Brain Anatomy
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
fissure
deep grooves that separate gyri
gyri
elevated ridges of the brain
sulci
shallow grooves that separate gyri
longitudinal fissure
deep groove running from the anterior to the posterior of the brain, separating the two cerebral hemispheres
transverse fissure
deep groove that separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum
parietoccipital sulcus
groove that separates the parietal and occipital lobes and is found on the internal surface of the cerebrum
lateral sulcus
groove that separates the temporal lobe from the inferior aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes
precentral gyrus
ridge anterior to the central sulcus
postcentral gyrus
ridge posterior to the central sulcus
central sulcus
shallow groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes.
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing, reading, writing, and language.
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose function includes processing sensory information
cerebrum
most superior part of the brain, making up 60% of the total brain weight
diencephalon
also known as the interbrain and includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
brain stem
the most inferior part of the brain. Merges with the spinal cord. Contains three subparts
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the posterior and inferior end; functions include coordinating movement output and balance
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
basal nuclei
islands of gray matter buried within the white matter of the cerebrum
thalamus
inner room which acts as a relay station for the sensory cortex
hypothalamus
helps regulate water balance, metabolism, thirst, and hunger
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's master gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, it regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
mammillary bodies
hangs from the posterior floor of the hypothalamus and helps control sense of smell
pineal body
part of the endocrine system; releases melatonin and regulates sleep/wake cycles
choroid plexus
a highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles that make and secretes cerebrospinal fluid.
