Exam 2 - study guide
1/131
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
What are we made of?
all organisms are made of cells
Eukaryotic cells
Protists, fungi, animal, plants
DNA in nucleus that is bounded by a membranous nuclear envelope
membrane bound organelles
cytoplasm in the region between plasma membrane and nucleus
(generally larger)
Prokaryotic cells
Bacteria and Archaea
No nucleus
DNA in unbound region called nucleoid
no membrane bound organelles
cytoplasm bound by the plasma membrane
all cells
plasma membrane
semifluid substance called cytosol
chromosomes (carry genes)
ribosomes
Plasma membrane
selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell
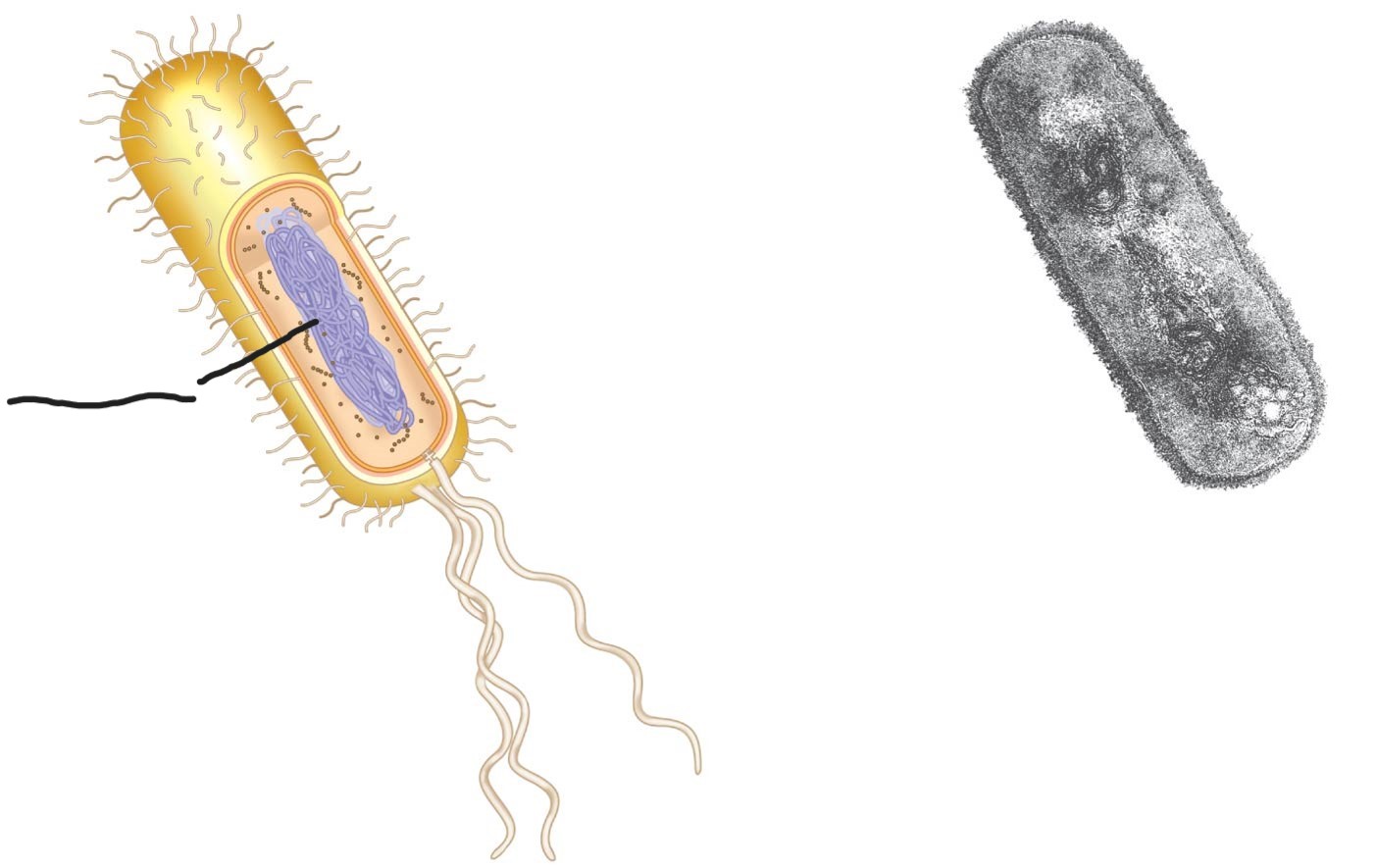
What is this (typical rod-shaped bacterium)
bacterial chromosome
Bacterial chromosome
to carry the genetic information for that species of bacteria
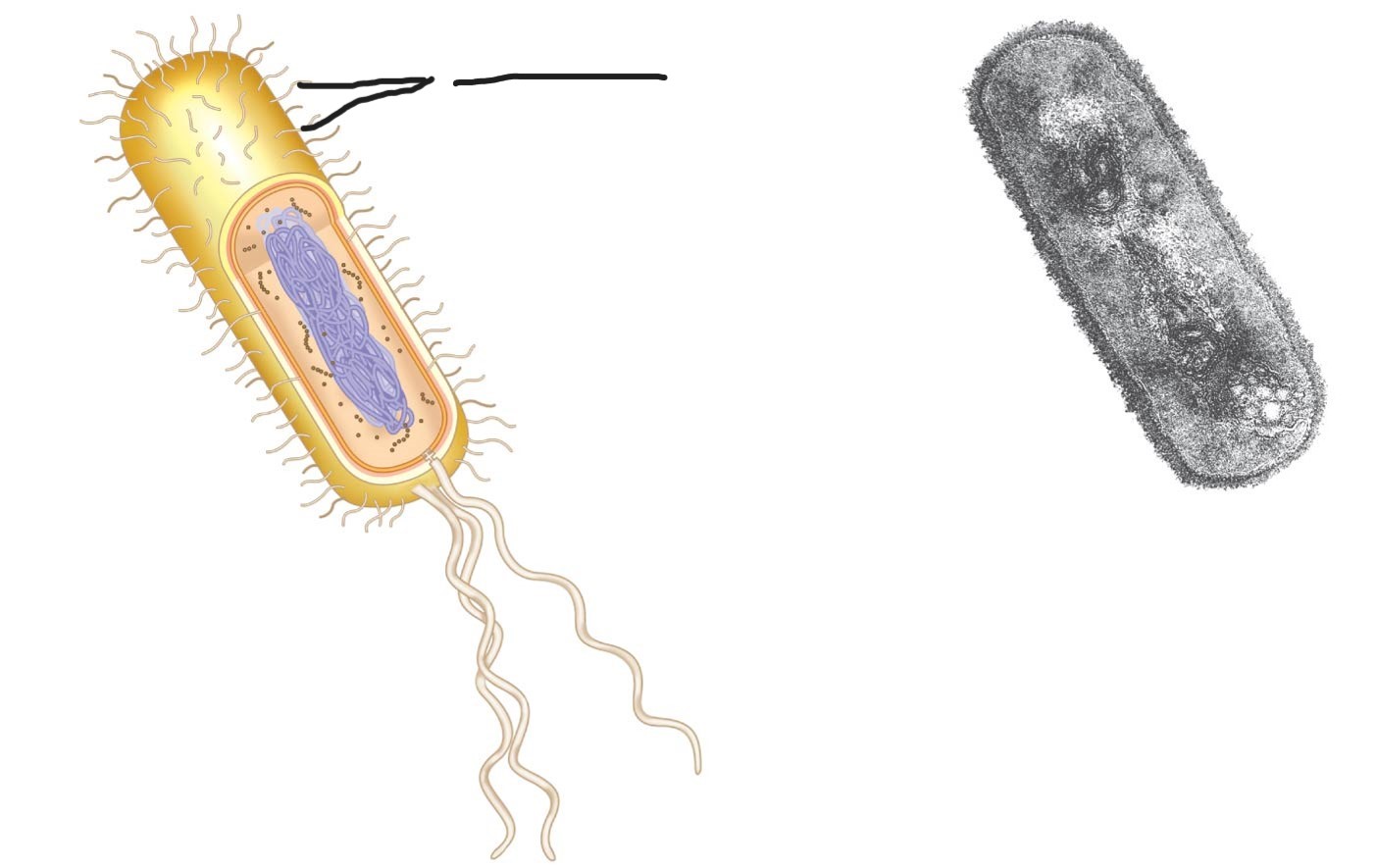
what is this (a typical rod-shaped bacterium)
fimbriae
Fimbriae
enable the bacteria to bind to specific receptor structures and thereby to colonise specific surfaces
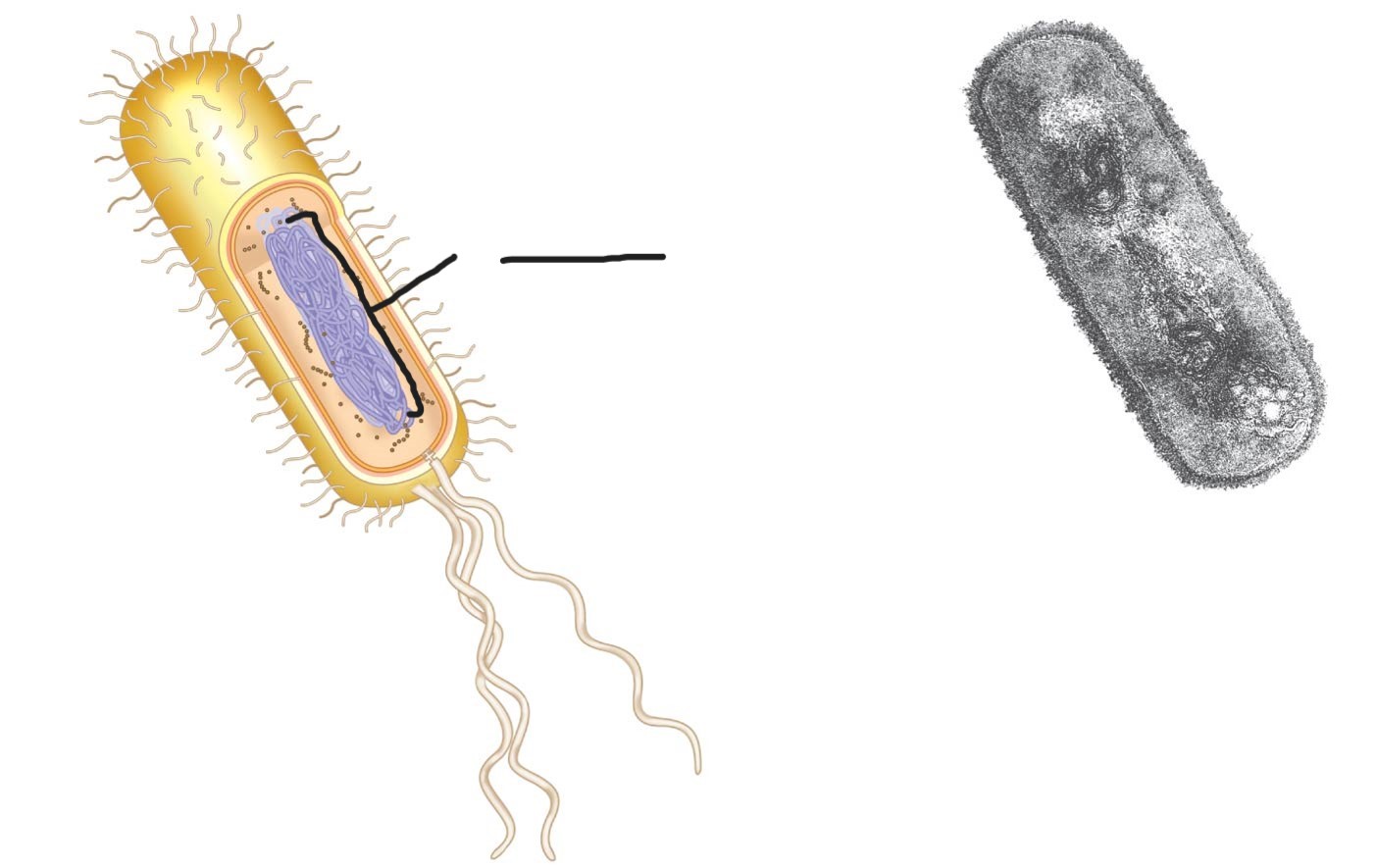
what is this (a typical rod-shaped bacterium)
Nucleoid
nucleoid
regulates the growth, reproduction, and function of the cell
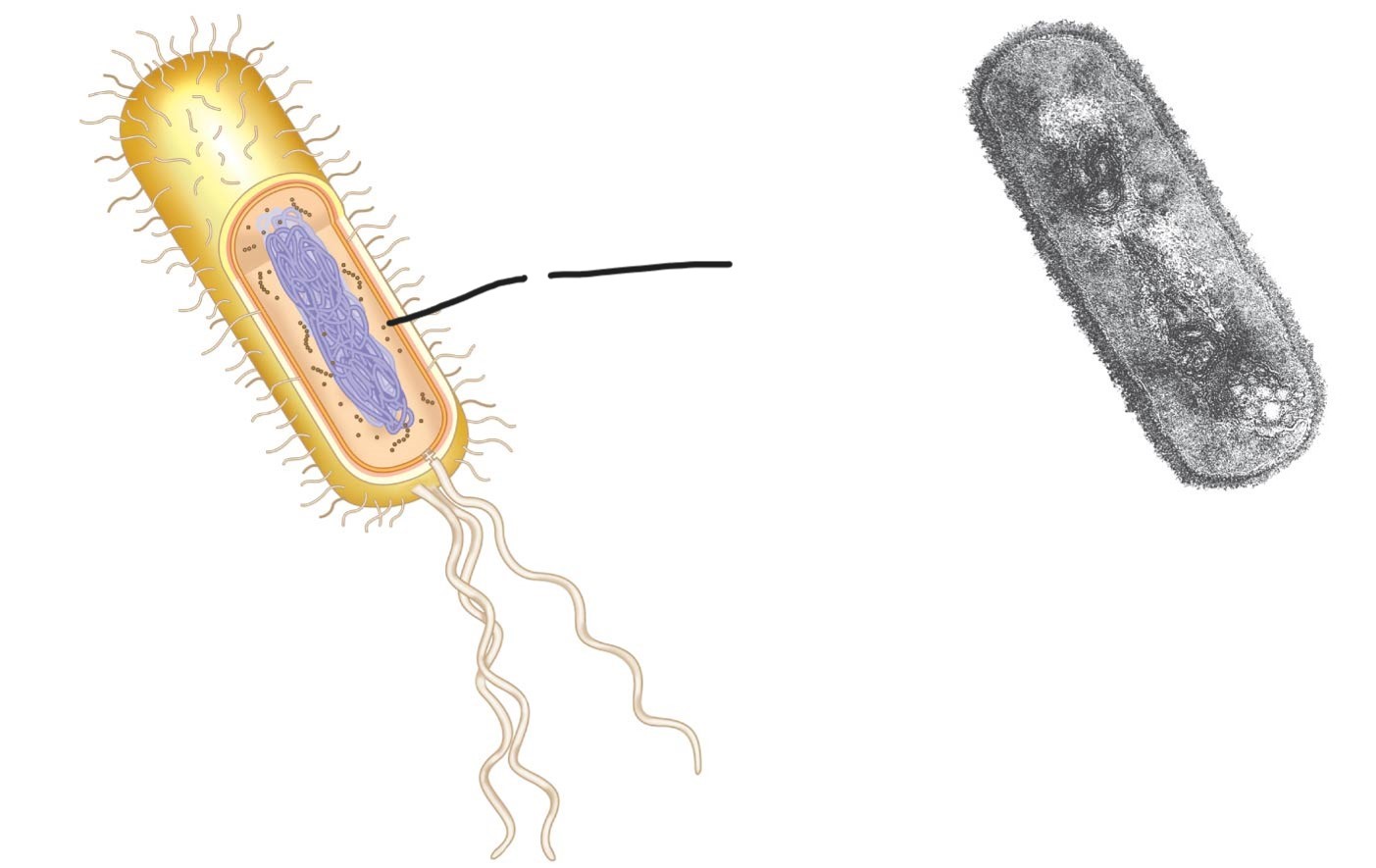
what is this (a typical rod-shaped bacterium)
Ribosome
ribosome
