Honors Global Tsars
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
History
- 800-900 CE Vikings moved south along the rivers
- Became known as the "Rus" --> mixture of Scandinavian and Slavic peoples
Where was Russian civilization centered?
Kiev (Kyiv)
Vladimir the Great (980-1015)
Introduced Christianity
Yaroslav the Wise (1019-1054)
- Legal code with fixed punishments
- Divided kingdom among sons
Why did they decline after Yaroslav?
Lack of clear heir led to civil war
Time period (1242)
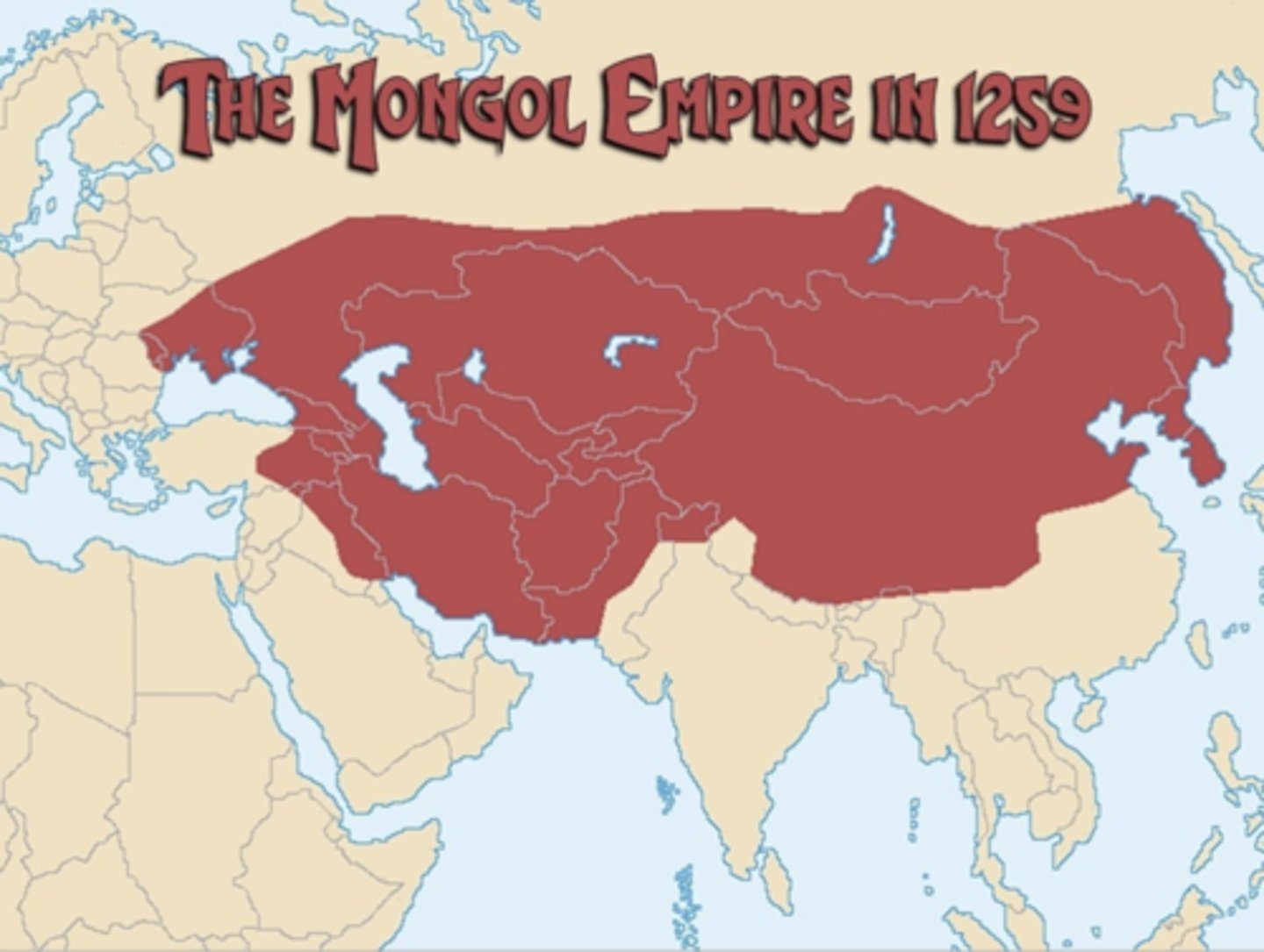
- The Golden Horde (Mongols) sacked Kiev
- Local princes acted as tax collectors
- Moscow princes became most powerful
Power of Moscow rose as power of __ declines (1242)
Khan
The Mongol Empire in 1259
The Tatars
- Descendants of the Mongols
- 2nd largest ethnic group (after Russians)
- Dominate Kazan and other Volga cities
- Predominantly Muslim
- Became a political force in new Russia
Tributary State
Muscovite princes paid tribute to the Mongol Empire until 1480
1480
The Mongols retreated leaving Muscovy to be an independent kingdom
Ivan III (1462-1502)
- First Tsar of Russia
- Proclaims Muscovy to be independent in 1480
- Moscow prince who led rebellion against Mongol rule
The Byzantine Empire (11th Century)
Buffer state between Islamic empires and Christian Europe
The Fall of Constantinople (1453)
- Constantinople falls to the Ottoman Empire
- Changes name to Istanbul
Who did Ivan III (1462-1502) marry into?
A Byzantine royal family
What does Russia begin to see themselves as?
The next defender of Christendom
Divine Right
The belief that the right to rule is given direvt
Russian Orthodox Church
- Dominant religion in Russia
- Tsar rules by Divine Right
- Slavic language (not Latin)
Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584)
KEY POINTS
- Consolidated power
- Expands borders
- Terror as political tool
- Time of Troubles
How does Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584) consolidate power?
- Solidifies the power of the Tsar and eliminates rivals
- Tsar at 3, suffers abuse and neglect at the hands of the Boyars
- At 16 he pushes them aside and takes power
What did Ivan do in 1564?
Abdicates throne
- Alleges corruption of clergy and boyars
- Boyars beg him to return
- He agrees, with conditions --> absolute power
Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584)
Terror as a Political Tool
- Uses torture and murder as a way to gain power
Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584)
Expansion of borders
- Expands Russia past the historic Moscow borders
- Conquered Mongol strongholds of Kazan and Astrakhan
Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584)
Time of troubles
Dies without strong heir --> leads to chaos
- Ivan kills his own son
- Other son (Fyodor) takes over
- Many pretenders "False Dmitrys"
- Invasions by Sweden and Poland
Boyars
Noble class in Russia
Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584) Expansion of Russia shown on map
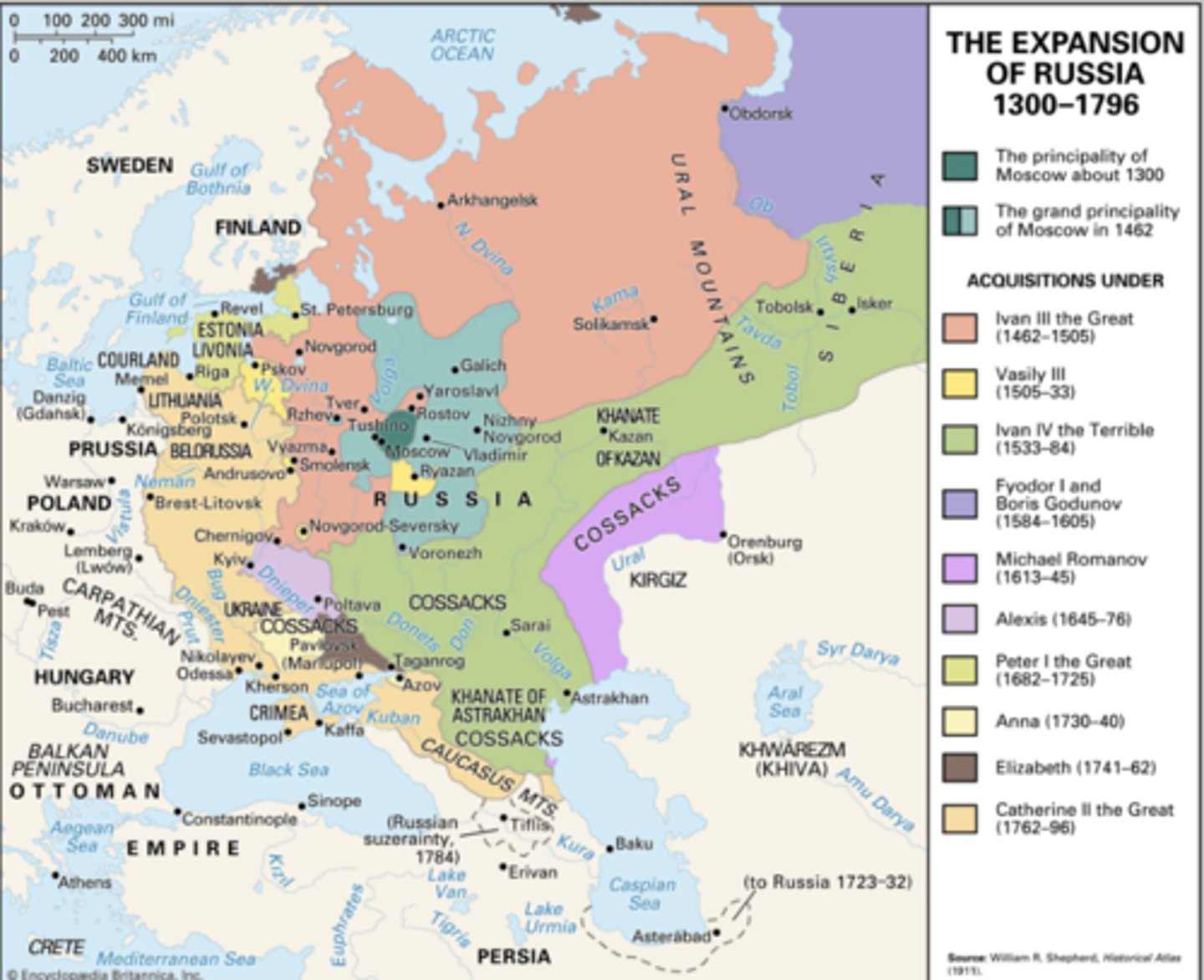
Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584)
Oprichnina
Oprichnina - State policy that allowed mass executions, torture, and oppression of boyars and peasants
Oprichnik - Group of "bodyguards" to carry out orders
Ivan IV The Terrible (1533-1584)
Son - Fyodor
- Son that took over
- Weak, Boyars mostly rule
- No clear heir after him
Romanov Dynasty
- Dynasty elected in 1613 at end of Time of Troubles; ruled Russia until 1917
- One of the longest ruling dynasties in European history
