AP Unit 2: Tissue Level of Organization
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are the two broad tissue membranes found in the human body?
connective tissue membranes
epithelial membranes
What is an example of a connective tissue membrane?
synovial membranes
Synovial membranes
found in the synovial joints, these membranes secrete synovial fluid, which lubricates the joints and reduces friction during movement
What are examples of epithelial membranes?
mucous membranes, serous membranes, and the cutaneous membranes (skin)
Where are mucous membranes found?
lining body cavities that are open to the exterior, such as the respiratory and digestive tracts
What do mucous membranes do?
they produce mucous to protect, moisten, and trap debris
Where are serous membranes found?
lining body cavities that do not open to the exterior, such as the pericardium around the heart and the pleura around the lungs
What do serous membranes do?
they secrete serous fluid to reduce friction between organ surfaces
Where are epithelial membranes typically located?
lining body cavities
covering internal organs
forming the outer layer of the skin
What do epithelial membranes consist of?
epithelial tissue and an underlying layer of connective tissue
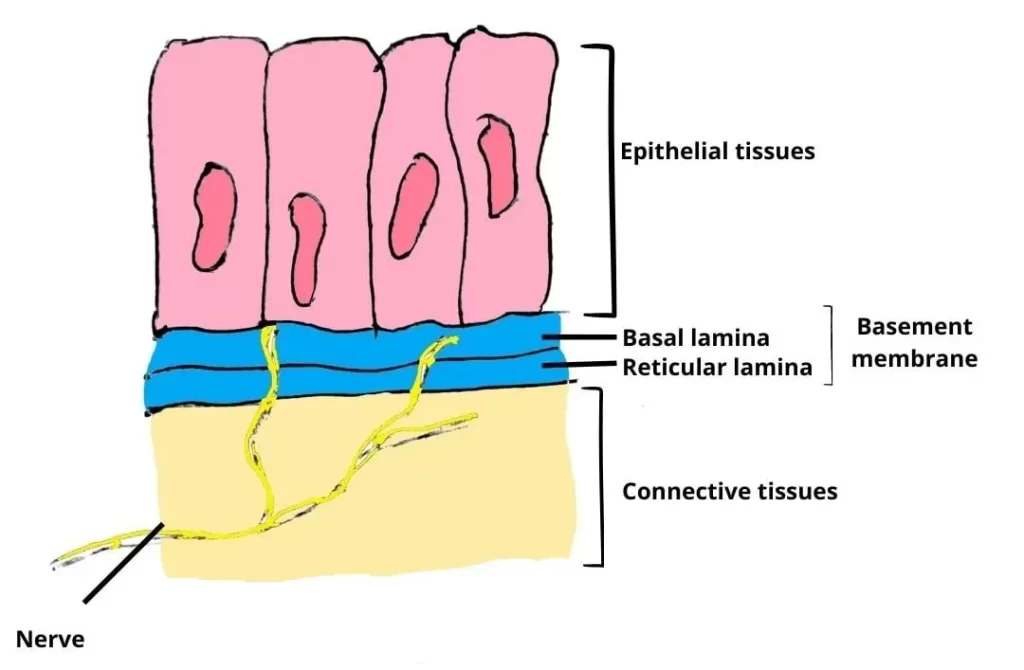
What are the three types of cell junctions?
tight junctions
gap junctions
anchoring junctions
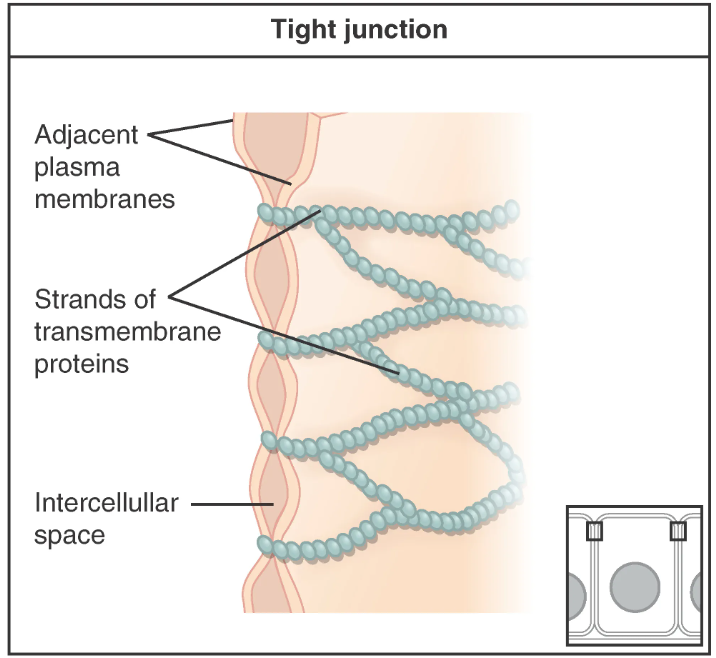
Tight Junction
these junctions form a continuous seal around adjacent epithelial cells, preventing the leakage of extracellular fluids between them
What do tight junctions play a crucial role in?
