AS level OCR Chemistry
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Isotopes
Different atomic forms of the same element. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
Relative atomic mass
The mean mass of an atom of an element, compared to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Concentration=
Number of moles ÷ Volume
One mole
6.02×10^23
Number of moles=
mass ÷ molar mass
r.t.p
25 ºC
100 kPa (1 atm)
Molar gas volume
24 dm³ / mol
One mole of any gas always has the same volume at r.t.p
Number of moles=
Volume (dm^3) ÷ Molar gas volume (24 dm^3 / mol)
R- Gas constant
8.314 J / K / mol
Gas equation
pV = nRT
(Pa)(m³)(K)
Assumes forces between molecules are negligible and the molecules have a negligible size
Empirical formula
The smallest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
Molecular formula
The actual number of atoms of each element in a compound
Ions:
Nitrate
Carbonate
Sulfate
Hydroxide
Ammonium
Zinc ion
Silver ion
Formula:
NO3-
CO3²-
SO4²-
OH-
NH4+
Zn²+
Ag+
Acids
Proton donors - produce H+ ions in water
Alkalis
Proton acceptors - produce OH- ions in water
Acid + Base=
Metal oxide + Acid=
Metal hydroxide + Acid=
Salt + Water
Metal + Acid=
Metal salt + Hydrogen
Metal carbonate + Acid=
Metal salt + Carbon dioxide + Water
Ammonia + Acid=
Ammonium salt
Methyl orange
Yellow in alkali, red in acids
