Psych of Learning (Exam 3)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:15 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Structural Verbal Behavior
focuses on how the grammar, syntax, & processes of language influence our behavior
2
New cards
Functional Verbal Behavior
focuses on the operating contingencies in the environment that control the speaker's behavior
3
New cards
Consequences of Verbal Behavior
reinforced through another person's behavior which is evoked by stimulus (visual, auditory, tactile)
4
New cards
Non-verbal Stimulus
object, object property, action, relation
5
New cards
Verbal Stimulus
written or spoken word, number, symbol
6
New cards
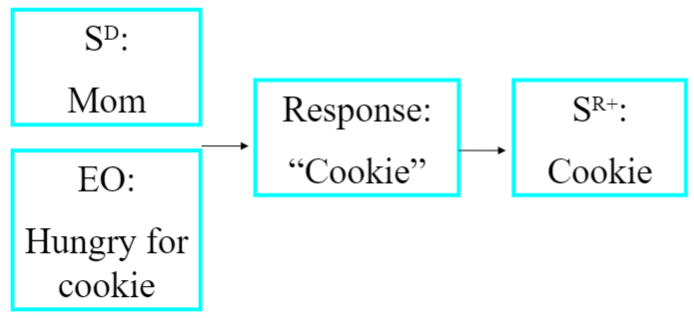
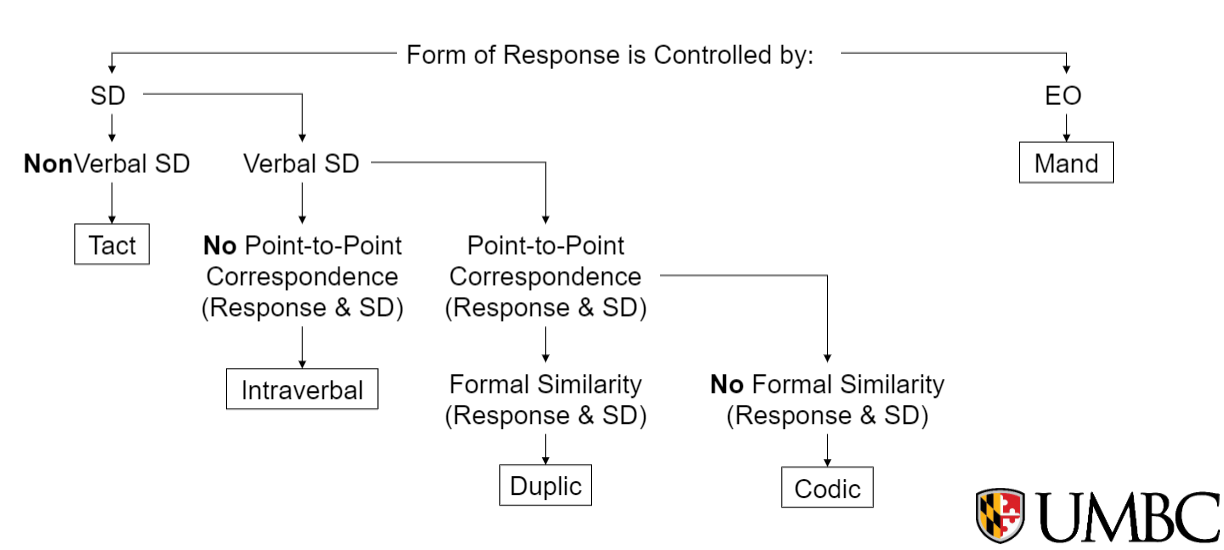
Manding / The Mand Relation
response form controlled by CURRENT ESTALISHING OPERATION, or controlled by what the speaker wants from the listener
(from the word "command" or "demand")
ex. kid asks for ball when they want to play with it
(from the word "command" or "demand")
ex. kid asks for ball when they want to play with it
7
New cards
Things Manded For & Examples
- Attention ("hey!")
- Objects ("water")
- Actions ("come here")
Ex. speaking, writing, signing, finger spelling, morse cord, point at words, symbol, or pic
- Objects ("water")
- Actions ("come here")
Ex. speaking, writing, signing, finger spelling, morse cord, point at words, symbol, or pic
8
New cards
Mand Applied Examples

9
New cards
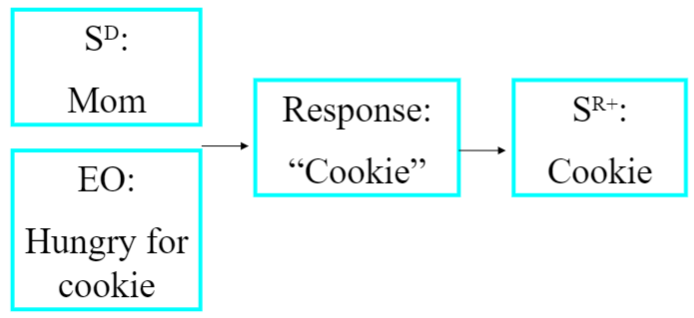
The Tact Relation
response form controlled by an immediately prior NON-VERBAL DISCRIMINATIVE STIMULUS, such as labeling something within their environment
(from the word "contact")
ex. you smell popcorn & say, "mmm, popcorn!"
