APBio Unit 5 Heredity
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

56 Terms
chromosomes
Threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes.
genes
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait/protein
genetics
Scientific study of heredity and variation.
heredity
Transmission of traits from one generation to the next.
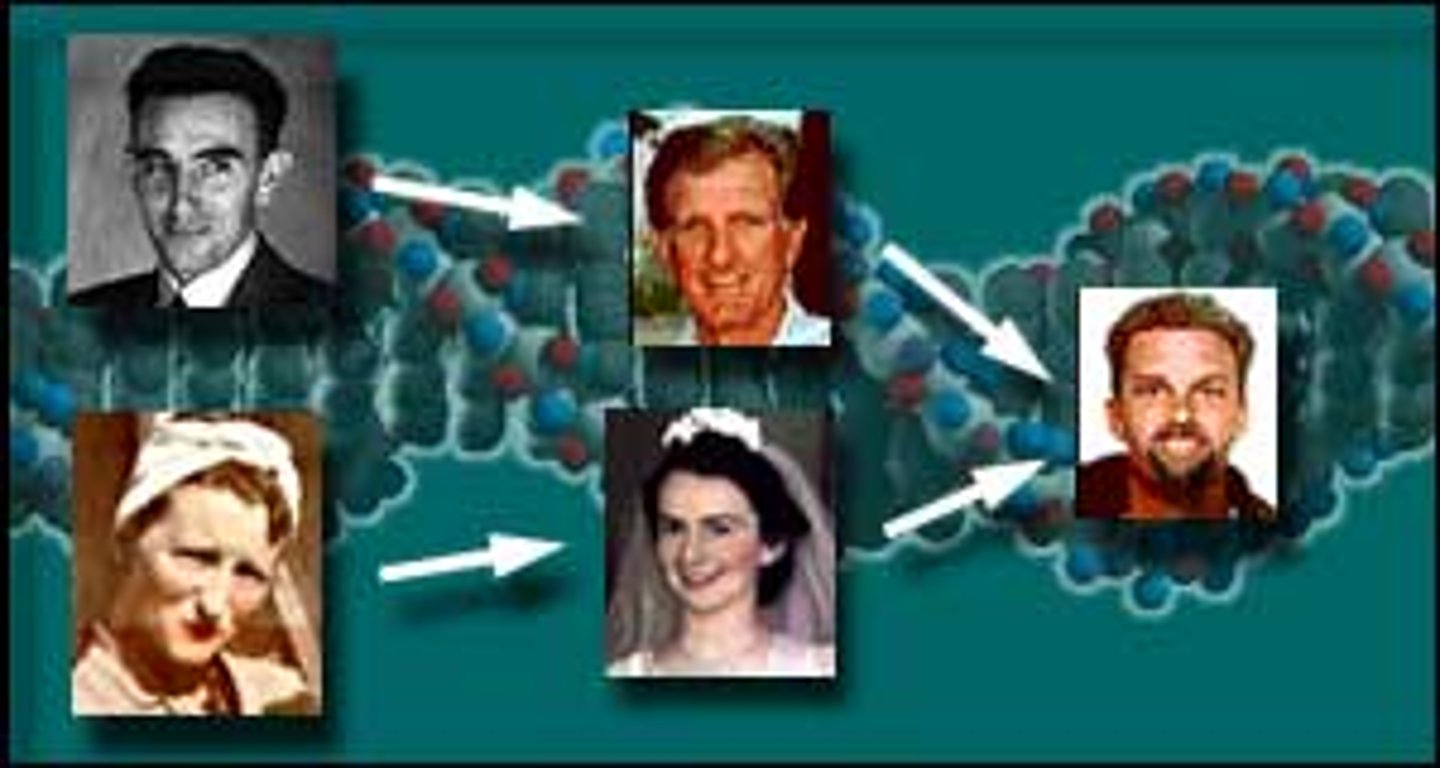
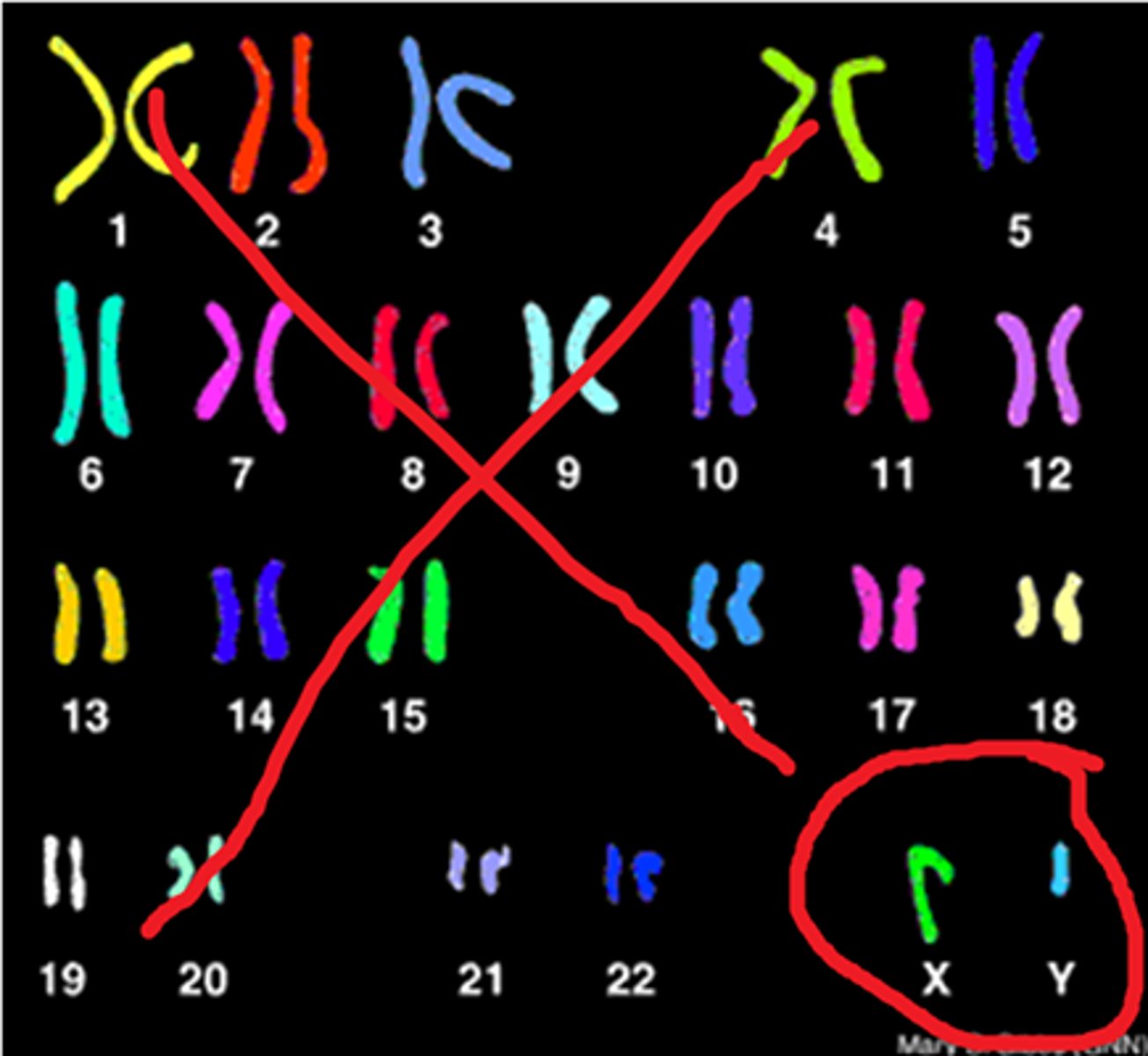
sex chromosomes
X and Y chromosomes.
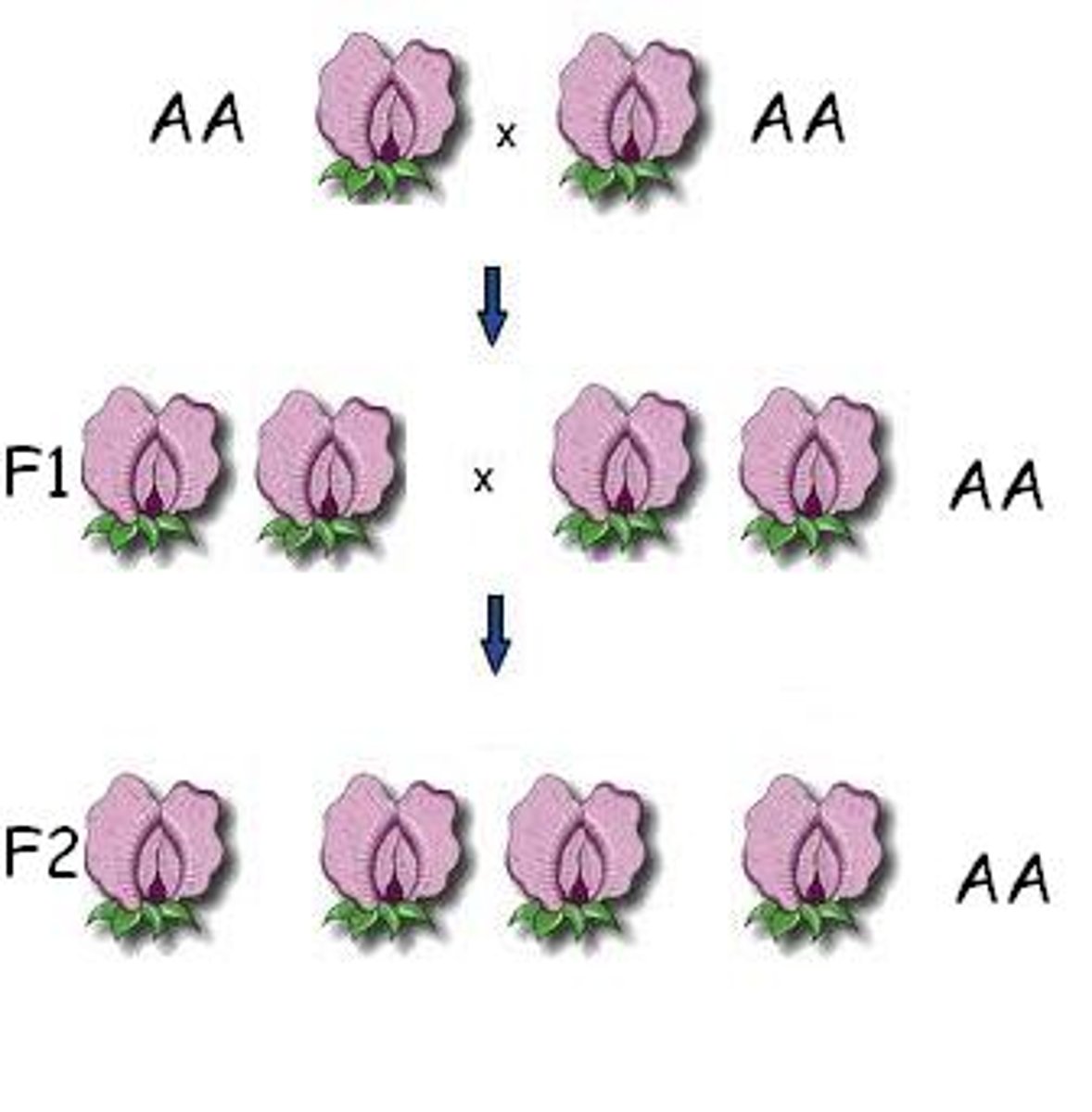
true-breeding
Organisms that, when reproducing, create offspring of all the same variety.
hybridization
The crossing of two true-breeding parents.
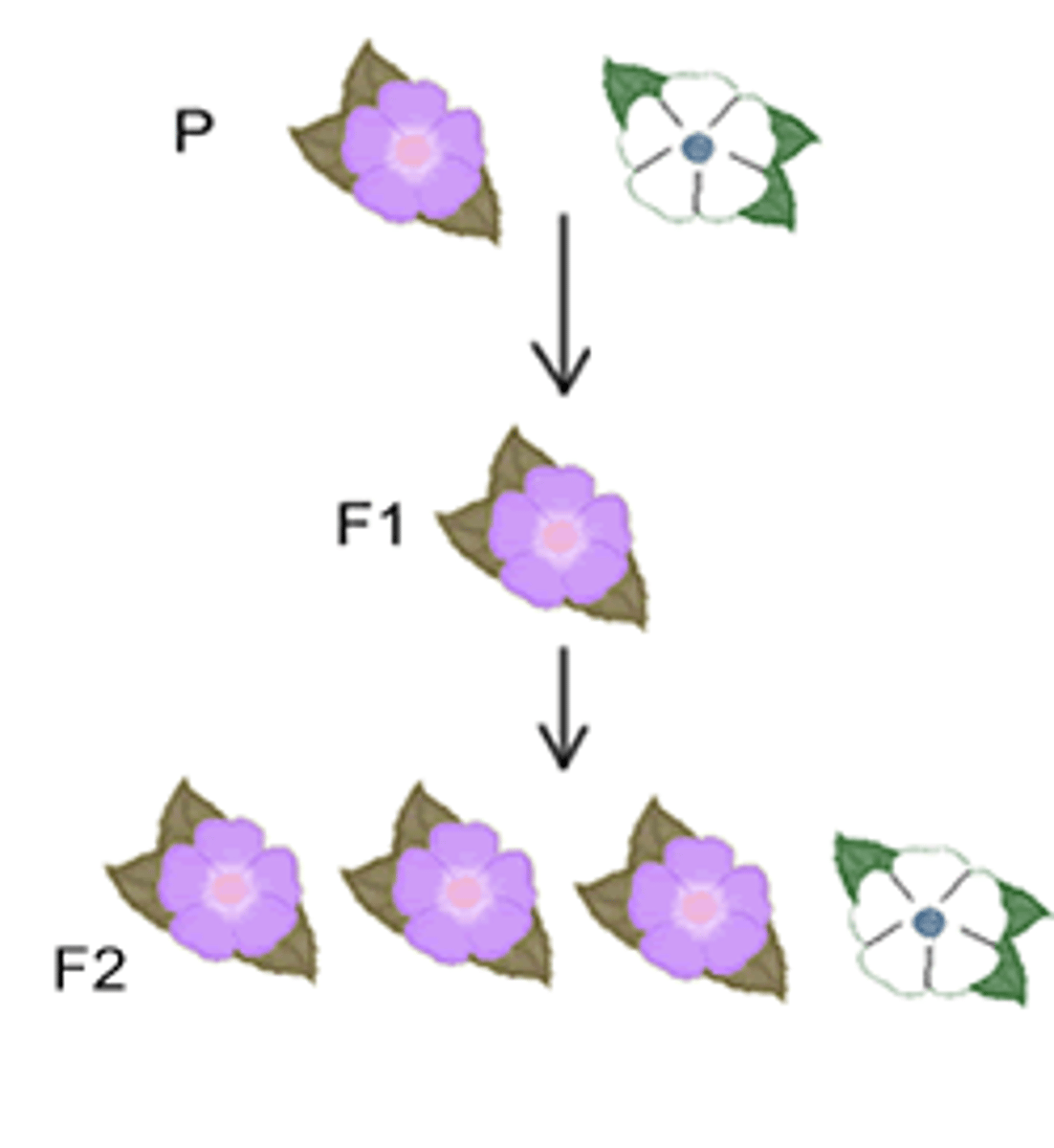
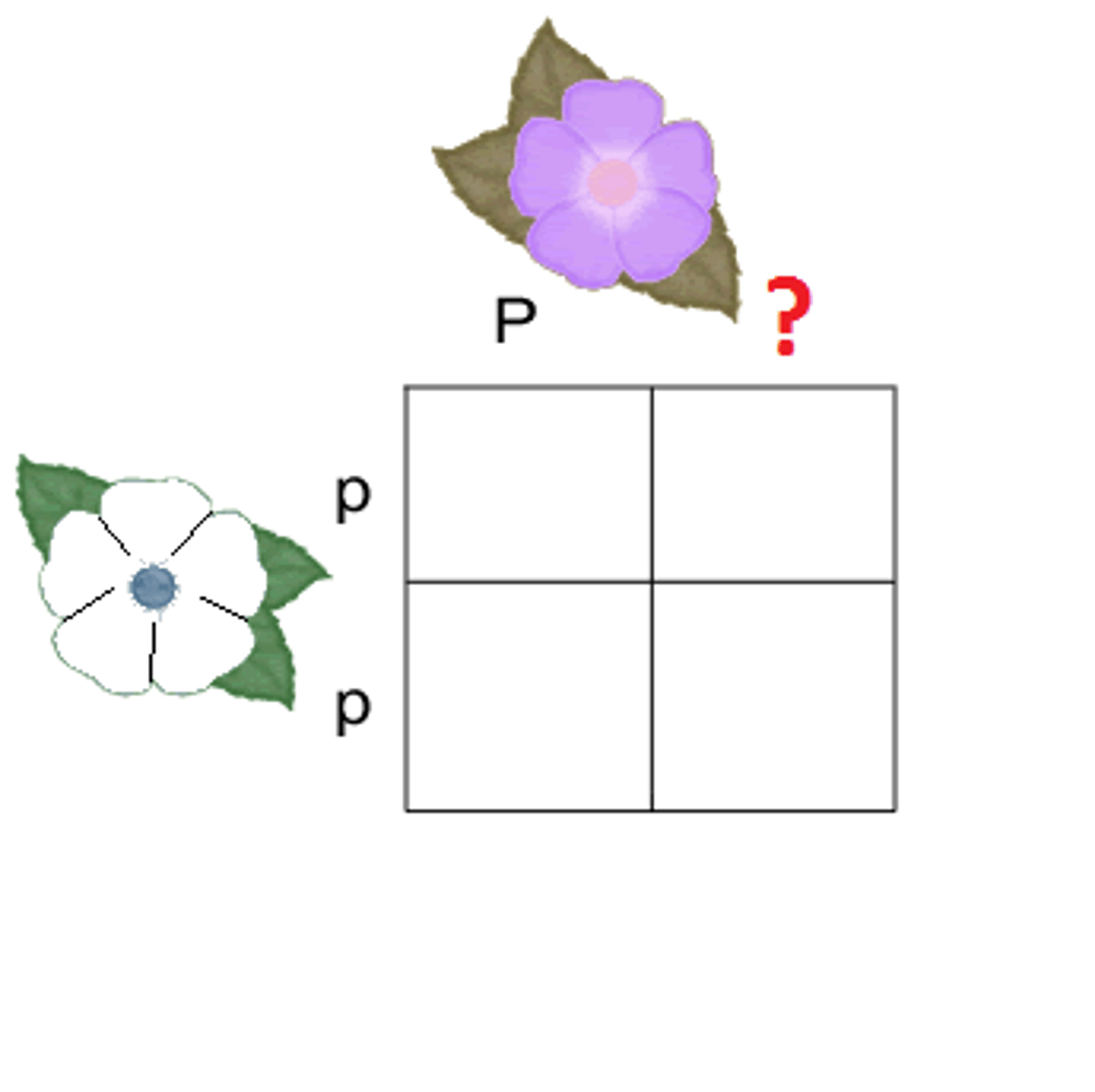
P generation
The name for the true-breeding parents.