Phenolphthalein
Pink in alkali, colourless in acids
Oxidation number of oxygen
Nearly always -2, except in peroxides where it is -1 and 0 in molecular oxygen
Oxidation number of hydrogen
Nearly always +1, except in metal hydrides where it is -1 and 0 in molecular hydrogen
Sub-shells:
s
p
d
f
Orbitals:
1
3
5
7
Ionic bonding
The electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
Covalent bond
The electrostatic forces of attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms
Exceptions to covalent bonding
Boron trifluoride- 6 electrons in the outer shells
Sulfur hexafluoride- 12 electrons in the outer shells
Dative covalent bonding (coordinate bonding)
Both electrons from one atom
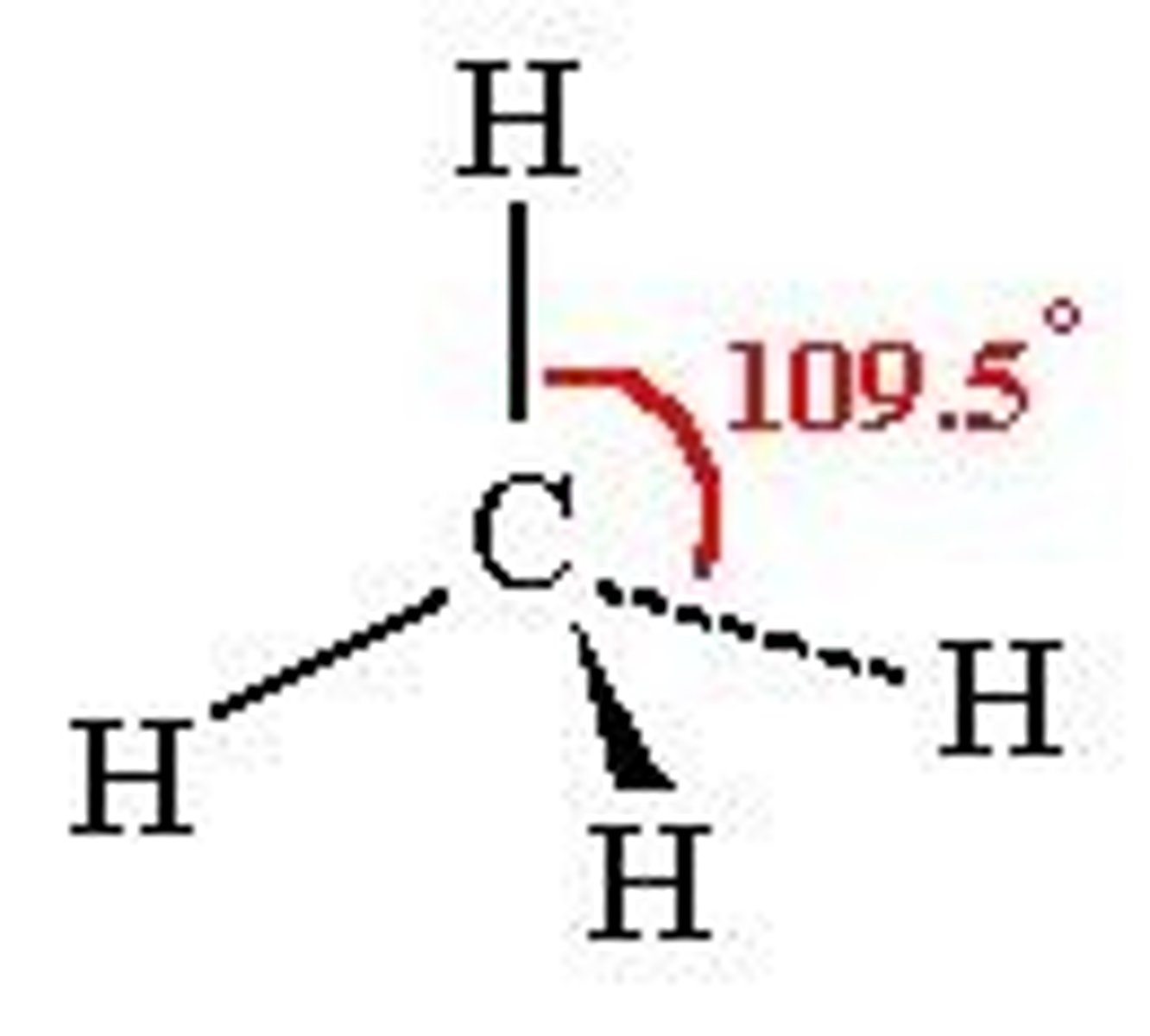
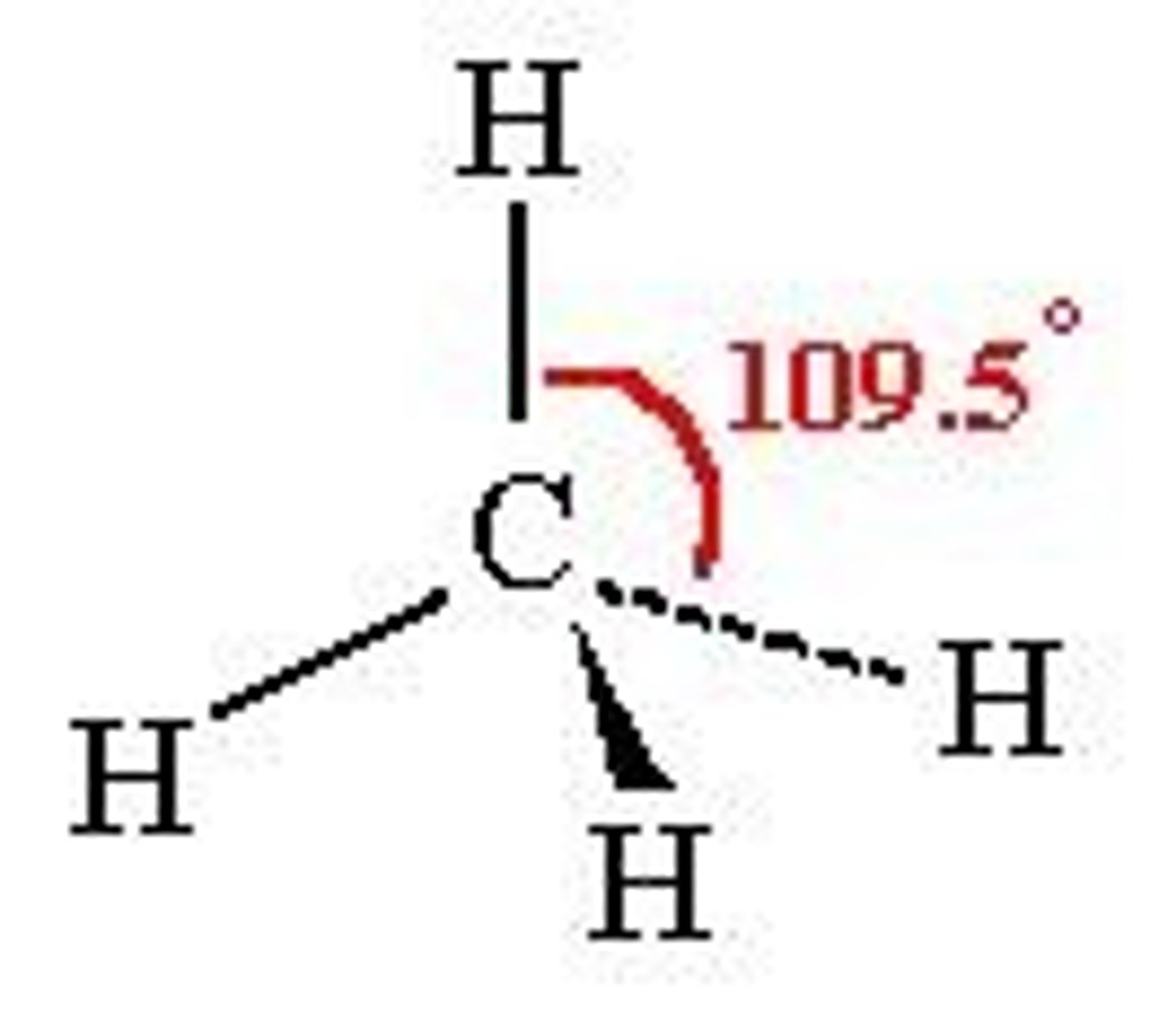
Shape of methane molecule
No lone pairs
Bond angle- 109.5º
Shape of ammonia molecule
1 lone pair
Bond angle- 107º
Shape of water molecule
2 lone pairs
Bond angle- 104.5º
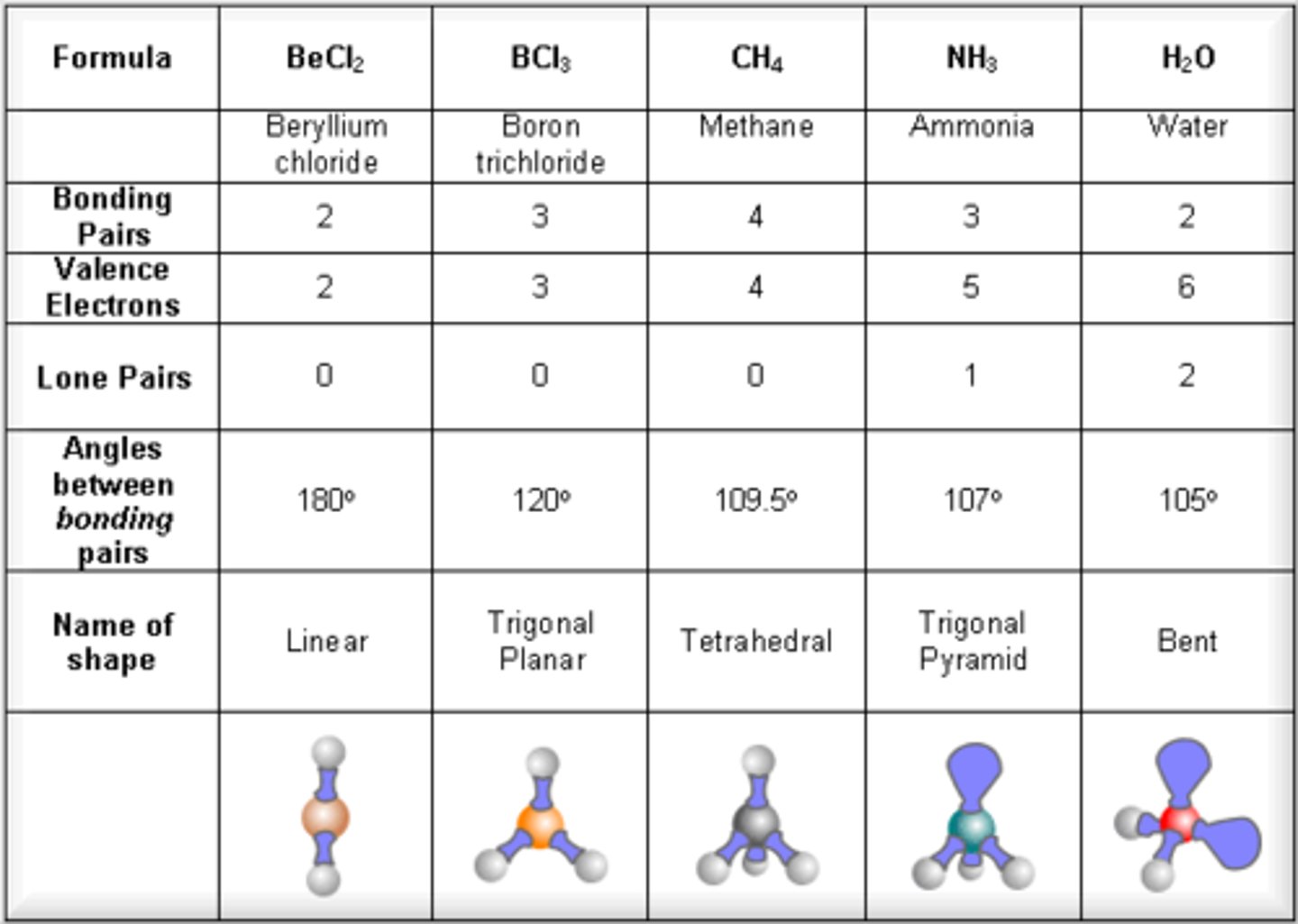
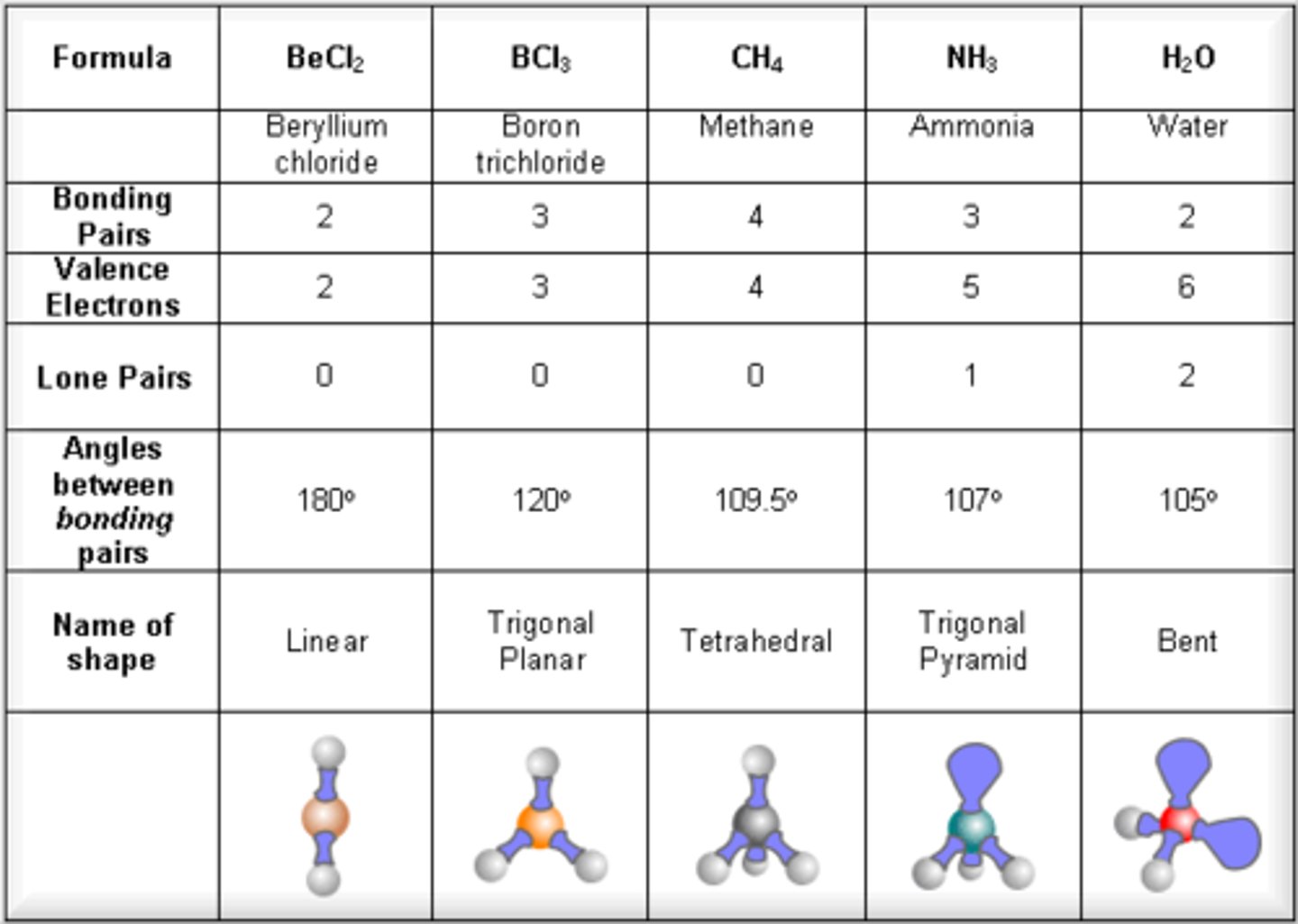
Linear molecules
2 electron pairs around central atom
Bond angle- 180º
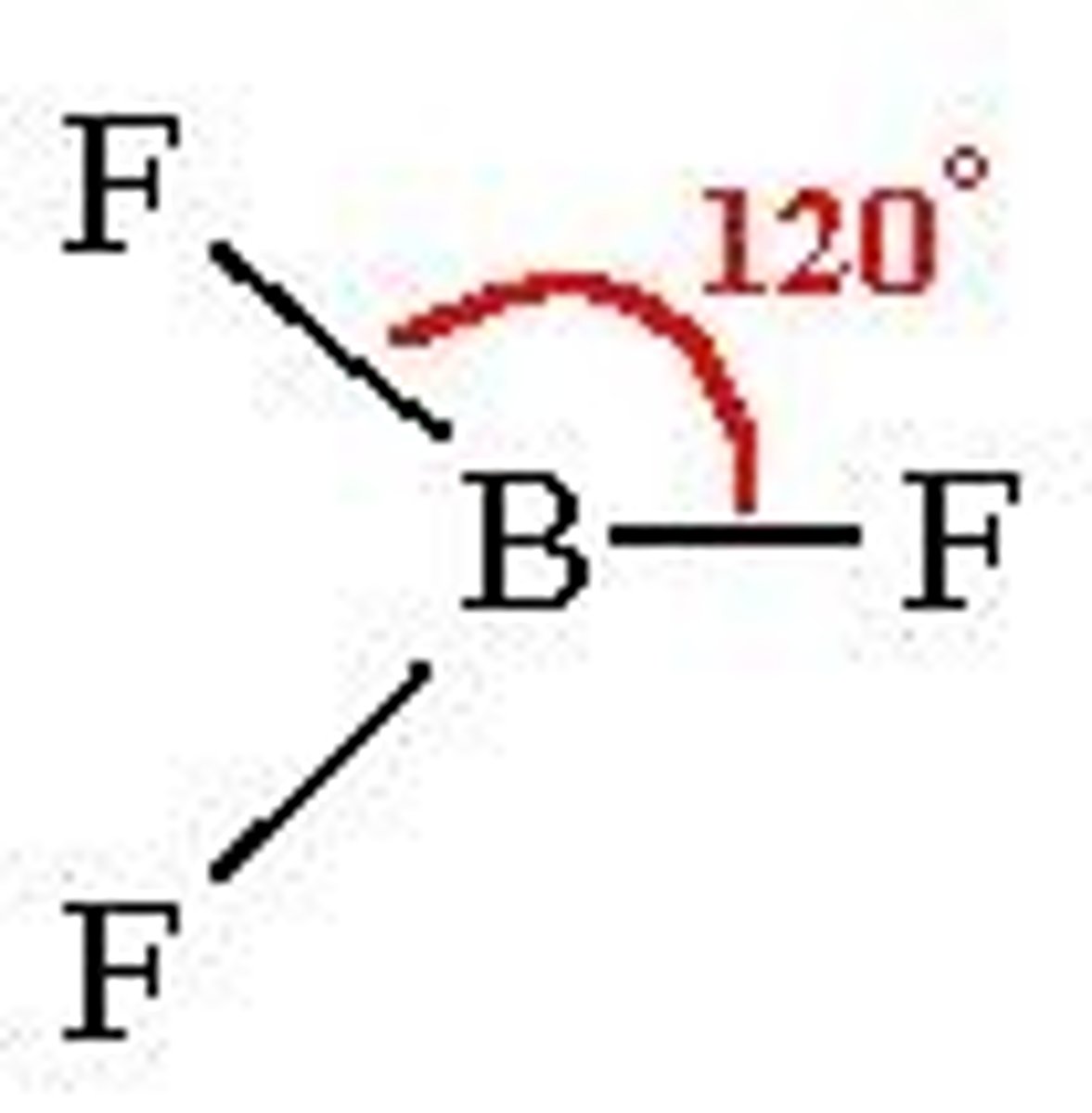
Trigonal planar
3 electron pairs around central atom
No lone pairs
Bond angle- 120º
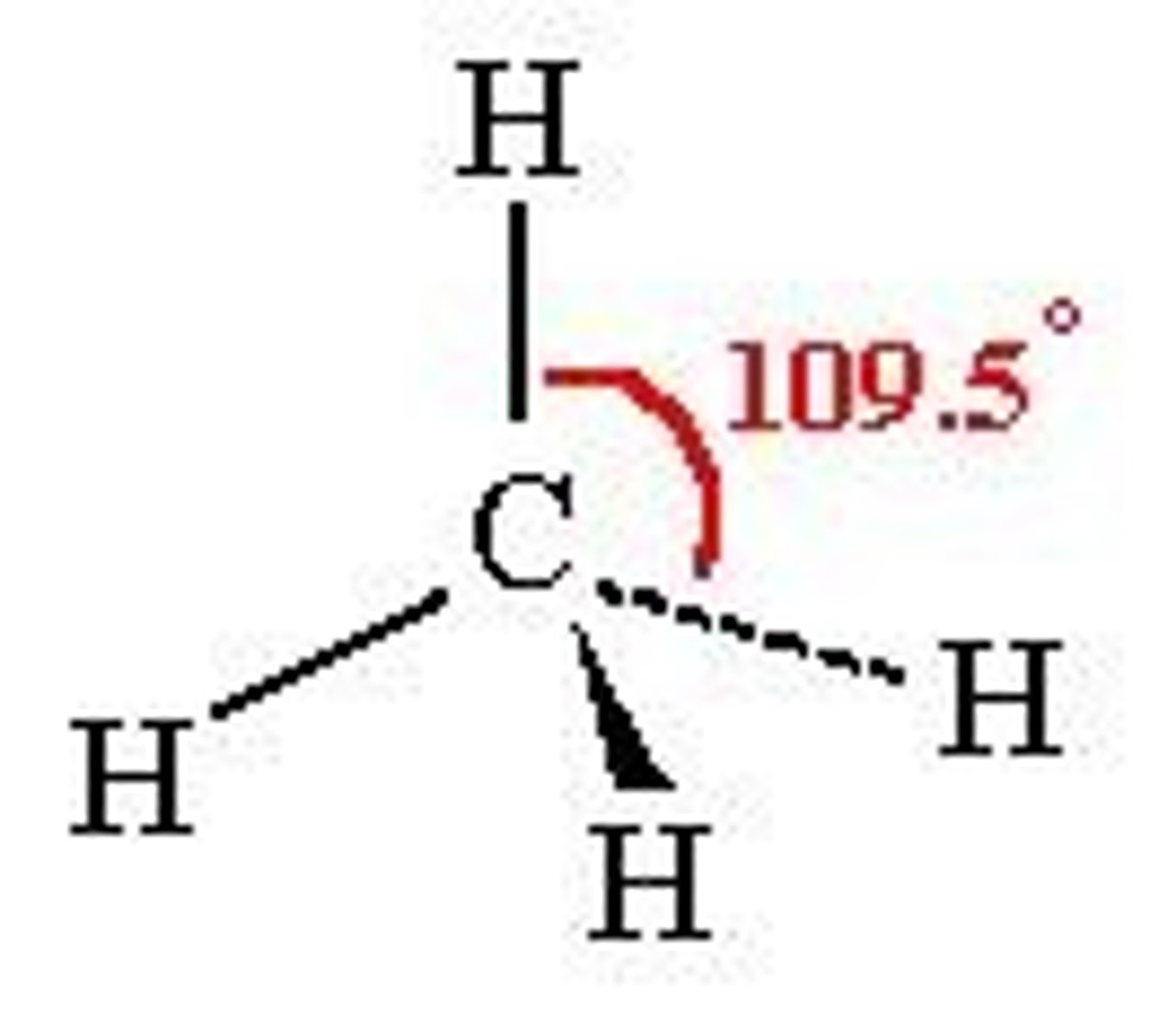
Tetrahedral
4 electron pairs around central atom
No lone pairs
