APES Final Terms I do not know
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Nitrogen Fixation
78% of earth is Nitrogen but to be used by other organisms nitrogen must be fixed into ammonia or nitrates which can happen by lightning storms/soil bacteria to be made biologically available
Nitrification
Second step when soil bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and then to one of the forms that can be used as plants called nitrate
Assimilation
plants absorb ammonia, amonia ions, and nitrate ions through their roots and then heterotrophs recieve energy by consuming other organisms then obtain nitrogen when they consume plants’ proteins and nucleic acids
Ammonification
decomposing bacteria step 4 convert dead organisms into ammonia or ammonium ions which are reused by plants or volatized into the atmosphere
Denitrification
In denitrification specialized bacteria (anaerobic) convert amonia back into nitrites and nitrates and then into nitrogen gas and nitrous oxide gas to go back into the atmosphere #5
Phosphorus found in
soil/rock/sediments through chemical weathering, symbiotic relationship between fungi and plants and phosphorus is a limiting factor which controls the population growth becayse it is needed for plant growth.
Terrestrial cycle
movement of essential elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and water within land based ecosystems
Eutrophication
When a body of water receives excess nutrients (BAD)
how do organisms get sulfur
plants get sulfur in the water through their roots while animals eat plants that have sulfur.
Autotrophs
capable of making their own organic compounds from inorganic chemicals
heterotrophs
get food energy from eating other organisms or products created by them
chemotrophs
chemosynthetic organisms found in hydrothermal vents deep in the ocean
Net primary productivity
amount of energy plants give to the herbivores in an ecosystem found by taking the GPP - amount of energy plants use it is a limiting factor for it’s consumers
GPP
amount of sugar the plants produce in photosynthesis
Detritivores vs. Decomposers
Detri. physically eats dead organisms to get energy such as termites while Decom. chemically breakdown by releasing enzymes.
Species Richness
number of different species found in an ecosystem
Law of Tolerance
degree to which organisms are capable of tolerating changes in the environment (basis of evolution)
Law of the minimum
Living organisms will continue to live eating anything available until there is nothing left
Provisioning services
category benefits that humans recieve which provide humans with water/food medicine energy etc.
Regulating services
waste decomposition and detoxification, purification of water and air
cultural services
use of nature for science/education/recreation
supporting services
ones that make other services possible ex. primary production, nutrient cycling etc.
Indicator Species and Keystone Species
Species used as a standard to evaluate the health of an ecosystem ex: trout subject to polution disease so if they dissapear there is a pollutant and Keystone species whos existence allows diversity of other animals/the ecosystem would drastically change.
Primary succession
starts on bare rock with no soil after severe events
secondary succession
existing soil with nutrients and seeds/roots from a previous community
Pioneer species
first organism to have wide ranges of ecological tolerance
climax community
final stage of succession in which balance between abiotic/biotic components referred to as the climax community
Lichens
pioneer organisms that take bare rock and turn it into soil
Habitat fragmentation
development isolates a habitat into parts and isolates ecosystems
edge effect
more species live on the edge of with more biological and species diversity than inside of it
ecotones
overlapping boundaries of two ecosystems
selective pressure
any cause that reduces reproductive success/fitness in a population
genetic drift
random changes in the frequency of gene variants/alleles driven by chance and not by fitness
Ecological extinction
so few individuals of a species that this species can no longer perform it’s ecological function (what it gives to the ecosystem)
Commercial/economic extinction
few individuals of the population DO exist but the effort and cost it take to hunt them down is not worth the expense
Gause’s principle
no two species can occupy the same niche at the same time and the species less fit will die/move out
realized niche
move to occupy a smaller niche than it would in absense of competiion they compromise size
resource partitioning
different species use slightly different parts of the habitat
ecozones or ecoregions are
geographic areas that have similar land and climate
Decidious forest
75-250cm rainfall hardwood trees
Grasslands
Sod forming grasses (think plantation) 10-60cm rain
Conficerous forest (taiga)
20-60 cm cpnficerous trees

Savanna
10-30 during rainy season and has grasses with widely spaced trees
epilimnion
uppermost oxygenated layer of freshwater
hypolimnion
lower colder denser layer of freshwater
thermocline
line between these two layers that is when the temperature shifts dramatically
Littoral zone
very shallow water at the shoreline and plants/animals that live here get lots of sunlight LIT zone includes the species that go back and forth to shore like turtles
Limnetic Zone
open sunlit surface of a freshwater body away from the shore, where photosynthetic organisms live
Profundal zone
water deep enough that sunlight cannot penetrate through it where photosynthetic plants cannot live and organisms have adapted to little light and cold temp
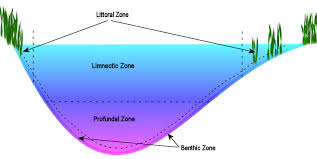
Benthic Zone
surface and sub layers of the river, lake, and pond, are characterized by very low temperatures and low oxygen levels inhabited by organisms that live on/below SEDIMENT surface
estuary
mouth of ocean meets river
barrier islands
created by buildup of deposited sediments and their boundaries are constantly shifting as water moves around them
Euphotic Zone
similar to the limnetic zone in freshwater but in salt water it is the upper warm layers of the ocean with the highest level of dissolved oxygen
Bathyal Zone
middle region colder and darker and does not have enough sunlight to promote photosynthesis similar to the profundal zone inhabited by sharks/whales
Abyssal zone
deepest region of the ocean extremely cold temperatures high levels of nutrients organisms live off of bioluminescence
commensalism
one benefits while the other does not benefit nor get harmed
lithosphere vs. pedosphere
Lithosphere is solid rocky outer layer of earth including earths crust and UPPERMOST mantle while the pedosphere is the soil layer at earth’s surface and forms where each of the four spheres interact key in nutrient cycling essentially lithosphere below surface while pedosphere is at surface.
Exosphere
above 500km highest absolutely thinnest gases
Thermosphere
2nd to highest 80-500km gases very thin and where northern lights take place
Mesosphere
middle region meteors burn here 3
Stratosphere
20-50km temperatures increase with distance from earth holds crucial ozone layer which shields earth by absorbing most UV radiation
ozone layer
17-30km 2nd to closest to earth O3 thin band of O3 traps radiation from the sun
troposphere
closest layer to earth where weather takes place
chemical weathering
result of chemical reactions to rock with water air or dissolved materials and results in minerals that are broken down or restructured into different minerals this tends to dominate in warm enviorments EX rust when iron touches water
Biological weathering
weathering that happens because of physical or chemical means through activities of LIVING organisms like when trees gain cracks as they grow bigger
Rock cycle is what interacting
time pressure and heat
Igneous
when rock is melted by heat and pressure below the crust and then cooled into solid igneous rock from molten lava ex. basalt
Sedimentary
formed as sediment when eroded rocks and remains of plants and animals builds up and gets compressed forms under water as sediments on ocean floor compressed and then cemented together example limestone
Metamorphic
formed by pressure and heat which causes physical/chemical changes to an existing rock when sedimentary rocks sink deeper into the earth and are heated by high temperatures in the earth’s mantle ex: slate from shale.