10.G BIO, C1 Patterns of Evolution (PART G)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Microevolution
Allele frequencies diverge within a species occurs over years or decades due to mutations, genetic drift, gene flow and natural selection. Evidence comes from analyzing organisms and populations
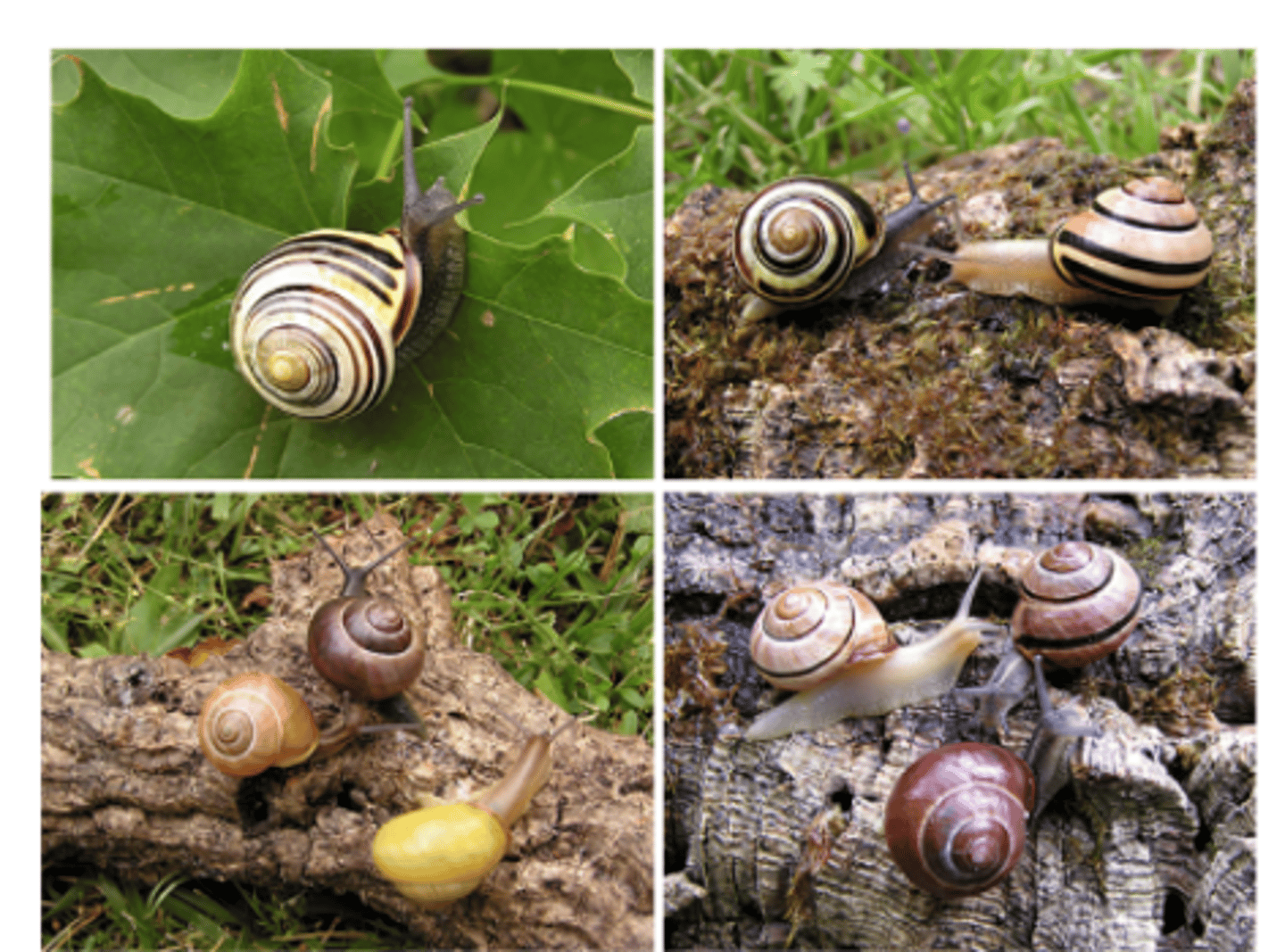

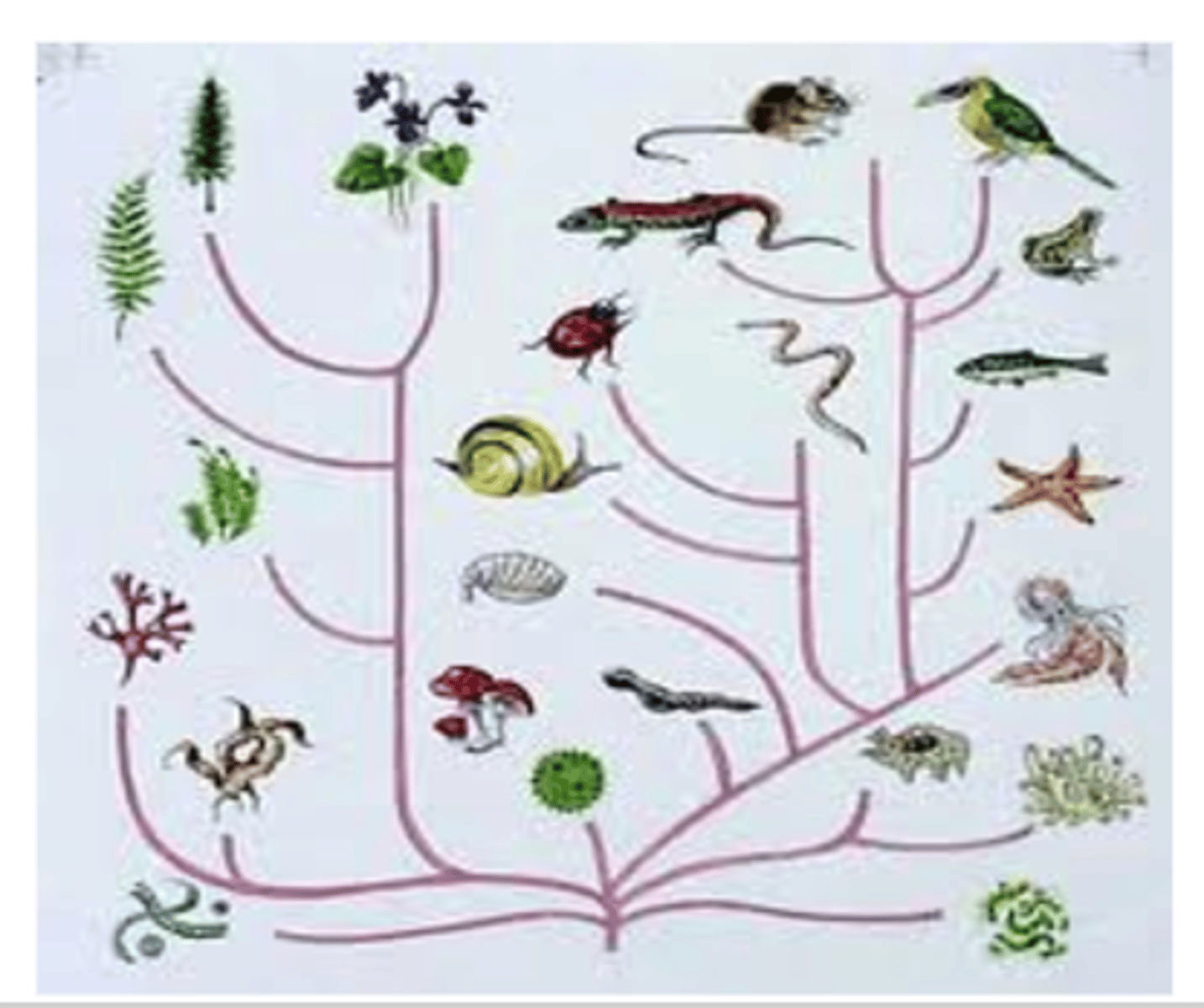
Macroevolution (Description)
Large scale changes in allele frequencies within a species that results in the formation of a new species. Typically occurs over thousands or millions of years due to geographic and reproductive isolation.
