OPT 223 IVFA
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
While not always required and somewhat invasive, why do we sometimes perform IVFA?
necessary to diagnose and manage for some conditions
What are some indications to potentially perform IVFA (if necessary to diagnose these)?
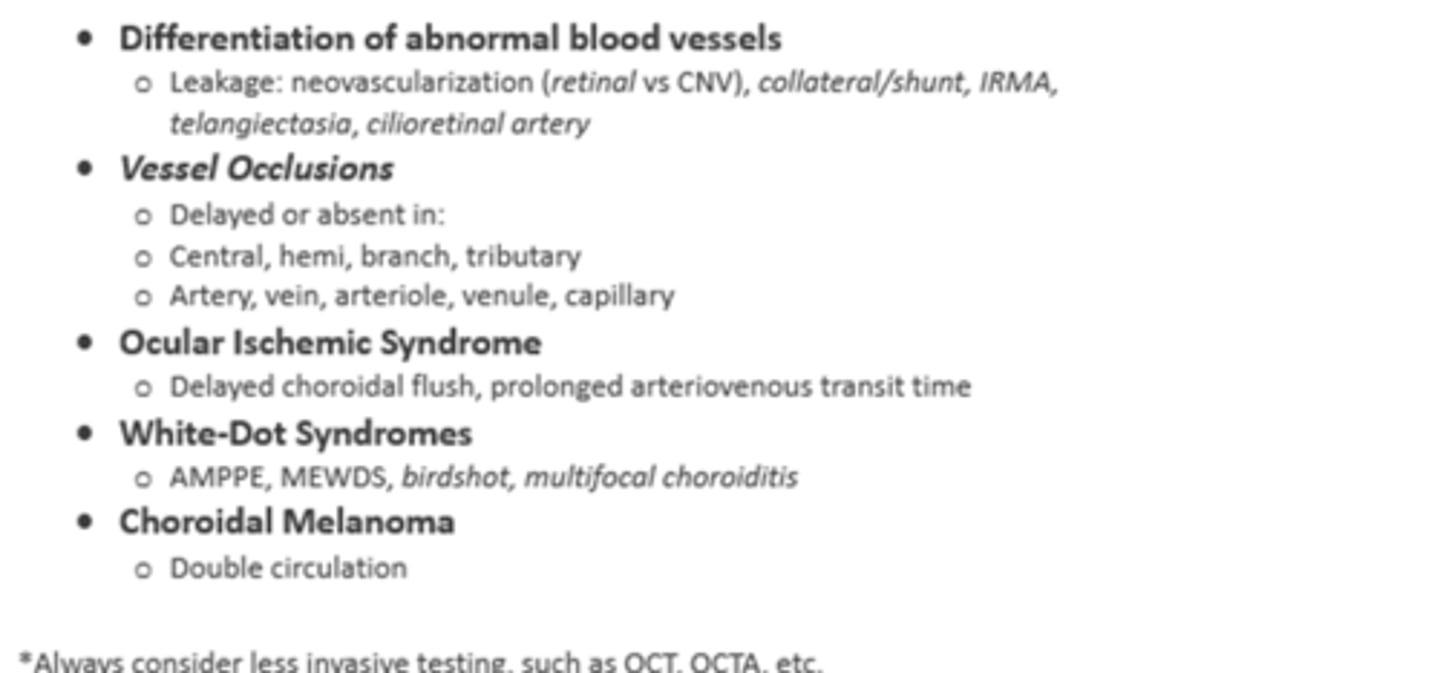
differentiate abnormal BV (neo)
proliferative DR
exudative MD
ocular ischemic syndrome
BV occlusions
white dot syndromes
choroidal melanoma
What are 3 contraindications to performing IVFA?
allergy to fluorescein dye
pregnancy (category C)
poor GFR (glomerular filtration rate, approx. <90) like in kidney disease, elderly
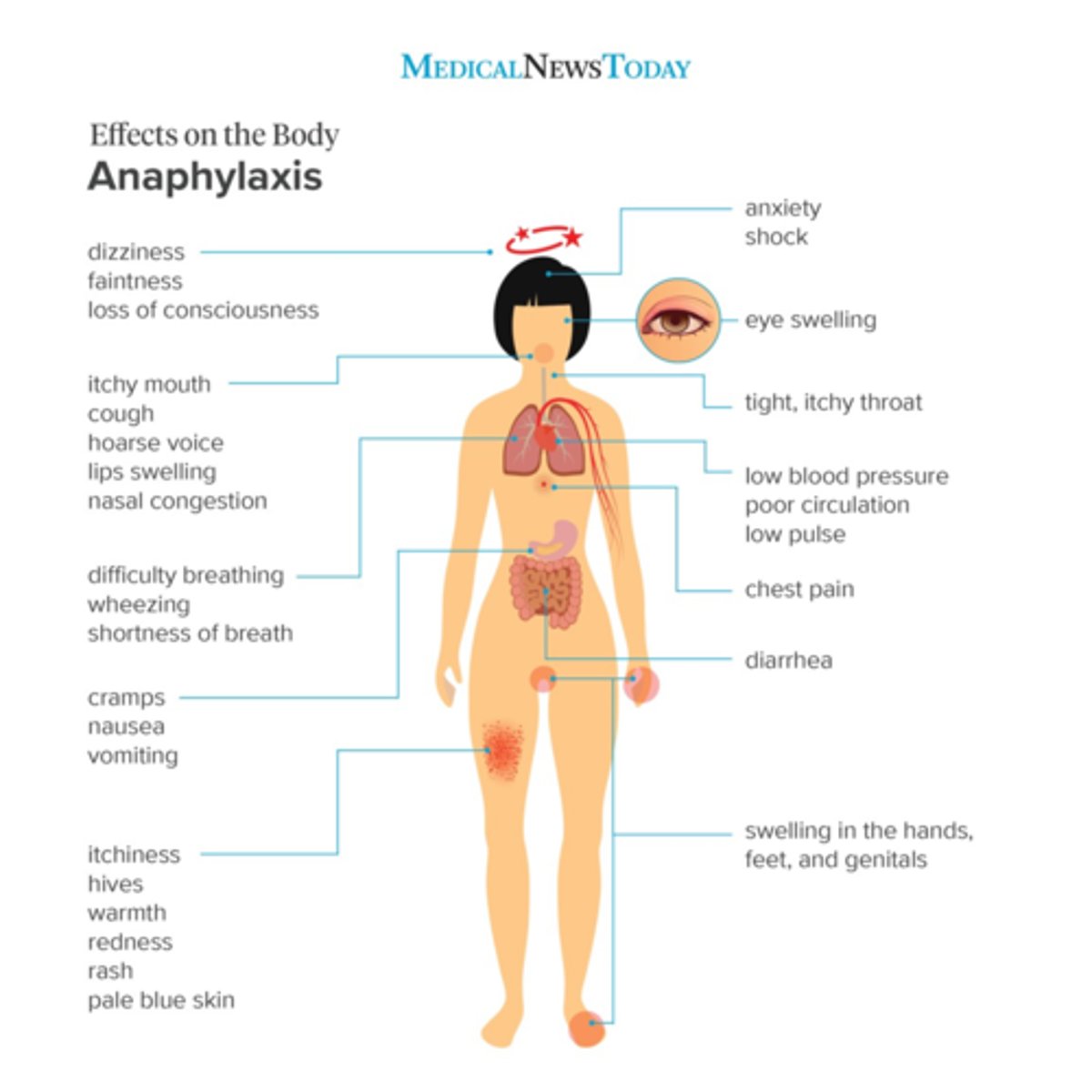
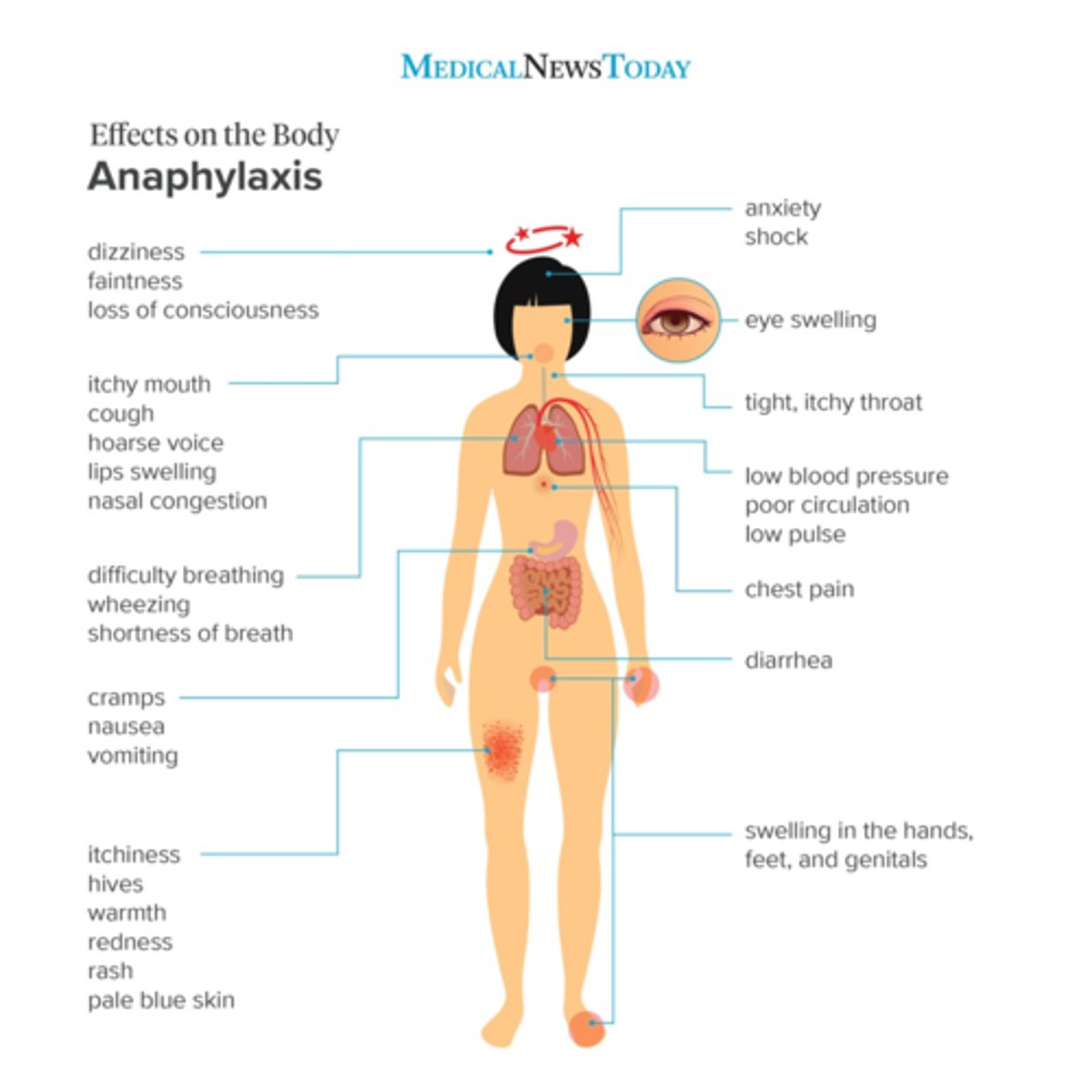
What are 6 common adverse effects of IVFA?
yellowing of skin and urine
transient nausea (3-15% of cases)
vomiting (7% of cases)
pruritis (itching)
extravasation of dye (leakage of dye into ECF)
mild pain and redness/bruising
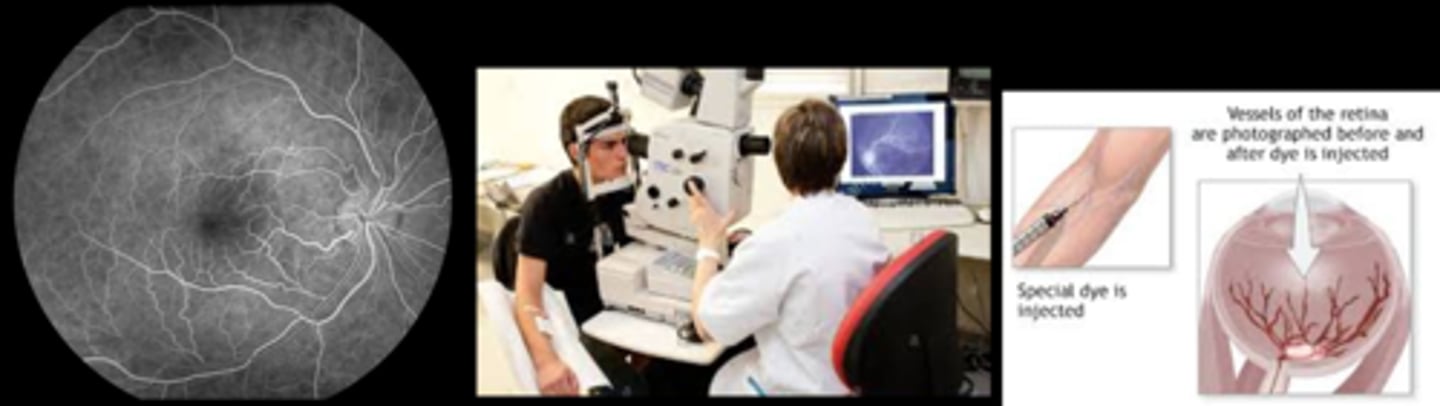
What are 7 rare adverse effects of IVFA?
urticaria (hives)
pyrexia (fever)
thrombophlebitis
syncope (fainting)
bronchospasm
anaphylaxis
cardiac arrest
To prepare for IVFA, what do we need to get in patient Hx?
review diagnoses and safety for procedure
demographic (visibility of veins)
medical history (contraindications or considerations)
age/weight (access to veins)
allergies (contraindications)
To prepare for IVFA, what do we need to consider for our exam findings?
abnormalities (which eye, location desired) as we cannot capture both eyes in early phase
ability to visualize retina = if we cannot see the retina on fundoscopy, we won't be able to see it on FA
fixation and cooperation ability = can they fixate for 10-20min? Rx?
non-invasive testing
What is included in the consent process for IVFA?
description of procedure
preparation before appt
indications
RBA

What tests do we perform same-day before the IVFA?
vitals
BCVA
dilate for imaging
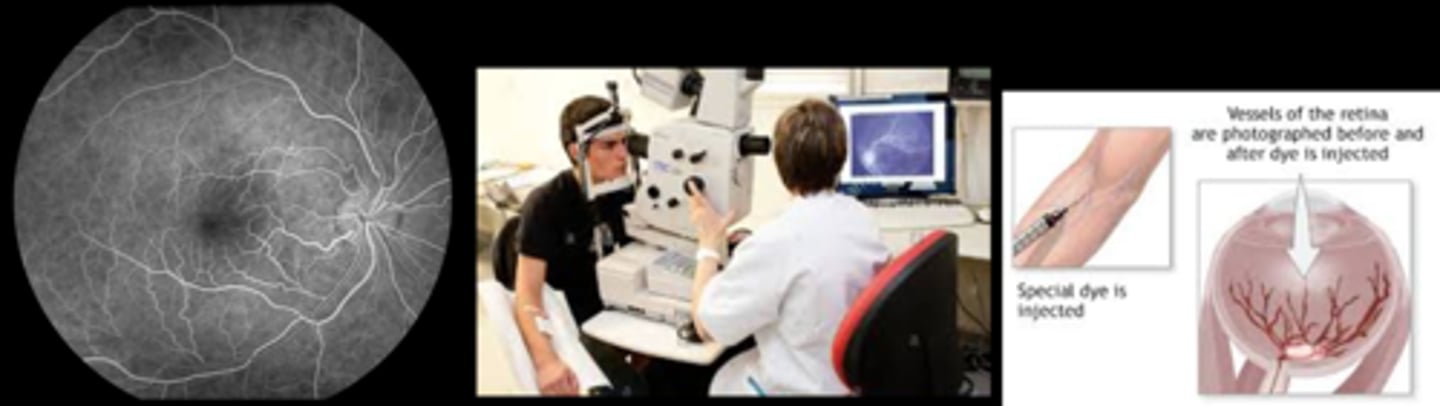
What do you document after IVFA?
drug, dose, delivery method, location
interpretation of results
complications
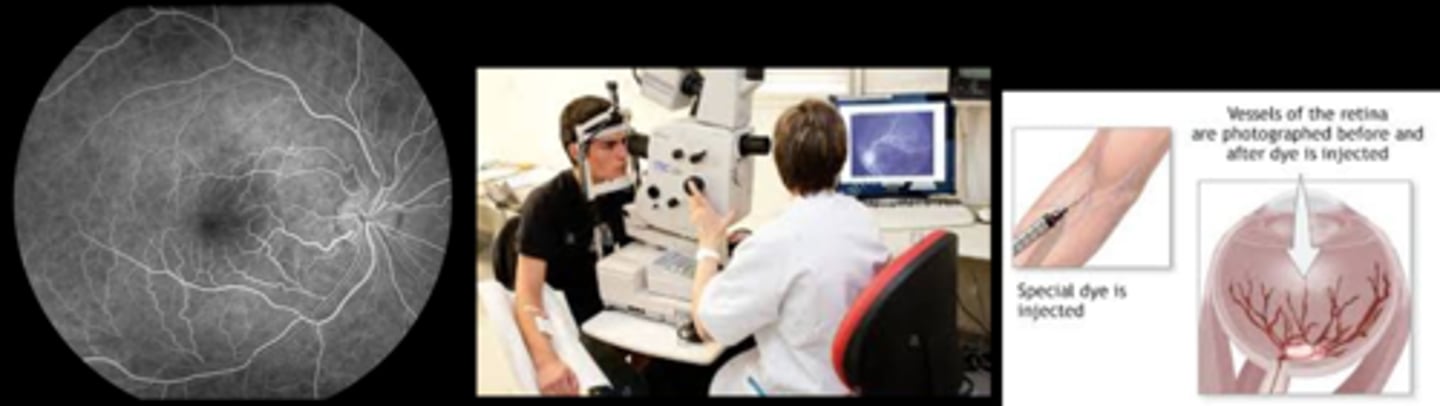
What equipment do we need for IVFA?
anti-septic enviro
IV fluorescein (3mL of 25% NaFl or 5mL of 10% NaFl)
IM epinephrine in case of allergic rxn
diphenhydramine for itching
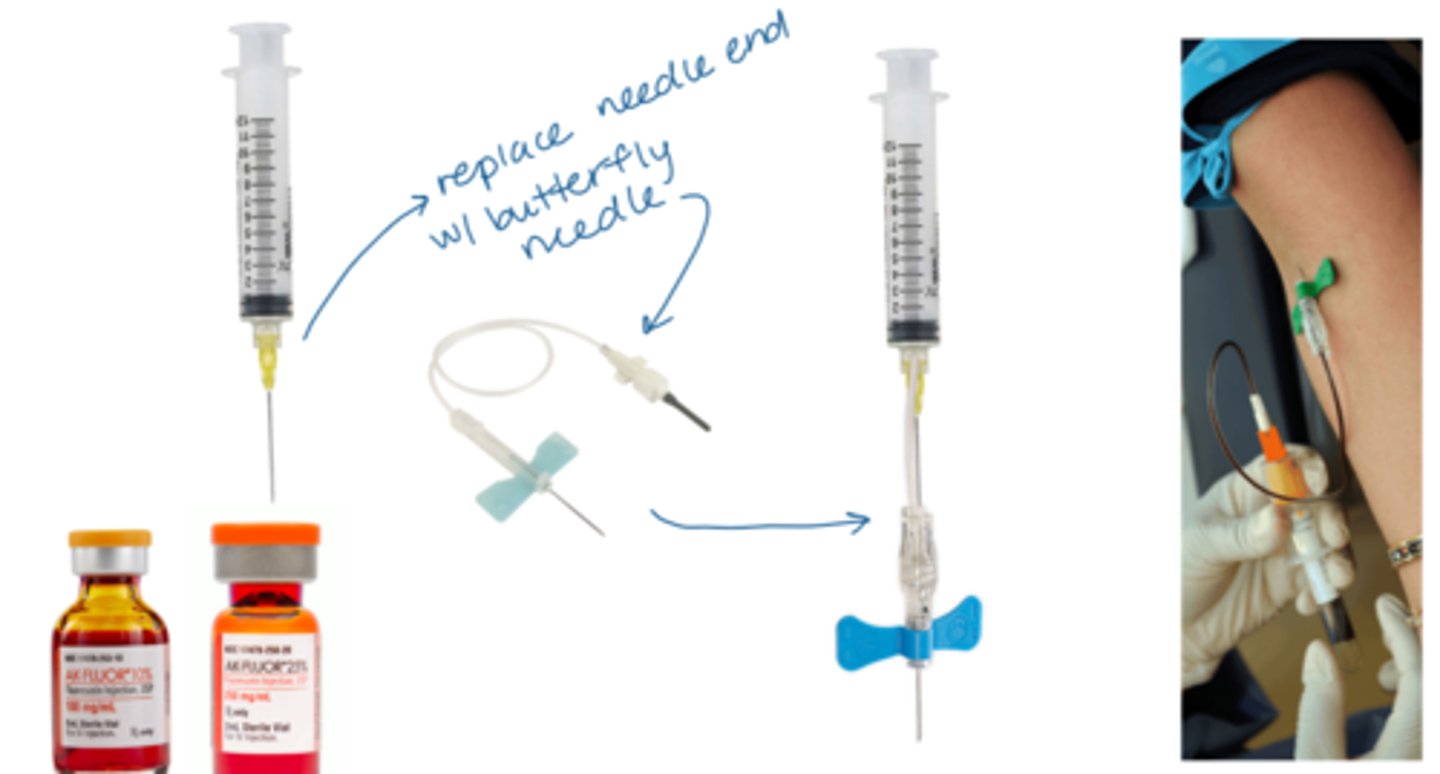
Why do we not use oral fluorescein as often for IVFA?
