unit #6a: digestive system
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/48
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
what are the 4 functions of the digestive system?
* mechanical processing of food (ex. chewing)
* chemical/enzymatic processing of food
* absorption of nutrients
* compaction/excretion of undigested residual foods
* chemical/enzymatic processing of food
* absorption of nutrients
* compaction/excretion of undigested residual foods
2
New cards
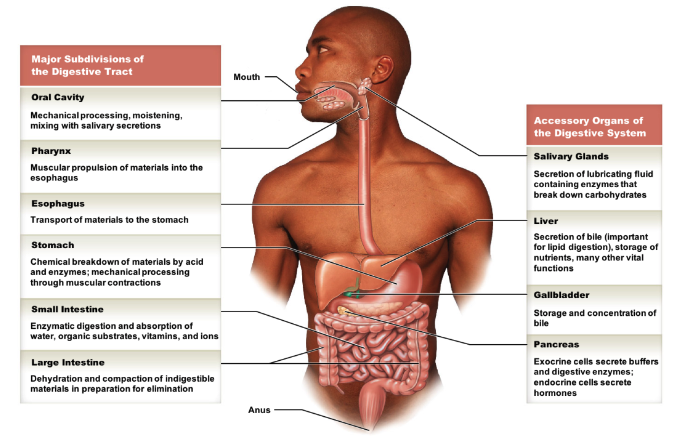
in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, list the main vs. accessory parts of the digestive system.
* main GI tract parts
* oral cavity
* pharynx
* esophagus
* stomach
* small intestine
* large intestine
* accessory parts
* salivary glands
* liver
* gallbladder
* pancreas
* oral cavity
* pharynx
* esophagus
* stomach
* small intestine
* large intestine
* accessory parts
* salivary glands
* liver
* gallbladder
* pancreas
3
New cards
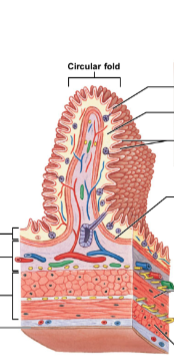
what are the four histological layers (and their possible subdivisions/types) of the digestive tract, from deep to superficial? describe their constitution and associations.
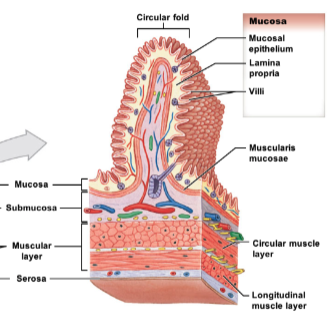
* mucosa: lines lumen, made of epithelial layer
* includes: lamina propria (areolar connective tissue) and muscularis mucosa (thin band of smooth muscle; controls movement of villi/mucosa)
* submucosa: layer of areolar connective tissue with larger blood vessels, glands, nerves
* muscularis externa (muscular layer): double layer of muscle
* includes: inner circular layer, outer longitudinal layer
* outermost layer: either serosa or adventitia
* serosa: visceral peritoneum, found around organs in peritoneal cavity
* adventitia: collagen fiber network binding organs not in peritoneal cavity → retroperitoneal
* includes: lamina propria (areolar connective tissue) and muscularis mucosa (thin band of smooth muscle; controls movement of villi/mucosa)
* submucosa: layer of areolar connective tissue with larger blood vessels, glands, nerves
* muscularis externa (muscular layer): double layer of muscle
* includes: inner circular layer, outer longitudinal layer
* outermost layer: either serosa or adventitia
* serosa: visceral peritoneum, found around organs in peritoneal cavity
* adventitia: collagen fiber network binding organs not in peritoneal cavity → retroperitoneal
4
New cards
what are the 2 types of mechanical digestion in the muscular layer? describe the 2 in where the occur and what sublayers are involved.
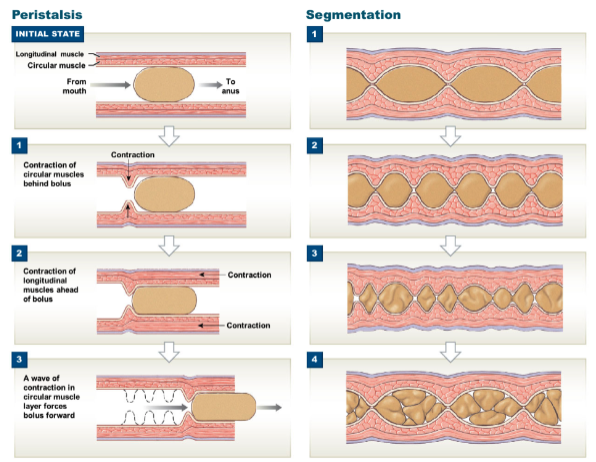
* segmentation: contractions of circular layer breaks bolus (small mass of food) into smaller chunks and mixes them together
* occurs mostly in small and large intestine
* peristalsis: alternating contractions of circular and longitudinal layers that pushes bolus down GI tract
* occurs throughout GI tract; can be seen a lot in esophagus
* occurs mostly in small and large intestine
* peristalsis: alternating contractions of circular and longitudinal layers that pushes bolus down GI tract
* occurs throughout GI tract; can be seen a lot in esophagus
5
New cards
describe sphincters. how many are there in the GI tract? name all of them and their location.
* sphincters: allow one-way movement of bolus thru gut
* 6 sphincters in total
* upper esophageal
* lower esophageal
* pyloric (stomach → duodenum)
* ileocecal valve (ileum → large intestine)
* internal anal sphincter (involuntary at rectum)
* external anal sphincter (voluntary at anus)
* 6 sphincters in total
* upper esophageal
* lower esophageal
* pyloric (stomach → duodenum)
* ileocecal valve (ileum → large intestine)
* internal anal sphincter (involuntary at rectum)
* external anal sphincter (voluntary at anus)
6
New cards
describe the peritoneal cavity. what is it lined with?
* peritoneal cavity: subspace within abdominal cavity
* lined with serous membrane called parietal peritoneum
* lined with serous membrane called parietal peritoneum
7
New cards
what are organs within the peritoneal cavity called, and what are they covered with? give examples of GI tract parts that are a part of this classification.
* w/in peritoneal cavity = “intraperitoneal”
* covered by serous membrane, visceral peritoneum; covered by serosa
* ex. stomach, liver, spleen, jejunum, ileum, transverse and sigmoidal colon, cecum
* covered by serous membrane, visceral peritoneum; covered by serosa
* ex. stomach, liver, spleen, jejunum, ileum, transverse and sigmoidal colon, cecum
8
New cards
what are organs behind the peritoneal cavity called, and what are they covered with? give examples of GI tract parts that are a part of this classification.
* behind peritoneal cavity = “retroperitoneal”
* covered by adventitia
* ex. pancreas, kidneys, duodenum, ascending and descending colon
* covered by adventitia
* ex. pancreas, kidneys, duodenum, ascending and descending colon
9
New cards
describe mesenteries. what are they made out of and what is their function?