Macroevolution (Examples)
Examples include:
- Extinction
- Adaptive Radiation
- Evolution
- Coevolution
- Punctuated Equilibrium
- Changes in Genes
Extinction
A term that typically describes a species that no longer has any known living individuals.
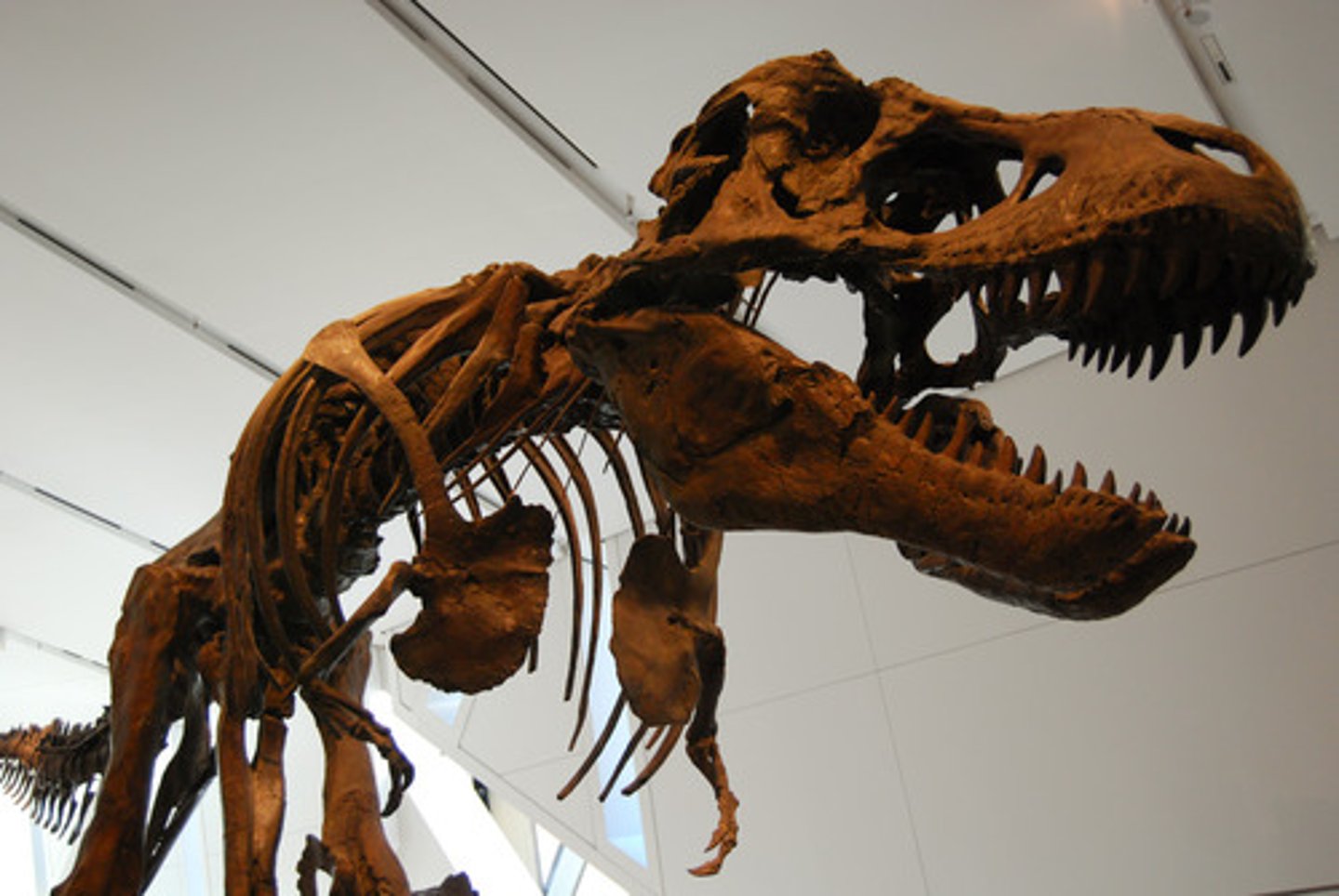

Adaptive radiation
The process by which many related species evolve from a single ancestral species. This is also referred to as divergent evolution.