Bond angle- 109.5º
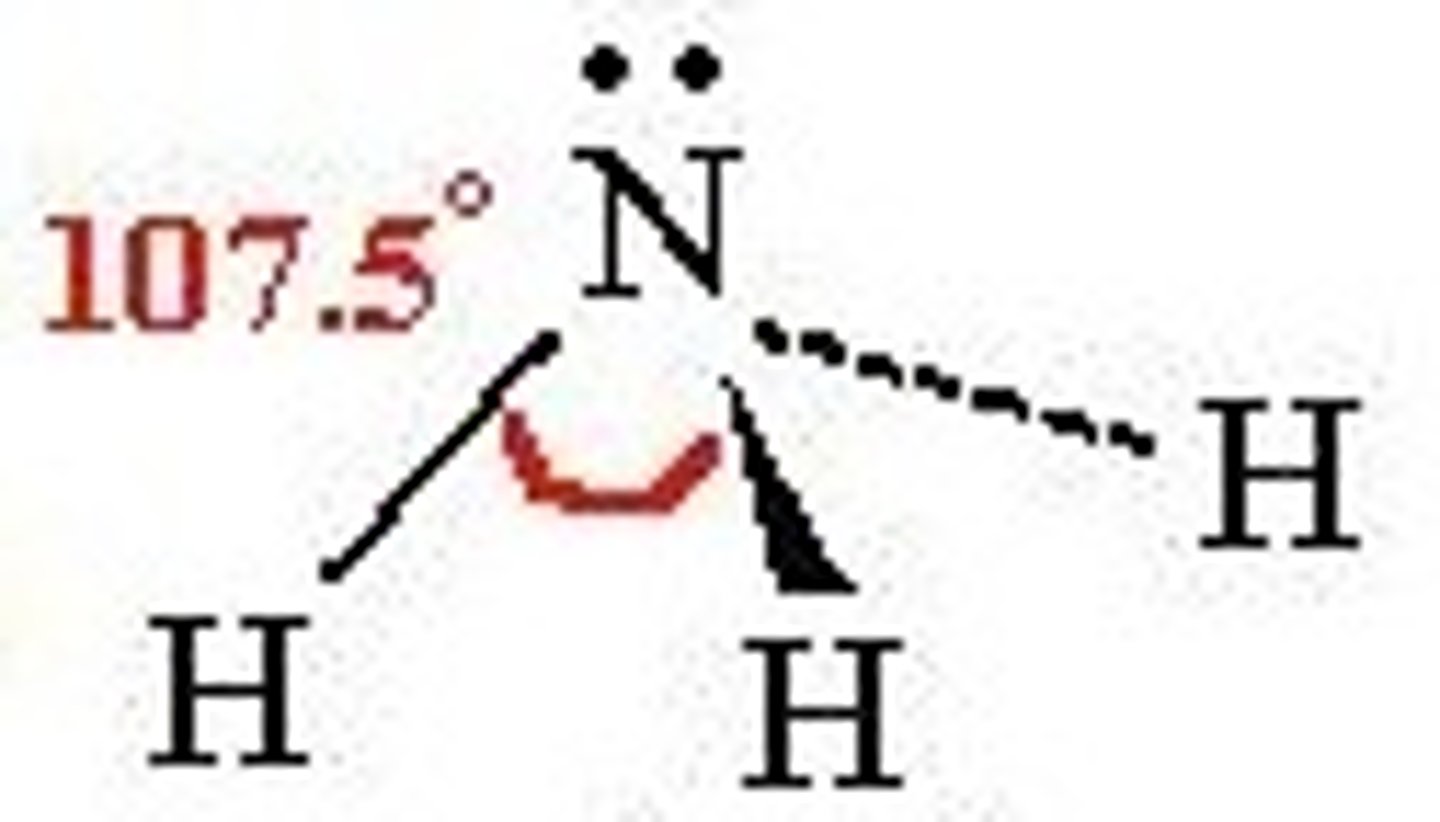
Pyramidal
4 electron pairs around central atom
1 lone pair included
Bond angle 107º
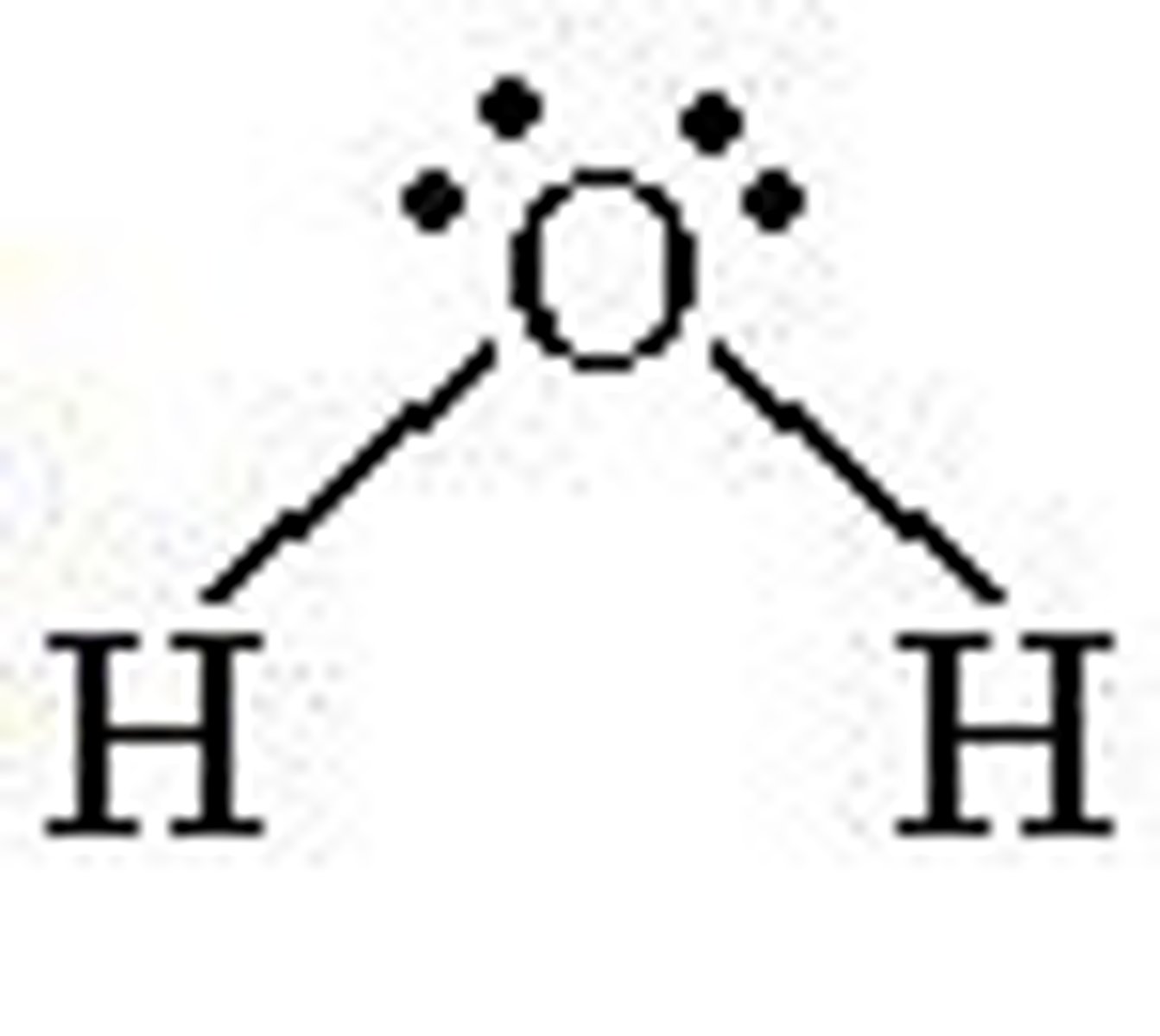
Nonlinear
4 electron pairs around central atom
2 lone pairs
Bond angle- 104.5º
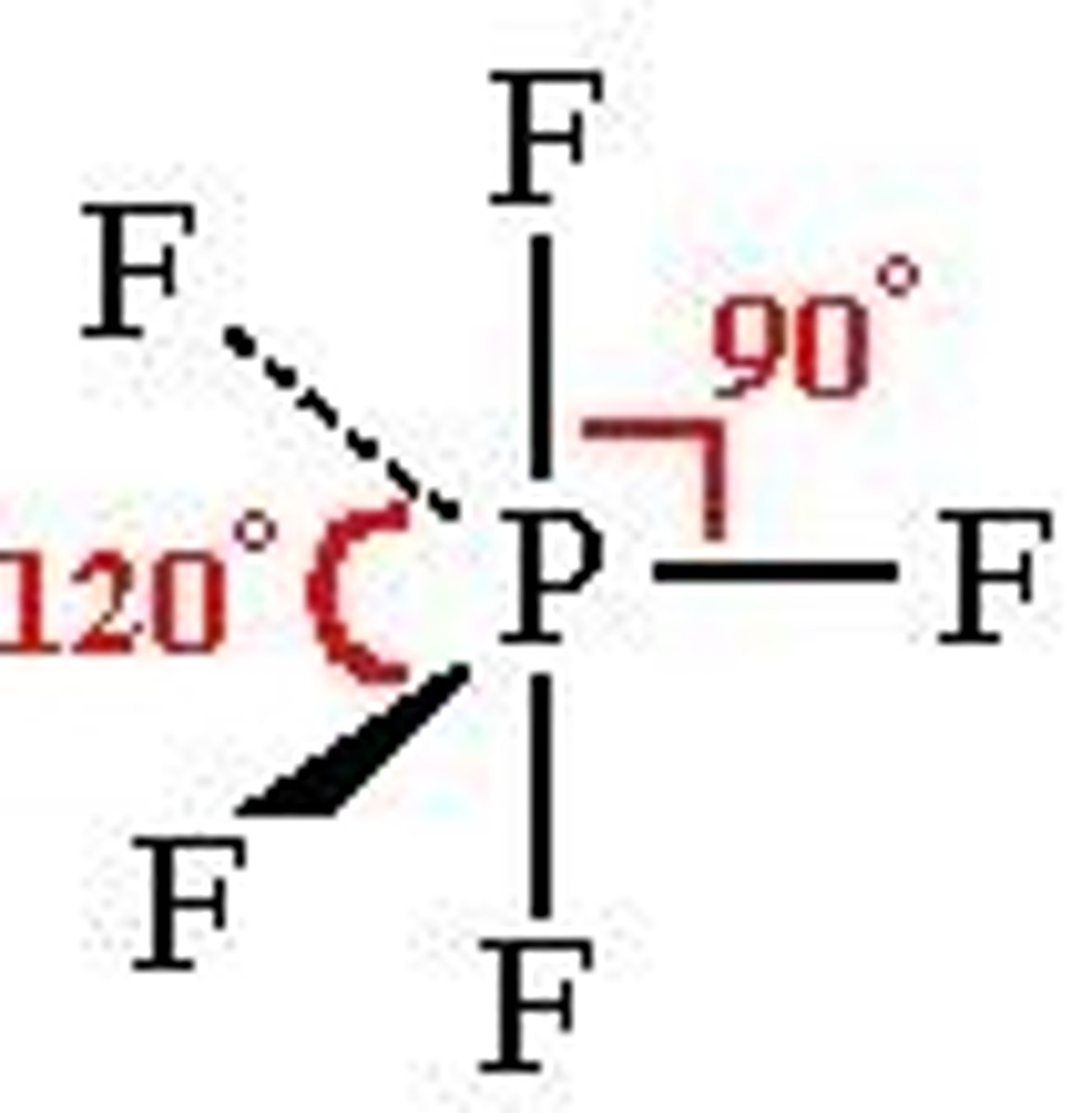
Trigonal bipyramidal
5 electron pairs around central atom
No lone pairs
Bond angle- 120º, 90º
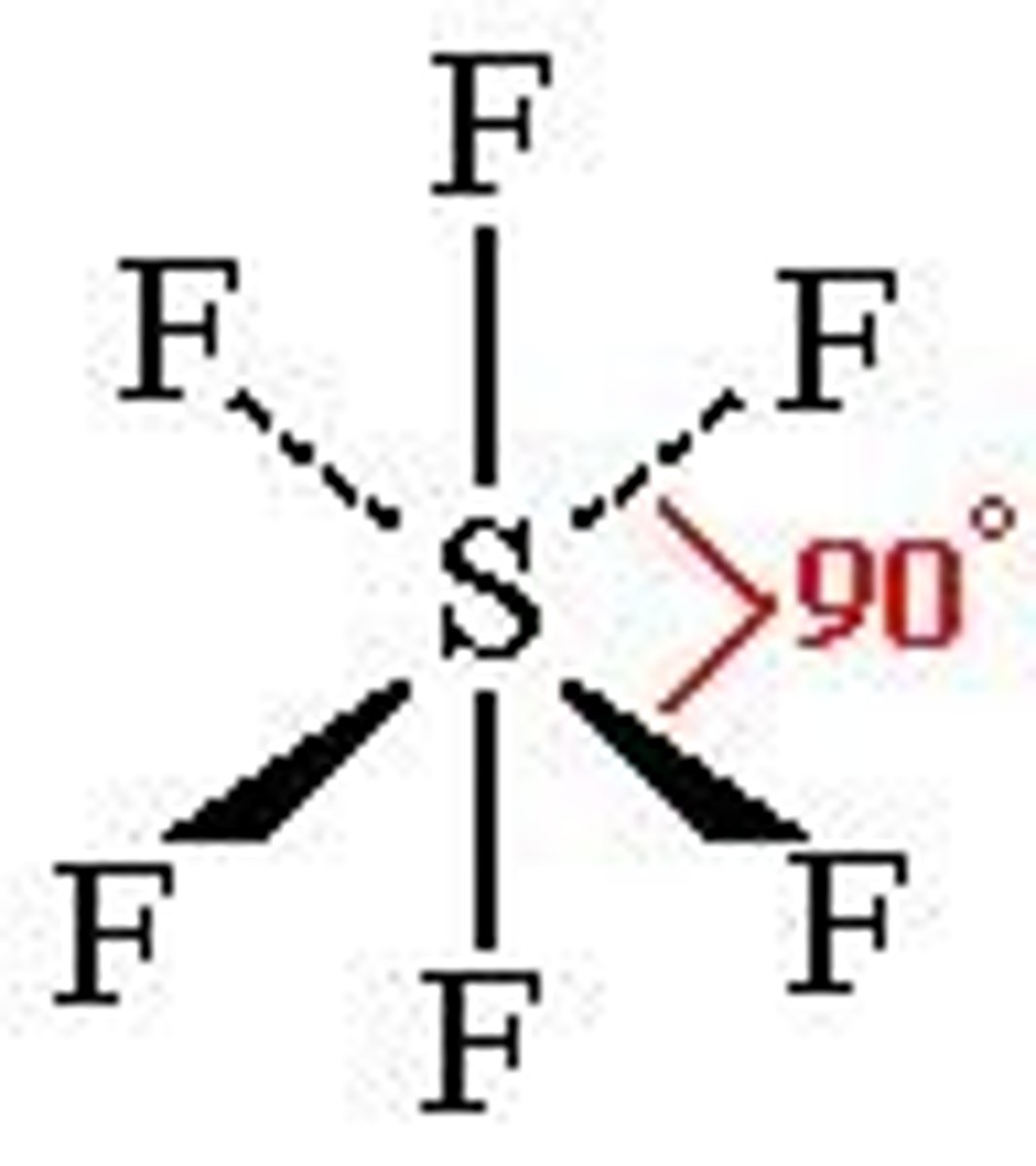
Octahedral
6 electron pairs around central atom
No lone pairs
Bond angle- All 90º
Electronegativity
An atom's ability to attract the electron pair in a covalent bond
Three types of intermolecular forces
Induced dipole-dipole
Permanent dipole-dipole interactions
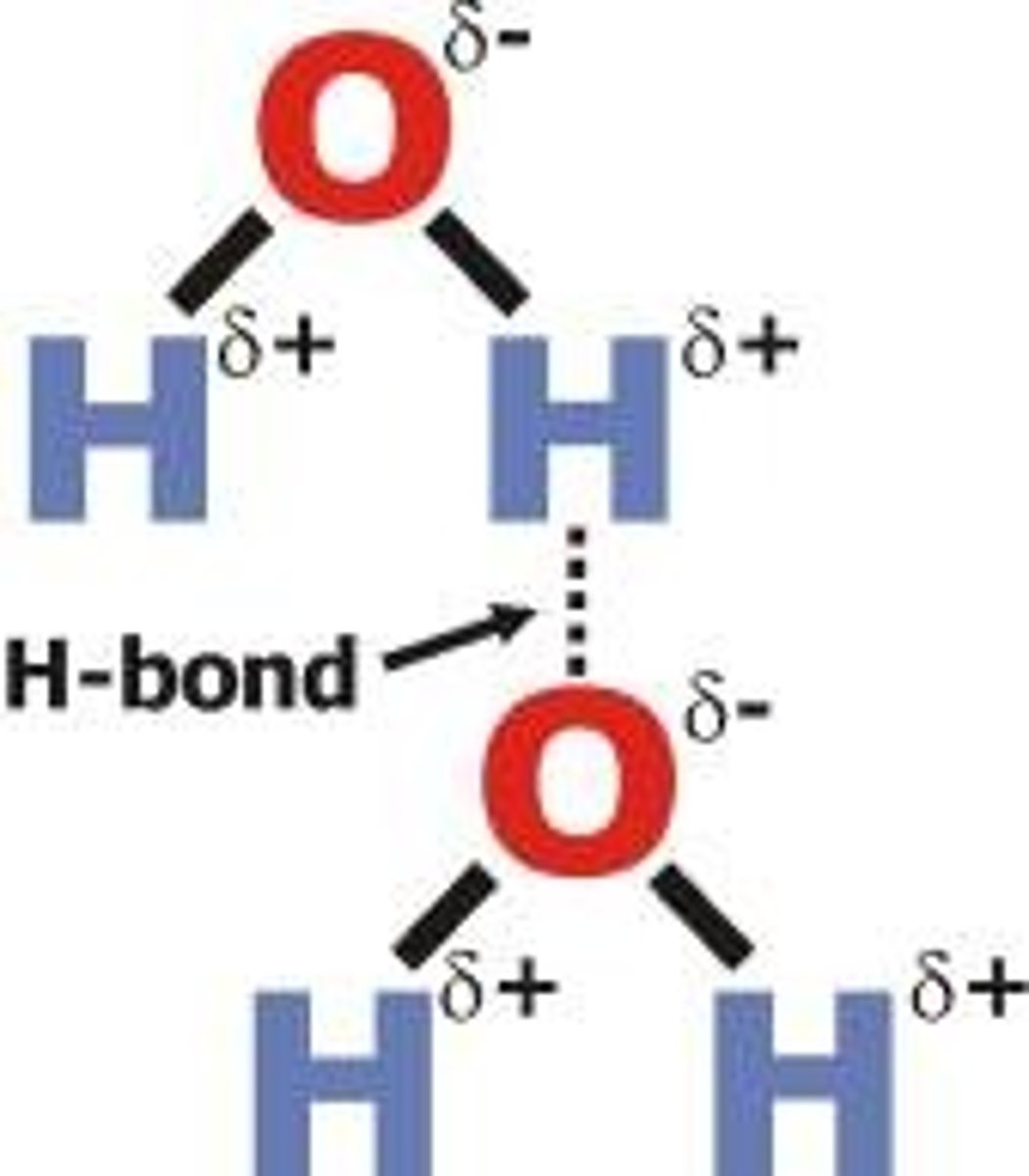
Hydrogen bonding
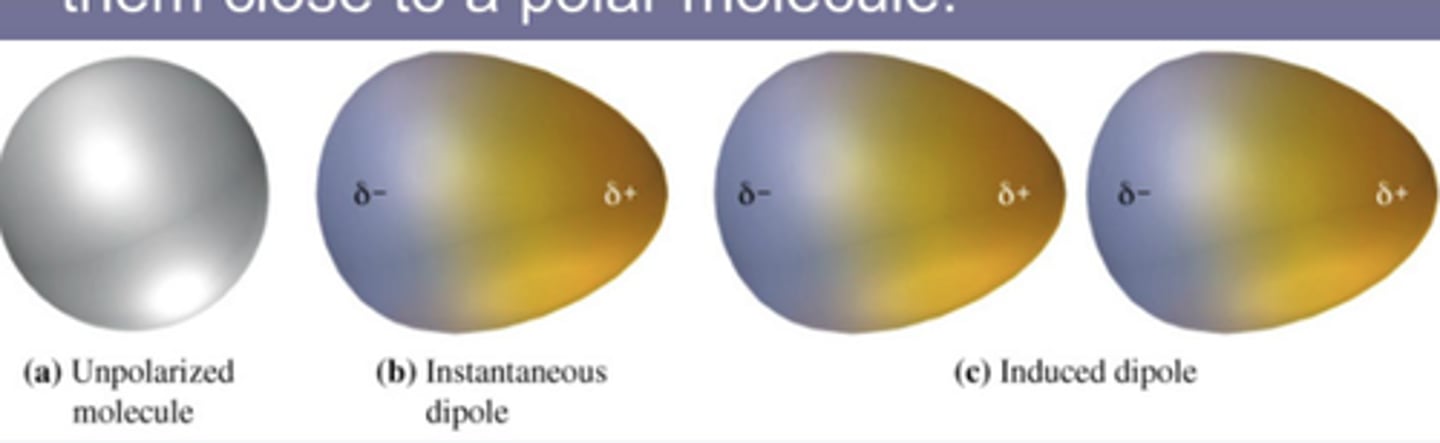
Induced dipole-dipole
All atoms and molecules are attracted
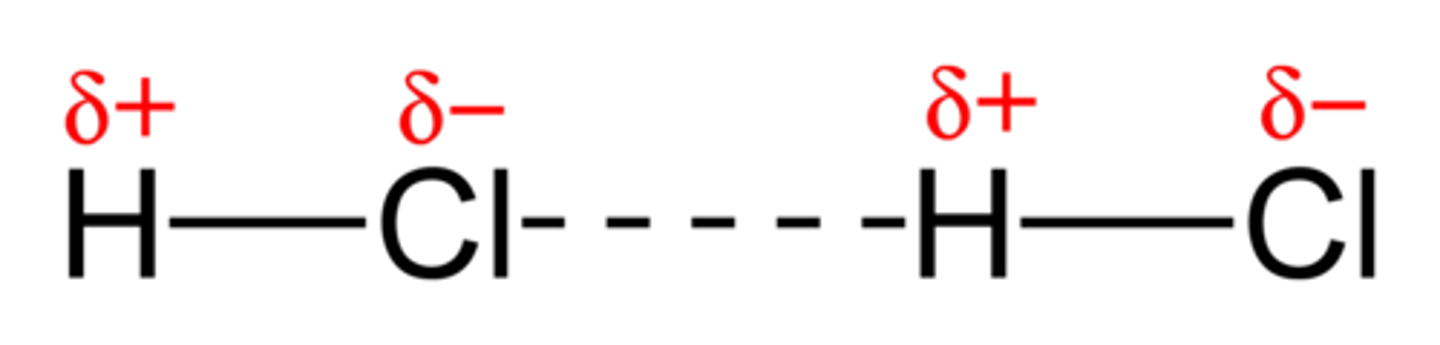
Permanent dipole-dipole interactions
Weak electrostatic forces of attraction between polar molecules
Hydrogen bonding
Only possible when hydrogen is bonded to fluorine, nitrogen or oxygen
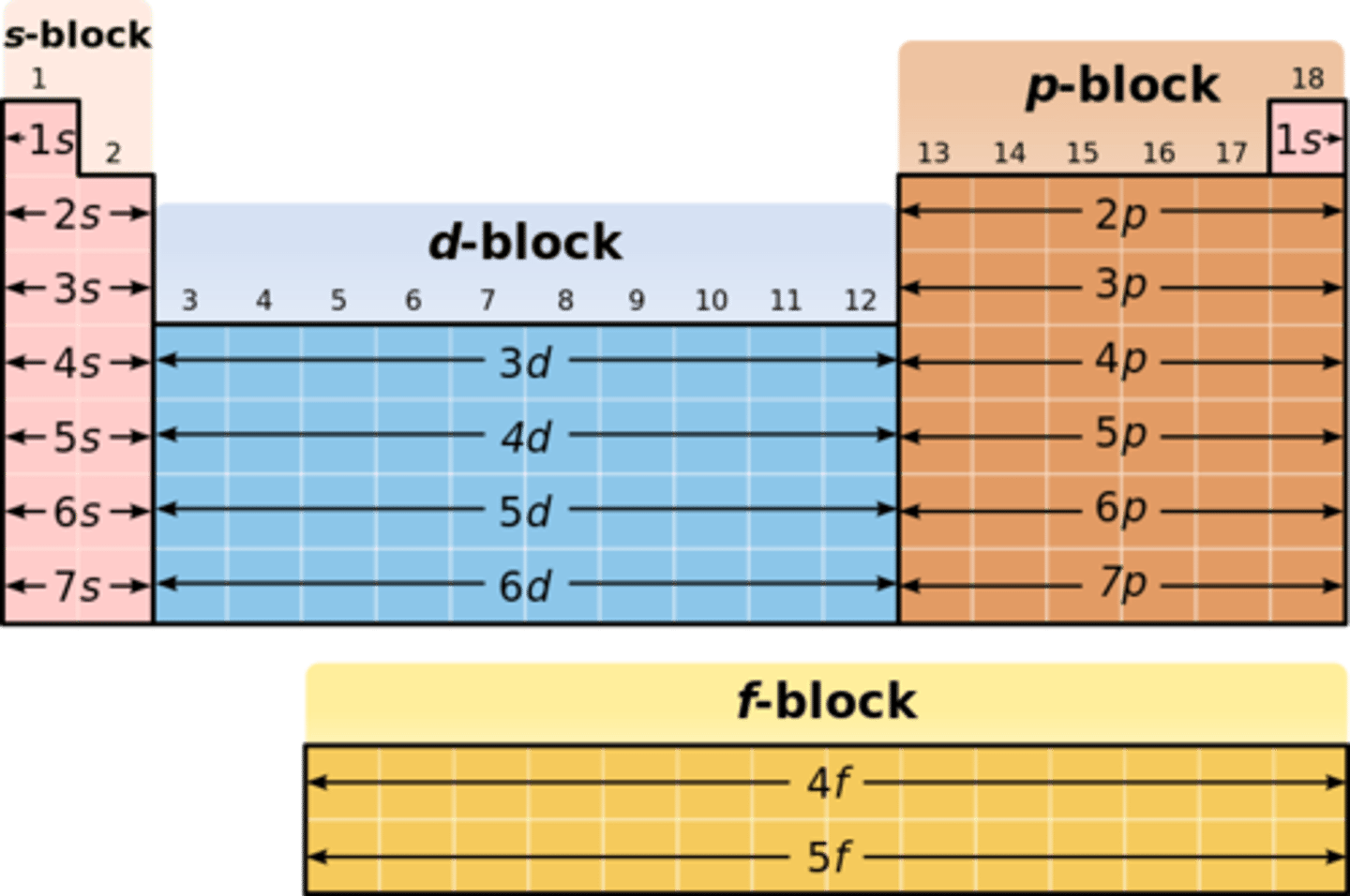
Periodic table blocks
First ionisation energy
The energy needed to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms
Factors affecting ionisation energy
Nuclear charge
Atomic radius
Shielding
