unit 5: heredity
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms

diploid cells
• two full sets/pairs of chromosomes
• chromosome pairs differ in size, shape, genetic information, centromere location
• cell contains one set from each parent
• represented by 2n
• ex. skin cells, leaf cells, hypha cell

haploid cells
• cell contains one set of chromosomes
• represented by n
• ex. gametes, sex cells
purpose of meiosis
ensures the formation of haploid gamete cells in sexually reproducing diploid organisms
results of meiosis
four genetically varied daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell

prophase I
• nuclear envelope begins to disappear
• fibers begin to form
• DNA coils into visible duplicated chromosomes made up of sister chromatids
• Double chromosomes pair up based on size, shape, centromere location, & genetic information
• while paired, chromatids exchange genetic information with chromatids from the other chromosome (nonsister chromatids exchange genetic information)

metaphase I
• double chromosomes remain in pairs
• fibers align pairs across the center of the cell

anaphase I
• fibers separate chromosome pairs
• each double chromosome, from the pair, migrates to opposite sides of the cell
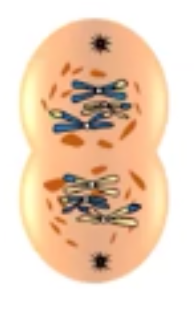
telophase I
• nuclear envelope reappears and establishes two separate nuclei
• each nucleus contains only one double chromosome from each pair
• nucleus only contains half of the total information the parent nucleus contained
• chromosomes will begin to uncoil

cytokinesis I
separates the cell into two daughter cells
daughter cells are haploid and genetically different from each other and the parent

prophase II
• nuclear envelope begins to disappear
• fibers begin to form

metaphase II
• fibers align double chromosomes across the center of the cell

anaphase II
• fibers separate sister chromatids
• chromatids (single chromosomes) migrate to opposite sides of the cell
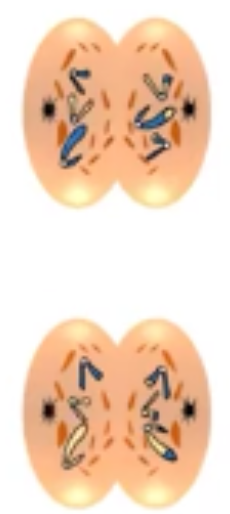
telophase II
• nuclear envelope reappears and establishes separate nuclei
• each nucleus contains single chromosomes
• chromosomes will begin to uncoil
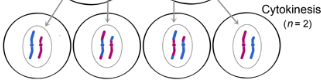
cytokinesis II
separates the two cells into four daughter cells
daughter cells are haploid and genetically different from each other and parent cell
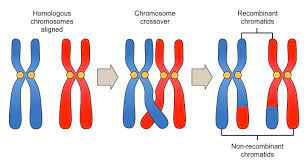
crossing over
prophase I
occurs when nonsister chromatids exchange segments
results in recombinant chromosomes
random assortment of chromosomes
metaphase I
order of homologous pairs affect which chromosmes end up in each gamete
random fertilization
information from each parent is contributed to the fertilized egg
one gamete from each parent fuse together to form a diploid offspring
any gamete can contribute to the diploid nature of genomes in offspring
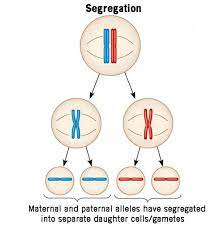
mendel’s law of segregation
• chromosomes carry alleles
• homologous chromosomes carry alleles for the same trait
• when chromosomes are separated into daughter cells during meiosis, the alleles for each trait are also separated
• separation of alleles allows for genetic variation among gametes

mendel’s law of independent assortment
• two or more genes assort independently of each other
• one trait is not automatically inherited with another trait
• alleles for separate traits can be packaged in every possible combination into gametes
gene
unit of heredity coding for a trait; they can be transferred from one generation to the next
trait
a genetically determined characteristic of an organism
allele
a specific variation of a gene; inherited from both parents
dominant allele
always shows in the phenotype if inherited
recessive allele
only shows in the phenotype when the dominant allele has not been inherited
genotype
combination of inherited alleles
homozygous
genotype containing two of the same alleles
heterozygous
genotype containing two different alleles
phenotype
the physical result or expression of the genotype
monohybrid cross
examination of how one trait is inherited
dihybrid cross
examination of how two traits are inherited
pedigree
a visual representation of tracing the history of a trait through familial generations

autosomal dominant trait
shows pattern of affected offspring with affected parents
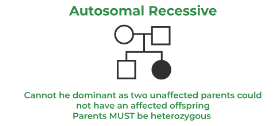
autosomal recessive trait
shows pattern of affected offspring with unaffected parents
chi-square goodness-of-fit test
used to determine if the observed results are significantly varied from the expected results/ if there is a relationship between two groups of data
null hypothesis
states there is no relationship or no difference between two groups of data in an investigation
alternative hypothesis
states the observed results are due to a nonrandom cause
linked genes
genes that are adjacent and close to one another on the same chromosome and that are inherited together; less likely to be separated during crossing over
sex-linked traits
traits that are determined by genes located on sex chromosomes
map distance
• tells you how close together a pair of linked genes is
• determined by how frequently a pair of genes participates in a single crossover event
non-nuclear inheritance occurs in ___ & ___
chloroplasts & mitochondria
traits from chloroplasts and mitochondrial DNA are ___ inherited
maternally
phenotypic plasticity
the ability of one genotype to produce more than one phenotype
cause of phenotypic plasticity
changes in environmental conditions
nondisjunction
the failure of chromosomes to fully separate during the formation of gamtes; results in too many or too few chromosomes in sex cells