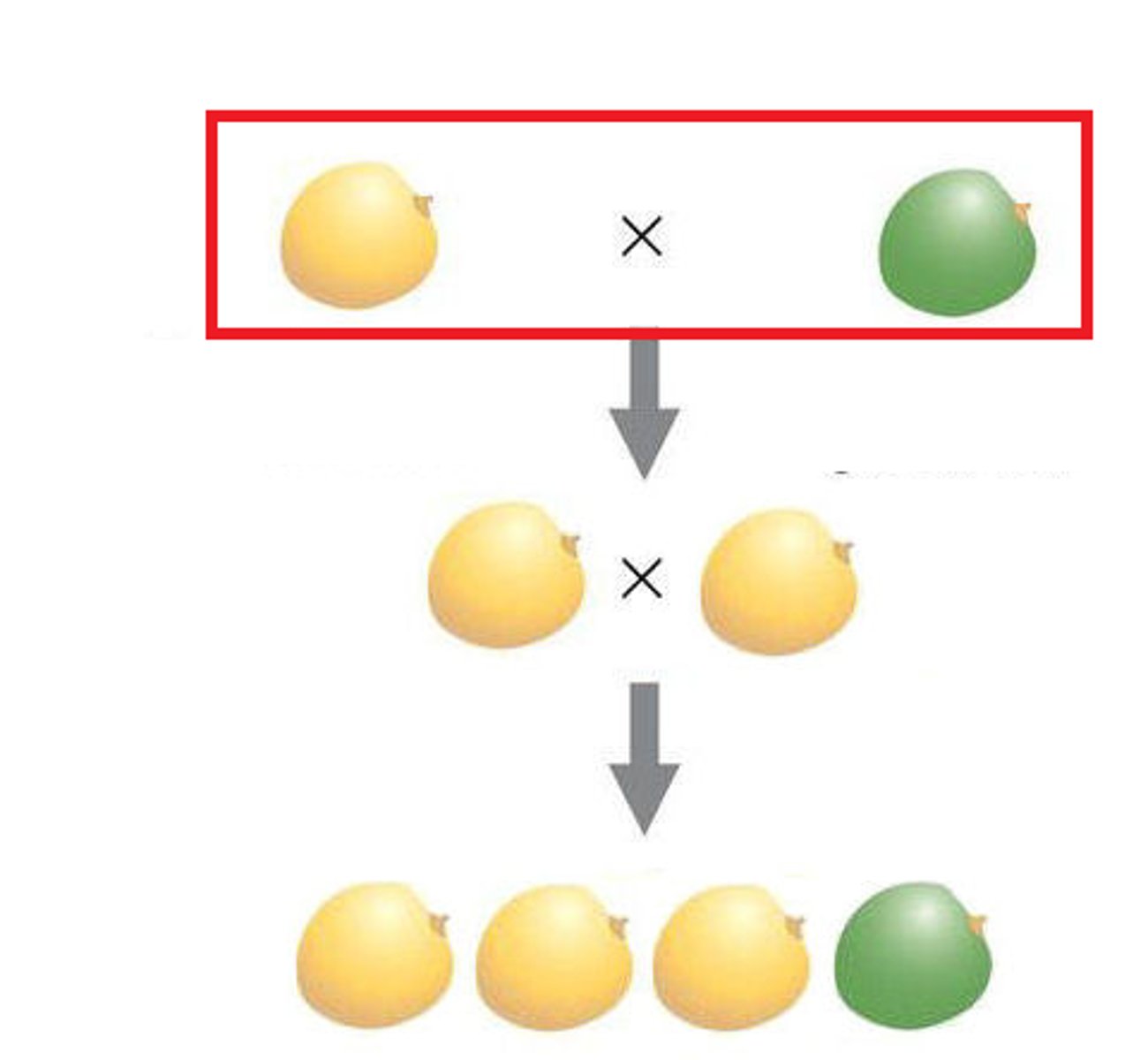
F1 Generation
The hybrid offspring of true-breeding parents.
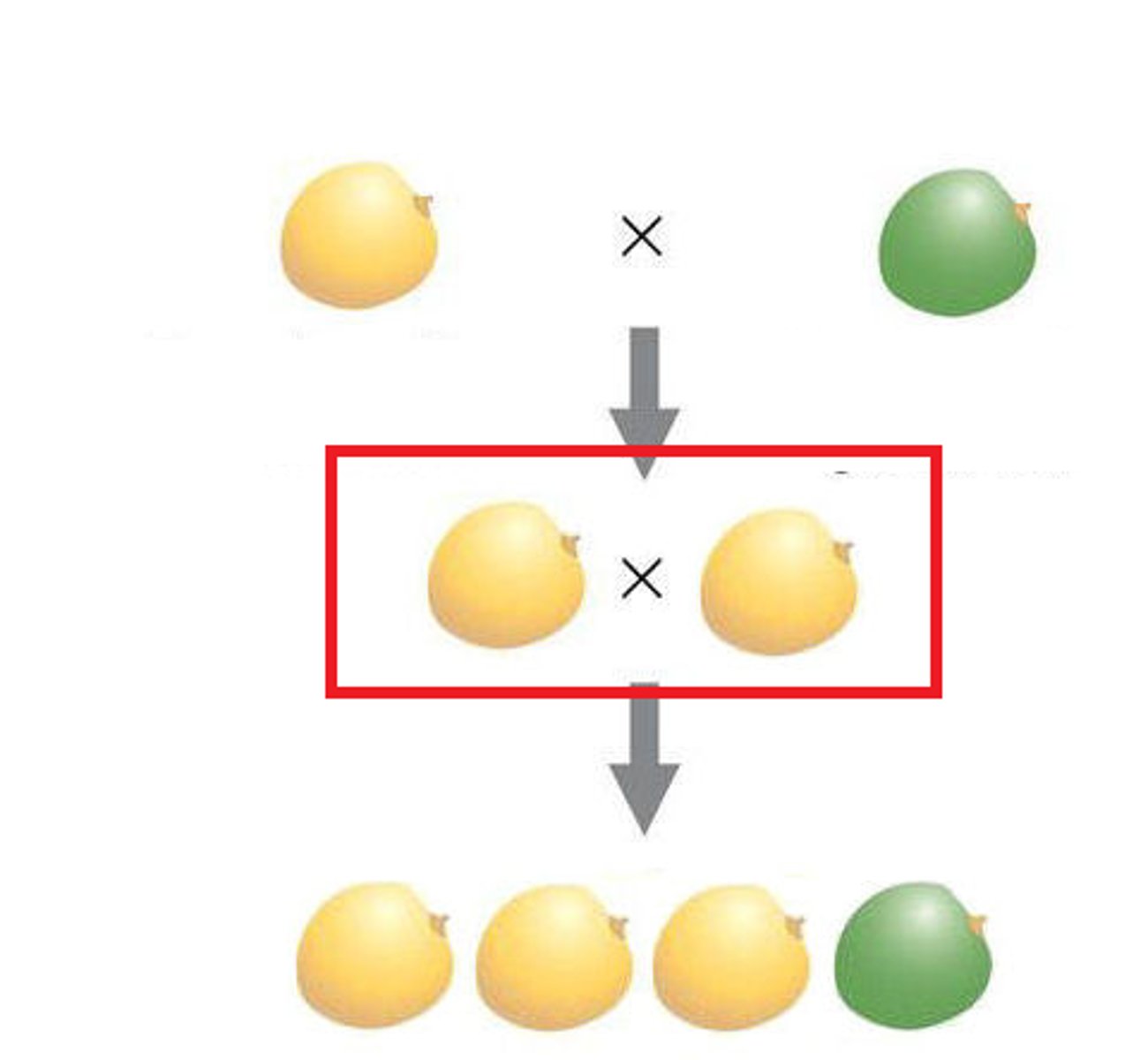
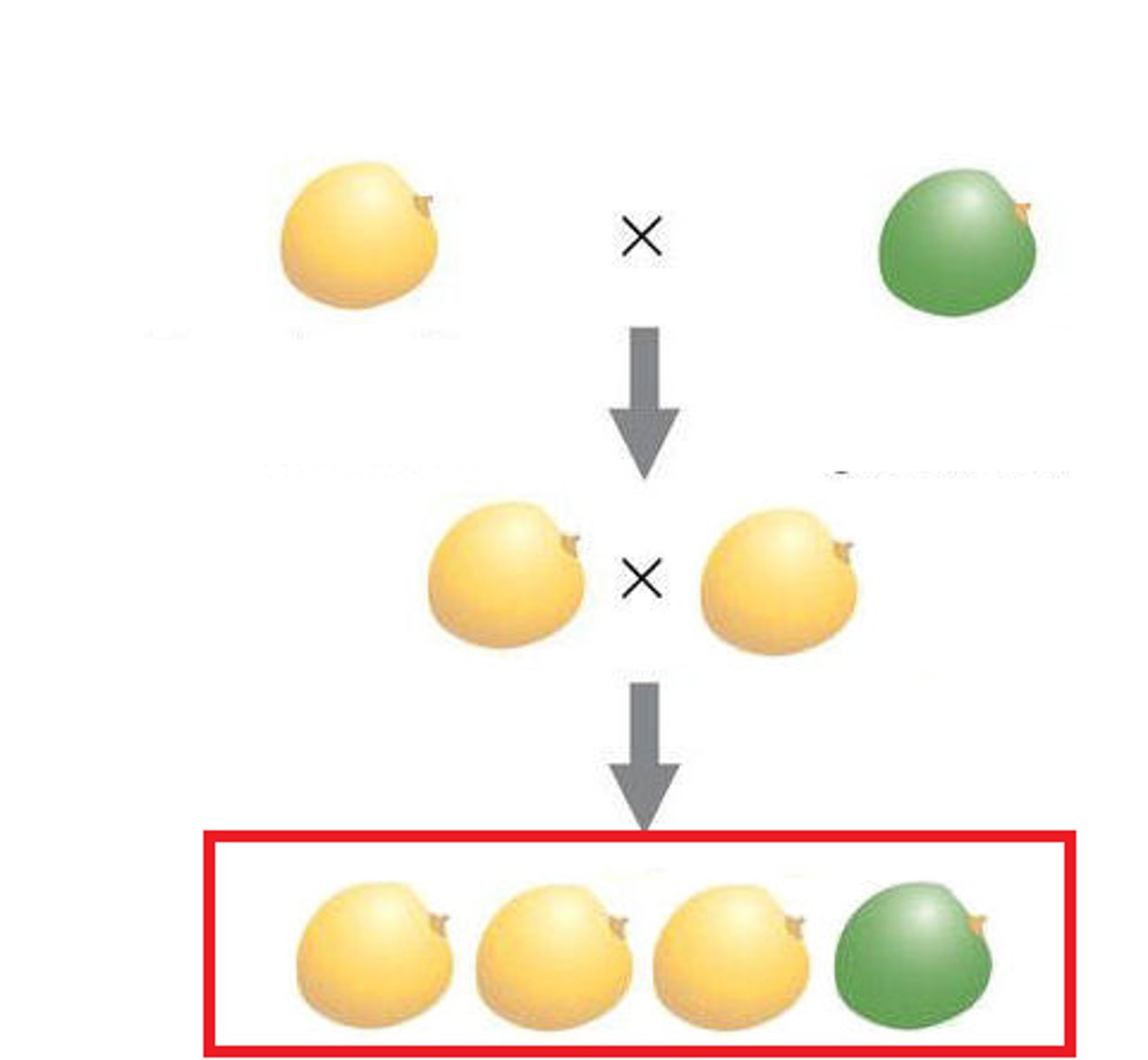
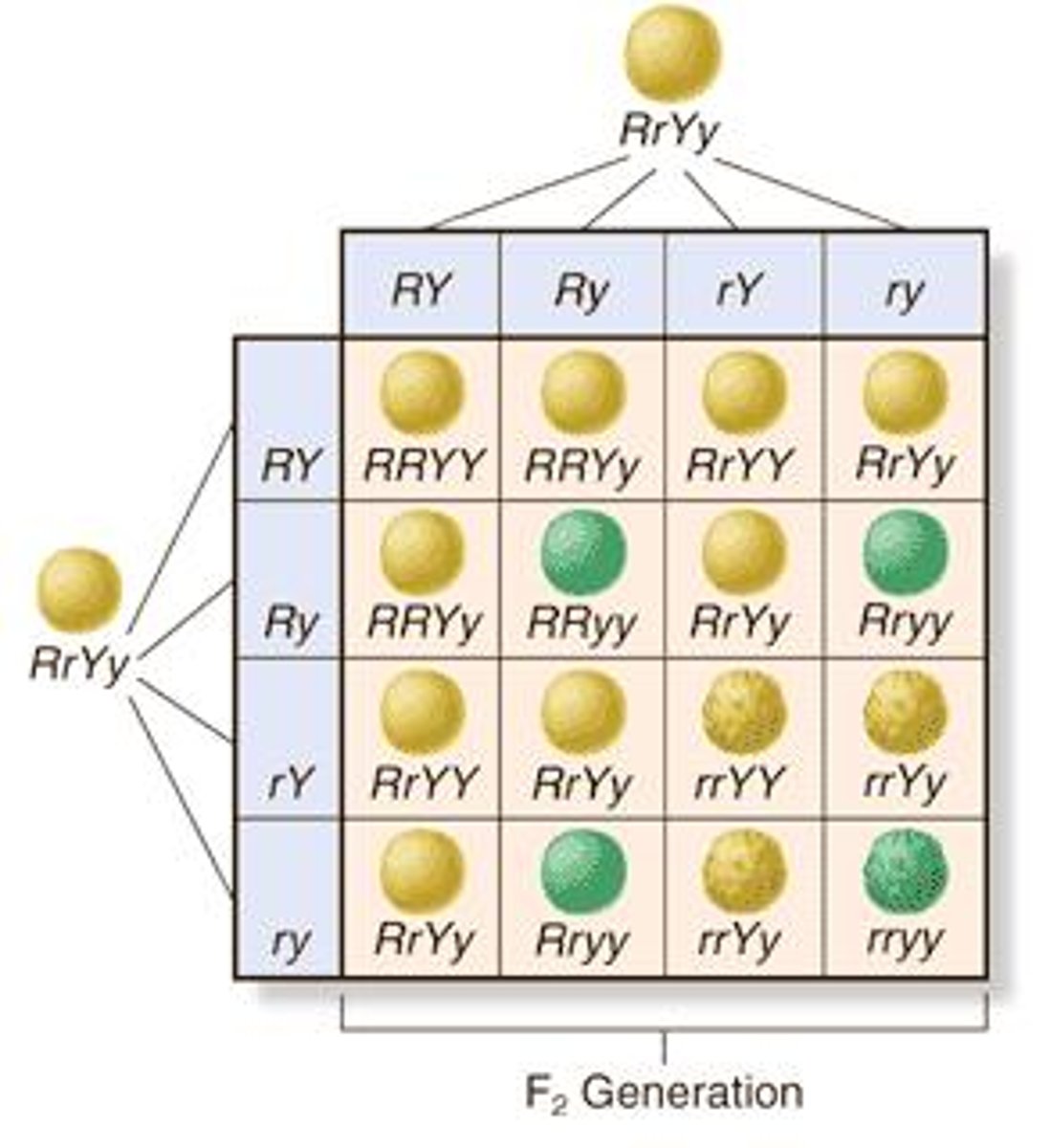
F2 Generation
After the self-pollenization of the F1 generation, this is produced.
The Law of Segregation
Two alleles separate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes because they are on on homologous chromosomes.
dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present.