intercellular structure made of both RNA and protein, and it is the site of protein synthesis in the cell
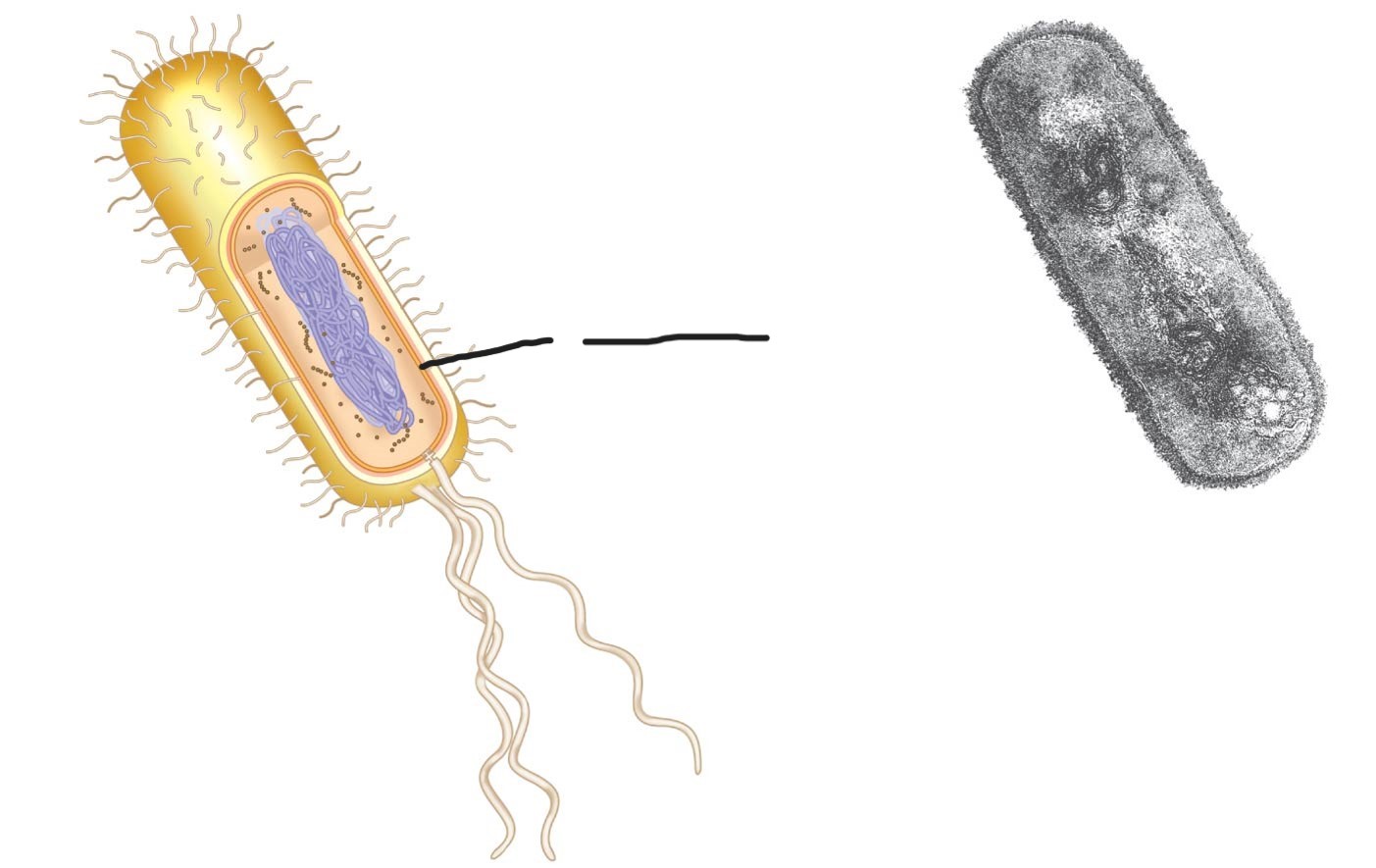
what is this (a typical rod-shaped bacterium)
Plasma membrane
plasma membrane
provides protection for a cell
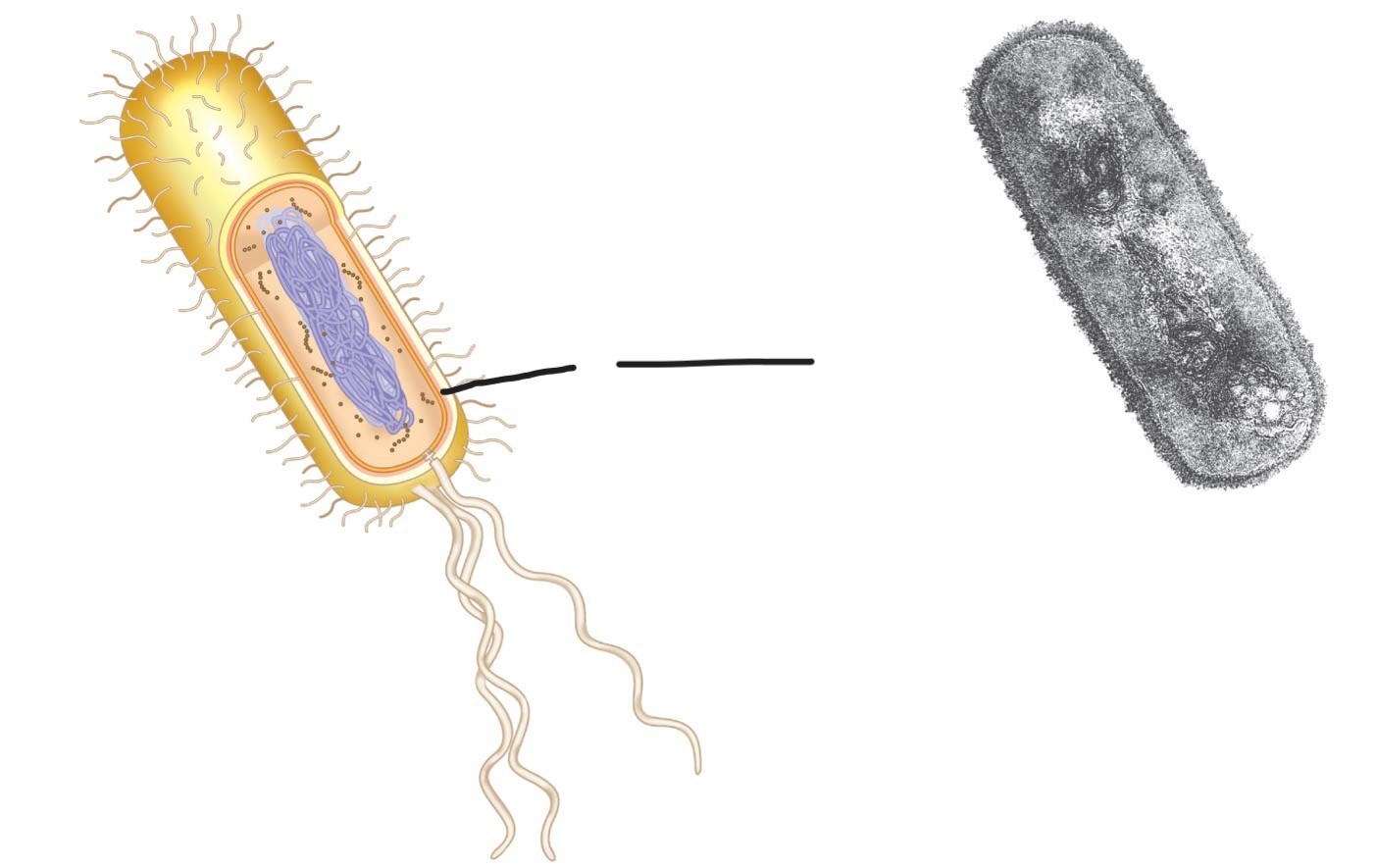
what is this (a typical rod-shaped bacterium)
cell wall
cell wall
surrounds the plasma membrane of plant cells and provides tensile strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress
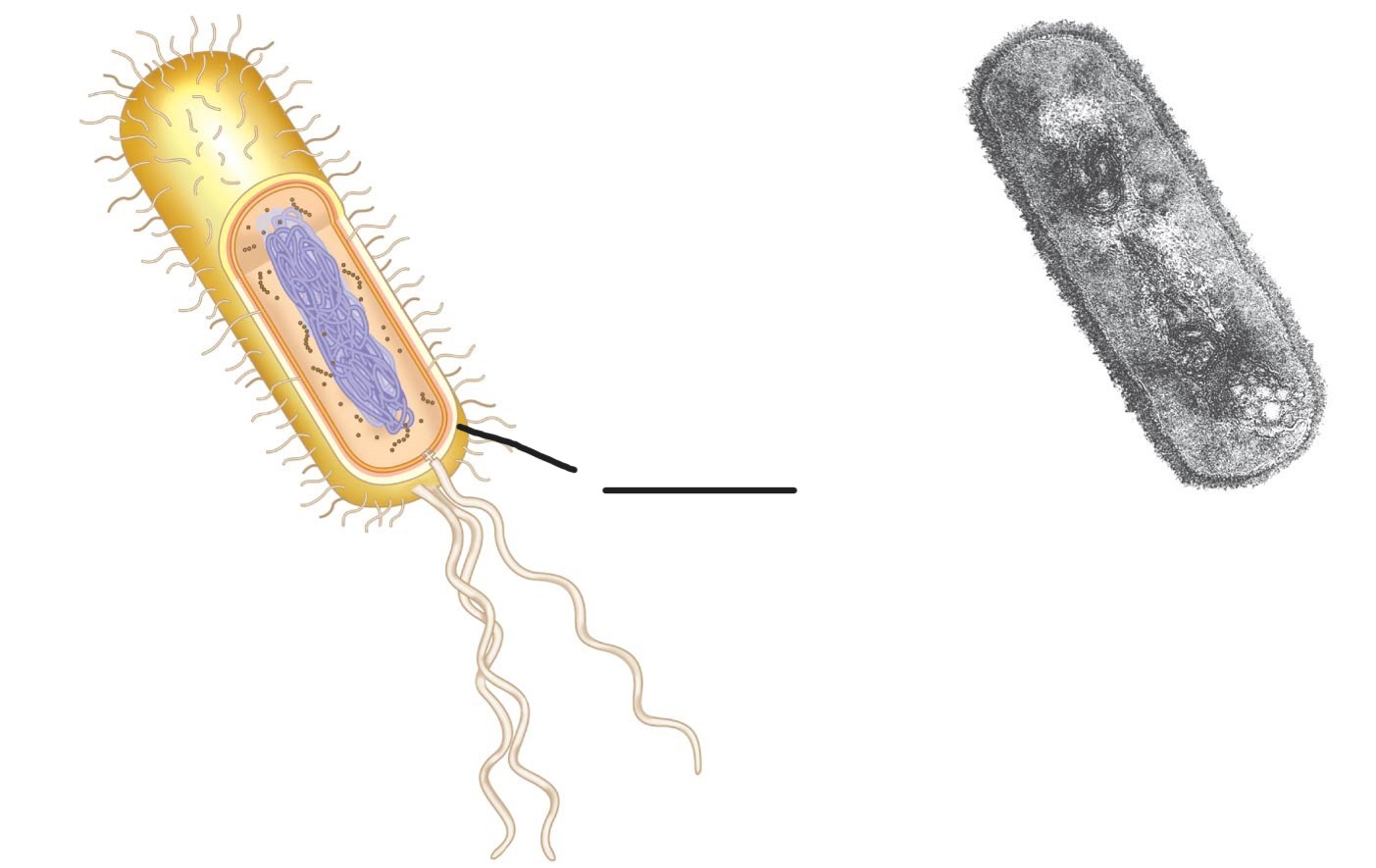
what is this (a typical rod-shaped bacterium)
capsule
capsule
protecting bacteria from toxic compounds and desiccation and allowing them to adhere to surfaces and to escape the immune system of the host
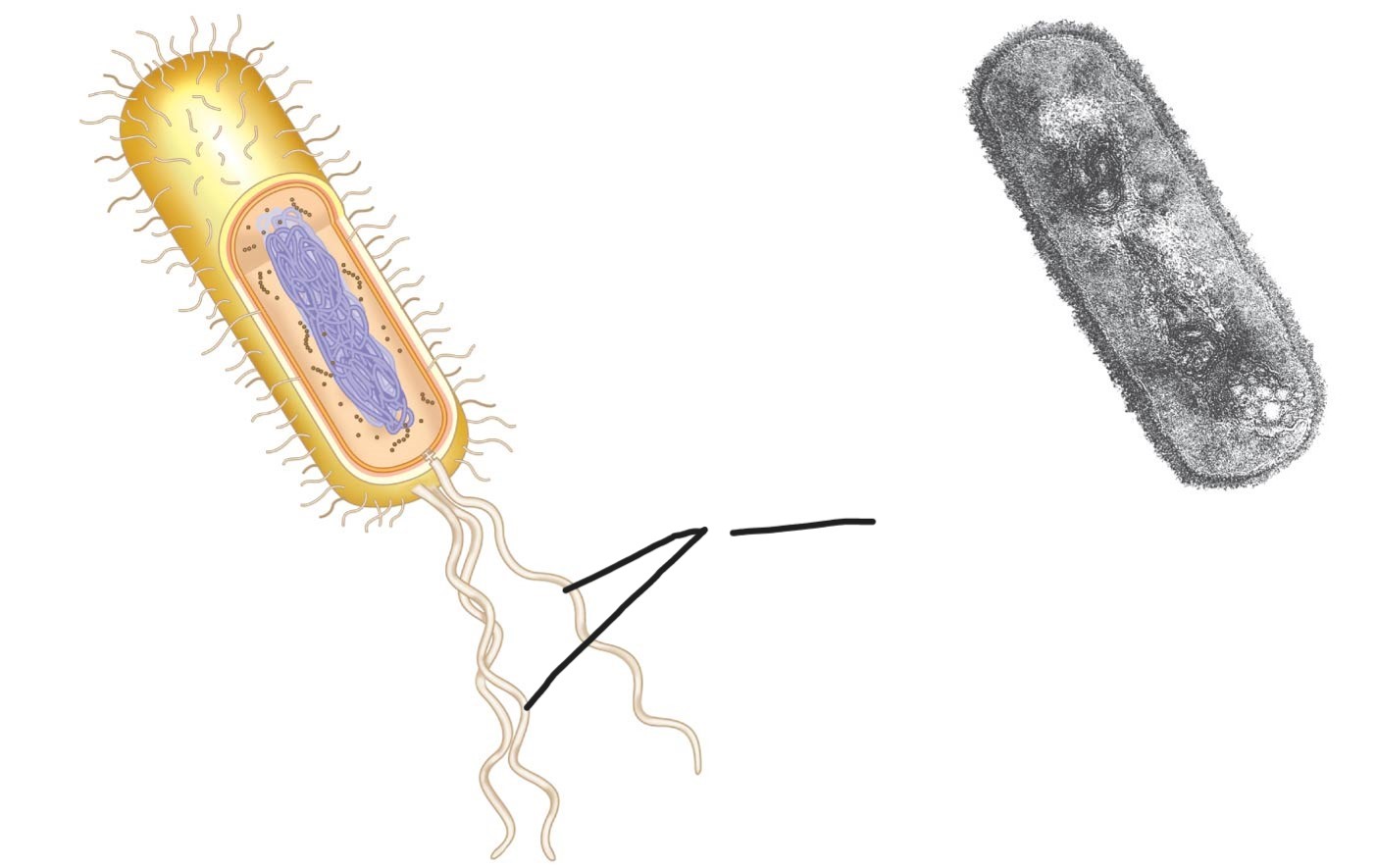
what is this (a typical rod-shaped bacterium)
Flagella
flagella
microscopic hair-like structures involved in the locomotion of a cell
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes
synthesizes lipids
metabolizes carbohydrates
detoxifies drugs and poisons
stores calcium ions
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) biosynthetic factory
ER membrane is continuous with the nuclear envelope
there are two distinct regions of ER
Smooth and Rough
Rough ER
surface is studded with ribosomes
Has bound ribosomes, which secrete glycoproteins (proteins covalently bonded to carbohydrates)