* fused double sheets of peritoneal serous membrane; surround and stabilize organs within peritoneal cavity → no tangling
10
New cards
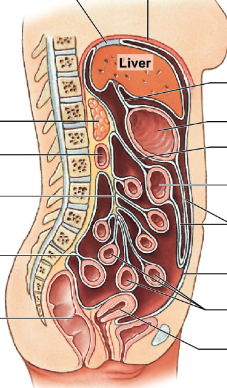
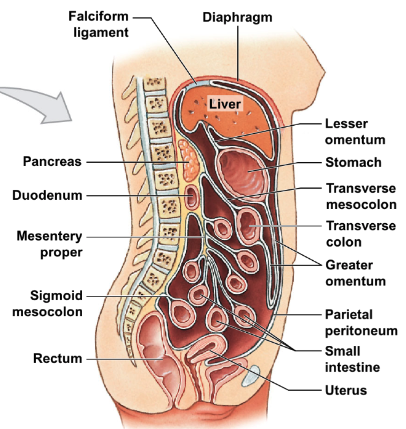
list and describe the 6 main mesenteries in the GI tract, including what parts they connect.
* falciform ligament: holds liver → anterior abdominal wall
* lesser omentum: holds liver → stomach
* greater omentum: holds anterior stomach, forms pouch inferiorly, turns → anterior side of transverse colon
* transverse mesocolon: holds transverse colon → body wall
* mesentery proper: holds majority of small intestine → body wall
* sigmoid mesocolon: holds sigmoid colon → body wall
* lesser omentum: holds liver → stomach
* greater omentum: holds anterior stomach, forms pouch inferiorly, turns → anterior side of transverse colon
* transverse mesocolon: holds transverse colon → body wall
* mesentery proper: holds majority of small intestine → body wall
* sigmoid mesocolon: holds sigmoid colon → body wall
11
New cards
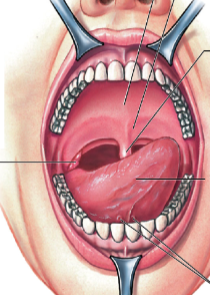
what is the function of the mouth? describe the parts it has.
* mouth made for mechanical and some chemical digestion
* hard palate: anterior roof
* soft palate: posterior roof
* uvula: prevents food from entering pharynx too soon
* salivary glands: secrete some enzymes for digestion
* hard palate: anterior roof
* soft palate: posterior roof
* uvula: prevents food from entering pharynx too soon
* salivary glands: secrete some enzymes for digestion
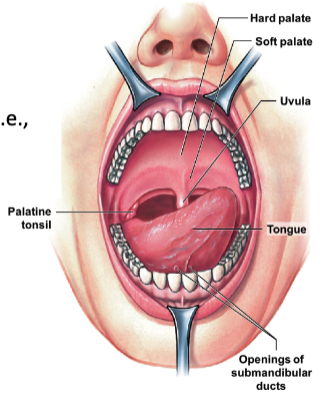
12
New cards
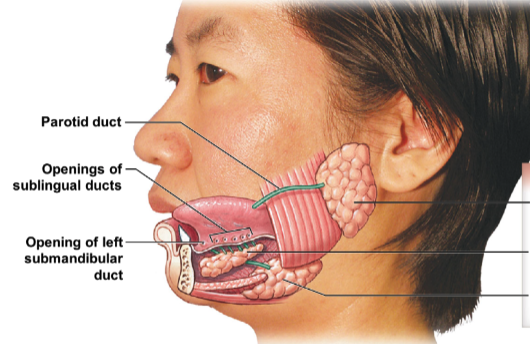
identify and name the 3 salivary glands.
* parotid gland
* sublingual gland
* submandibular gland
* sublingual gland
* submandibular gland
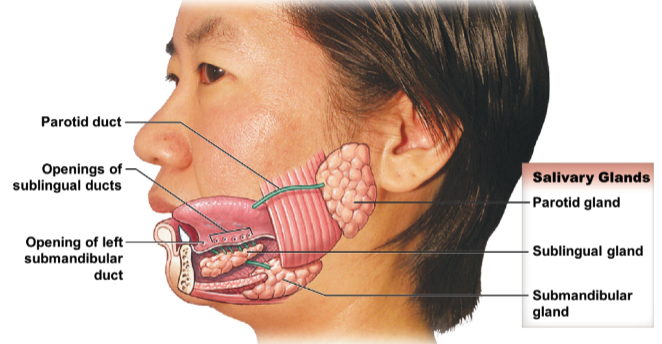
13
New cards
what parts of the pharynx and esophagus are included in the digestive system?
* pharynx → oropharynx, laryngopharynx
* esophagus → lower esophageal sphincter
* esophagus → lower esophageal sphincter
14
New cards
what is the main function of the stomach? what does it form?
* main function: mechanical and some chemical digestion
* forms chyme from digested food
* forms chyme from digested food
15
New cards
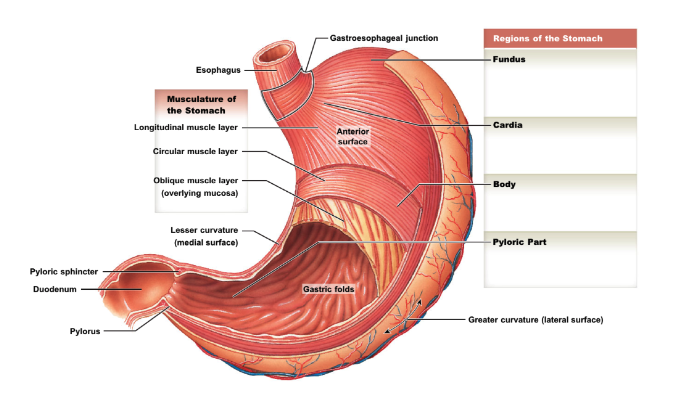
identify and describe the regions and parts of the stomach.
* cardia: adjacent to gastroesophageal junction
* fundus: superior “pocket”
* body: largest region
* pylorus: distal tapering end
* greater curvature: external, lateral surface
* lesser curvature: external, medial surface
* oblique muscle layer: btwn circular muscle layer and mucosa → allow extra food churning
* gastric folds (rugae): present when stomach empty; allow expansion when full
* pyloric sphincter: btwn pylorus and duodenum
* fundus: superior “pocket”
* body: largest region
* pylorus: distal tapering end
* greater curvature: external, lateral surface
* lesser curvature: external, medial surface
* oblique muscle layer: btwn circular muscle layer and mucosa → allow extra food churning
* gastric folds (rugae): present when stomach empty; allow expansion when full
* pyloric sphincter: btwn pylorus and duodenum
16
New cards
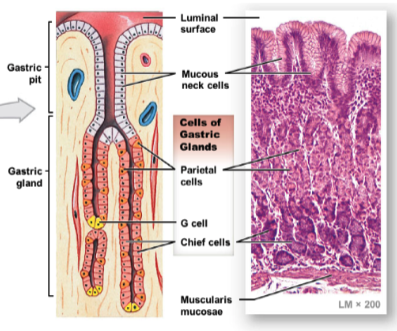
describe gastric pits in stomach wall. what do they contain, and how many type of secretory cells do they have?
* contain gastric glands with 4 types of secretory cells
17
New cards
name and describe the 4 types of secretory cells found in gastric glands. what do they all produce respectively?