(from the word "contact")
ex. you smell popcorn & say, "mmm, popcorn!"
10
New cards
Tacts Applied Examples

11
New cards
Mands vs Tacts
- Mands: allow speakers to alter environment through listeners' behavior
- Tacts: permits listeners to react to stimuli affecting speakers
*reinforcing verbal behavior enhances the effectiveness of the entire verbal community*
- Tacts: permits listeners to react to stimuli affecting speakers
*reinforcing verbal behavior enhances the effectiveness of the entire verbal community*
12
New cards
Functional Independence
verbal operants have to be functionally independent, if they're learned separately then they can't say it in all contexts and the word only developed a single function
ex. you ask a child "what is this?" - "banana" then ask to "tell me a yellow fruit" - no response
ex. you ask a child "what is this?" - "banana" then ask to "tell me a yellow fruit" - no response
13
New cards
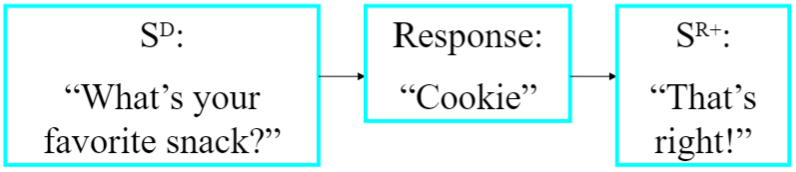
Intraverbals / The Interverbal Relation
- verbal response form controlled by a VERBAL STIMULUS
- no point-to-point correspondence between the response & verbal stimulus
- no point-to-point correspondence between the response & verbal stimulus
14
New cards
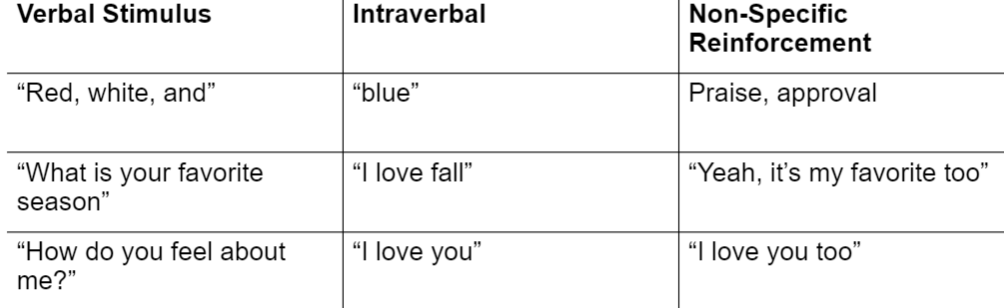
Intraverbal Applied Examples
15
New cards
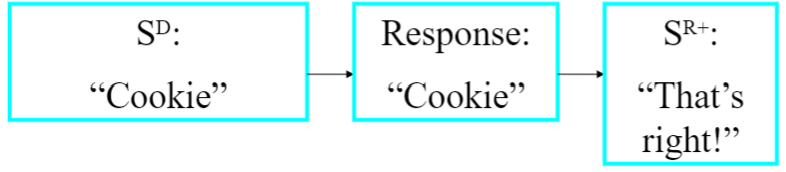
Duplics (Echoic) Relation
- response form controlled by verbal stimulus
- formal similarity between response & verbal stimulus (speaker repeats what's heard)
- point-to-point correspondence between response & verbal stimulus
- formal similarity between response & verbal stimulus (speaker repeats what's heard)
- point-to-point correspondence between response & verbal stimulus
16
New cards
Duplic/Echoic Applied Examples
17
New cards
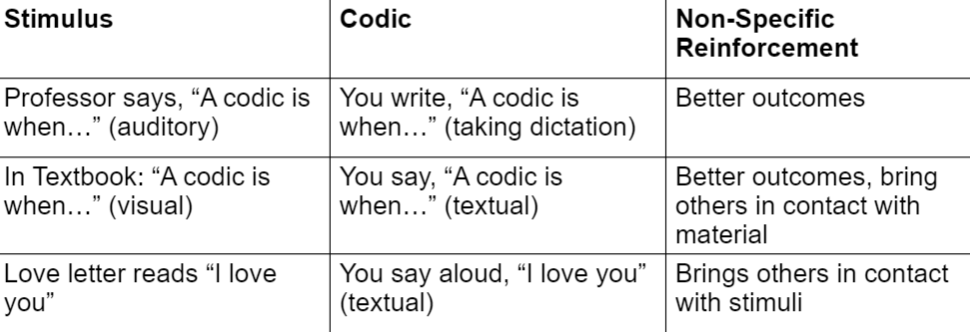
Codic Relation
response form controlled by a verbal stimulus with point-to-point correspondence
18
New cards
Textuals (codic) vs Echoic (duplic)
- Textuals: visual stimulus = vocal response (ex. reading text out loud)
- Echoic: auditory stimulus = written response (ex. writing down what you hear)
- Echoic: auditory stimulus = written response (ex. writing down what you hear)
19
New cards
Codic Applied Examples
20
New cards
Forms of Verbal Responses