midbrain
part of the brain stem that helps with vision and hearing
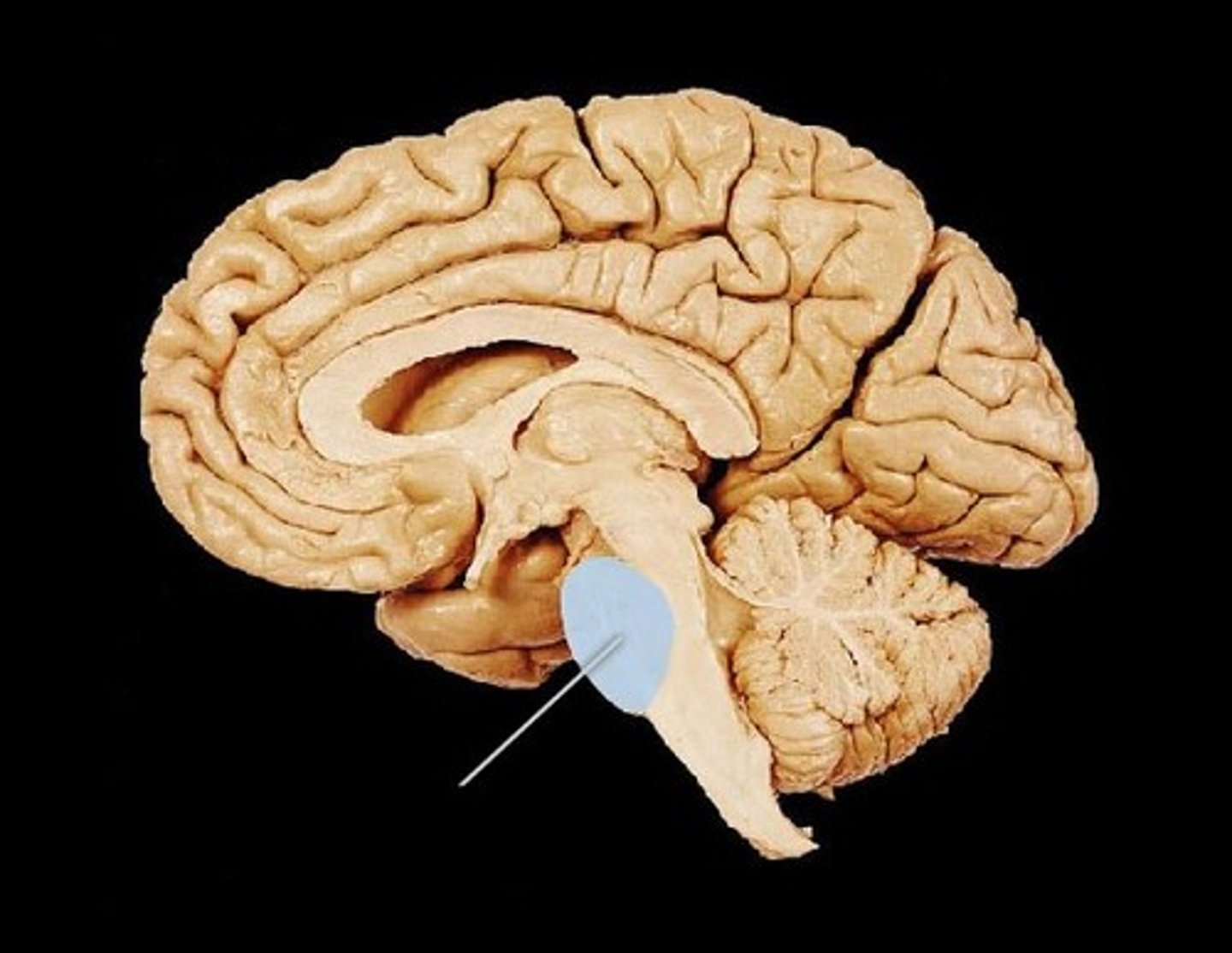
pons
it's name means bridge and is involved in breathing
medulla oblongata
part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
pineal and pituitary
two endocrine glands within the brain
Parkinson's disease
a progressive disease that destroys basal nuclei cells, reduces dopamine and is identified by muscular tremors, slowing of movement, and partial facial paralysis
Huntington's disease
a hereditary disease marked by degeneration of brain cells in the basal nuclei and causes chorea and progressive dementia.
CTE
tau proteins build up in the brain which causes memory loss, aggression, and depression long after hits to the head have stopped
Alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder characterized by an abnormal production of amyloid protein and causes gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
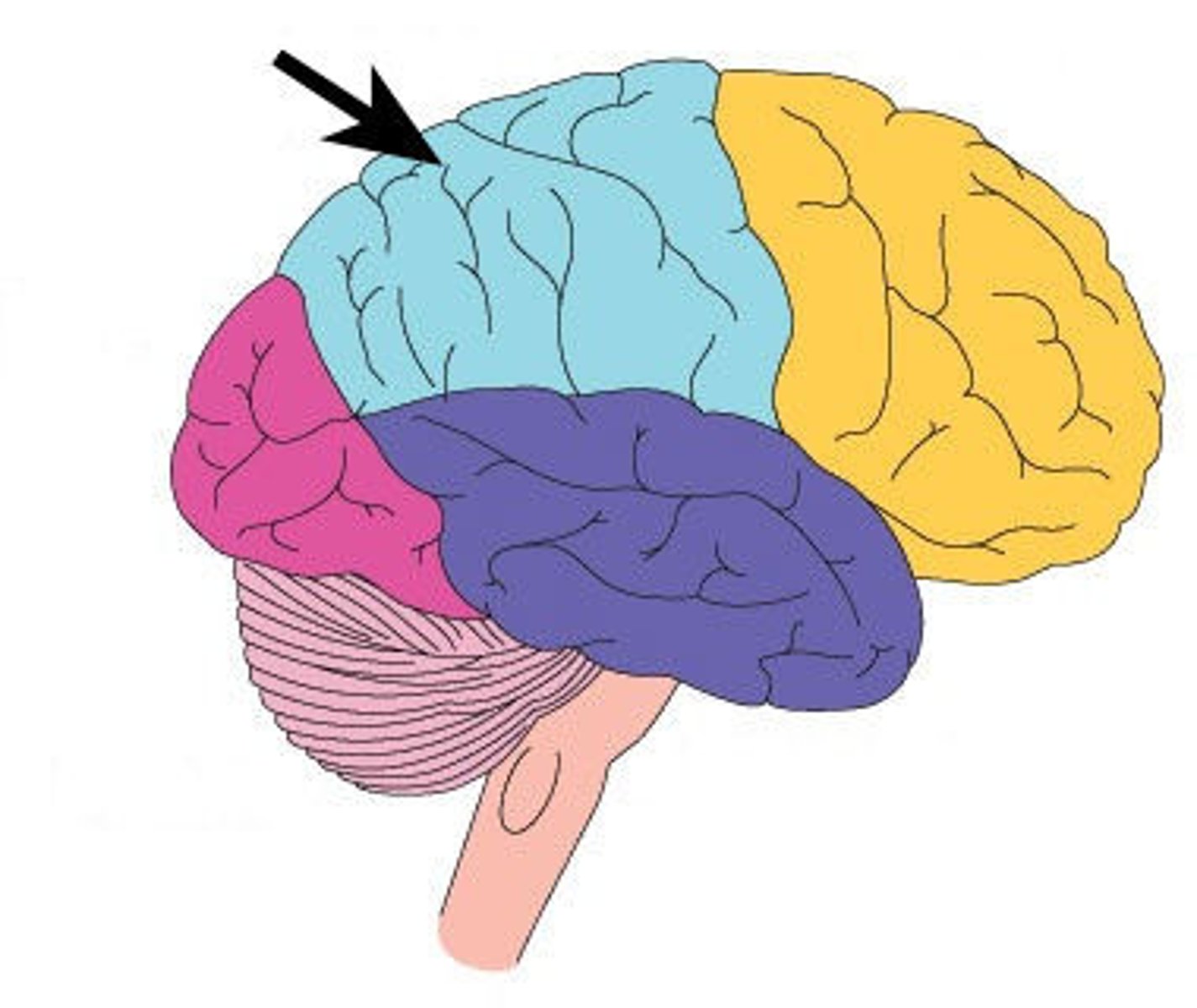
frontal lobe
which lobe is shown here in yellow?
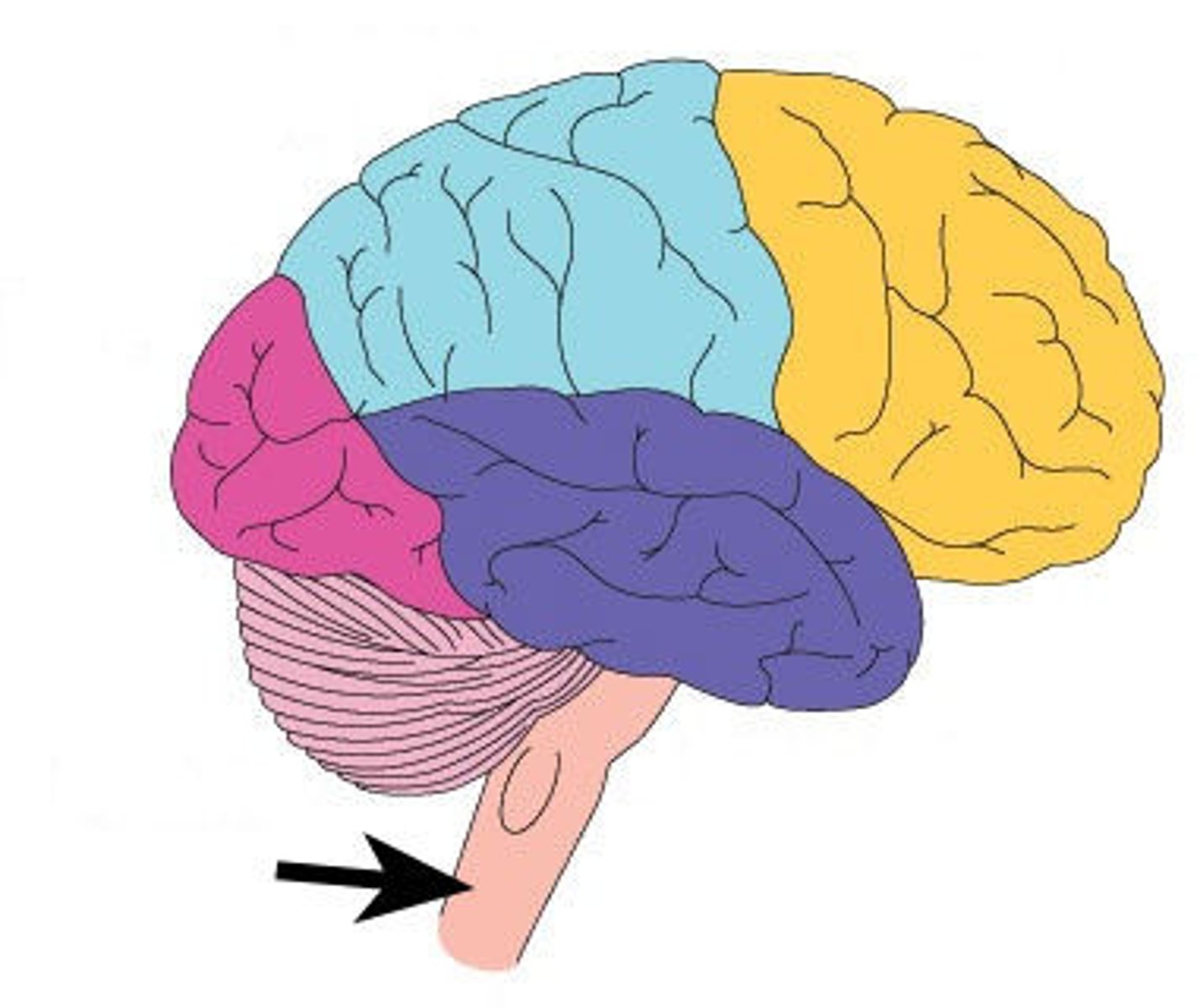
temporal lobe
which lobe is shown here in purple?
