PSY124-prejudice,stereotypes,discrimination
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Prejudice
negative feelings towards ppl based on their membership in a soc group
discrimination
negative behaviour towards ppl because of their membership in a certain group
stereotypes
belief that link a group of ppl w/ specific traits
prescriptive stereotypes
Beliefs about how a group should be (women should be nurturing)
descriptive stereotypes
Beliefs about how a group is (women are nurturing)
types of prejudice
racism
sexism
ageism
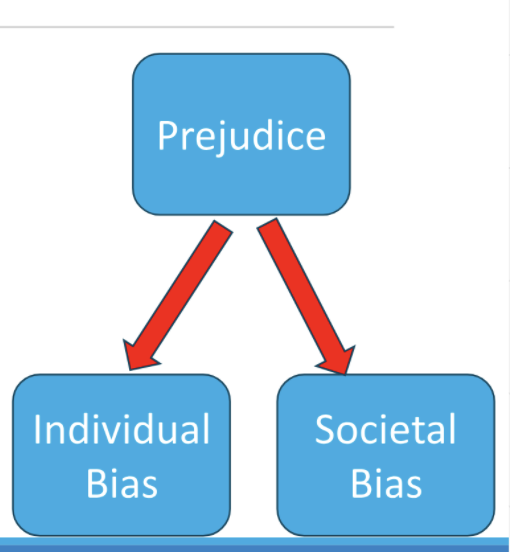
individual bias
a person has unfair beliefs, uses fixed labels, or treats others unfairly.
systemic bias
rules, organizations and traditions keep giving advantages to some groups while making life harder for others.
implicit bias
operates unconsciously and unintentionally
aversive racism
someone truly believes in equality but still shows racist behavior without realizing it
(Jury decisions, hiring)
moral credentialing
doing something good first so they feel it’s okay to act unfairly later (supporting minor group charity but make racist jokes)
virtual signalling
Publicly talk about their values to look fair or cover bias
microagressions
subtle but harmful form of discrimination
common themes of microagressions
Perpetual alien (“Where are you really from?”)
Ascribing positive traits (“You’re smart for a girl”)
Differential treatment (based on group membership)
Colourblindness
Denial of bias in meritocracy (“Stop complaining”)
Environmental (offensive names/places)
dehumanization
seeing people from other groups as less human, comparing them to animals or natural forces
infrahumanization
seeing people from other groups as less human by thinking they feel only simple emotions (like fear or anger) but not complex ones
ambivalent sexism
hostile sexism - negative resentful feelings towards women
benevolent sexism - women need protection, women are morally pure
stereotype threat
fearing you’ll be evaluated by negative stereotypes about your group (girls cant do math)
can become a self-fulfilling prophecy
can be reduced with intervention
meta stereotypes
outgroup will view ppl from your group which can make you worried they’ll see you in a negative way
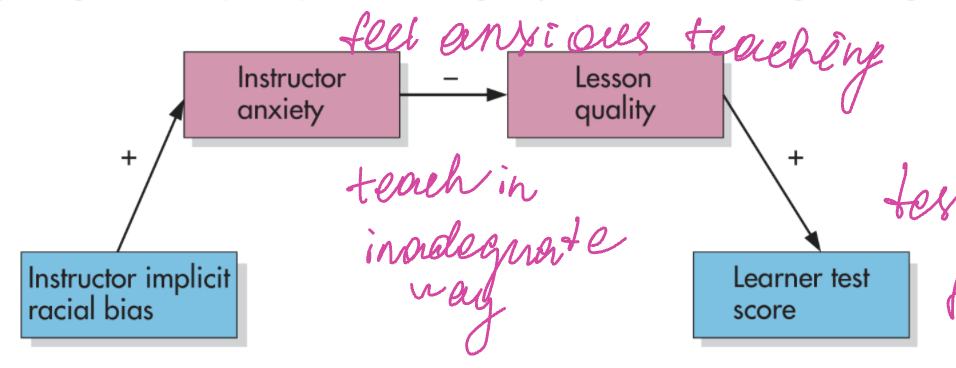
socialization
ppl learn the norms, rules and info of their culture or group. (learning gender norms, racial attitudes, other social biases)