recessive allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
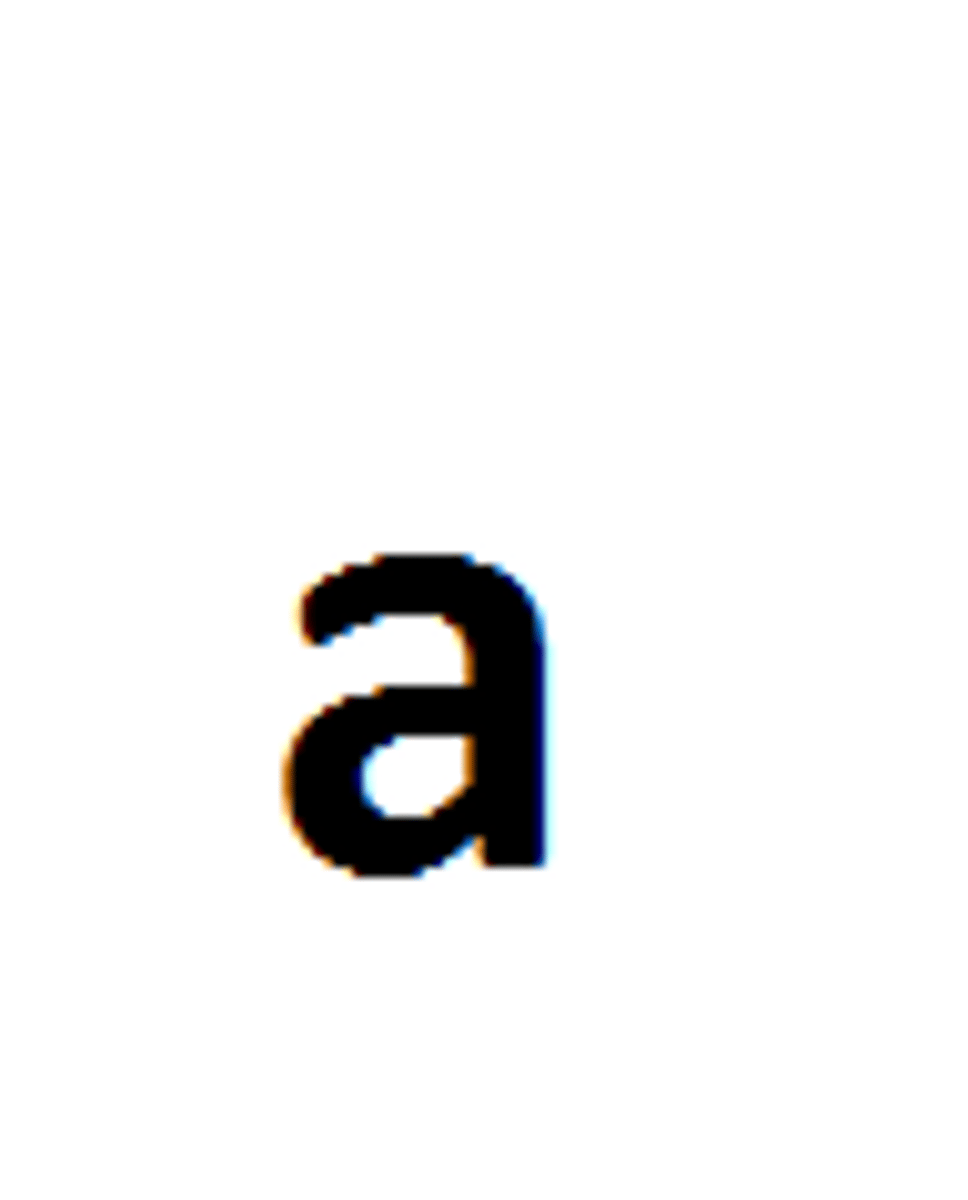
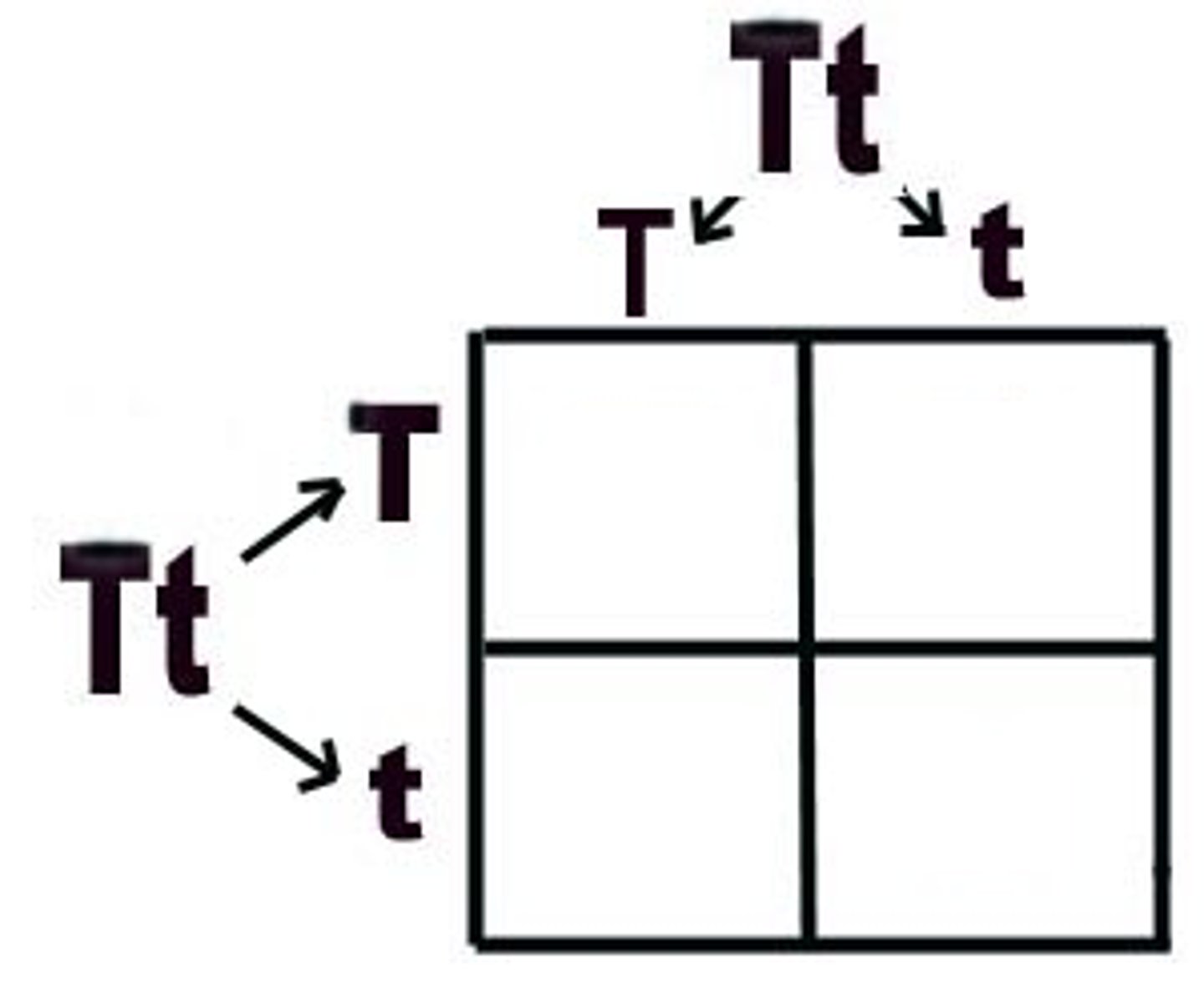
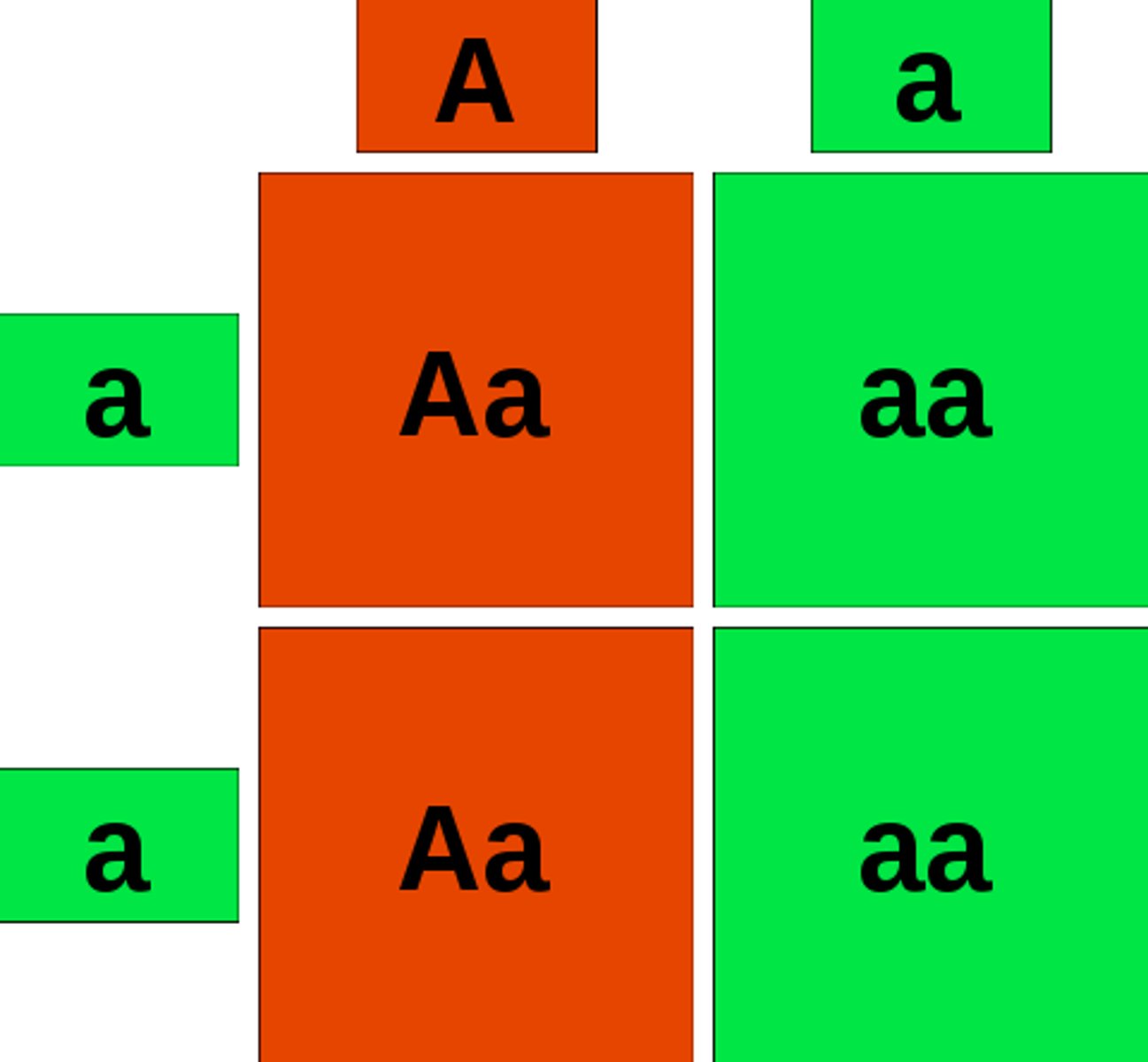
Punnett square
A diagram for predicting the allele composition of offspring from a cross between individuals of known genetic makeup.
homozygous
An organism having a pair of identical alleles for a character, either dominant or recessive.
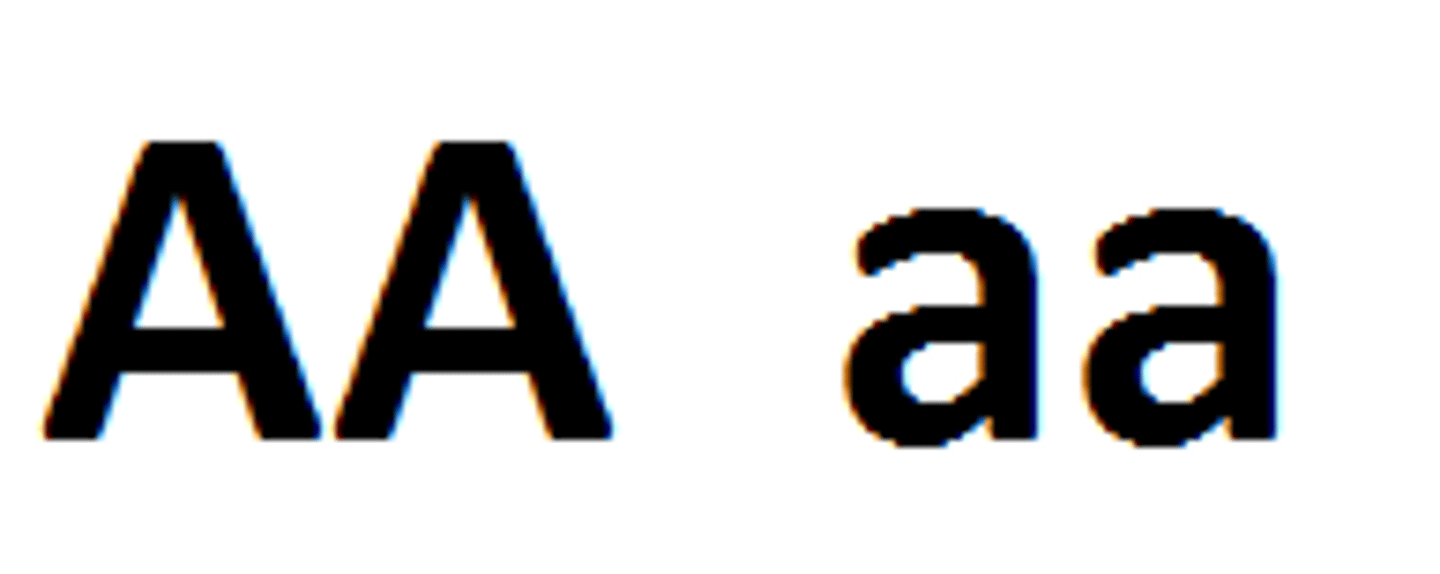
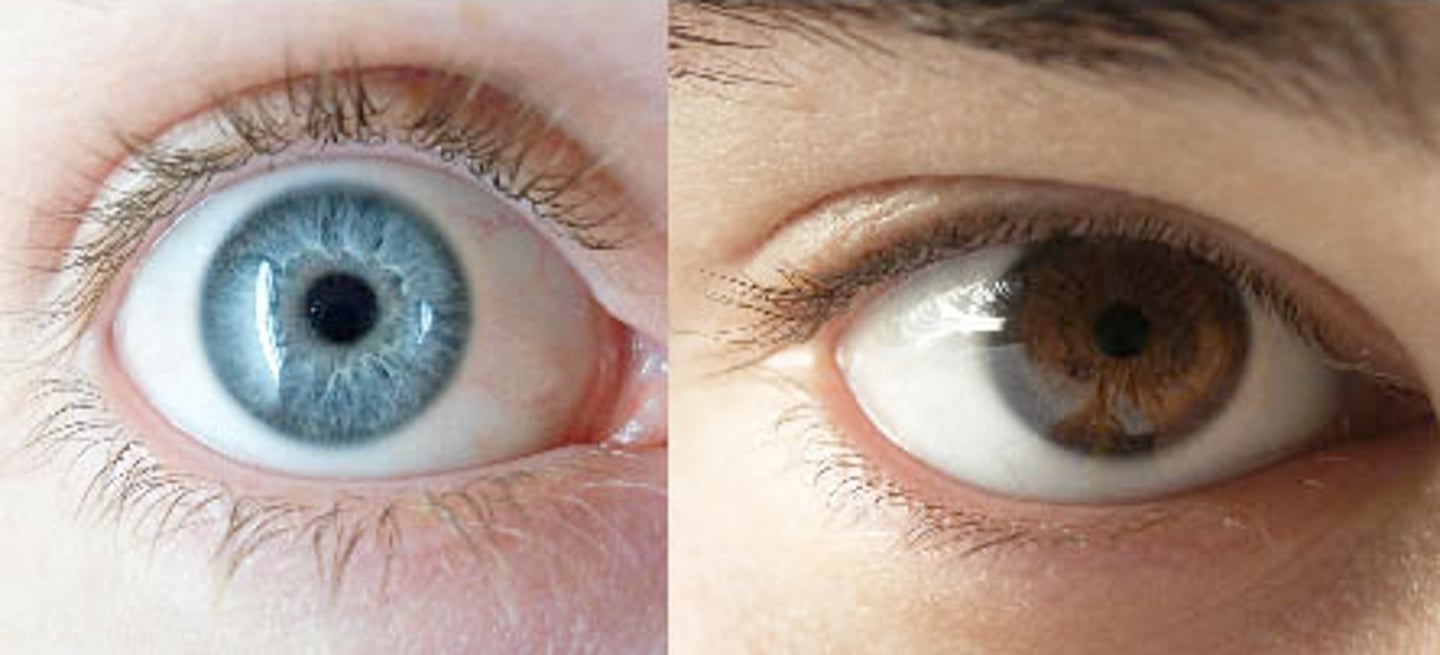
phenotype
An organism's traits.
genotype
An organism's genetic makeup.
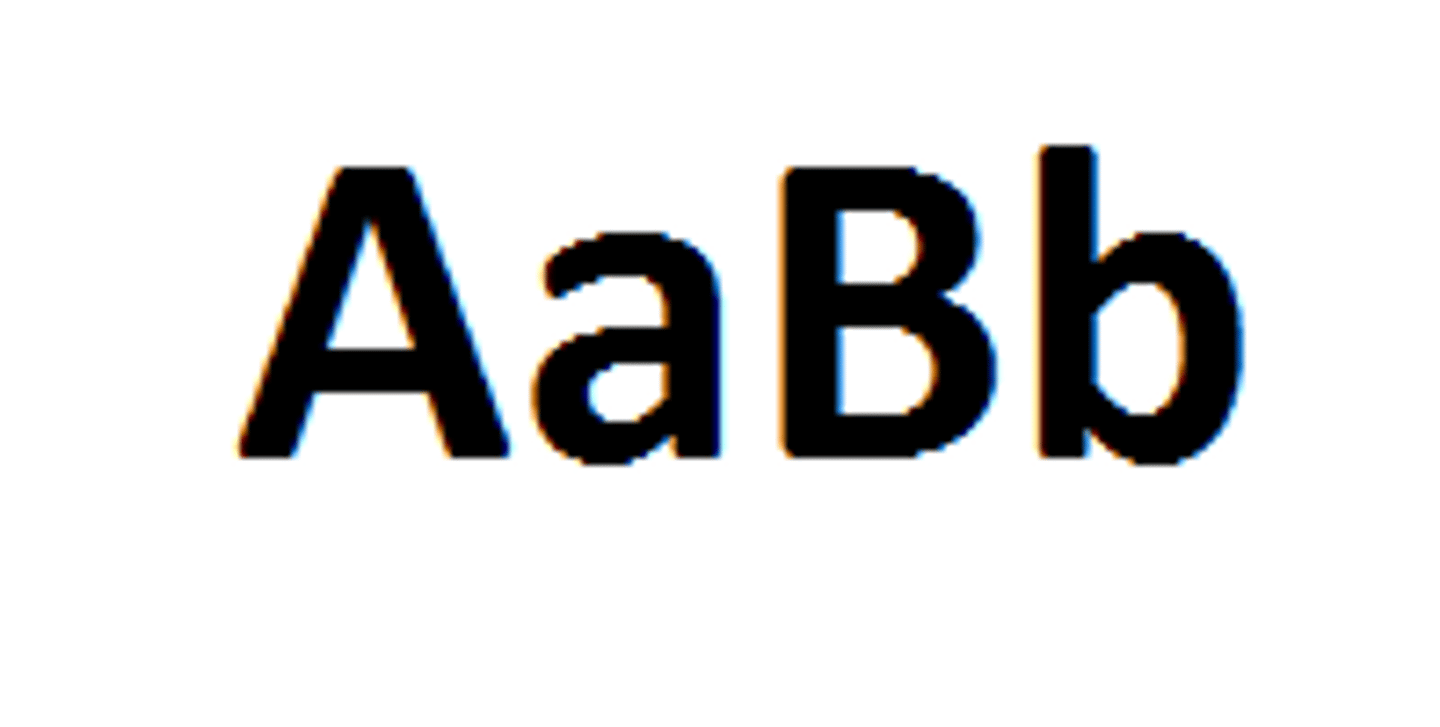
testcross
The result of breeding a recessive homozygote with an organism of dominant phenotype but unknown genotype.