maintaining the integrity of epithelial barriers
What are the two types of anchoring junctions?
desmosomes
adherens
Adherens Junctions
these junctions provide mechanical stability to tissues by linking adjacent calls through cadherin proteins
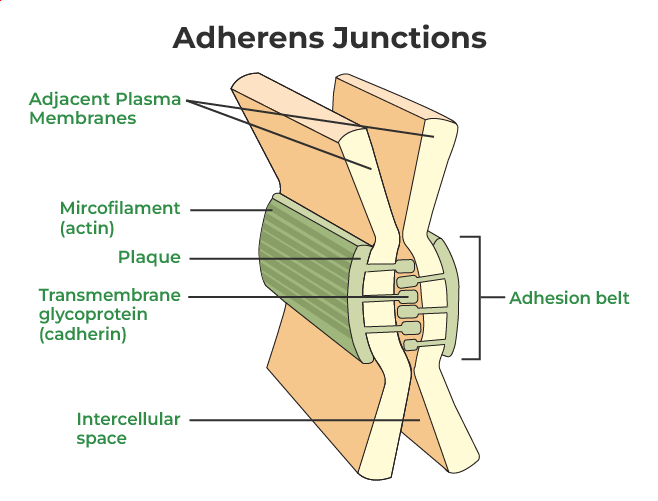
Where are adheren junctions typically located?
just below tight junctions
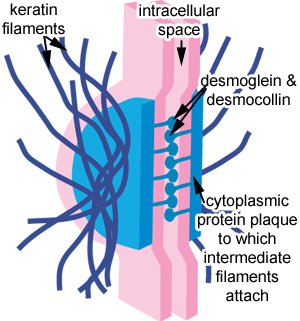
Desmosomes
these are strong junctions that provide additional mechanical support to epithelial tissue
What are desmosomes characterized by?
the presence of desmocollin and desmoglein proteins that link adjacent cells
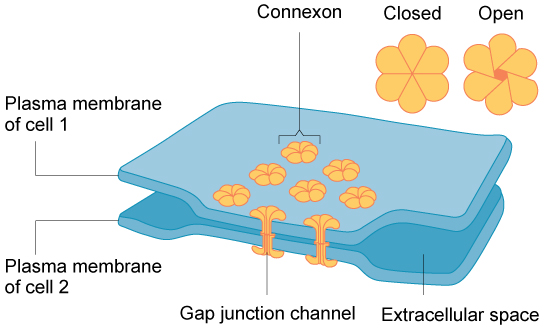
Gap junctions
junctions that allow for the direct exchange of ions and small molecules between neighboring cells.
Gap junctions are essential for _______ between cells in tissues like cardiac muscle and smooth muscle.
communication
What are the four types of tissue in the body?
nervous tissue
epithelial tissue
cardiac tissue
connective tissue
What are the four functions of epithelial tissue?
Protection
Secretion
Absorption
Sensory perception
What role does epithelial tissue play in protection?
Epithelial tissues on the skin provide a barrier against physical, chemical, and microbial threats. Similarly, mucus membranes lining the respiratory tract protect underlying tissues from harmful substances by trapping debris
What role does epithelial tissue play in secretion?
epithelial cells secrete various substances, including hormones, enzymes, and mucus
What role does epithelial tissue play in absorption?