takes hours to absorb
AND
will only see late phase of angiogram
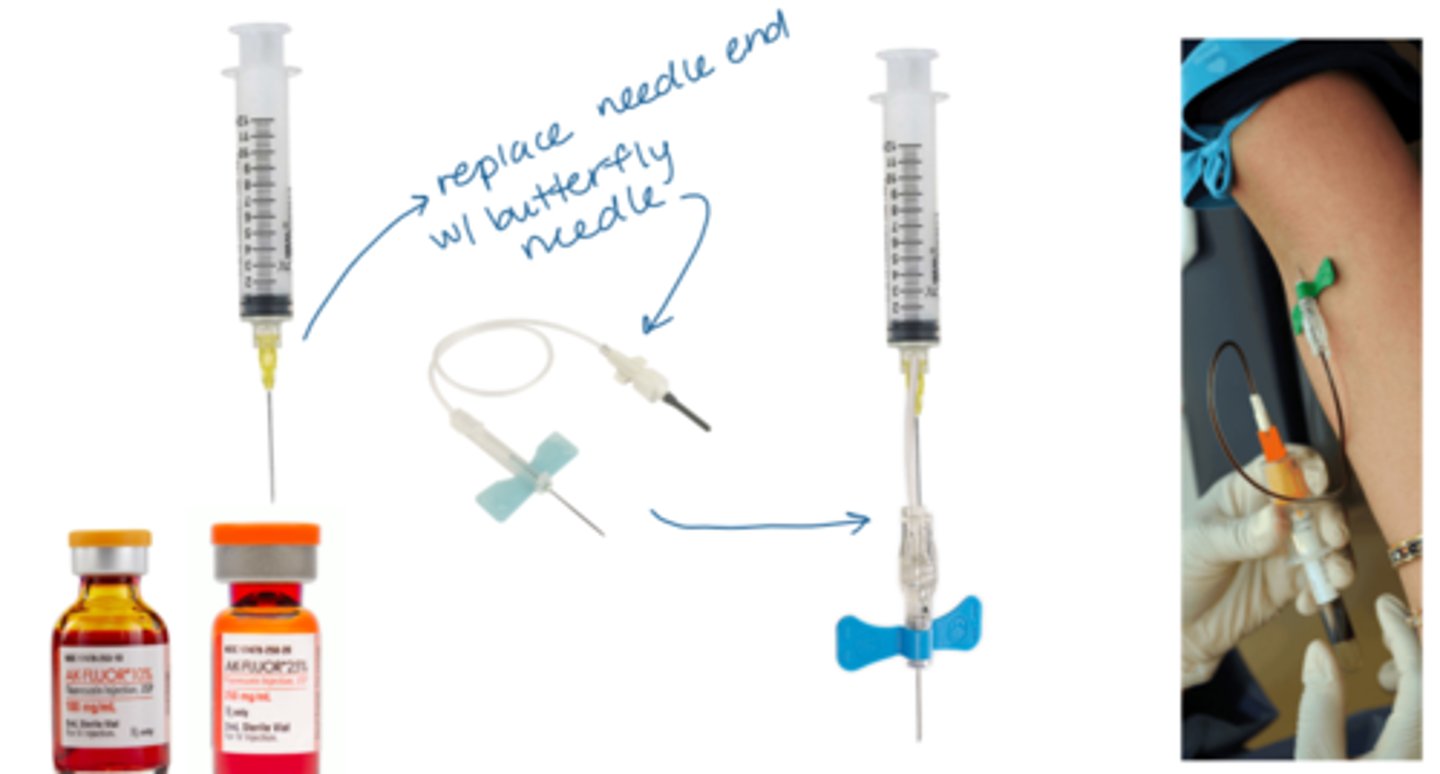
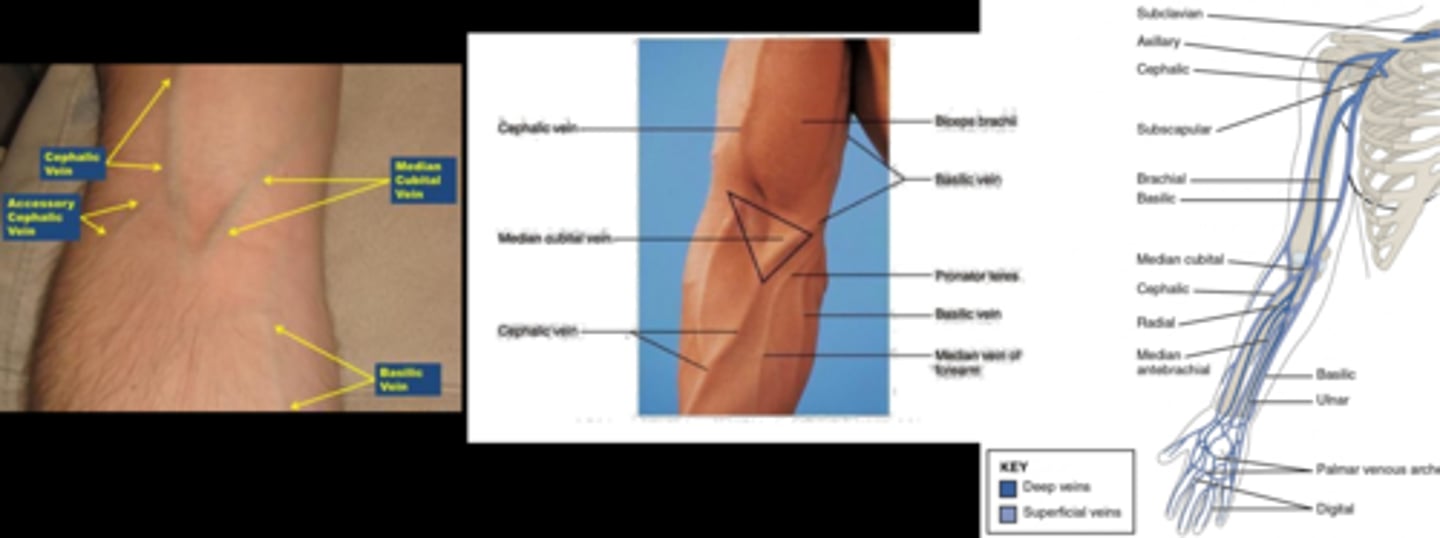
What is the most preferred venipuncture option?
medial cubital vein in antecubital space = prominent, non-rolling vein
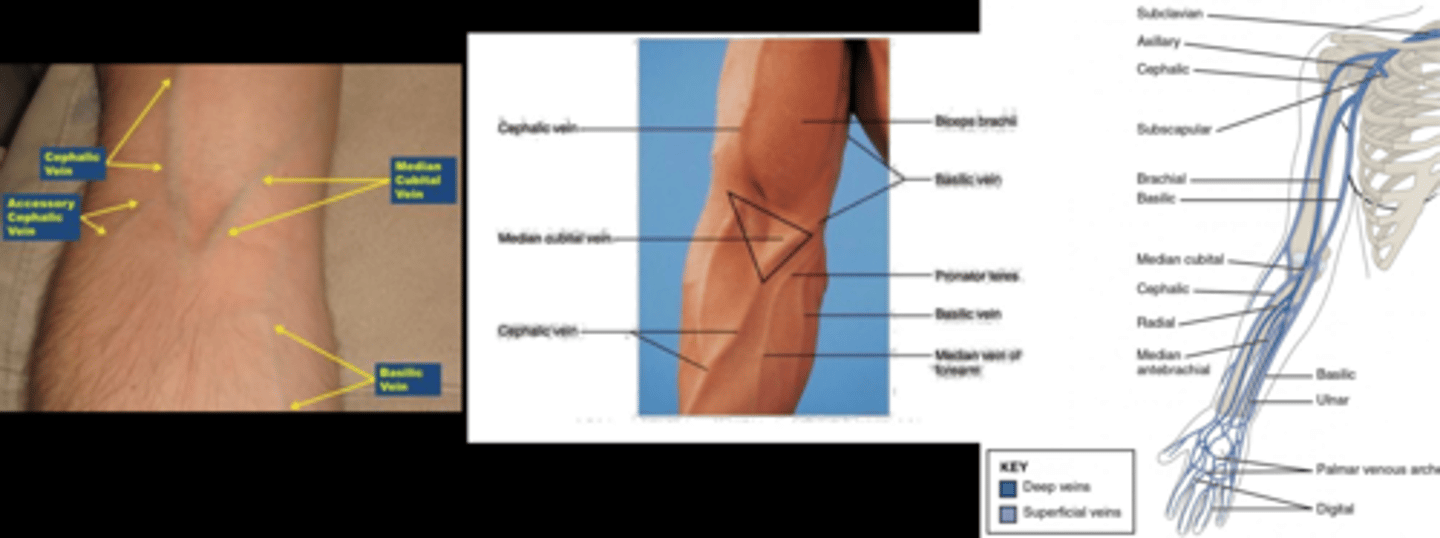
What are 2 alternative venipuncture locations?
cephalic vein in antecubital space, but can roll
dorsal hand veins but painful
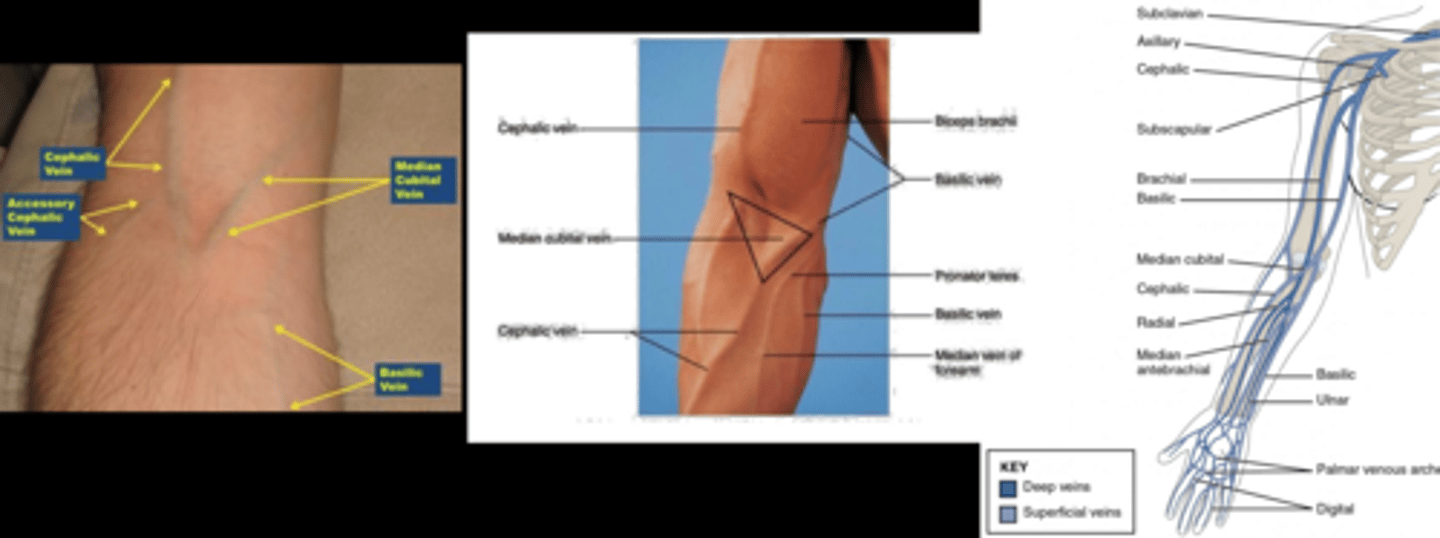
What artery do we always avoid during IVFA?
basilic bc nearby the brachial artery and nerve
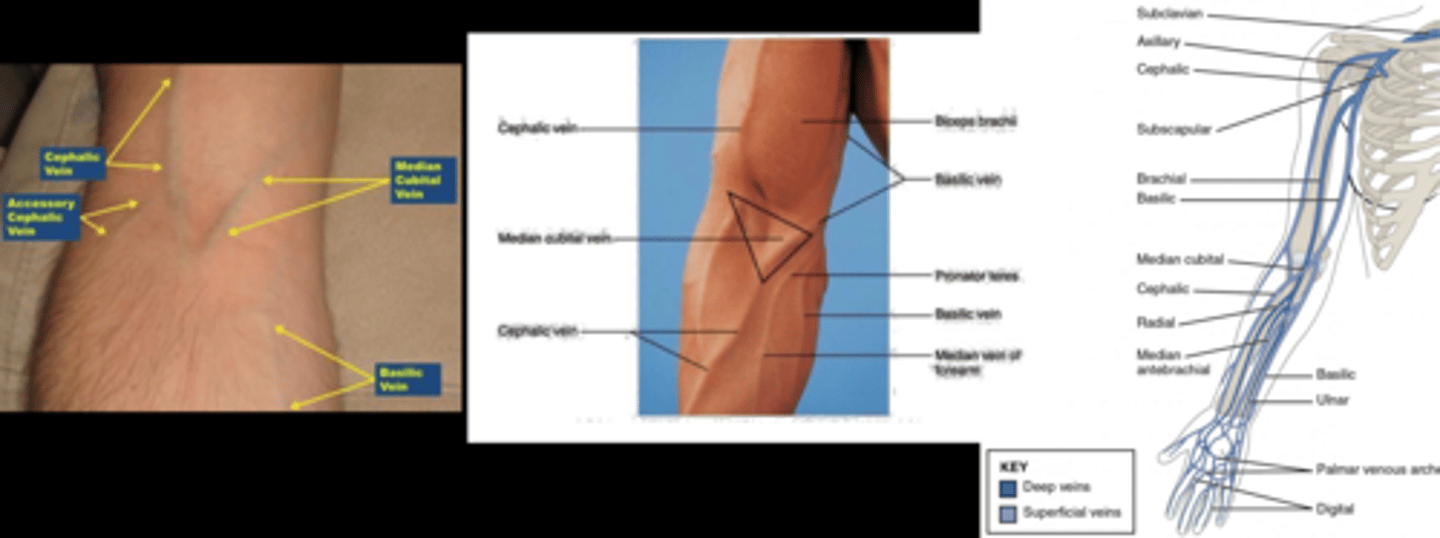
How can we palpate veins when deciding which to puncture?
clenching
warm compress
downward gravity
= brings blood into arm veins
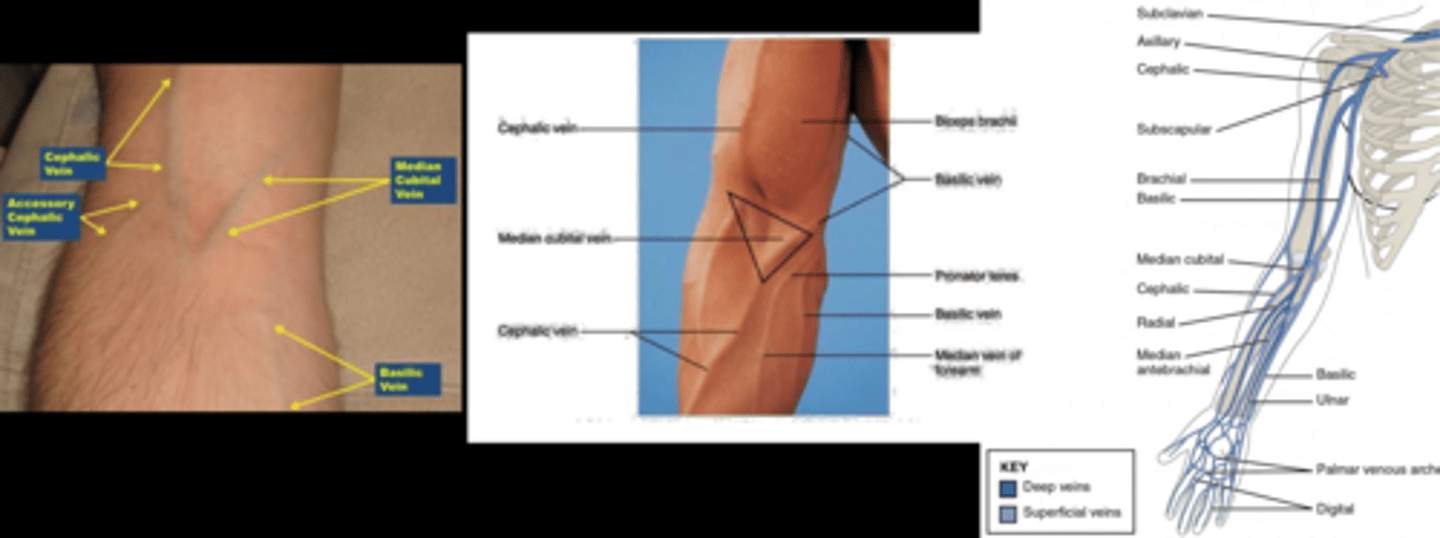
How do we position the pt before injecting fluorescein?
in the machine
Where and how do we apply the torniquet to increase venous filling?
2-6 inches above site, tightly cross & tuck a loop in from the top (but don’t pull the end through) so that you can pull the short end away from injection site
Never leave a tourniquet on for more than _________.
1-2 minutes
How do we clean the injection site?
Alcohol wipe - circular motion outward
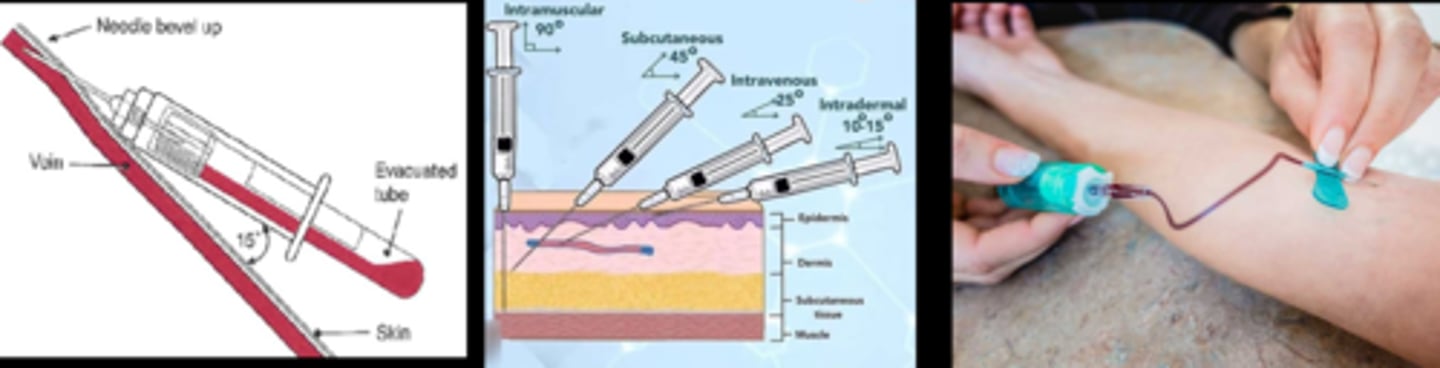
Explain how to insert a needle.