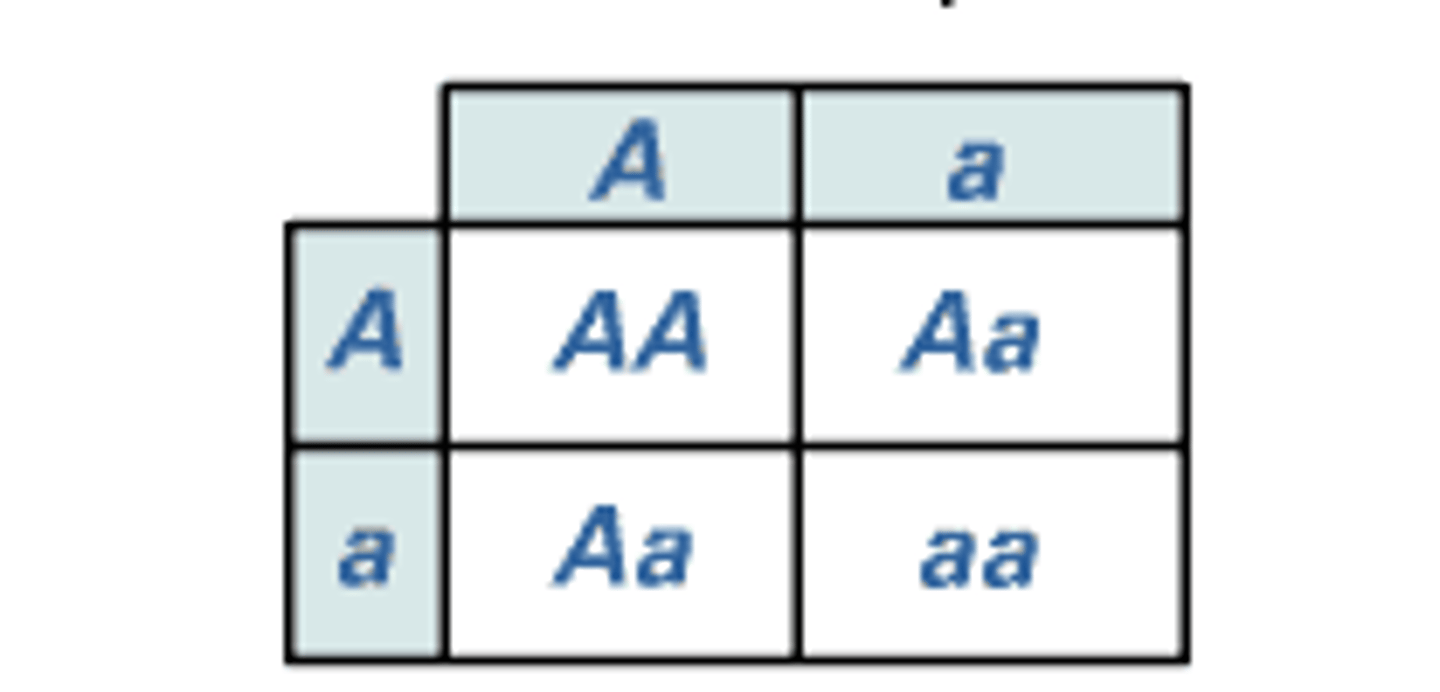
monohybrids
Parents that are heterozygous for one character.
dihybrids
Parents that are heterozygous for two characters.
multiplication rule
To determine the probability of 2 independent events occurring, we multiply the probability of one event by the probability of another. (they cannot occur at the same time) Example is child one, child two
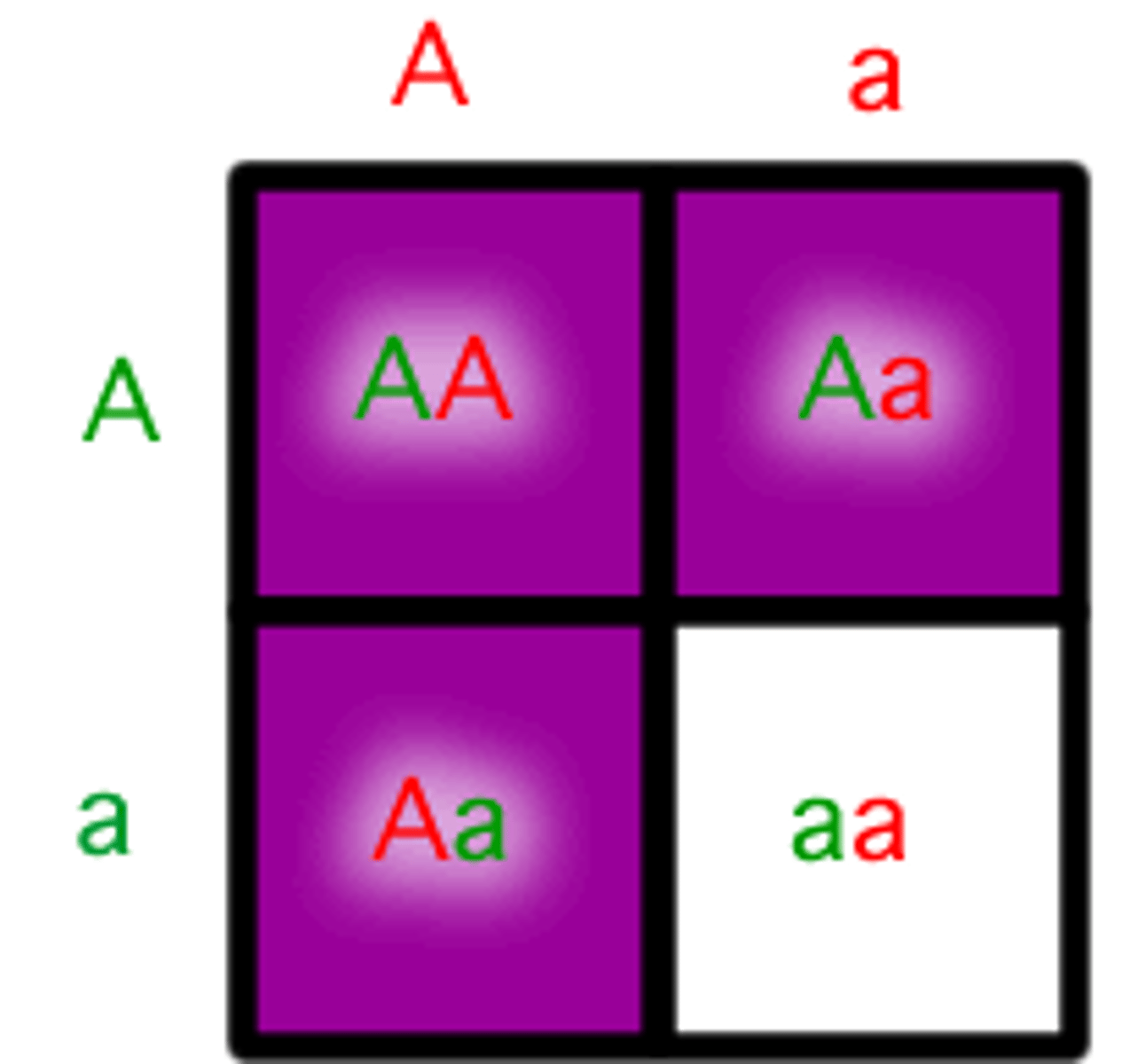
complete dominance
When the phenotypes of the heterozygote and dominant homozygote are indistinguishable.
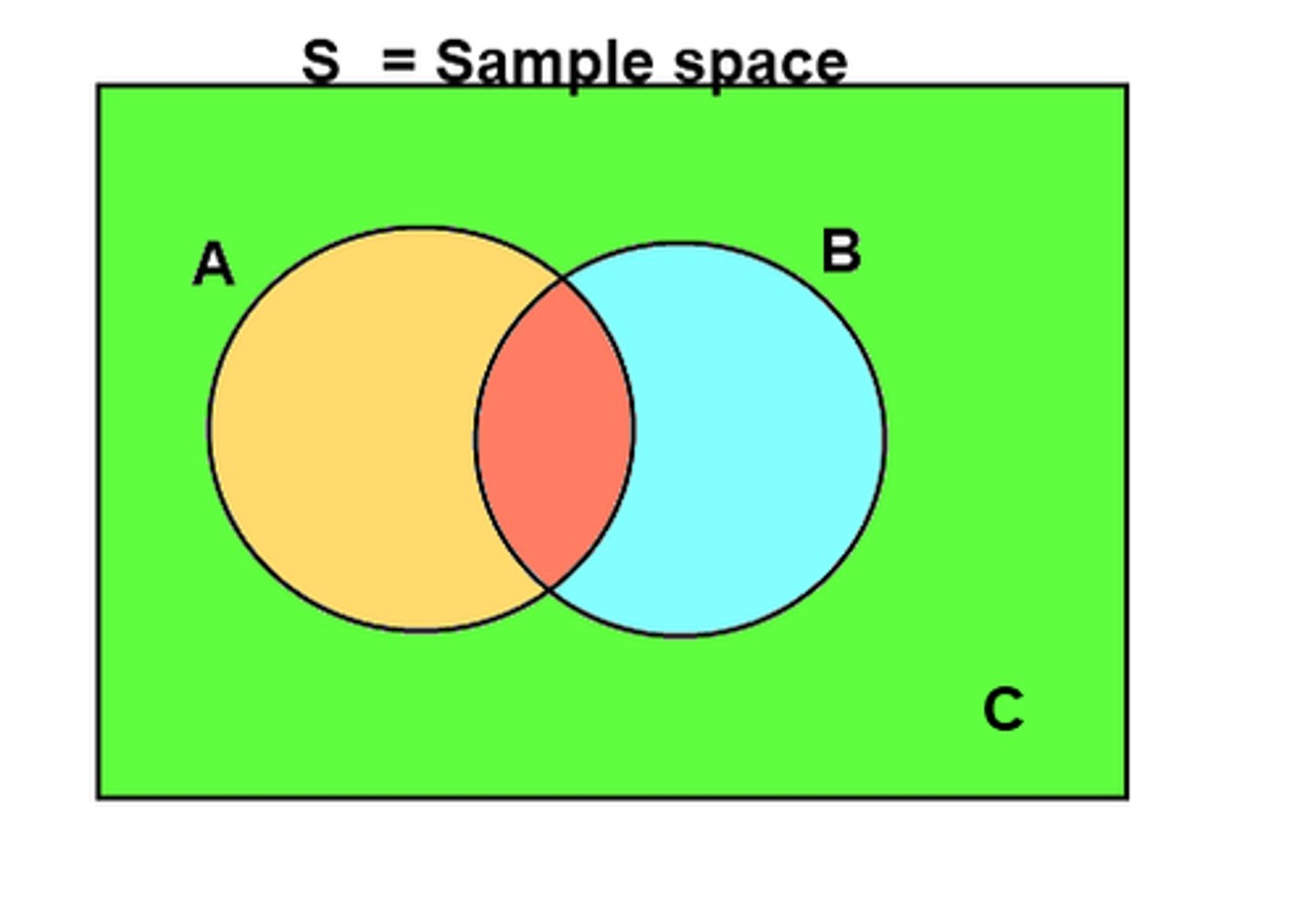
codominance
When which the phenotypes of both alleles are exhibited in the heterozygote.
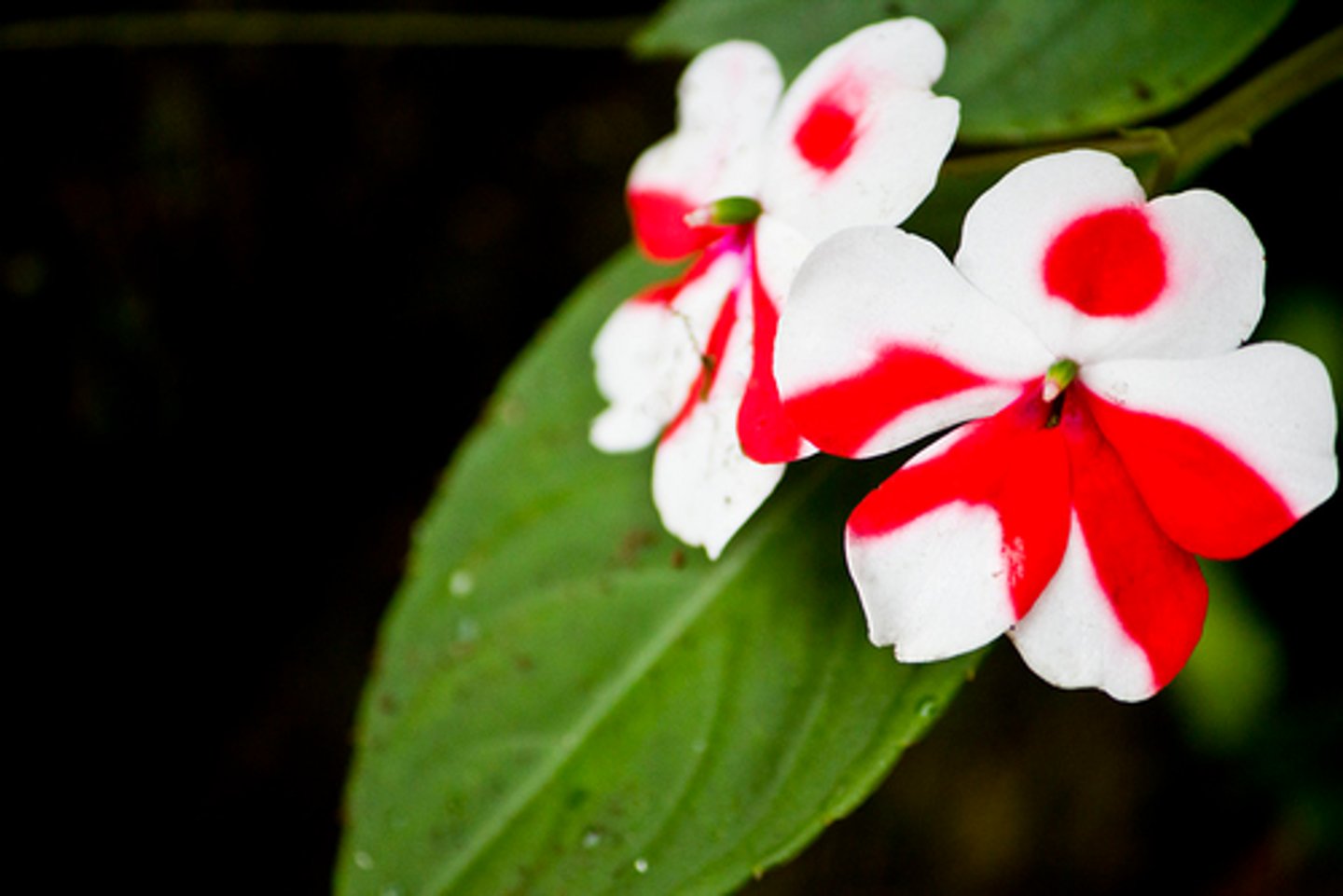

incomplete dominance
Creates a blended phenotype; one allele is not completely dominant over the other.

Tay-Sachs disease
A human genetic disease caused by a recessive allele that leads to the accumulation of certain lipids in the brain. Seizures, blindness, and degeneration of motor and mental performance usually become manifest a few months after birth.
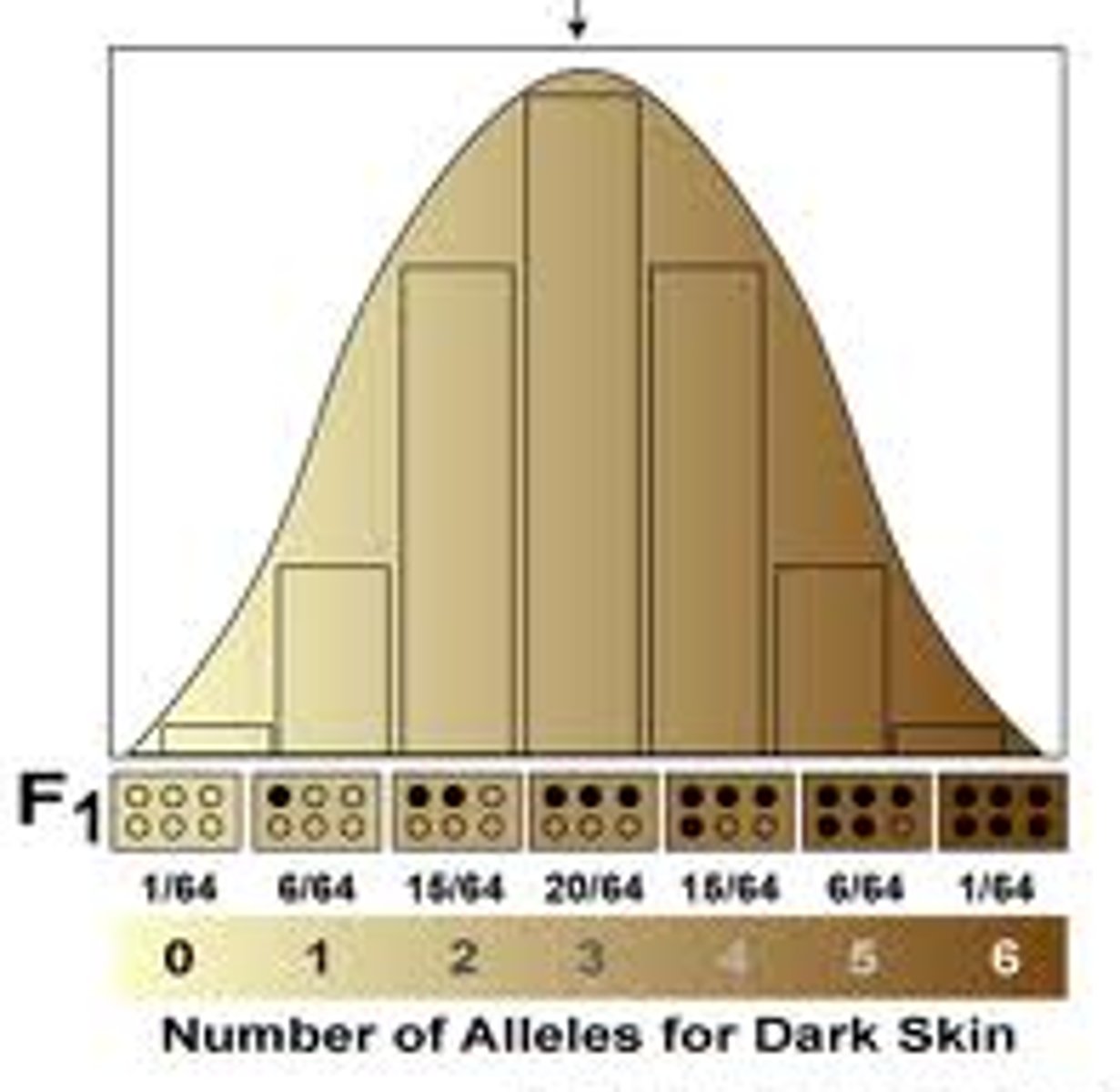
polygenic inheritance
An additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character.
pedigree
A diagram that shows the occurrence of a genetic trait in several generations of a family.