Epithelial tissue in the intestines absorbs nutrients and water from digested food, allowing for efficient nutrient uptake into the bloodstream.
What role does epithelial tissue play in sensory perception?
Epithelial cells in the sensory organs respond to stimuli such as touch, taste, and smell, facilitating sensory perception and communication with the environment.
How is simple epithelial tissue organized?
in a single layer of cells
How is stratified epithelial tissue organized?
in multiple layers of cells
What are the types of epithelial cells?
squamous cells
cuboidal cells
columnar cells
transitional cells
Transitional cells are unique to the ____ system.
urinary
What do transitional cells do? Why is this important?
they can change shape from squamous to cuboidal or columnar when the tissue is stretched
this allows the urinary tracts to accommodate changes in volume
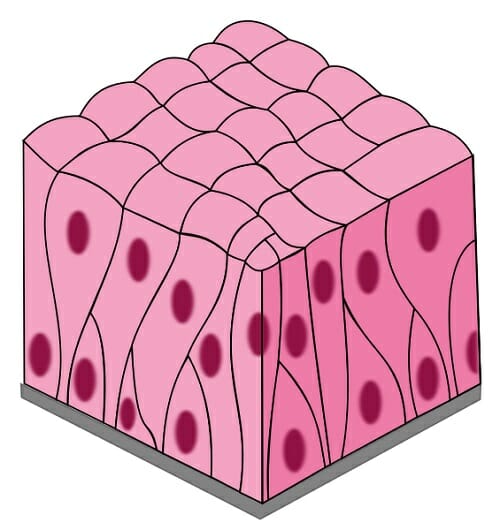
Pseudostratified Epithelial Cells
A type of epithelial cell that has a single layer but appears stratified due to varying cell heights. They often contain cilia and are found in the respiratory tract, playing a role in secretion and movement of mucus.
What is a Goblet Cell?
A type of specialized epithelial cell that secretes mucus, helping to protect and lubricate the surfaces of various tissues.
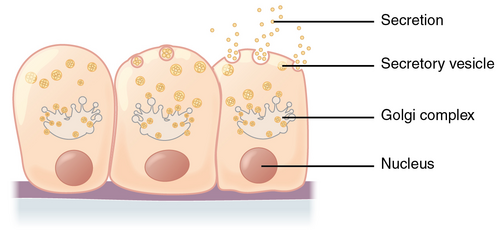
What are the three modes of Glandular Secretion?
Merocrine secretion
Apocrine secretion
Holocrine Secretion
In merocrine secretion, the cell ____ ____.
remains intact
In apocrine secretion, the _____ portion of the cell is released.
apical
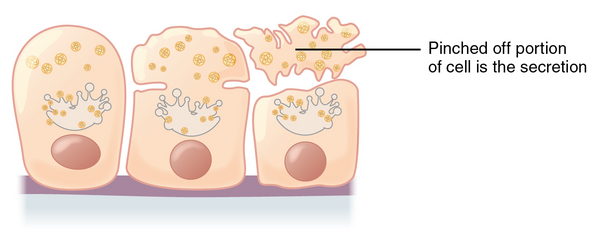
In holocrine secretion, the cell is ____ as it releases its product, and…
destroyed; the cell itself becomes part of the secretion
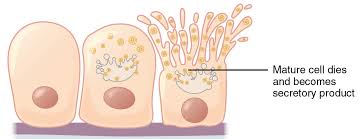
Sebaceous Glands
secrete oils that lubricate and protect the skin
Sebaceous Glands are a type of ______ gland.
holocrine
Where are sebaceous glands found?
next to a hair follicle
What are the four functions of connective tissue?
Structural Support
Transport
Storage
Immunity
What role does connective tissue play in structural support?
connective tissue, such as bones and cartilage, provide support and structure to various body parts. They protect internal organs, and tendons connect muscle to bone.
Tendons
a fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
What role does connective tissue play in transport?
Blood is a connective tissue responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body
What role does connective tissue play in storage?
Adipose tissue stores energy in the form of fat, and cartilage serves as a shock-absorbing and supportive structure in joints
What role does connective tissue play in immunity?