* mucous neck cells: prod. mucus
* parietal ells: prod. HCl
* G cells: prod. gastrin (hormone promoting stomach wall contractions → mix/churn food)
* chief cells: prod. pepsinogen (enzyme that helps break down proteins in food)
* parietal ells: prod. HCl
* G cells: prod. gastrin (hormone promoting stomach wall contractions → mix/churn food)
* chief cells: prod. pepsinogen (enzyme that helps break down proteins in food)
18
New cards
what is the main function of the small intestine?
site of majority of chemical breakdown and absorption
19
New cards
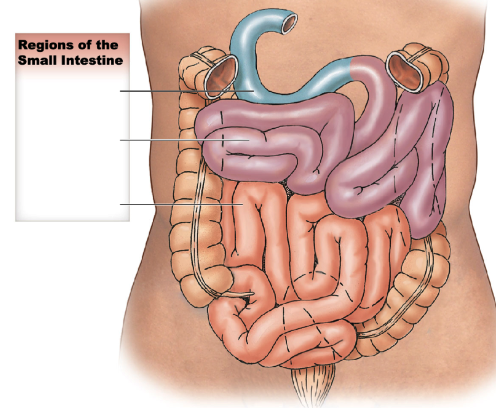
what are the 3 regions of the small intestine? describe their length and if they’re intraperitoneal vs. retroperitoneal.
* in order of GI tract
* duodenum: after pylorus, \~25cm long; retroperitoneal
* jejunum: \~2.5m long; intraperitoneal
* ileum: ending at ileocecal valve, \~3.5m long; intraperitoneal
* has thinner wall and smaller diameter compared to jejunum
* duodenum: after pylorus, \~25cm long; retroperitoneal
* jejunum: \~2.5m long; intraperitoneal
* ileum: ending at ileocecal valve, \~3.5m long; intraperitoneal
* has thinner wall and smaller diameter compared to jejunum
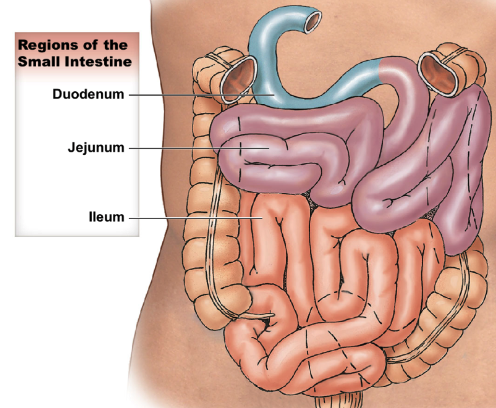
20
New cards
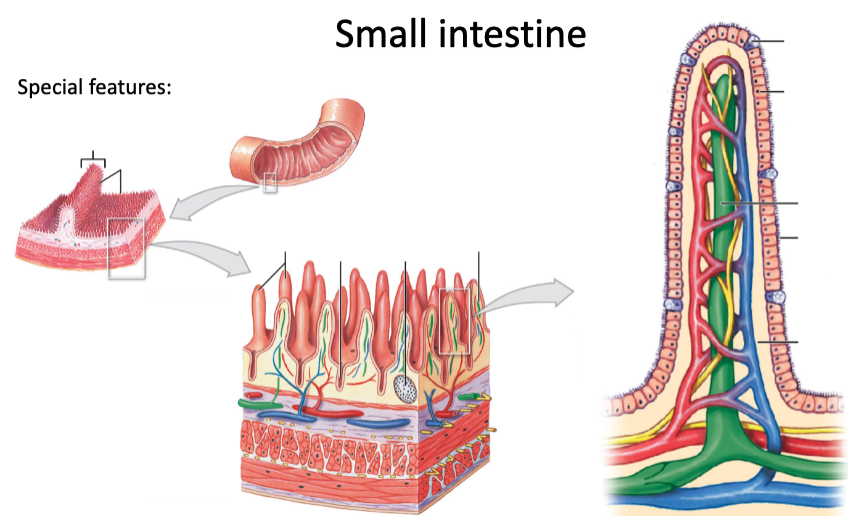
what are some special features general to the small intestine? describe them.
* circular folds (plicae circulares): increase digestive surface area
* villi: mucosa projections; have microvilli on apical surface (forming brush border) of epithelial columnar cells
* goblet cells: prod. mucus, found btwn epithelial cells
* lacteal: lymphatic capillaries located in center of villi
* intestinal glands (intestinal crypts): located in submucosa
* MALT: located in mucosa
* villi: mucosa projections; have microvilli on apical surface (forming brush border) of epithelial columnar cells
* goblet cells: prod. mucus, found btwn epithelial cells
* lacteal: lymphatic capillaries located in center of villi
* intestinal glands (intestinal crypts): located in submucosa
* MALT: located in mucosa
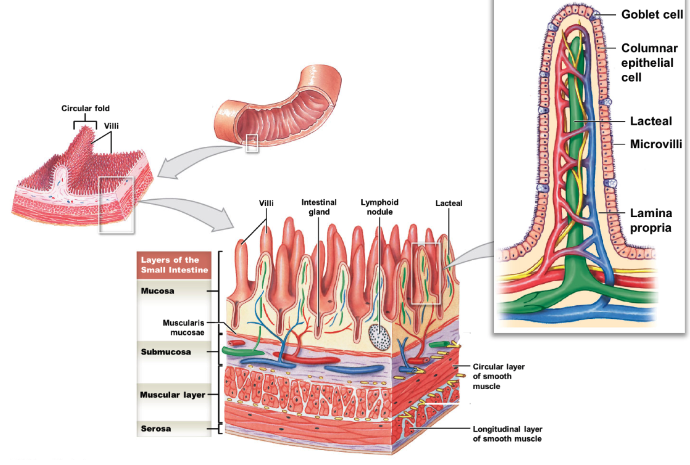
21
New cards
what is a special feature of the duodenum? of the ileum?
* duodenum → duodenal submucosal glands: prod. mucus
* also, duodenal papilla: opening for figestive enzymes from pancreas/gallbladder
* ileum → Peyer’s patches (aggregated lymphoid nodules): located in submucosa
* also, duodenal papilla: opening for figestive enzymes from pancreas/gallbladder
* ileum → Peyer’s patches (aggregated lymphoid nodules): located in submucosa
22
New cards
what are the 2 functions of the large intestine?
