Nuclear Chemistry
1/27
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
nuclear fission
bombard the nucleus with neutrons, splits nucleus into smaller fragments; releases energy
nuclear fission chain reaction
neutrons are also products of this reaction and can be used to start another reaction
nuclear fusion
light mass nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus
example of nuclear fusion
hydrogen bomb, sun
why is nuclear fusion better than fission?
generates more energy and doesn’t produce radioactive substance
what type of reactions do nuclear power plants use?
nuclear fission
nuclear half life
time required for half the atoms of a particular radioisotope to decay into another isotope
half life formula
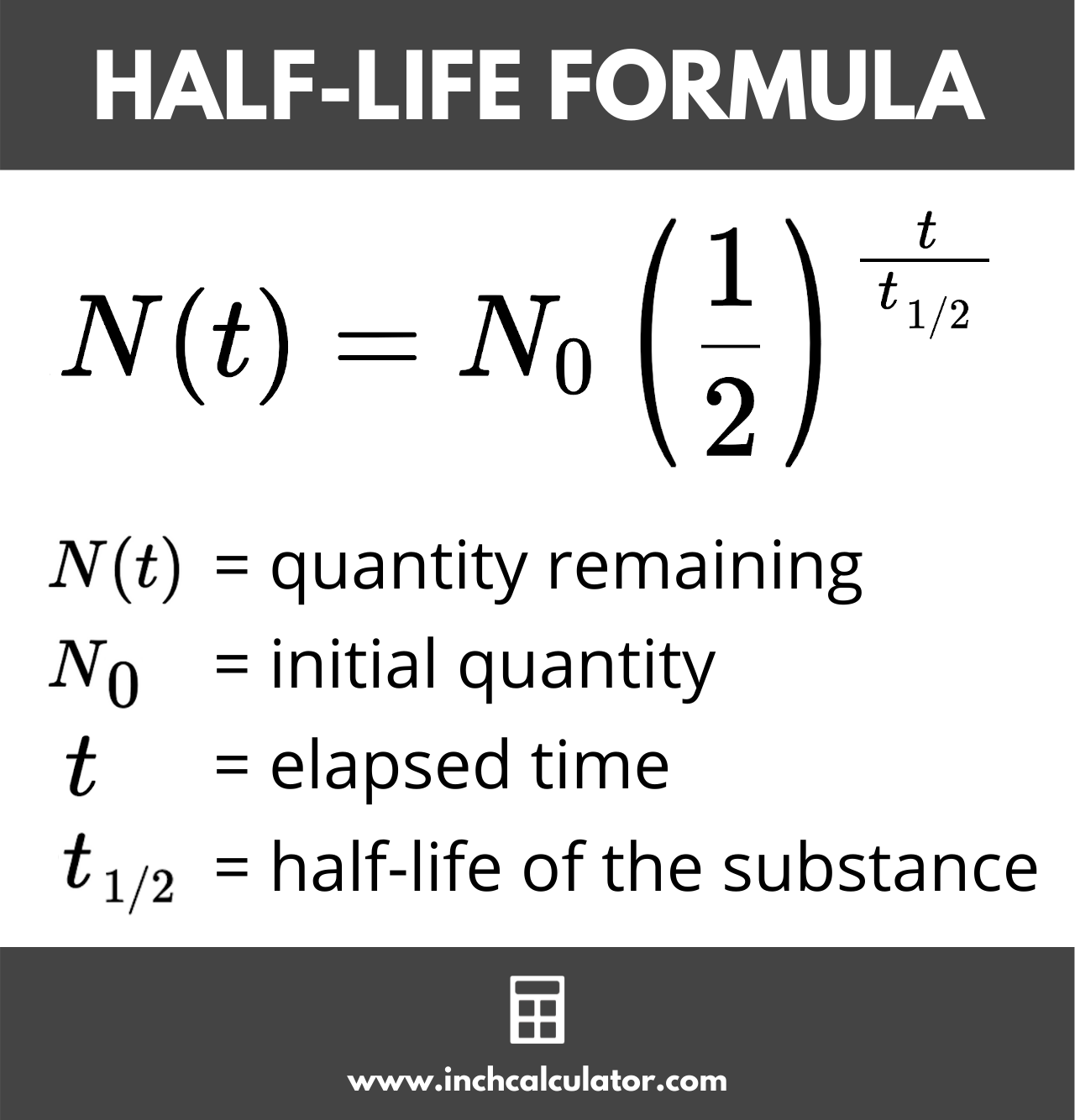
The half life of cobalt-60 is 10.47 minutes. How much cobalt is remaining after 180 minutes starting with 2000 grams?
0.01 grams left
radioactive decay
spontaneous disintegration of nucleus into slightly lighter nucleus accompanied by emission of particles, electromagnetic radiation, or both
alpha decay
releases α particle, or a helium nucleus (42He)
what blocks alpha rays?
paper
beta decay
loss of β- particle (high energy electron); neutron turns into proton, emits electron (0-1e)
what blocks beta rays?
metal foil
gamma decay
loss of γ high-energy radiation (00γ), usually occurs immediately following other types of decay
what blocks gamma rays?
lead/concrete
what is the most dangerous radiation?
gamma rays
positron/beta plus decay
proton converted to a neutron, and a positron + neutrino is sent out (don’t need to show neutrino)
neutrino
“ghost particle” has no mass or charge
positron
anti matter equivalent of an electron
neutron emission
one or more neutrons are ejected from a nucleus; atom becomes a different isotope
band of stability
diagram that plots N (neutrons) vs Z (protons) to show stability of known elements
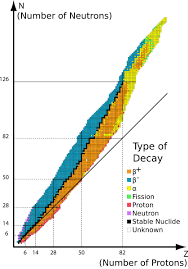
for which elements is the N:Z ratio about 1:1?
elements with less than 20 protons
when do elements undergo beta decay?
when the dot is above the band of stability (more neutrons, less protons)
when do elements undergo positron decay?
when the dot is below the band of stability (less neutrons, more protons)
when do elements undergo alpha decay?
for elements with 82+ protons
how does a pressurized water reactor work?
it uses nuclear fission to heat up water that turns into steam and drives a turbine to generate electricity
what do control rods do?
control chain reactions by absorbing neutrons