8 D2 | Fixed Prosth | Restoration of Endodontically Treated Teeth
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
T/F endodontically treated tooth get weaker and more brittle as time goes on
FALSE
it does not!!! but can get structural damage
what it the purpose of a post?
a) provide strength to the remaining tooth structure
b) provide fracture resistance
c) retain the core
d) improve survivability of endo tx
c) to retain the core
what are ideal components of the post for the coronal section of the tooth?
- maximum retention of core and crown
- high strength and fatigue resistance
- esthetics
- simple to use
- cost effective
what are ideal characteristics of the post for the apical section of the tooth?
- maximum protection of root
- adequate retention within the root
- biocompatibility/noncorrosive
- radiopaque
of the following in the picture, which ones are prefabricated posts and which ones are custom?
ones with colored background are cast custom posts
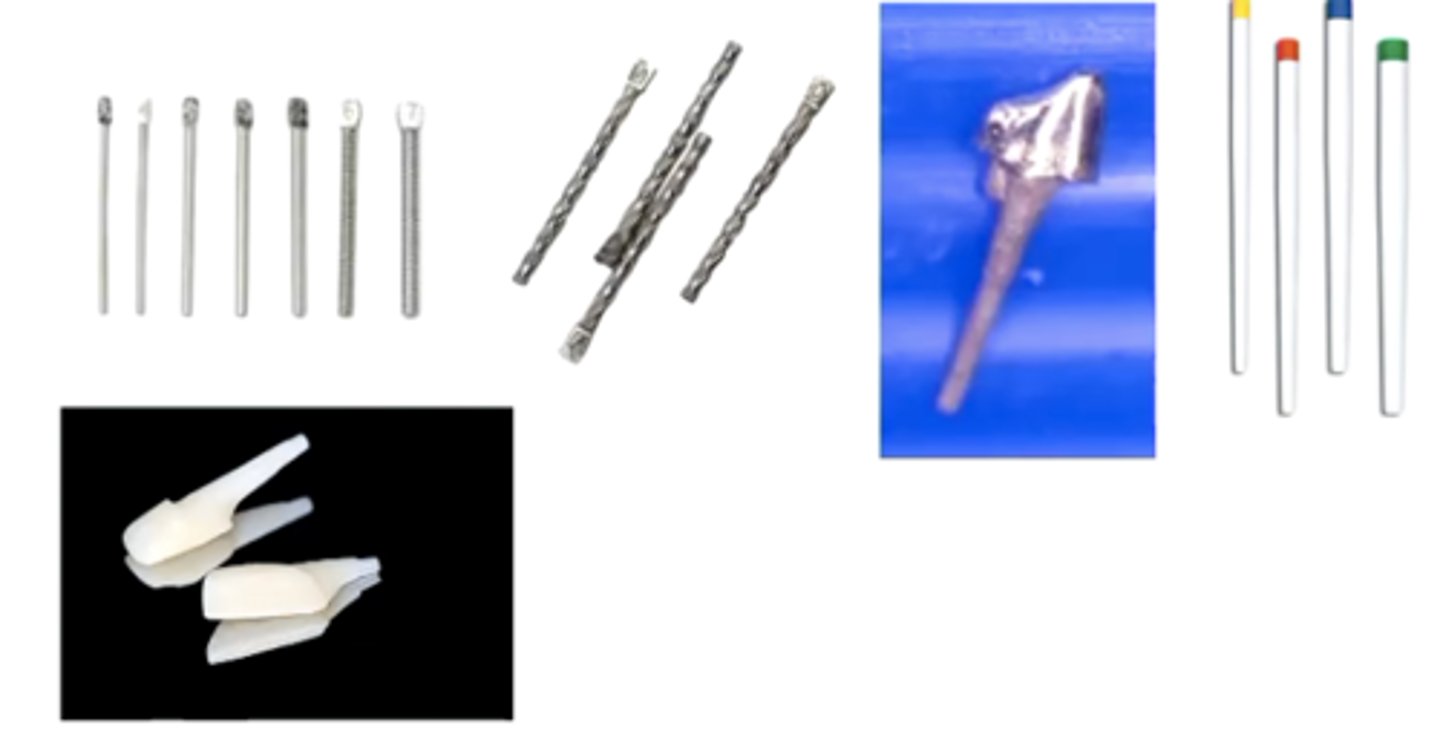

if you have a funnel shaped canal, you should use
a) cast custom posts
b) prefabricated posts
a) cast custom posts
which quality of a post is strongly associated with the amount of retention?
a) width
b) type of material
c) length
d) custom vs prefabricated
c) length
the optimal post length should be at least equal to ___________
clinical crown length
T/F the post should be at least 1/2 of the root length, though some studies suggest 2/3 to 4/5 of root length. ideally, it should be as long as possible without disturbing the apical seal
TRUE
how much apical seal should the ETT have?