Micheal Romanov
- Started the Romanov Dynasty
- Boyars elect him to end troubles
- 16 years old, boyars thought he would be easy to control
- Gives Boyars total control over serfs
Serfs
Peasant in Russia tied to the land they worked on. Similar to slavery
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
KEY POINTS
- Modernization
- Westernization
- Expansion
- Absolutism
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Modernization
- Modernizes technology and military
- Peter moved Russia away from old Russian ways
- No beards
- Empahsis on modern science
- Baroque art
- Modernizes military
- Builds a Navy
- Prussian-inspired tactics
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Westernization
- Orients Russia towards Western Europe
- Peter wants to make Russian culture more "western"
- Beard Tax
- Western clothes
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Expansion
- Expands borders, captures a warm water port
- He desperately wants a warm water port
- Can't trade efficiently without one
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Absolutism
- Expands power of Tsar, limits opposing factions
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Background
- Peter's father dies when he is young
- Co-rules with half brother
- Sister really is in charge
- Overthrows sister, brother dies
- He takes over as sole ruler in 1696
- Puts down Streltsy rebellion in 1698
Streltsy
Russian infantry class
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Touring Europe
- Learns shipbuilding
- Modern medicine
- Military tactics
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Great Northern War
War with Sweden
Russian wins land that becomes St. Petersburg
What does Peter the Great (1682-1725) create?
