Neurobiology of Neurons and Neuroglia
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Neuron
Nerve cell specialized for impulse conduction.
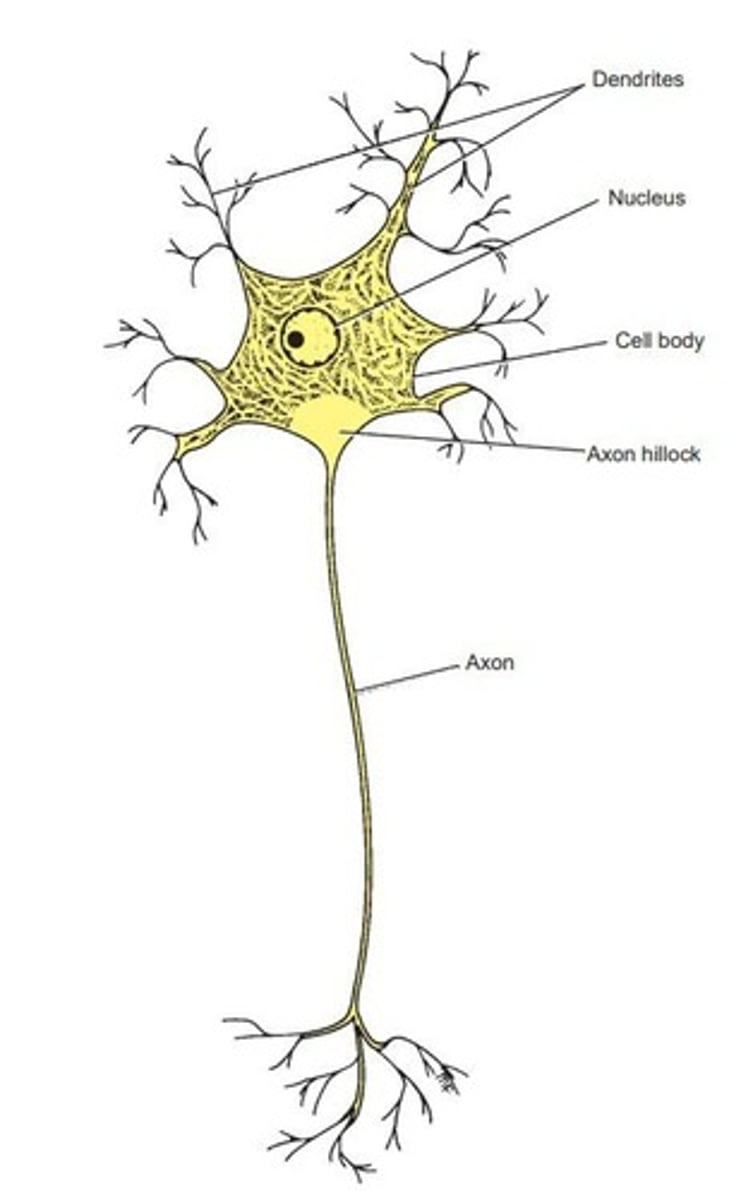
Neurites
Processes projecting from a neuron's cell body.
Dendrites
Receive information and conduct it to cell body.
Axon
Single long neurite conducting impulses away from cell.
Unipolar Neuron
Single neurite dividing into two branches.
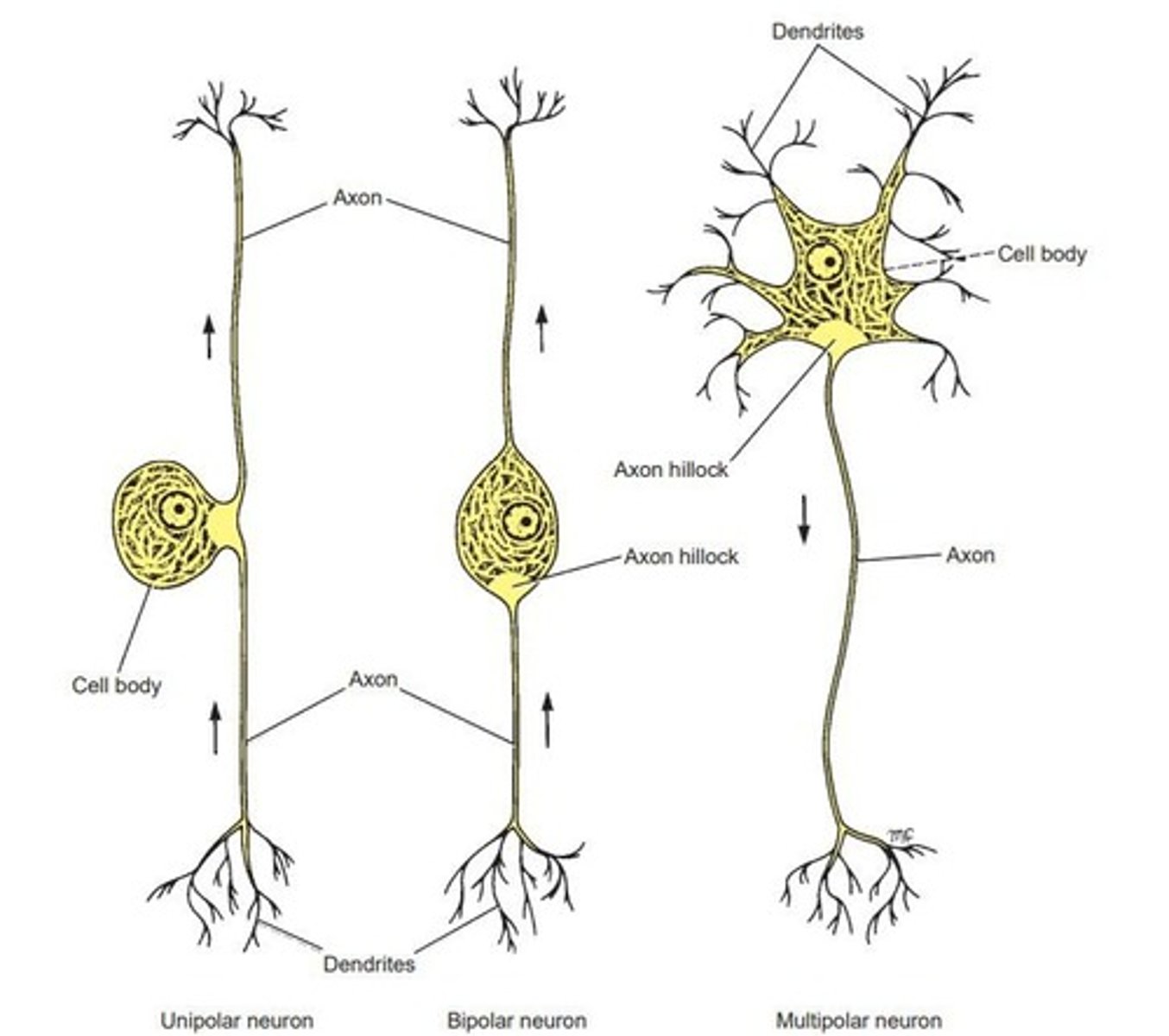
Bipolar Neuron
Two neurites emerging from an elongated cell body.