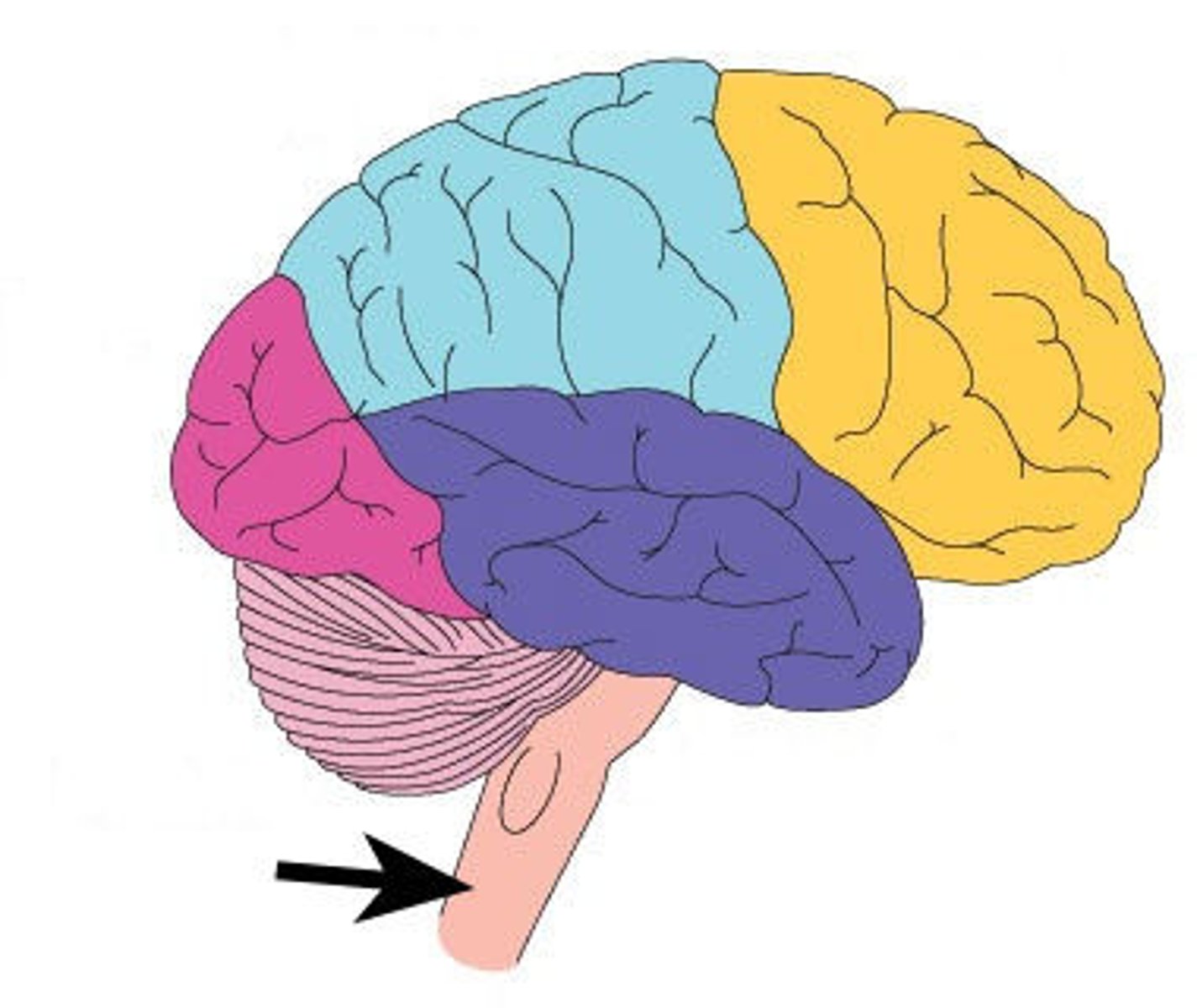
parietal lobe
which lobe is shown here in blue?