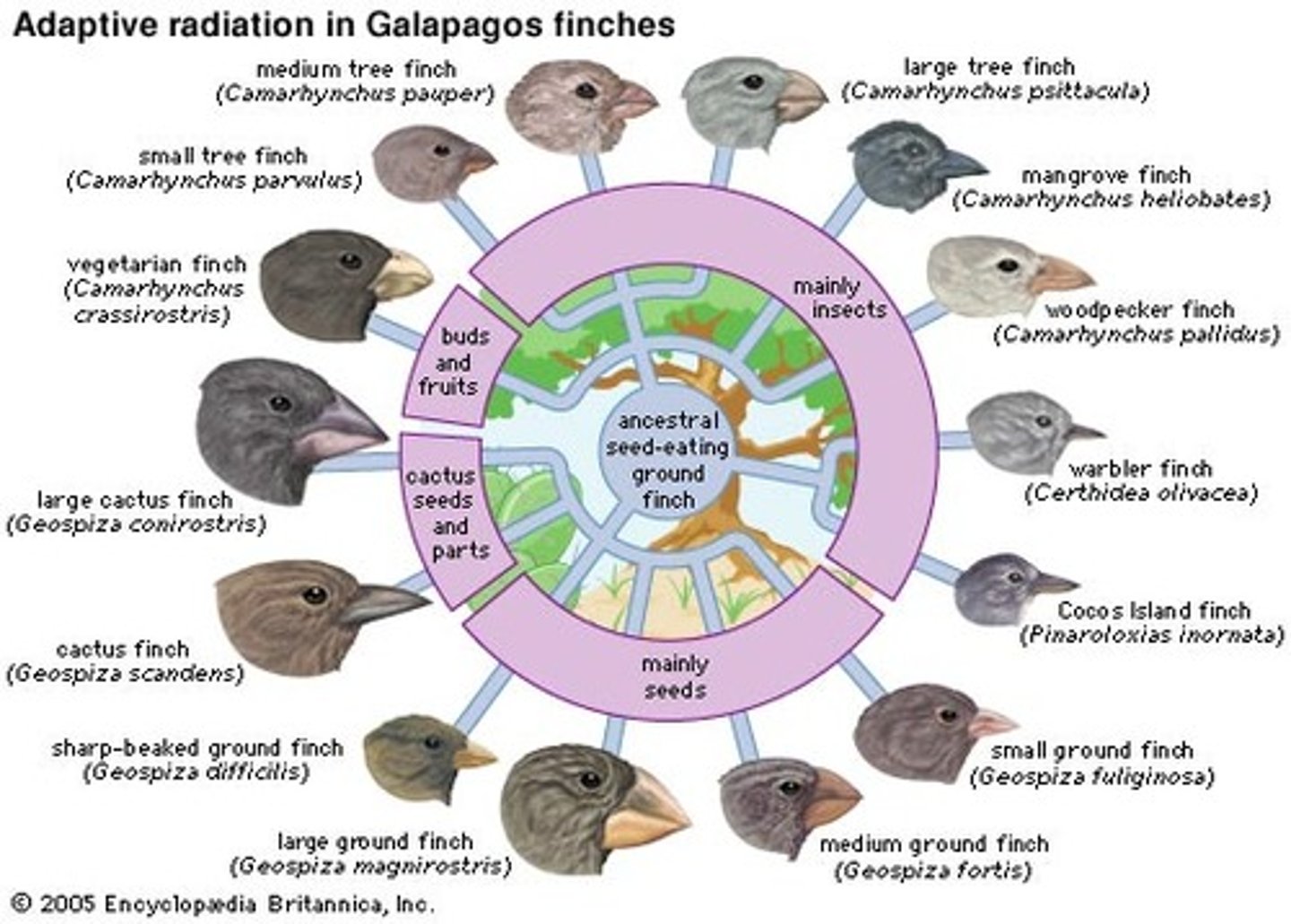
Divergent evolution
The process by which many related species evolve from a single ancestral species. Also referred to as adaptive radiation.