Ionisation energy drop between groups 2 and 3 is due to sub-shell structure
The outer electron in group 3 elements is in a p orbital rather than an s orbital.
A p orbital has a slightly higher energy than an s orbital in the same shell so the electron is further from the nucleus.
The p orbital has additional shielding provided by the s electrons which override the effect of increased nuclear charge.
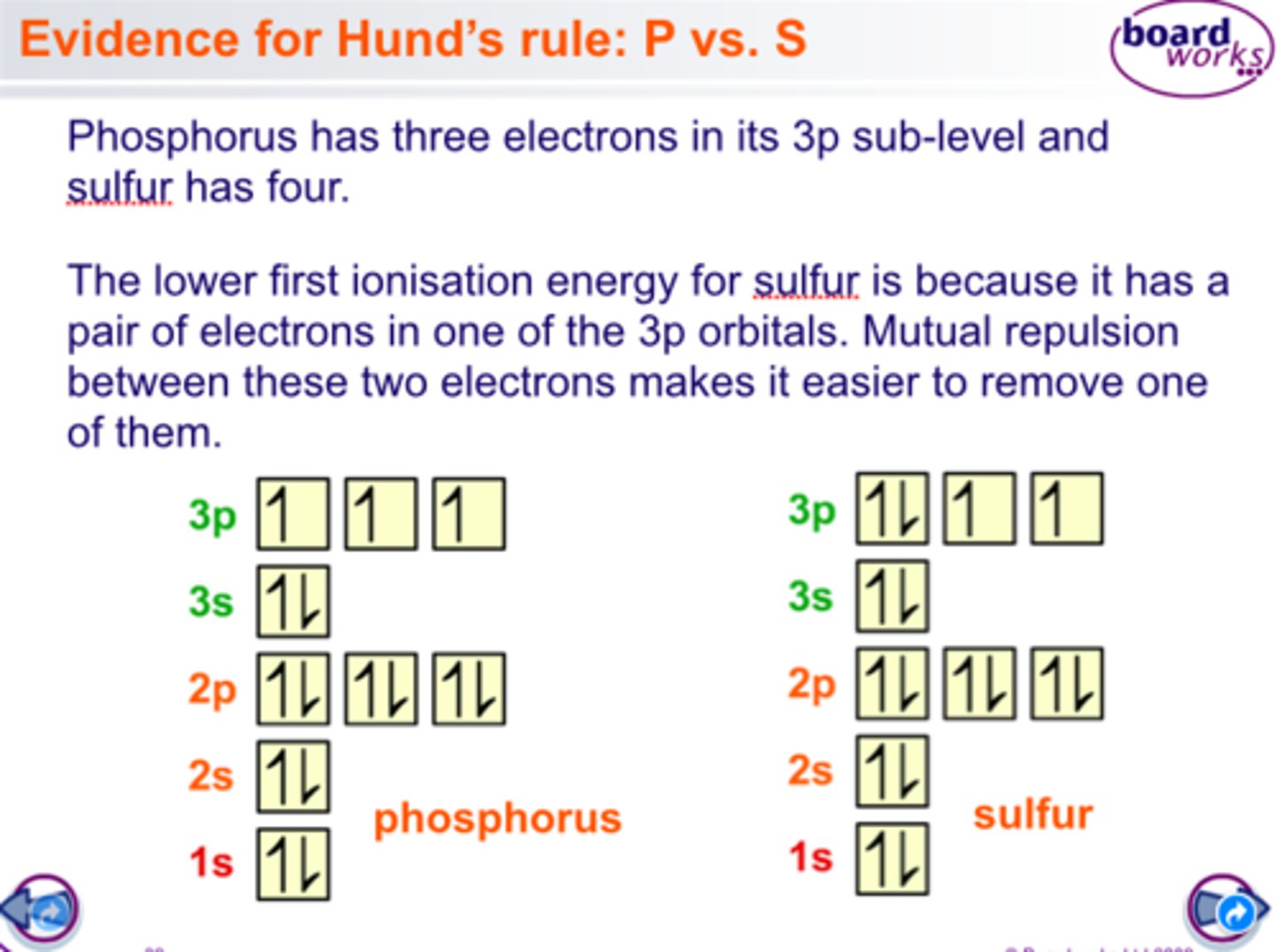
Ionisation energy drop between groups 5 and 6 is due to p orbital repulsion
The repulsion between two electrons in a p orbital in group 6 elements means they are easier to remove than a singly-occupied p orbital in group 5 elements.
Carbon allotropes- high melting and boiling points, also insoluble
Diamond- Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral shape.
Silicon also forms a crystal lattice structure with similar properties as each silicon atom can form four covalent bond
Graphite- Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds so there is one delocalised outer electron
Graphene- One layer of graphite in a hexagonal sheet, one atom thick. Transparent and incredibly light in one layer
Halogens (25ºC):
Fluorine- gas
Chlorine- gas
Bromine- liquid
Iodine- solid
Colour:
Pale yellow
Green
Red-brown
Grey
Test for halides
Silver nitrate solution
First add dilute nitric acid
Silver halides
