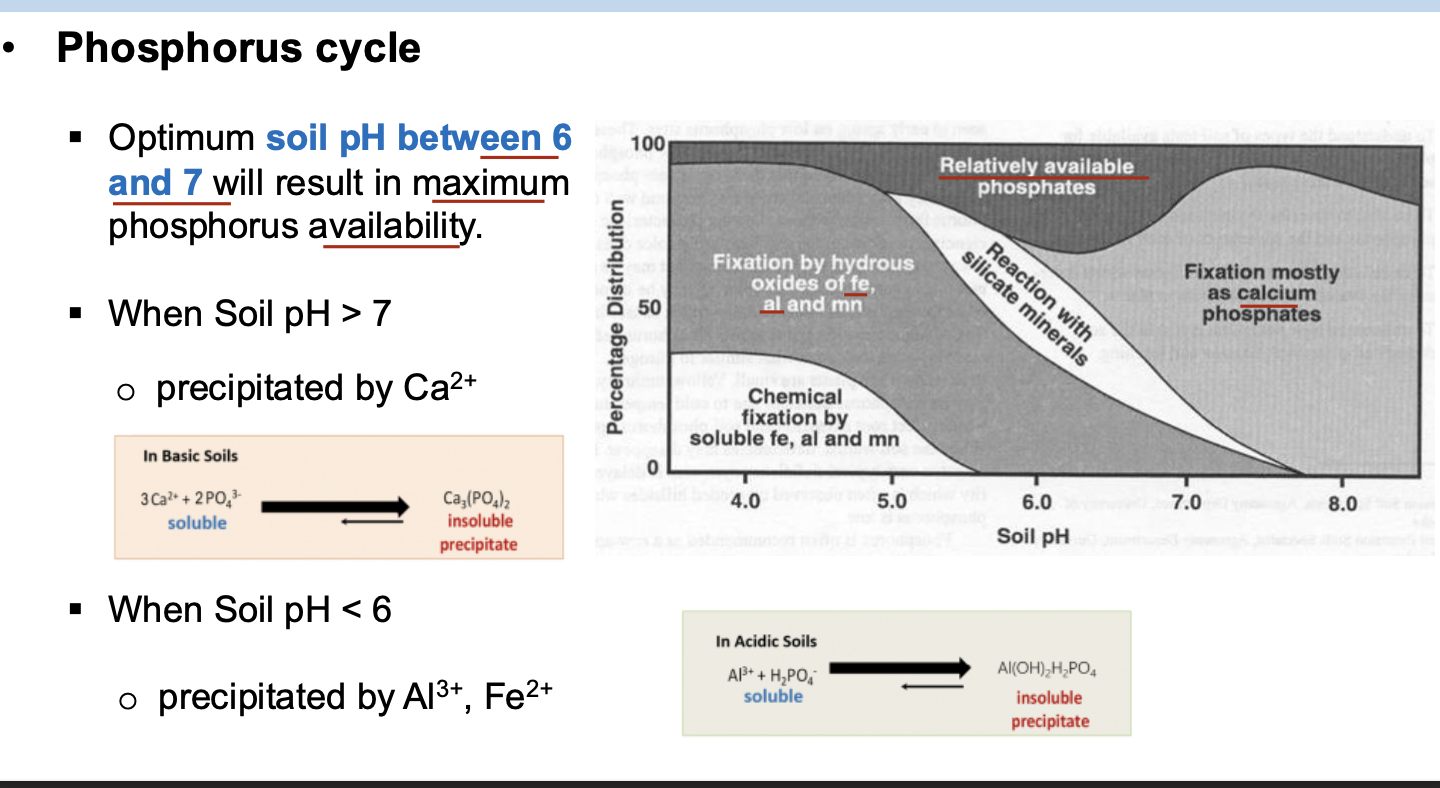
In a relatively young ecosystem with limited vegetation, what is the primary source of phosphorus for plants?