distributes transport vesicles, proteins surrounded by membranes
is a membrane factor for the cell
Endomembrane system
Nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
vacuoles
plasma membrane
(components are either continuous or connected through transfer by vesicles)
nuclear envelope (endomembrane system)
separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm and provides the structural framework of the nucleus
endoplasmic reticulum (endomembrane system)
Accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
continuous with nuclear envelope
two distinct regions: smooth ER and rough ER
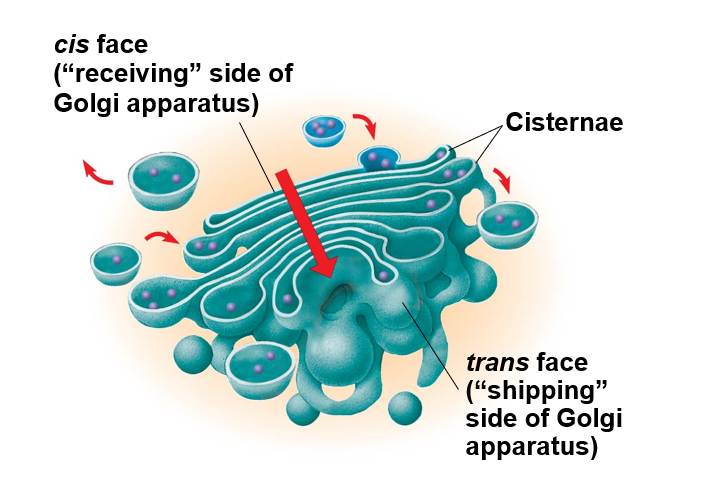
golgi apparatus (endomembrane system)
consists of flattened membranous sacs called Cisternae
Functions:
modifies products of the ER
manufactures certain macromolecules
sorts and packages material into transport vesicles
lysosomes (endomembrane system)
a membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules
the enzymes can: hydrolyze proteins, fats, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids
work best the acidic environment inside the lysosome
vacuoles (endomembrane system)
large vesicles derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus
certain vacuoles in plants and fungi carry out enzymatic hydrolysis like lysosomes
helps in storage of salts, minerals, pigments and proteins within the cell