Silver chloride- White precipitate, dissolves in ammonia
Silver bromide- Cream precipitate, dissolves in concentrated ammonia
Silver iodide- Yellow precipitate, insoluble in concentrated ammonia
Disporportionation
The same element is both oxidised and reduced
Halogen + alkali ---->
X2 + 2NaOH ---->
Disproportionation reaction
Metal halogen-ate + Metal salt + Water
NaXO + NaX + H2O
Chlorine and sodium hydroxide make bleach, Sodium chlorate(I)
2NaOH + Cl2 ----> NaClO + NaCl + H2O
0 +1 -1
Chlorine + Water ↔
Cl2 + H2O ↔
Hydrochloric acid + Chloric(I) acid
HCl + HClO
Chloric(I) acid + Water ↔
HClO + H2O ↔
Chlorate ion + Hydronium
ClO- + H3O+
Chlorate ions kill bacteria
Chlorine alternatives
Ozone (O3)- Strong oxidising agent, but is expensive and has a short half-life
Ultraviolet light- Damages DNA of microorganisms, but ineffective in cloudy water
Test for carbonates
First add dilute hydrochloric acid
If carbonate ions (CO3 2-) are present carbon dioxide will be released and will turn limewater cloudy
Test for sulfates
Barium chloride solution
First add dilute hydrochloric acid
A white precipitate (Barium sulfate) will form if sulfates are present
Test for ammonium compounds
Warm the mixture and add sodium hydroxide
If the damp red litmus paper turns blue, ammonia (alkali) is given off which means ammonium compounds are present.