* absorption of electrolyte/vitamin/water
* compaction of feces for excretion
* compaction of feces for excretion
23
New cards
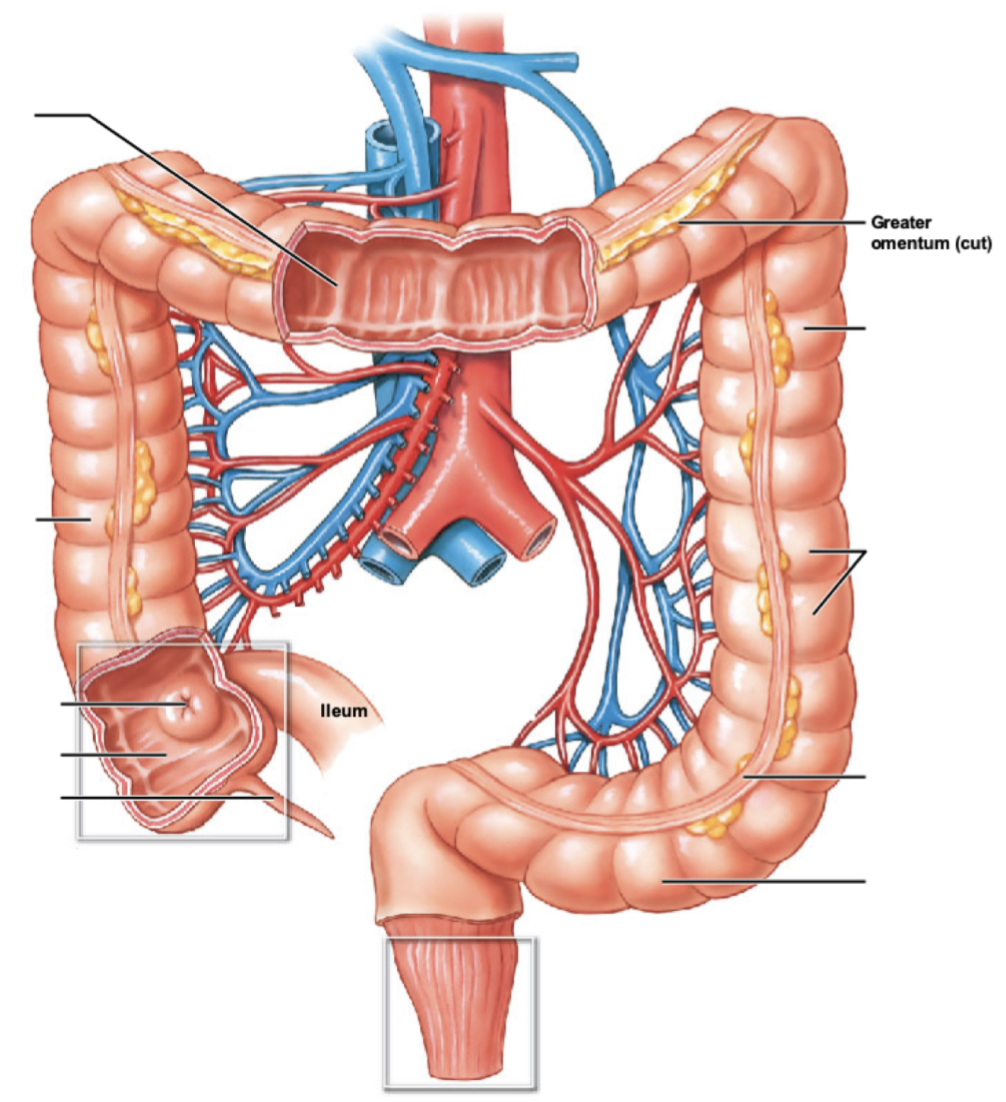
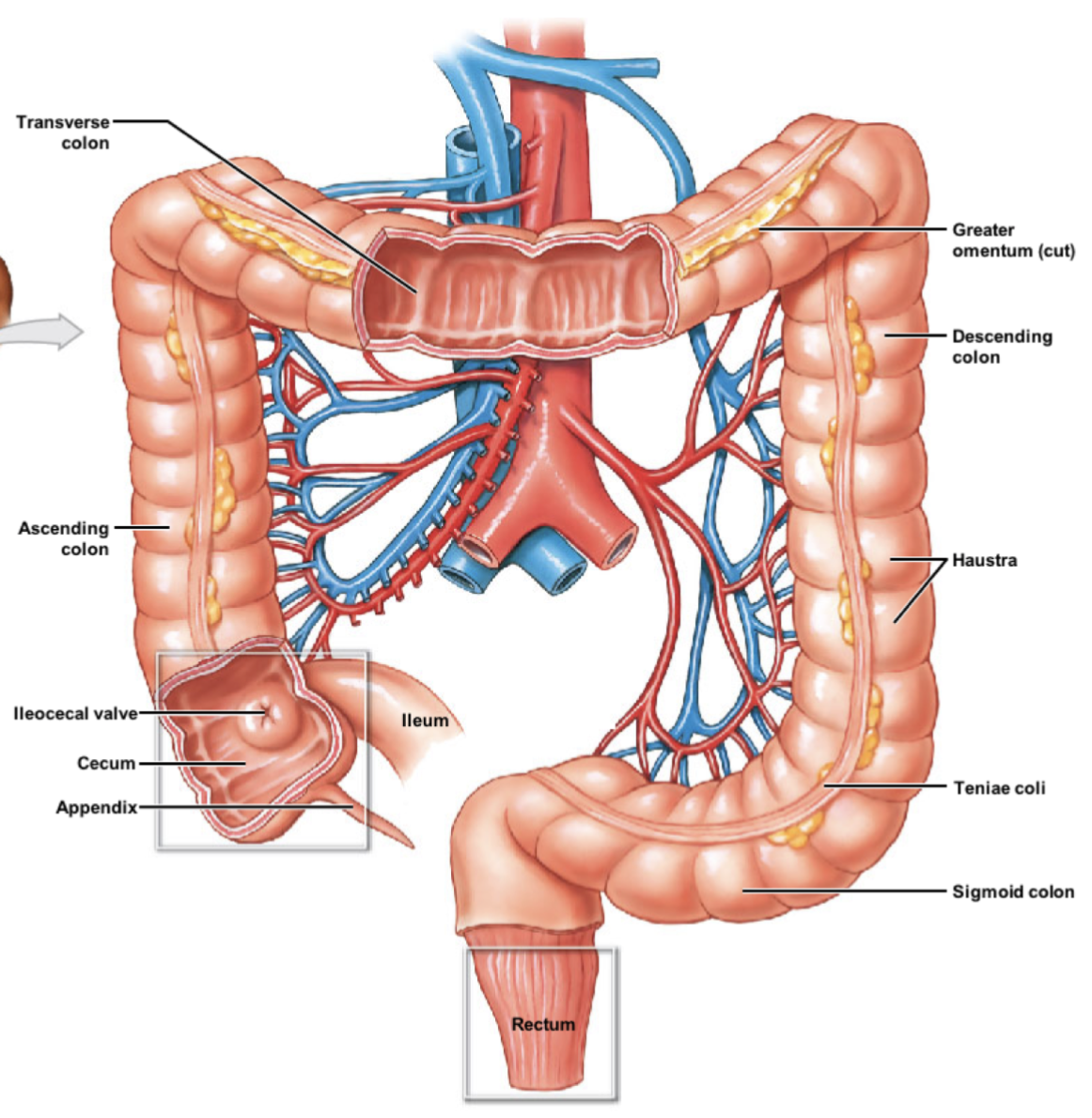
describe the order of travel within the large intestine, from ileocecal valve to rectum.
ileocecal valve → cecum → ascending colon → transverse colon → descending colon → sigmoid colon → rectum
24
New cards
describe the cecum and appendix of the large intestine. what connects the cecum and ileum? is the cecum intraperitoneal or retroperitoneal?
* cecum: expended pouch receiving digested food from ileum; thru ileocecal valve
* intraperitoneal
* appendix: small extension of cecum containing lymphatic tissue
* intraperitoneal
* appendix: small extension of cecum containing lymphatic tissue
25
New cards
describe the 4 regions the colon has. which are intraperitoneal vs. retroperitoneal?