Multipolar Neuron
Multiple neurites arising from the cell body.
Golgi Type I
Long axon, may exceed 1 meter in length.
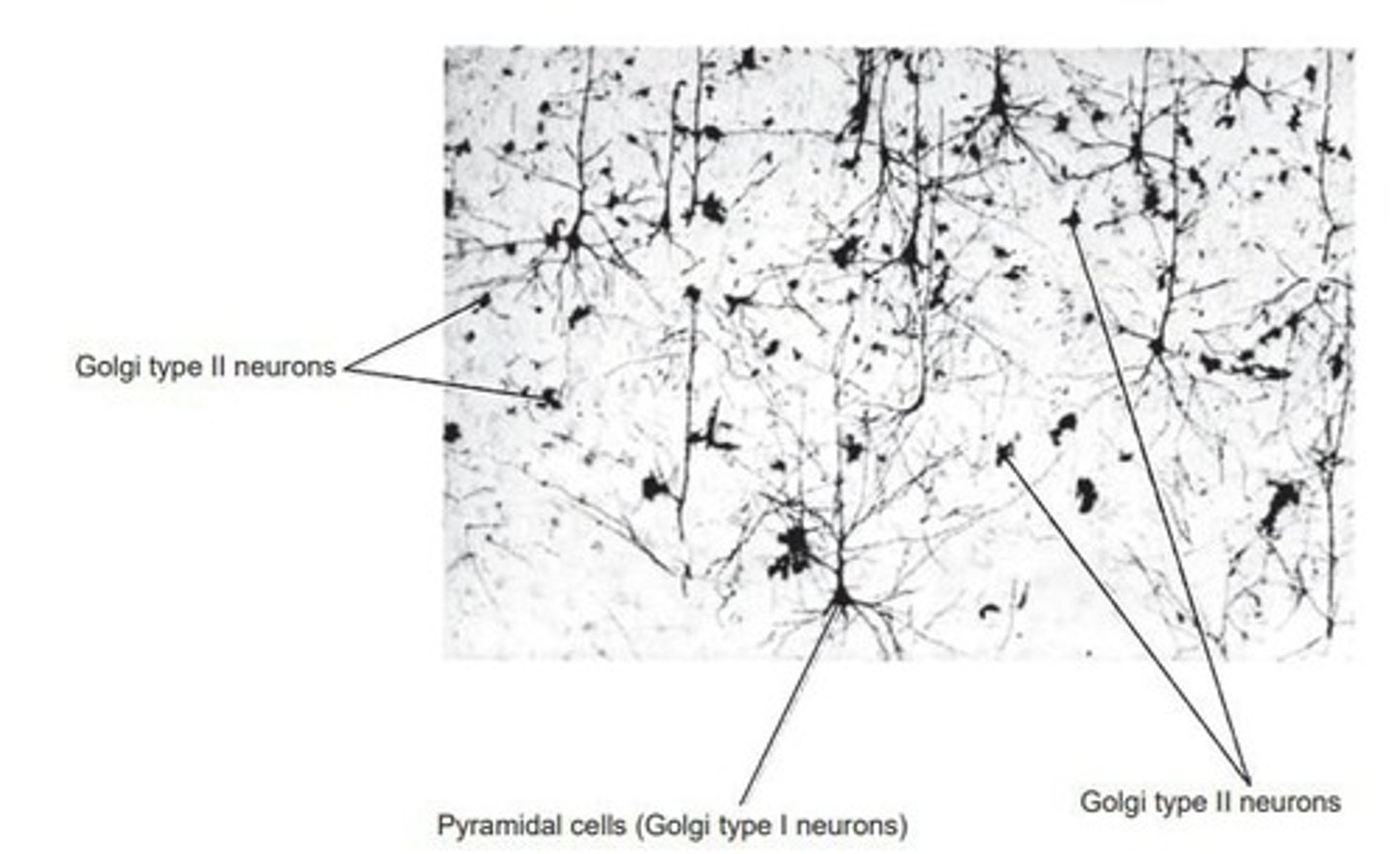
Golgi Type II
Short axon, often terminates near cell body.
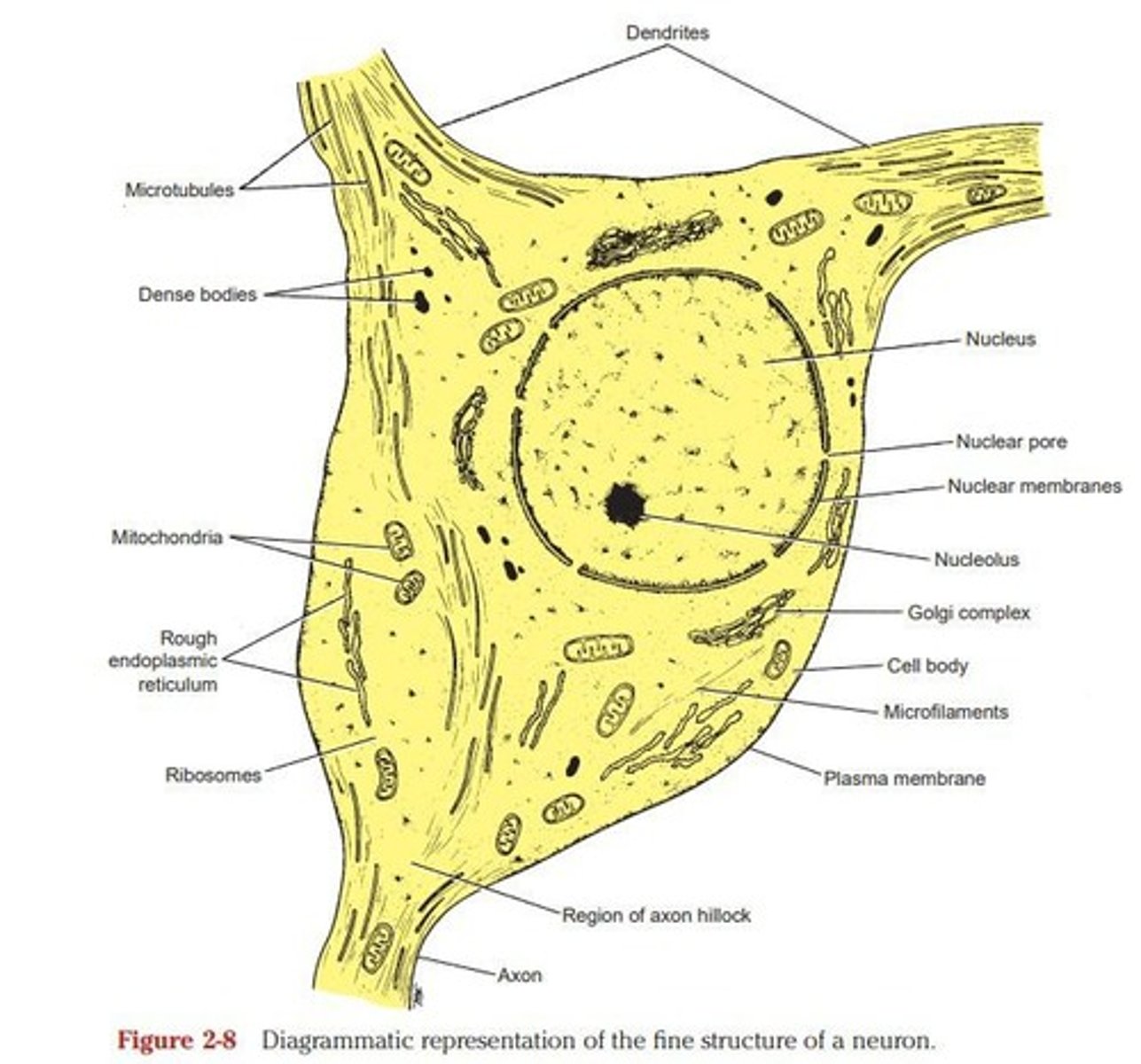
Nerve Cell Body
Mass of cytoplasm containing the nucleus.