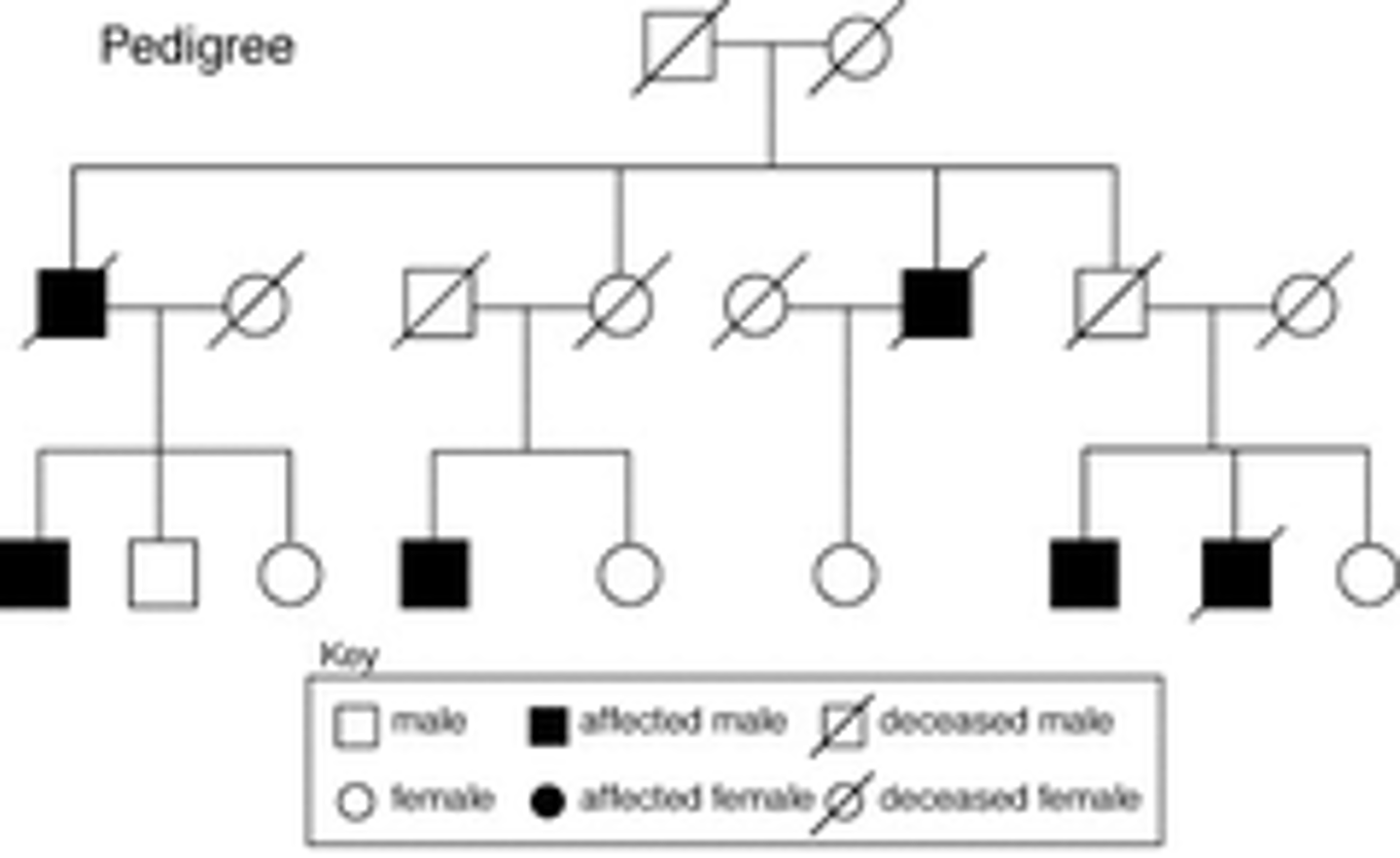
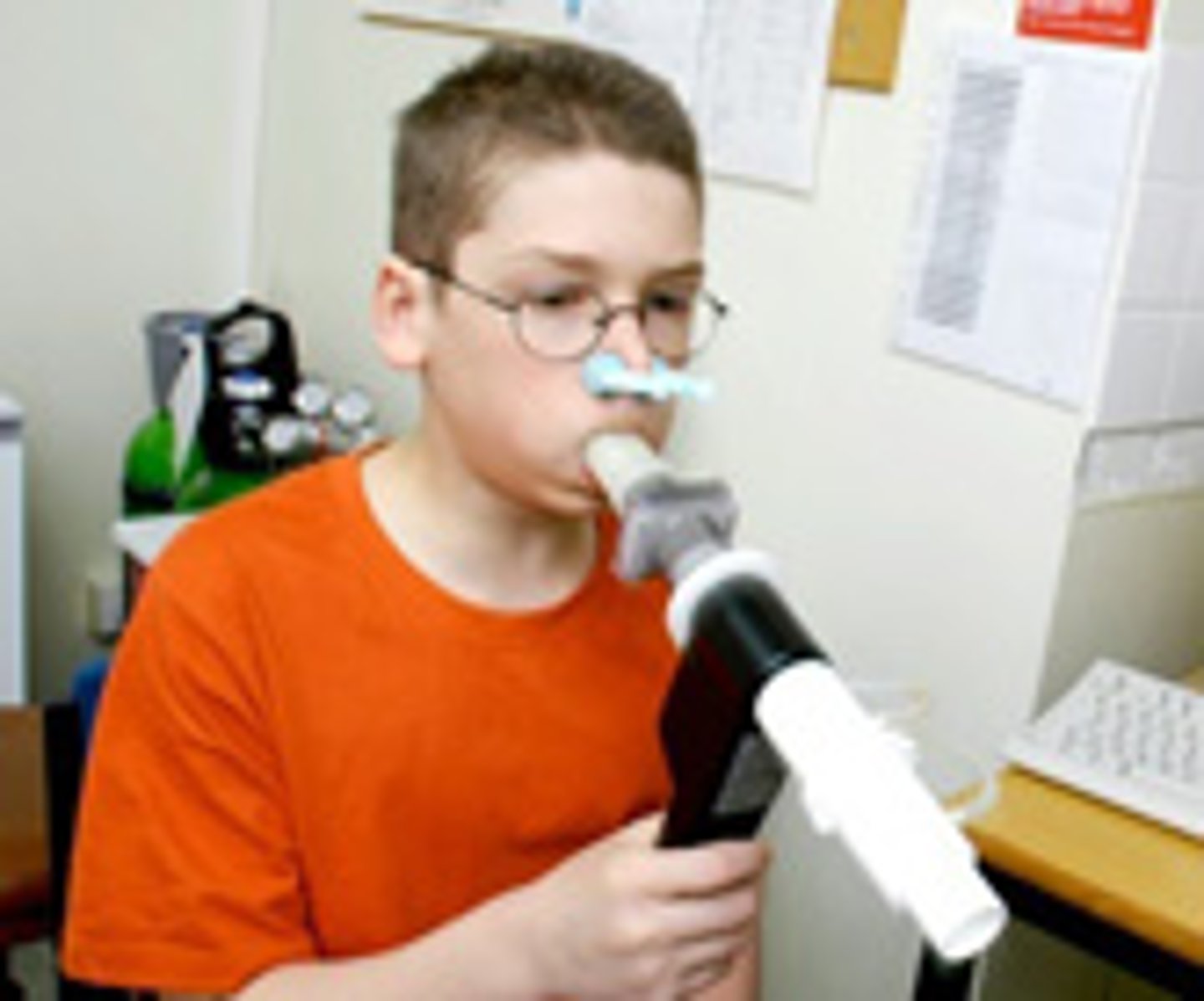
cystic fibrosis
A genetic disorder that is present at birth and affects both the respiratory and digestive systems.
sickle-cell disease
Genetic disorder in which red blood cells have abnormal hemoglobin molecules and take on an abnormal shape.

Huntington's disease
Genetic disorder that causes progressive deterioration of brain cells. caused by a dominant allele. symptoms do not appear until about the age of 30.

sex linked genes
Genes located on the sex chromosomes.
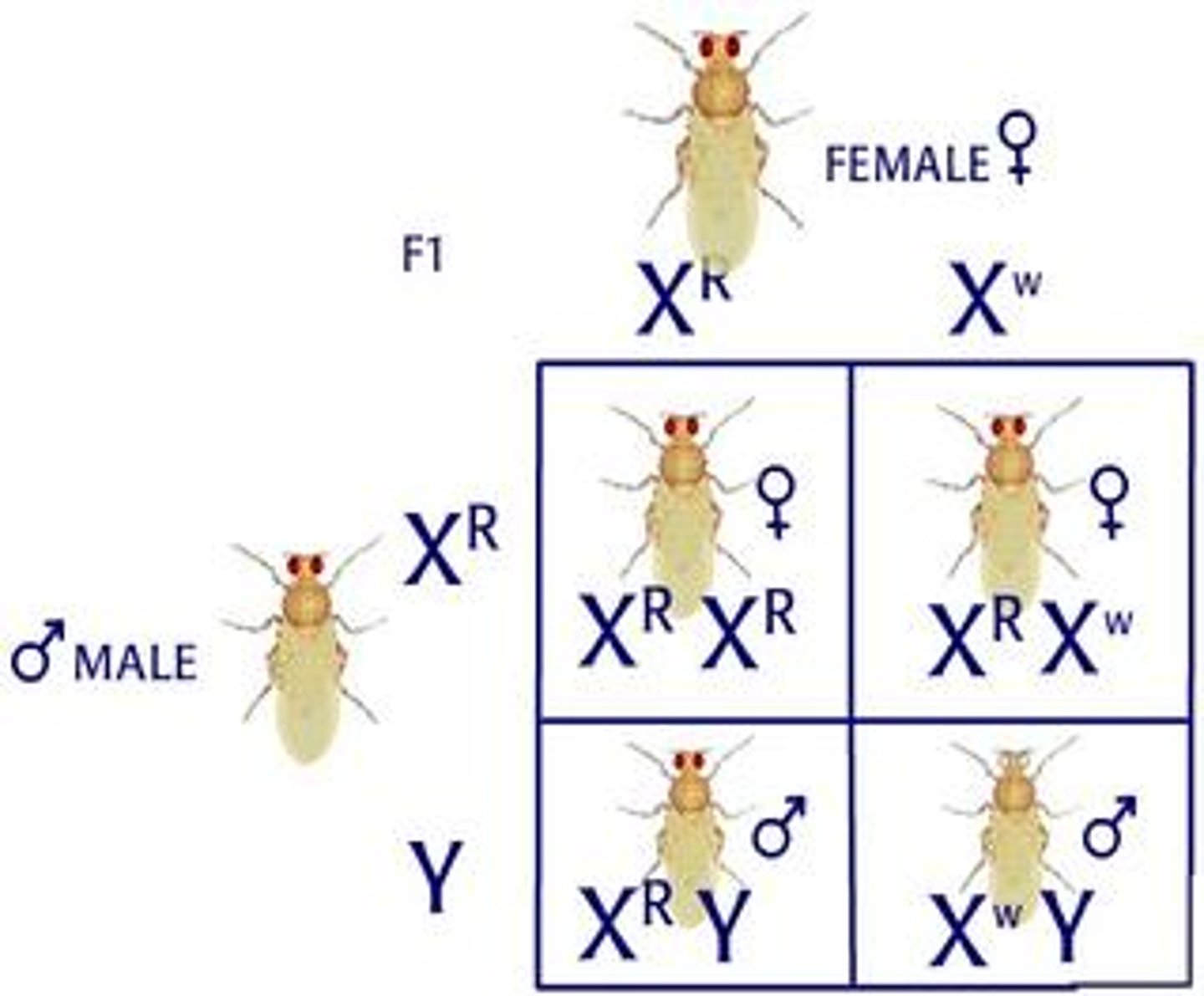
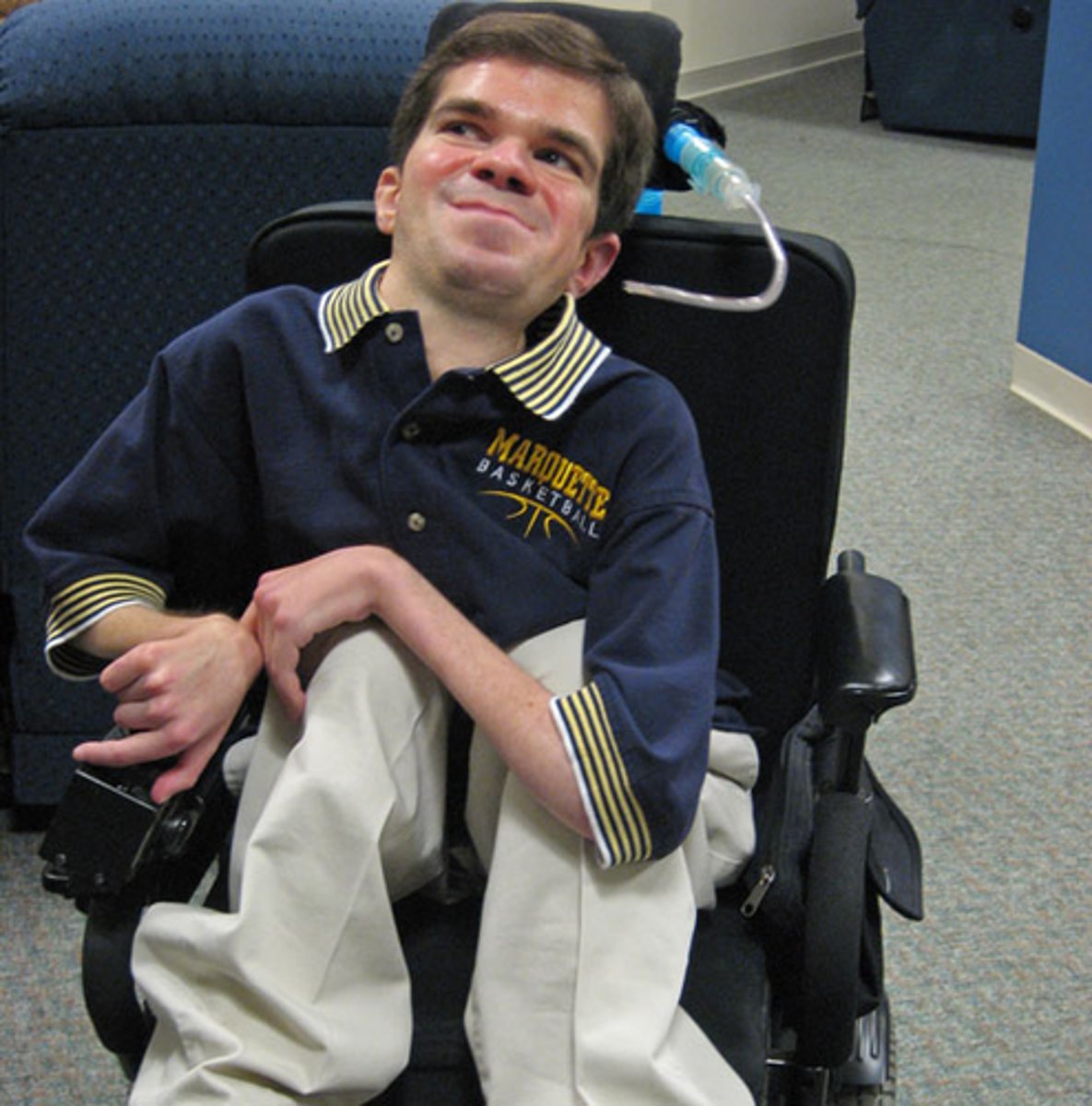
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
A human genetic disease caused by a sex-linked recessive allele; characterized by progressive weakening and a loss of muscle tissue.
barr body
A dense body formed from a deactivated X chromosome.
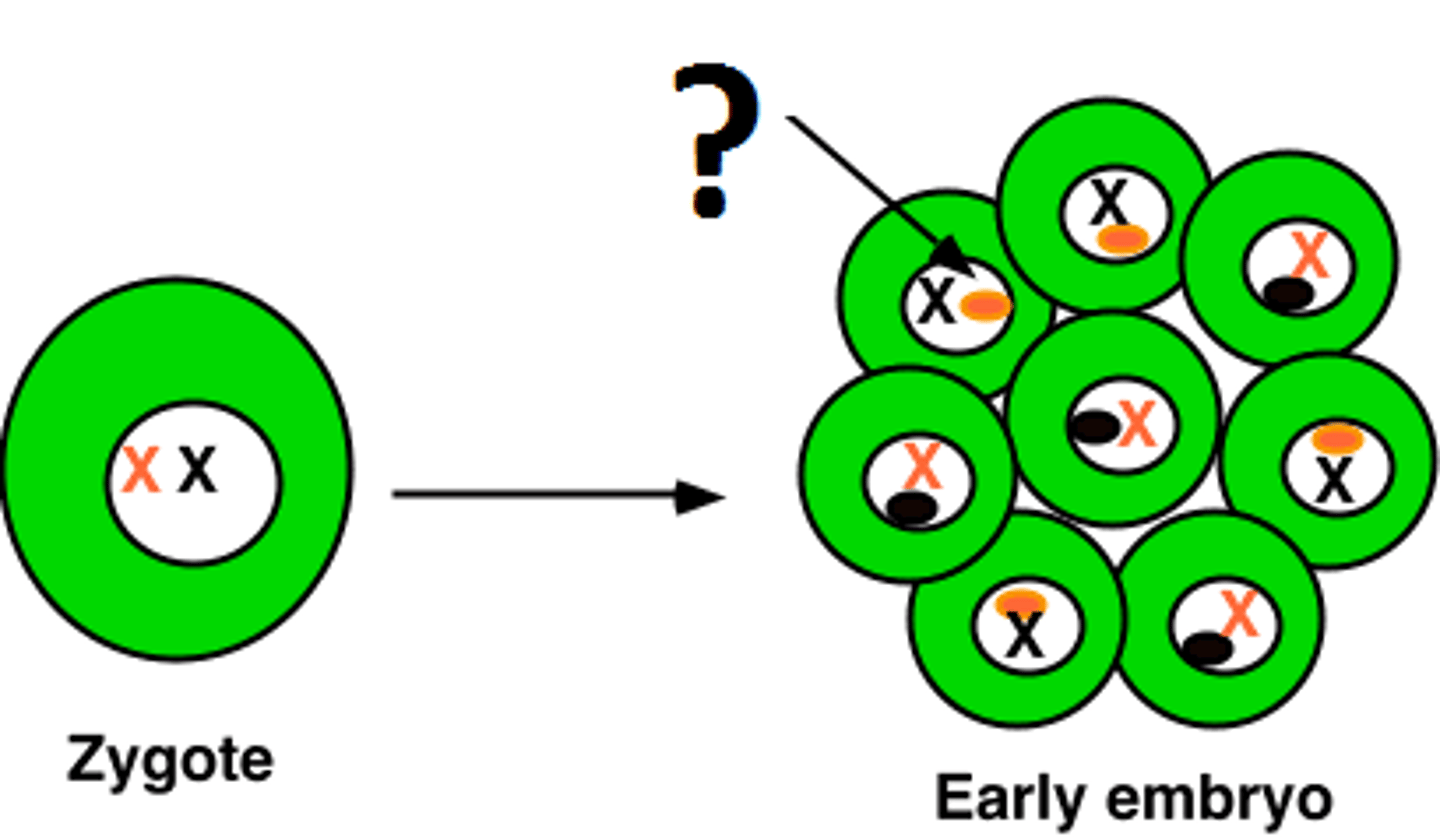
hemophilia
An X-linked recessive disorder in which blood fails to clot properly, leading to excessive bleeding if injured.