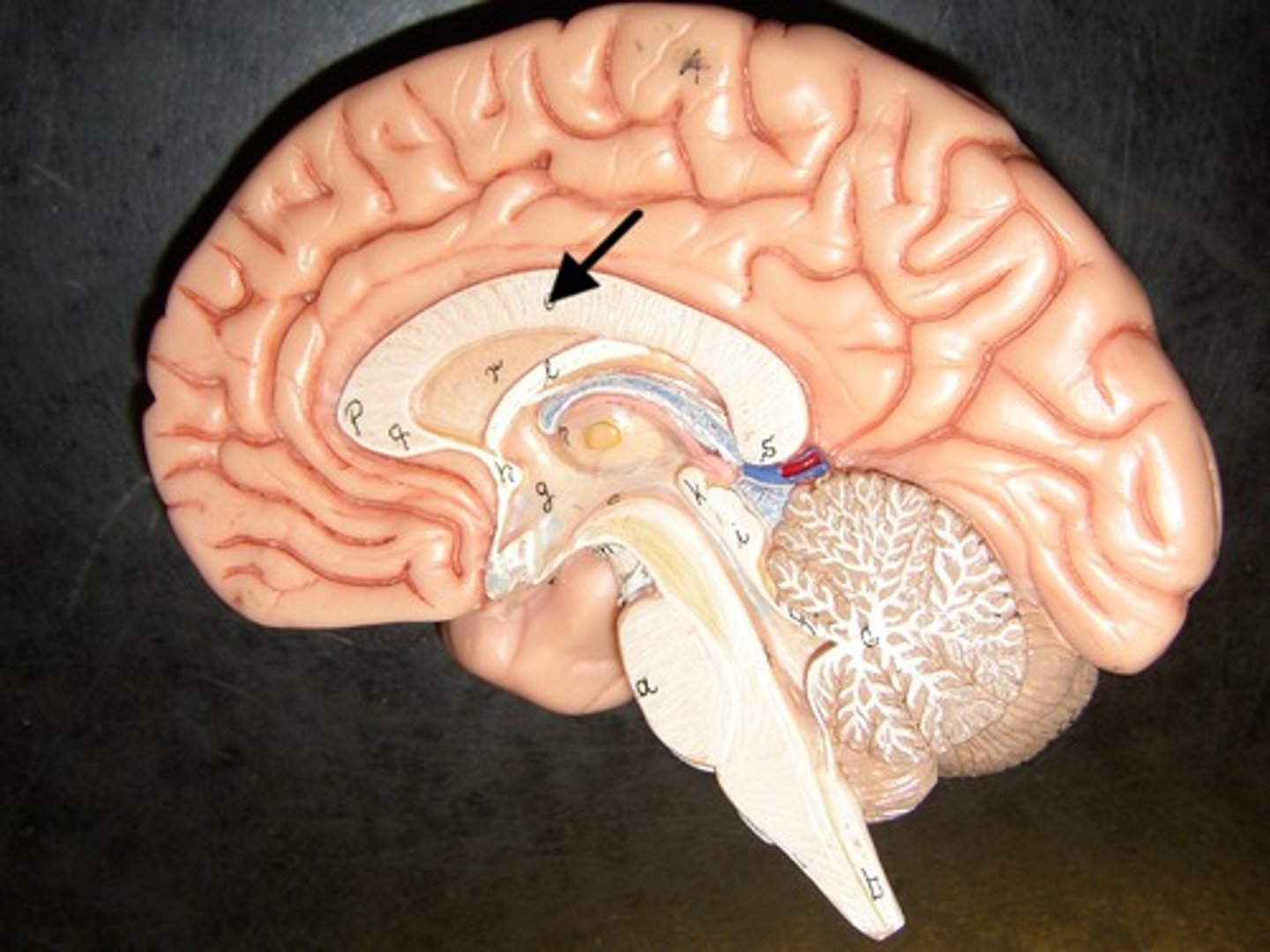
corpus callosum
which structure is the arrow pointing to?