plasma membrane (endomembrane system)
provides protection
phagocytosis
one cell engulfing another cell forming food vacuole
contractile vacuoles
pump excess water out of cell
central vacuoles
hold organic compounds and water
ribosome
bound to ER, free in cytosol
site of protein synthesis in cell
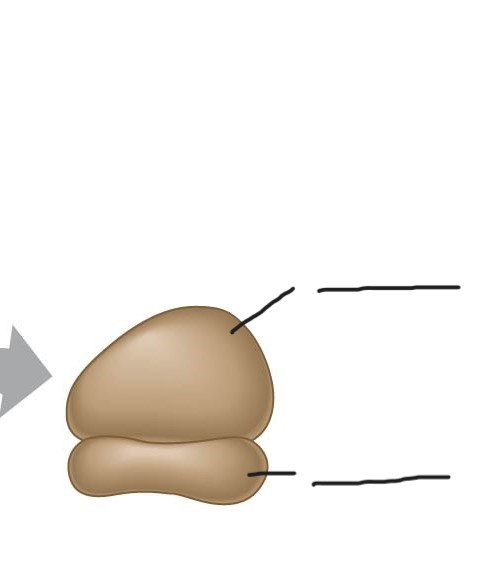
Ribosome
Top: large subunit
bottom: small subunit
Mitochondria
sites of cellular respiration
(metabolic process that uses oxygen to generate ATP)
Chloroplasts
sites of photosynthesis
(contain chlorophyll, enzymes, other photosynthesis molecules)
Mitochondria chloroplasts (and bacteria)
enveloped by a double membrane
contain free ribosomes and circular DNA molecules
grow and reproduce somewhat independently in cells
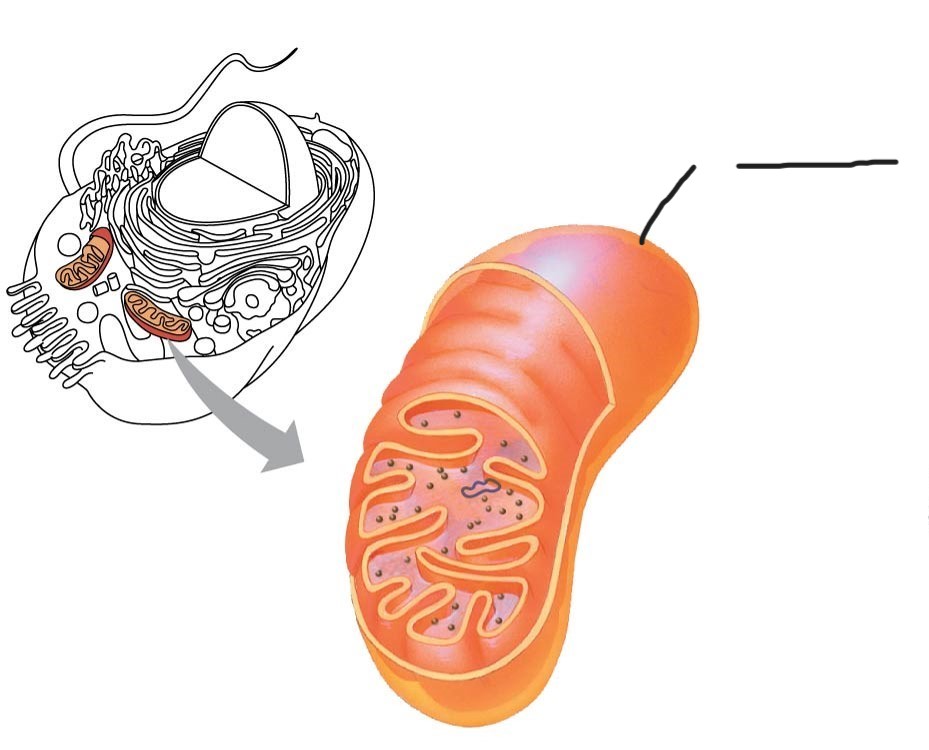
1 Mitochondrion
Outer membrane
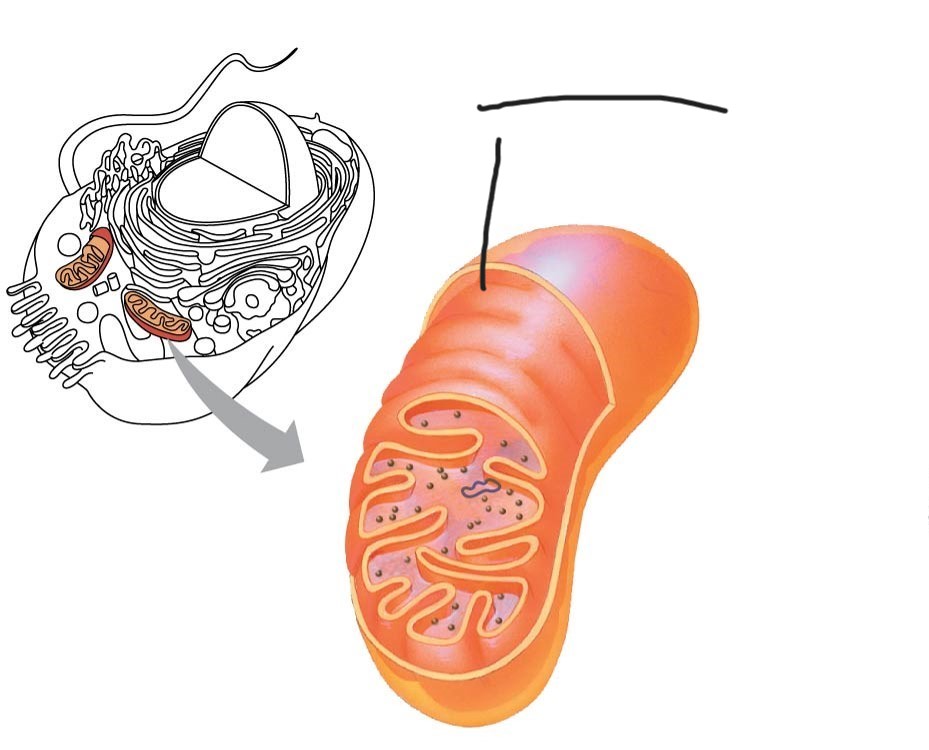
2 Mitochondrion
intermembrane space
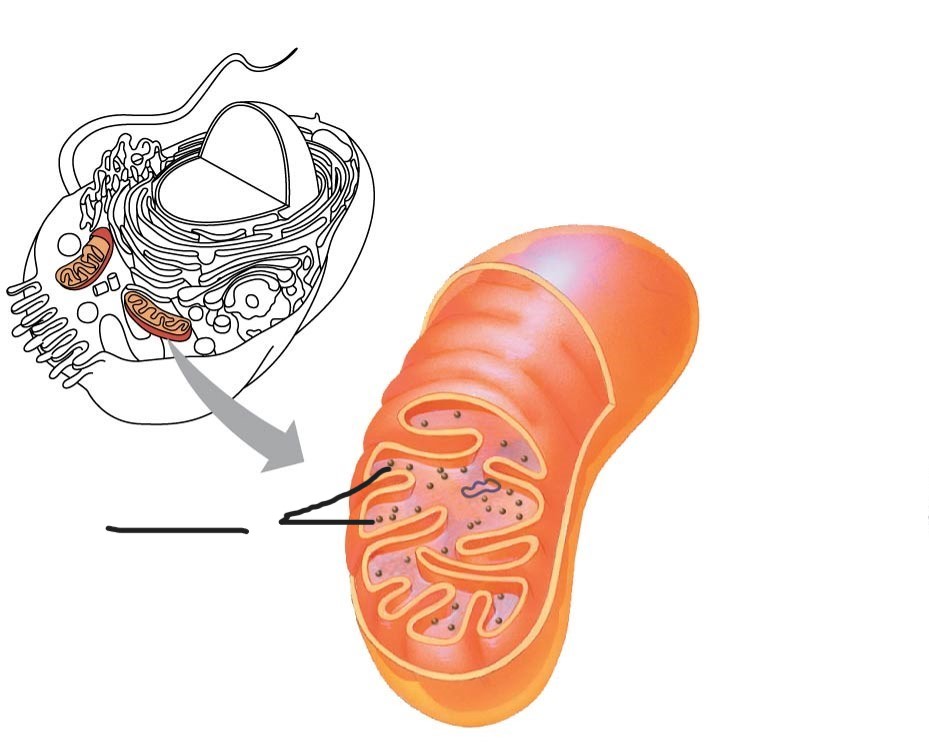
3 Mitochondrion
Free ribosomes in the mitochondrial matrix
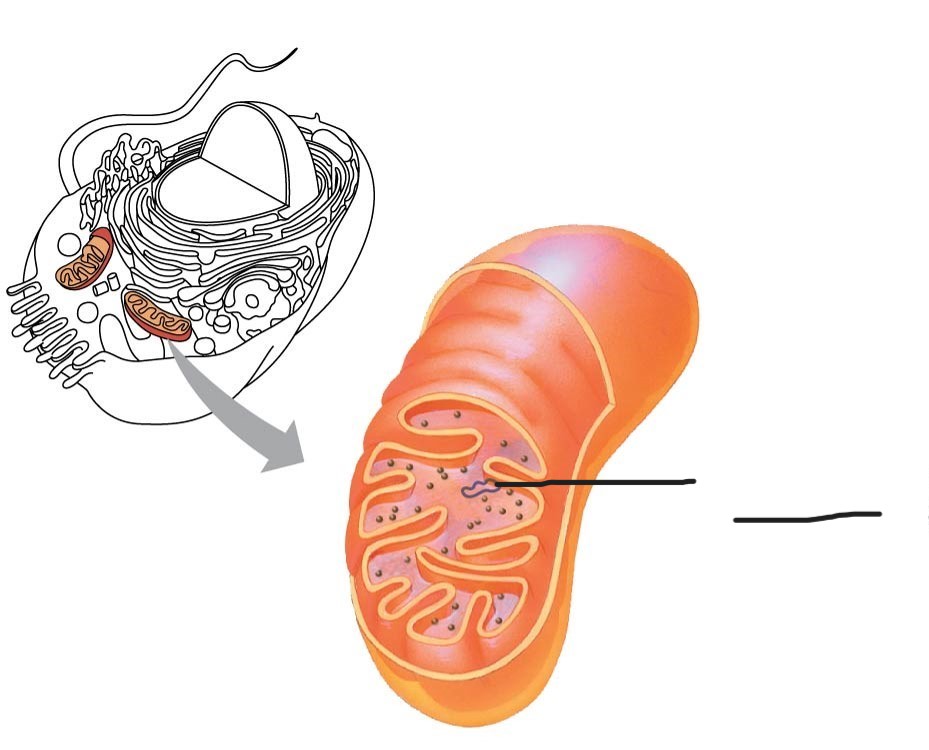
4 mitochondrion
DNA
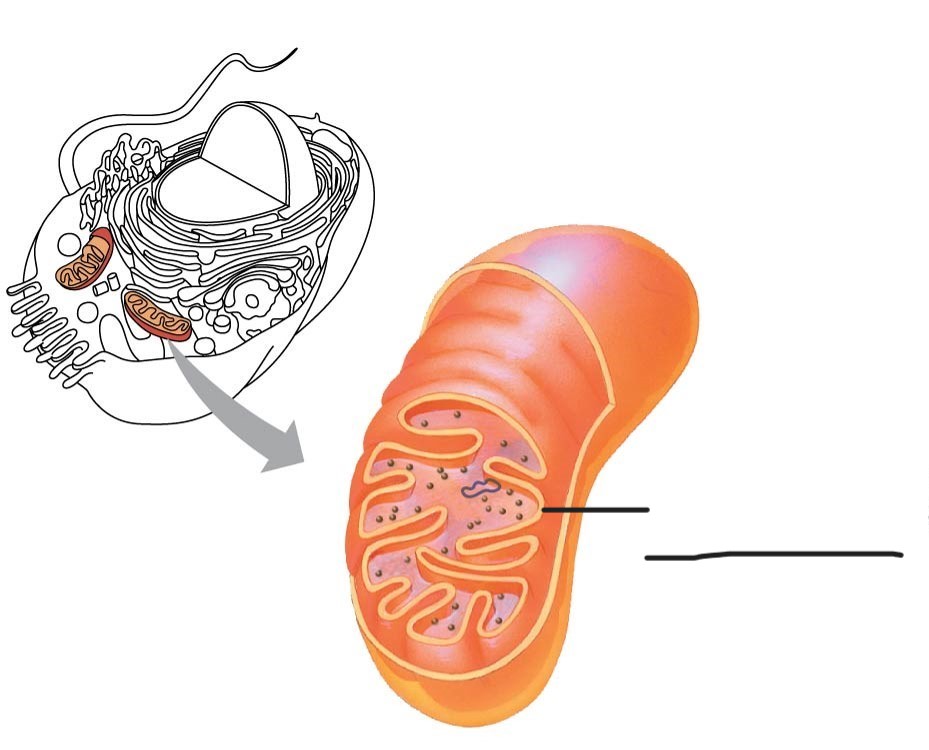
5 Mitochondrion
inner membrane
(creates intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix)
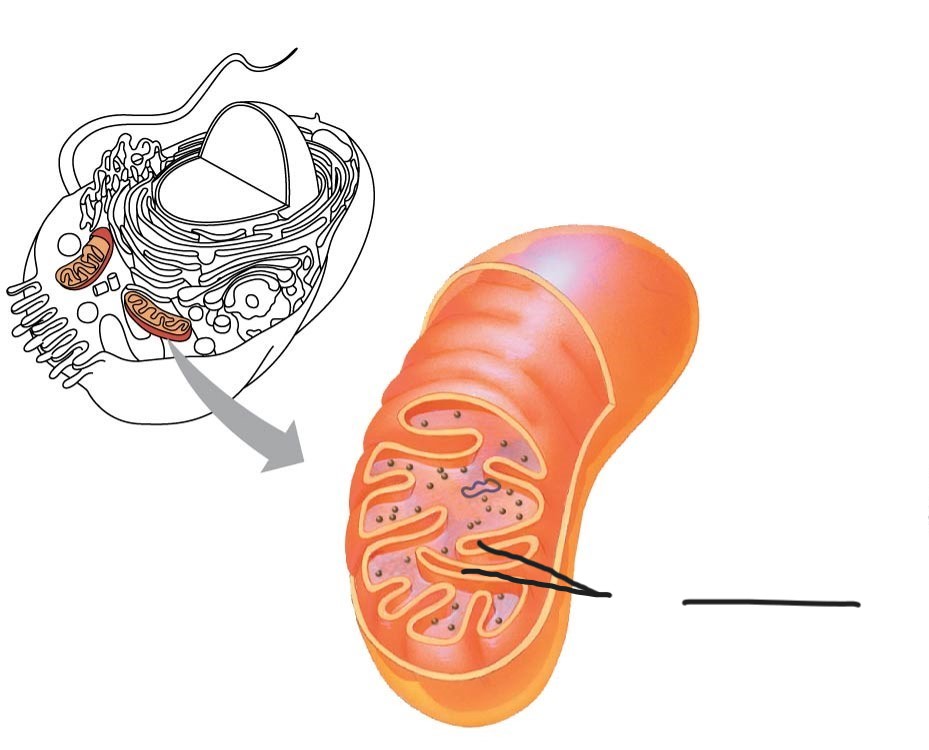
6 Mitochondrion
Cristae
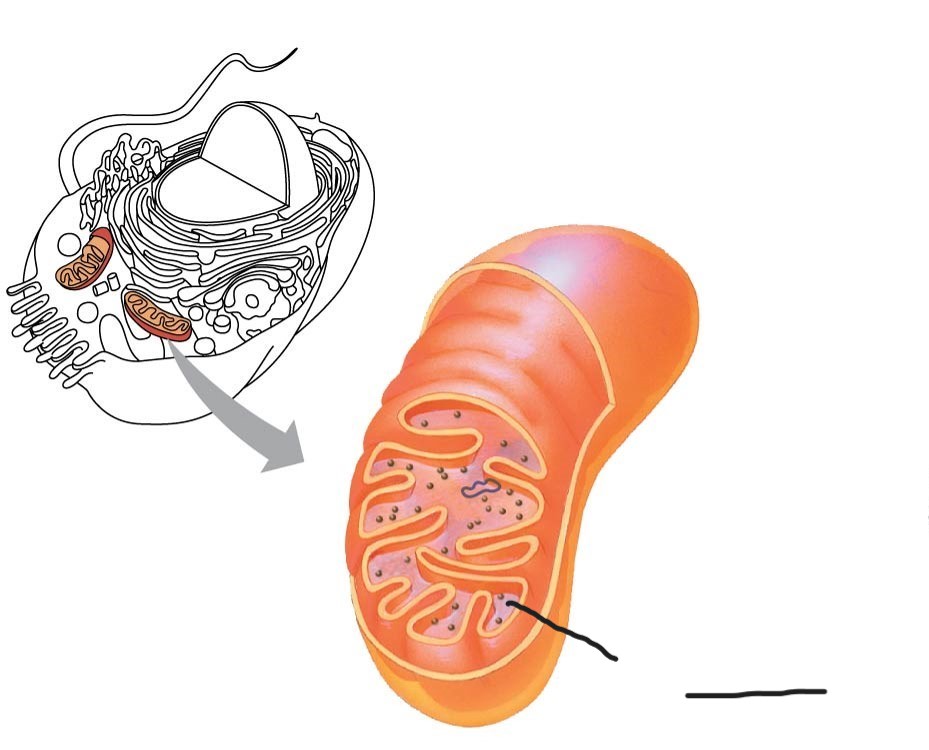
7 Mitochondrion
Matrix