Nucleus
Stores genes, centrally located in cell body.
Cytoplasm
Contains organelles and structures for cellular function.
Nissl Substance
Granules synthesizing proteins in neuron cytoplasm.
Golgi Complex
Organelle involved in modifying and packaging proteins.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, produces energy.
Microfilaments
Thin filaments providing structural support to cells.
Microtubules
Cylindrical structures aiding in cell shape and transport.
Lysosomes
Organelles containing enzymes for cellular digestion.
Centrioles
Cell structures involved in cell division.
Lipofuscin
Pigment granules indicating cellular aging.
Melanin
Pigment responsible for coloration in cells.
Glycogen
Stored form of glucose in cells.
Plasma Membrane
Boundary of the cell, regulates material transport.
Chromatolysis
Nissl substance disperses due to neuronal damage.
Neurofibrils
Main component of the neuron's cytoskeleton.
Kinesin
Motor protein for anterograde transport away from cell.
Dynein
Motor protein for retrograde transport towards cell.
Melanin Granules
Involved in dopamine formation.
Glycocalyx
Part of plasma membrane aiding in ion diffusion.
Resting Membrane Potential
Steady potential difference of about -80mV.
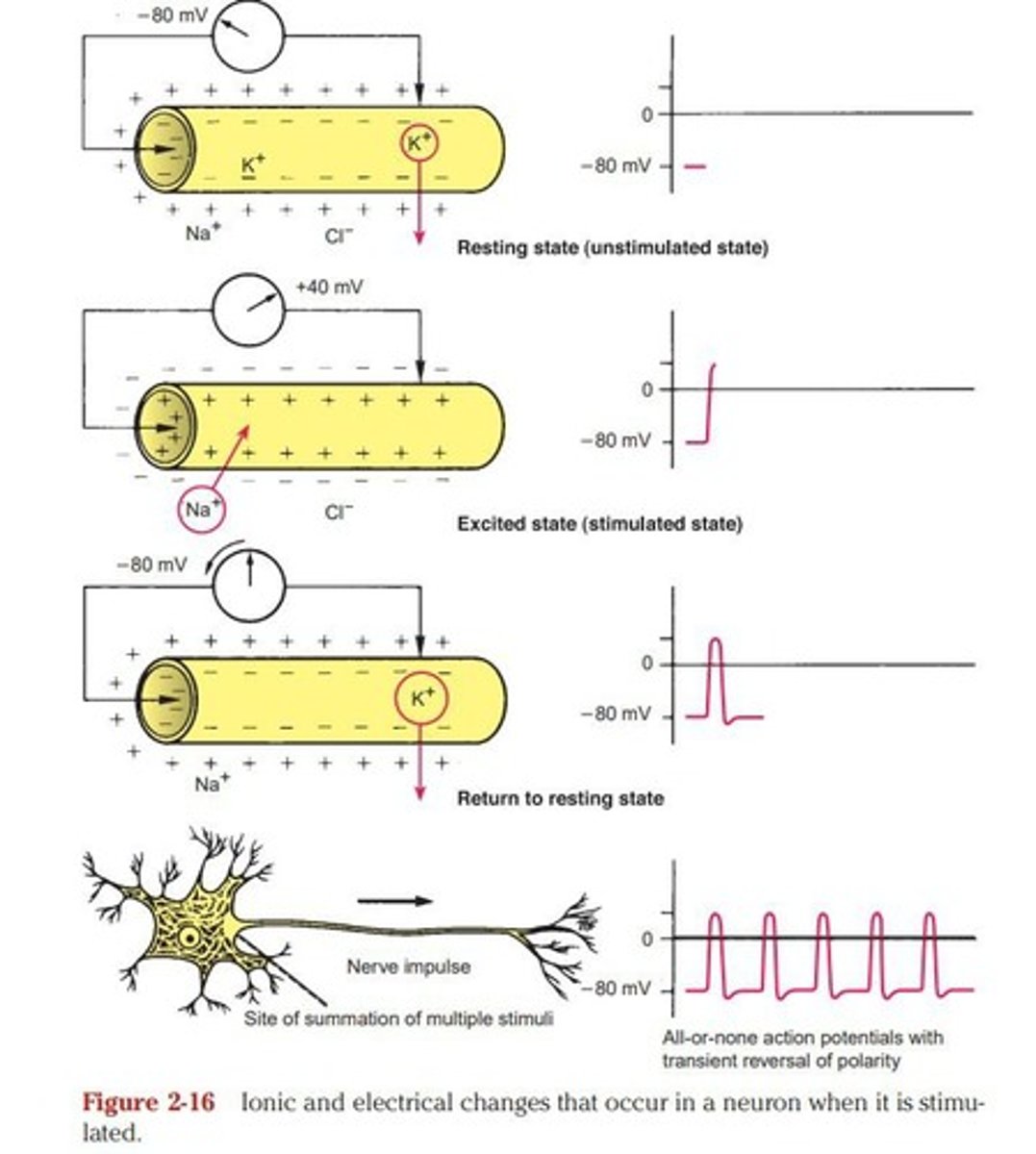
K+ Ion Permeability
Greater than Na+ ions in resting state.