Modern Navy
Peter the Great (1682-1725)'s new city
- Builds new city
- Moves capital
- Forced labor and forced residency
What is Peter the Great (1682-1725) reign defined by?
War
St. Petersburg
Russia's "Window to the West"
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Absolutism - Boyars
- Creates service nobility based on merit system
- Kills and exiles dissenters
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Absolutism - Russian Orthodox Church
Gets rid of Patriarch, rules as a secular Tsar
Patriarch
Leader of the Russian Orthodox Church
Similar to the Pope
Peter the Great (1682-1725)
Absolutism - Streltsy
- harshly puts down rebellion
- Tortures and kills over 1,000
- Disbands group
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Key Points
- Government Reform
- Westernization
- Expansion
- Enlightenment
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Government Reform
- Tries to move away from terror as a political tool
- Increased control of landowning boyars
- Good for boyars, bad for serfs
- Financially supported foreign philosopers
- Not so much Russian ones
- Some religious toleration
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Westernization
- Creates western/Eurppean-style court
- Catherine is German wants to bring western sophistication to Russian court
- Patron of western philosophers and artists
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Expansion
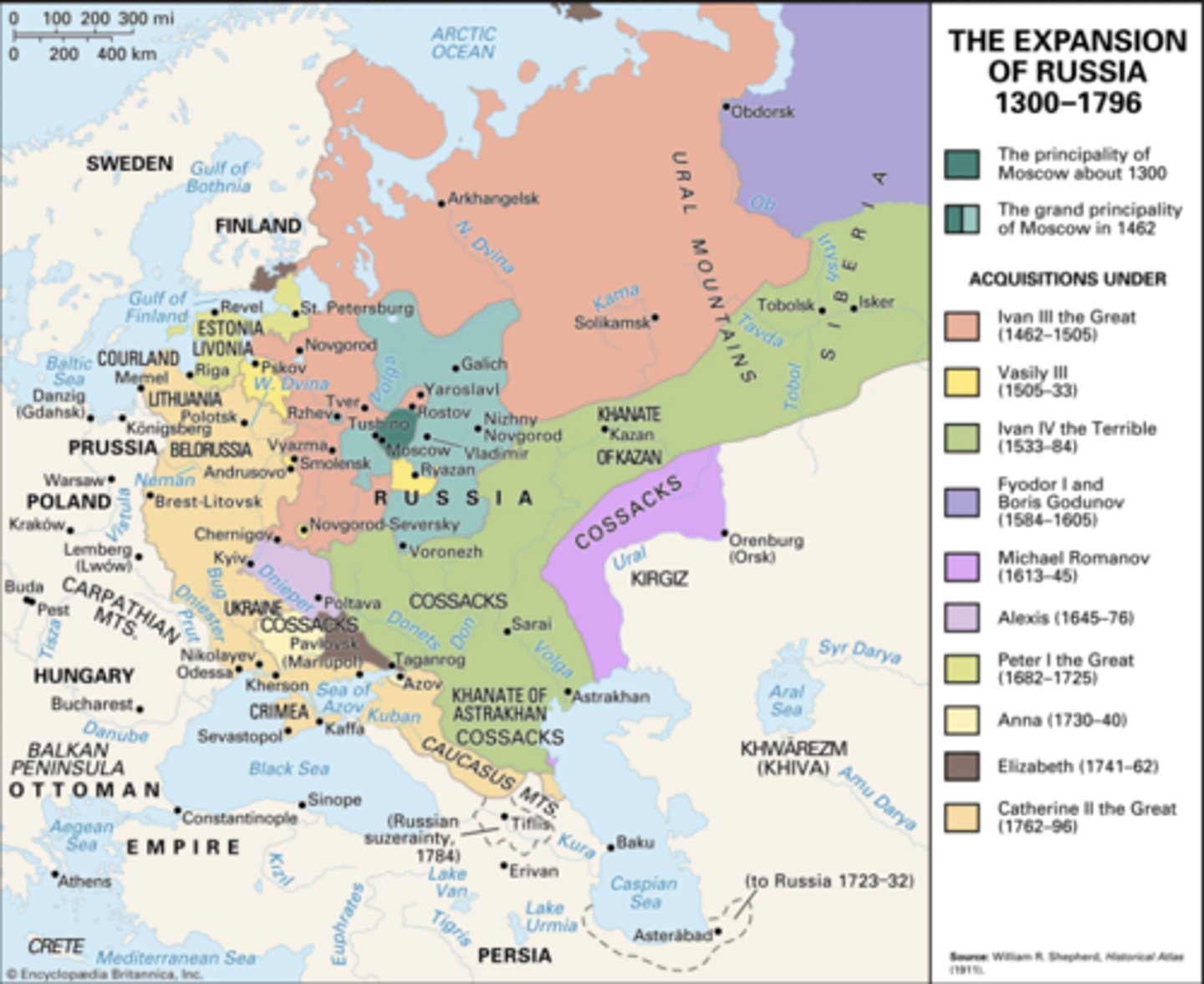
Significantly expands borders, including Crimean Peninsula
- Expanded west into Crimea, Black Sea, Poland, Belarus, and Lithunia
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Enlightenment
- Supported art, education (especially for women), and public health
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Background
- Born as a German princess
- Name was Sophie von Anhalt-Zerbst
- Married Peter the Great's grandson (Peter III)
- Converts to Russian Orthodox, takes new name
Peter III (CTG's wife)
- Horrible rule
- Obsessed with Prussia
- Hated Catherine (feeling was mutual)
Peter III and Catherine the Great's son
Paul I
Paternity is questioned
Peter III assassination - 1762
Coup led by Catherine's lover and supported by Catherine
Pugachev Rebllion - 1773-1775
Cossack rebellion, put down by Catherine
Pugachev
A peasant who claimed to be Peter III and led a peasant revolt against Catherine but it resulted in worse conditions for them than before