Avoiding false positives
Test for carbonates ----> Test for sulfates ----> Test for halides
Enthalpy change (ΔH)
The heat energy transferred in a reaction at constant pressure
Unit- kJ / mol
Standard enthalpy change of reaction
The enthalpy change when the reaction occurs in the molar quantities shown in the chemical equation, under standard conditions
Standard enthalpy change of formation
The enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states, under standard conditions
Standard enthalpy change of combustion
The enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen, under standard conditions
Standard enthalpy change of neutralisation
The enthalpy change when an acid and alkali react together to form one mole of water, under standard conditions
Average bond enthalpy
The energy needed to break one mole of bonds in the gas phase, averaged over many different compounds
Enthalpy change, q (Joules)=
m×c×ΔT
Specific heat capacity
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one kelvin
Specific heat capacity of water
4.18 J / g / K
Hess's law
The total enthalpy change is (always the same) independent of the route taken
Enthalpy change of reaction=
Total energy absorbed (bond breaking) - Total energy released (bond making)
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. The catalyst remains chemically unchanged
Production of ethanol
Ethene and steam are reacted
60-70 atmospheres
300ºC
phosphoric (V) acid catalyst
Equilibrium constant, Kc
When you have a homogenous reaction that's reached dynamic equilibrium, the larger the value of Kc the further the equilibrium lies to the right and vice versa
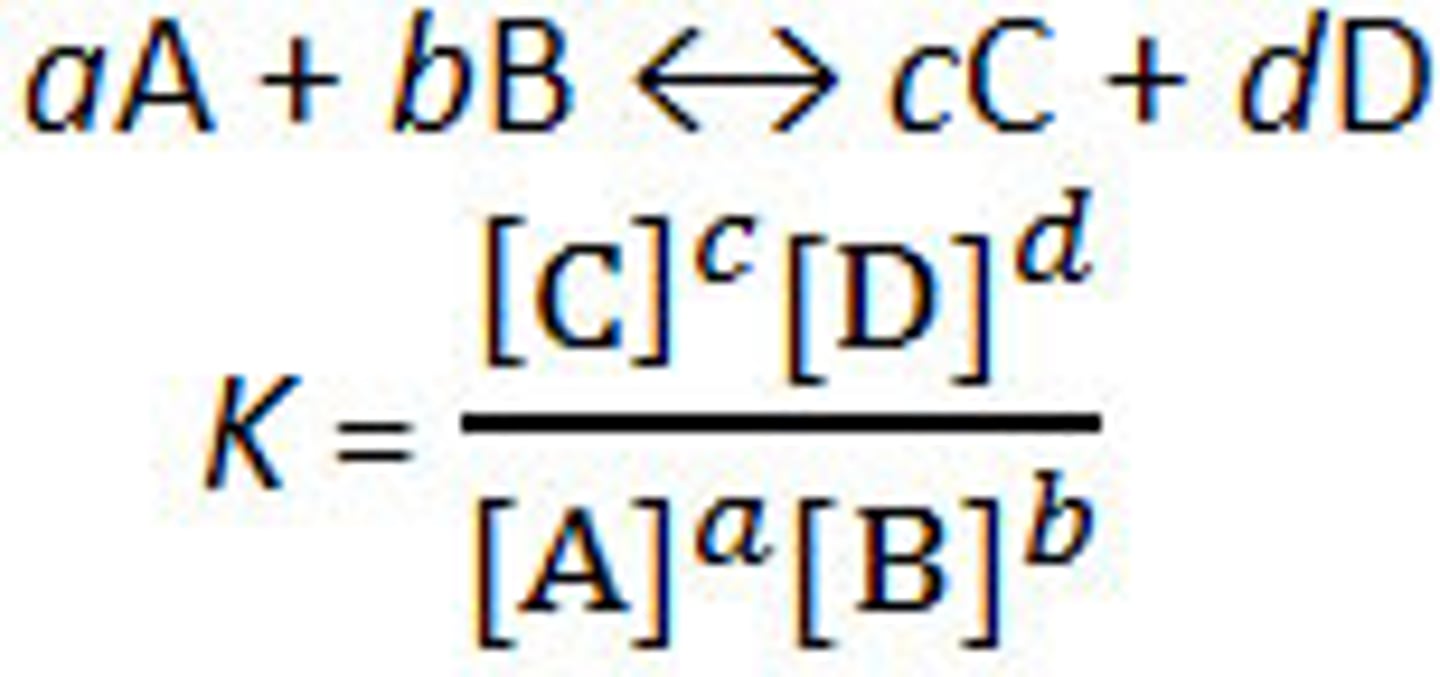
Structural formula
The arrangement of atoms carbon by carbon with attached hydrogen and functional groups
Skeletal formula
The bonds of the carbon skeleton only, with any functional groups