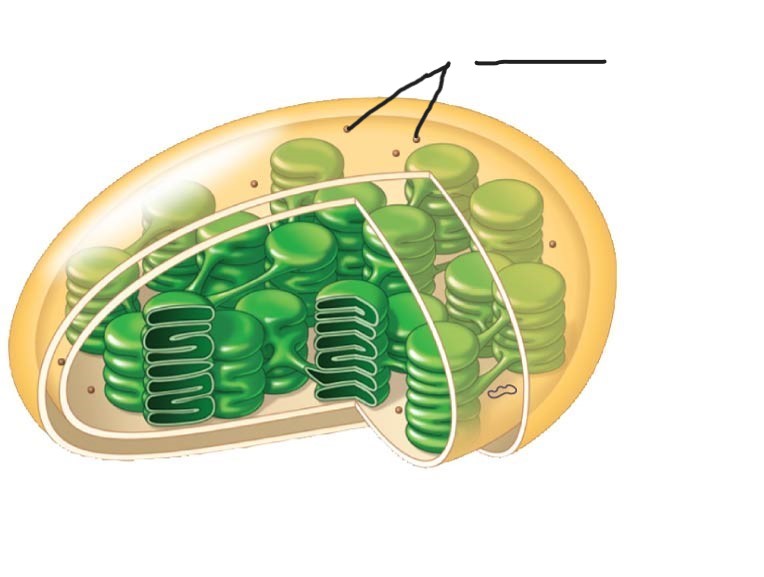
Chloroplast
Ribosomes
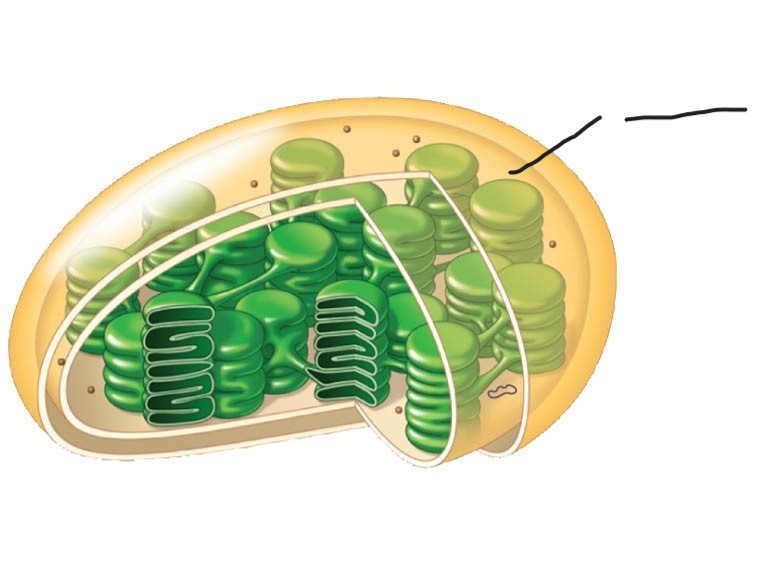
2 Chloroplast
Stoma
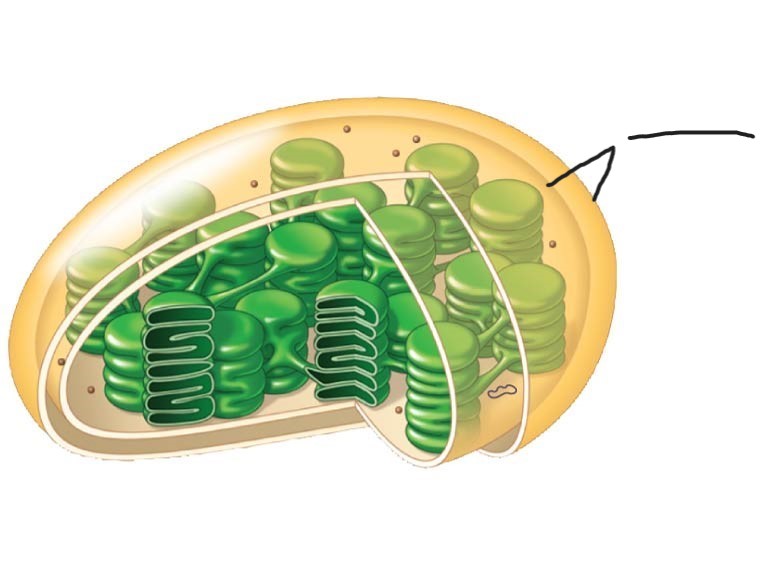
3 Chloroplast
Inner and outer membranes
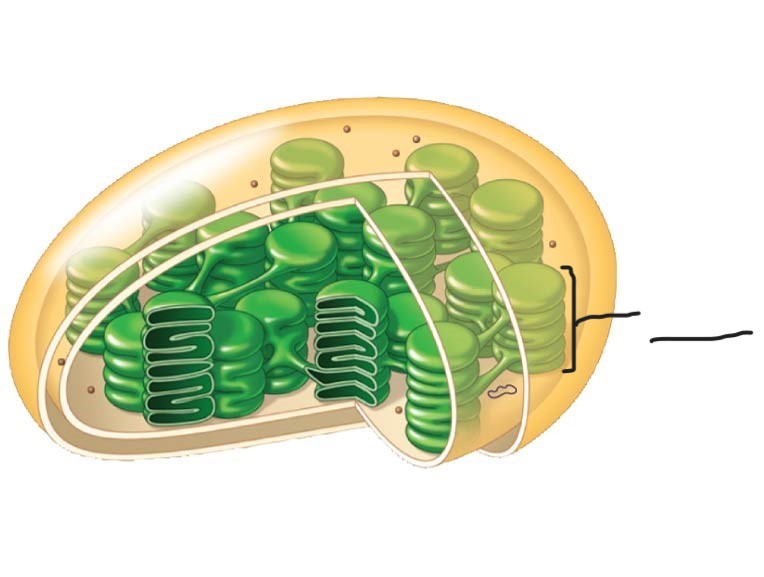
4 Chloroplast
Granum
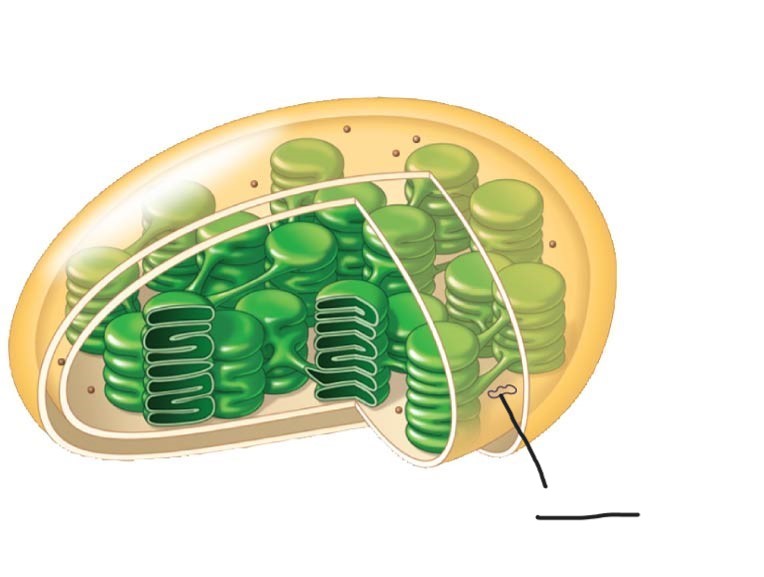
5 Chloroplast
DNA
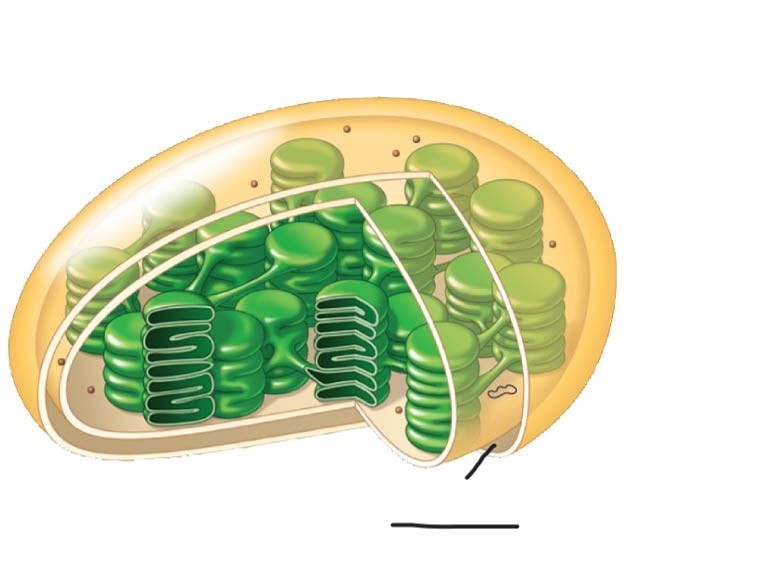
6 Chloroplast
Intermembrane space
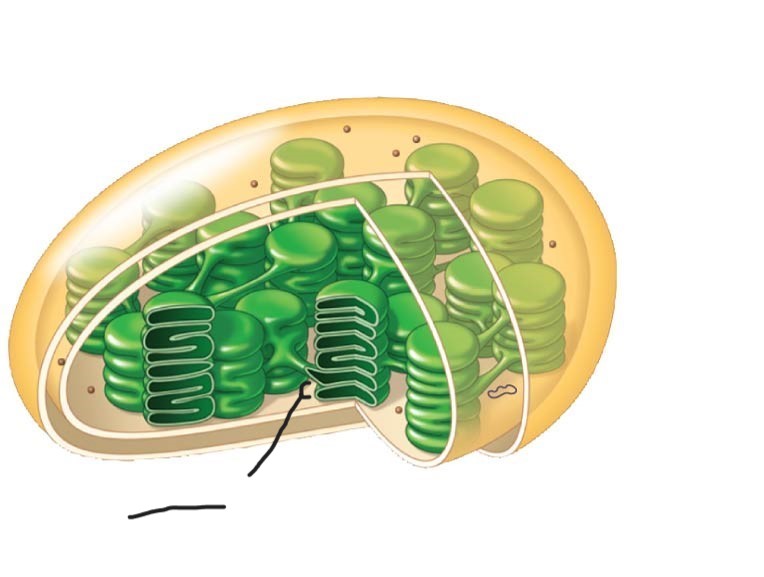
7 Chloroplast
Thylakoid
thylakoid
membranous sacs, stacked to form granum
stoma
internal fluid
Cytoskeleton
network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm
organizes cells structures and activities, anchoring many organelles (helps to support cell and maintain its shape)
interacts with motor proteins to provide mobility (vesicles can “walk” along tracks provided by it
3 types of fibers make up cytoskeleton
Microtubules - thickest
microfilaments - (actin filaments) thinnest
intermediate filaments - middle
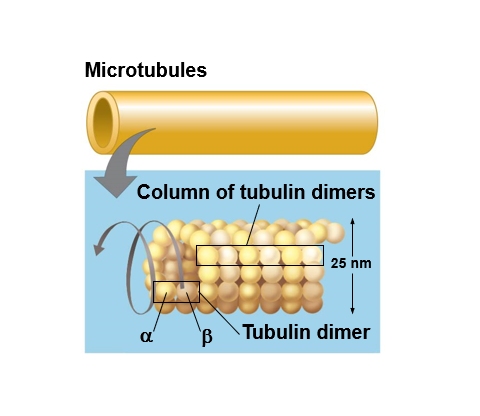
Microtubules
hollow rods constructed from globular protein dimers called tubulin
Functions
shape and support cell
cell mobility (cilia or flagella)
guide movements of organelles
separate chromosomes during cell division
microtubules (tubulin polymers)
hollow tubes; wall consists of 13 columns of tubulin molecules
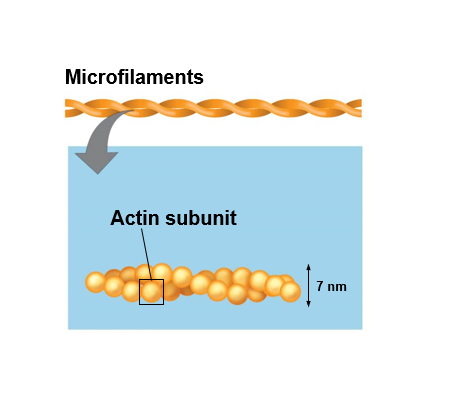
Microfilaments