* ascending colon: located along right side; retroperitoneal
* transverse colon: intraperitoneal
* descending colon: located along left side; retroperitoneal
* sigmoid colon: S-shaped regions \~15cm long; intraperitoneal
* covered by sigmoid mesocolon
* transverse colon: intraperitoneal
* descending colon: located along left side; retroperitoneal
* sigmoid colon: S-shaped regions \~15cm long; intraperitoneal
* covered by sigmoid mesocolon
26
New cards
describe the rectum of its length and function. what is the last portion of the rectum, and what is the exit called? for the exit, what does it have the controls passage?
* rectum: final 15cm tract that stores feces
* last portion of rectum → anal canal
* exit of tract → anus; has internal (involuntary) and external (voluntary) anal sphincters
* last portion of rectum → anal canal
* exit of tract → anus; has internal (involuntary) and external (voluntary) anal sphincters
27
New cards
what are 2 special features of the large intestine? (hint: band along intestine & pouches)
* teniae coli: modification of longitudinal muscle layer → forms 3 bands of muscle
* haustra: series of pouches along colon forms by teniae coli
* haustra: series of pouches along colon forms by teniae coli
28
New cards
describe the stomach by its:
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. special features
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. special features
1. simple columnar epithelium with lamina propria
2. NO villi
3. presence of gastric pits, rugae, oblique muscle layer
29
New cards
describe the duodenum by its:
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. relative presence of intestinal glands
6. special features
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. relative presence of intestinal glands
6. special features
1. simple columnar epithelium with lamina propria
2. some villi
3. some plicae
4. __few__ goblet cells
5. some intestinal glands
6. presence of duodenal submucosa glands
30
New cards
describe the jejunum by its:
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. special features..?
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. special features..?