A. Rock weathering
B. Precipitation deposition
C. Air deposition
D. Organic matter decomposition
A. Rock weathering
At what soil pH level is phosphorus most available to plants uptake?
A. 4.0-5.0
B. 5.0-6.0
C. 6.0-7.0
D. 8.0-9.0
C. 6.0-7.0
Which of the following statements is correct about the difference between N and P cycles?
A. Phosphorus exists in gaseous forms but nitrogen generally does not.
B. Human activities do not affect the P cycle in a significant way.
C. Plants only take up inorganic forms of nitrogen and organic forms of phosphorus.
D. The N cycle is relatively fast and the P cycle is relatively slow
D. The N cycle is relatively fast and the P cycle is relatively slow
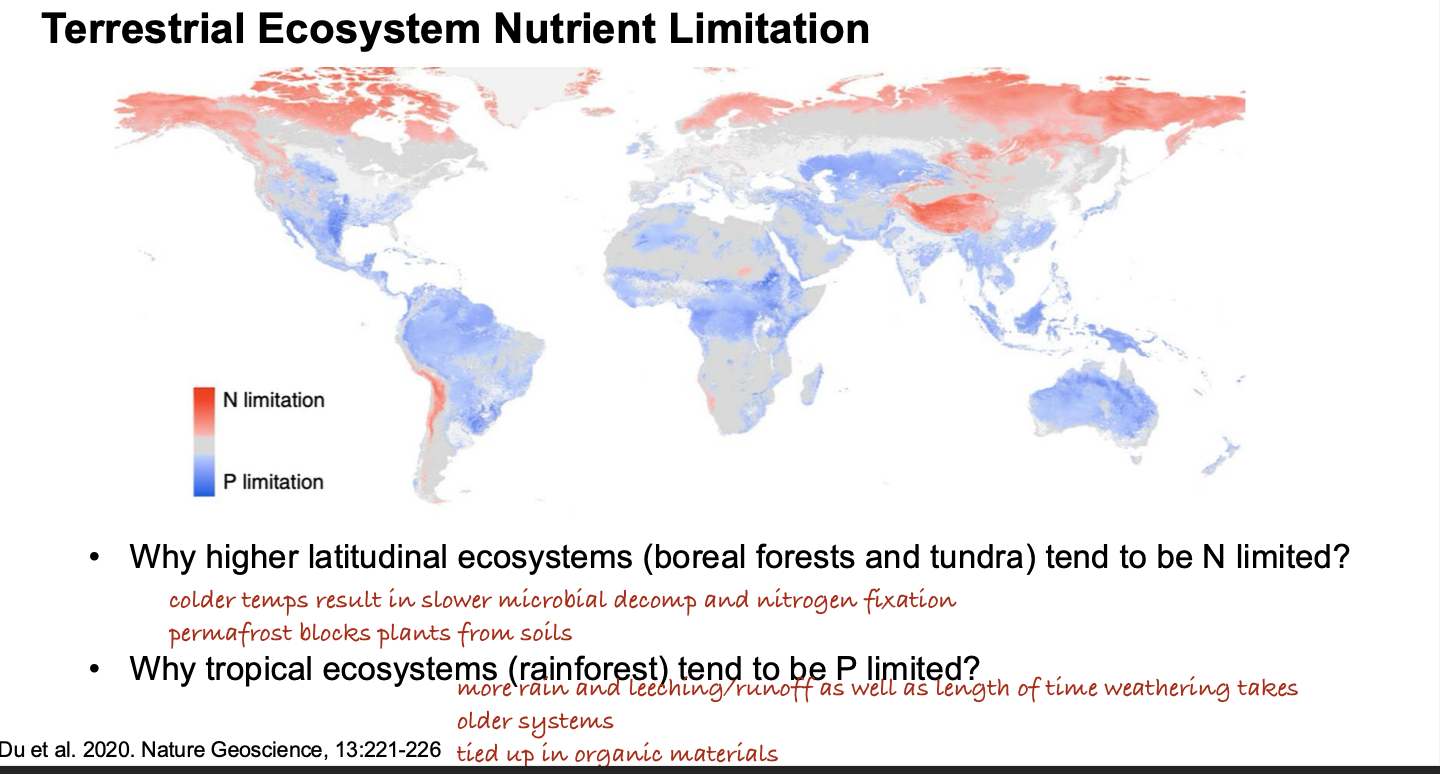
Which of the following ecosystems is more likely to be limited by phosphorus?