thin solid rods, built from molecules of globular actin subunits (bundles make up intestinal cells)
structural role: bear tension, resisting pulling forces within cell
Function:
maintain cell shape
changes in cell shape
muscle contraction
cytoplasmic streaming in plants
cell mobility
division of animal cells
microfilaments (actin filaments)
two intertwined strands of actin each a polymer of actin subunits
Intermediate filaments
fibrous proteins supercoiled into thicker cables
Functions:
maintains cell shape
anchors nucleus and other organelles
formation of nuclear lamina
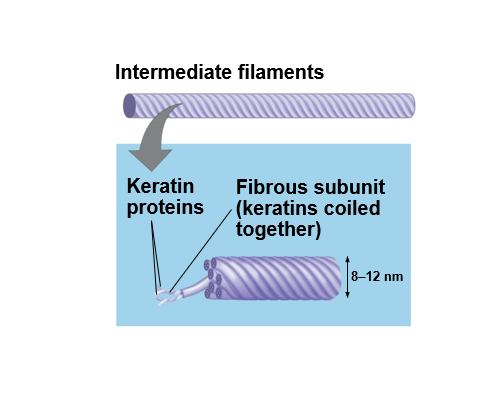
Intermediate filaments (keratin fibers)
Fibrous proteins supercoiled into thicker cables
(only animal cells have these)
Peroxisomes
specialized metabolic compartments bounded by a single membrane
produce hydrogen peroxide and convert it to water
motor protein
protein that can move with the help from ATP
centrosome
microtubules grow out from
cell wall
extracellular structure - made of cellulose fibers embedded in other polysaccharides and protein
cell wall layers
Primary cell wall: relatively thin and flexible
middle lamella: thin layer between primary walls of adjacent cells
secondary cell wall: (in some cells) added between plasma membrane and primary cell wall
cell junctions
neighboring cells in animal or plants - adhere, interact, and communicate through direct physical contact