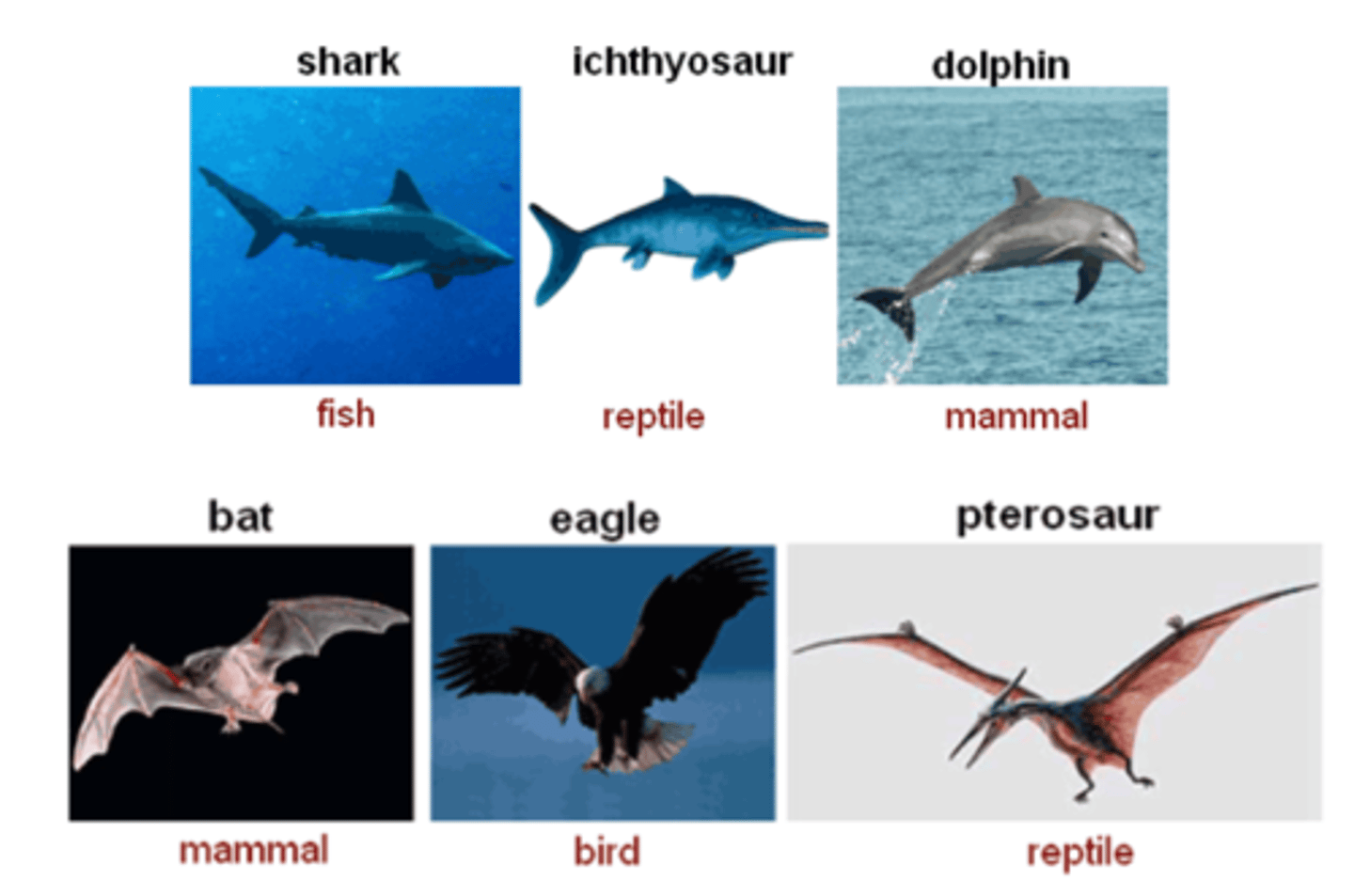
Convergent evolution
The process by which unrelated organisms come to resemble one another due to being subjected to similar selective pressures that result in