4-5mm
T/F the post should be at least 1/2 of the root length
T/F the post should extend more than 6mm apical to the bone
T/F for molars, the post should be no more than 7mm (measured from the canal orifice)
T/F shorter posts put less stress on the tooth, and are less prone to fracture but also lesser retention
TRUE
FALSE -- more than 4mm apical to the bone
TRUE
FALSE -- shorter posts put MORE stress on tooth, and are more prone to root fracture as well as lesser retention
the width of the post affects what aspect of the ETT?
nothing to do with amount of retention
according to the proportionist approach, the post width should be ____________
a) minimal canal preparation and preserve as much root structure as possible
b) post should be surrounded by at least 1mm of sound dentin
c) should be no greater than 1/3 of the root width at its narrowest dimension
c) should be no greater than 1/3 of the root width at its narrowest dimension
according to the conservationist approach, the post width should be ____________
a) minimal canal preparation and preserve as much root structure as possible
b) post should be surrounded by at least 1mm of sound dentin
c) should be no greater than 1/3 of the root width at its narrowest dimension
a) minimal canal preparation and preserve as much root structure as possible
according to the preservationist approach, the post width should be ____________
a) minimal canal preparation and preserve as much root structure as possible
b) post should be surrounded by at least 1mm of sound dentin
c) should be no greater than 1/3 of the root width at its narrowest dimension
b) post should be surrounded by at least 1mm of sound dentin
what can happen if you have a wide post?
wide post can cause a wedging effect, and can potentially cause root fracture, especially with forces directed off the long axis
ferrule
band of restoration that encircles the external dimension of residual tooth structure (part of the crown that braces the tooth to provide resistance to dislodgment and prevent fracture)
or amount of coronal tooth structure left
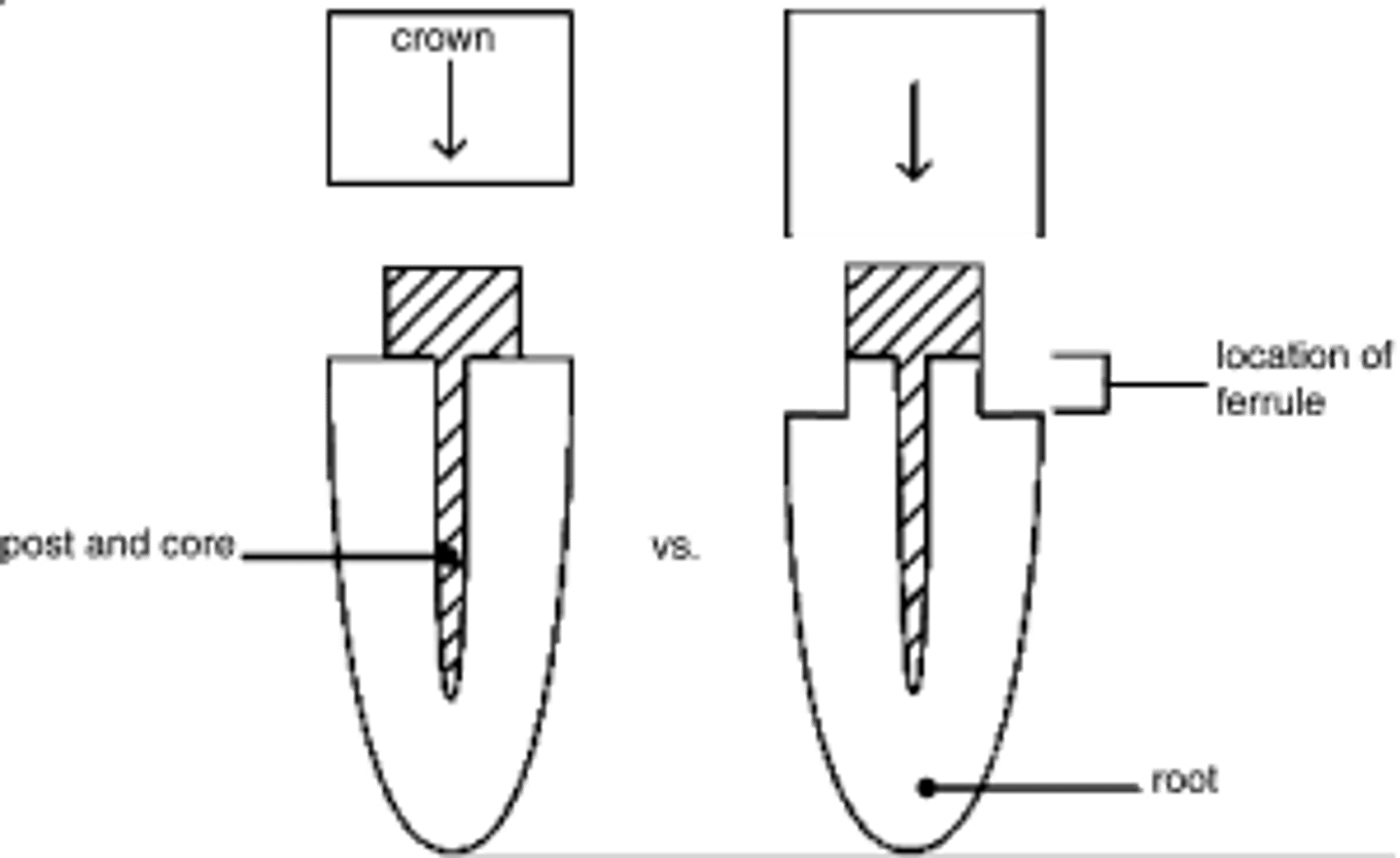
what is the optimal ferrule height?
2mm
T/F with at least 2mm ferrule height, it significantly reduces the incidence of fracture in ETT
T/F if we cannot provide adequate ferrule, it is better to extract the affected tooth
TRUE
TRUE
how does C/R ratio play a role in fracture resistance? how does it play a role in obtaining the optimum ferrule?
the lower the crown:root ratio, the higher the load needed to cause it to fail