Homologous series
Same general formulas and functional groups
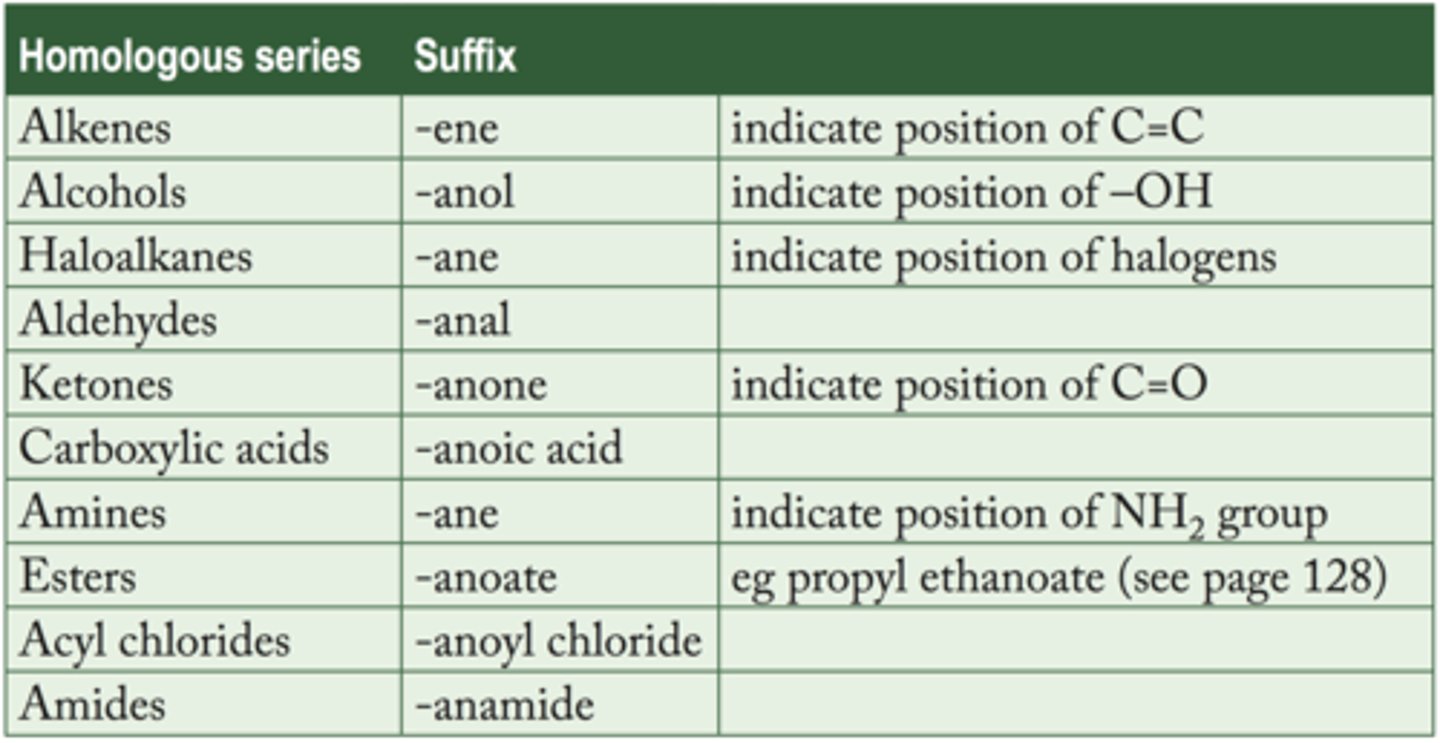
Carbon skeleteon
Aromatic or aliphatic
Aromatic compounds contain a benzene ring
Aliphatic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen joined in straight chains, branched chains or non-aromatic rings (alicyclic)
Isomers
Same molecular formula but different structural formula, the atoms are arranged differently
Types- Structural isomers and stereoisomers
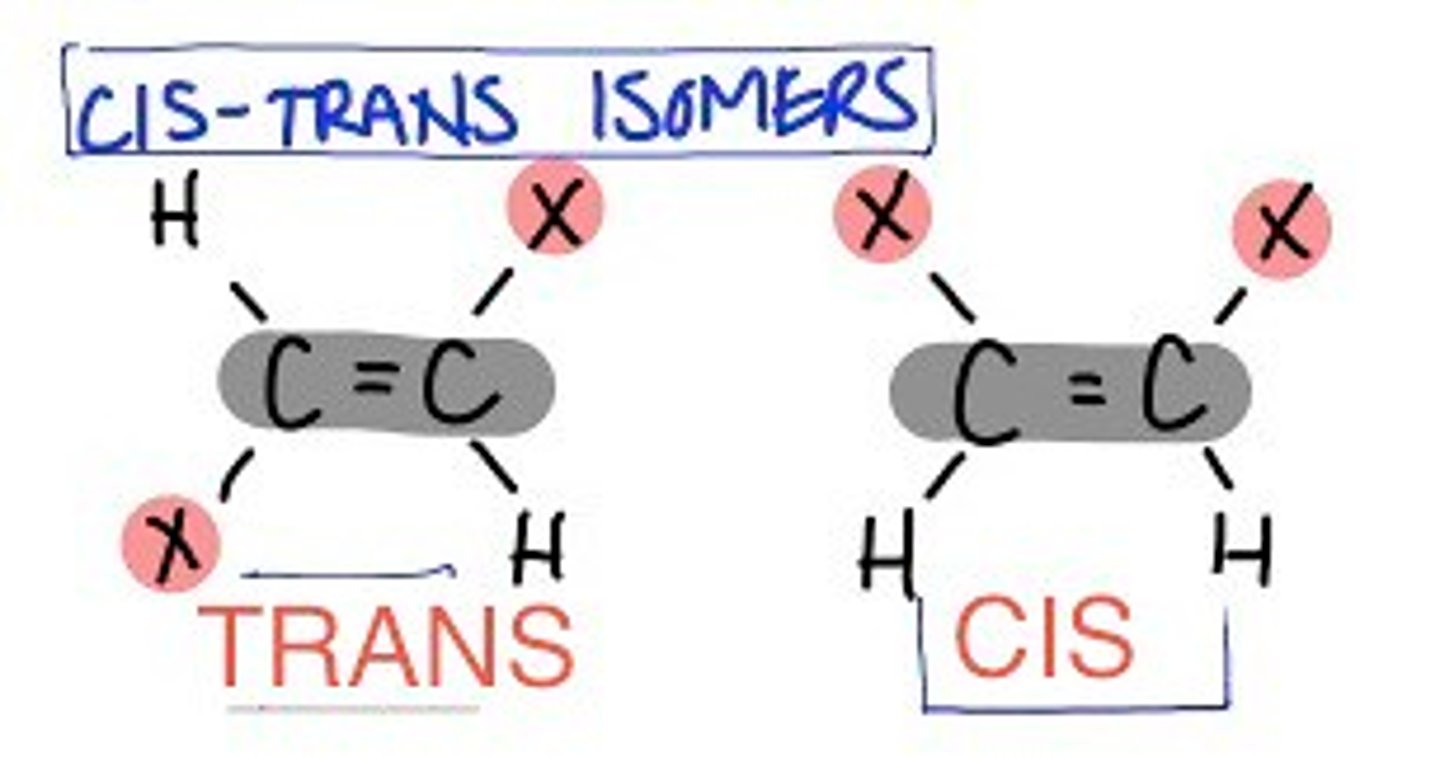
Structural isomers
Chain isomers- The carbon skeleton can be arranged differently (straight or branched)
Similar chemical properties but different physical properties
Positional isomers- The functional group could be attached to a different carbon atom
different physical and maybe chemical properties
Functional group isomers- The same atoms can be arranged into different functional groups
Very different physical and chemical properties
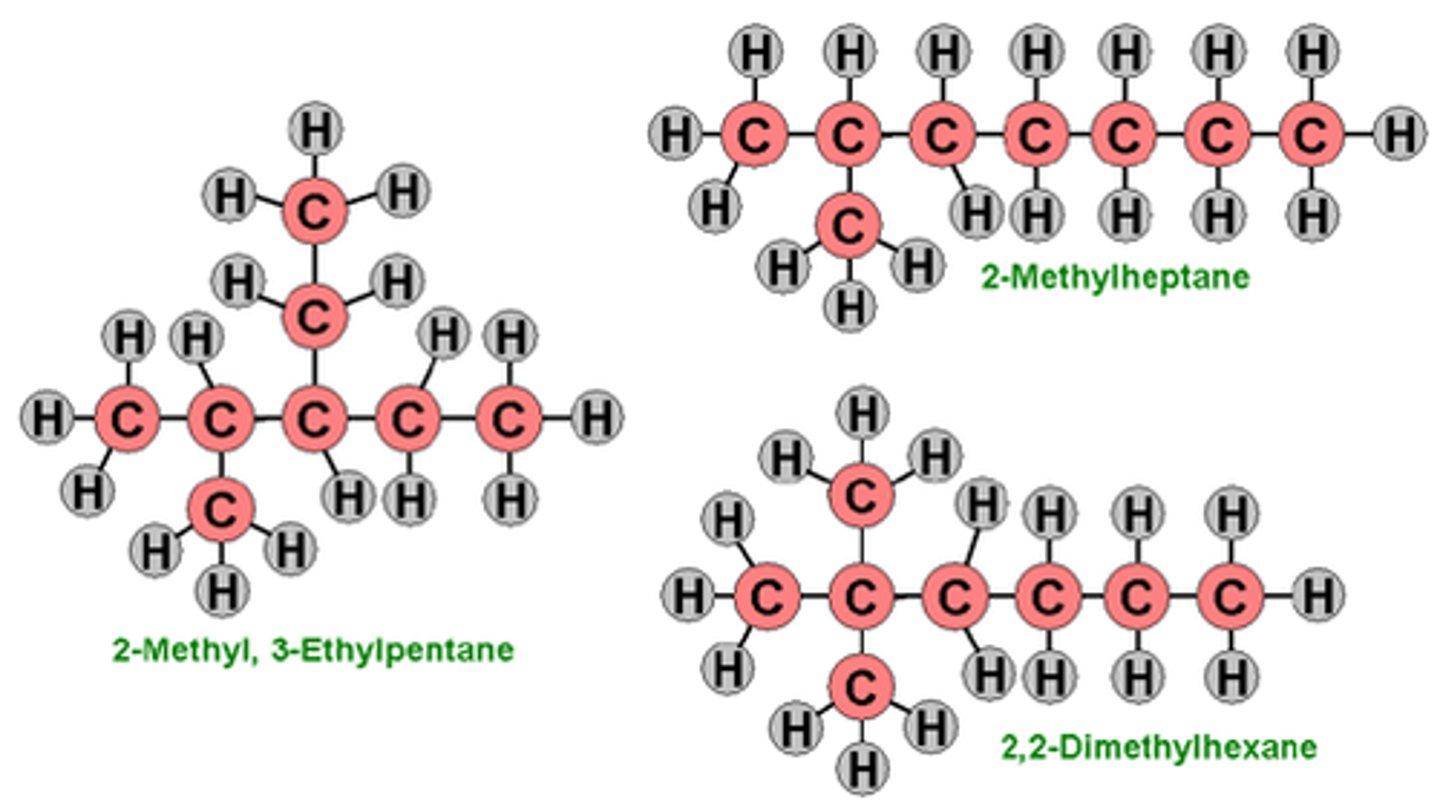
Alkane molecule shape
Alkane molecules are tetrahedral around each carbon atom
Each carbon atom has four pairs of bonding electrons around it
Bond angle- 109.5º
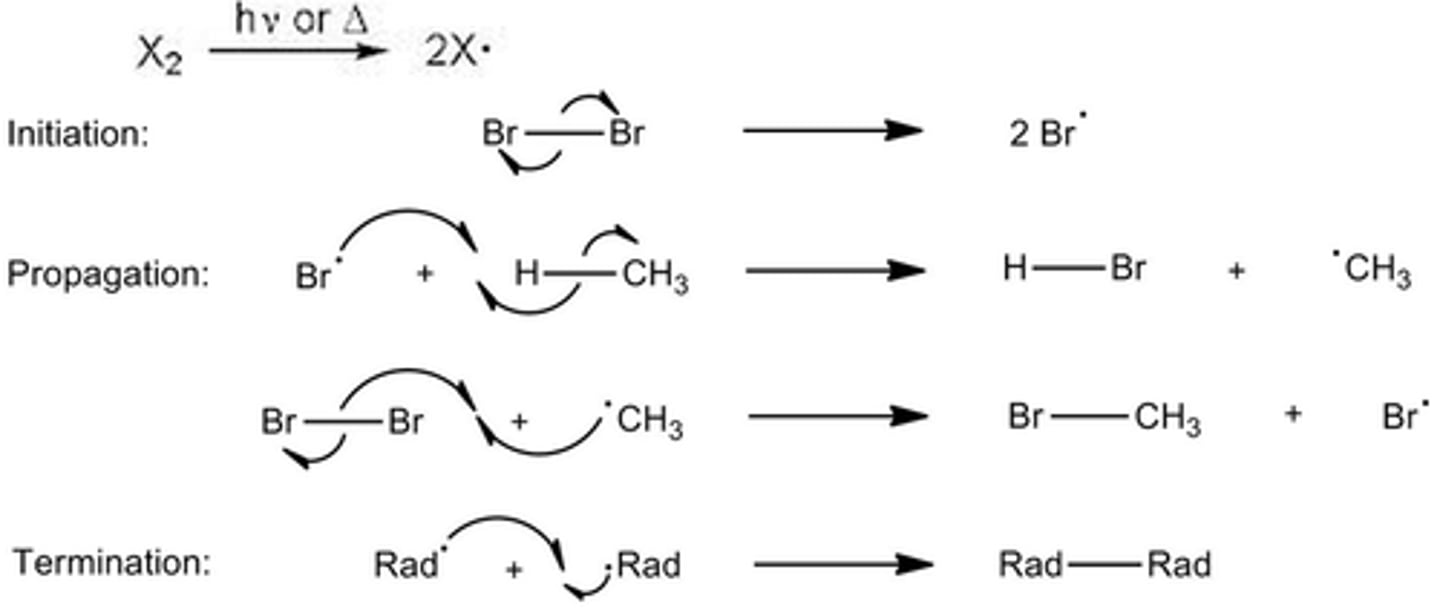
Halogen + Alkane=
Haloalkane (photochemical reaction)
Free-radical substitution reaction
1) Initiation- Free radicals are produced
2) Propagation- Free radicals are used up and created
3) Termination- Free radicals are mopped up
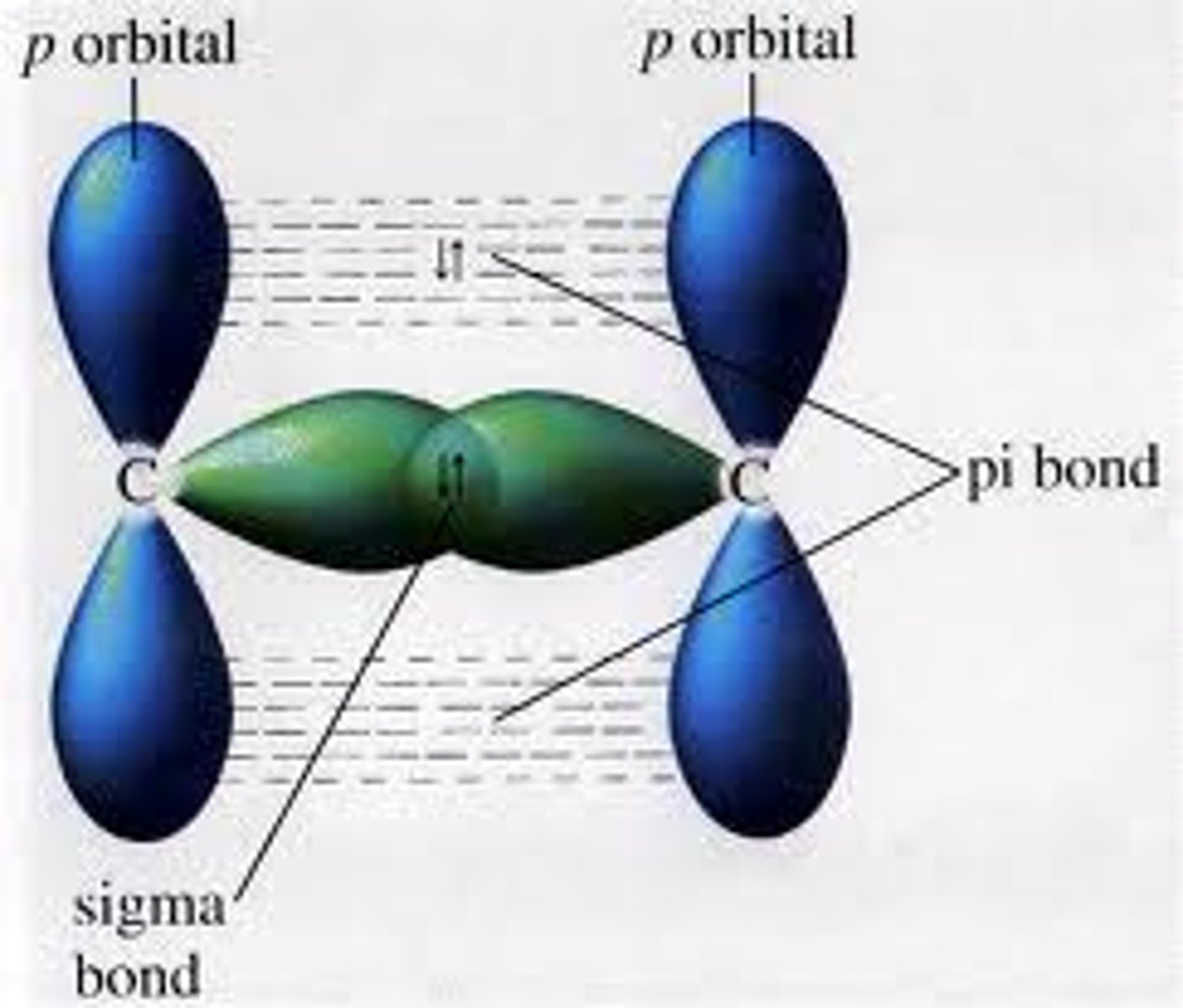
Alkene double bond
Sigma bond- Two s orbitals overlap, C-C or C-H in alkanes (high bond enthalpy)
Pi bond- Sideways overlap of two adjacent p orbitals (low bond enthalpy)
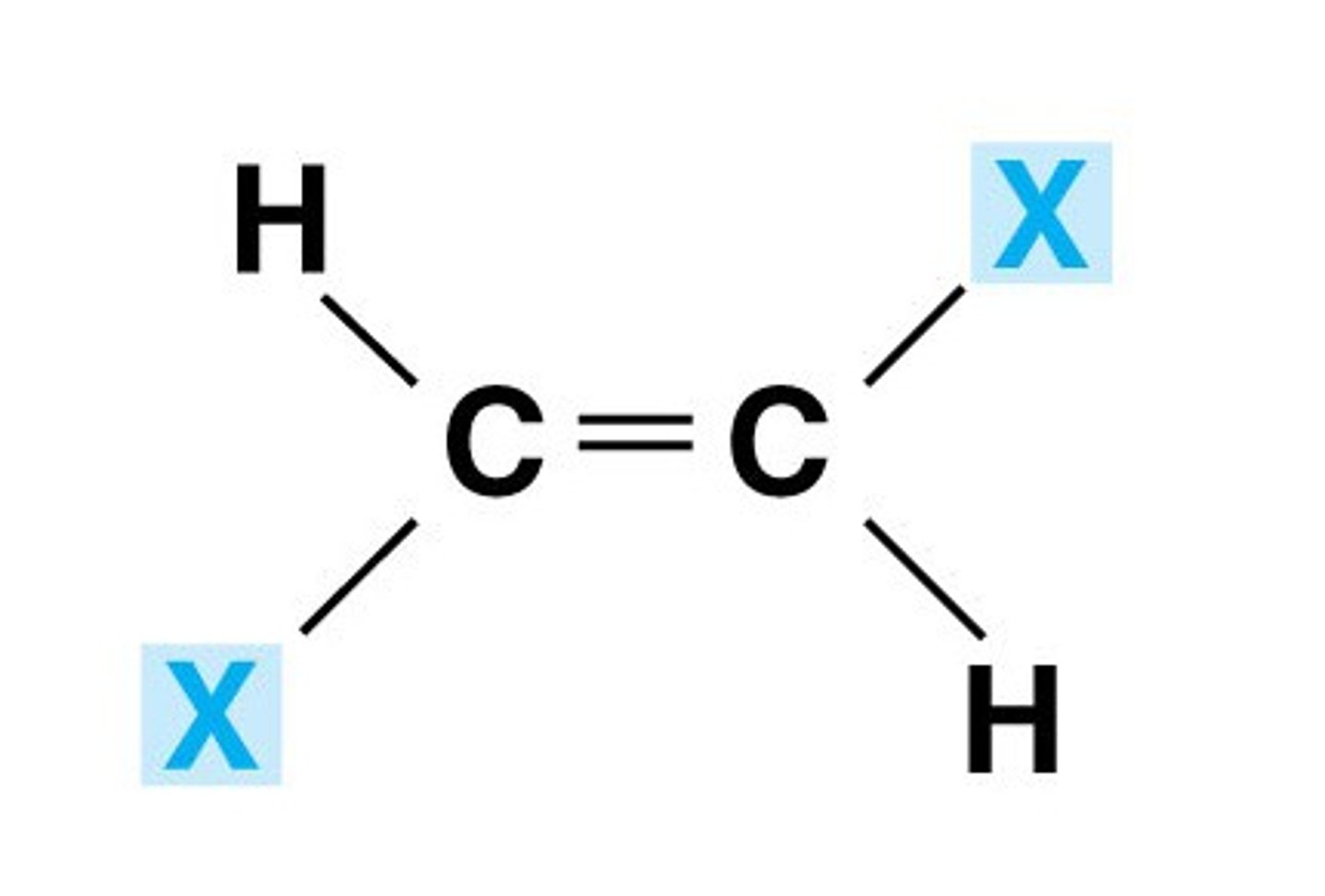
E/Z isomerism
Stereoisomerism because of the lack of rotation around the carbon-carbon double bond
E-isomer
The same groups are across the double bond