1. hold skin taut at distal end
2. needle bevel up at 15-30 deg to the skin
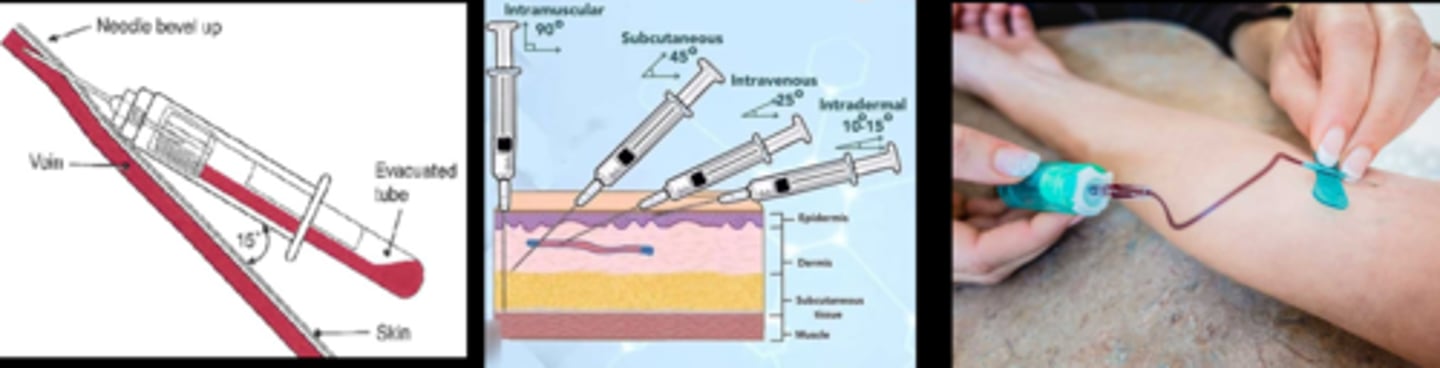
We establish blood flow by seeing blood in the needle tube. What 2 things can we do if we see none?
1. move needle slightly further in/out/left/right
2. try different vein (alcohol wipe if need to re-palpate)
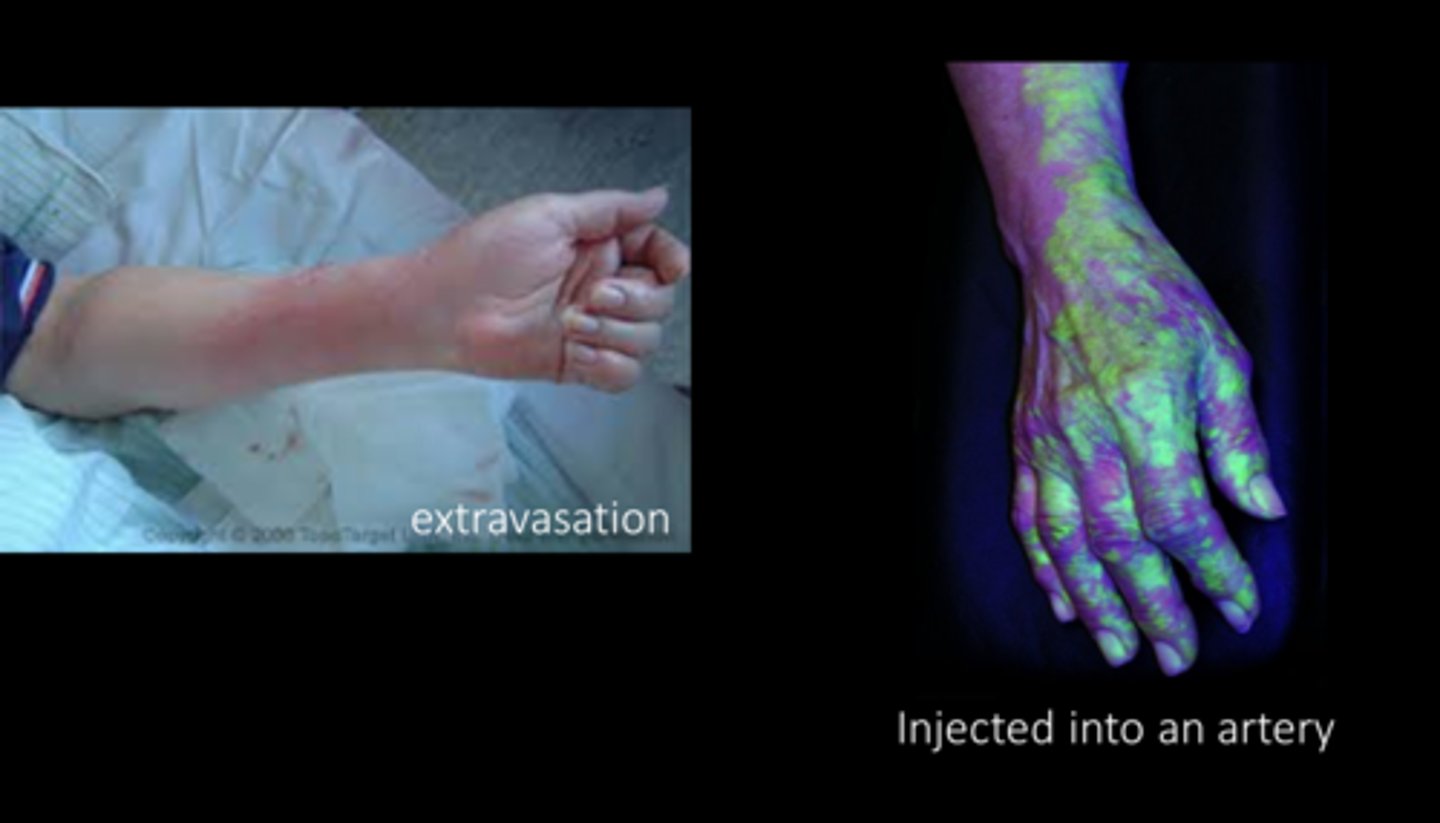
What is the last step before removing the tourniquet? Explain the 3 things we are looking for.
inject a small amount of NaFl to look for...
1. pain/burning = needle is in artery or extravascular tissue, pH 9 of NaFl burns
2. extravasation = site discoloration, edema
3. yellowing distal to injection site = artery injection
After removing the tourniquet, how do we inject the NaFl?
1. pt looks at target in OCT
2. check the time
3. inject NaFl over 5 sec
How do we remove the needle after the IVFA?
place cotton ball over injection site
withdraw needle at same angle as insertion
bandaid over cotton
needle into sharps
Why might we not remove the needle right away after IVFA?
diphenhydramine (IV benadryl) can be injected if itching
How do we use an epipen if the pt has an allergic reaction during IVFA?
1. lateral thigh (bunch skin if no fatty tissue; keep skin taut if fatty tissue present)
2. pierce quickly at 90 deg
3. inject 1mL per 1 sec
4. remove slowly
How do we use IM epinephrine if the pt has an allergic reaction during IVFA?
deltoid mm injection
How does the NaFl travel in the blood? Free or bound?
60-80% of fluorescein binds to serum proteins/albumin
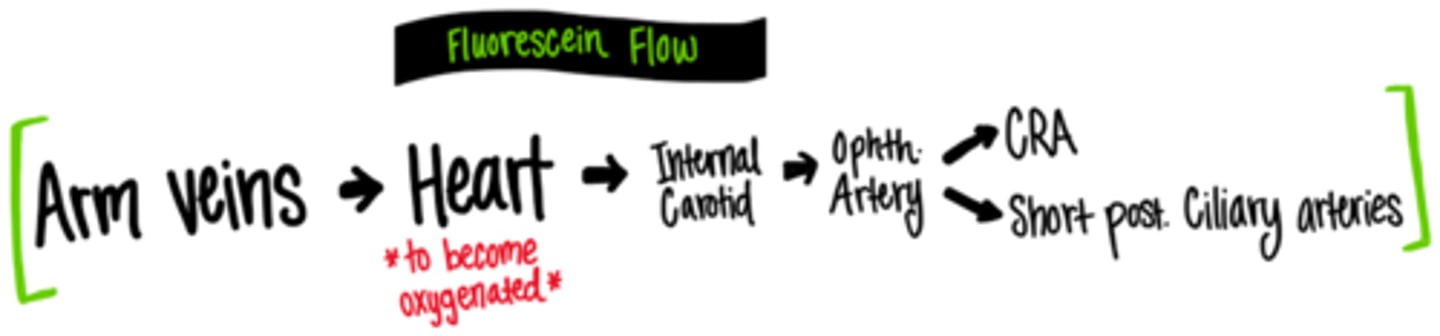
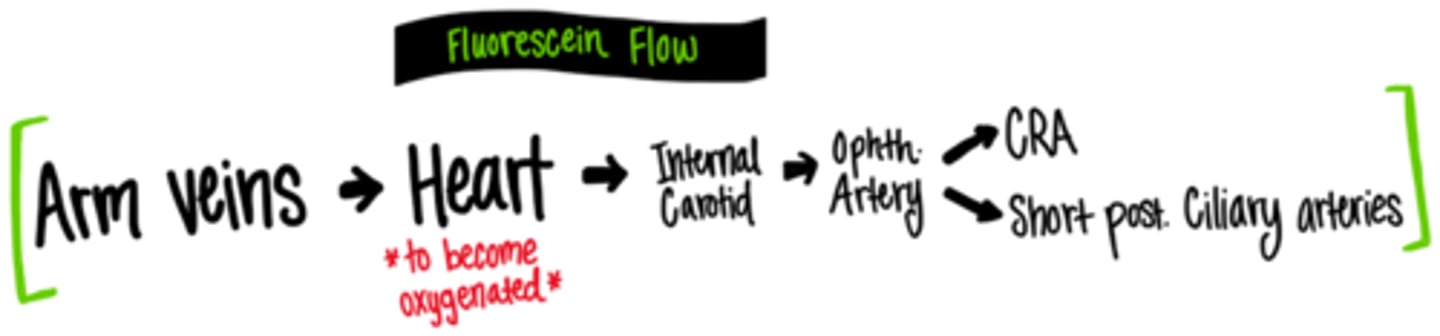
Explain the path of NaFl flow from the arm veins to the retina.
medial cubital -> basilic -> axillary -> subclavian -> brachiocephalic -> sup vena cava -> R heart -> lungs -> L heart -> internal carotid -> ophthalmic artery -> CRA and SPCA -> retina and choroid
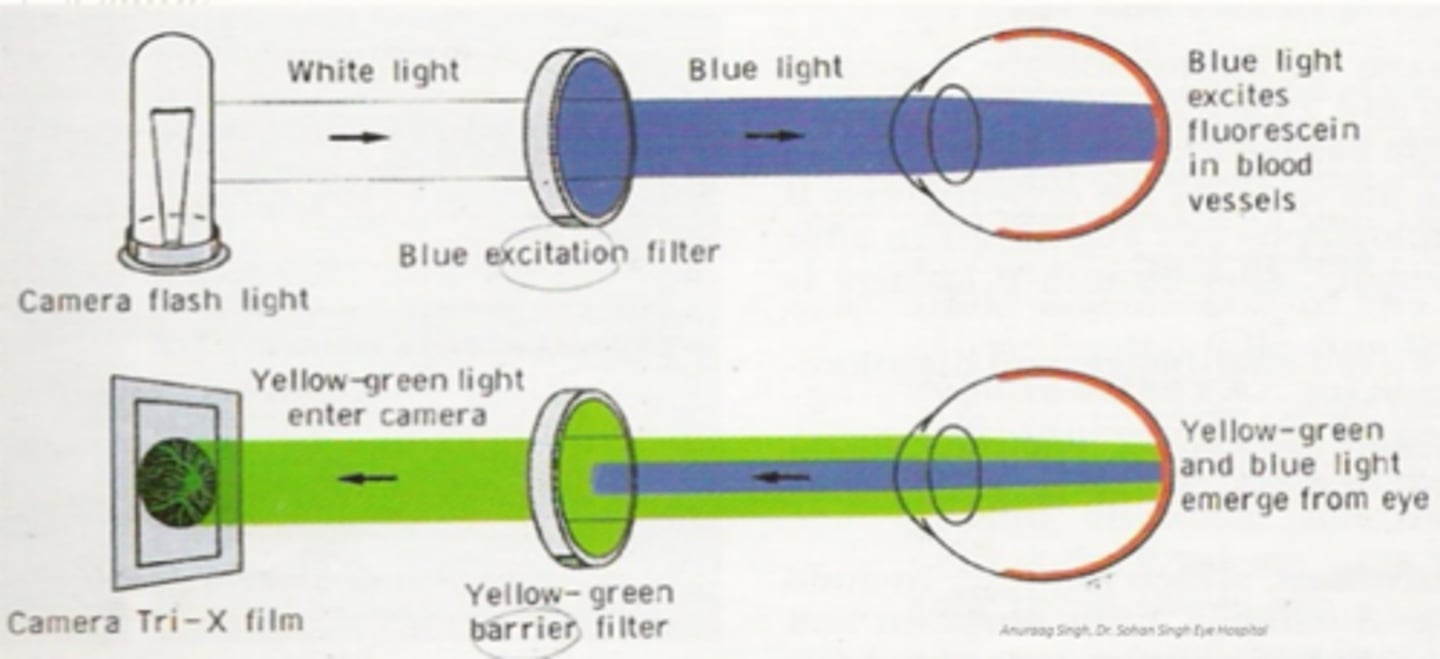
How does the IVFA platform on the OCT machine work?
white light from flash passes through blue filter = blue light hits retina = fluorescein in blood is excited = yellow-green and blue light leaves eye = yellow-green filter allows only Y-G light through to camera, no B light
How do we change the mag for IVFA?
different lens attachments
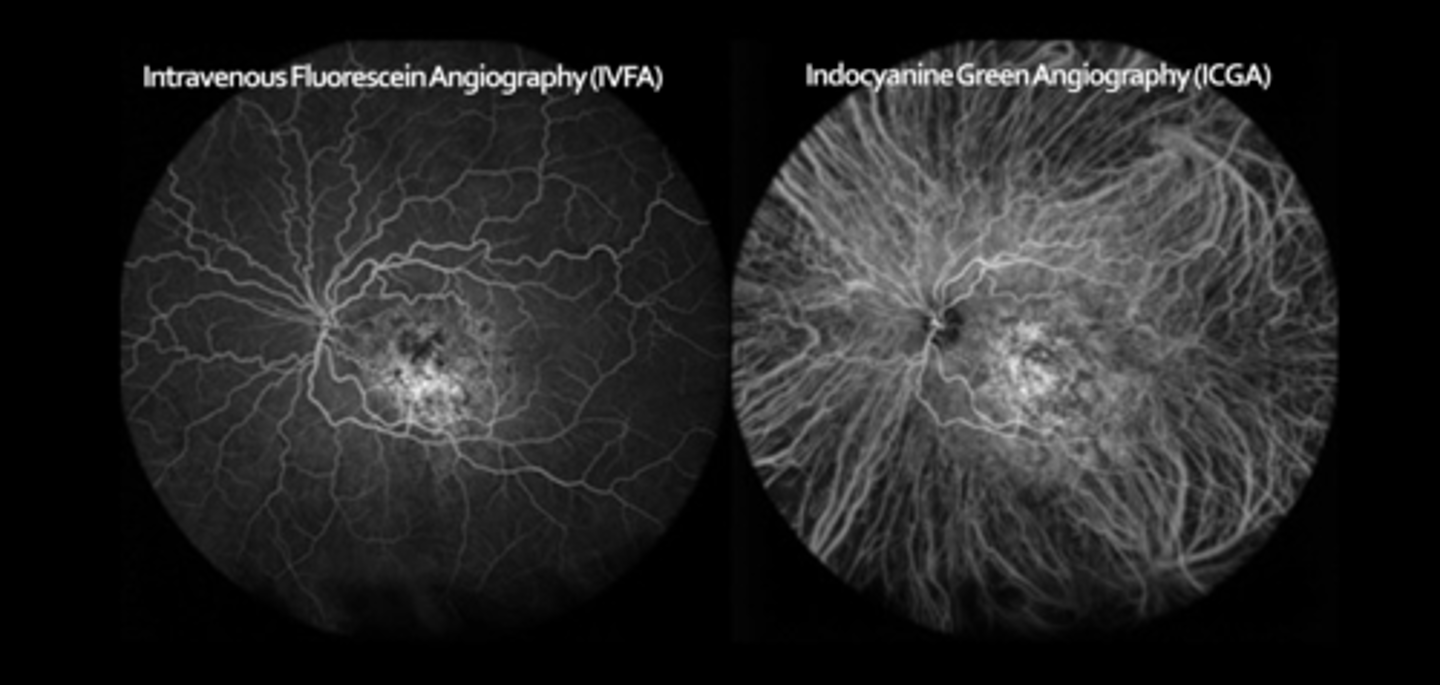
ASIDE: why do we use indocyanine green angio (ICGA)?
