Hesi anatomy review part 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/114
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
1
New cards
What minerals are stored in bone?
calcium and phosphorus
2
New cards
what are the two types of bone tissue?
compact (dense) and spongy (cancellous)
3
New cards
Spongy bone contains a
latticework of plates of bone with spaces in between (trabeculae)
4
New cards
Cells that form bone tissue
osteoblasts
5
New cards
Osteocytes
osteoblasts that become fixed in the dense bone matrix and stop dividing but continue to maintain bone tissue
6
New cards
Osteoclasts
break down the bone tissue
7
New cards
Epiphysis
on a long bone; the site of bone growth in length
8
New cards
Diaphysis
the shaft of a long bone
covered by compact bone
has a hollow center called the medullary cavity
covered by compact bone
has a hollow center called the medullary cavity
9
New cards
Axial skeleton
skull, vertebral column, 12 pairs of ribs, and sternum
10
New cards
Appendicular skeleton
shoulder and hip girdles, and extremities
11
New cards
how many bones in the skull
28
14 facial bones
14 cranial vault bones
14 facial bones
14 cranial vault bones
12
New cards
How many sections of the vertebral column and what are they?
5
7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
(5 fused) sacrum
(4 fused) coccyx
7 cervical vertebrae
12 thoracic vertebrae
5 lumbar vertebrae
(5 fused) sacrum
(4 fused) coccyx
13
New cards
Contractile units of muscle
sarcomere
14
New cards
myofibril
long, rod-shaped organelles that nearly fill the sarcoplasm (cytoplasm of muscle cell)
15
New cards
what myofilaments are within contractile proteins?
actin and myosin
16
New cards
actin
thin protein
17
New cards
myosin
thick protein
18
New cards
muscle contraction occurs through the
sliding filament model
19
New cards
what is the sliding filament model?
myosin binds to actin and pulls it toward the center of the sarcomere
20
New cards
agonist
muscle that performs a given movement (prime mover)
21
New cards
antagonist
muscle that produces the opposite movement
22
New cards
synergists
muscles that work in cooperation with the agonist
23
New cards
flexors
reduce the angle at a joint
24
New cards
extensors
increase the angle
25
New cards
abductors
draw a limb away from the midline
26
New cards
adductors
return the limb back toward the body
27
New cards
central nervous system
the brain and spinal cord
28
New cards
peripheral nervous system
all other nerves in the body, namely cranial nerves and peripheral nerves
29
New cards
peripheral nervous system is divided into the
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
\
autonomic nervous system
\
30
New cards
somatic nervous system
skin, muscles, bones, joints
31
New cards
autonomic nervous system
digestion, heart rate, blood pressure, urination
32
New cards
what are the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
parasympathetic and sympathetic
33
New cards
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
34
New cards
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
35
New cards
all actions of the nervous system depend on the transmission of
nerve impulses over neurons
36
New cards
functional unit of the nervous system
neuron
37
New cards
what are the main parts of a neuron
the cell body, axon and dendrites
38
New cards
dendrites transmit the impulse
toward the cell body
39
New cards
axons transmit the impulse
away from the cell body
40
New cards
afferent neurons transmit impulses
toward the CNS
41
New cards
examples of effector organs
muscles, glands, digestive organs
42
New cards
four major parts of the brain
cerebrum
cerebellum
diencephalon
brainstem
cerebellum
diencephalon
brainstem
43
New cards
function of cerebrum
sensory interpretation, movement, thinking and personality
44
New cards
function of the cerebellum
responsible for muscle coordination
45
New cards
function of the diencephalon
thalamus- routes incoming sensory info to appropriate part of the cerebrum
hypothalamus- monitors autonomic nervous system and endocrine system
hypothalamus- monitors autonomic nervous system and endocrine system
46
New cards
function of brainstem
respiration and heart rate
47
New cards
which layer of the skin undergoes mitosis?
stratum (germinativum) basale
48
New cards
sensory impulses enter the ____ spinal cord
posterior
49
New cards
motor impulses leave through the ____ spinal cord
anterior
50
New cards
where do the nervous and endocrine systems meet?
the hypothalamus and pituitary gland
51
New cards
what governs the pituitary gland?
the hypothalamus
52
New cards
two major groups of hormones are?
steroid and non-steroid hormones
53
New cards
what do steroid hormones do?
enter the target cell and have a direct effect on the DNA of the nucleus
54
New cards
what do non steroid hormones do?