1. simple columnar epithelium with lamina propria
2. some villi
3. **many** plicae
4. __few__ goblet cells
5. NO unique features
31
New cards
describe the ileum by its:
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. special features
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. special features
1. simple columnar epithelium with lamina propria
2. __few__ villi
3. __few__ plicae
4. some goblet cells
5. presence of Peyer’s patches, ileocecal valve
32
New cards
describe the colon by its:
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. relative presence of intestinal glands
6. special features
\
1. mucosa histology
2. relative presence of villi
3. relative presence of plicae
4. relative presence of goblet cells
5. relative presence of intestinal glands
6. special features
1. simple columnar epithelium with lamina propria
2. NO villi
3. NO plicae
4. **many** goblet cells
5. some intestinal glands
6. presence of MALT, teniae coli
33
New cards
where is the liver located it? is it intraperitoneal or retroperitoneal?
* located in right hypochondriac region; intraperitoneal
34
New cards
describe the 4 functions of the liver.
* regulate metabolic needs (sugar, fats, amino acids storage)
* hepatic portal system! filters blood containing absorbed nutrients & toxins from stomach, small & large intestine
* recycles erythrocytes & prod./secretes plasma proteins
* prod. bile → aid in digestion of lipids (fats)
* hepatic portal system! filters blood containing absorbed nutrients & toxins from stomach, small & large intestine
* recycles erythrocytes & prod./secretes plasma proteins
* prod. bile → aid in digestion of lipids (fats)
35
New cards
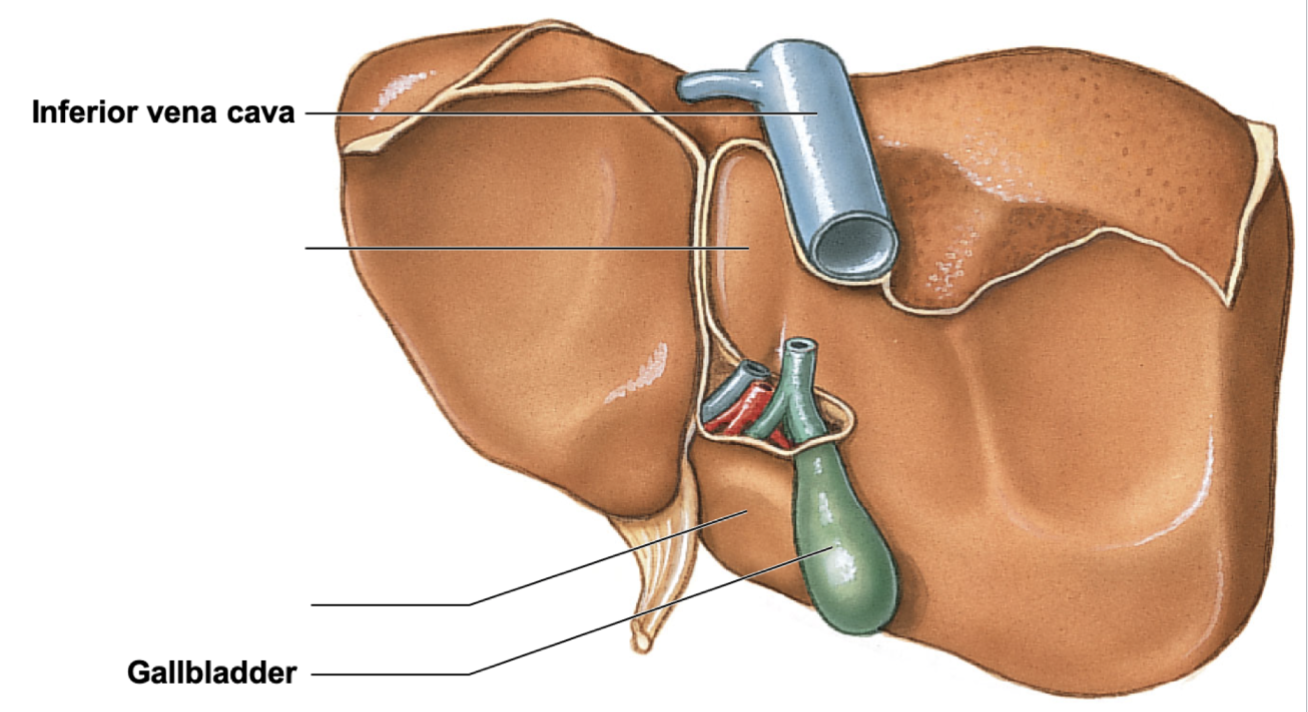
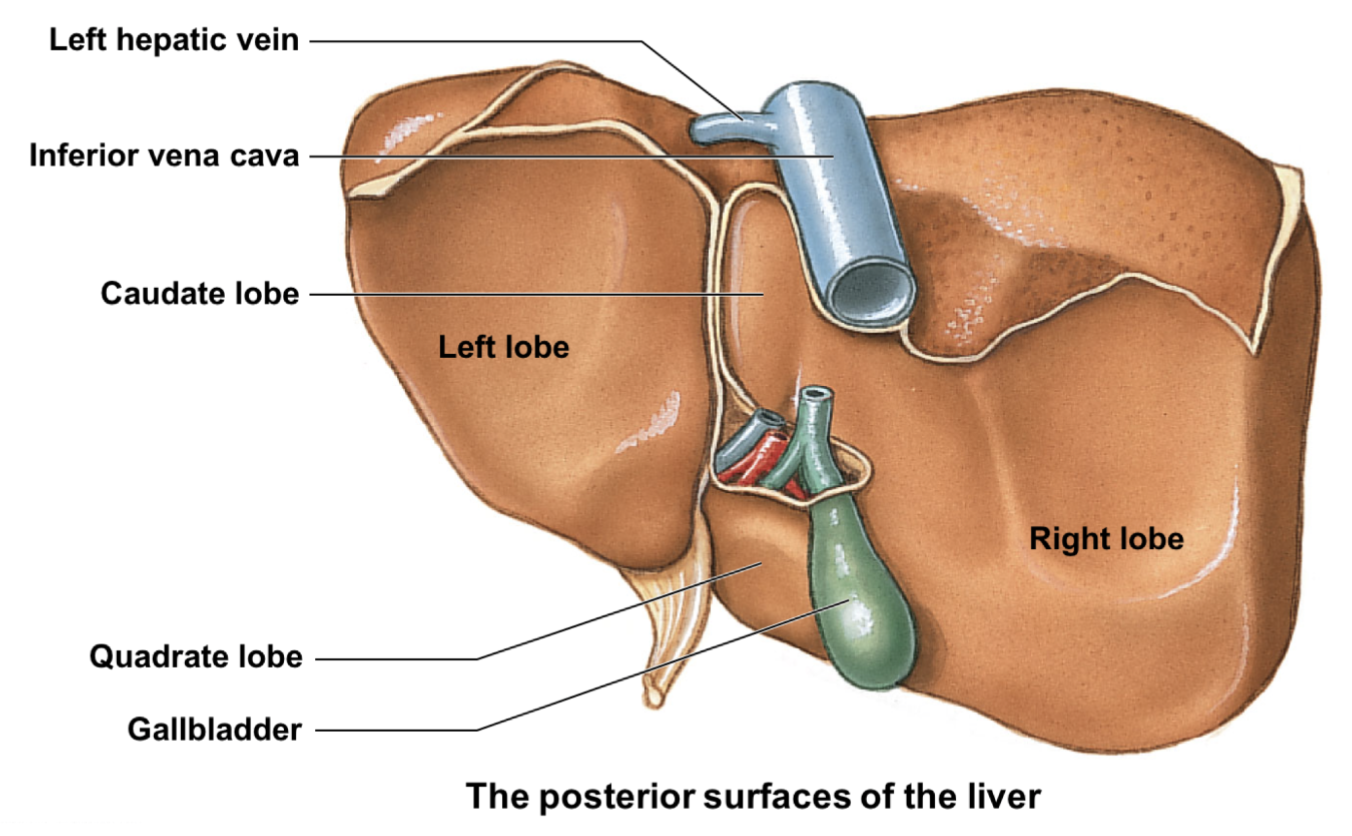
what are the 4 gross regions of the liver?
* right lobe
* left lobe
* caudate lobe: btwn right lobe and inferior vena cava
* quadrate loba: located inferior to caudate lobe
* left lobe
* caudate lobe: btwn right lobe and inferior vena cava
* quadrate loba: located inferior to caudate lobe
36
New cards
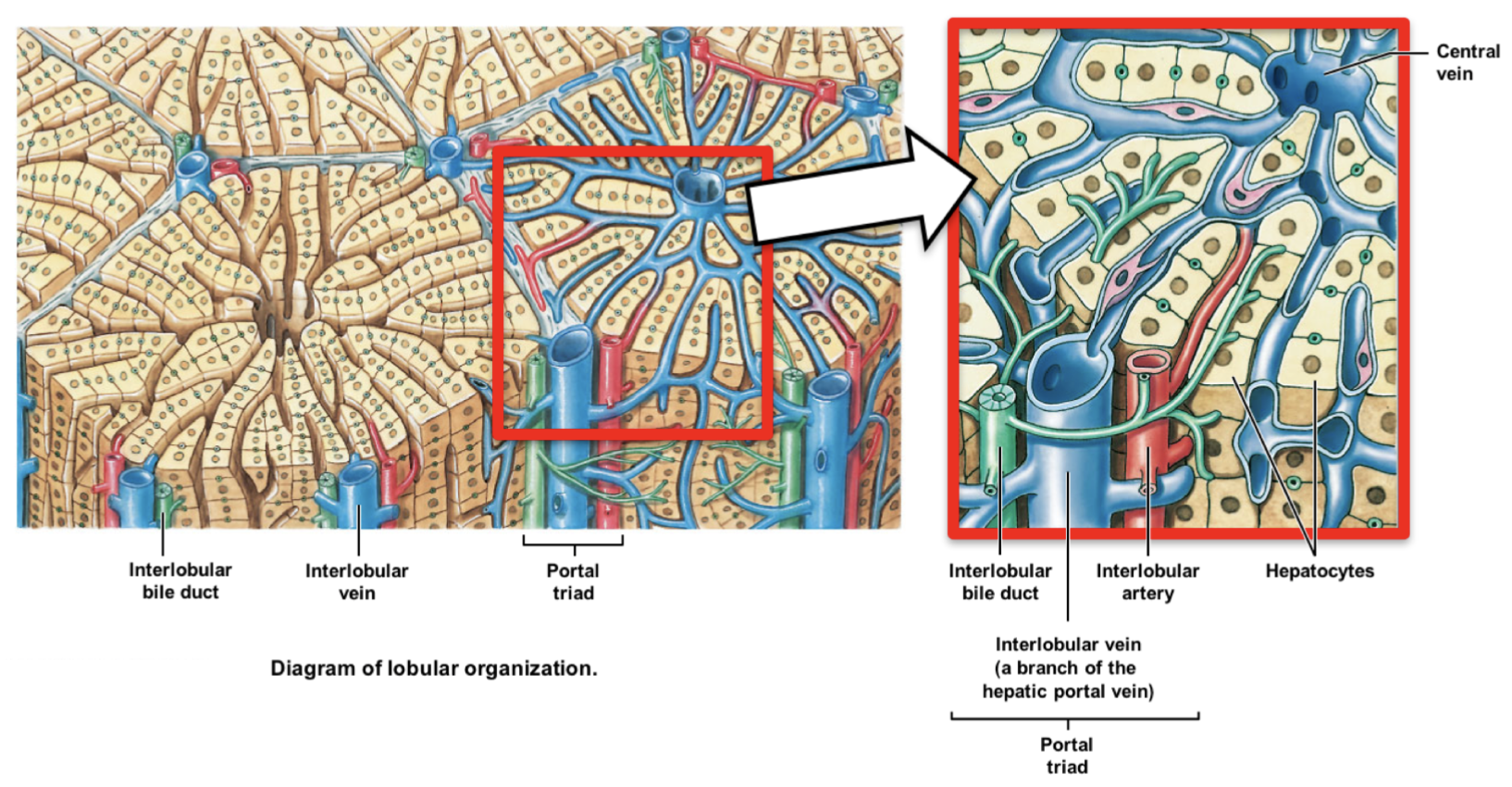
what is the functional unit of the liver? what are they composed of?