ICG emits higher wavelengths = penetrates beyond RPE = 98% serum protein bound = won't diffuse out of choriocapillaris = better choroid visualization
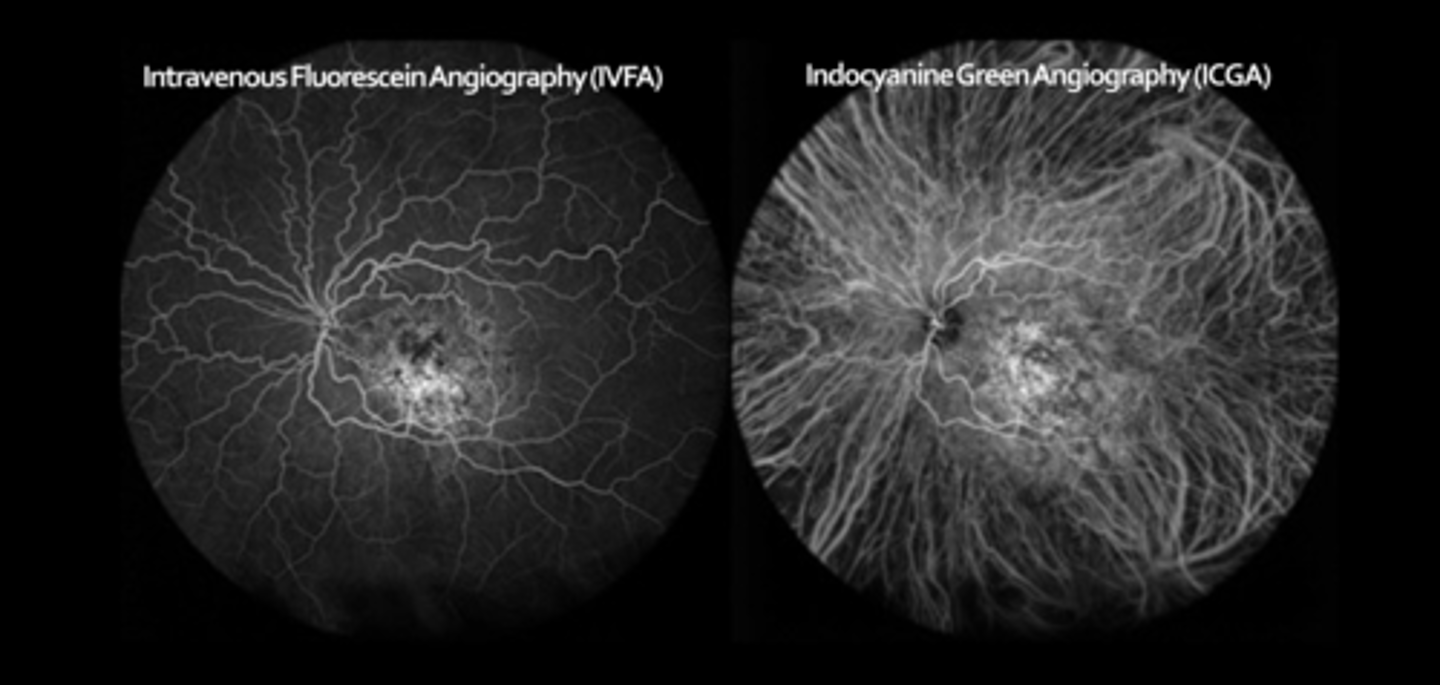
What are the 3 phases of ICGA?
early (0-3 min): maximal hyperF within 1 min, medium and large choroidal BV are filled
middle (5-15 min): choroidal BV become less distinct, diffuse/homogenous choroidal fluorescence
late (18-22+ min): details fade, ONH becomes dark, can see contrast of abnormal hyperF lesions at this stage
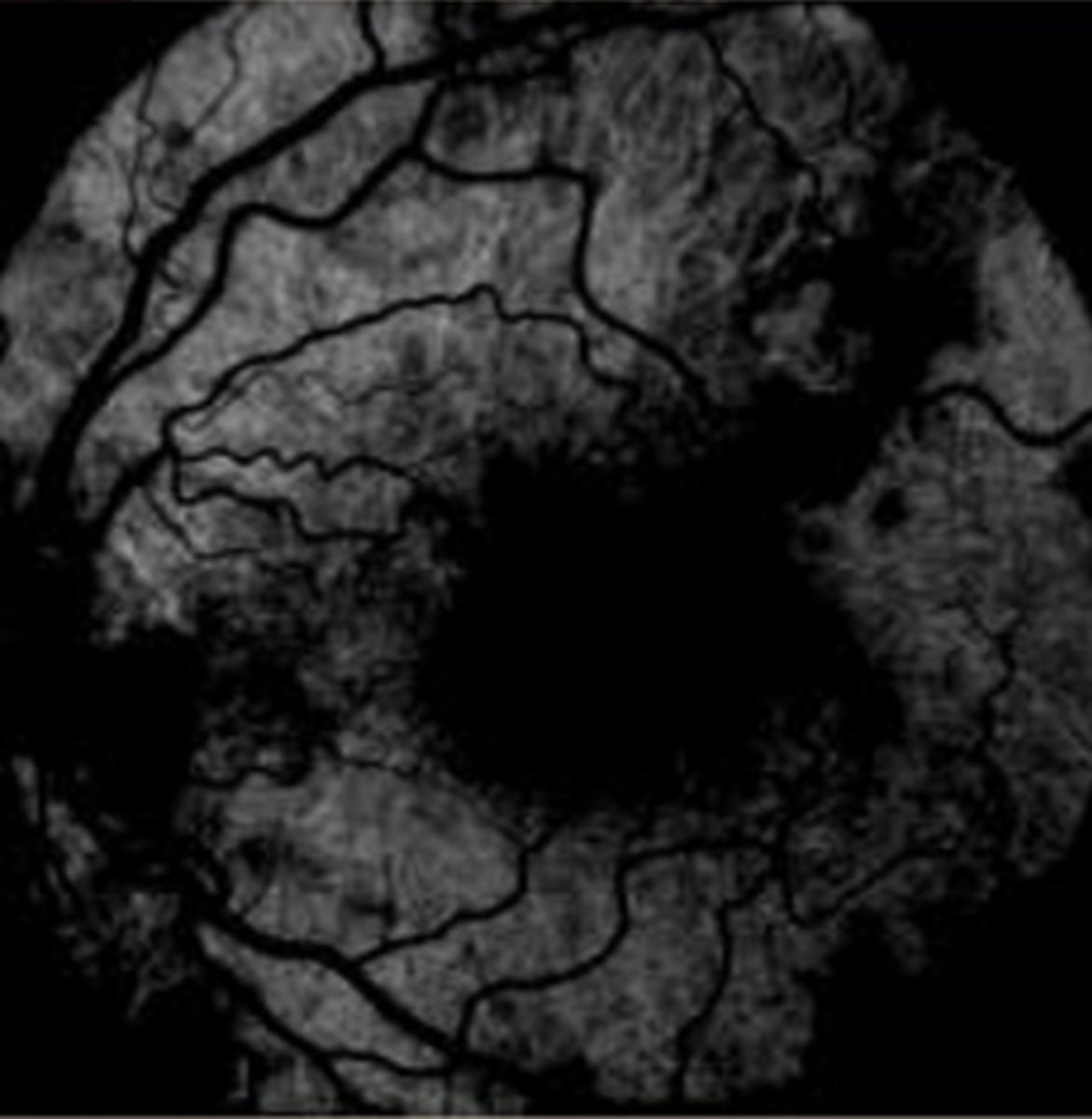
What does the posterior segment look like before NaFl reaches the eye?
fairly dark, hypoF
What structure remains dark/hypoF over all the angio phases?
macula bc of heavy pigment carotenoids and FAZ
What are the 7 IVFA phases in order?
1. pre-arterial / choroidal flush
2. arterial
3. arteriovenous
4. peak
5. venous laminar
6. venous complete
7. late
What is the approx post-injection time of the pre-arterial / choroidal flush phase?
8-12 sec
can be up to 20 in some pt's based on age, CV status, speed of injection
Describe the appearance of the pre-arterial / choroidal flush phase.
patchy/lobular hyperF followed by overall hyperF glow of retina (due to fenestrated choriocapillaris that blood and NaFl moves freely through)
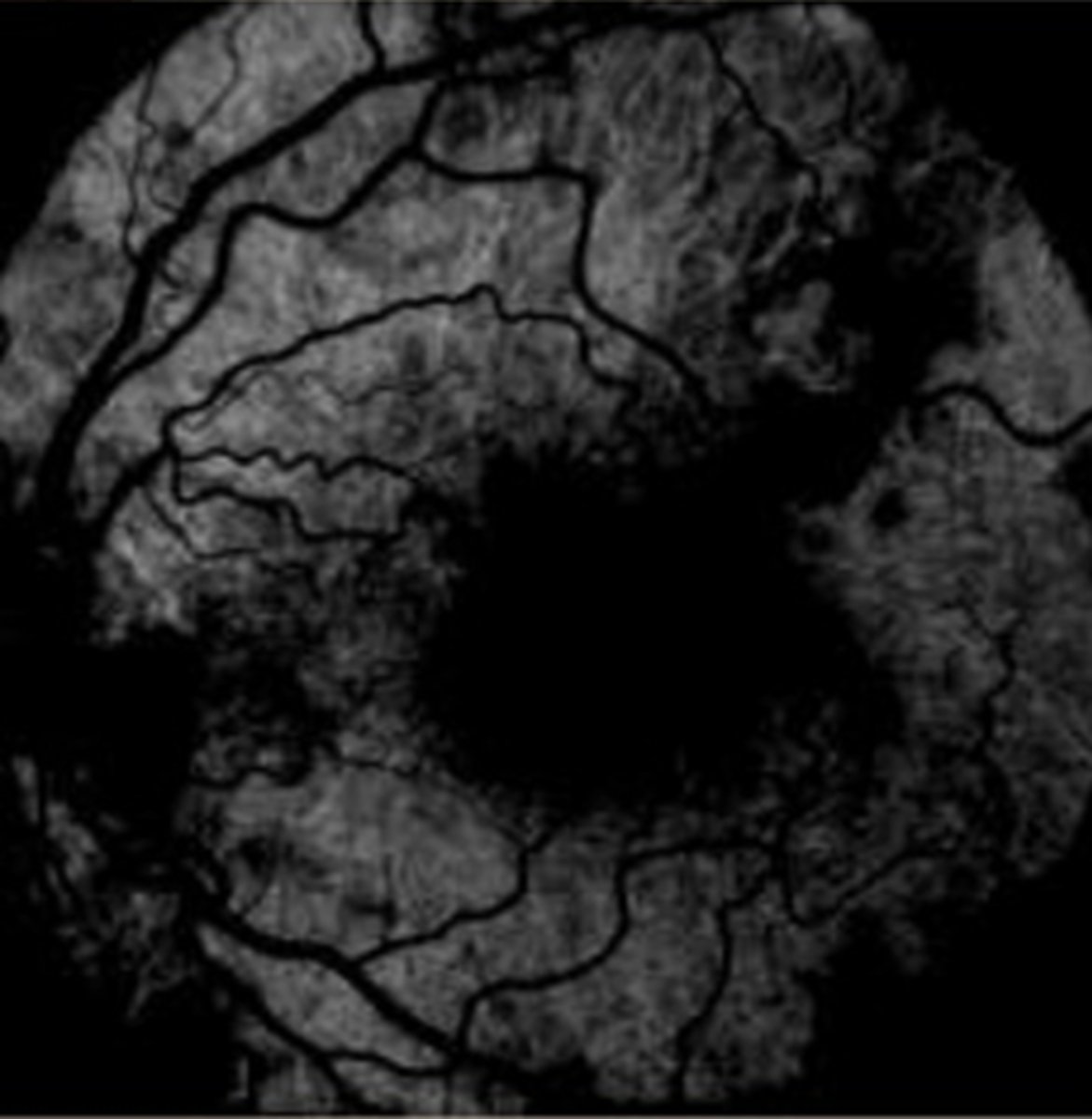
What is the approx post-injection time of the arterial phase?
12-15 sec
(1-3 sec after choroidal flush)
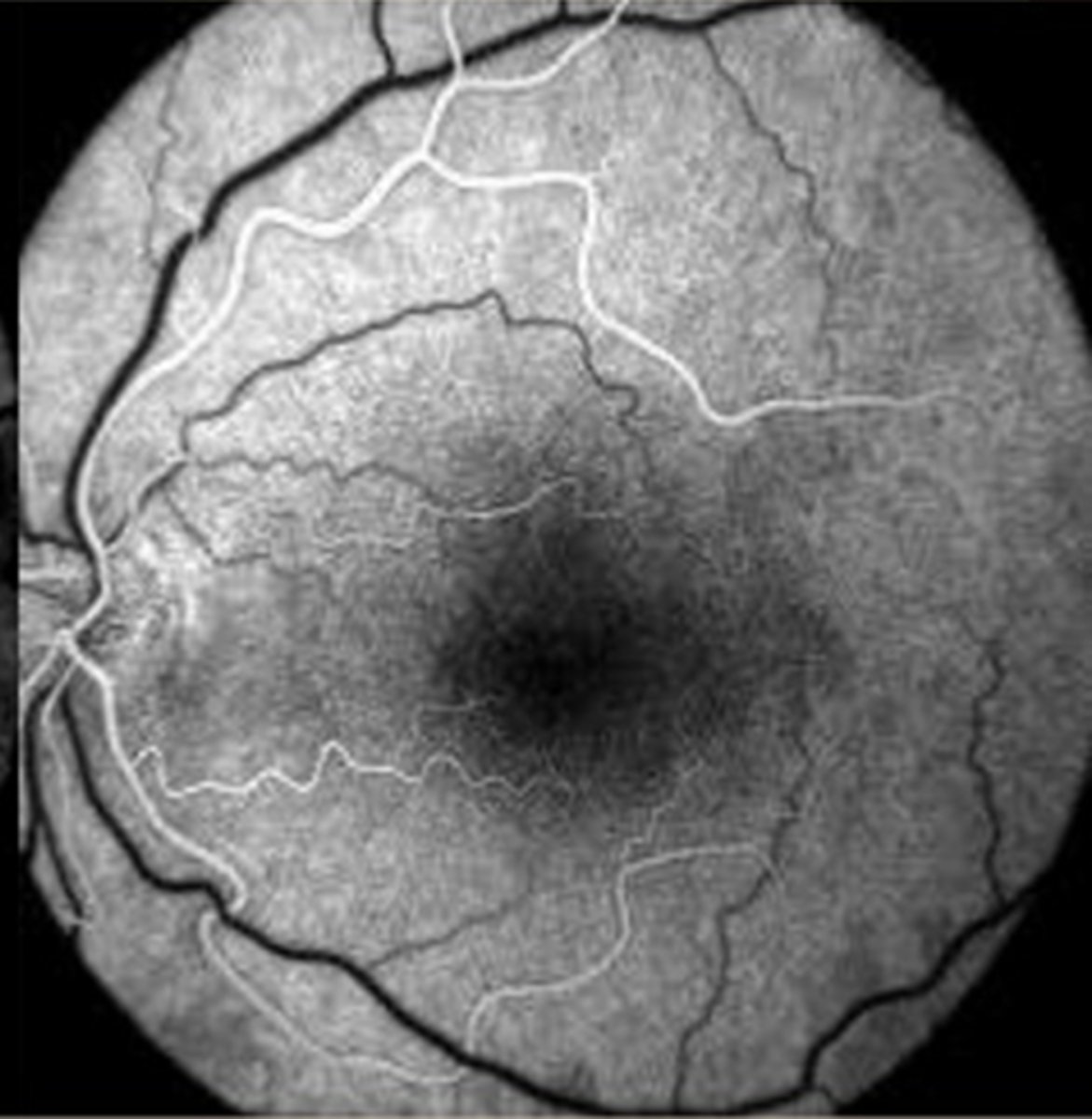
Describe the appearance of the arterial phase.
all 4 artery branches fill simultaneously
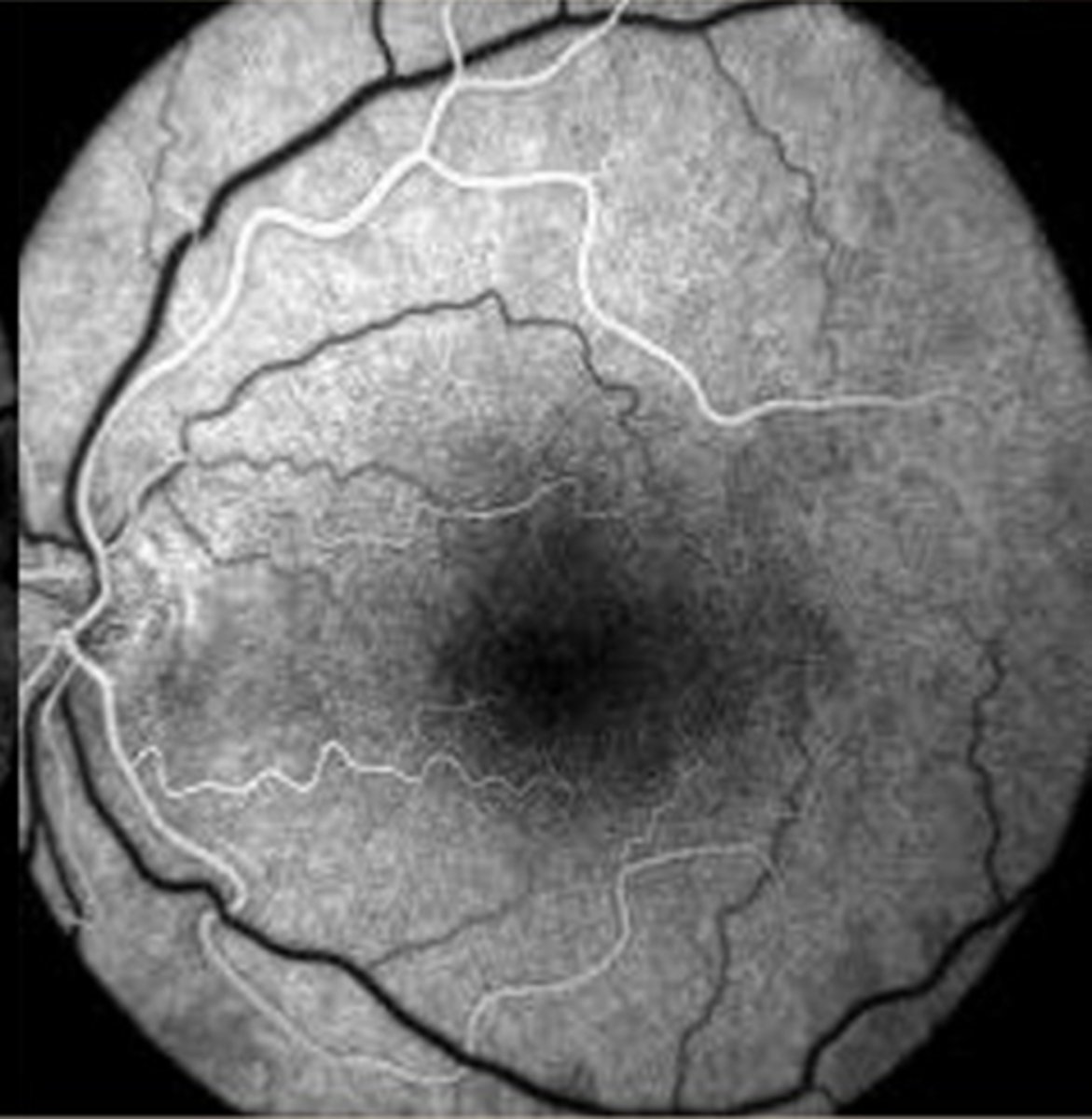
What is the approx post-injection time of the arteriovenous phase?
quick, negligible
Describe the arteriovenous phase.
transition from artery to vein via capillaries
What is the approx post-injection time of the peak phase?
20-30 sec
Describe the appearance of the peak phase.
max [ ] of dye = optimal time to see FAZ
What is the approx post-injection time of the venous laminar phase?