Depolarization
Na+ influx changes membrane potential positively.
Action Potential
Rapid change in membrane potential to +40mV.
Duration of Action Potential
Lasts approximately 5 milliseconds.
Repolarization
K+ efflux returns membrane to resting state.
Self-Propagation of Impulse
Nerve impulse spreads without altering size or frequency.
Refractory Period
Period after impulse where another cannot occur.
Absolute Refractory Period
No further electrical change from second stimulus.
Relative Refractory Period
Strong stimulus can trigger action potential.
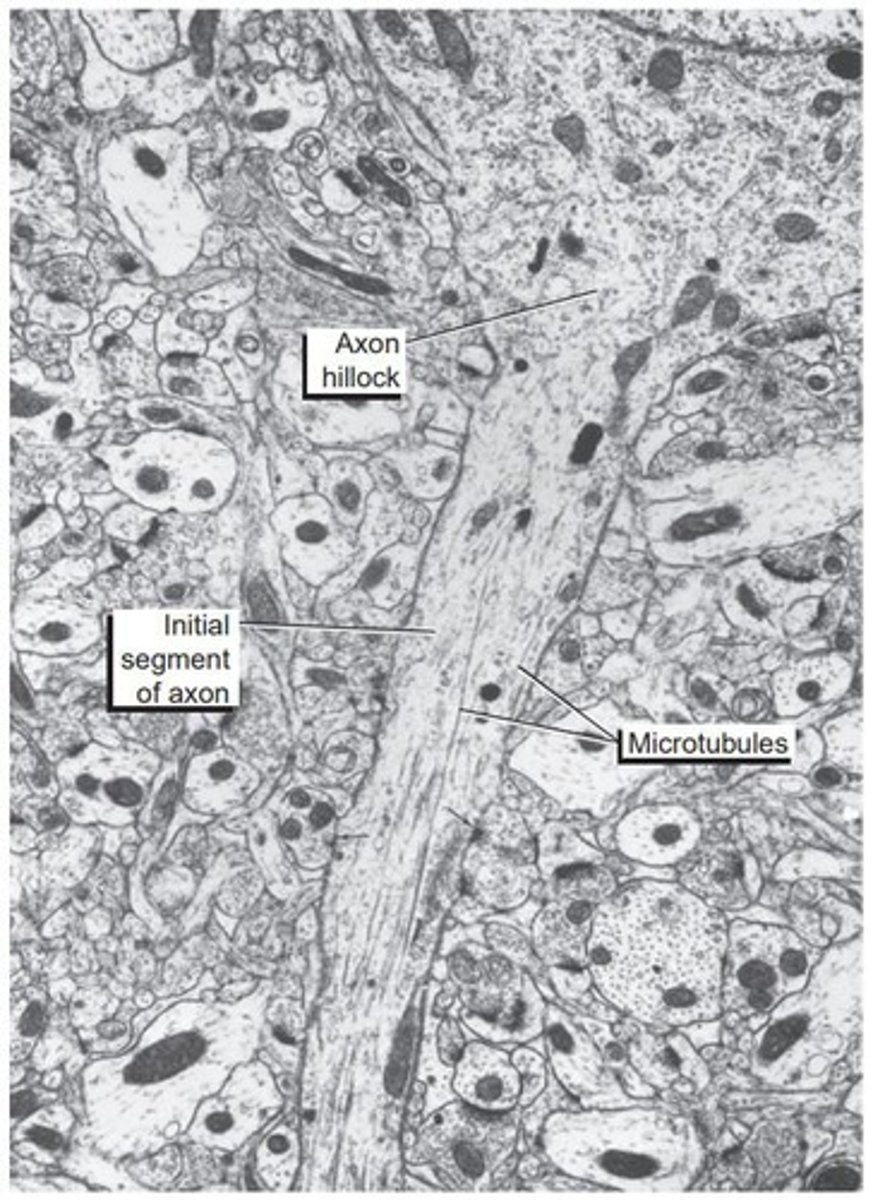
Axon Hillock
Site where action potential originates, lacks Nissl granules.
Axon Terminals
Distal ends of axon branches, often enlarged.
Axolemma
Plasma membrane surrounding the axon.
Axoplasm
Cytoplasm contained within the axon.
Initial Segment
First 50-100um of axon after axon hillock.
Axonal Transport
Transport of materials between cell body and axon terminals.
Anterograde Transport
Transport away from the cell body.
Retrograde Transport
Transport towards the cell body.
Synapses
Junctions for communication between two neurons.
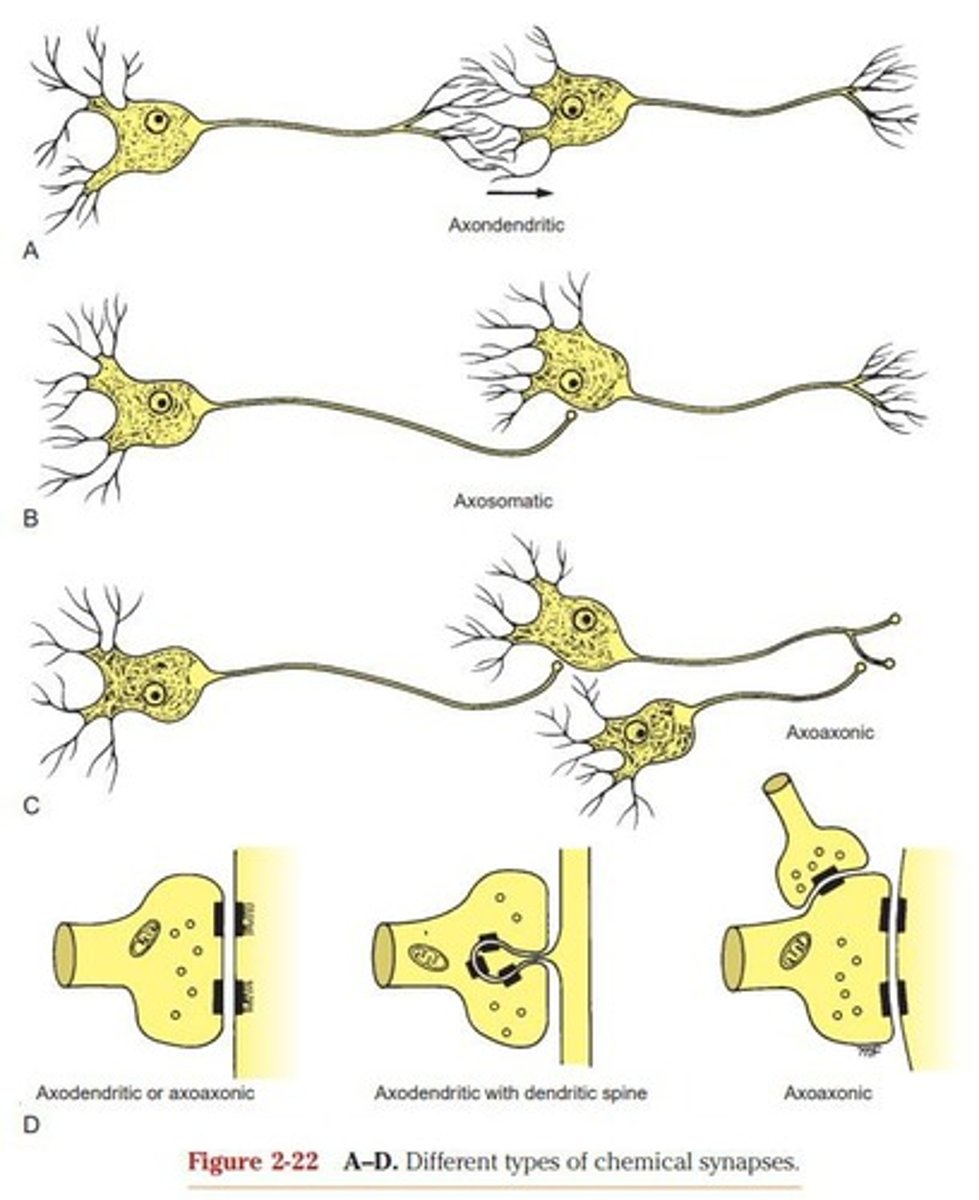
Axoaxonic Synapse
Synapse between two axons.