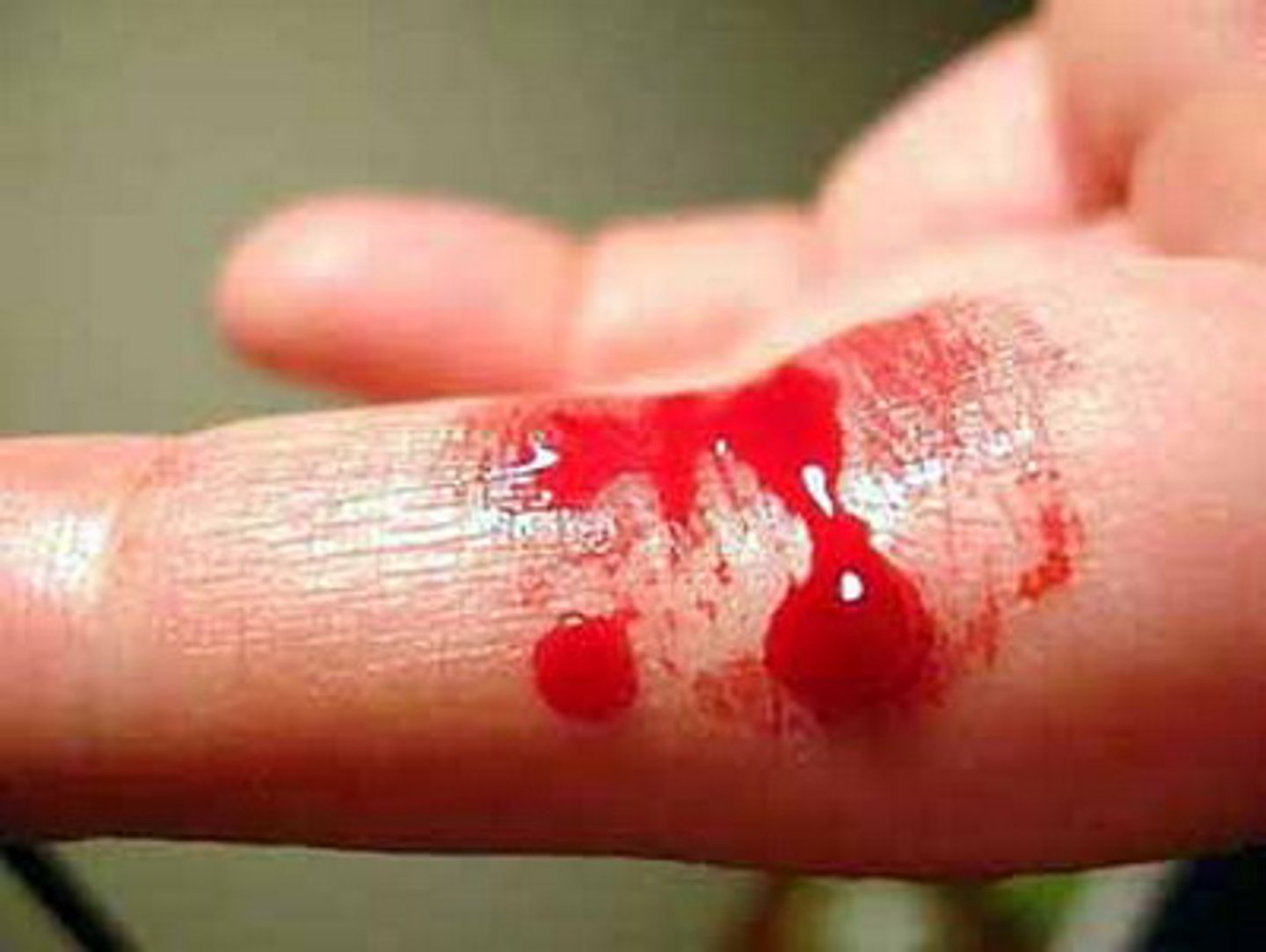
linked genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
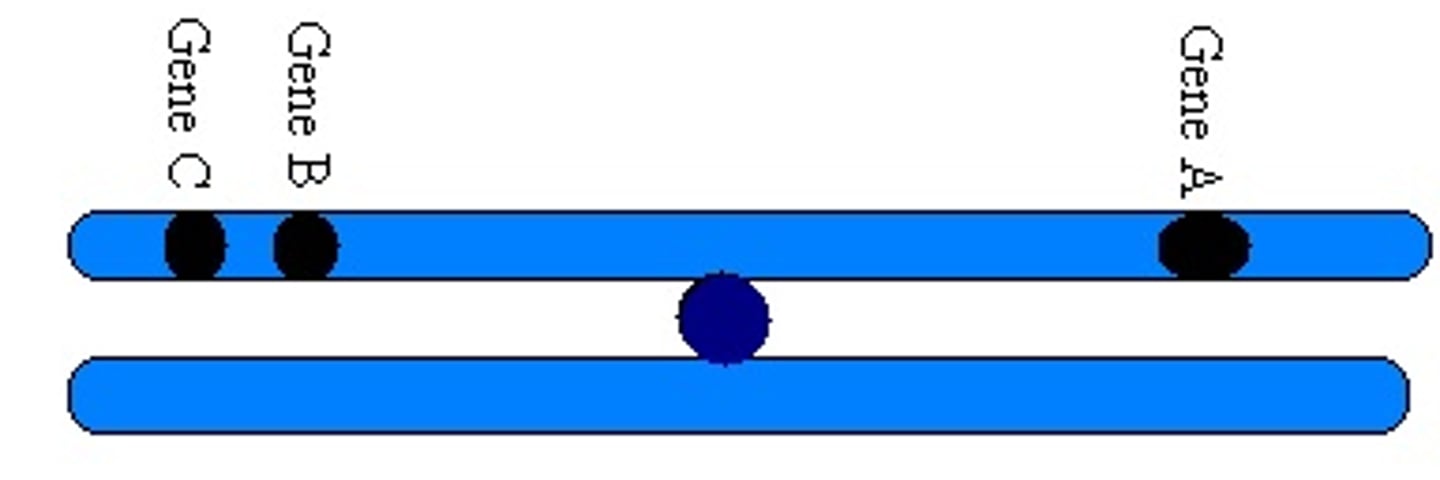
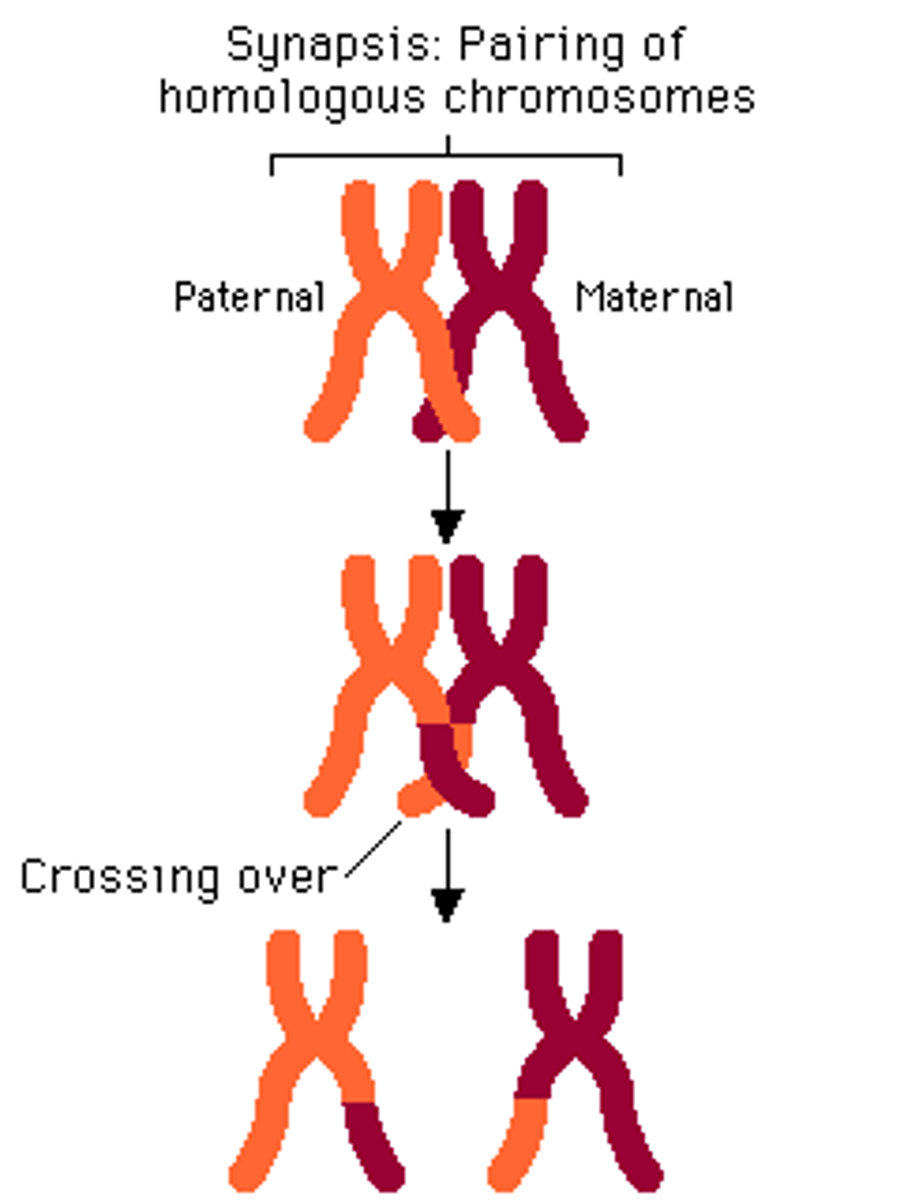
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
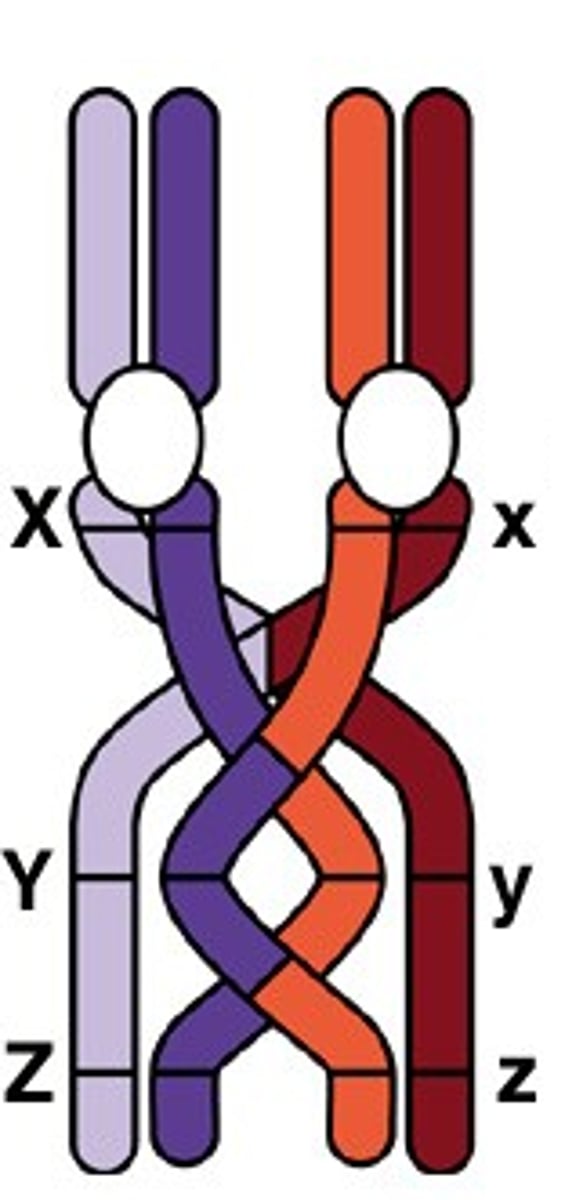
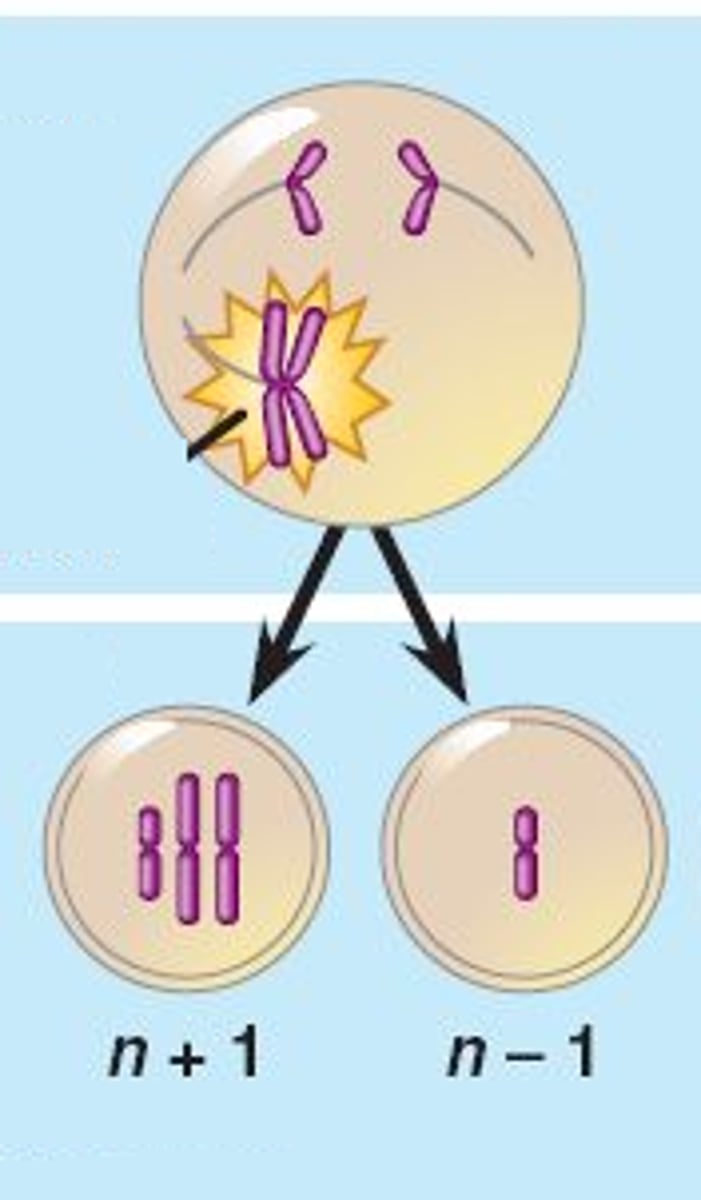
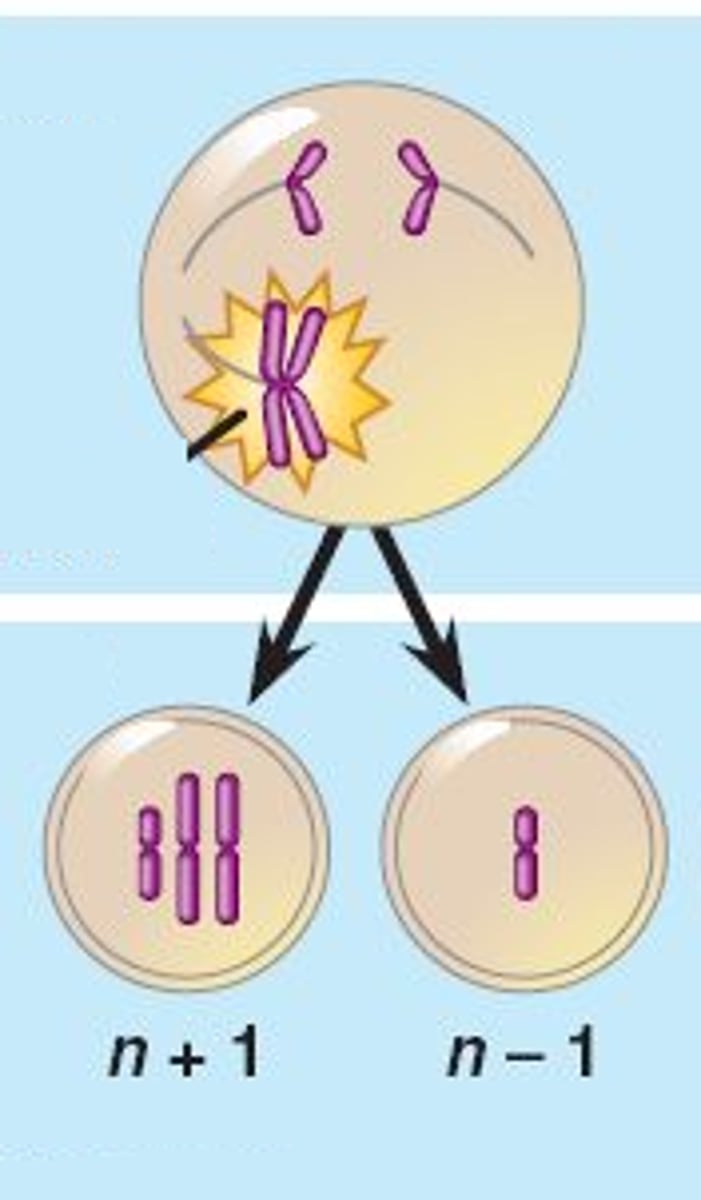
nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
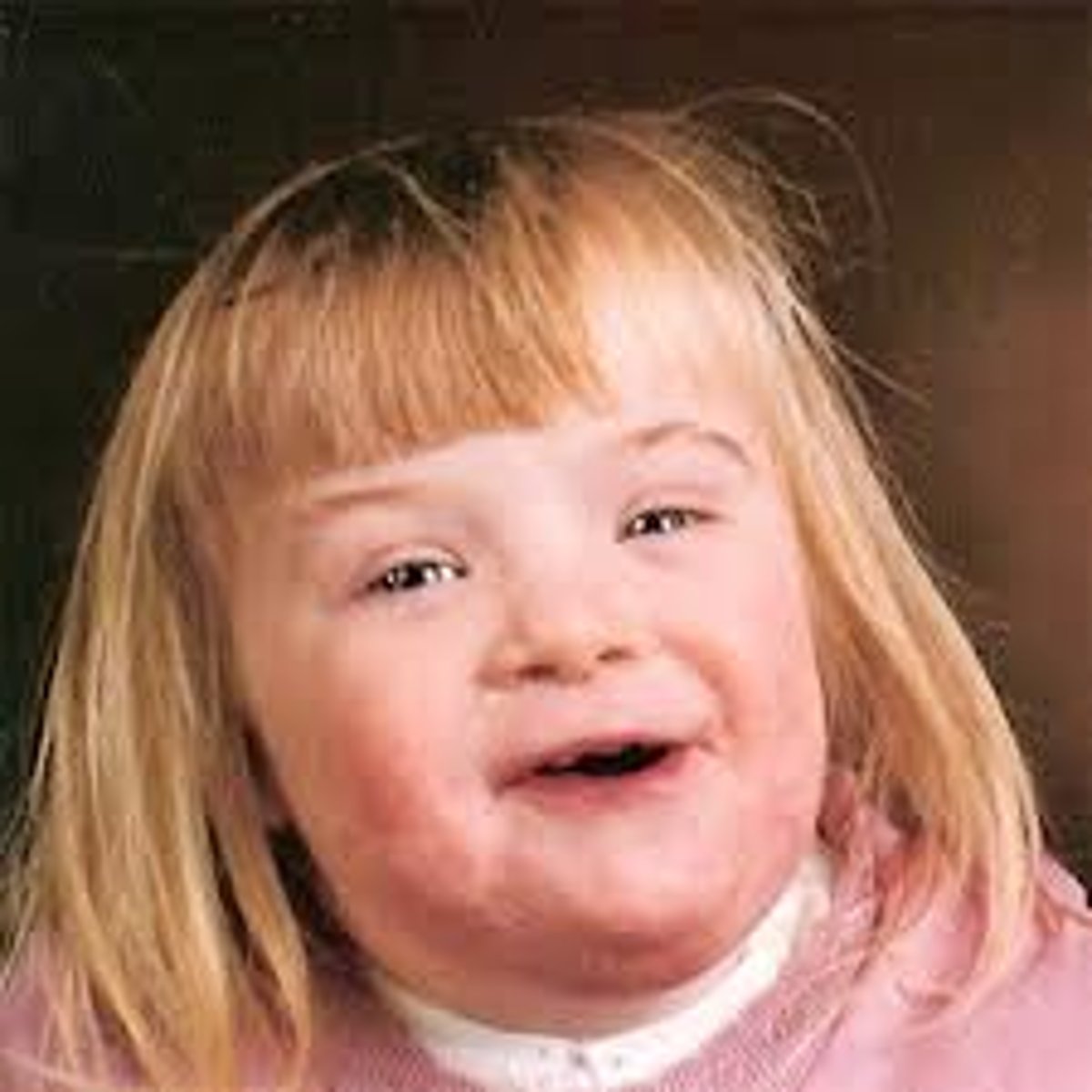
Downs Syndrome
A congenital disorder caused by having an extra Chromosome 21.