A. Tropical rainforest
B. Boreal forest
C. Tundra
D. Glacier ecosystem
A. Tropical rainforest
There is more rain leeching P from the soils, it is an older system with less nutritious soils, and it is tied up in organic materials.
What are the potential reasons an ecosystem becomes phosphorus-limited over time? [Select all that apply]
A. Phosphorus is continuously lost from the ecosystem through leaching and runoff.
B. Phosphorus is gradually incorporated into soil organic matter, making it unavailable to plants.
C. Phosphorus is physically bounded to soil minerals, making it unavailable to plants.
D. Phosphorus is lost to the atmosphere through volatilization over time
A. Phosphorus is continuously lost from the ecosystem through leaching and runoff.
B. Phosphorus is gradually incorporated into soil organic matter, making it unavailable to plants.
C. Phosphorus is physically bounded to soil minerals, making it unavailable to plants.

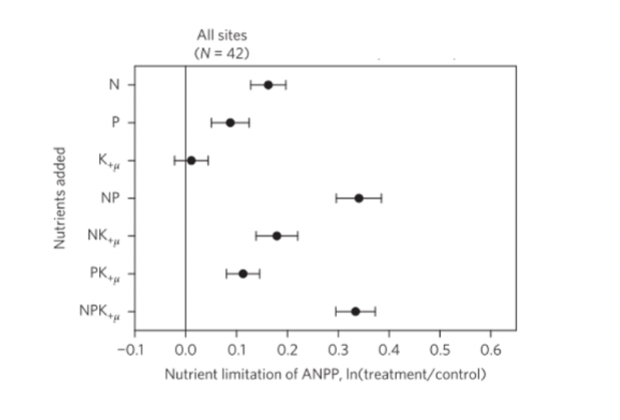
Experimentally adding nutrients to an ecosystem is an effective way to test whether a specific nutrient limits ecosystem productivity. The 'Nutrient Network' is a collaborative, global research initiative studying nutrient limitation in grassland ecosystems. Review this figure and select the correct statements.
A. Global grassland ANPP is more likely limited by nitrogen (N) than by phosphorus (P).
B. Adding phosphorus (P) along with nitrogen (N) does not enhance global grassland ANPP.
C. Global grassland ANPP are less likely limited by potassium (K)
D. Adding potassium (K) together with nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) significantly promote global grassland ANPP.
A. Global grassland ANPP is more likely limited by nitrogen (N) than by phosphorus (P).
C is true too, K does not have an effect on the landscape, but the answer they’re looking for is A.
Which of the following statements is correct about biodiversity assessment?
A. High species richness always implies high species evenness.
B. High species evenness always implies high species richness.
C. High species richness does not necessarily indicate high species evenness.
C. High species richness does not necessarily indicate high species evenness.
In a community with high species richness and low evenness, what would thisommunity look like?
A. Many different species, each with similar abundance.
B. Many different species, with one or a few dominating the community.
C. Few different species, each with similar abundance.
D. Few different species, with one or a few dominating the community.
B. Many different species, with one or a few dominating the community.
If a community exhibits low species richness and high evenness, what does this indicate?
A. Few different species, with one or a few dominating the community.
B. Few different species, each with similar abundance.
C. Many different species, each with similar abundance.
D. Many different species, with one or a few dominating the community
B. Few different species, each with similar abundance.
Which of the following statements regarding biodiversity and ecosystem functions are correct? [Select all that apply]
A. Diverse ecosystems are often more stable and resilient in the face of environmental disturbances or invasions.
B. Diverse ecosystems often lead to increased competition for resources, which reduces ecosystem productivity.
C. Diverse ecosystems are likely to sequester more carbon (e.g., through biomass accumulation) than ecosystems with few species or monoculture stands.