Axodendritic Synapse
Synapse between an axon and a dendrite.
Axosomatic Synapse
Synapse between an axon and a cell body.
Bouton Terminal
Terminal expansion of a synapse.
Chemical Synapses
Involve presynaptic and postsynaptic clefts.
Synaptic Cleft
Space separating terminal axon and postsynaptic surface.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers released at synapses.
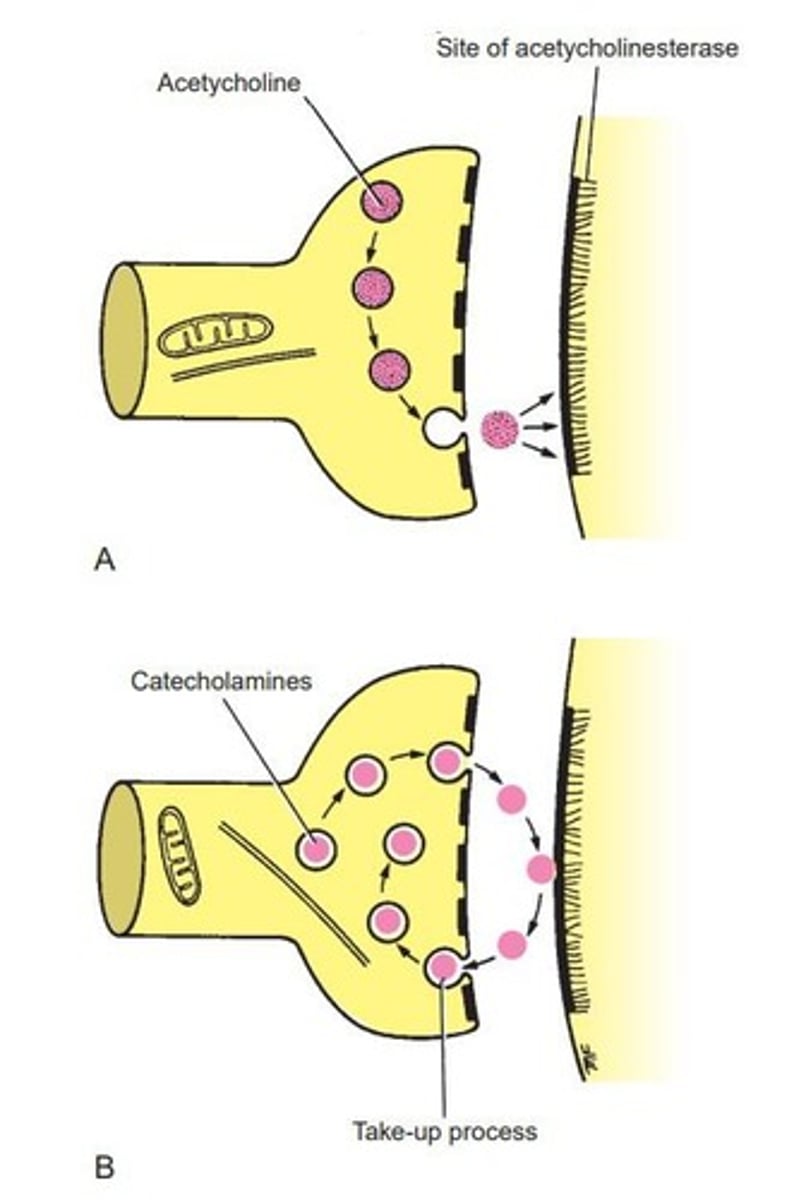
Acetylcholine
Common neurotransmitter in central and peripheral nervous systems.
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter released by substantia nigra neurons.
Glycine
Neurotransmitter primarily in spinal cord synapses.
Vesicles
Contain neurotransmitters released into synaptic cleft.