intercellular junctions
plasmodesmata
tight junctions
desmosomes
gap junctions
plasmodesmata
channels that perforate plant cell walls
water and small solutes (sometimes proteins and RNA) pass from cell to cell
Junctions in animal cells
tight junctions
desmosomes
gap junctions
tight junctions
prevent fluid from moving across a layer of cell
desmosomes
mediate direct cell-cell contacts and provide anchorage sites for intermediate filaments important for the maintenance of tissue architecture
Gap junctions
aggregates of intercellular channels that permit direct cell–cell transfer of ions and small molecules
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
animal cells version of cell wall
made up of glycoproteins - collagen, proteoglycans, fibronectin
ECM proteins bind to integrins
integrins
receptor proteins in plasma membrane
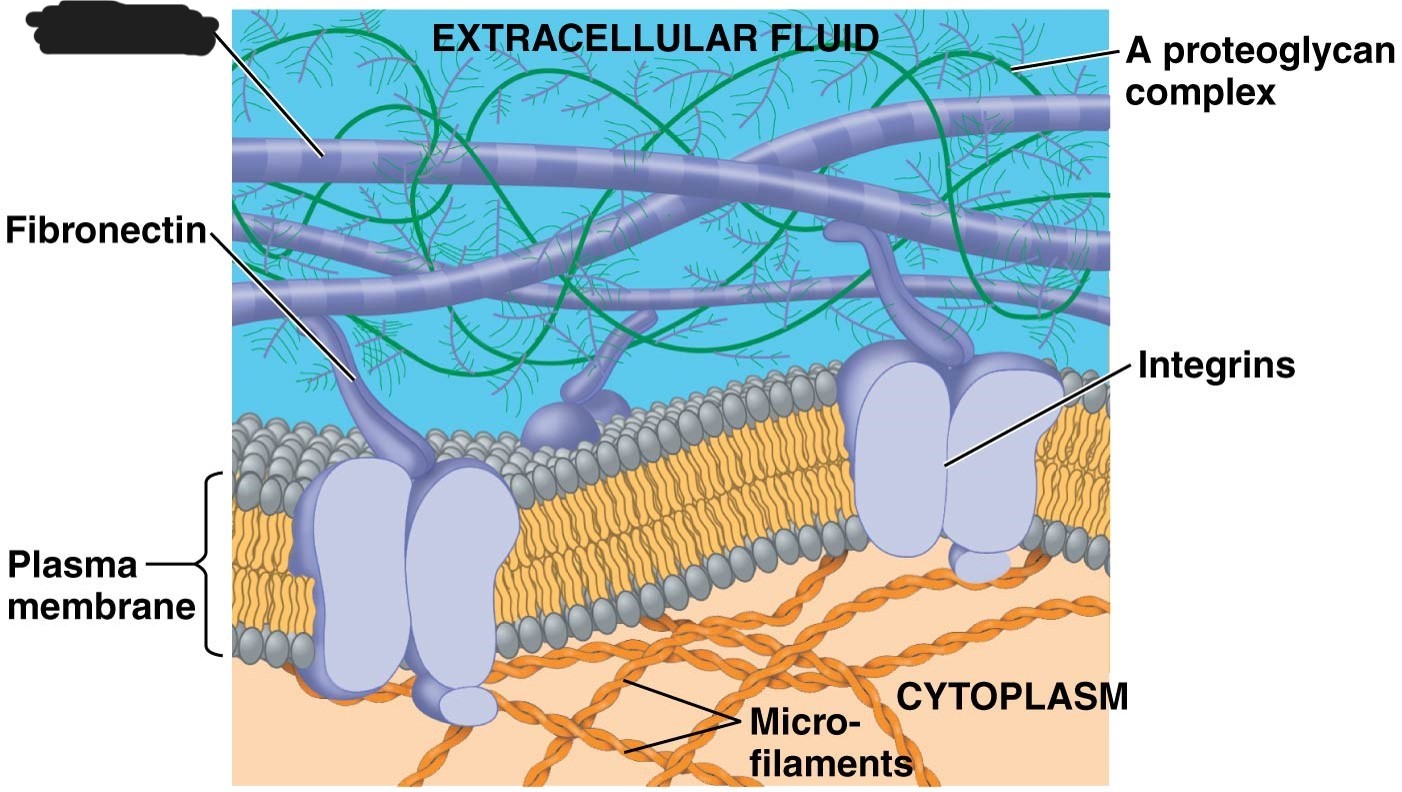
1 extracellular matrix (ECM)
collagen
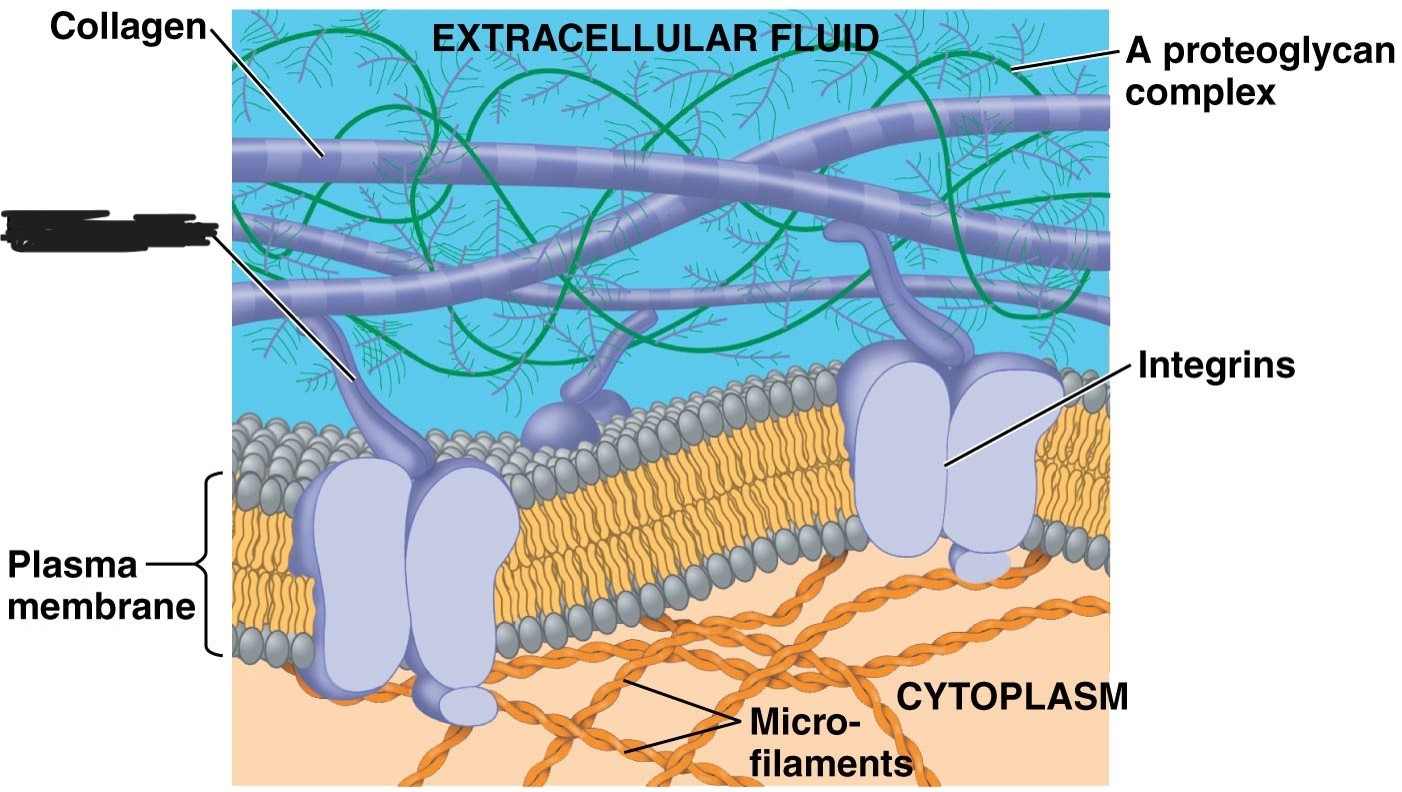
2 Extracellular matrix (ECM)
Fibronectin
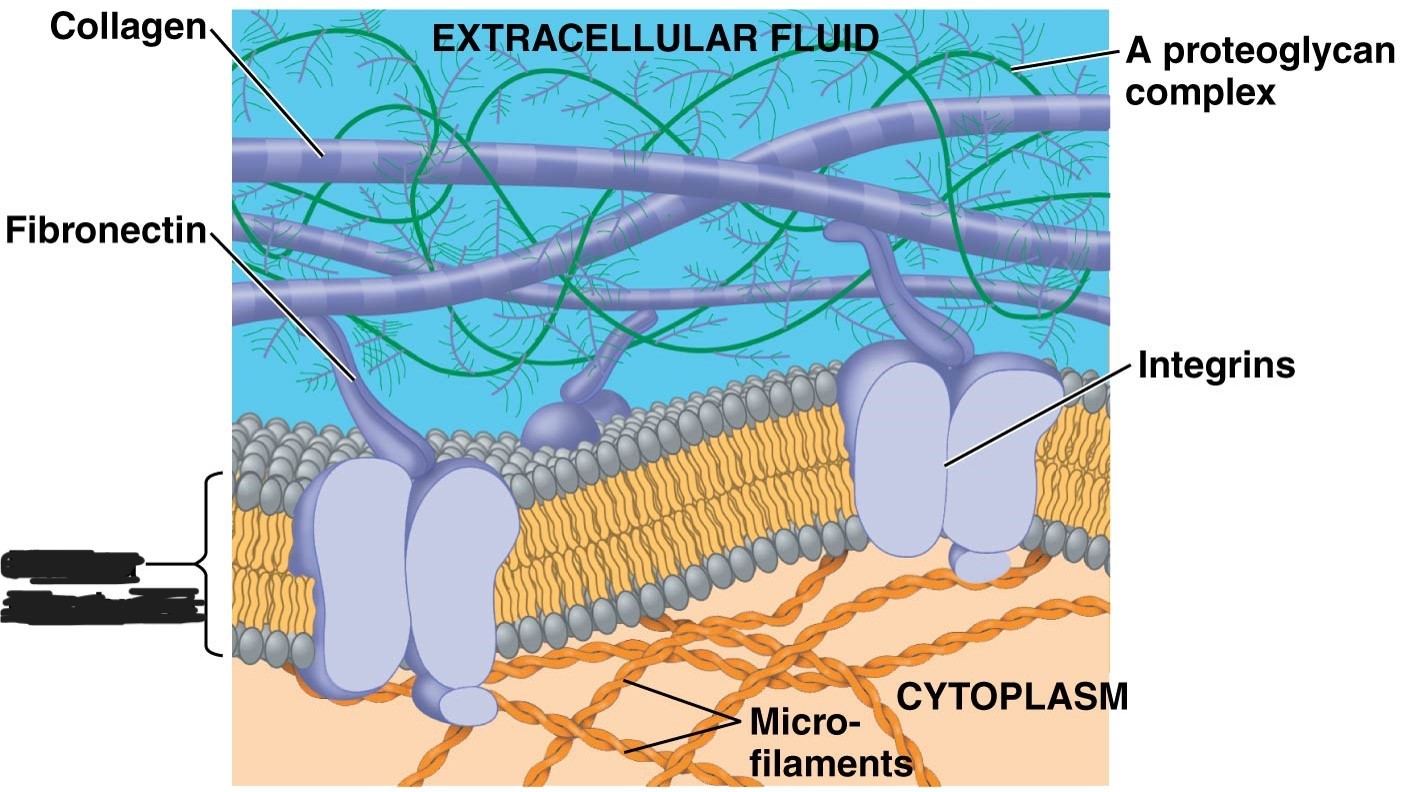
3 Extracellular matrix (ECM)
plasma membrane
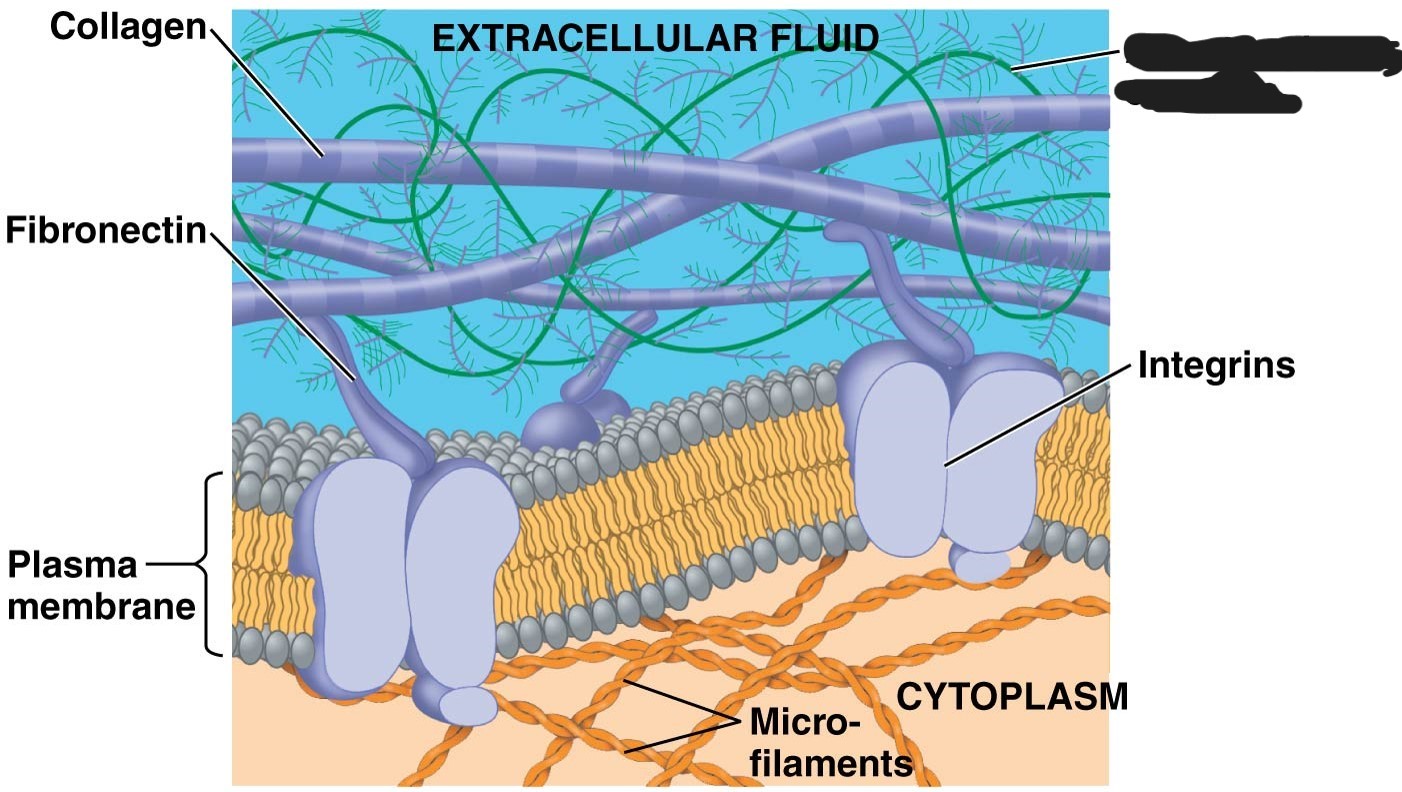
4 extracellular matrix (ECM)
A proteoglycan complex
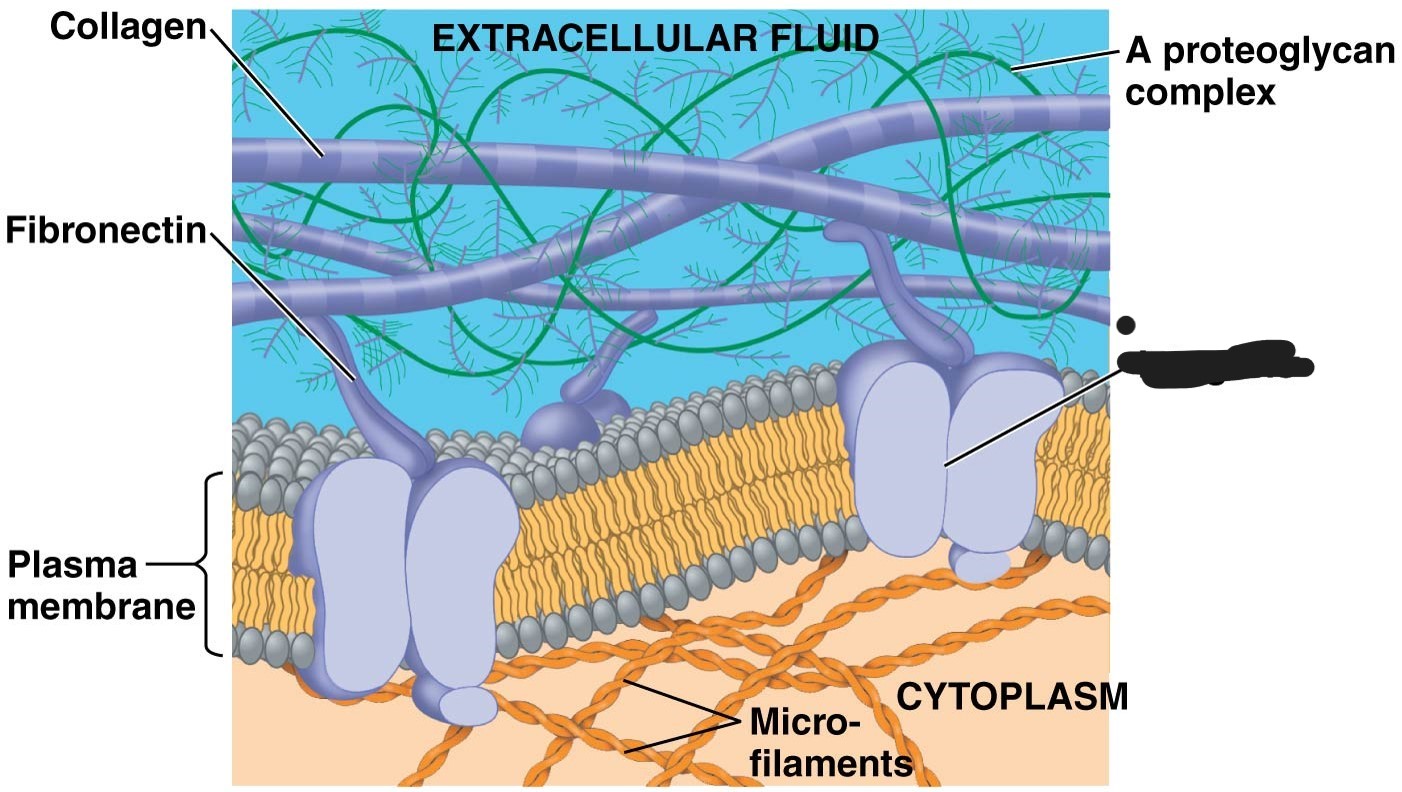
5 extracellular matrix (ECM)
integrins
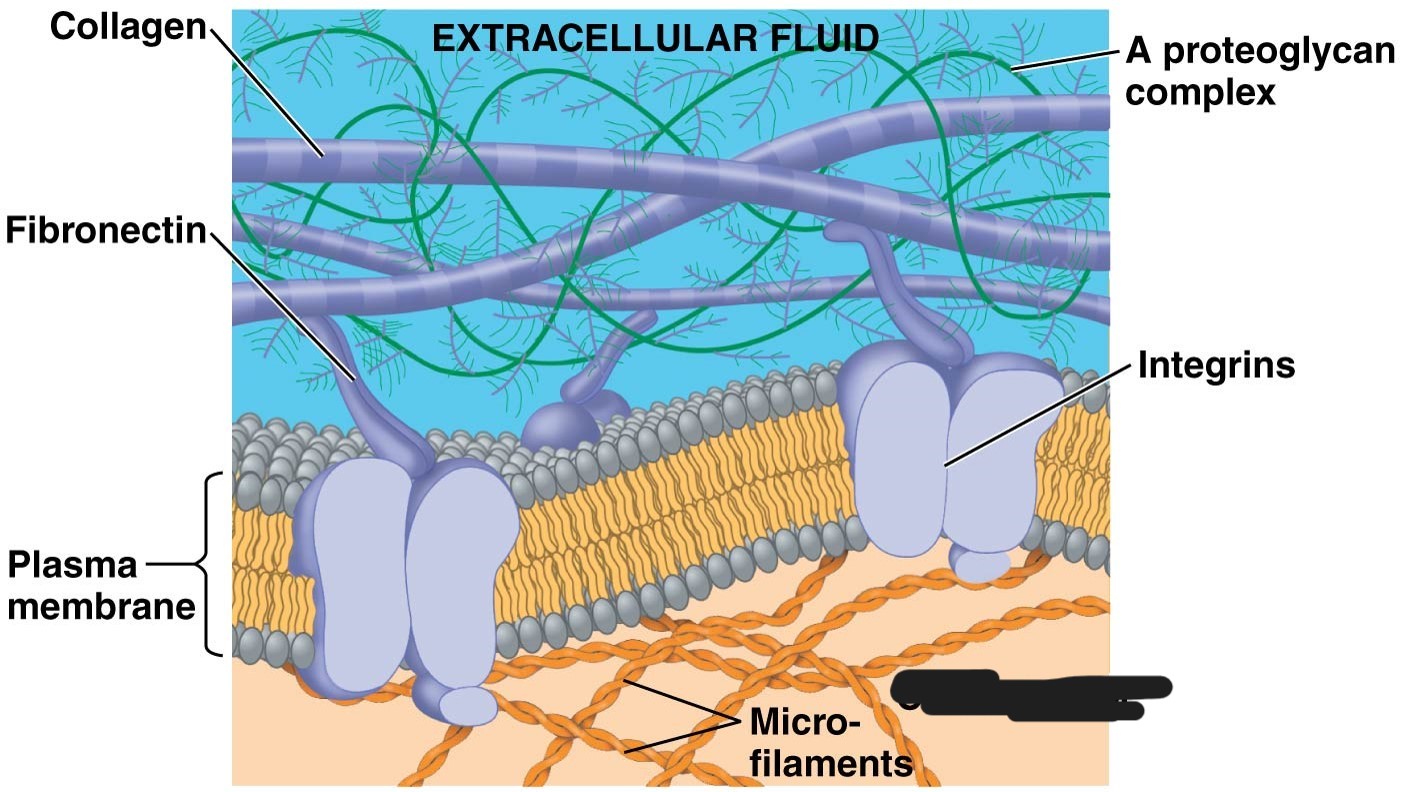
extracellular matrix (ECM)