* functional liver unit = liver lobules (6-sided units); composed of hepatocytes
37
New cards
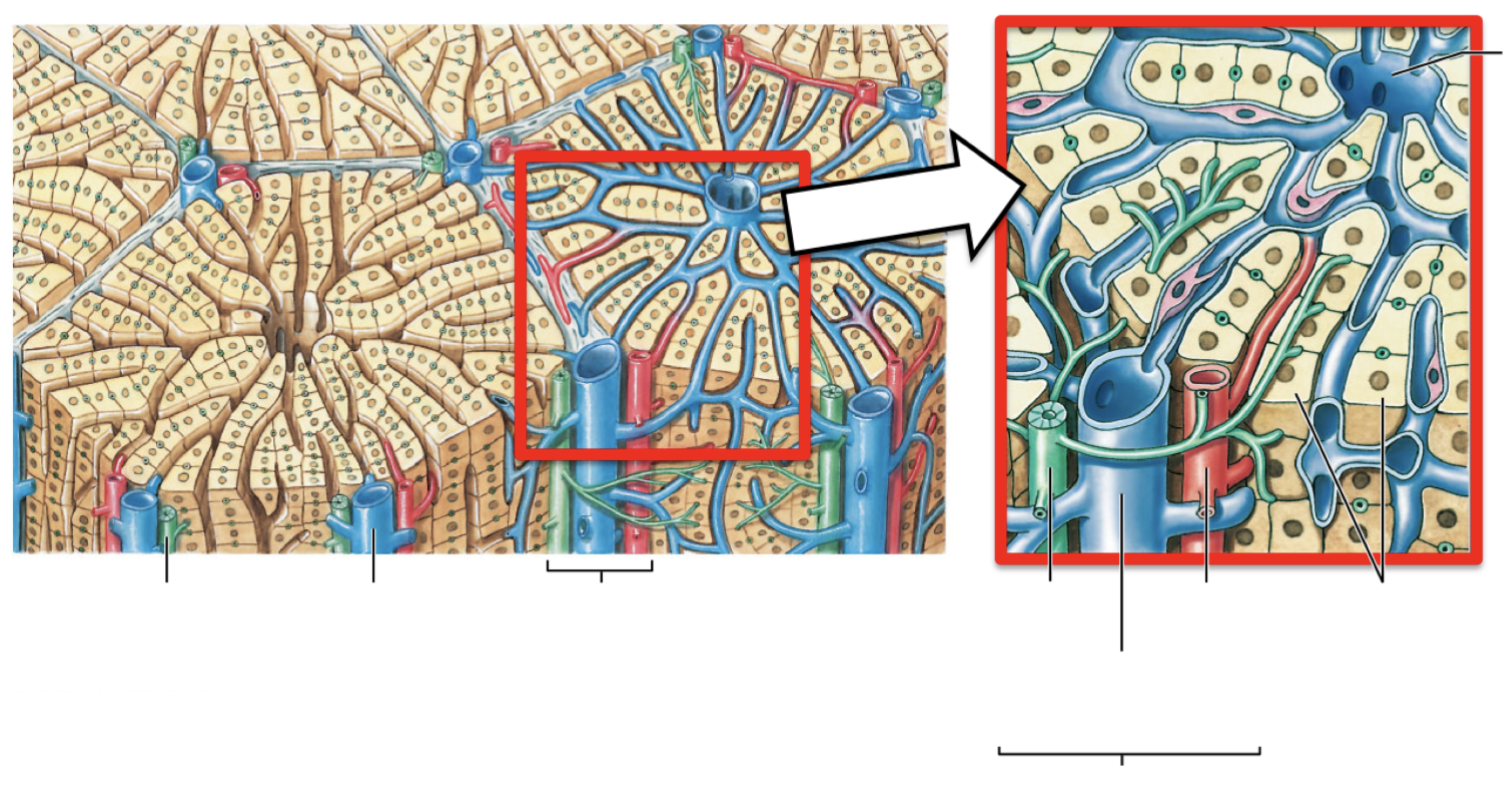
describe the portal triad. what 3 vessels do they contain? describe them and their purpose.
* portal triad: blood vessels bundle at each corner
* interlobular artery: carry oxygenated blood from hepatic artery
* interlobular vein: carries deoxygenated blood from hepatic portal system
* interlobular bile duct: carries bile formed by hepatocytes to right & left hepatic ducts, thru common hepatic duct, then to gallbladder
* opposite direction of blood flow
* interlobular artery: carry oxygenated blood from hepatic artery
* interlobular vein: carries deoxygenated blood from hepatic portal system
* interlobular bile duct: carries bile formed by hepatocytes to right & left hepatic ducts, thru common hepatic duct, then to gallbladder
* opposite direction of blood flow
38
New cards
describe the flow of blood in the liver.
* blood from interlobular artery & vein → through lobule → drains into central vein @ center of lobule → out to inferior vena cava
39
New cards
describe the bladder. what is its function? how does bile enter the gallbladder?
* gallbladder: small sac adjacent to liver; stores, concentrates, secretes bile
* bile from common hepatic duct → enters gallbladder thru cystic duct
* bile from common hepatic duct → enters gallbladder thru cystic duct
40
New cards
how does bile leave the gallbladder, and where does it exit through? what duct does the exit in question merge with, and where does it go into?
* gallbladder is stimulated → bile leaves out cystic duct, which merges with bile duct → into hepatopancreatic ampulla
41
New cards
how is bile released into the duodenum? through what?
bile released into duodenum when hepatopancreatic sphincter relaxes; through duodenal papilla
42
New cards
describe the flow of bile, from the hepatocytes to the gallbladder, where it’s stored until needed.
hepatocytes → interlobular bile duct → right & left hepatic ducts → common hepatic duct → cystic duct → gallbladder (stored)
43
New cards
during digestion, describe the flow of bile, from the gallbladder to the duodenum.