15-20 sec
(by 30 sec)
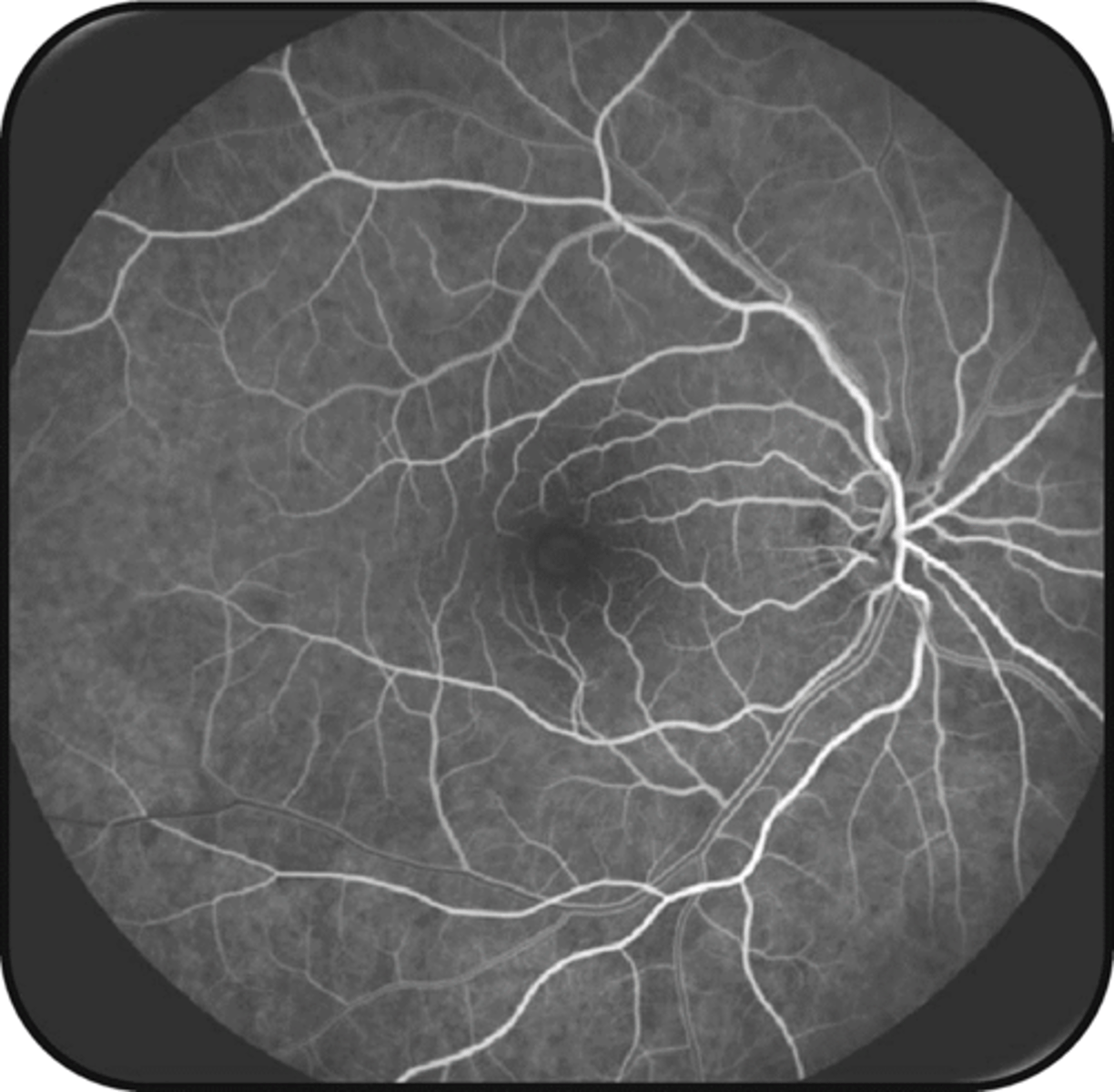
Describe the appearance of the venous laminar phase.
plasma w/ NaFl is rapidly moving along walls bc central lumen has more RBC = vein walls appear hyperF but center lumen appears hypoF (esp noticeable in large caliber veins)
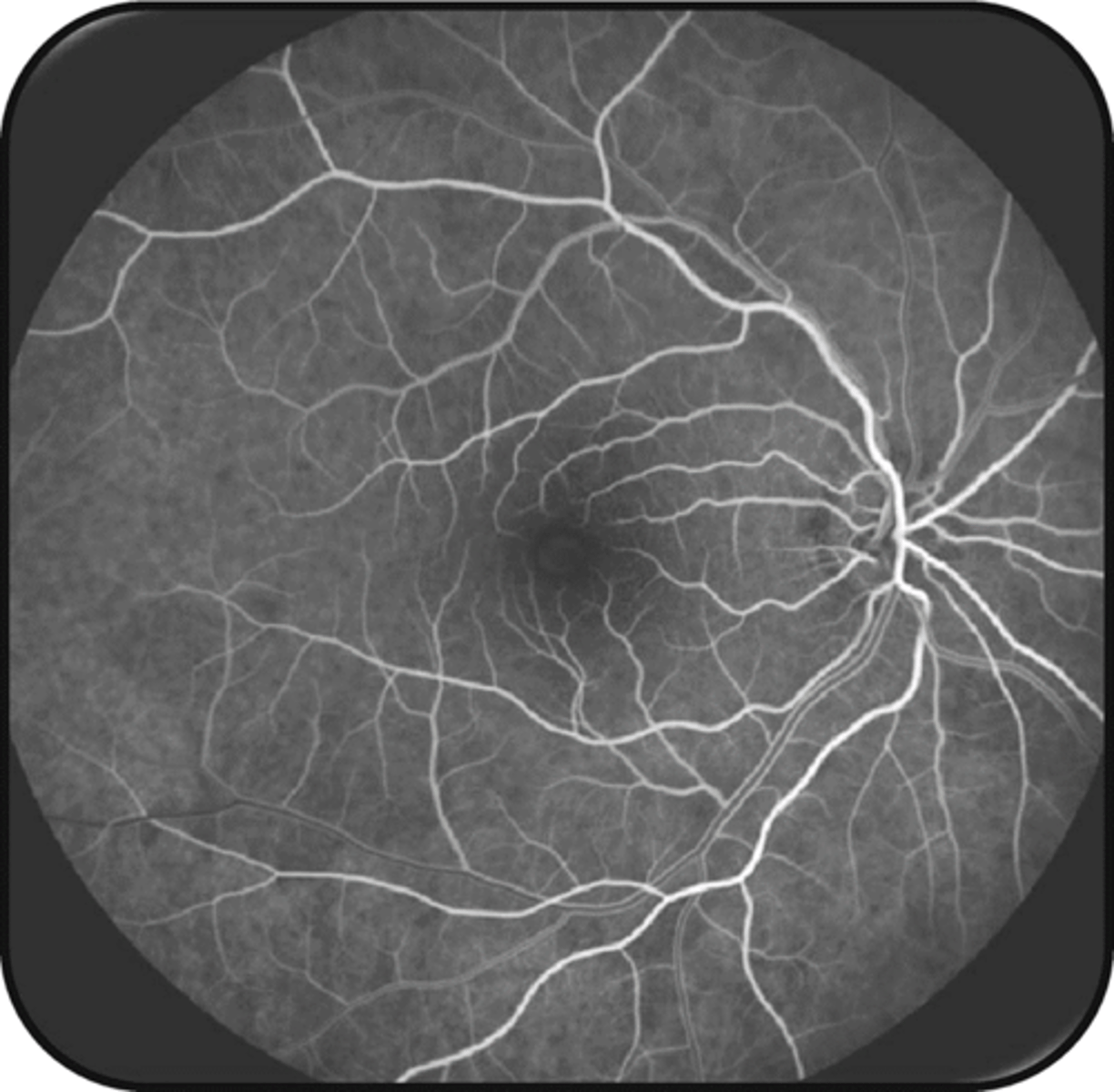
What is the approx post-injection time of the venous complete phase?
45-60 sec
Describe the appearance of the venous complete phase.
all BV hyperF, including the vein lumen
ONH hyperF due to capillary perfusion
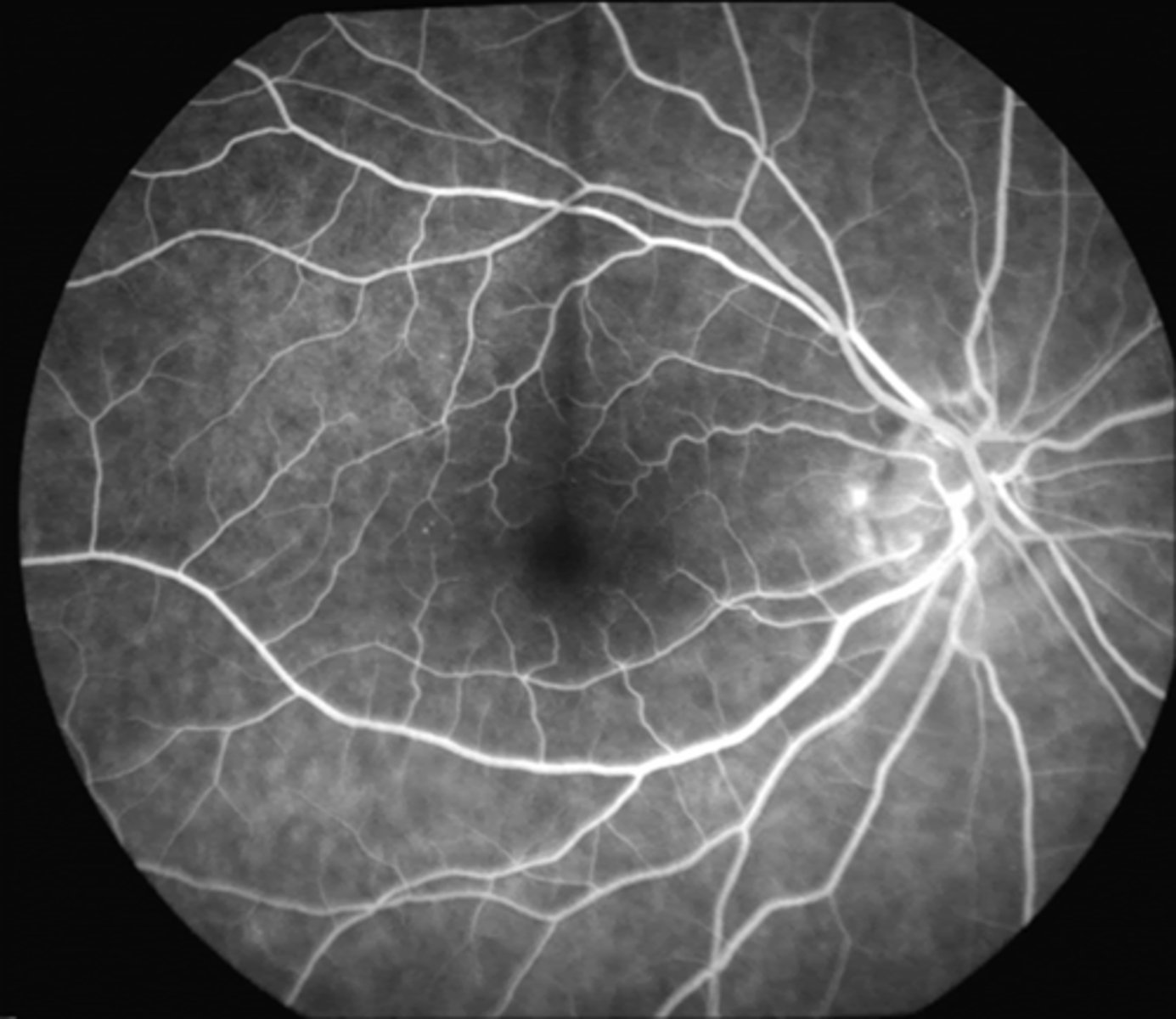
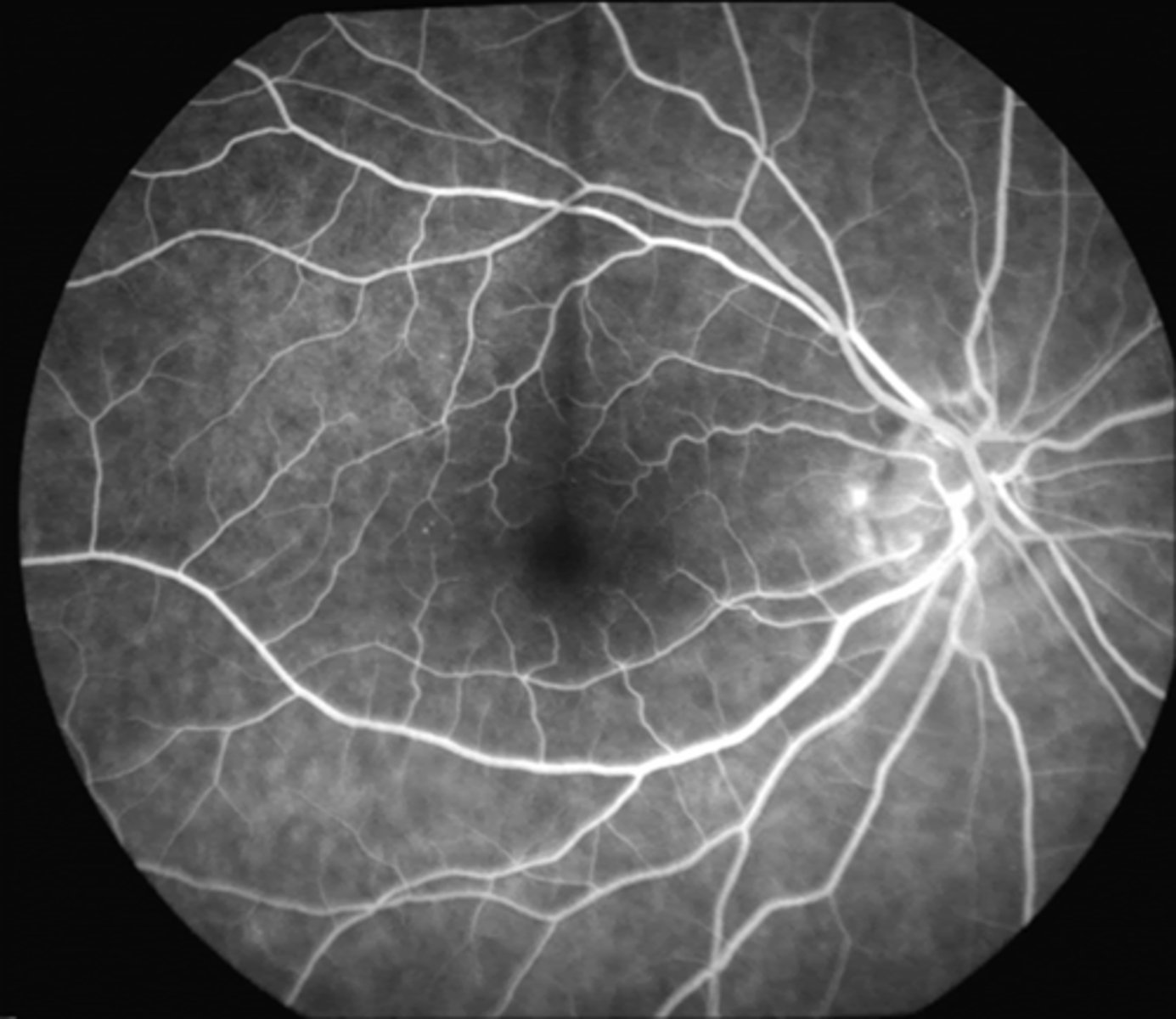
What is the approx post-injection time of the late phase?
2-5 min
(up to 20 min)
Describe the appearance of the late phase.
gradual reduction of fluorescein
after ~10 min, retinal BV are devoid of fluorescein and choroidal flush is barely visible
= optimal time to identify late leakage
Ex) if a pt has a cilioretinal artery, what phase will it fill in?
pre-arterial bc it's supplied by the choroid
What are 3 possible abnormalities of the IVFA timing?
1. choroidal flush noted after 12-20 sec = delayed arm to eye time
2. patchy choroidal flush
3. delayed filling of a branch like in a BRAO
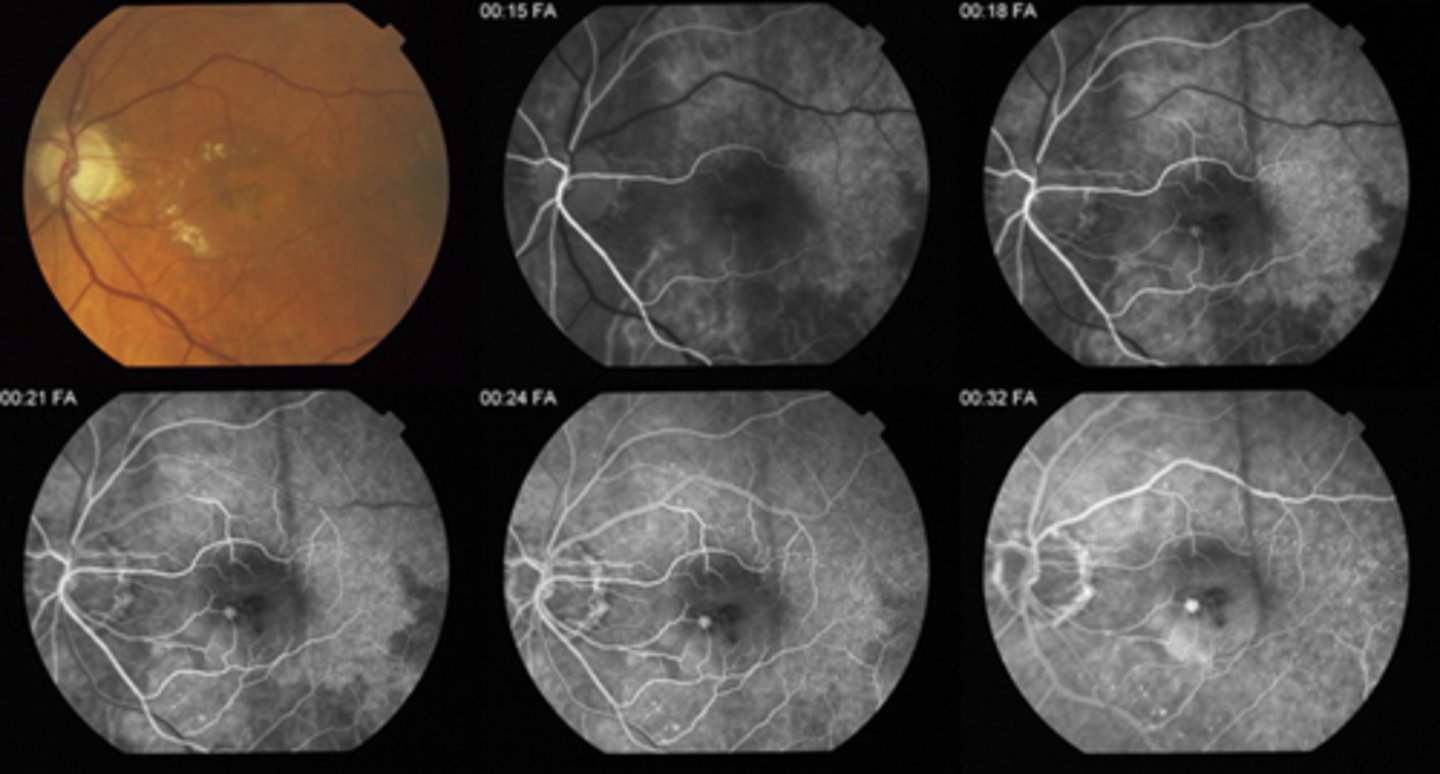
What are 3 possible abnormalities that show as IVFA hypoF?
