Lab Meiosis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Sex cell cycle involves
Meiosis I and Meiosis II; production of gametes
Gametes
genetically unique haploid cells; sex cells; sperm and egg
Fertilization
the sperm fuses with the egg; results in a diploid zygote
4 major stages of the sex cell cycle
interphase, Meiosis I, interkinesis, and Meiosis II
how many nuclear divisions are in the sex cell cycle
2; meiosis I and meiosis II, results in 4 haploid daughter cells
what performs the sex cell cycle
germline cells found in male and female reproductive organs
male and female reproductive organs
testes and ovaries
Oogenesis
the oogonia produces eggs in the ovaries
spermatogenesis
spermatogonia produce sperm in the testes
parent germline cell is
diploid; contains homologous pair
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes of the same number, length, locus of genes etc, held together at the synapsis forming a tetrad
tetrad
pair of sister chromosomes
where does crossing over occur
where non sister chromatids pair up, this exchanges DNA and scrambles genetic variation
ploidy
number of sets of chromosomes; diploid or haploid
interphase G0
germline cell functions normally, DNA is still in chromatin form, only one centrosome
interphase G1
centrosomes duplicate
interphase S
DNA replication, DNA still in chromatin form
interphase g2
histones form beads on a string
Meiosis I Early Prophase I
DNA condenses into tetrads, spindle fibers begin forming, nuclear envelope begins dissolving
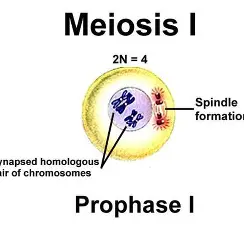
Meiosis I late prophase I
crossing over occurs between non sister chromatids, tetrads begin going to poles, nuclear envelope gone
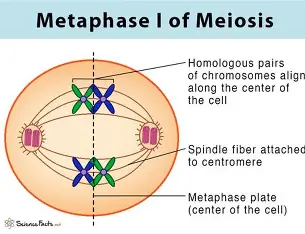
meiosis I metaphase I
spindle fibers attach, independent assortment occurs, tetrads line up along metaphase plate
Meiosis I Anaphase I
Tetrad splits at synapse, move to opposite sides of cell
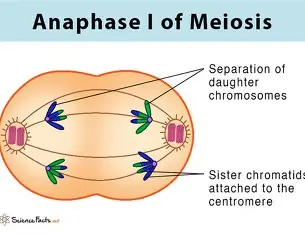
Meiosis I Telophase I
New nucleus nuclear envelope reforms, DNA unravels into chromatin, actin begins forming cleavage furrow or cell plate begins forming
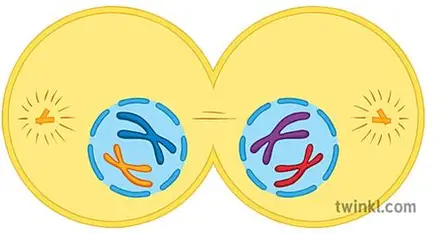
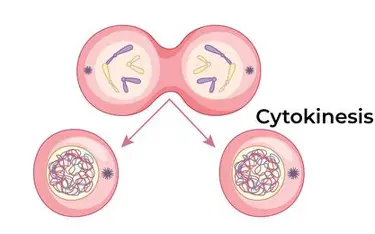
Meiosis I Cytokinesis I
cell splits into 2 haploid cells
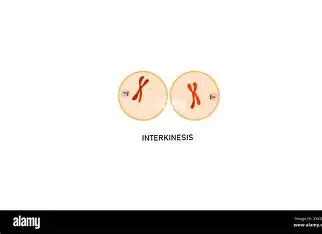
Interkinesis G1
centrosomes duplicate
Meiosis II early prophase II
DNA condenses, nuclear envelope dissolving
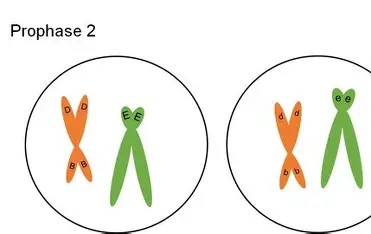
Meiosis II late prophase II
Spindle fibers attach, start moving to opposite poles, nuclear envelope gone
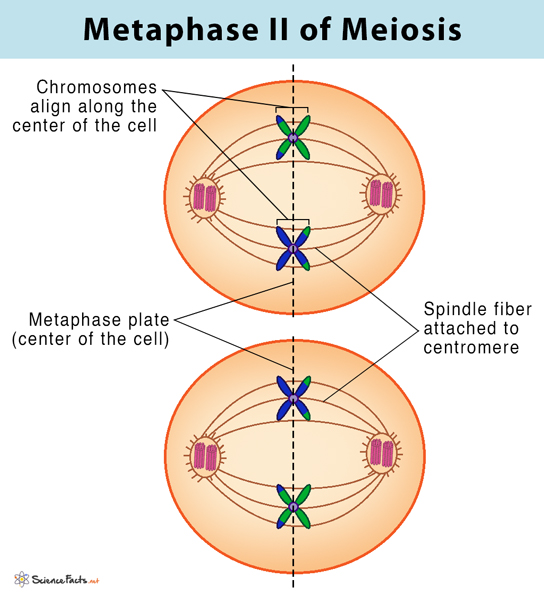
Meiosis II Metaphase II
Chromosomes alight at centromeres
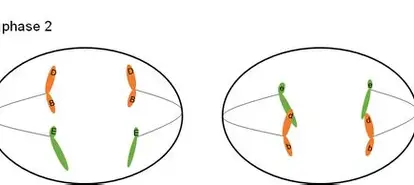
Meiosis II Anaphase II
sister chromatids separated, cleavage furrow begins forming
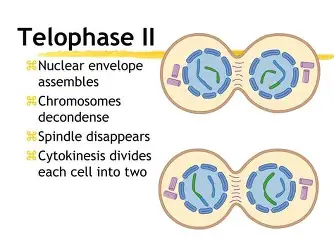
Meiosis II Telophase II
Nuclear envelope is back
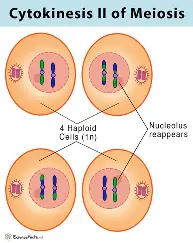
Meiosis II Cytokinesis II
4 haploid gametes produced