similar adaptations (e.g. shark/dolphin; bat/bird)

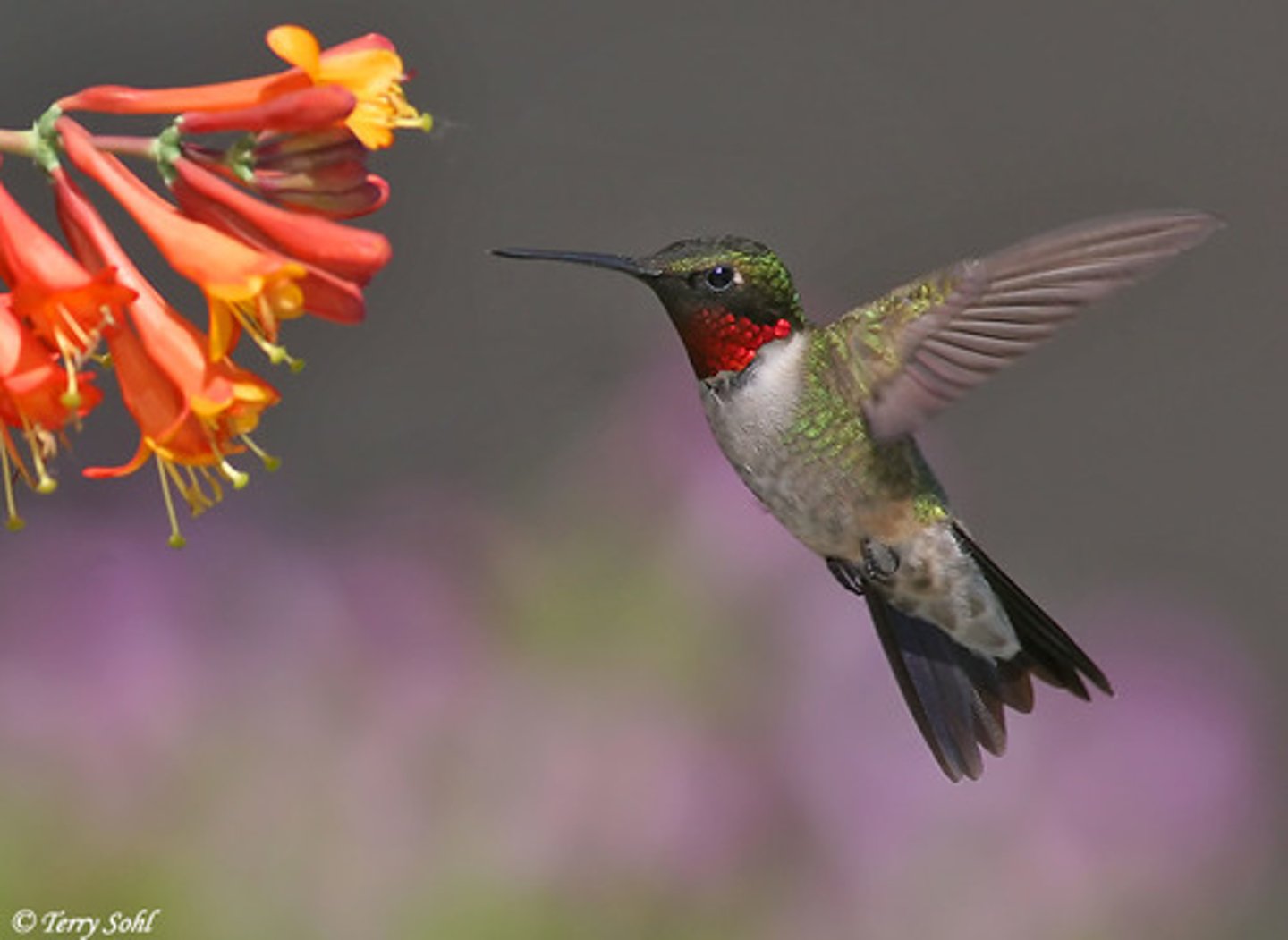
Coevolution
The process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other over time (e.g. flowers and insects)