cytoplasm
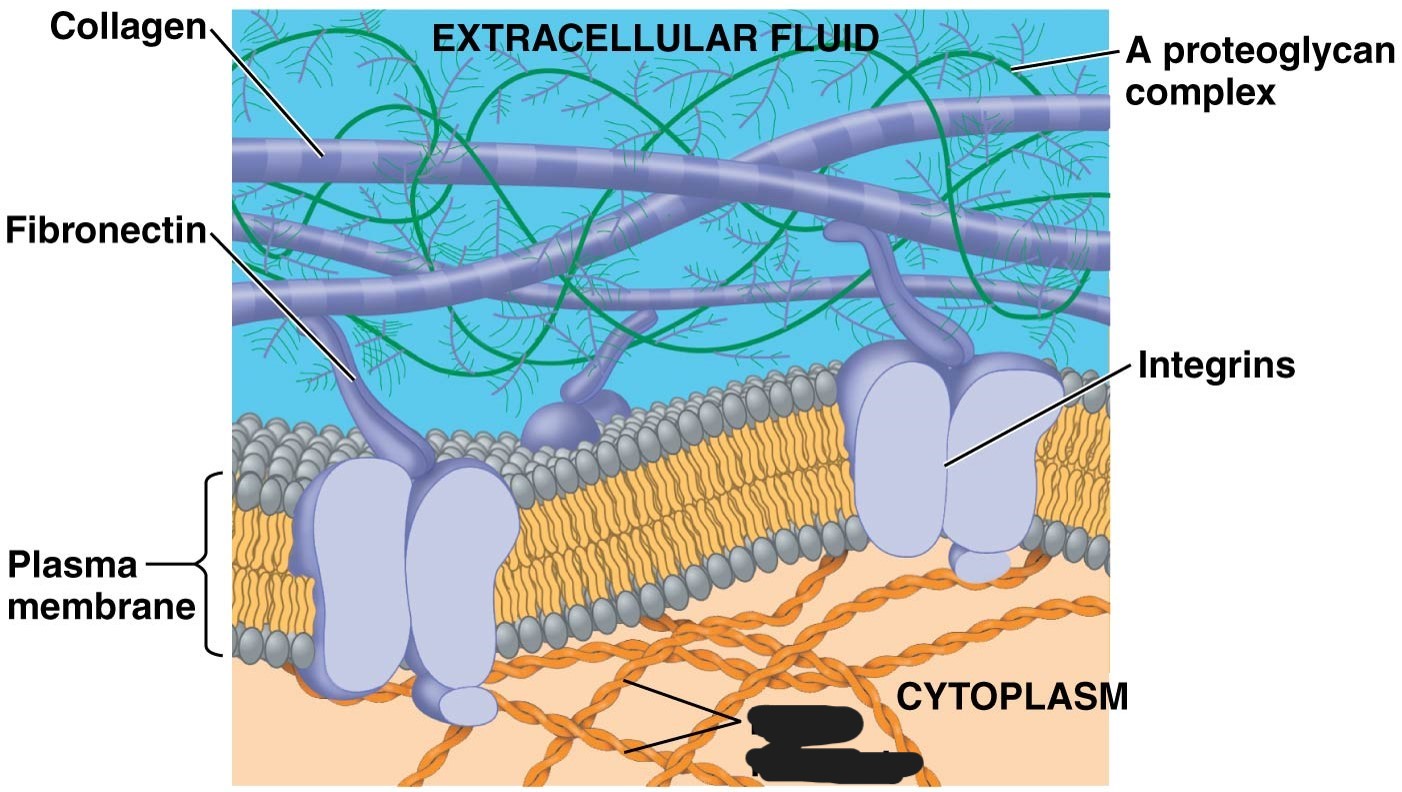
extracellular matrix (ECM)
micro-filaments
Plasma membrane
selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell
(general structure is double layer of phospholipids)
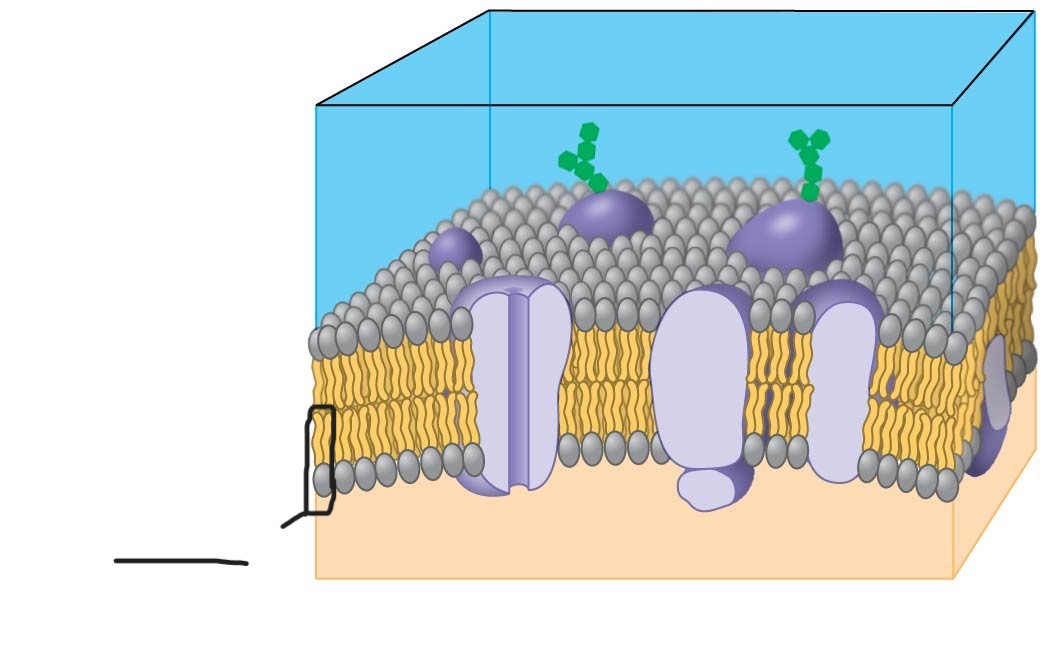
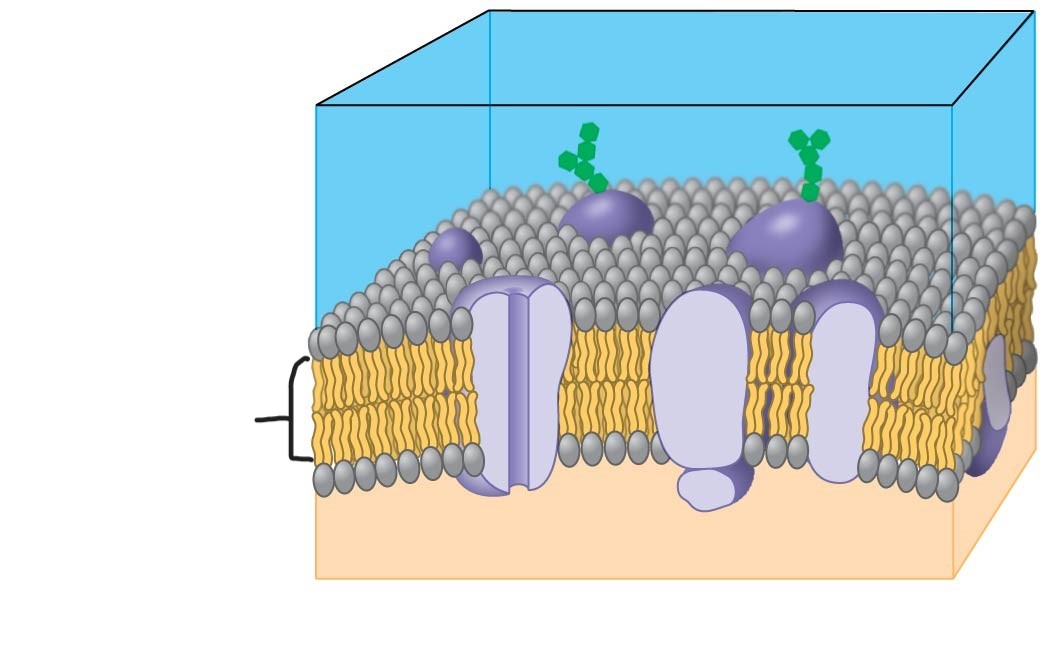
1 plasma membrane
phospholipid
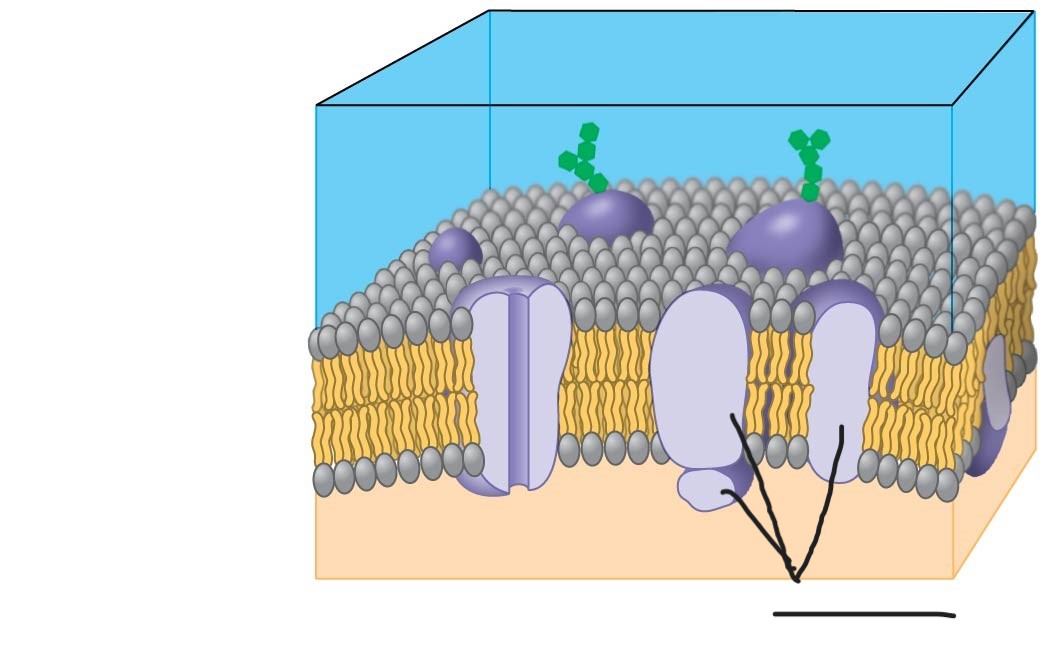
2 plasma membrane
proteins
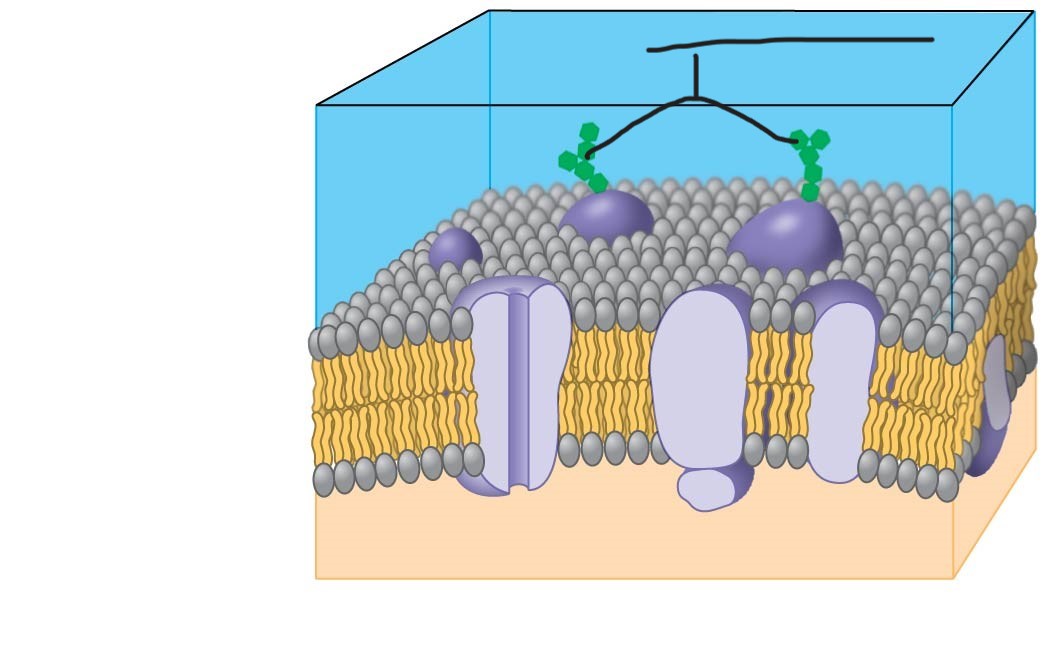
3 plasma membrane
Carbohydrate side chains
4 plasma membrane
hydrophilic region
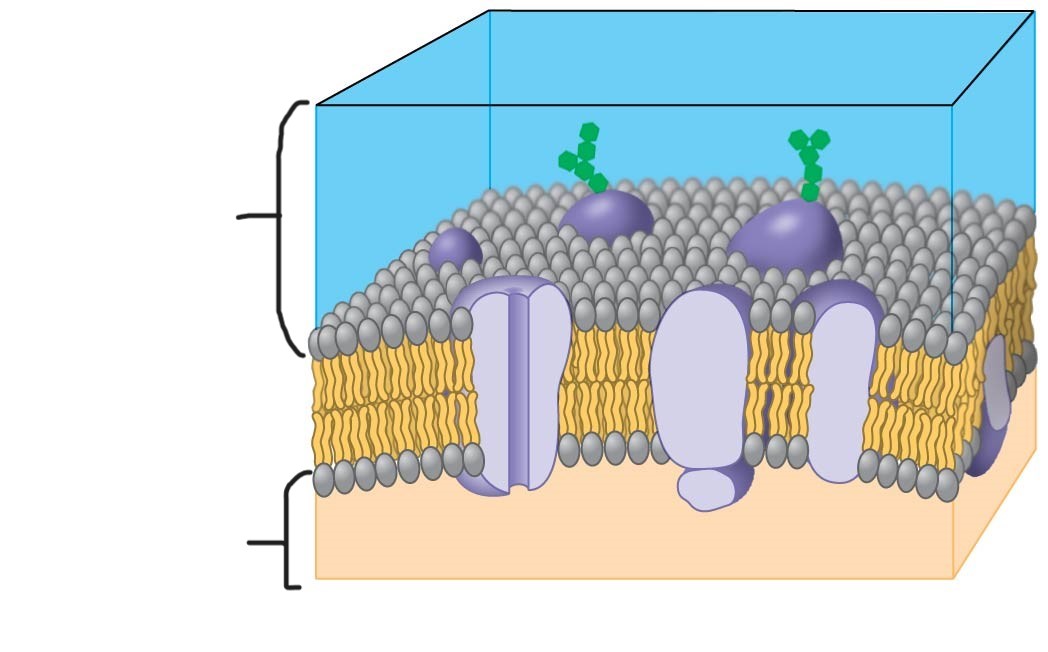
5 plasma membrane
hydrophobic region
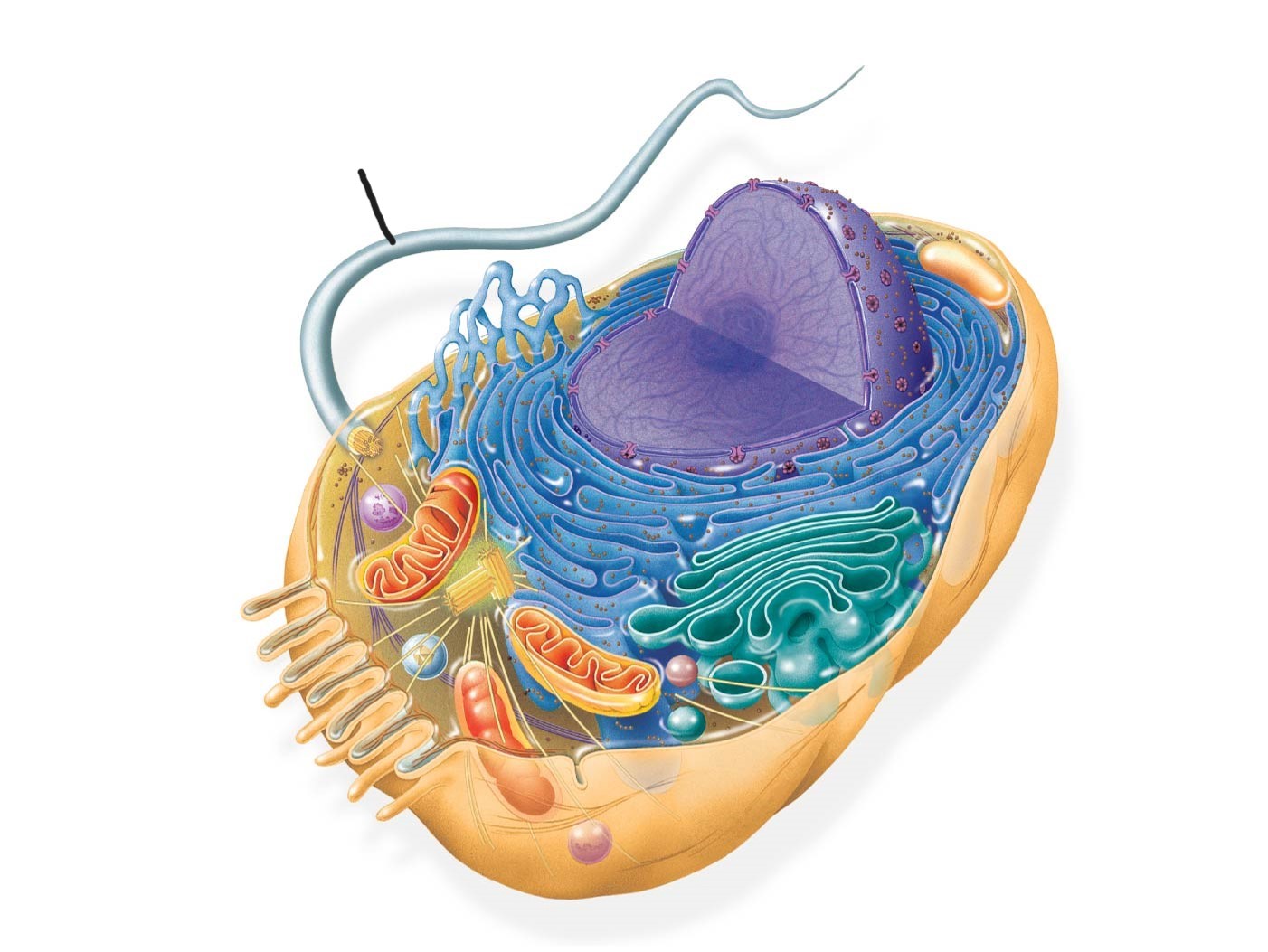
animal cell
flagellum
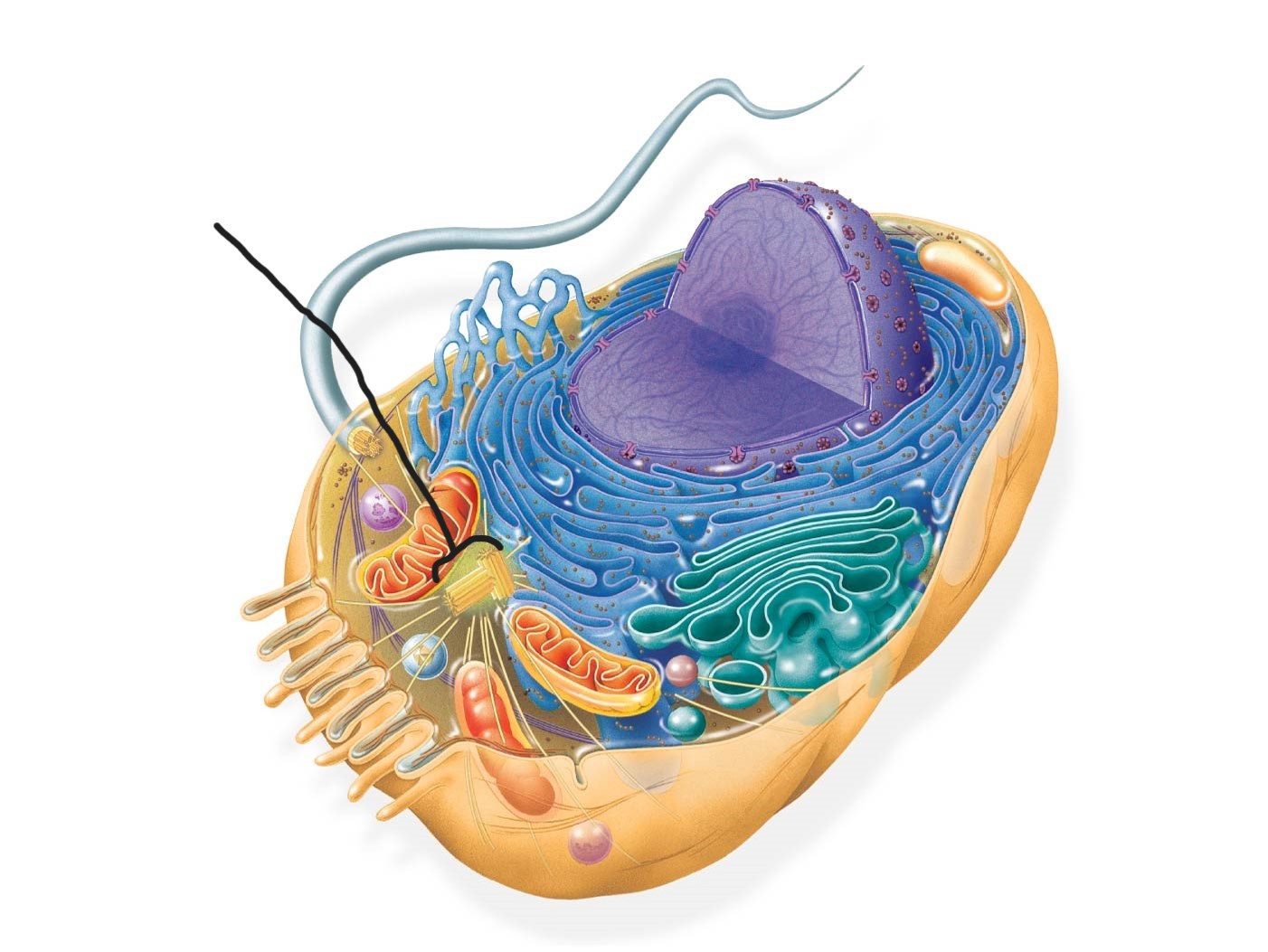
2 animal cell
centrosome
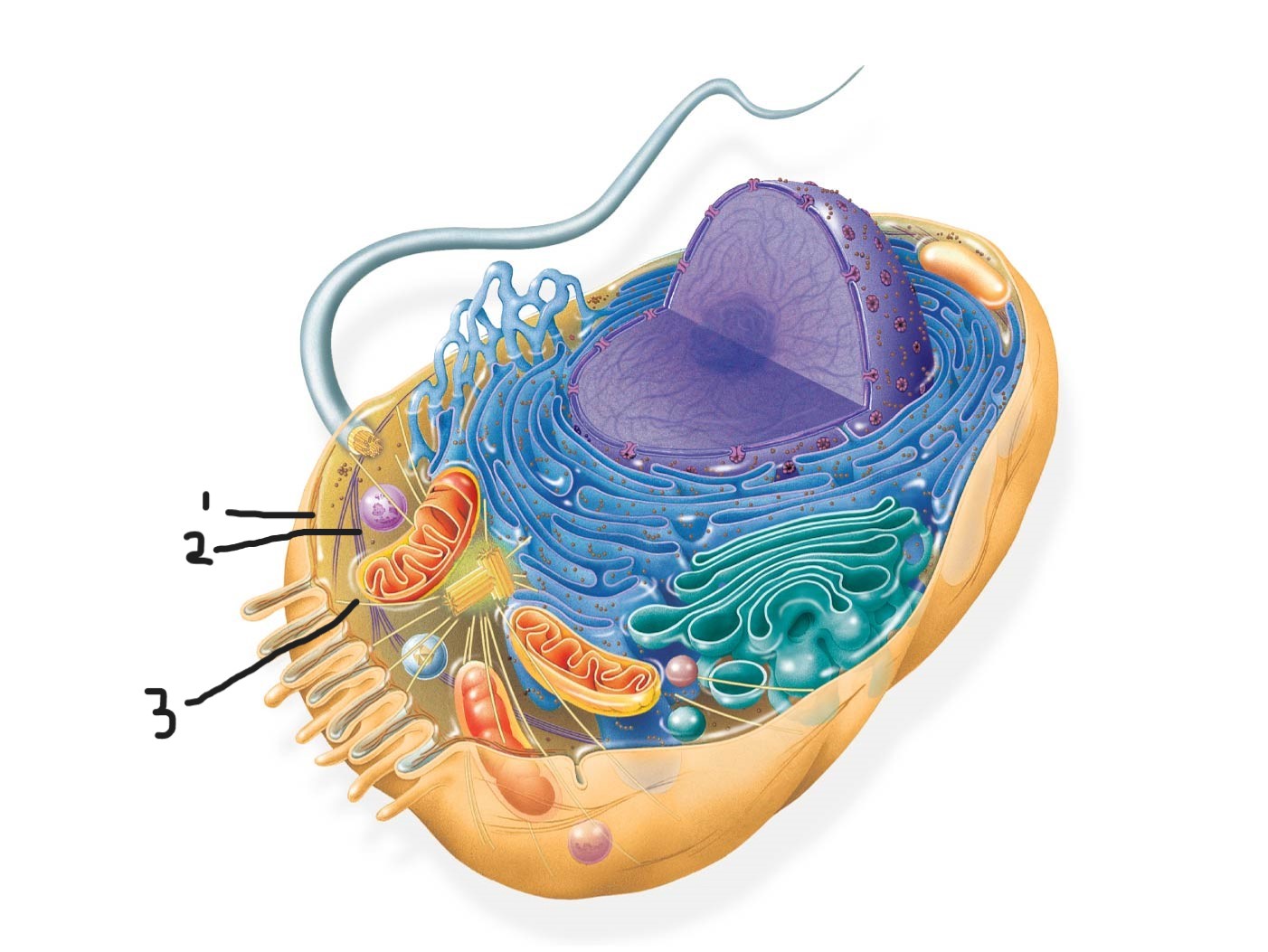
3 animal cell (Cytoskeleton )
microfilaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
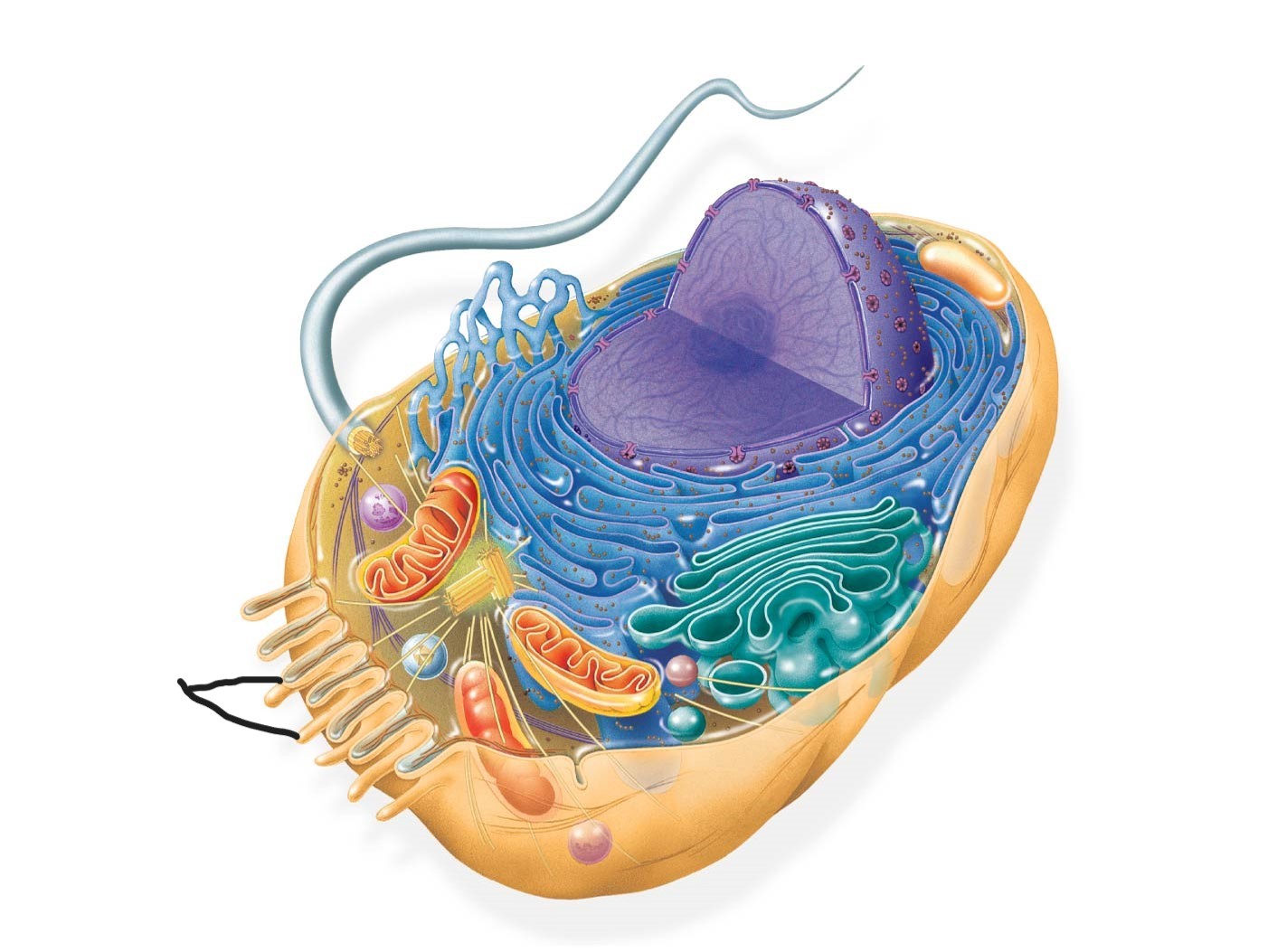
4 animal cell
microvilli
microvilli
digestion and absorption of intestinal contents by increasing surface area of cell
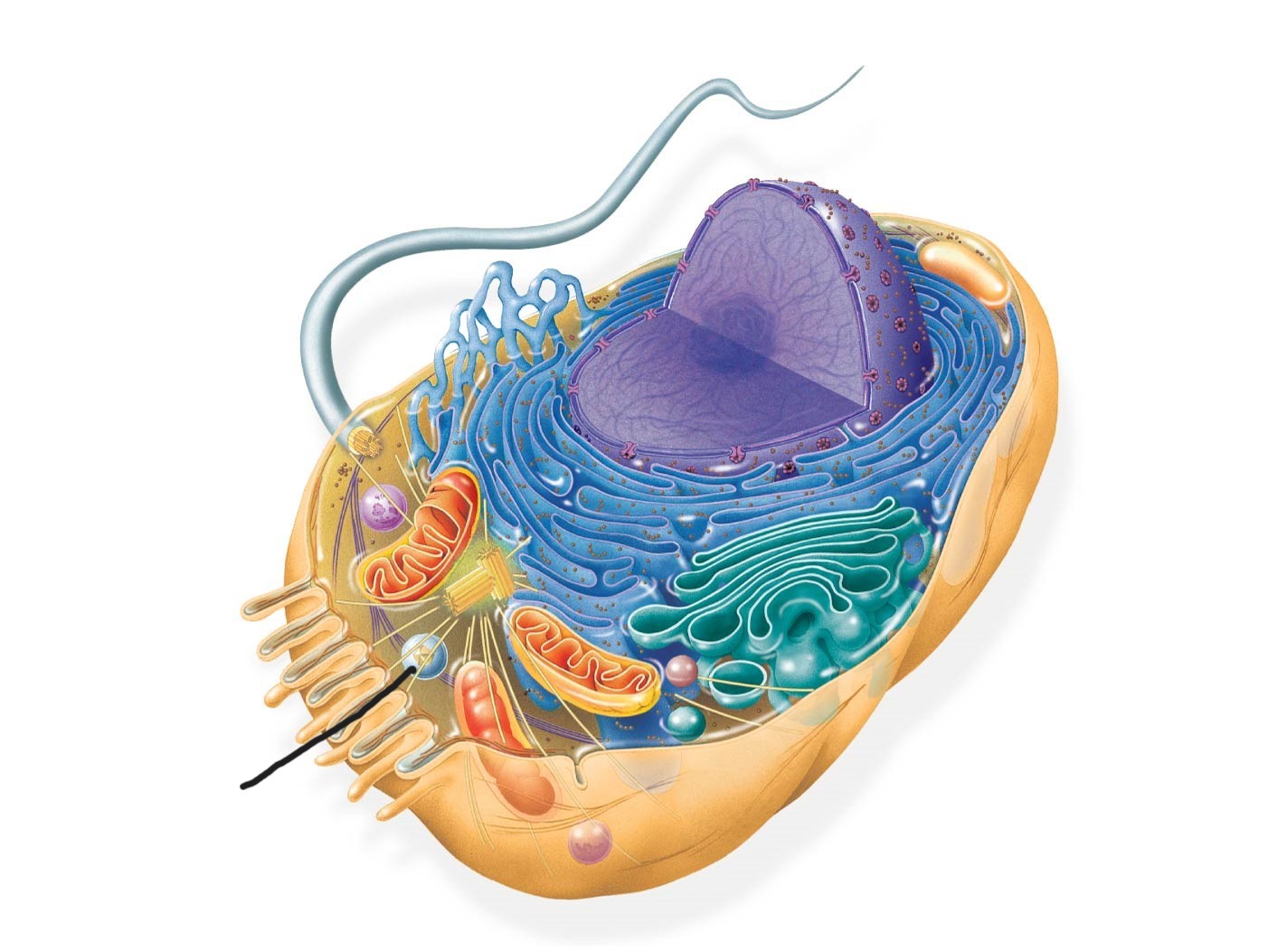
5 animal cell
peroxisome
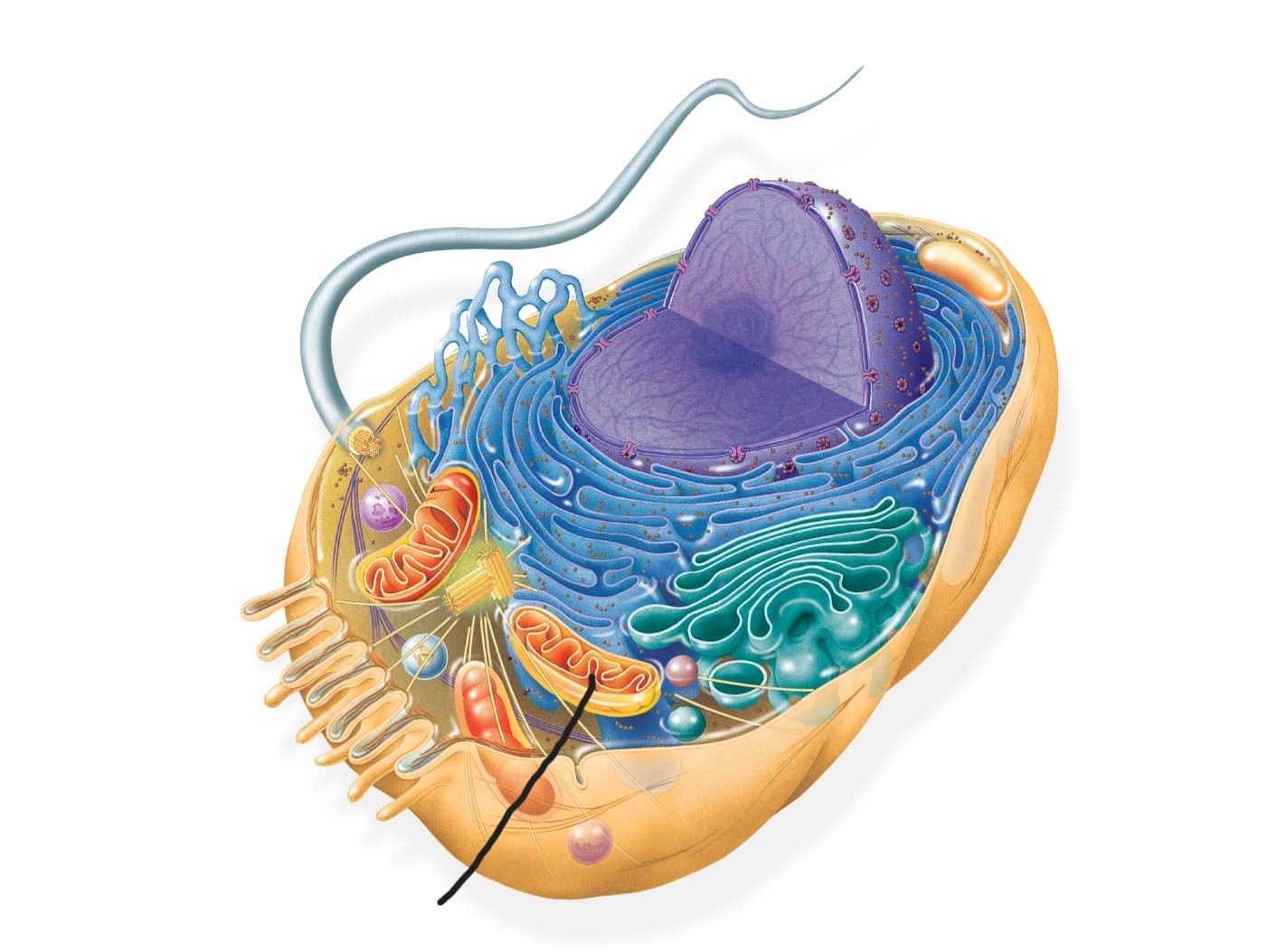
6 animal cell
mitochondrion
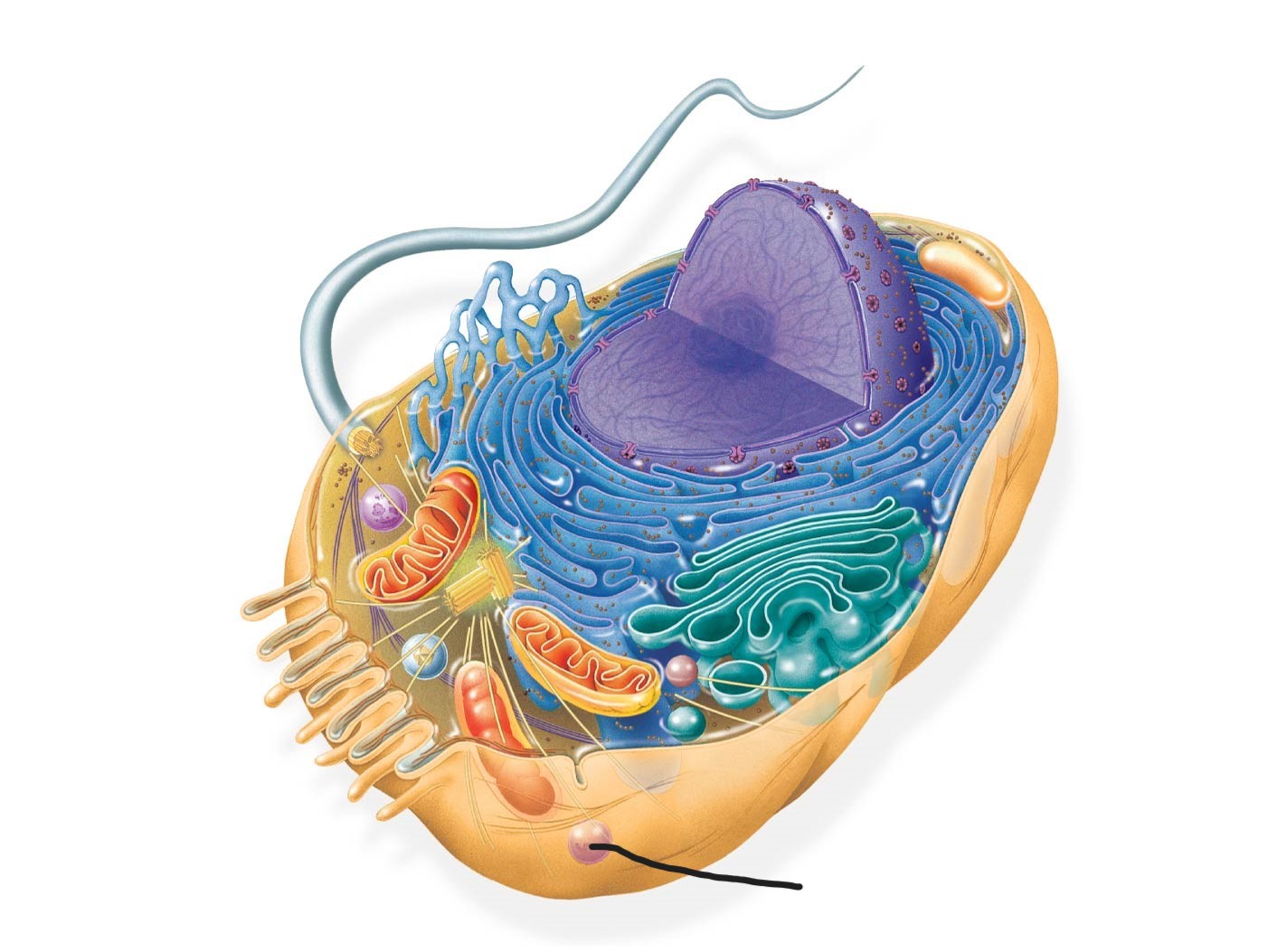
7 animal cell
lysosome
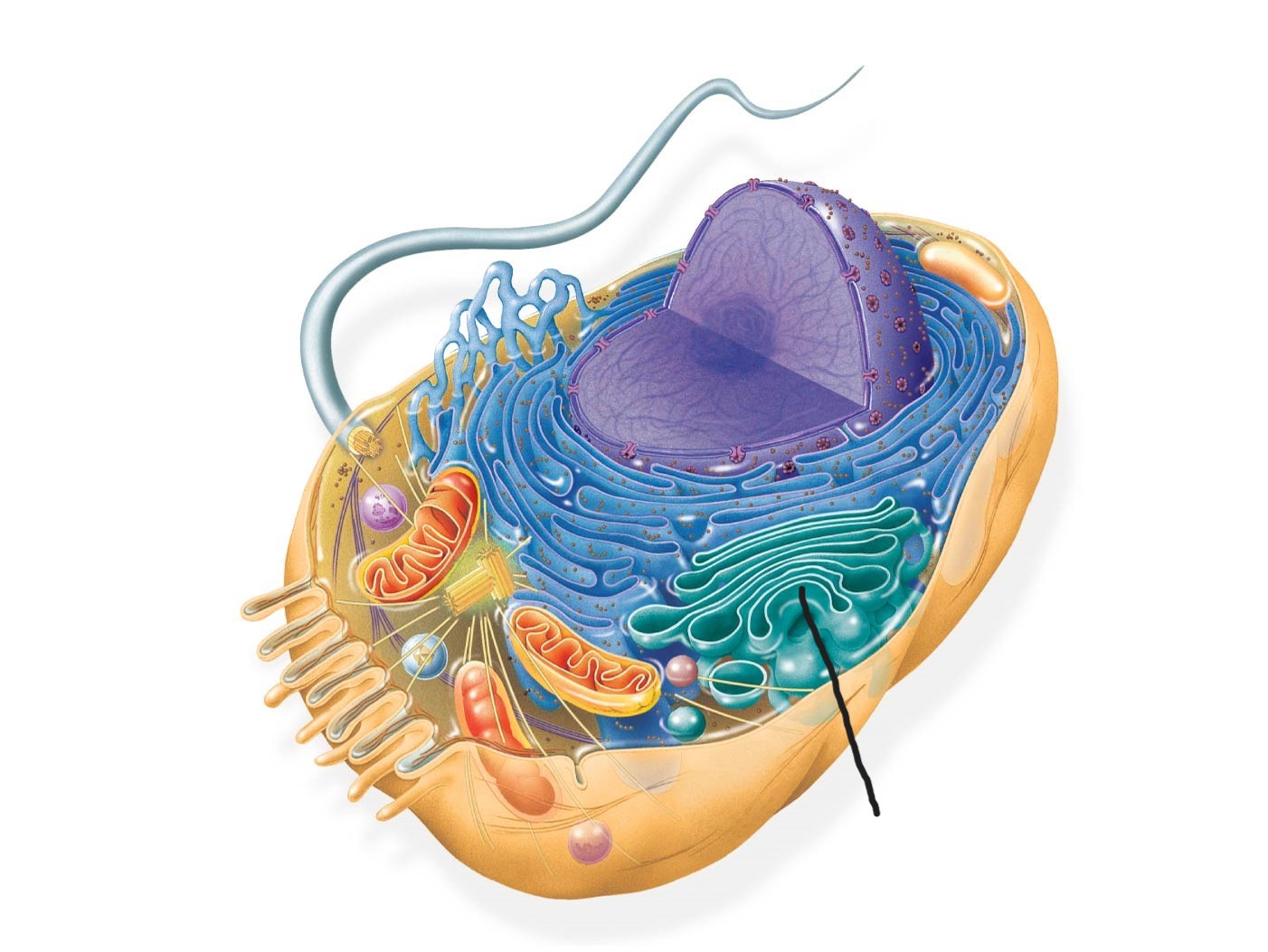
8 animal cell
golgi apparatus
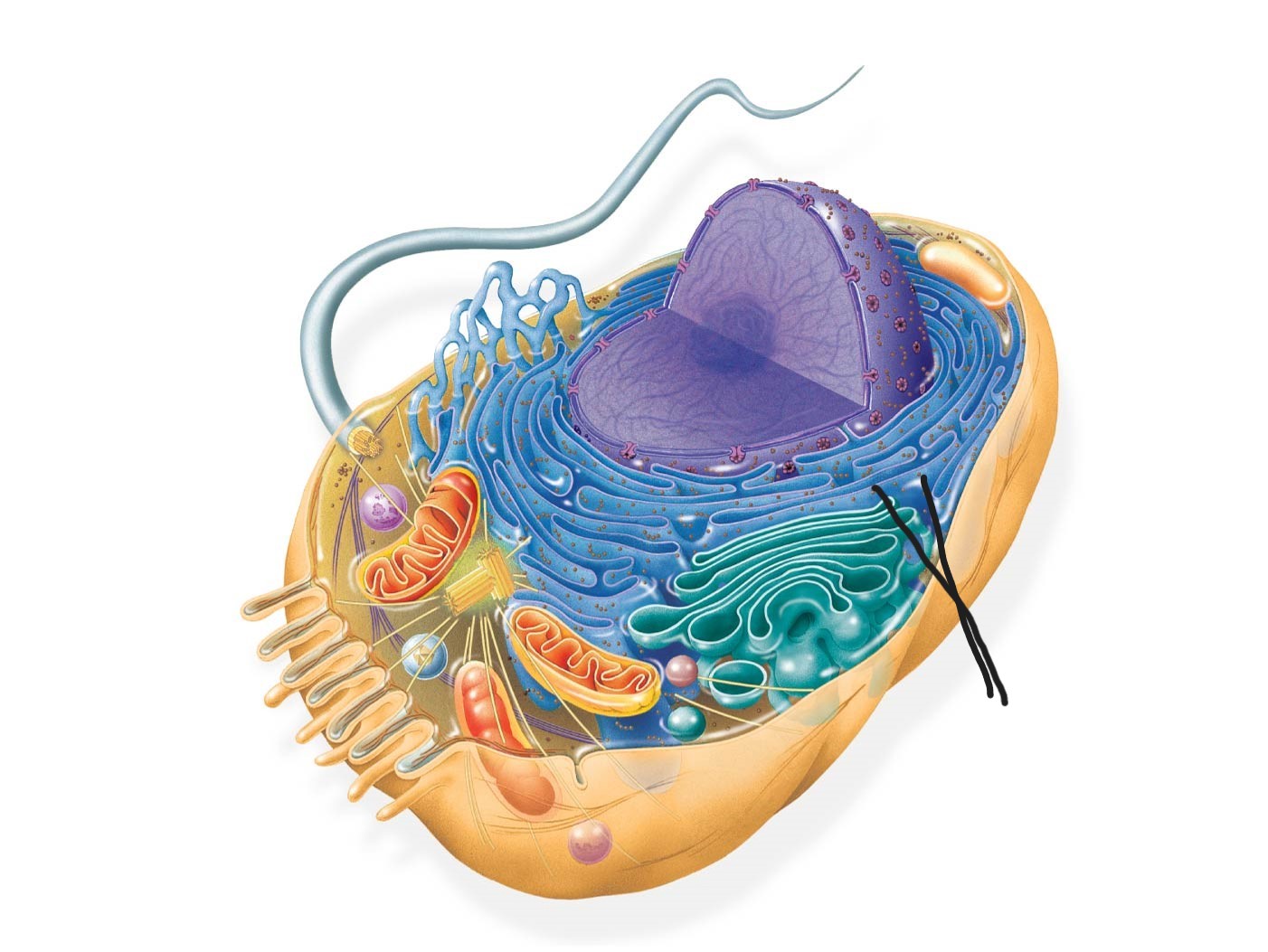
9 animal cell
ribosomes