Cossack
Peasent group in Eastern Russia
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Westernization - The Hermitage
Art gallery started by Catherine
Largest gallery in the world by area today
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Expansion Map
Potemkin Villages
- To avoid upsetting CII Potemkin would create "false fronts"
- Idyllic peasant villages
- In reality --> poor, hungry & cold
- Becomes the pattern in Soviet Union
What is Catherine the Great (1762-1796) considered as
One of the Enlightened Monarchs
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)
Death and Aftermath
- Never remarried
- Hated her only "legitimate" son
- Wanted to skip him in succession and name grandson (Alexander 1) heir
- Catherine died suddenly before that could happen
Catherine the Great (1762-1796)'s son Paul 1
Proceeds to undo most of Catherine's reforms until he is asassinated
Alexander I (1801 - 1825)
Russia V. Napoleon
- Napoleon had conquered much of Europe, moved East against Russia in 1812
- Scorched earth
- Russia sets strategic parts of Moscow on fire to hurt French troops
- Russian winter forces retreat
- Napoleon weakened and never recovers
Alexander I (1801 - 1825)
Russia Defeats Napoleon
- Alexander welcomed as hero in Europe
- Invited to Congress of Vienna in 1814 to decide future of Europe
- Earns respect and recognition from Europe
Nicholas I (1825-1855)
Background
- Becomes king after Alexander dies and older brother refuses
- Interegnum period led to "Decembrist revolt"
- Orhtodoxy, autocracy, nationalism
Interregnum
Period between two monarchs
Nicholas I (1825-1855)
Decembrist Revolt
- Soldiers loyal to Nicholas's older brother (Constantine) revolted to put him in power
- NI put down revolt quickly, harshly punished leaders and sent many to Siberia
Nicholas I (1825-1855)
Military
- Expanded Military
- Many wars
- Army large but weak
- Lost Crimean war
Nicholas I (1825-1855)
Rule
- Strict, harsh rule
- Used police spies
Nicholas I (1825-1855)
Anti-Westernization
- Banned books
- Strictly controlled education
Nicholas I (1825-1855)
Reforms
- Issued some actual reforms
- New legal code
- Economic reform
- Industrialization
- Considered ending serfdom
- Decided not to, didn't want to upset the boyars
Alexander II the Liberator (1855-1881)
Emancipation Reform
1861
- Abolished serfdom on private land
- Made serfs free citizens, could marry, move, own land, etc.