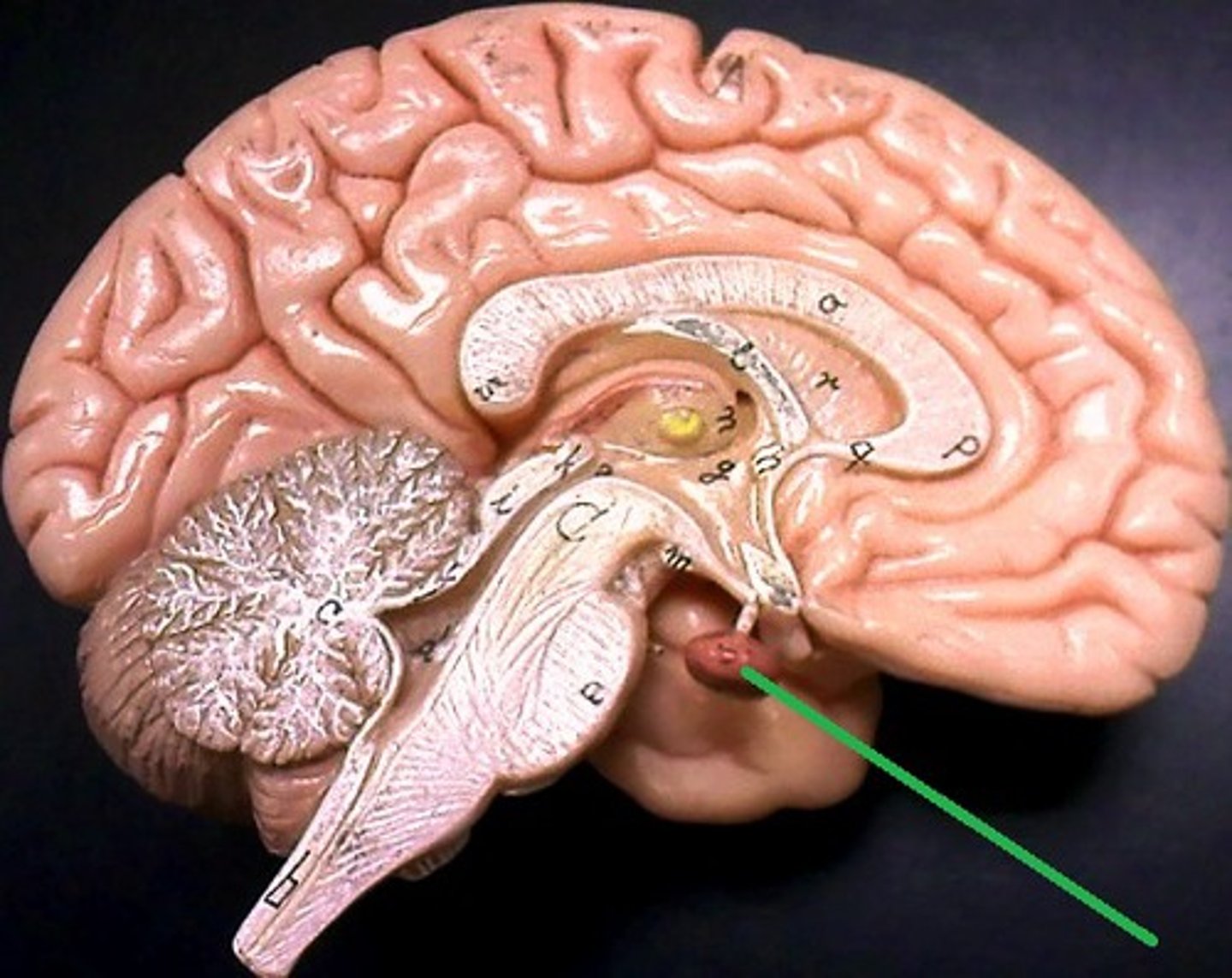
pituitary gland
which structure is the green line pointing to?
pons
which area is highlighted in blue?