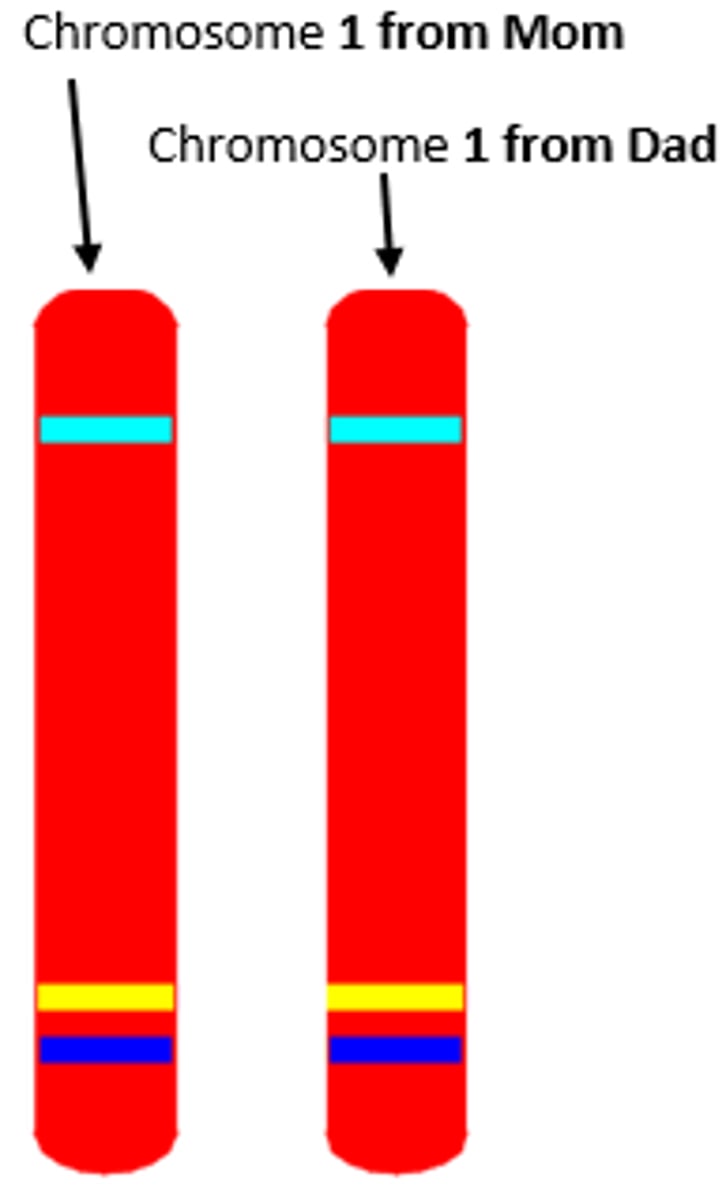
Homologous Chromosome
Chromosomes that are similar in size, shape, and genetic content
Chiasma
The X-shaped, microscopically visible region representing homologous chromatids that have exchanged genetic material through crossing over during meiosis.
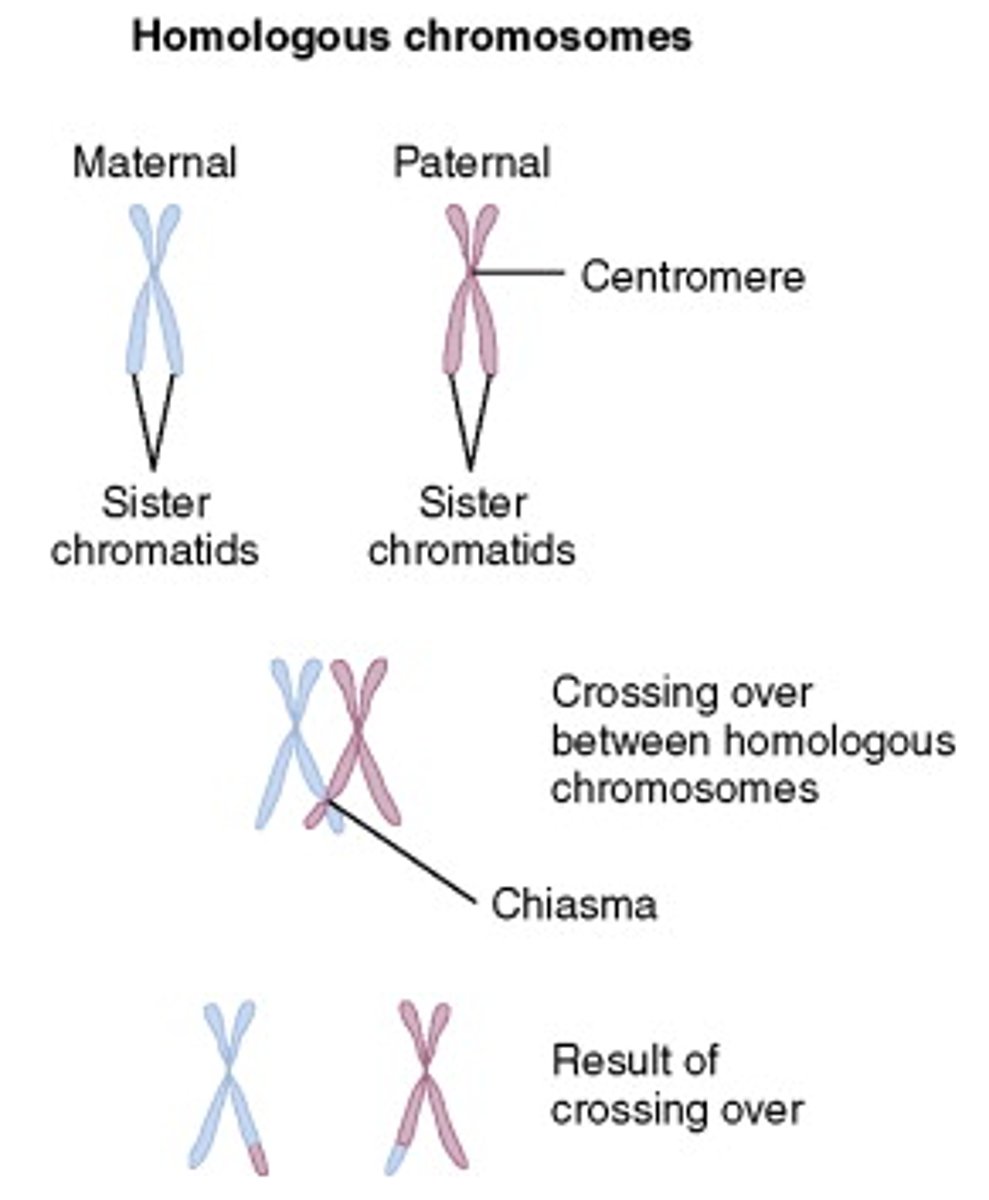
Crossing Over
the exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes, resulting in a mixture of parental characteristics in offspring.
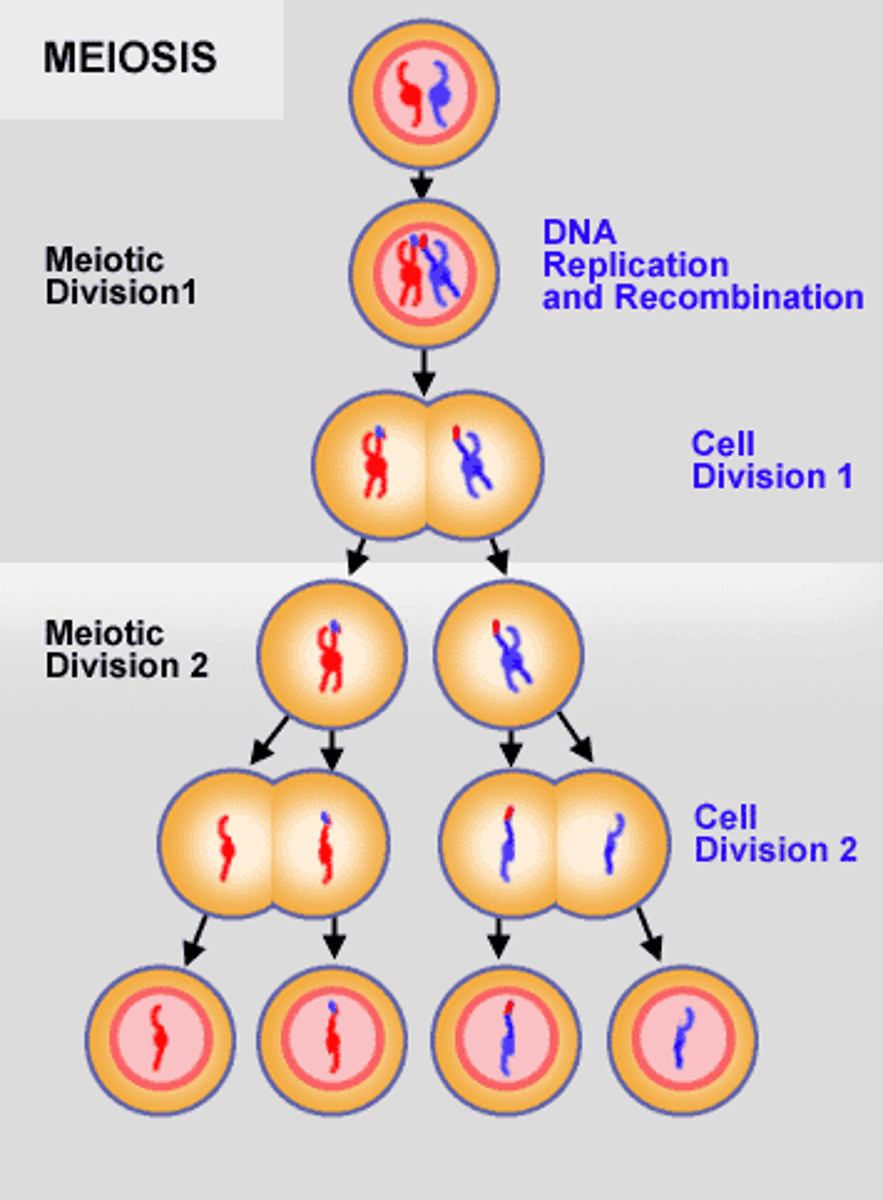
Meiosis 1
Crossing over occurs during
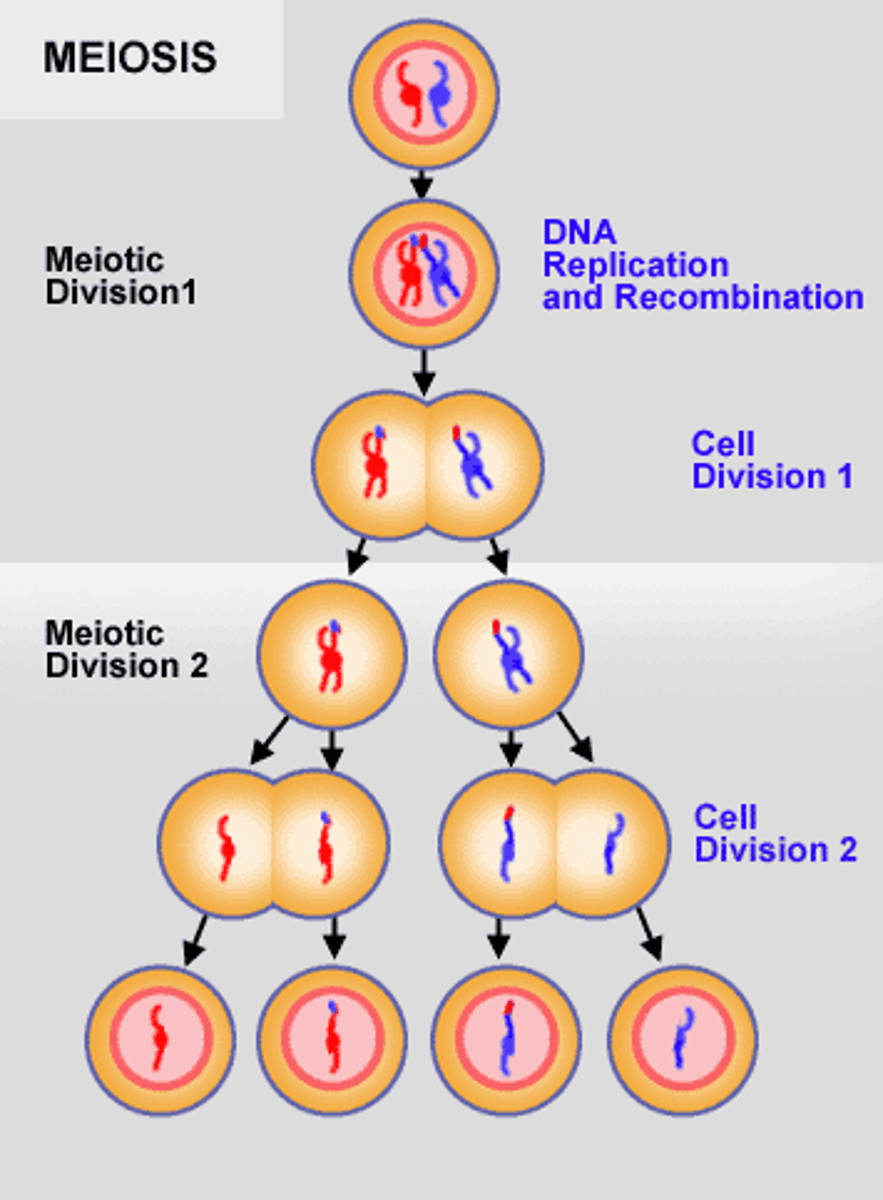
Meiosis 2
Cellular division without DNA replication results in haploid cells.
Nondisjunction
Error in meiosis in which the homologous chromosomes fail to separate properly
Haploid
Having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
Diploid
A cell that contains two complete sets of chromosomes, (homologous chromosomes) one from each parent.
