ppt. - work and energy
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
total amount of energy in the universe
conserved
energy can be transformed from one time to another, or even from one object to another
total amount is always the same
principle of conservation of energy - no exceptions
remains constant as long as the same amount of energy is added and removed
as long as no energy enters or leaves the system, and no work is done on or by the system
principle of conservation of energy
no work is created or destroyed
no exceptions
energy
the ability to do work; a scalar quantity
Joules (J) or Newton-meters (N-m)
Joules
N-m
kinetic energy (K or KE)
associated with the state of motion of an object
stable energy: 0 __
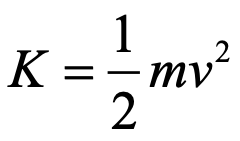
potential energy symbol
PE or U
potential energy (PE or U)
energy associated with an object’s position relative to another object or the arrangement of a system of objects
sometimes referred to as stored energy
types of potential energy, U
gravitational potential energy
elastic potential energy
electric potential energy
chemical potential energy
elastic potential energy
energy stored in a stretched (or compressed) spring
a system such as a spring that has a defined spring constant - k - that is extended a distance x from a position of equilibrium
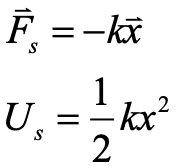
gravitational potential energy
UG, - is the PE of a system due to interactions of gravitational fields
such as the change in U when you lift an object from the floor to a height, h, from the floor - DU = mgDh
mgh vs -GmM/r
UG = mgh near the surface
UG = -GmM/r “farther afield)
it is negative b/c U is at infinity and gets larger and larger negative as a mass moves closer to the earth
electric potential energy
such as the energy stored in the capacitor of a camera flash unit
chemical potential energy
charged car battery
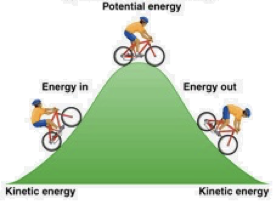
mechanical energy
includes kinetic and potential energy of an object or system due to its motion or position
falling object mechanical energy neglecting air friction
the gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy as the object falls
maintaining constant total mechanical energy
falling object mechanical energy including air friction
total mechanical energy is not constant as the object falls
some is converted to thermal energy in the molecules of the object in the air
means a temperature increase in both the object and the air
work is a
scalar quantity
measured in joules
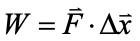
work is negative or porsitive
force and displacement in same direction: posiitive
different direction: negative
perpindicular: zero
(+/-) work on a system (increases/decreases) the mechanical energy of the system
positive work on the system increases the mechanical energy of the system
negative work on a system decreases the mechanical energy of the system
friction usually does NEGATIVE work on systems
ball rolling across a floor mechanical energy
gravitational potential energy does not change
friction does negative work on the energy (in opposite direction that the ball rolls)
eventually decreasing its kinetic energy to zero as it converts the balls mechanical energy to thermal energy
mechanical energy is
potential and kinetic
work and energy
scalar qualities that can be measured in joules or calories
1J = 1 kg-m2/s2
1 cal = the amount of energy needed to raise the temp of 1 g of water by 1°C
4.186 J = 1 cal
1 nutritional calorie = 1,000 cal or 1 kcal
if there is no work ON the system
its total mechanical energy remains constant
work done On the system will change the energy of the system
work-energy theorem
work done on an object or system changes the mechanical energy of the system
•W = DK + DU
work done BY a system decreases the energy of the system
On = +
by = -
spring
work done in stretching a spring is = to the amount of Us stored in the sprng
½ kx2
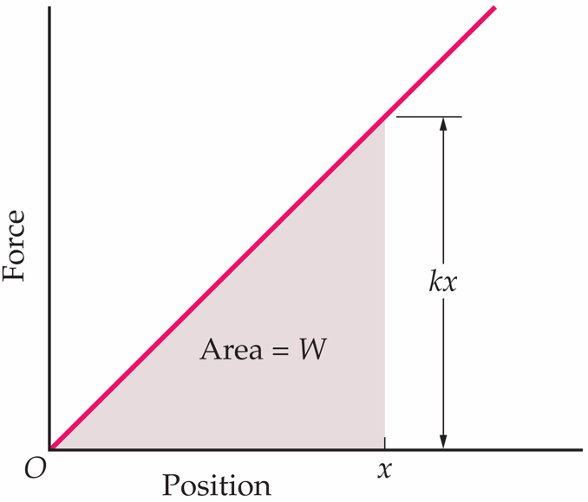
you can find the spring constant by graphing force vs position
slope is k
determining work by graphing
the work done on an object is equal to its change in mechanical energy
work is the area under a curve of a force vs position graph
total mechanical energy of a pendulum
remains constant throughout the pendulum’s motion (neglecting friction)
power
the rate at which energy changes or the rate at ehich work is done
measured in WATTS