Trans isomer
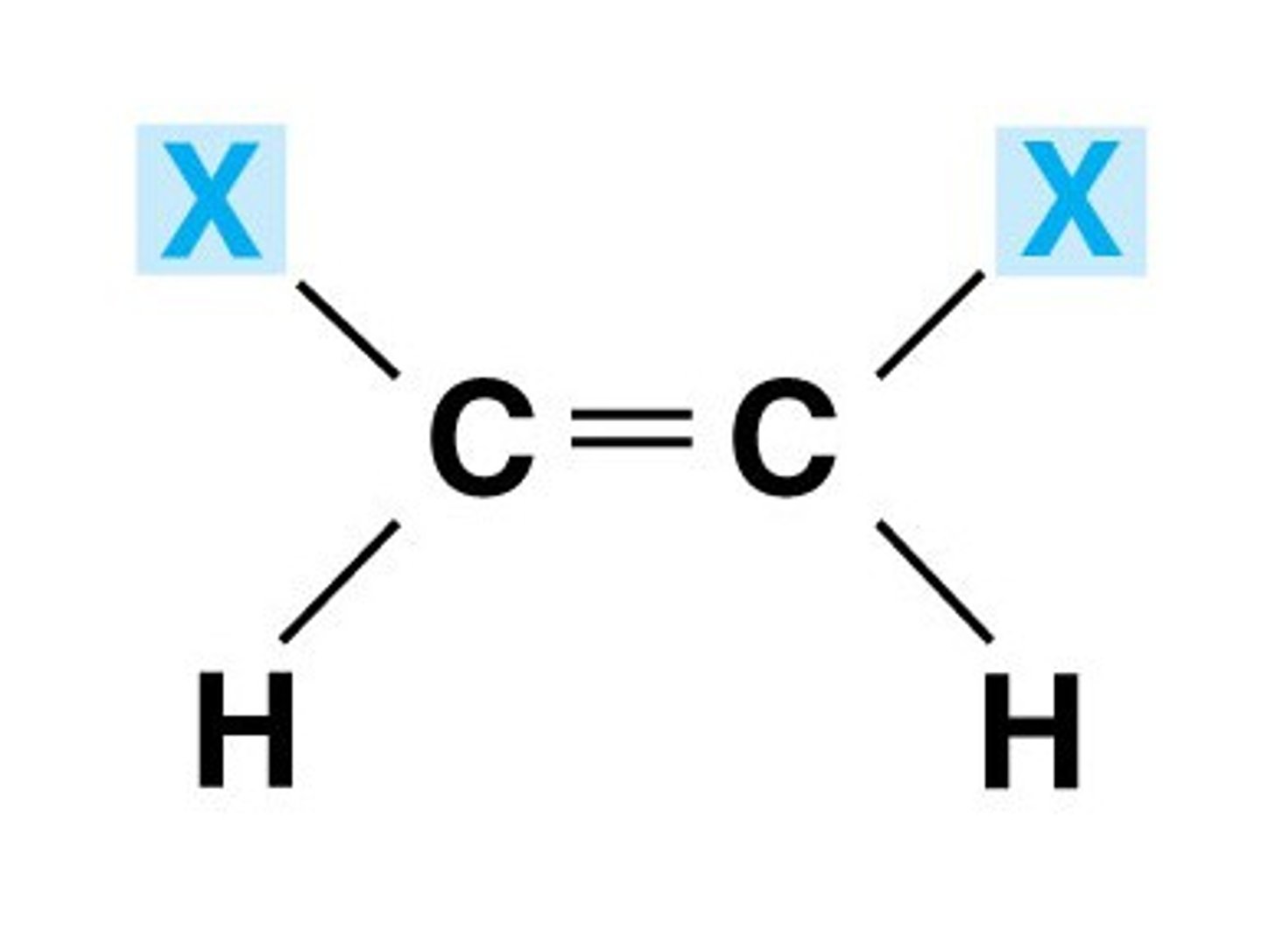
Z-isomer
The same groups are on the same side of the double bond
Cis isomer
Adding hydrogen to C=C bonds produces alkanes
Ethene will react with hydrogen in an electrophilic addition reaction to produce ethane
Nickel catalyst
150ºC
Halogens react with alkenes to form dihaloalkanes
Electrophilic addition
Orange bromine water decolourises when mixed with an alkene and forms a dibromoalkane
Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition with hydrogen halides
Two haloalkanes are formed
Markownikoff's rule- The major product is the one where hydrogen adds to the carbon with the most hydrogens already attached
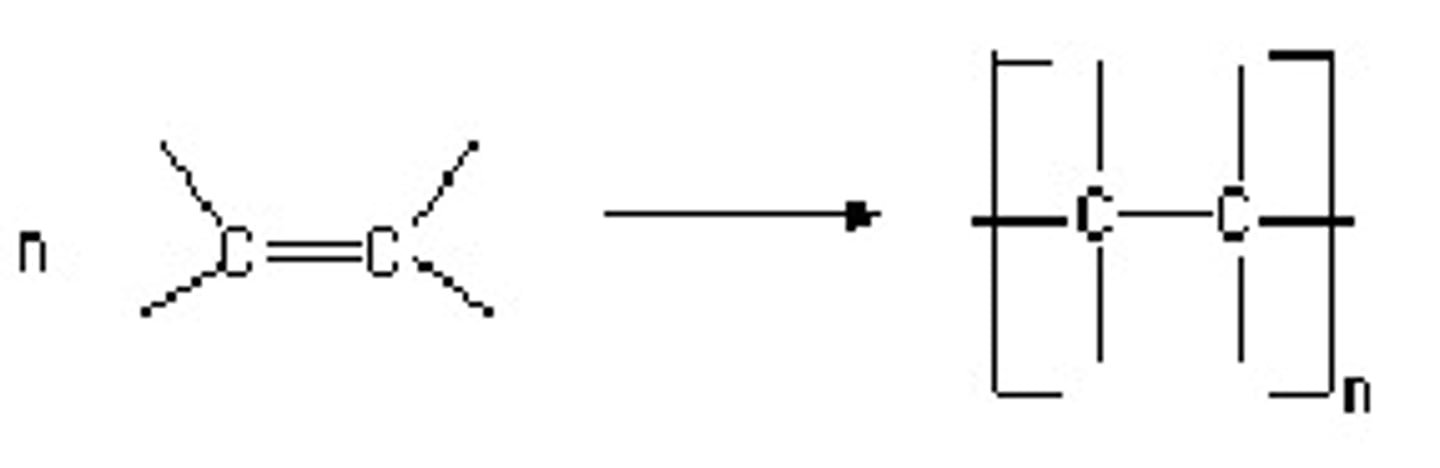
Addition polymers
Alkenes (monomers) join up and the double bond is removed
Alcohols
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Halogen + Alcohol ---->
Haloalkane
The -OH is substituted by the halide
Acid catalyst required such as sulfuric acid
Dehydration
Alcohols can be dehydrated to form alkenes
Concentrated sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid
Heated
Oxidising alcohols
Oxidising agent- acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
Primary alcohols ----> Aldehydes (distill) and then carboxylic acids (reflux)
Secondary alcohols ----> Ketones
Tertiary alcohols will only oxidise by being burnt
Hydrolysis
Haloalkanes can be hydrolysed to make alcohols in a nucleophilic substitution reaction
Warm aqueous alkali solution (Sodium hydroxide)
CFCs (Haloalkanes)
Stable, volatile, non-flammable and non-toxic
Refluxing
Vertical Liebig condenser
Prevents loss of volatile substances
Continuously boils,evaporates and condenses the vapours
Seperation
Separating funnel with water added to mixture
Anhydrous salt (Magnesium sulfate) can be added to remove water after separation