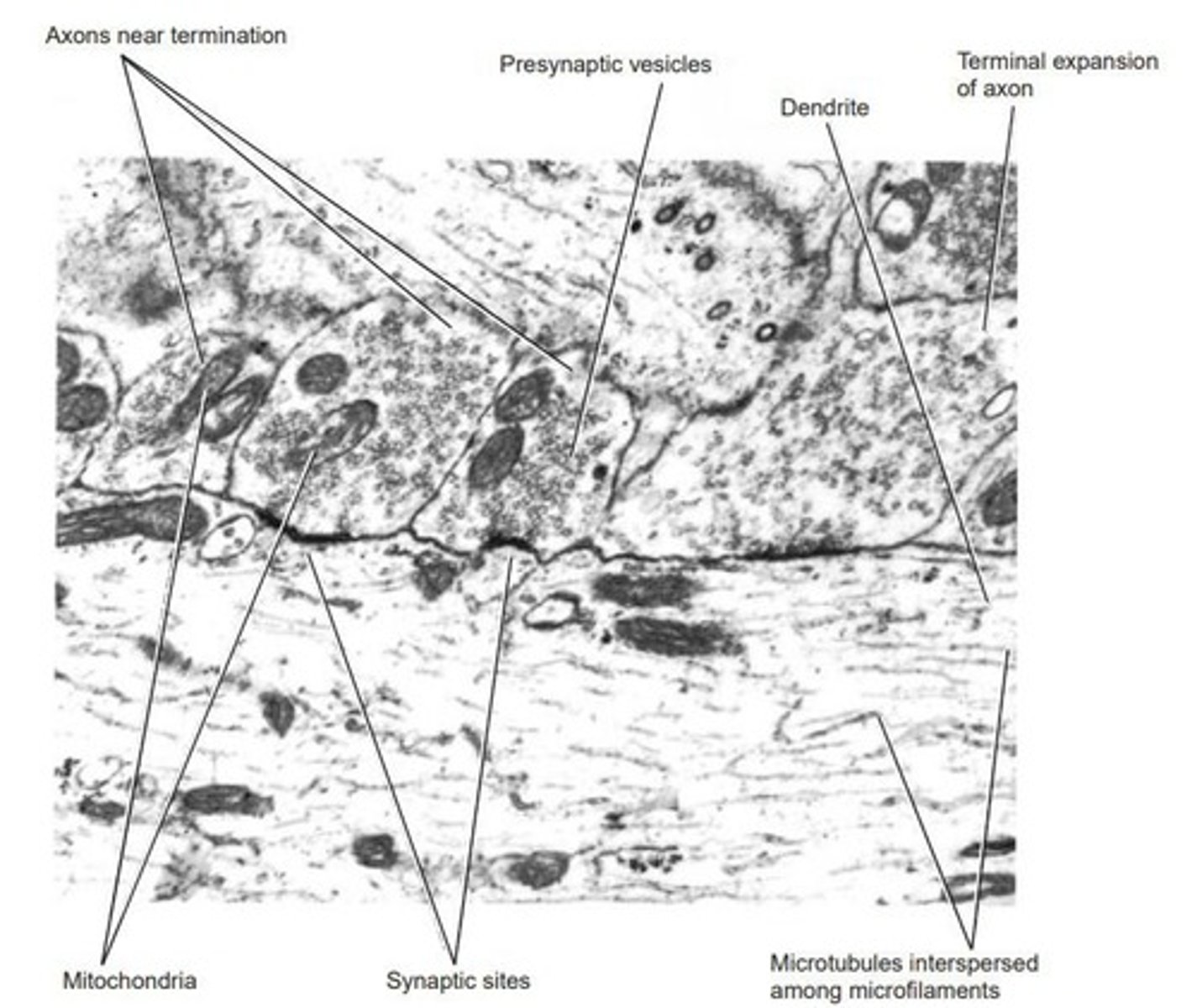
Neurotransmitter
Chemical released to transmit signals between neurons.
Calcium Influx
Calcium entry that facilitates neurotransmitter release.
Synaptic Vesicles
Membrane-bound structures storing neurotransmitters.
Postsynaptic Membrane
Membrane receiving neurotransmitter signals.
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP)
Temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane.
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)
Temporary hyperpolarization of postsynaptic membrane.
Hyperpolarization
Increase in membrane potential, neuron inhibition.
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter at sympathetic nerve endings.
Neuromodulators
Substances modifying postsynaptic neuron activity.
Astrocytes
Supportive cells forming framework for neurons.
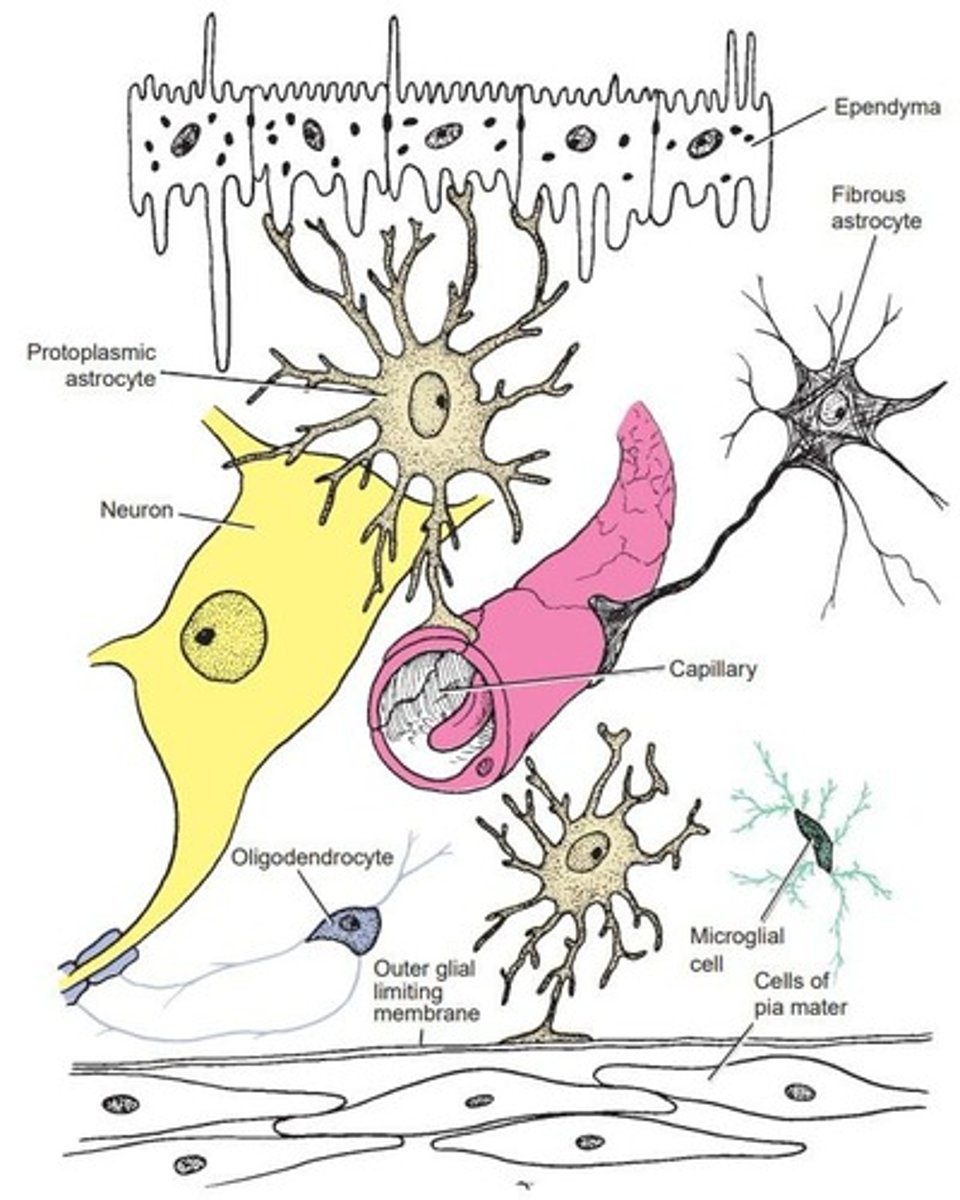
Oligodendrocytes
Cells forming myelin sheath in CNS.