Alexander II the Liberator (1855-1881)
Judicial Reform
- New penal code
- Trial in open court
- Jury stsem
- Lifetime tenure for judges
- Considered elected assembly to advise Tsar
Zemstvo
Local self-government set up in Russia under Alexander II
What did Alexander II the Liberator (1855-1881) sell and to who?
Sold Alaska to the US
Alexander II the Liberator (1855-1881)
Assassination
- Survived 5 assassination attempts from 1866-1880
- Assassinated in 1881 by group called "The People's Will"
Alexander III (1881-1894)
Relationship with father
- Did not get along with his father
- Disagreed about many policy decisions
Alexander III (1881-1894)
Changes
- Undid AII's reforms
- Limited power of zemstvo
- Stopped creation of advisory board to Tsar
Who did Alexander III (1881-1894) kill?
- Hunted down members of "The People's Will" and killed them
- Hung Vladimir Lenin's brother
Alexander III (1881-1894)
Political Ideal (Russification)
- A nation containing only one nationality, language, & religion
Alexander III (1881-1894)
Russification
Imposed Russian language and schools on non-Russian ethnic minorities
Alexander III (1881-1894)
Progroms
- Assassination of AII led to a series of pogroms from 1881-1884
- AIII passed harsh laws against Jews in Russia (part of Russification)
- Caused many to flee, many to America
Pogroms
Violent riots aimed at expelling a particular ethnic group, usually Jews
Alexander III (1881-1894)'s death
Died younger than expected
Nicholas II The Last Tsar (1894-1917)
Background
- Not well prepared for throne
- Strong believer in Divine Right
- Wrongly believed all Russians loved and adored him
Nicholas II The Last Tsar (1894-1917)
Russo-Japanese War
1904-1905
- Russia soundly defeated, embarassing for NII
Revolution of 1905
Four main causes
- Agrarian problem
- Nationality problem
- Labor problem
- Educated class problem
Revolution of 1905
Bloody Sunday
- Unarmed group came to present petition to NII
- Imperial guard fired on them and killed many
Revolution of 1905
Result
- Creation of Duma
- New Constitution
- October Manifesto
Duma
Russian parliament, initially created to advise Tsar and create laws (with Tsar veto)
Nicholas II The Last Tsar (1894-1917)
Family
Wife, Alexandra, hated by Russians
5 children, 1 boy who was only chance for an heir
Nicholas II The Last Tsar (1894-1917)'s son
Alexei
Had hemophilia which is a hereditary blood disease
Rasputin
Context
- Self proclaimed healer and mystic
- Befriended NII and Alexandra, claimed he could heal Alexei
Rasputin
Influence
- Increased influence
- At one point was commanding WWI troops
Rasputin
Death
- Assassinated by noblemen who opposed his influence