21
New cards
Point-to-Point Correspondence
response is the same word (or phoneme) as stimulus
22
New cards
Formal Similarity
response & stimulus are in the same sense mode
23
New cards
Audience Control
a non-verbal stimulus that controls the form of a verbal response (not necessarily a person)
24
New cards
Generalized Imitation
learning to imitate others
(we learn "imitation" as a behavior rather than learning to imitate specific response)
(we learn "imitation" as a behavior rather than learning to imitate specific response)
25
New cards
Precurrent Behavior
many rules are designed to evoke precurrent behavior which is behavior that precedes & mediates other behavior
ex. making a grocery list = Sd for certain items
ex. making a grocery list = Sd for certain items
26
New cards
Rules
- Specifies behavior: may not be exact behavior, but the effects of it
- Specifies the contingency: clarifies the consequences associated w/ certain actions
- Specifies the contingency: clarifies the consequences associated w/ certain actions
27
New cards
Contingency-Shaped Behavior
the contingency is actually contacts
ex. if you speed, then you'll receive a fine
ex. if you speed, then you'll receive a fine
28
New cards
Rule-Governed Behavior
you do something because of a rule
ex. you don't speed bc you known there's a fine if you do
ex. you don't speed bc you known there's a fine if you do
29
New cards
Applied (dimensions of applied behavior analysis)
behavior or organism is of interest to society
ex. studying how seat belt use increases likelihood of survival
ex. studying how seat belt use increases likelihood of survival
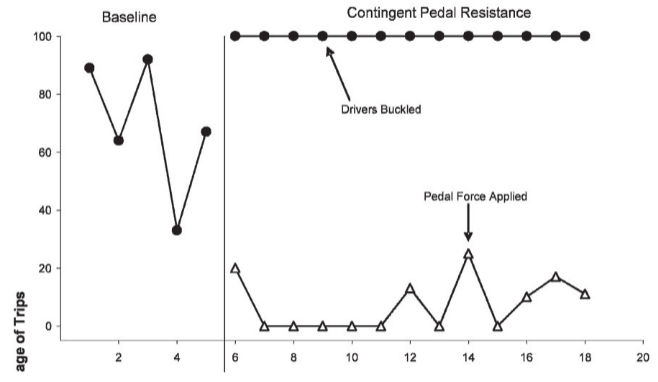
30
New cards
Behavioral (dimensions of applied behavior analysis)
specific behaviors are targeted for the interventions
ex. "does training mands also help in training echoics?"
ex. "does training mands also help in training echoics?"
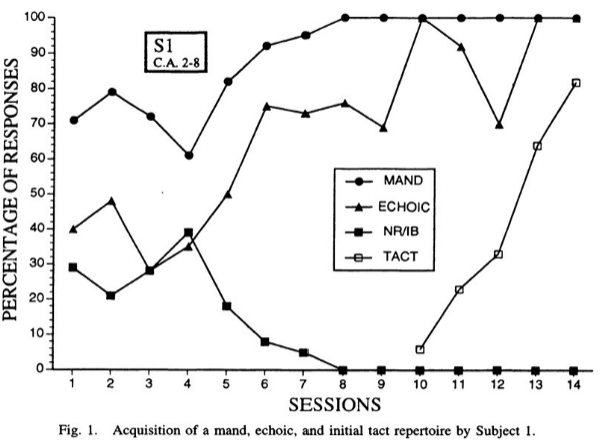
31
New cards
Analytic (dimensions of applied behavior analysis)
Identifies the functional relationship between behavior & environmental variables
ex. "what effect does the removal of the death penalty have on the rate of homicides?"
ex. "what effect does the removal of the death penalty have on the rate of homicides?"