this means that if you do a CL to obtain the proper ferrule length, that may increase the C/R ratio, which negatively affects the fracture resistance of the tooth. it might be better to orthodontically erupt the tooth to maintain the C/R ratio
parapost XP is used for _______
a) smaller teeth
b) larger teeth
a) smaller teeth -- used most often
parapost XH is used for _________
a) smaller teeth
b) larger teeth
b) larger teeth -- less used
when a post is required, how do you select the canal to avoid weakening of the root?
you want to place the post in the largest and straightest canal
T/F in the mandibular molars, you want to place the post in the mesial canal
T/F in the maxillary molars, you want to place the post in the palatal canal
T/F titanium post can be bend to accommodate for the bend in the canal
FALSE -- distal canal is bigger and straighter, so use the distal canal
TRUE
FALSE -- titanium post should NOT be bent to assist in retaining the core material where tooth structure was loss
how do you prepare a tooth to have a prefabricated post?
1) crown prep
2) remove unsupported tooth structure
3) canal is prepared with peeso reamers
4) dowel space prep is finished with a specific drill or reamer for the prefabricated dowel system being used
what do you do for post try-in?
- verify passive fit intracanal
- verify depth using PA radiograph, making sure post touches GP
-
after you've verified the post fits properly, if you want to adjust the length of the post so there is no excess post sitting above the prepped tooth, at which part would you cut it?
a) apical portion of post
b) coronal portion of post
a) apical portion of post
if you're doing a gold crown above the post, the post head should be approximately _____mm from the opposing dentition
1.0-1.5mm
if you're doing an all ceramic crown above the post, the post head should be approximately ____mm from the opposing dentition
2.0mm
what is the most common type of cement used to cement the post
self-adhesive resin cement -- popular and simple to use
all are the pros of using resin cement for post cementation except?
a) popular and simple to use
b) good retention
c) lowest solubility
d) high shearing strength
e) high compressive strength
d) high shearing strength
all the following are good physical properties of core material except:
a) high compressive strength
b) high tensile strength
c) dimensional stability
d) ease of manipulation
e) low setting time
f) ability to bond to tooth and post
b) high tensile strength
amalgam seems to be a good core material with a long history for success except for what concerns?