1. blockage = hemorrhage, pigment, exudate, media opacity in front of the BV
2. impaired vascular filling = choroidal BV, retinal arteries/veins/arterioles/venules/capillaries, ON capillaries
3. atrophy of a perfused structure = ON, choroid, retina
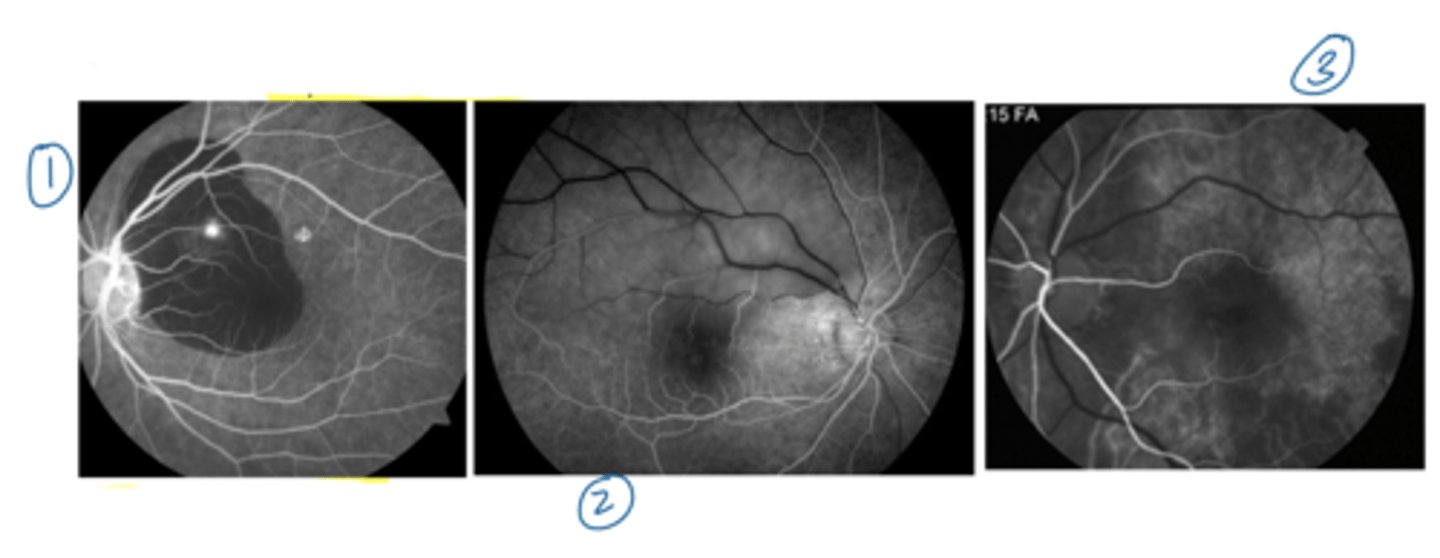
What are 4 possible abnormalities that show as IVFA hyperF?
leakage
pooling
staining
RPE atrophy
Why does leakage show as IVFA hyperF?
dye permeates out of leaky, incompetent BV = hyperF enlarges throughout angiogram with fuzzy borders
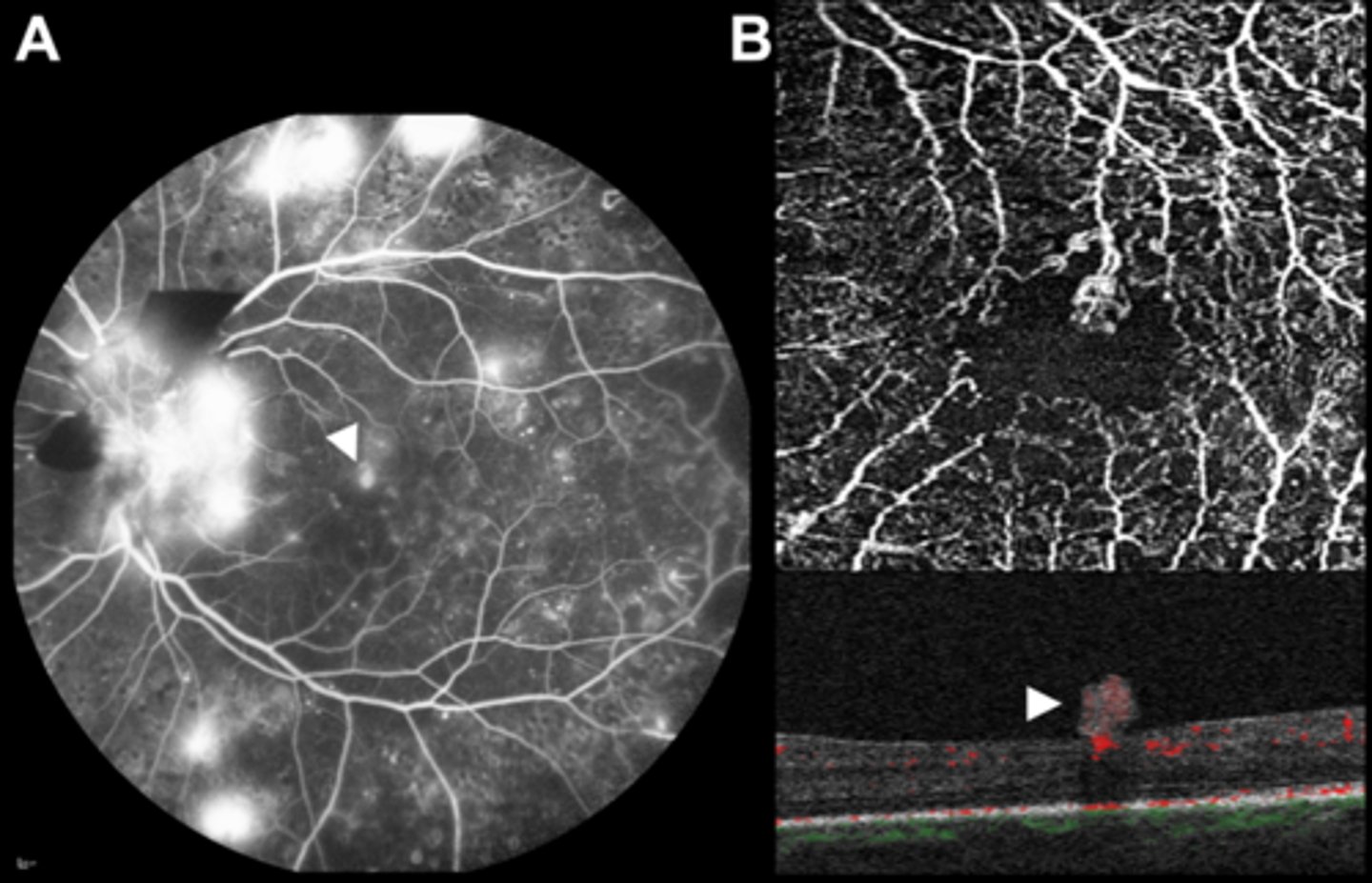
What are some examples of leakage showing as IVFA hyperF?
neovasc (breakdown of BRB = leakage)
disc edema
vascular malformations (aneurysms, arteriolar-venous shunts, telangiectatic vessels)
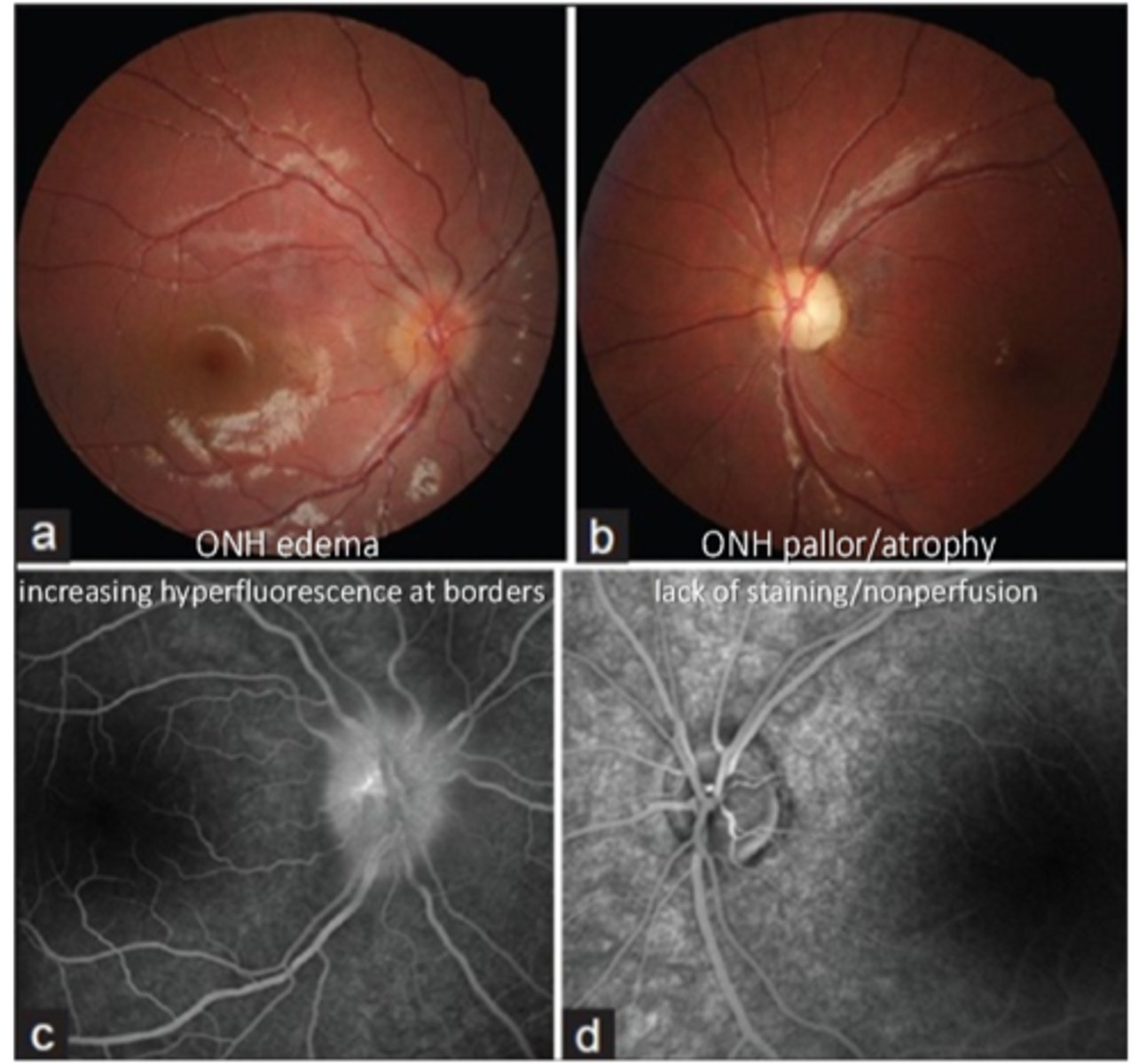
Why does pooling show as IVFA hyperF?
fluid with hyperF dye progressively enlarges to fill cavity (like subretinal or sub-RPE space) = then becomes fixed in size
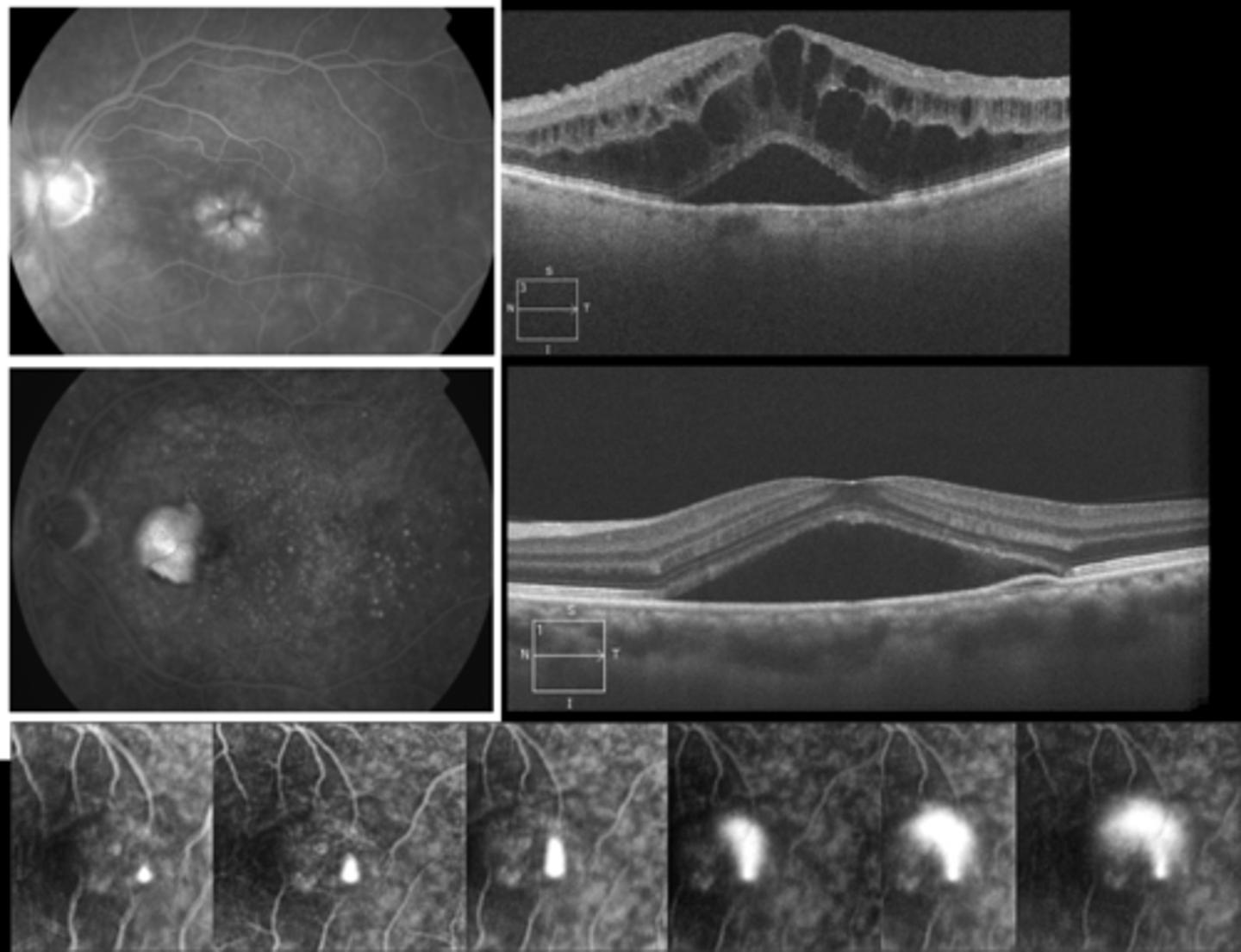
What are some examples of pooling showing as IVFA hyperF?
retinal edema like CSR
sensory retinal detachment (fuzzy borders)
RPE detachment (distinct borders)
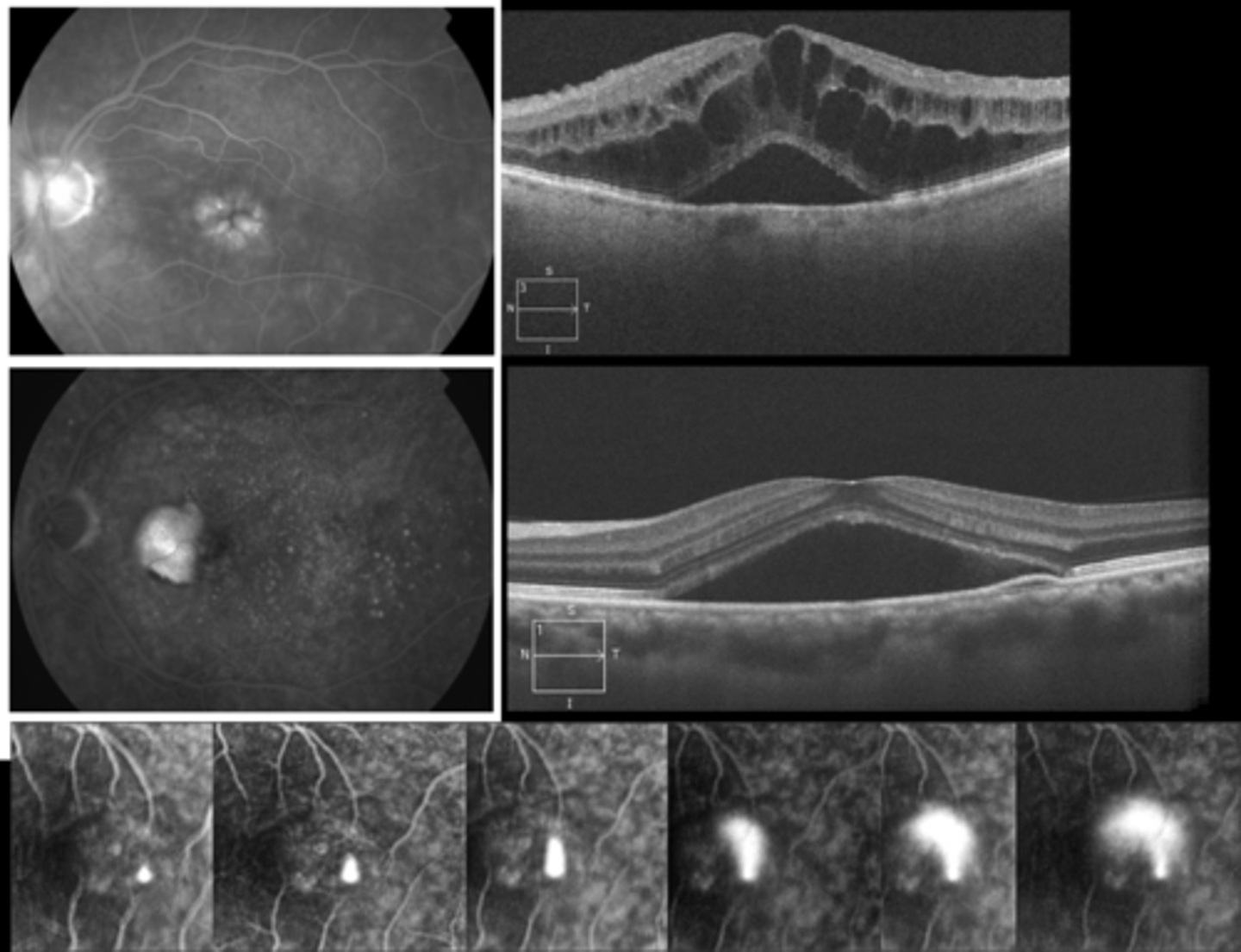
Why does staining show as IVFA hyperF?
NaFl dye accumulates = late hyperF gets gradually brighter (size stays the same)
What are some examples of staining showing as IVFA hyperF?
sclera
optic nerve head
drusen?