gallbladder → cystic duct → bile duct → hepatopancreatic sphincter & ampulla → duodenal papilla → duodenum
44
New cards
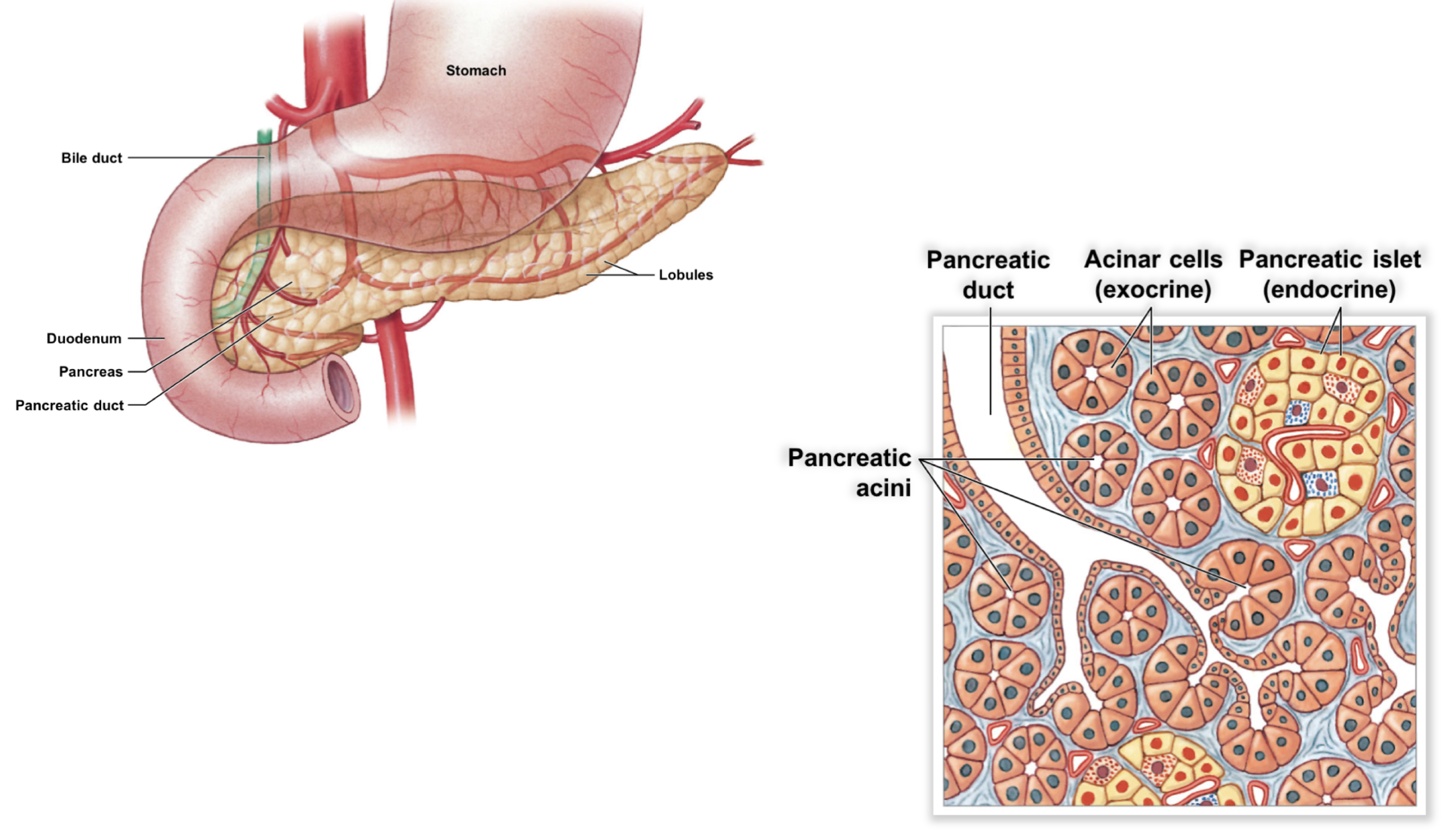
describe the pancreas of its location and if it’s intraperitoneal vs. retroperitoneal. what are its 4 functions?
* posterior to stomach; retroperitoneal
* produce digestive enzymes
* produce/secrete buffers (resist pH change) and hormones
* produce digestive enzymes
* produce/secrete buffers (resist pH change) and hormones
45
New cards
what 2 specialized cells help produce pancreatic juice (enzymes, buffers, hormones)?
* pancreatic acini
* pancreatic islets
* pancreatic islets
46
New cards
describe pancreatic acini. what cells do they have, and what type of glands are they? what do they produce? what are the 4 enzymes present in their product?
* acinar cells in exocrine glands; produce pancreating juice containing buffers (protect tissue from acidic chyme from stomach) and enzymes
* lipases, amylases, nucleases, proteinases/peptidases
* lipases, amylases, nucleases, proteinases/peptidases
47
New cards
describe pancreatic islets. what type of glands are they? what do they produce, and what is their products’ function?
* endocrine glands btwn pancreatic acini; produce hormones insulin and glucagon → regular sugar levels in blood
48
New cards
describe the flow of pancreatic juice, which is secreted during digestion, beginning from pancreatic acini to duodenum.
pancreatic acini → pancreatic duct → hepatopancreatic sphincter & ampulla → duodenal papilla → duodenum
49
New cards
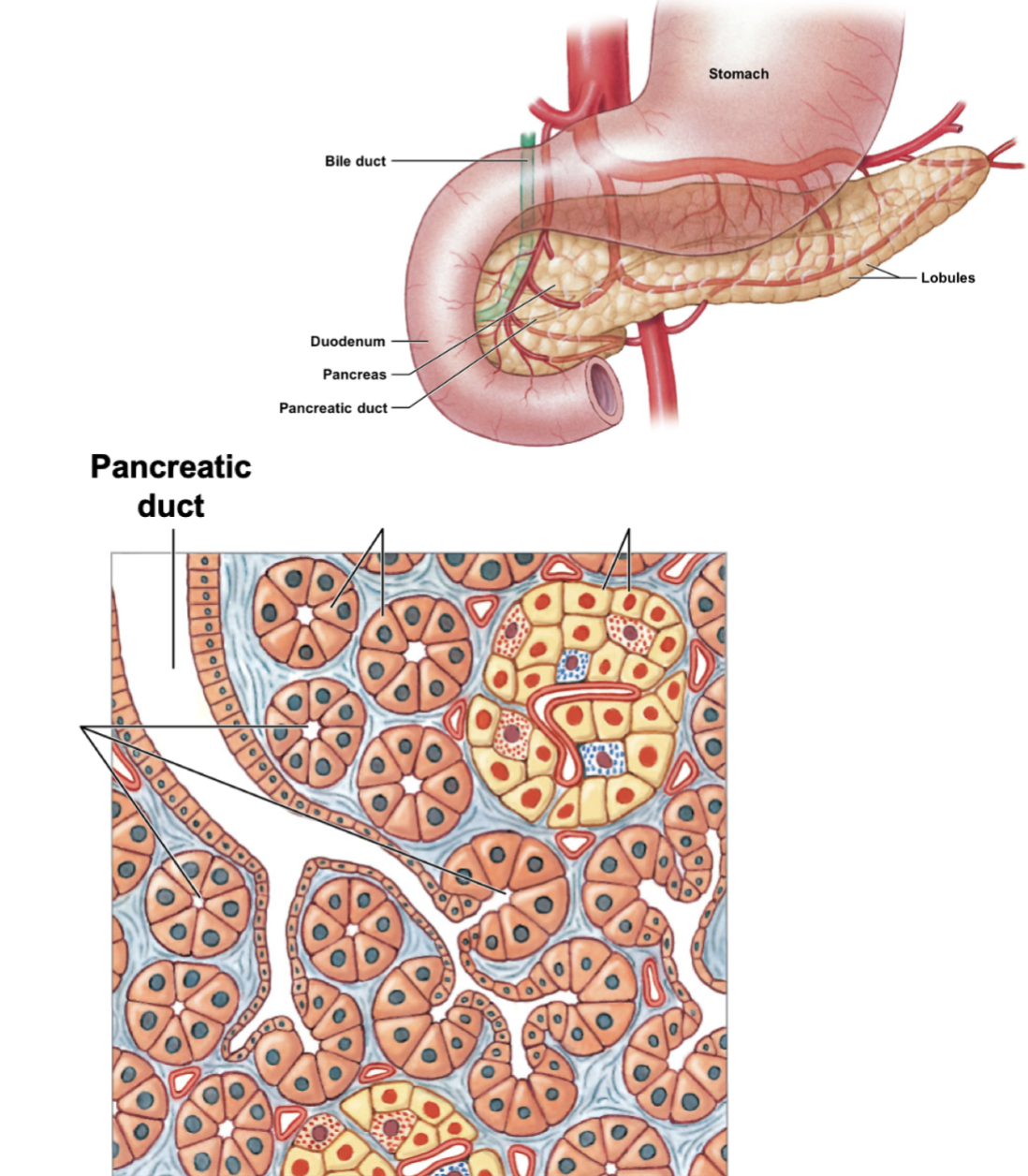
identify the various pancreatic parts.