- not esthetically pleasing
- does not bond to dentin
- requires more time to set
- pts are concerned about the presence of mercury in amalgam
T/F glass ionomer seems to be a better core material because if its good bonding characteristics and strong tensile and compressive strengths
FALSE -- glass ionomer should be avoided bc 1) weak tensile and compressive strengths and 2) low modulus of elasticity and poor bonding characteristics to dentin and enamel
has a low fracture resistance too
amalgam is a good core material but not really esthetic and poor setting time. glass ionomer is just a poor core material to use due to its physical properties. what should we use instead (and do use in clinic) and why?
resin-based composite
- compressive strength between amalgam and GI
- esthetic
- good strength characteristics
- can bond to dentin and easy to use
what are some of the negative features of using resin-based composite?
- polymeraziation shrinkage and hydroscopic expansion
resin-based composite is incompatible with ___________ in many root canal sealers, resulting in resin that is not cured completely
ZOE
a provisional crown is necessary to provide: __________
- coronal seal
- integrity of remaining tooth structure
- prevent drifting of adjacent teeth
- provide degree of oral function and esthetics
when would you want to do a custom cast post and core?
- irregular canal shapes
- extensive tooth structure damage
T/F it is required to prepare the tooth in both custom cast and prefabricated post/core techniques
FALSE
only REQUIRED in custom cast post/core technique. you have the option to not prepare the tooth in the prefabricated post/core technique
why is it required to prepare the tooth in custom technique?
to make sure there are no undercuts in the tooth
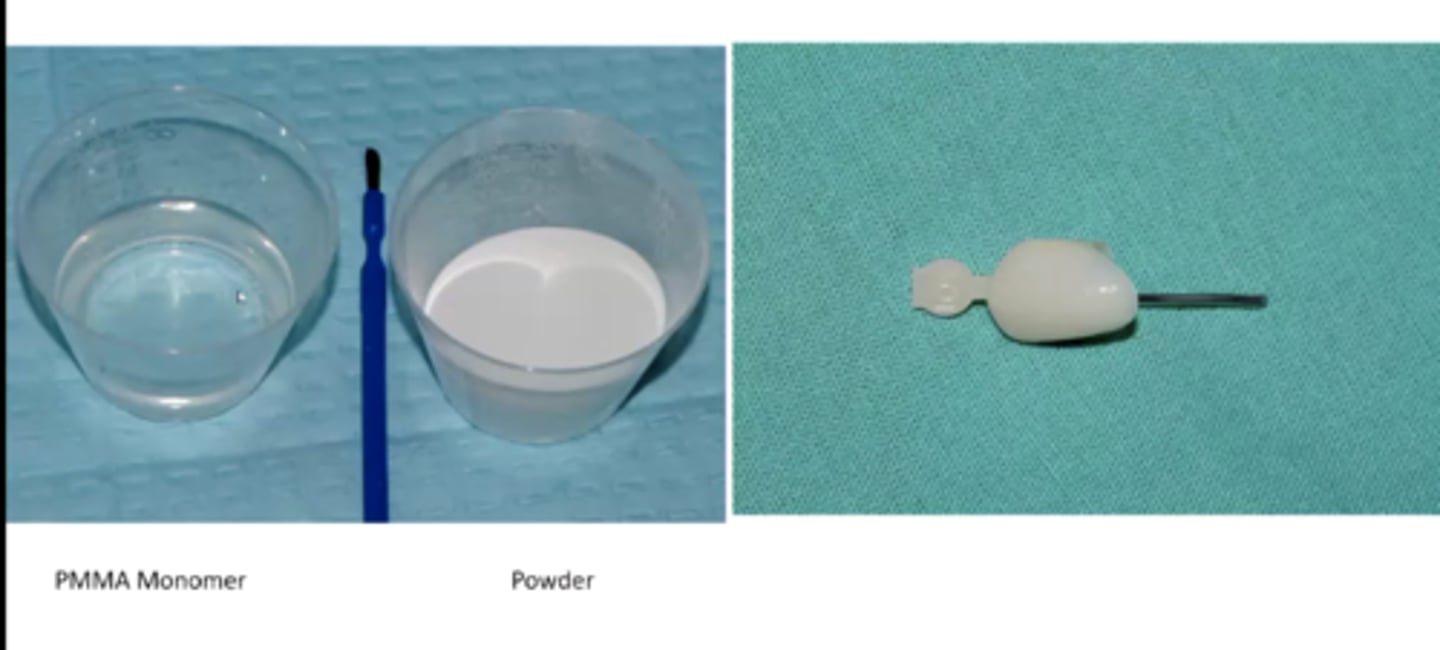
what do we use to create an impression of the canal for the custom technique?