Certain connective tissue, such as lymphoid tissue in the lymph nodes and spleen, are involved in immune responses by harboring immune cells
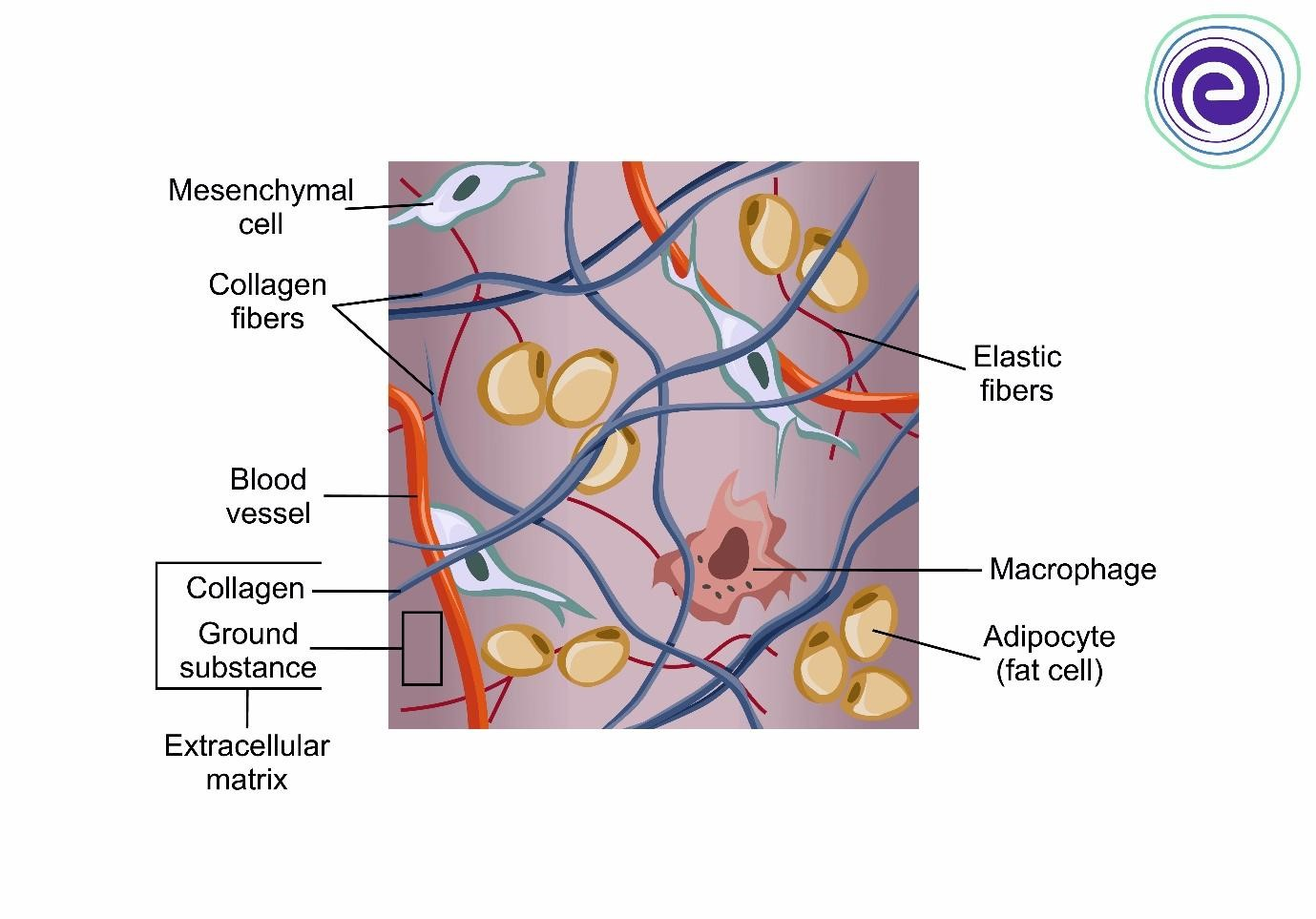
What is connective tissue made up of?
adipocytes, mesenchymal cells, elastic fibers, collagen fibers, fibroblasts, and macrophages
Collagen Fibers
the most abundant protein in the human body
provides strength to connective tissue
Elastic Fibers
Contain the protein elastin
provide elasticity to connective tissue
Reticular Fibers
composed of thin collagen fibers and form a network
provide structural support for soft organs like the liver and spleen
Ground Substance
part of the extracellular matrix that fills the spaces between cells and fibers
composed of water, proteins, and carbohydrates, contributing to tissue hydration and support.