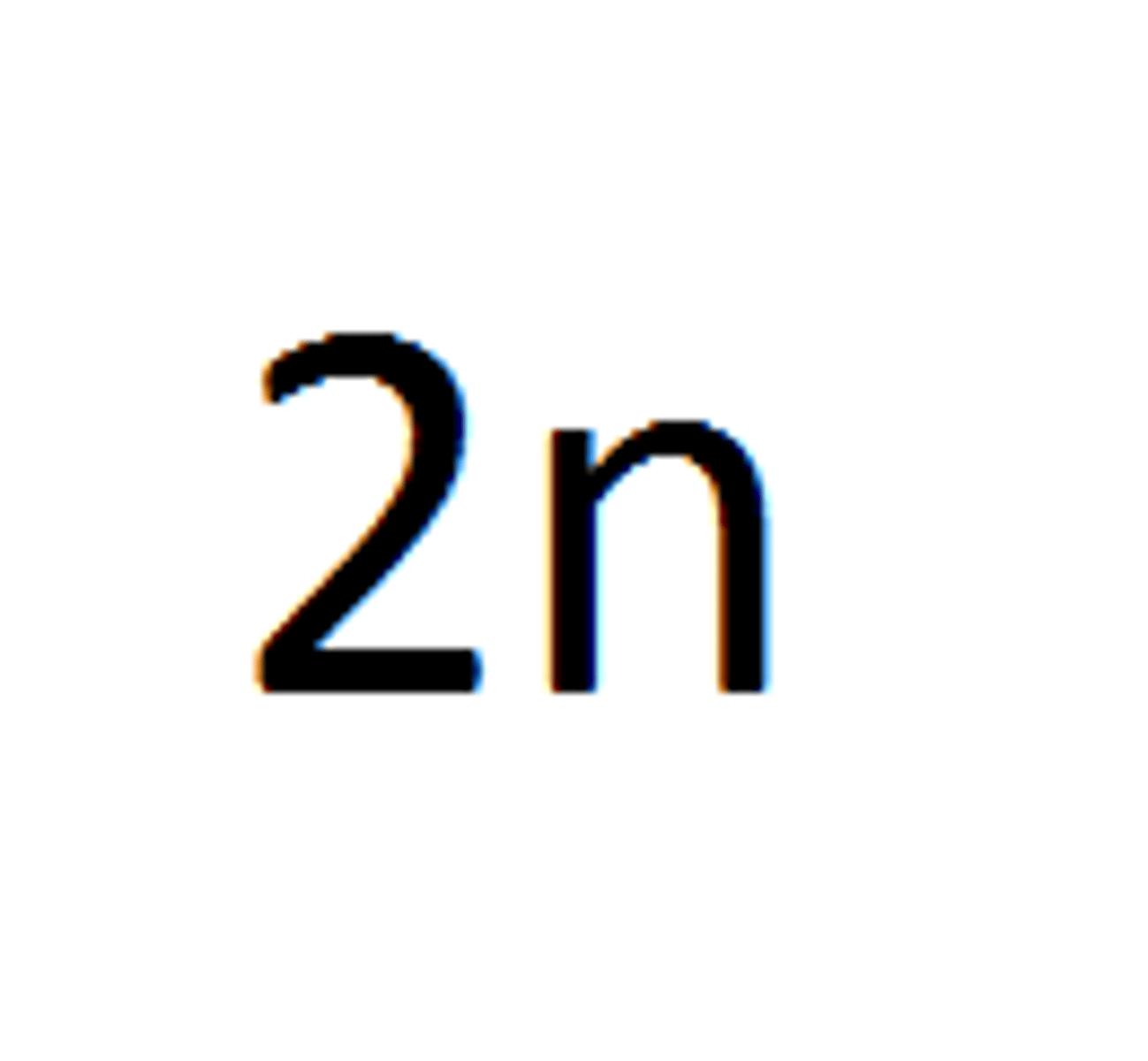
Parthenogenisis
A form of asexual reproduction in which a new individual develops from an unfertilized egg
Cloning
a general term for the research activity that creates a copy of some biological entity (a gene or organism or cell)

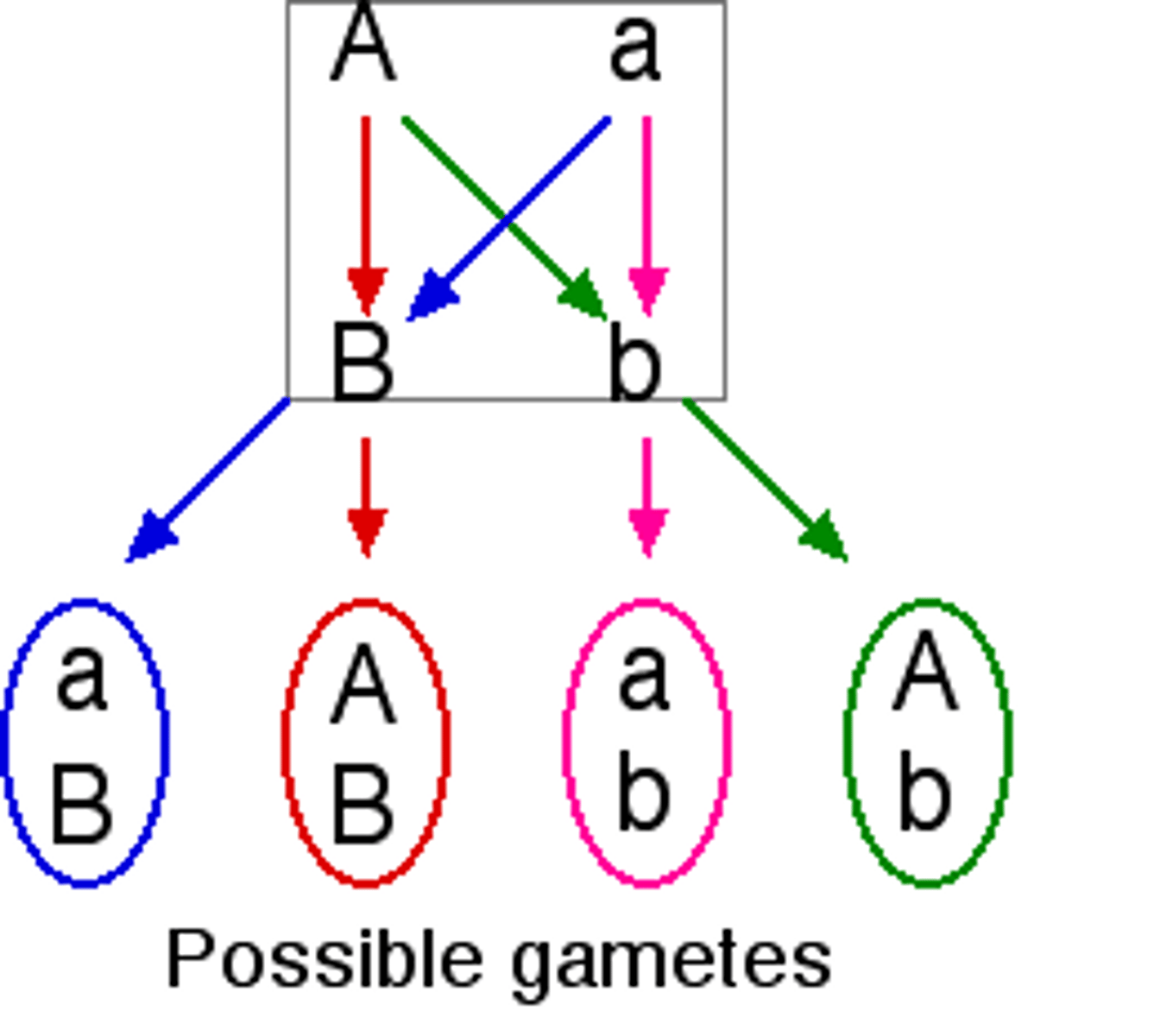
Independent Assortment
One of Mendel's principles that states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
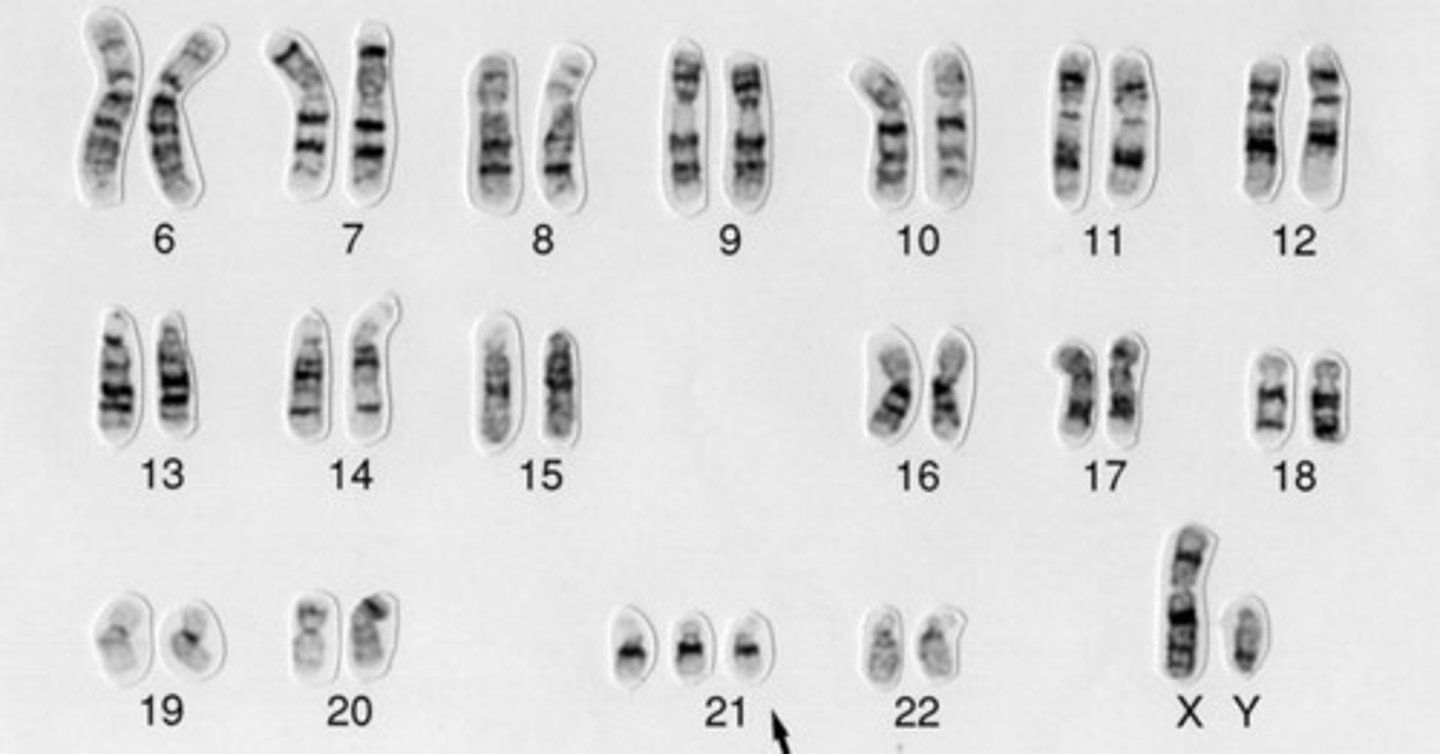
Trisomy 21
condition in which an individual has three number 21 chromosomes, resulting in Down syndrome
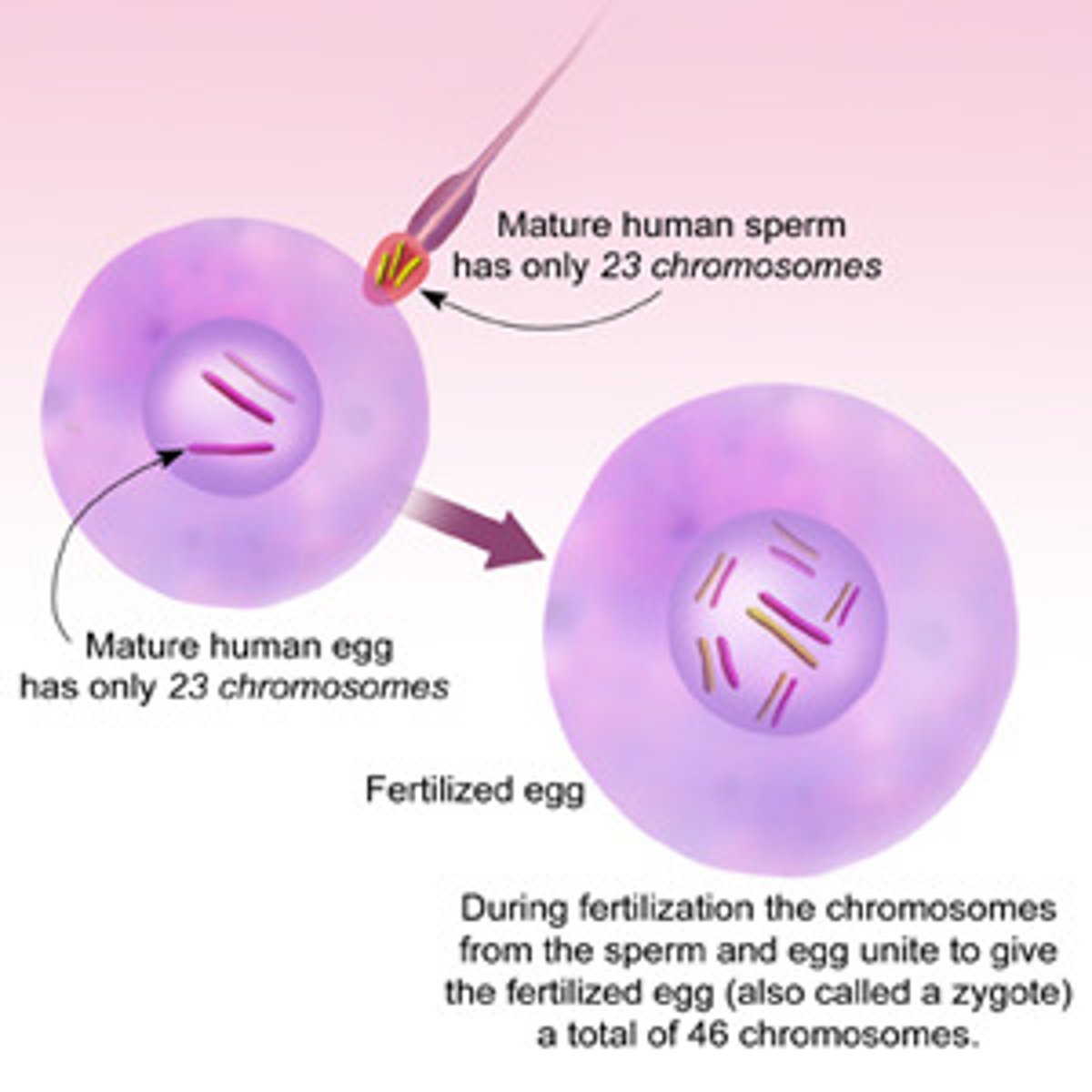
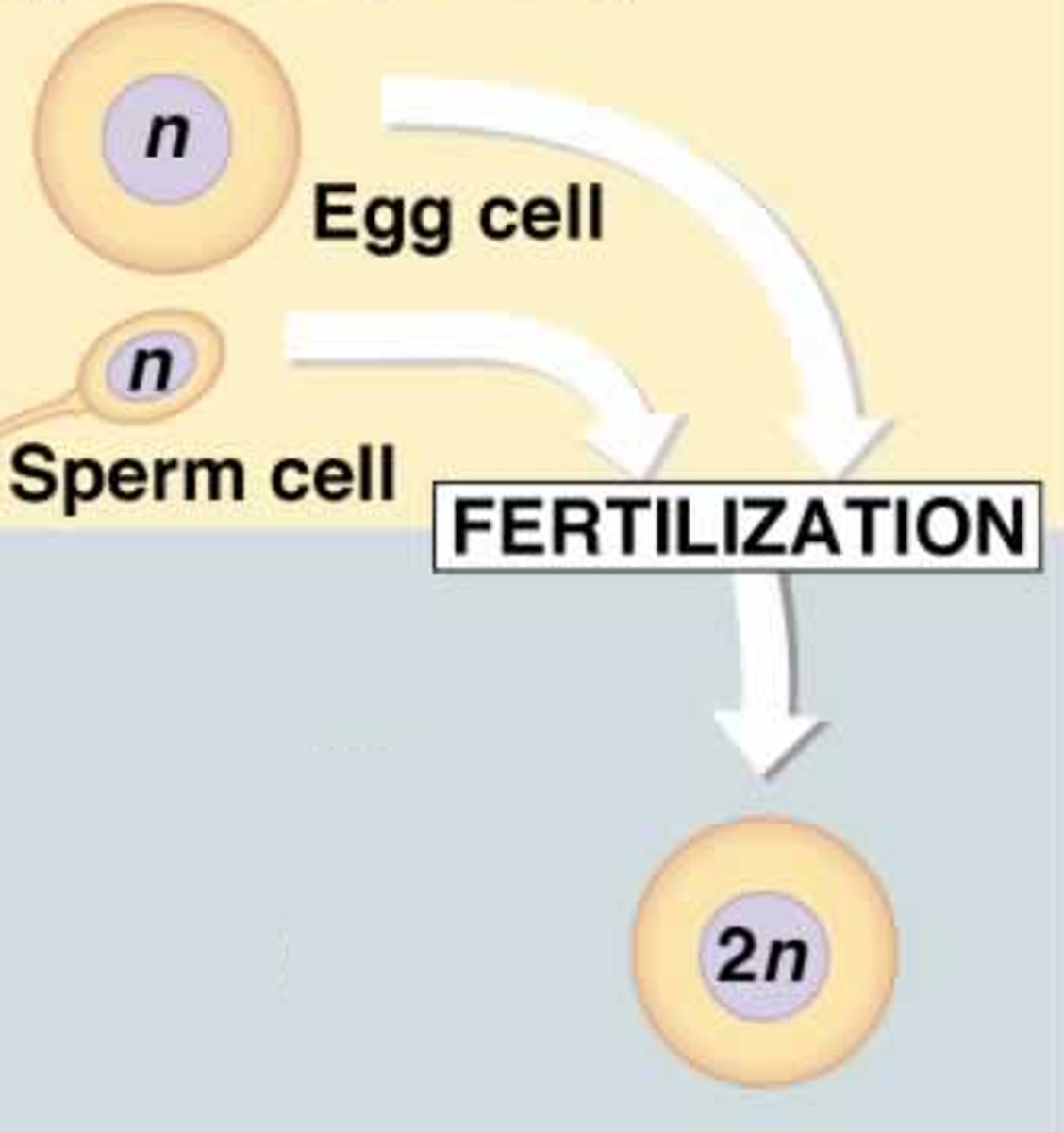
Gamete
A haploid cell such as an egg or sperm. unite during sexual reproduction to produce a diploid zygote.
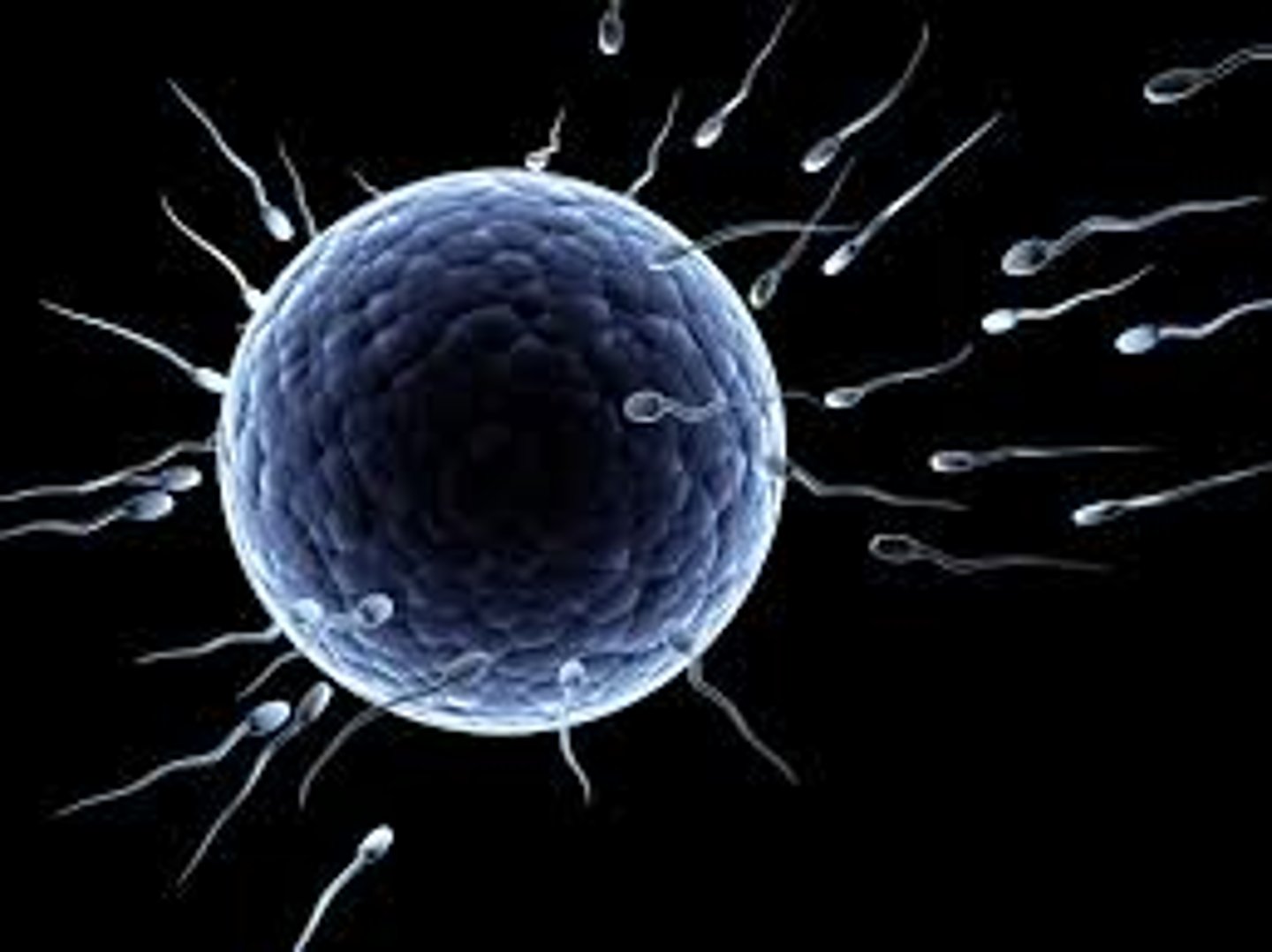
Zygote
Diploid cell formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg.
Asexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent.
Sexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents
Germ Cell
Reproductive cells that give rise to sperm and ovum
Chromatin
DNA and protein that makes up chromosomes