D. Diverse ecosystems often have different ecological niches that complement resource use among species
A. Diverse ecosystems are often more stable and resilient in the face of environmental disturbances or invasions.
C. Diverse ecosystems are likely to sequester more carbon (e.g., through biomass accumulation) than ecosystems with few species or monoculture stands. (Maybe)
D. Diverse ecosystems often have different ecological niches that complement resource use among species
Which of the following factors contribute to the high species richness in equatorial regions? [Select all that apply]
A. Stable climatic conditions over extended time periods allow for increased speciation and species accumulation.
B. High gross primary productivity supports a diverse array of herbivores and carnivores.
C. More complex and diverse habitats promote speciation and species coexistence.
D. Lower levels of predation and competition result in a higher abundance of species
A. Stable climatic conditions over extended time periods allow for increased speciation and species accumulation.
B. High gross primary productivity supports a diverse array of herbivores and carnivores. (maybe)
C. More complex and diverse habitats promote speciation and species coexistence.
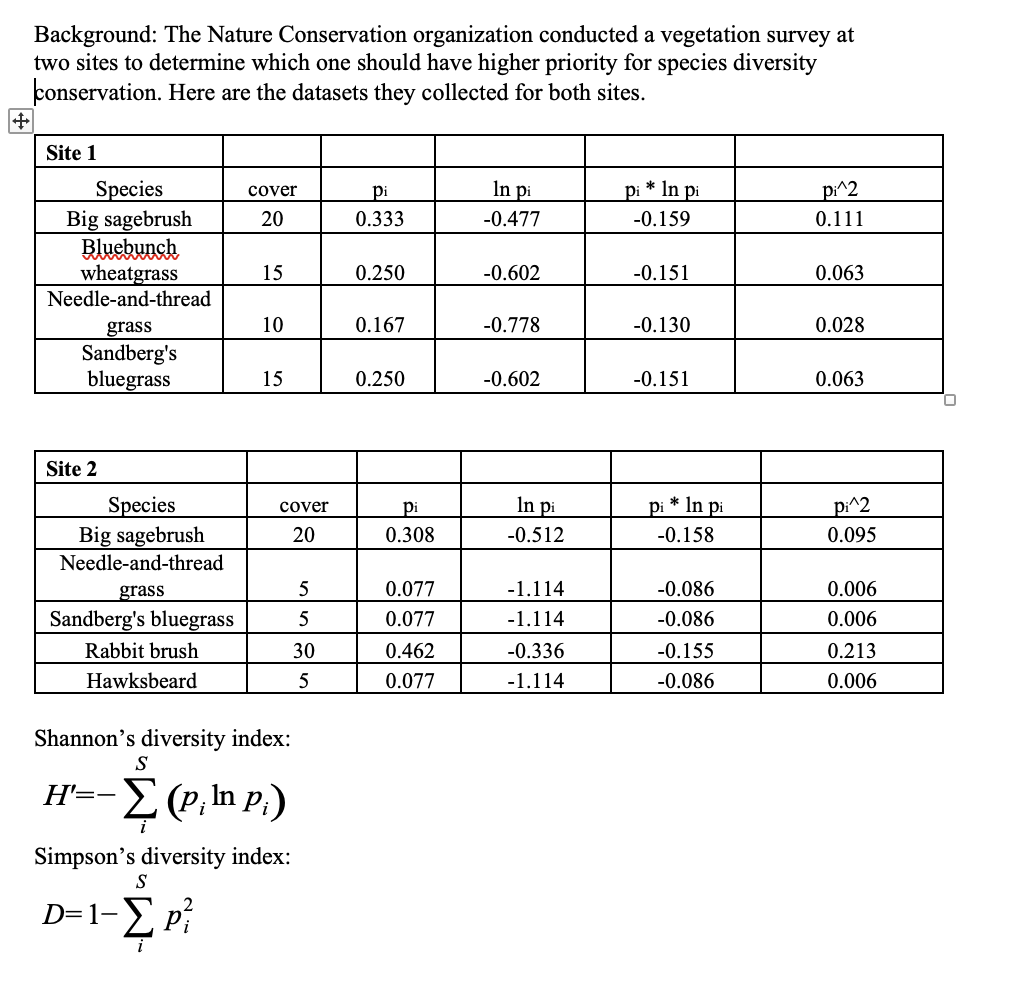
If the criteria are based on species richness, which site should the Nature Conservation organization select?