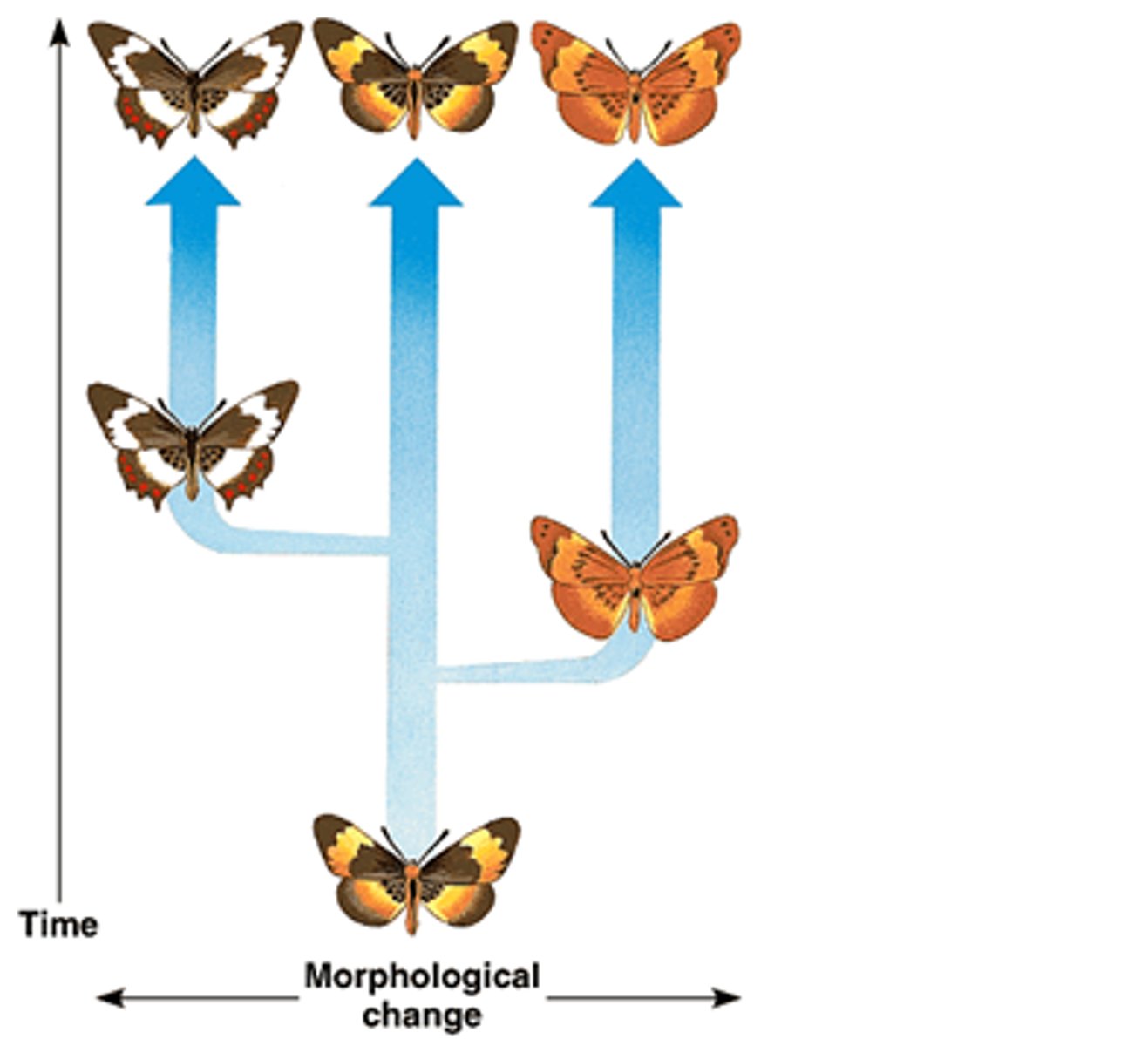
Hypotheses on Rate of Evolution
Gradualism
Punctuated Equilibrium
Gradualism
Idea that species originate through a gradual change of adaptations
