FBS 31_MODULE 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
‘Cell’ is derived from what Latin word that means chamber?
Cella
Eukaryotic cells that differ in several key respects from the cells of other eukaryotic organisms.
Plant cells
Type of plant cell that are found in young part of the plant and have thin, permeable primary walls
Parenchyma cells
Type of cell that is smaller and thicker than parenchyma cells. Contains pectin
Collenchyma cells
The thickest type of plant cell that are dead at maturity
Sclerenchyma cells
Principal type of collenchyma cells that are thickened at intercellular contact points
Angular collenchyma
Principal type of collenchyma cells that are arranged into ordered rows and thickened at the tangential face of the cell wall
Tangential collenchyma
Principal type of collenchyma cells that have intercellular space and thickening proximal to the intercellular space
Lacunar collenchyma
Major tissues of the Plant cell
Dermal
Ground
Vascular
Major tissue that includes the epidermis and peridermis
Dermal tissue
Major tissue for photosynthesis, food storage, regeneration, support and protection
Ground tissue
Major tissue for transport of water and minerals; for transport of food
Vascular tissue
Major tissue for protection and prevention of water loss
Dermal tissue
Major tissue that includes parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma tissues
Ground tissue
Major tissue that includes xylem and phloem
Vascular tissue
Parts of the Plant Cell (3Cs, NMREPGV)
Cell wall
Cytoplasm
Chloroplast
Nucleus
Mitochondrion
Ribosomes
Endoplasmic reticulum
Plasma membrane
Golgi bodies
Vacuole
Vacuoles are bound by a single membrane called the?
Tonoplast
What gives shape and structure to the cell and to the whole plant as well.
Cell wall
What is the living part of the cell where organelles are embedded.
Cytoplasm
What is a plastid containing the green pigment called the chlorophyll.
Chloroplast
What controls the activities of the cell; the presence of the DNA in the nucleus explains why it is this part of the cell that controls cellular activities.
Nucleus
What is the site of respiration?
Mitochondrion
What the site of protein synthesis?
Ribosomes
What part of the cell is involved in cell transport?
Endoplasmic reticulum
What is the cytoplasmic membrane separating the cytoplasm from the cell wall?
Plasma membrane
What controls the entry or exit of materials into the cell?
Plasma membrane
What is involved in the synthesis of new cell walls
Golgi bodies
What is the part of the cell that are fluid-filled organelles bound by a single membrane called the tonoplast, and contain a wide range of inorganic ions and molecules?
Vacuole
What do you call the substance that are non-protoplasm materials found in cells and can be found in protoplasm, vacuoles, or in the cell wall?
Ergastic substance
The main ergastic substances of plant cells
Cellulose
Starch
What is the chief component of the cell wall?
Cellulose
What is the main component of living protoplasm?
Proteins
Proteins can occur in an amorphous or crystalline (or crystalloid) form
What is a well-known amorphous ergastic protein?
Gluten
These are waste/metabolic products or protective in function. Plants mostly deposit such material in their tissues.
Crystals
What group of the plant cell structure is being described?
tri-/di-glycerides (storage, secretion)
fats (lipids) and oils are widely distributed in plant tissues
Fats, Oils, Waxes
Substances related to fats—waxes, suberin, and cutin—occur as protective layers in or on the cell wall.
The function of these grains are for storage and are made up of protein.
Aleurone grains
What are phenol derivatives (deter herbivory, deter infection)?
Tannins
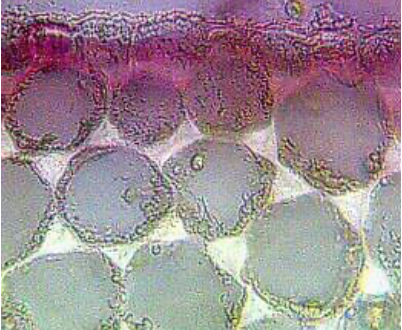
What type of collenchyma cell is this?
Angular
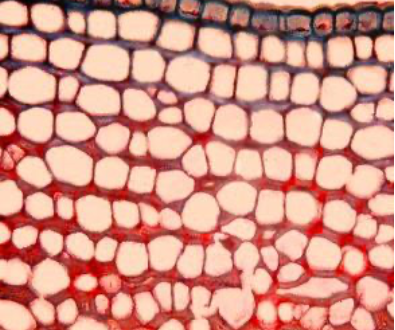
What type of collenchyma cell is this?
Tangential
What type of collenchyma cell is this?
Lacunar