A. Site 1
B. Site 2
A. Site 1
Site 1 only has 4 species while Site 2 has 5. Species Richness is simply the number of species at each site.
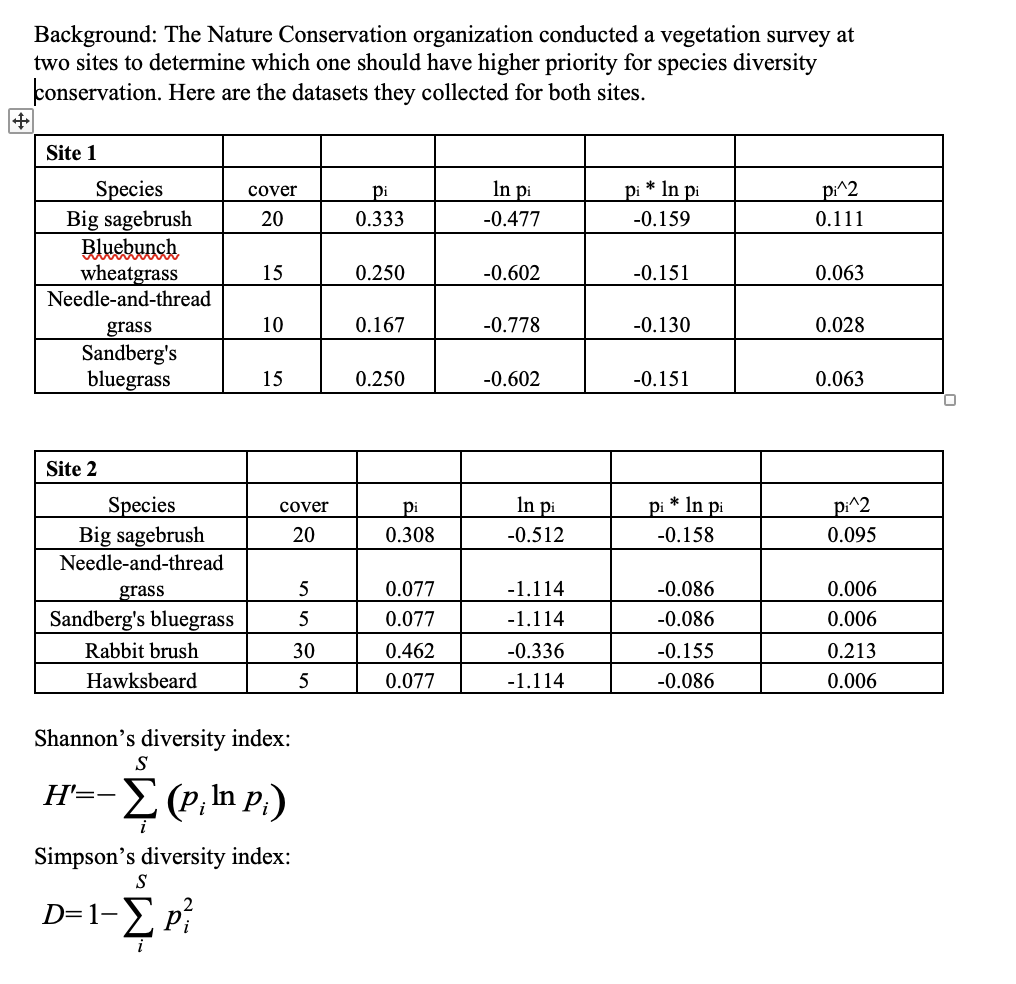
If the criteria are based on Shannon’s diversity index, which site should the Nature Conservation organization select?