gender norms
pervasive, lead to double standards
intersectionality
multiple overlapping social identities
soc categorization
classifying persons into groups based on common attributes
outgroup homogeneity effect
thinking that people from another group all seem the same, while seeing more differences among people in your own group
stereotypes
belief about what people are like just because they belong to a certain group
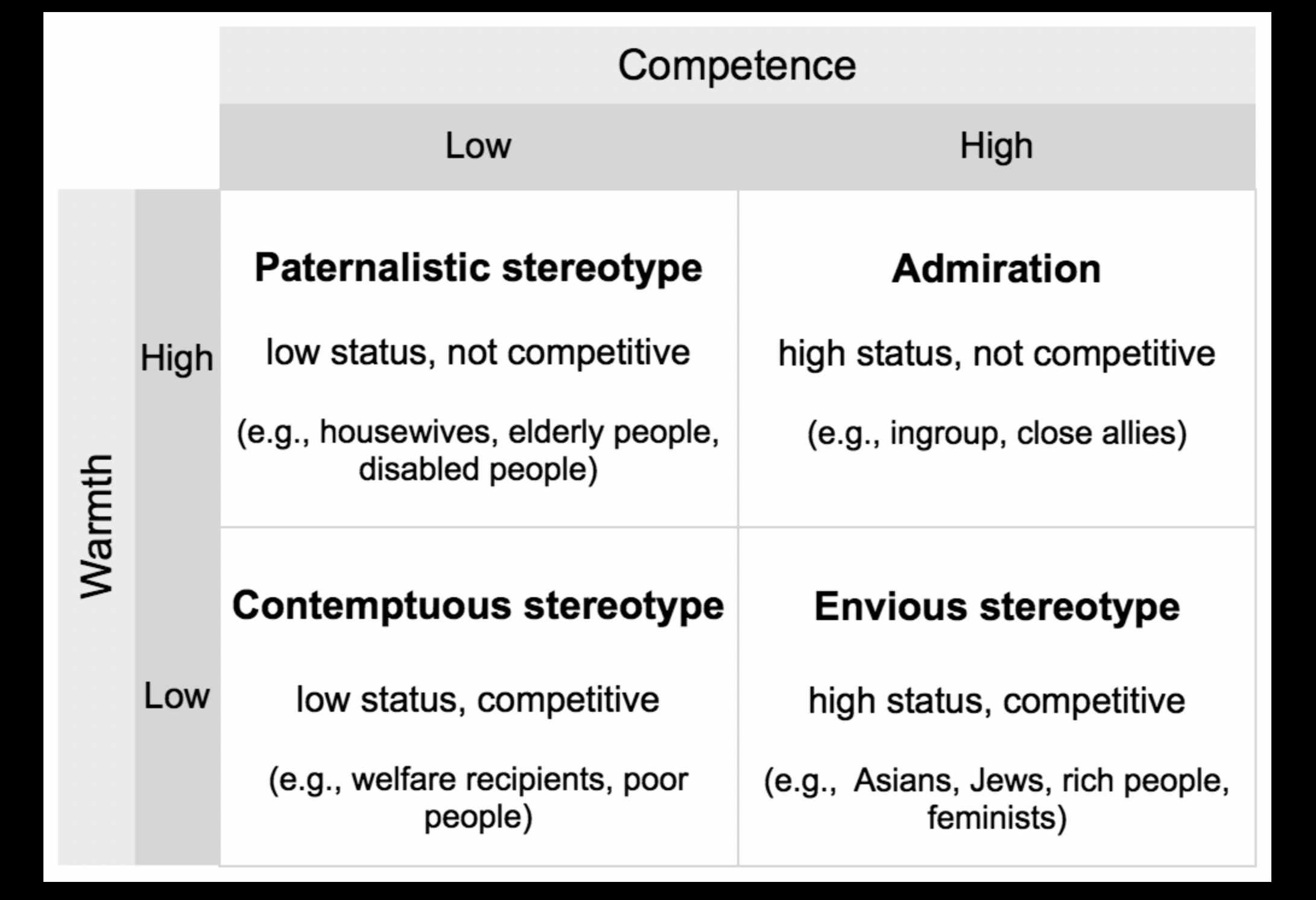
the stereotype content model
2 dimensions:
1 warmth - group is friendly
2 competence - group is capable/skilled
stereotype-consistent info
illusory correlation
confirmation bias
illusory correlation
imagining a connection between two things that don’t actually relate
confirmation bias
focusing on information that supports what you already believe and ignoring anything that disagrees with it
stereotype - inconsistent info
attributions - making excuses for behavior that doesn’t fit a stereotype( blaming the situation or the person so the stereotype still seems true)
subtyping - ppl lable the person as a exception, whent they dont match the stereotype
self control
suppressing stereotypes takes mental effort
extrinsic motivation
not wanting to apper prejudiced
intrinsic motivation
not wanting to be prejudiced
social identity th
we get much of our sense of who we are and our self-worth from the groups we belong to, so we want to view our own groups in a positive way
ingroup favoritism
discriminate against outgroups and favor ingroups
minimal group design
participants are randomly assigned, but told they belong to a specific group
realistic group conflict th
groups become hostile toward each other when they’re fighting over the same limited things (jobs, money)
Social Dominance Orientation
a desire to see one’s in-group as dominant over other groups and adopting values that facilitate oppression
system justification th
ppl are motivated to defend and justify the existing soc, political and econ conditions
contact hypothesis
group hostility will be reduced by:
equal status btwn the group
personal interaction btwn the members
cooperation on a shared goal
soc norms favor contact
common ingroup identity model
people from different groups start seeing themselves as part of one larger group, their attitudes toward each other usually become more positive
jigsaw classroom
children from diff backgrounds cooperate by learning diff parts of a larger project