glial tissue (Bergmeister)
fibrotic scarring
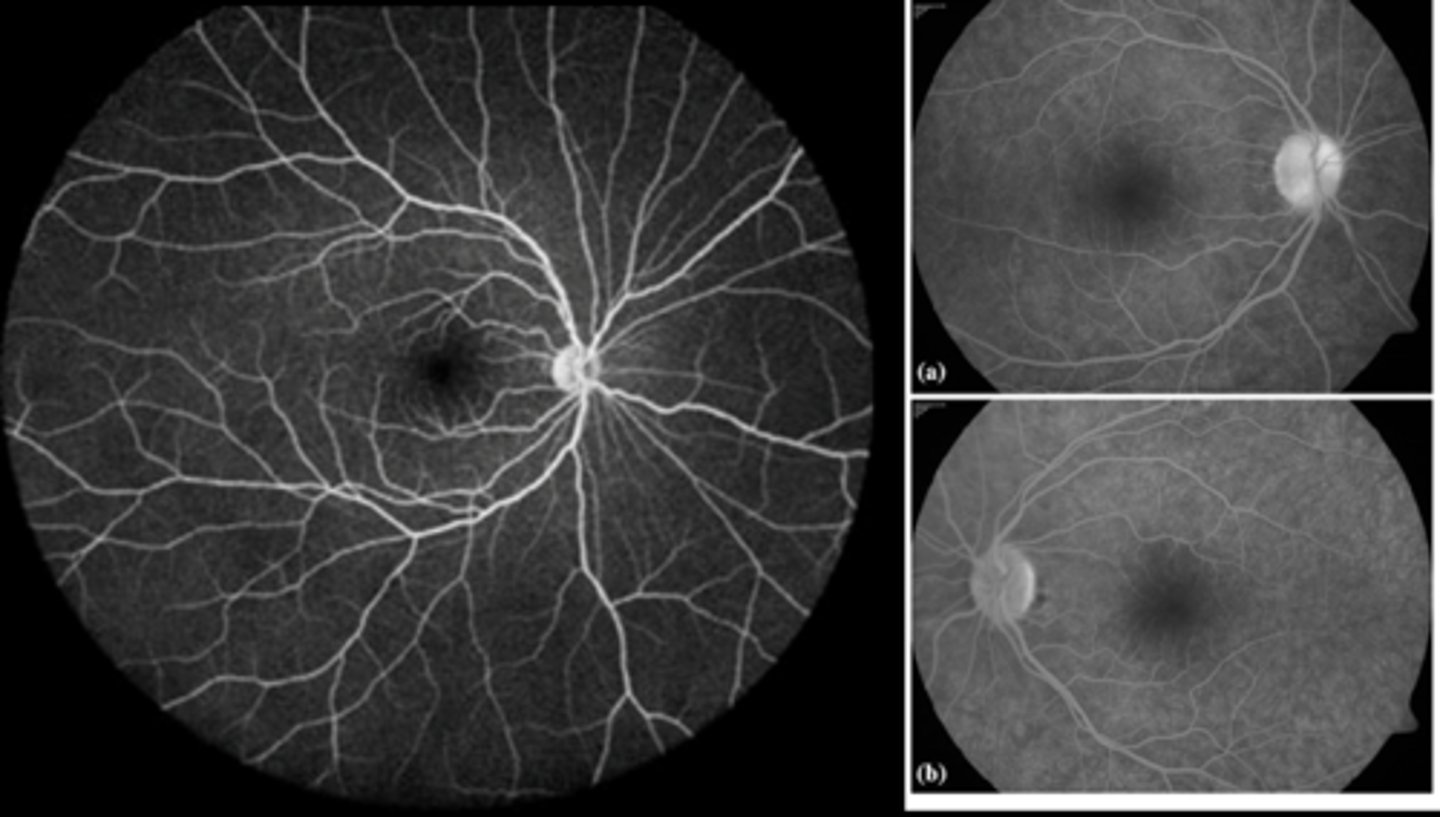
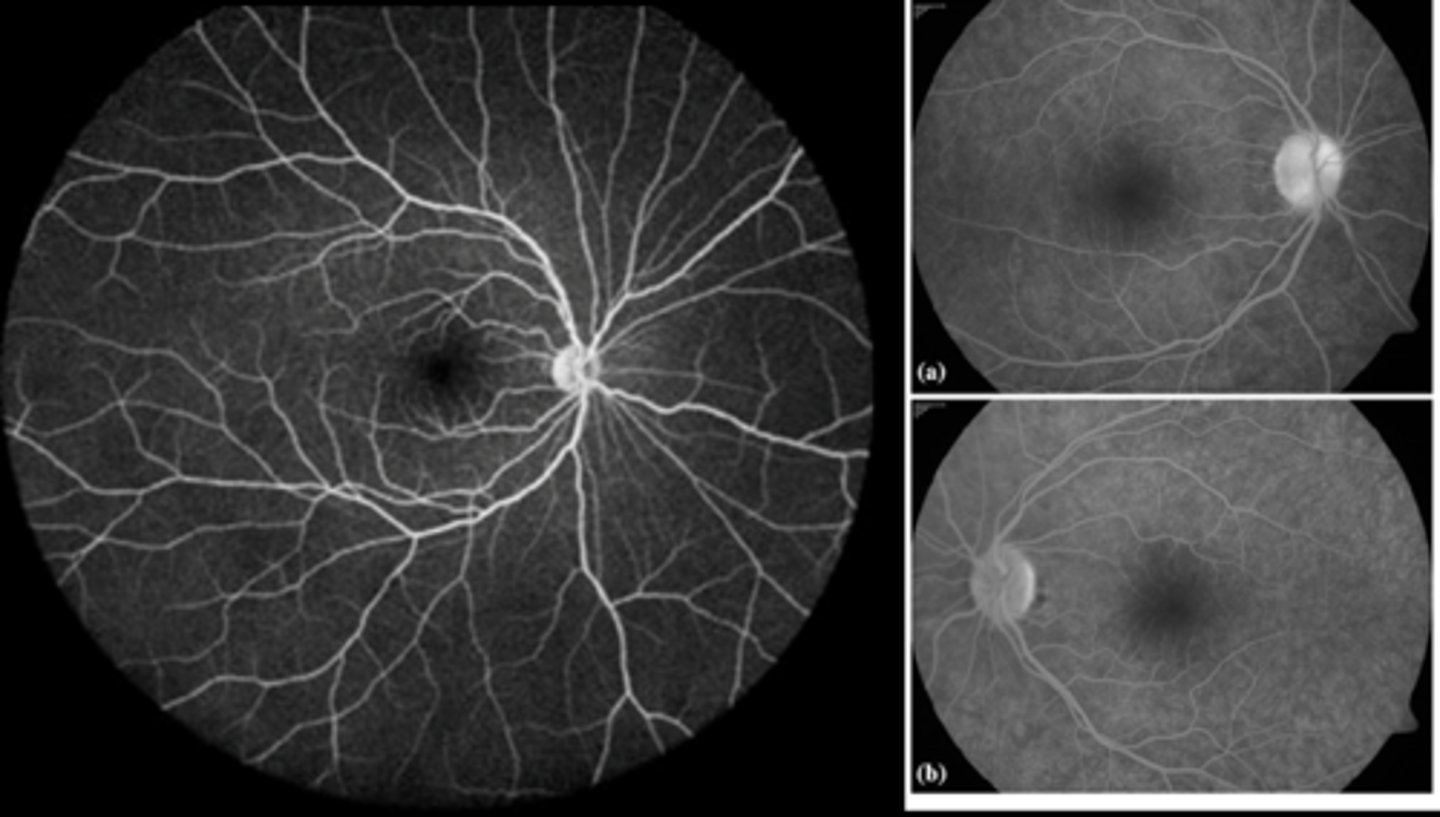
Why does RPE atrophy show as IVFA hyperF?
defect in RPE allows transillumination of the normal choroid hyperF (size and brightness stays the same) = becomes hyperF with the choroidal phase
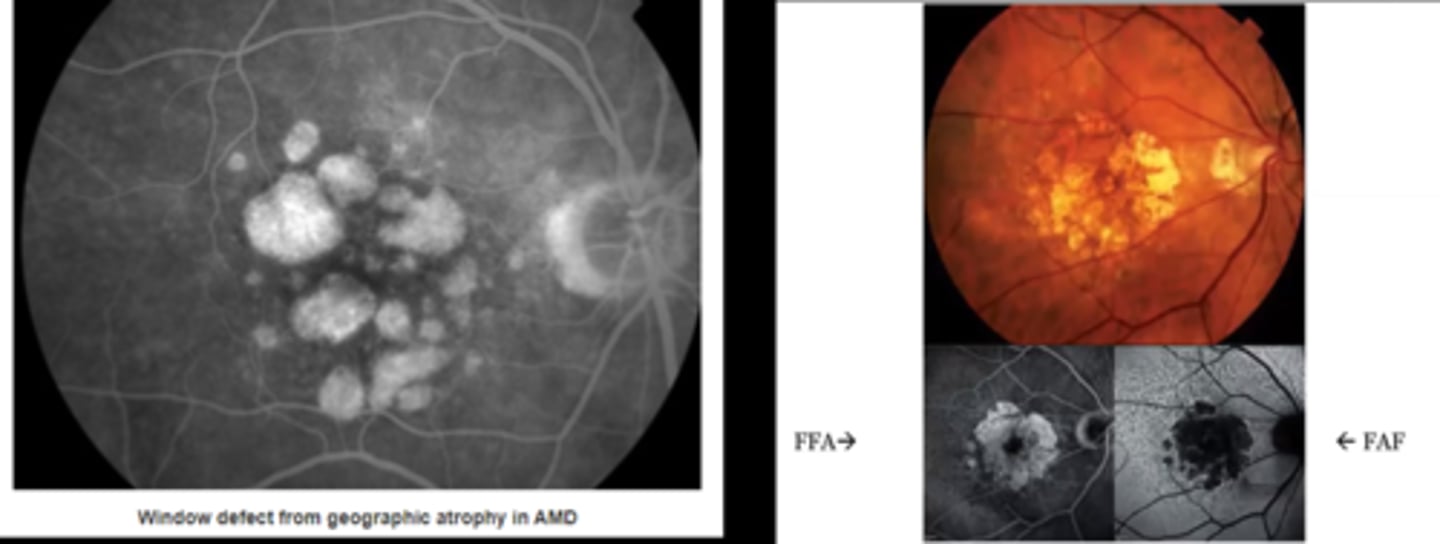
What are some examples of RPE atrophy showing as IVFA hyperF?
RPE loss (i.e. geographic atrophy from AMD)
retinal hole
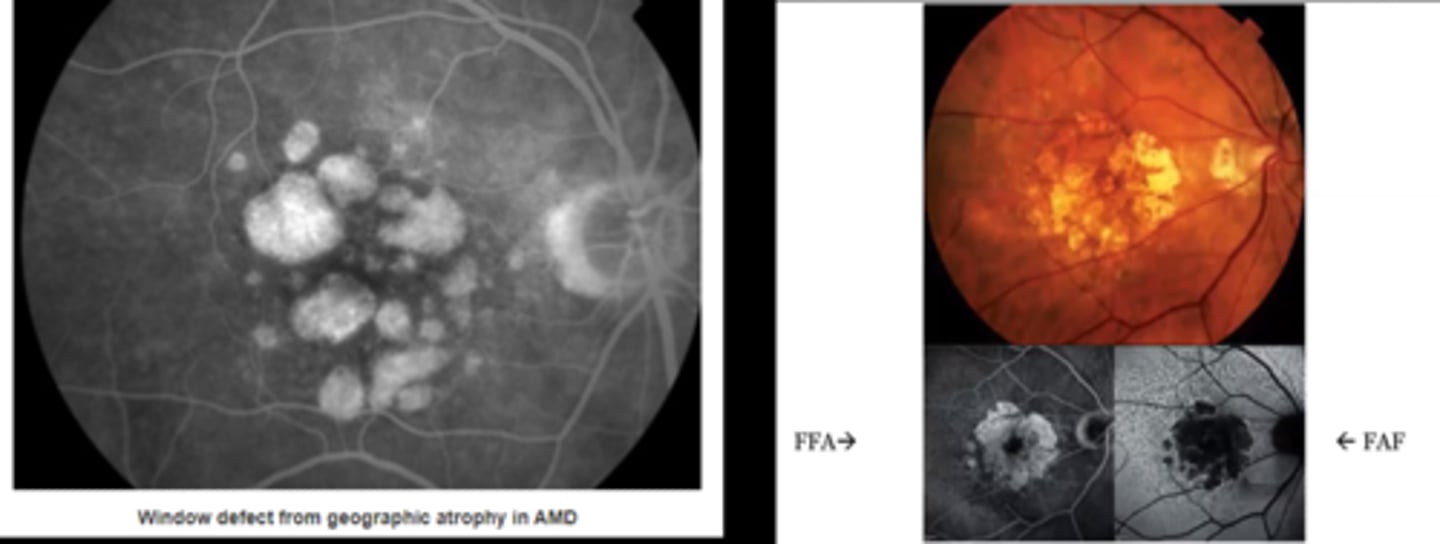
Why does loss of retina and RPE show as hyperF on IVFA but hypoAF on FAF?
can see choroid = hyperF on IVFA
no RPE lipofuscin = hypoAF on FAF
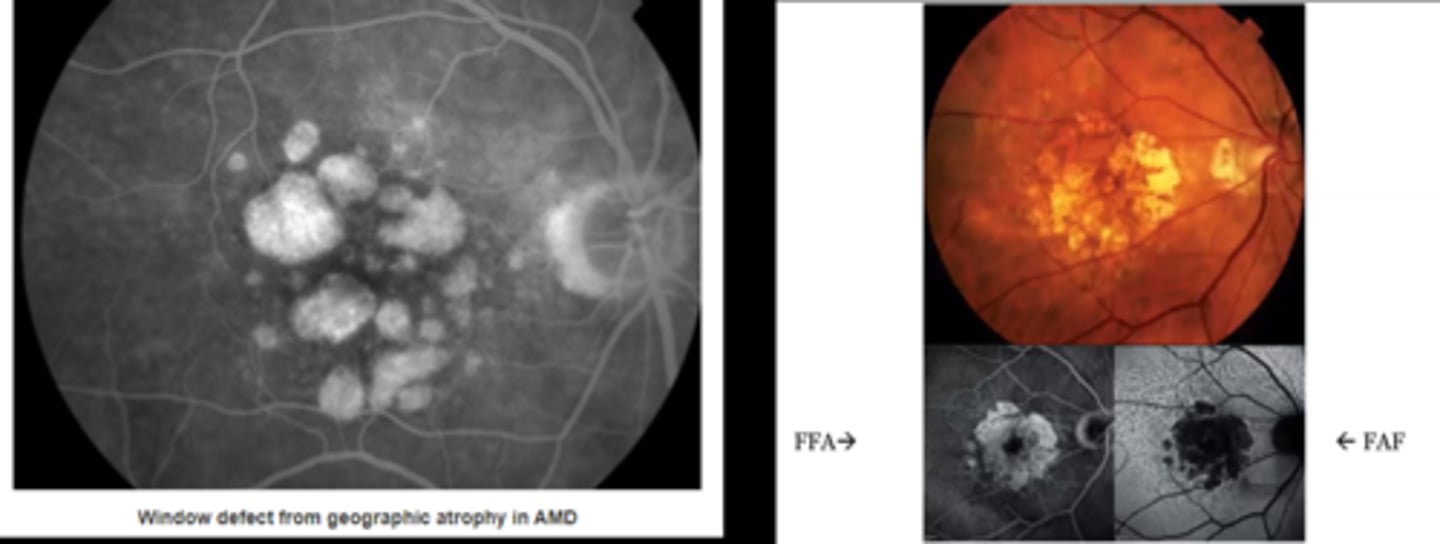
How do IVFA and FAF differ in terms of what will hyperF and hyperAF?
IVFA = blood
FAF = lipofuscin, drusen
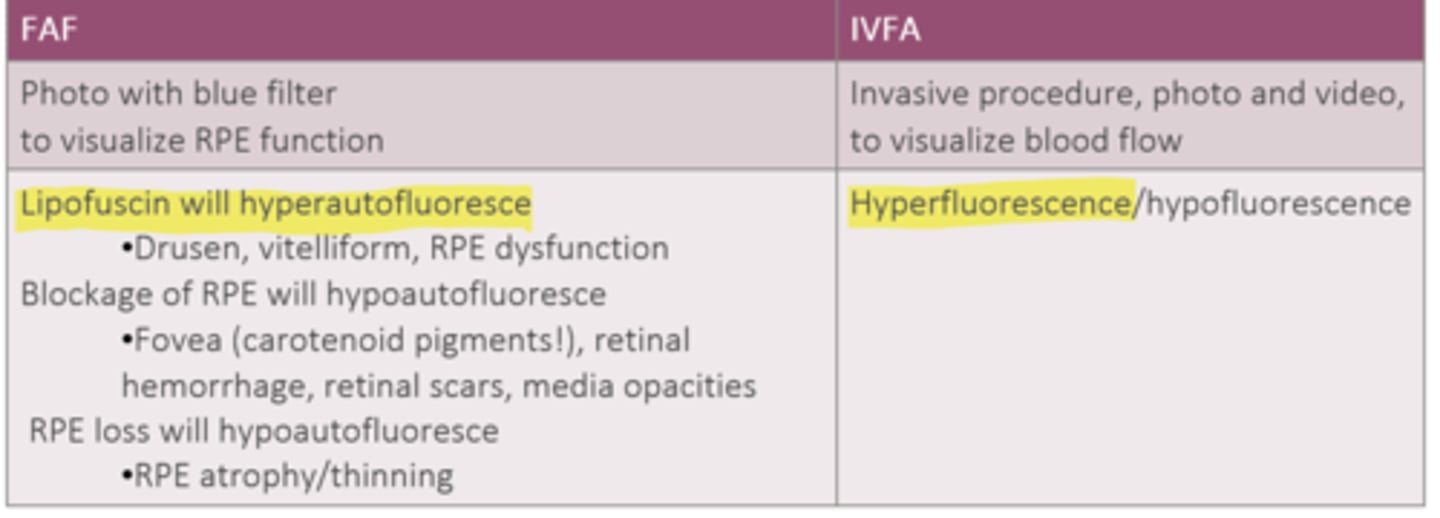
How do IVFA and FAF differ in terms of what will hypoF and hypoAF?
IVFA = lack of blood flow
FAF = RPE loss, RPE blockage from fovea carotenoids, hemorrhage, scar, opacities
How do IVFA and OCT/OCTA differ in terms of cost and duration?
IVFA = longer appt
OCT/OCTA = cheap, quick

How do IVFA and OCT/OCTA differ in terms of invasiveness?
IVFA = invasive
OCT/OCTA = non-invasive
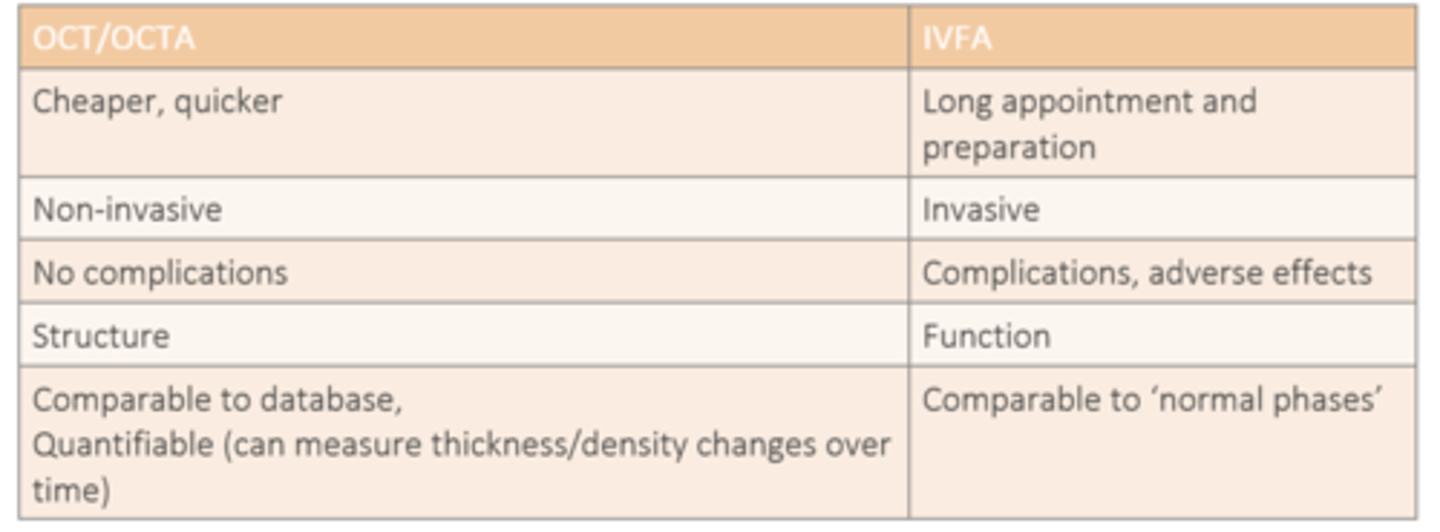
How do IVFA and OCT/OCTA differ in terms of complications?
IVFA = complications
OCT/OCTA = no complications
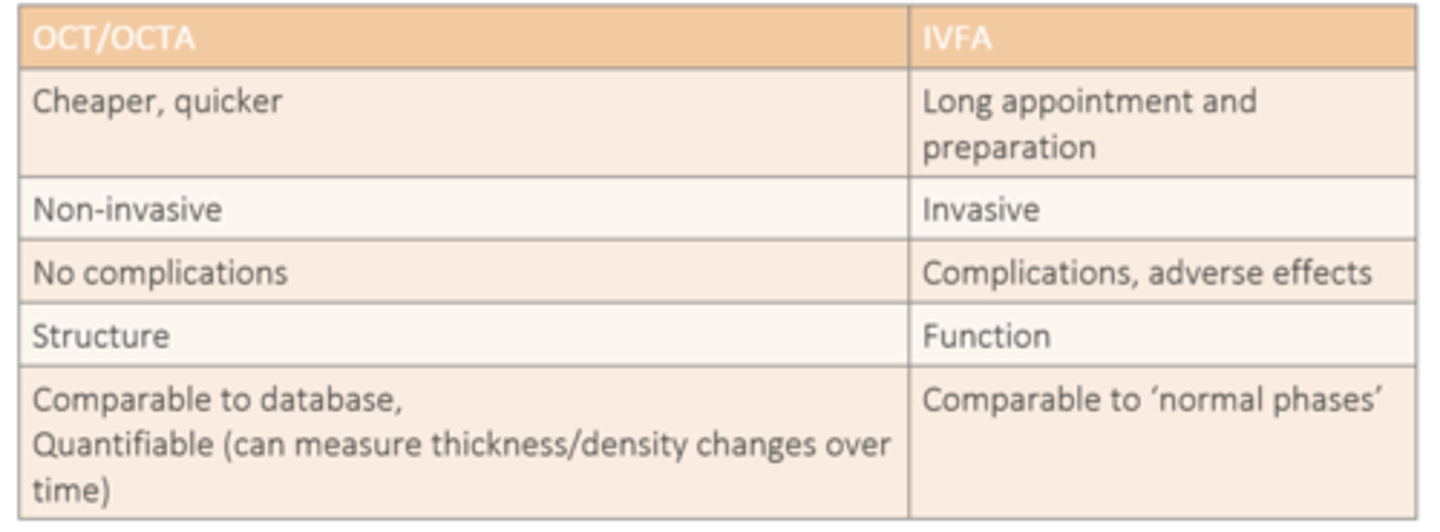
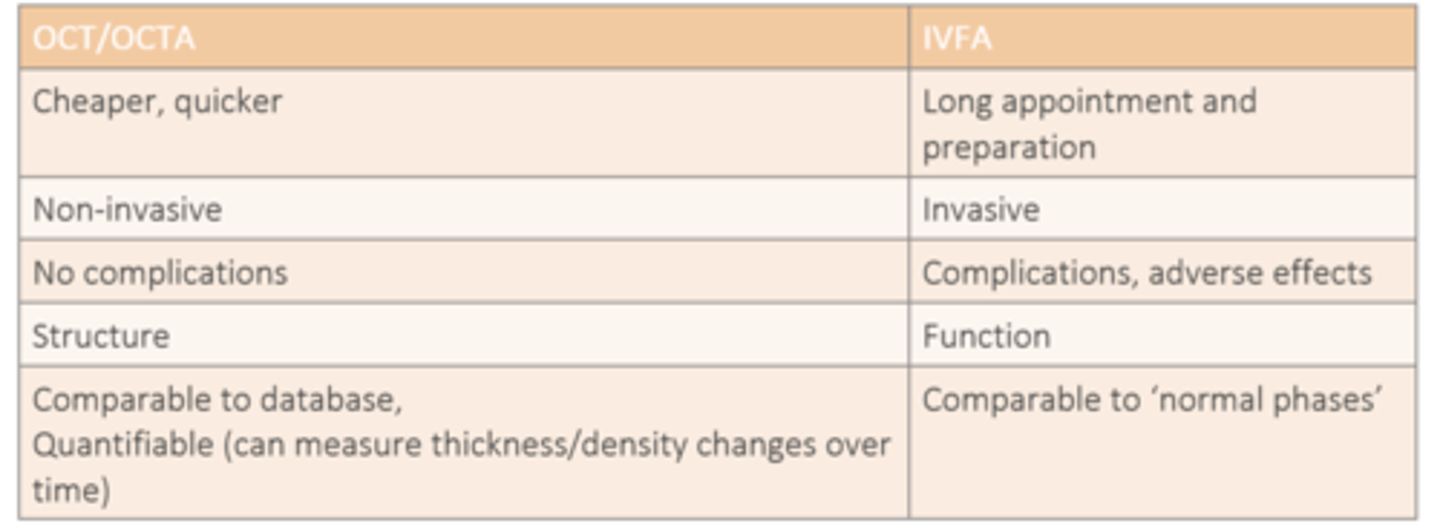
How do IVFA and OCT/OCTA differ in terms of structure vs function?