A. Site 1
B. Site 2
B. Site 2
H’ for Site 1 is 0.591 and for Site 2 it is 0.571, which means that Site 2 has lower diversity.
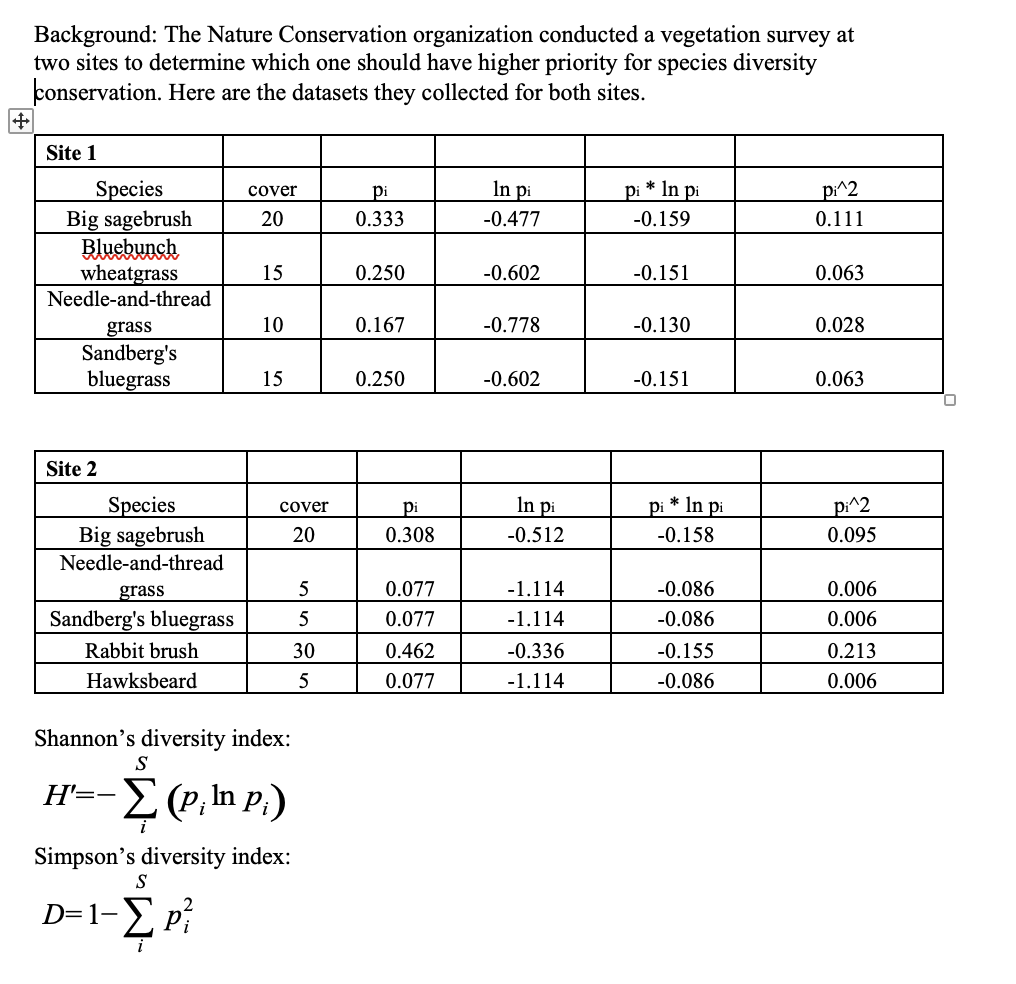
If the criteria are based on Simpson’s diversity index, which site should the Nature Conservation organization select?
A. Site 1
B. Site 2
A. Site 1
D for Site 1 is .265 and it is .362 for Site 2, which means that site 1 is less even (lower diversity).