Schwann Cells
Cells forming myelin sheath in PNS.
Microglia
Immune cells in CNS, perform phagocytosis.
Ependyma
Cells lining brain cavities and spinal canal.
Fibrous Astrocytes
Astrocytes providing structural support and insulation.
Protoplasmic Astrocytes
Astrocytes involved in nutrient storage and phagocytosis.
Neuroglia
Non-excitable cells supporting nervous system neurons.
Ion Channel
Protein allowing ions to flow across membranes.
Ependymocytes
Cells that circulate and absorb cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Tanycytes
Transport substances from CSF to hypophyseal-portal system.
Choroidal Epithelial Cells
Produce and secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Extracellular Space
Gap between neurons and neuroglial cells.
Blood-Brain Barrier
Endothelial cells prevent chemical permeability.
Neuron Injury Reaction
First reaction is loss of function.
Morphologic Changes
Cell becomes swollen, nucleus displaced peripherally.
Nissl Granules
Dispersed toward cell periphery during injury.
Hyperchromatism
Cytoplasm stains dark with basic dyes.
Rabies
Viral disease transmitted via infected animal bites.
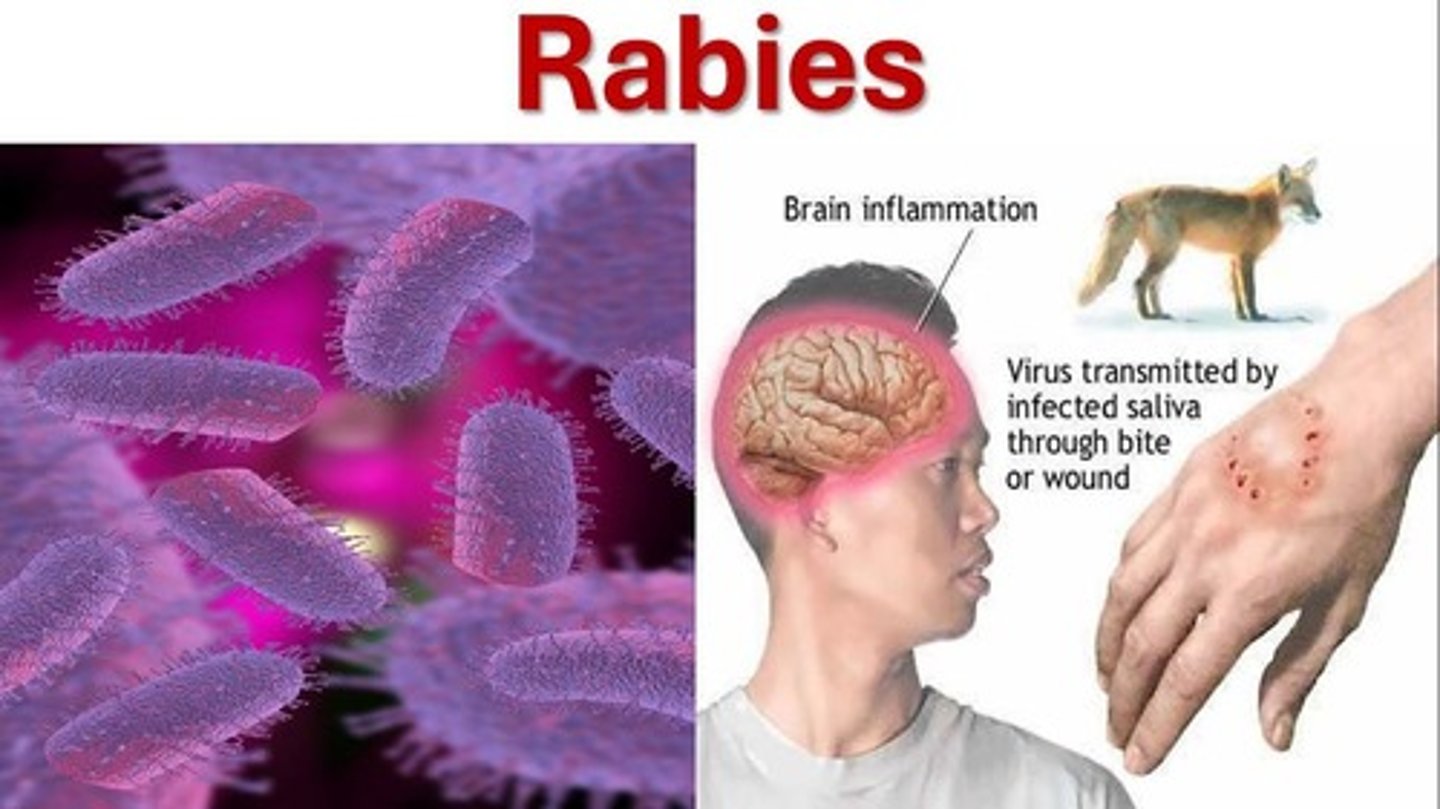
Incubation Period
Duration relates to peripheral nerve length.
Neuroblastoma
Malignant tumor associated with suprarenal gland.
Ganglioneuroma
Benign tumor in suprarenal medulla or ganglia.
Pheochromocytoma
Benign tumor secreting norepinephrine, causes hypertension.
Phenothiazines
Block dopamine receptors on postsynaptic neurons.
Procaine
Inhibits acetylcholine release from preganglionic fibers.
Nicotine
Mimics acetylcholine action on postsynaptic membrane.
Hexamethonium
Inhibits synaptic transmission resembling acetylcholine.
Multiple Sclerosis
Common CNS disease with demyelination patches.