spee dee plastic pin as the pin to apply a resin impression
how do you take the impression for the custom technique
1) loosely fit a resin sprue into the canal
2) apply GC-resin (quick set) in canal with lubrication -- should cover contrabevel
3) seat into canal, making sure there are no undercuts
4) bulk up the post head with resin to create shape of prepped tooth
5) wrap with moist gauze and send to lab asap
how do you set a temporary restoration for teeth that we are going to fit a custom cast post in?
since there is no post in it, create a makeshift post using WW or orthodontic wires with a retentive bend at the coronal and then reline using PMMA. then cement using temporary cement
T/F the temporary restoration for this custom post technique has a higher chance of dislodging
TRUE
for cementation of the post, what syringes should you use to make sure no air is trapped?
centrix syringe or extended tip that goes into canal using rely X unicem cement
posterior teeth with RCT should receive ___________ restorations
cuspal coverage restorations
anterior teeth with minimal loss of tooth structure can be restored with ___________
conservatively with bonded restorations
T/F preservation of coronal and radicular tooth structure is desirable
TRUE
purpose of the post is to ___________
retain the core build up, which is foundation restoration for future cuspal coverage restorations
a ferrule is highly desirable when a post is used. an adequate ferrule is considered __________
minimum of 2mm of vertical height and 1mm of dentin thickness
all the following are advantages to prefabricated posts except:
a) simple to use
b) less chair time and can be completed in one visit
c) provisional restoration is routine procedure
d) adaptable to large canals
d) adaptable to large canals -- it's not
all the following are disadvantages to prefabricated posts except:
a) cannot adapt well with various root canal configurations
b) may require additional removal of tooth structure to achieve passive path of insertion
c) core material can be chipped, fractured, or dislodged from post
d) limited application when affected tooth presents with severely damaged tooth structure
b) may require additional removal of tooth structure to achieve passive path of insertion -- this is a disadvantage for custom cast posts
all the following are advantages to custom cast posts except:
a) custom fit to canals in various root configurations
b) adaptable to large, irregularly shaped canals and orifices
c) only takes 2 visits
c) only takes 2 visits -- considered a disadvantage. pre-fabricated can do it all in one visit
all the following are disadvantages to custom cast posts except:
a) expensive
b) metal can show through restoration
c) fabrication of provisional restoration is difficult
d) risk of casting inaccuracies
e) may require additional removal of tooth structure to achieve passive path of insertion
f) core material can be chipped, fractured, or dislodged from post
f) core material can be chipped, fractured, or dislodged from post -- it's all one unit, so this wont happen
restorability test
inform pt of intended restorative plan and additional procedures such as RCT, post/core and/or CL, or extraction if affected tooth is severely damaged after tooth preparation
then provide tooth preparation as a planned restorative outcome. if emergency RCT is necessary, and affected tooth is deemed to be restorable, then refer pt to 3rd floor endo for pulpectomy. if not restorable, then refer to omfs to extract
severe structural damaged tooth refers to _________
loss of more than half of the coronal structure of the tooth
to ascertain that the tooth needs to be extracted rather than maintained, we need __________
all disciplines to deem the tooth hopeless
prosth: insufficient amount of coronal tooth structure to provide retention and resistance
perio: too much attachment loss
for prosth, what are three considerations to be made to determine whether the tooth is hopeless or not?
1) amount of remaining coronal tooth structure
2) strategic value of affected tooth with regard to remaining dentition
3) pt's preference
what is the most common complication for post/core?
post loosening (5%)
followed by root fracture (3%) and caries (2%)