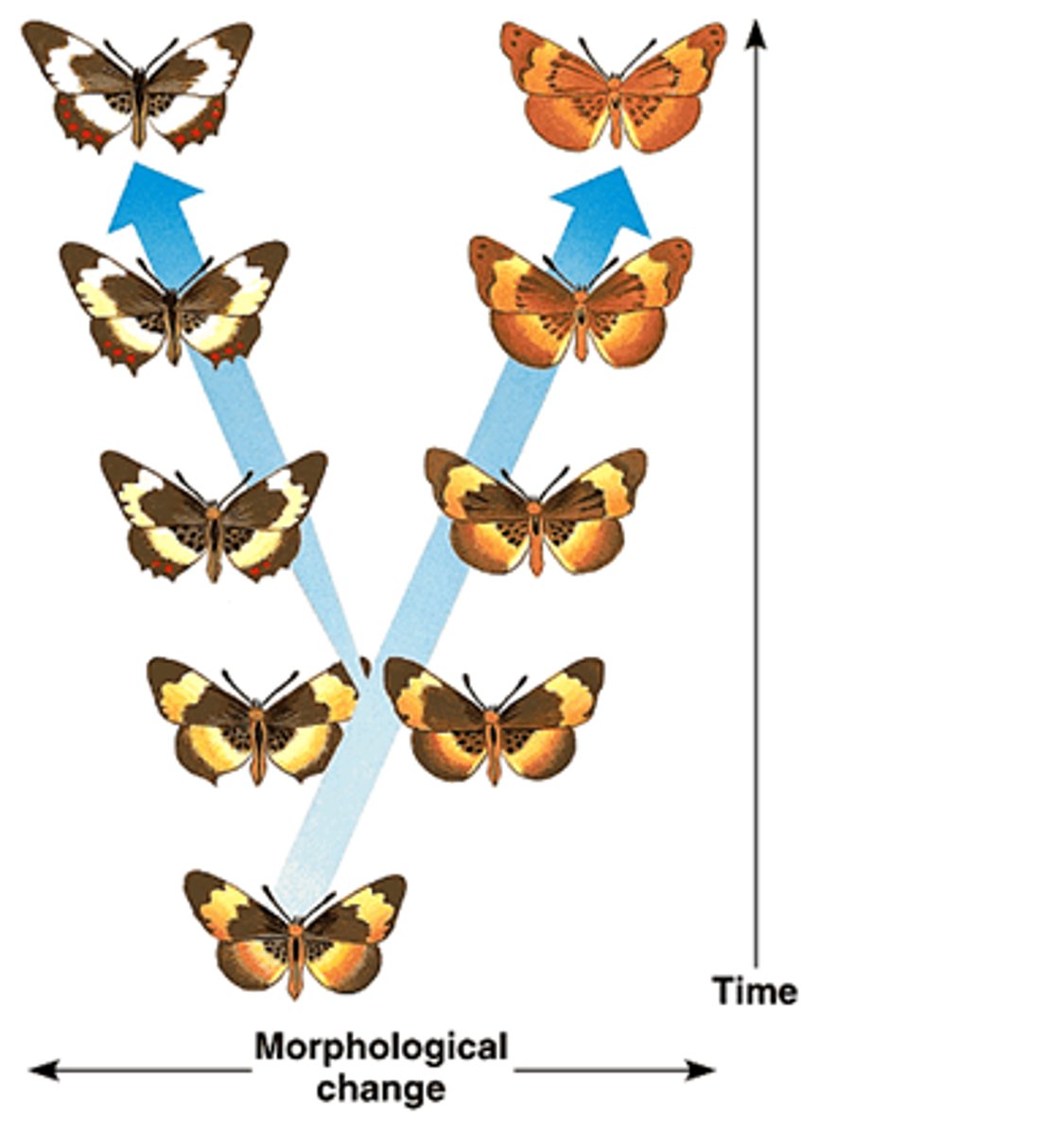
Punctuated equilibrium
Idea that speciation occurs relatively quickly in rapid bursts (due to environmental change) with long periods of genetic equilibrium in between