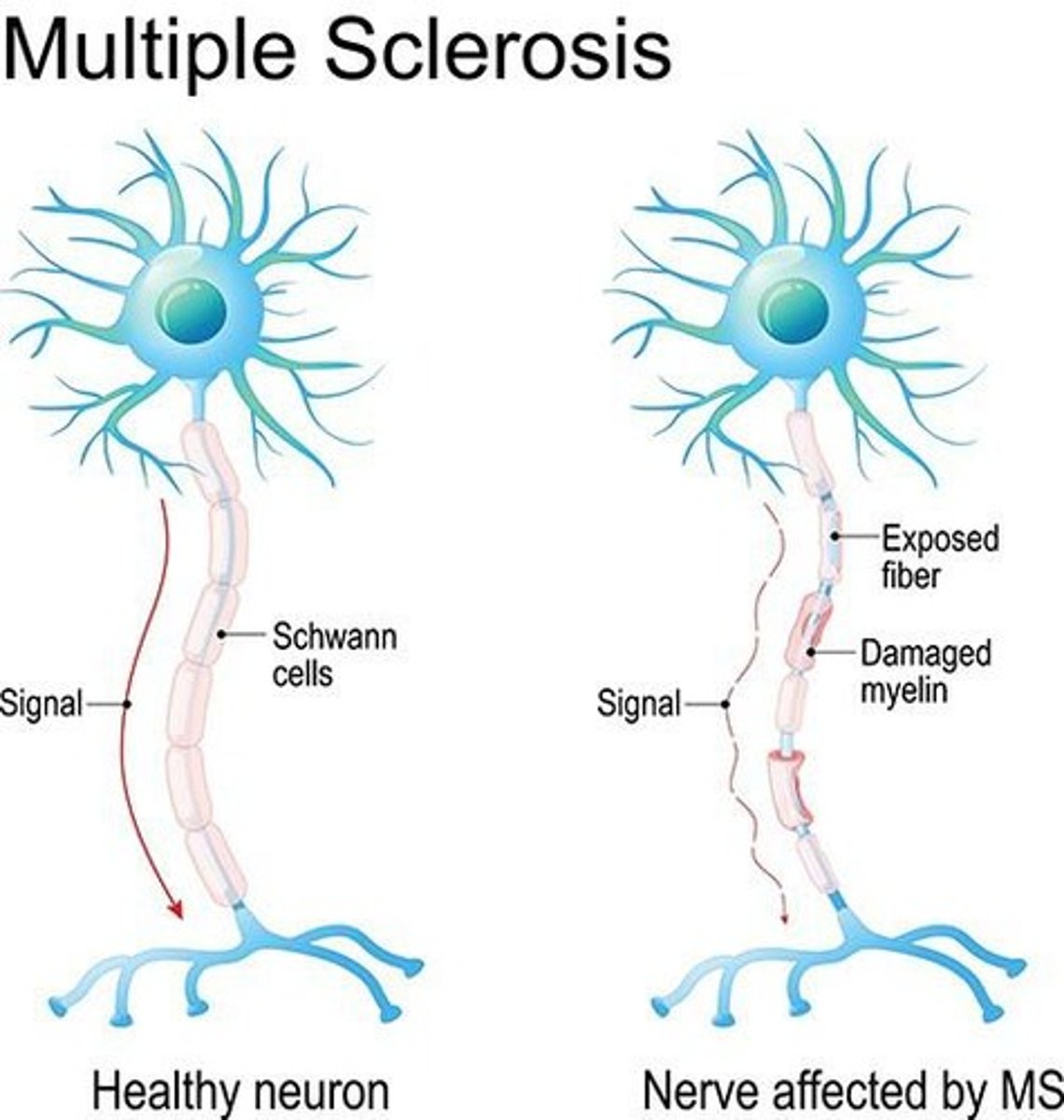
Gliotic Scar
Formed by astrocyte proliferation after demyelination.
Cerebral Edema
Condition following head injuries or infections.
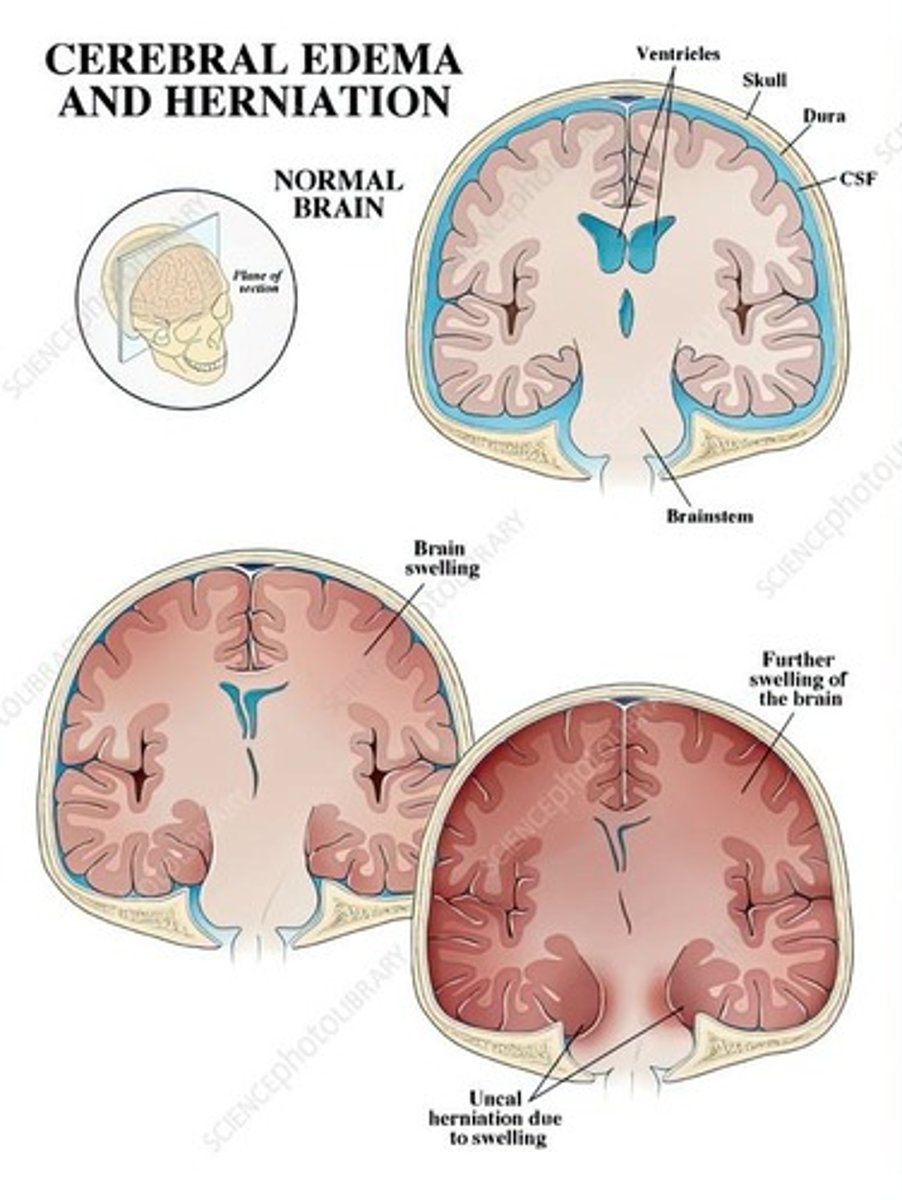
Vasogenic Edema
Fluid accumulation due to capillary wall damage.
Cytotoxic Edema
Fluid accumulation within nervous tissue cells.