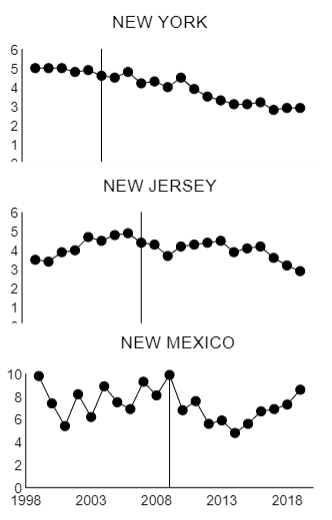
32
New cards
Generalizable (dimensions of applied behavior analysis)
★ Generalization: demo of control over behavior
- Stimulus: similar stimuli evoke same response
- Response: same stimulus evokes multiple types of responses
- Response Maintenance: response continues to occur long after treatment
- Stimulus: similar stimuli evoke same response
- Response: same stimulus evokes multiple types of responses
- Response Maintenance: response continues to occur long after treatment
33
New cards
Effective (dimensions of applied behavior analysis)
interventions produce socially significant changes in behavior
(p-value used as a test of statistical significance)
(p-value used as a test of statistical significance)
34
New cards
Technological (dimensions of applied behavior analysis)
interventions are clear & replicable
ex. following a recipe with specific steps
ex. following a recipe with specific steps
35
New cards
Conceptually Systematic (dimensions of applied behavior analysis)
procedures are described based on the behavioral principles
ex. a behavioral analyst is reviewing their client's treatment plan with the parents
ex. a behavioral analyst is reviewing their client's treatment plan with the parents
36
New cards
Differential Reinforcement of Other Behavior (DRO)
reinforcement contingent on absence of target behavior for set duration
ex. saying "nice job!" for every 5 mins w/o whining
ex. saying "nice job!" for every 5 mins w/o whining
37
New cards
Differential Reinforcement of Alternative Behavior (DRA)
reinforcement contingent on occurrence of specific behavior
ex. giving a cookie for asking nicely
ex. giving a cookie for asking nicely
38
New cards
Why might it be difficult to use a reversal design in the natural environment?
in natural settings, behavior is often resistant to a reversal procedure
39
New cards
Contingency Management Approach to Reduce Substance Abuse
managing the contingencies in place for use or non-use of harmful substances
40
New cards
In which cases do behavior analysts support the use of electric skin shock?
"we strongly oppose the use of contingent electric skin shock (CESS) under any condition"
41
New cards
NeuroDivergent
nonmedical term to describe people whose brain develops or works differently for some reason.
42
New cards
ABA Therapy
ABA services is to habilitate an individual
↪ habilitation involves teaching the skills needed to live as independently as possible
↪ habilitation involves teaching the skills needed to live as independently as possible
43
New cards
Overjustification Effect
- performance decreases below baseline levels after a reward is removed
- not an issue of ABA but of how/why reinforcers are delivered
- not an issue of ABA but of how/why reinforcers are delivered
44
New cards
What issues did Leaf et al. have with Kupferstein’s study?
1. Hypothesis testing bias
2. Indirect measures: surveys self-report inaccurate data
3. Respondent selection: bland group w/ some self-diagnosed w/ ASA
4. Ambiguity of ABA: research design flawed
5. Measurement: not using tools to full potential (PCL-5 assessment)
Kupferstein’s study had major methodological & conceptual flaws with a biased analysis that barely had evidence to support these claims. Should be more considerate that ABA-based interventions could be potentially traumatic for those receiving it.
2. Indirect measures: surveys self-report inaccurate data
3. Respondent selection: bland group w/ some self-diagnosed w/ ASA
4. Ambiguity of ABA: research design flawed
5. Measurement: not using tools to full potential (PCL-5 assessment)
Kupferstein’s study had major methodological & conceptual flaws with a biased analysis that barely had evidence to support these claims. Should be more considerate that ABA-based interventions could be potentially traumatic for those receiving it.
45
New cards
What metaphorical comparison is Skinner making between a hen having an egg and a poet having a poem (p. 351 – On Having a Poem)? What does he mean by “who deserves credit?” What control does he suggest a poet has over the poem produced?
He compares how the hen & the poet is responsible for producing the egg & poem. However, he inquires which deserve the credit, as if the poet originate the poem or did his behavior merely the product of his genetic & environmental histories.