What is the most common cell type found in connective tissue?
fibroblasts
What are fibroblasts responsible for?
producing fibers and ground substances in the extracellular matrix
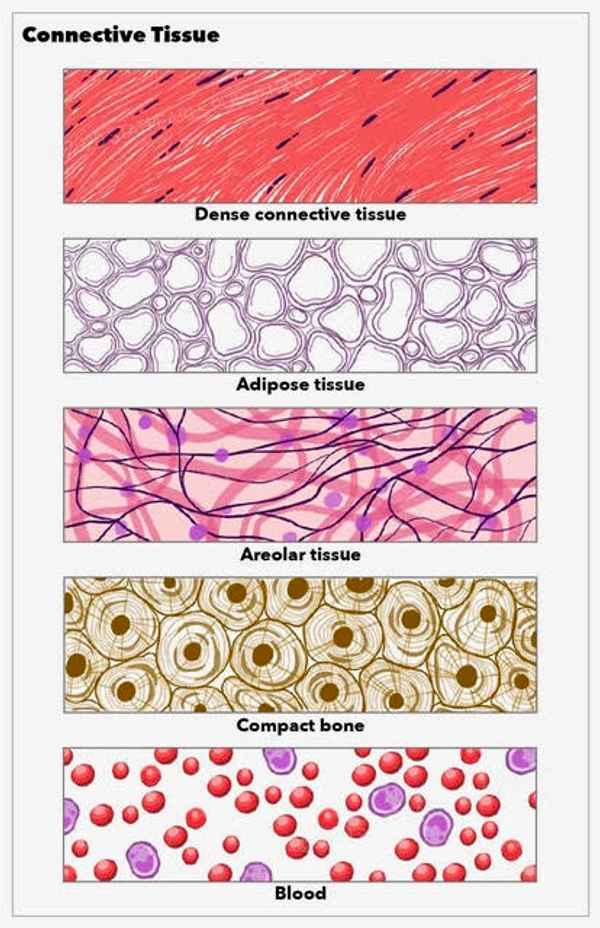
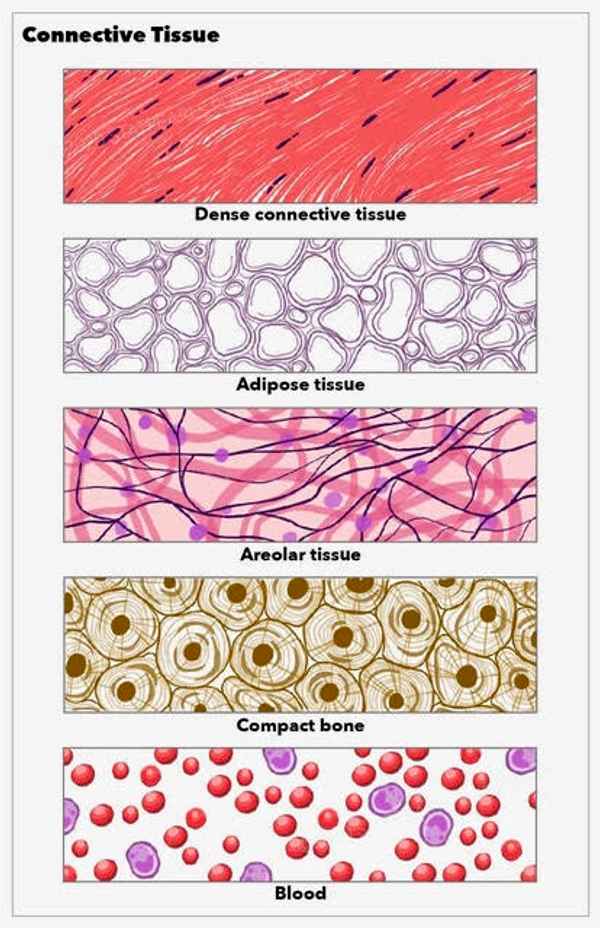
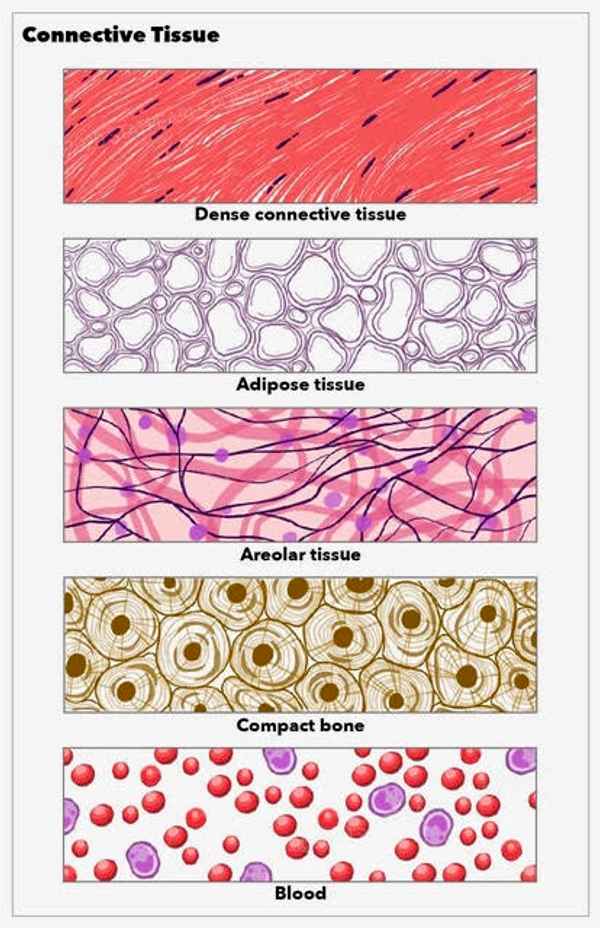
Adipose Tissue
a loose connective tissue that consists of fat cells with little extracellular matrix
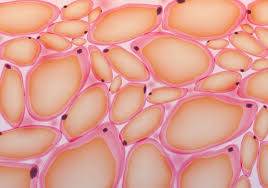
What does adipose tissue do?
it stores fat for energy and provides insulation
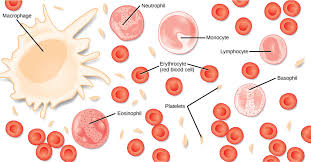
Blood
a fluid connective tissue containing erythrocytes and various leukocytes that circulate in a liquid extracellular matrix
What are the two types of dense connective tissue?
Dense regular connective tissue
Dense irregular connective tissue
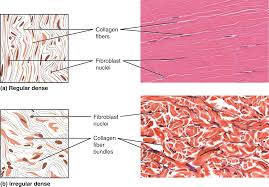
Dense regular
connective tissue that is tightly packed and provides strength in one direction, typically found in tendons and ligaments.
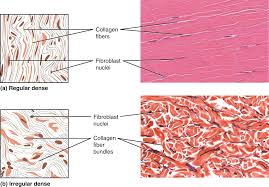
Dense Irregular
connective tissue that is not tightly packed, providing strength and support in multiple directions, commonly found in dermis of the skin and organ capsules.
Cartilage
a type of connective tissue that provides support and flexibility, found in joints, the rib cage, and the ear
What are the three types of cartilage?
Hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage.
Hyaline Cartilage
provides some support with some flexibility and is the most common type of cartilage, found in the nose, trachea, and ends of long bones
Fibrocartilage
provides some compressibility and can absorb pressure due to its dense, fibrous structure. It is found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and menisci of the knee.
Elastic cartilage
provides firm but elastic support and is found in structures such as the external ear
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
Skeletal Muscle
responsible for voluntary movements of the body and is striated in appearance, attached to bones by tendons.
Smooth Muscle
involuntary muscle tissue that is non-striated and found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the intestines and blood vessels.
Cardiac Muscle
involuntary muscle tissue that is striated and found only in the heart, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
What is nervous tissue made up of?
neurons and neuroglia, which work together to transmit and receive impulse signals