IVFA = function
OCT/OCTA = structure
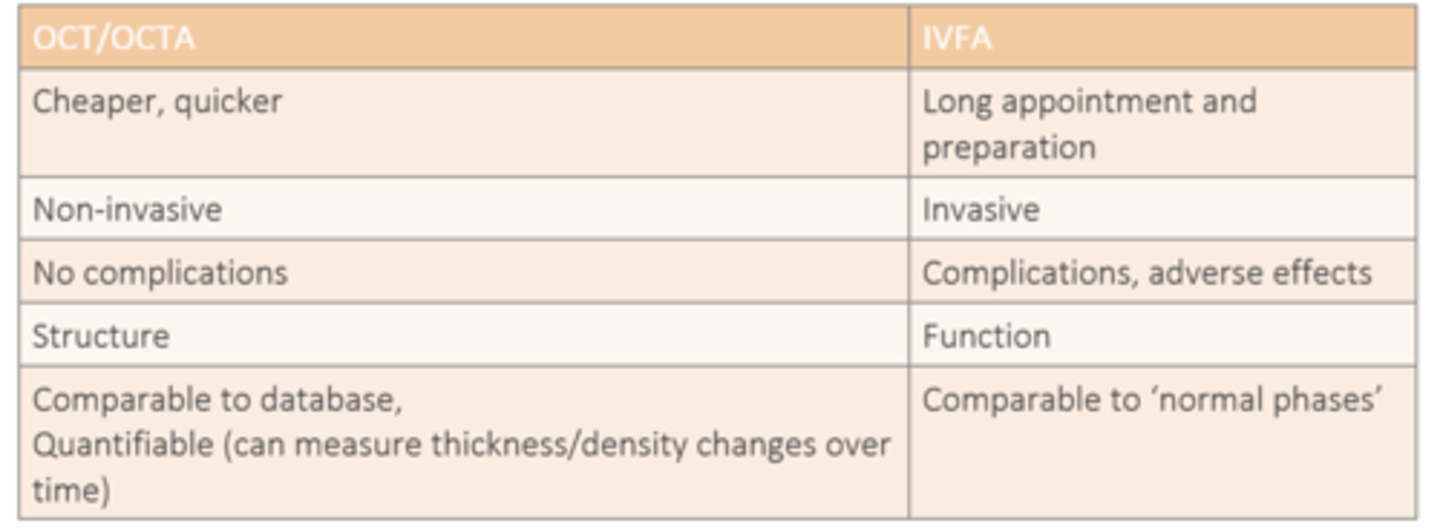
How do IVFA and OCT/OCTA differ in terms of data comparison?
IVFA = comparable to normal phases
OCT/OCTA = comparable to database, quantifiable/measurable over time
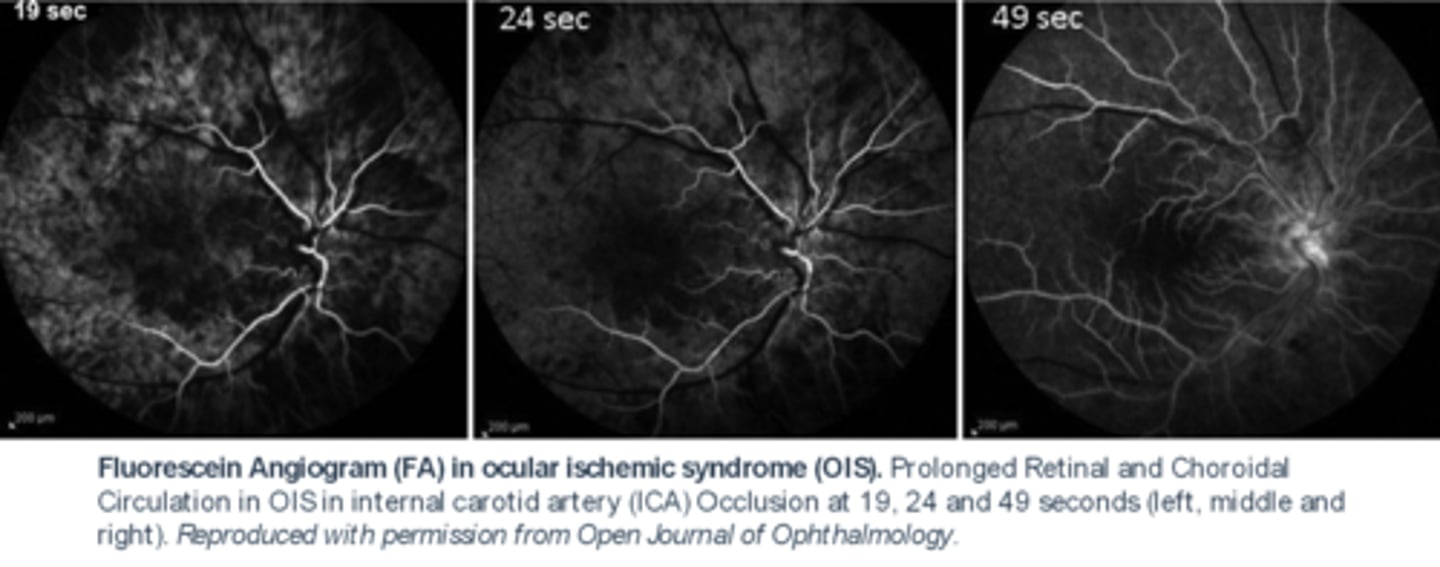
What do we see with ocular ischemic syndrome (OIS) on IVFA? 2 things.
delayed choroidal flush
AND
prolonged AV transit time bc veins still not filled at 24 sec here
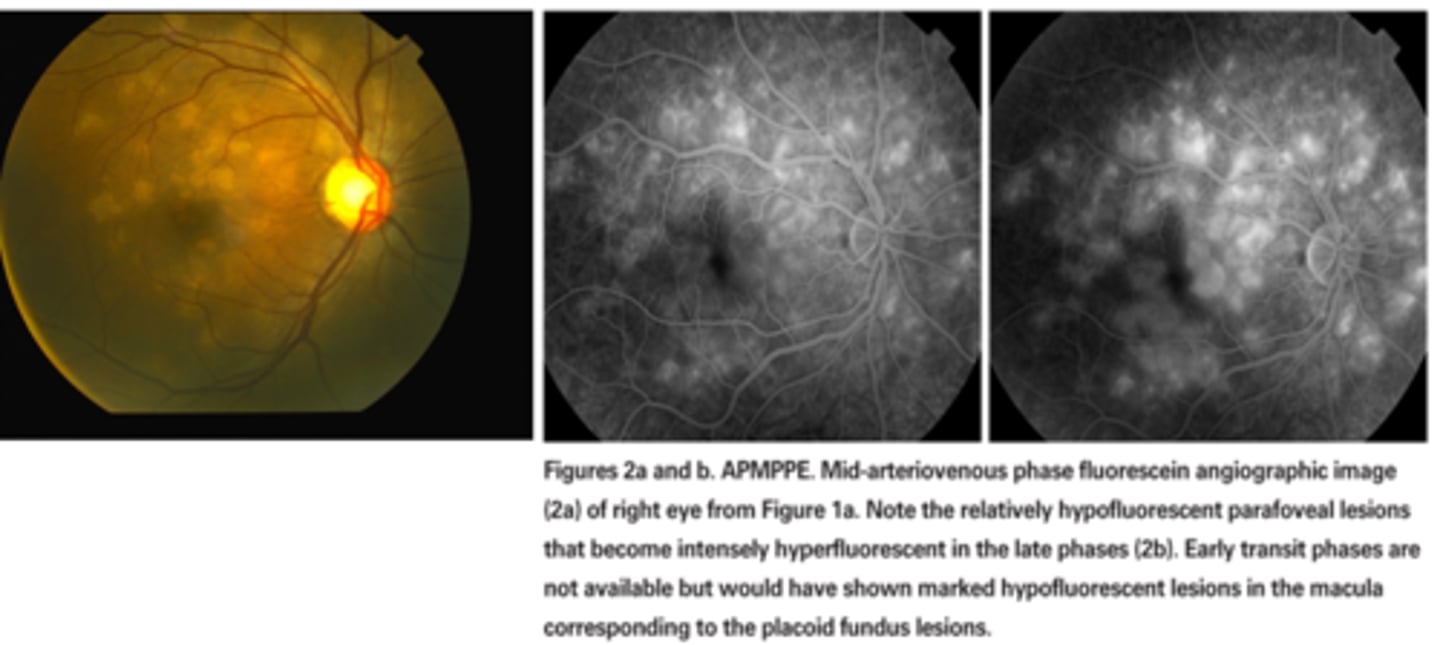
What do we see with white dot syndromes (retinal inflam) on IVFA?
ex) plaquoid pigment epitheliopathy = hyperF RPE lesions get brighter over the course of the IVFA = ischemic chorioretinal inflam spots will "stain"
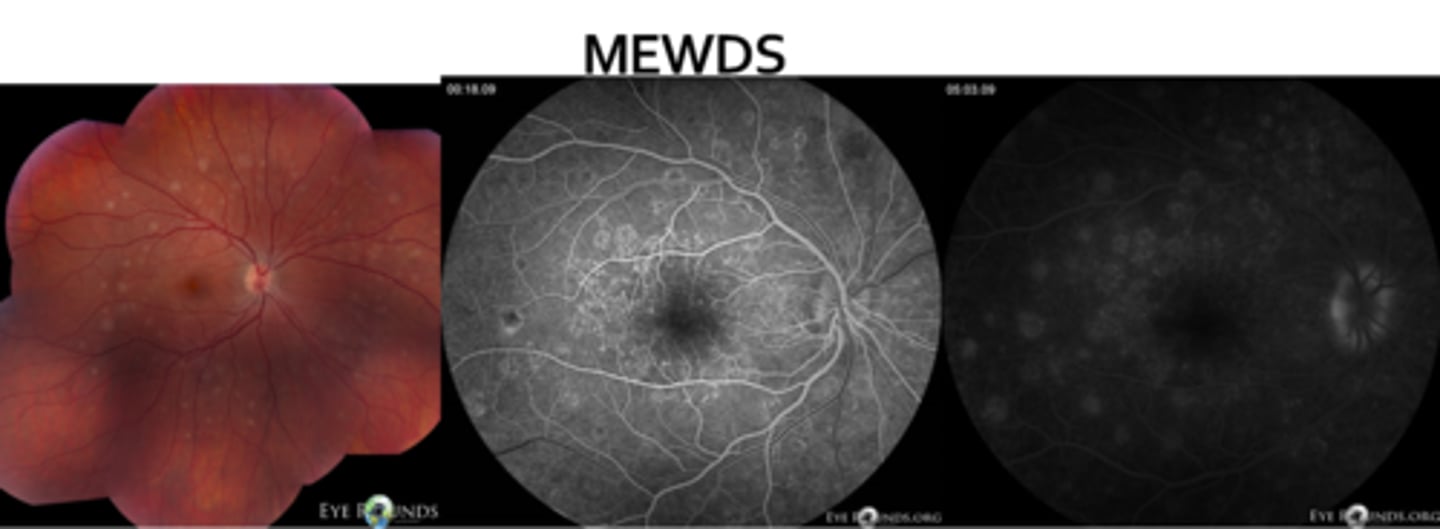
What do we see with MEWDS on IVFA?
early and late staining in a wreath pattern
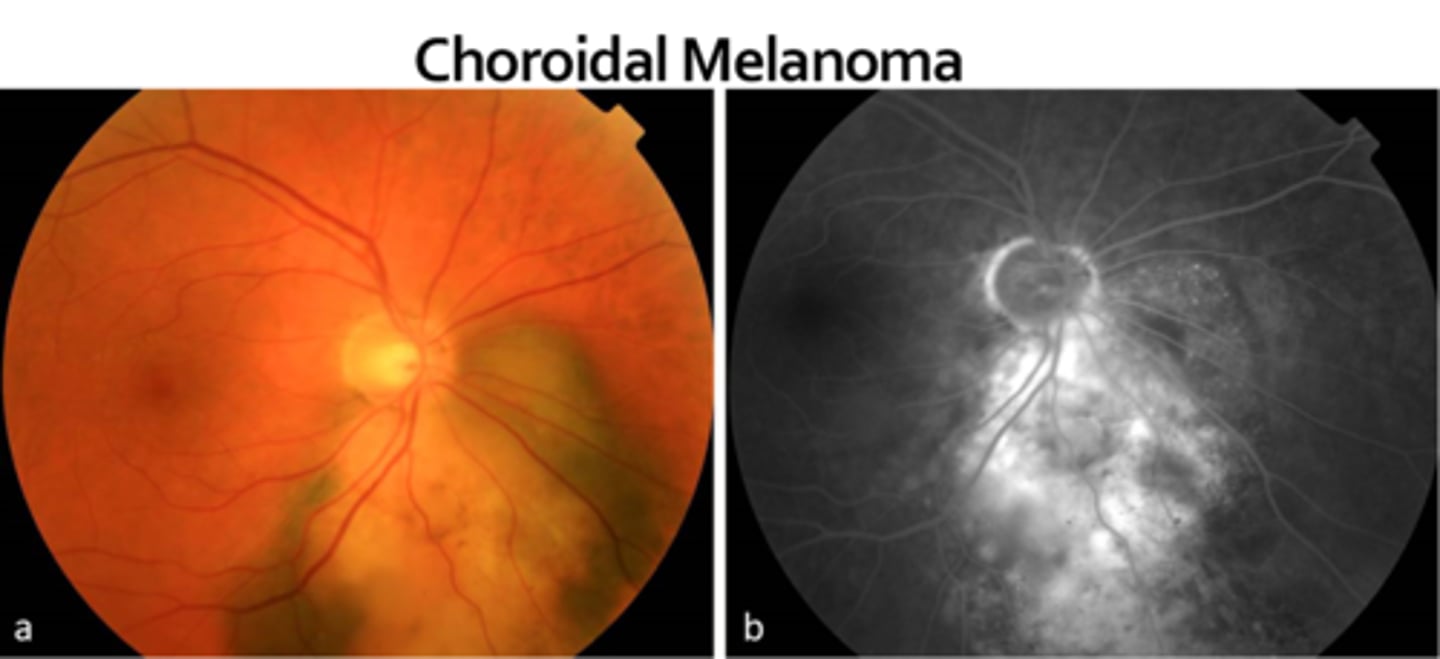
What do we see with choroidal melanoma on IVFA?
melanoma (but not nevus) will have a double circulation sign = internal circulation within lesion showing it's malignant (but ICGA may be best here bc choroidal)
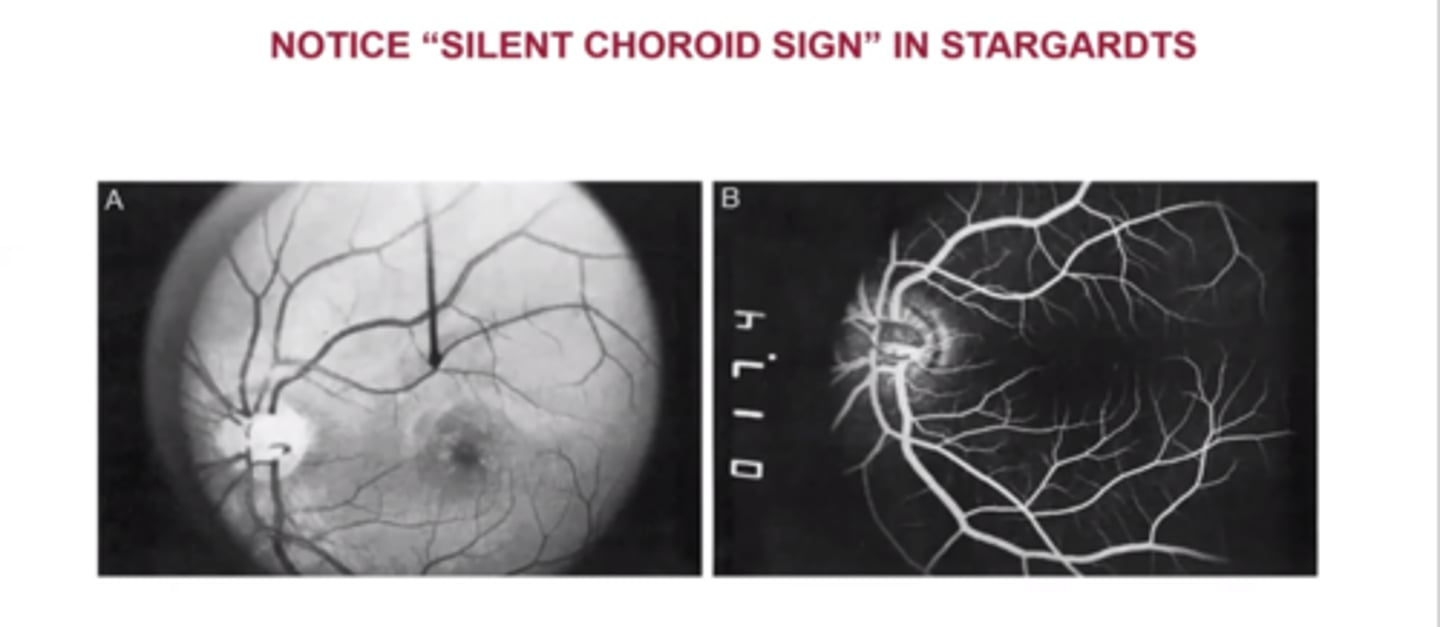
What do we see with Stargardt's on IVFA?
silent choroid sign = dark/silent choroid
NORMAL: lipofuscin accumulates in RPE = the fundus will hyperF on IVFA (initially choroid is dark)