remain at the cell surface and act through a second messenger, usually a substance called adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
55
New cards
how do most hormones affect cell activity?
by altering the rate of protein synthesis
56
New cards
hypothalamus attaches to the pituitary gland via the
infundibulum
57
New cards
somatotropin hormone also known as ______ does what?
growth hormone
stimulates growth in all organs
stimulates growth in all organs
58
New cards
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
stimulates secretion of adrenal cortex hormones
59
New cards
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
stimulates secretion of thyroid hormones
60
New cards
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
stimulates secretion of ovarian follicles and secretion of estrogens in females; stimulates sperm production in males
61
New cards
luteinizing hormone (LH)
triggers ovulation in females; stimulates secretion of testosterone in males
62
New cards
oxytocin
stimulates uterine contractions during labor; stimulates milk ejection from the mammary glands; also known as the bonding hormone
63
New cards
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
stimulates retention of water by the kidneys
64
New cards
thyroid gland
secretes thyroid hormones which regulate metabolism, and calcitonin which decreases blood calcium levels
65
New cards
parathyroid glands
secrete parathyroid hormone, which increases blood **calcium** levels
66
New cards
adrenal glands
cortex secretes cortisol
medulla secretes adrenaline (intensifies sympathetic response)
medulla secretes adrenaline (intensifies sympathetic response)
67
New cards
pancreas
secretes insulin, which decreases blood glucose levels, and glucagon, which increases blood glucose levels
68
New cards
gonads
ovaries secrete estrogens, which develop and maintain female sexual characteristics and progesterone, which maintains pregnancy; testes secrete testosterone, which develops and maintains male sexual characteristics
69
New cards
what are the hormones released from the posterior lobe of the pituitary
1. oxytocin
2. antidiuretic hormone
70
New cards
what are the tropic hormones (released from anterior lobe of pituitary)?
1. adrenocorticotropic hormone
2. thyroid-stimulating hormone
3. follicle-stimulating hormone
4. luteinizing hormone
5. growth hormone
6. prolactin
71
New cards
what are the tropic hormones?
1. adrenocorticotropic hormone
2. thyroid-stimulating hormone
3. follicle-stimulating hormone
4. luteinizing hormone
72
New cards
name the granular leukocytes
neutrophils
basophils
eosinophils
basophils
eosinophils
73
New cards
what do agranular leukocytes do
phagocytosis and production of antibodies
74
New cards
what are the granular leukocytes
neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils
75
New cards
what do granular leukocytes do?
antibody production
cellular immune responses
phagocytosis
cellular immune responses
phagocytosis
76
New cards
deoxygenated blood returning from the body is received by the
right atrium
77
New cards
the tricuspid valve is between the
right atrium and the right ventricle
78
New cards
bicuspid valve also known as the ____ is between the
mitral valve; left atrium and left ventricle
79
New cards
pulmonary valve
between the right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
80
New cards
aortic semilunar valve
between the left ventricle and the aorta
81
New cards
what node initiates heart beat?
sinoatrial node
82
New cards
cardiac cycle
period from the end of one ventricular contraction to the end of the next ventricular contraction
83
New cards
systole
contraction phase
84
New cards
diastole
relaxation phase
85
New cards
what is the structure responsible for the site of exchange of water, nutrients, and waste products between the blood and surrounding tissues?
capillaries
86
New cards
these drain blood from the capillaries and send it to veins
venules
87
New cards
walls of arteries are ________ and ________ and carry blood under _____ pressure__
thick, elastic, high pressure
88
New cards
respiratory control center?
medulla oblongata
89
New cards
external respiration
the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the blood through the alveoli
90
New cards
internal respiration
the exchange of gases between the blood and body cells
91
New cards
inhalation requires contraction of the ________
diaphragm
92
New cards
some carbon dioxide is carried on hemoglobin cells but most is converted to bicarbonate ion in the blood via the enzyme _______
carbonic anhydrase
93
New cards
what is a regulator of blood PH?
carbon dioxide
94
New cards
layers of the digestive tract from innermost to outer
mucous membrane
submucous layer
muscular layer
serous layer
submucous layer
muscular layer
serous layer
95
New cards
accessory organs of the digestive system?
liver, pancreas and gallbladder
96
New cards
mastication
chewing
97
New cards
name the three pairs of salivary glands
1. parotid glands
2. sublingual glands
3. submandibular glands
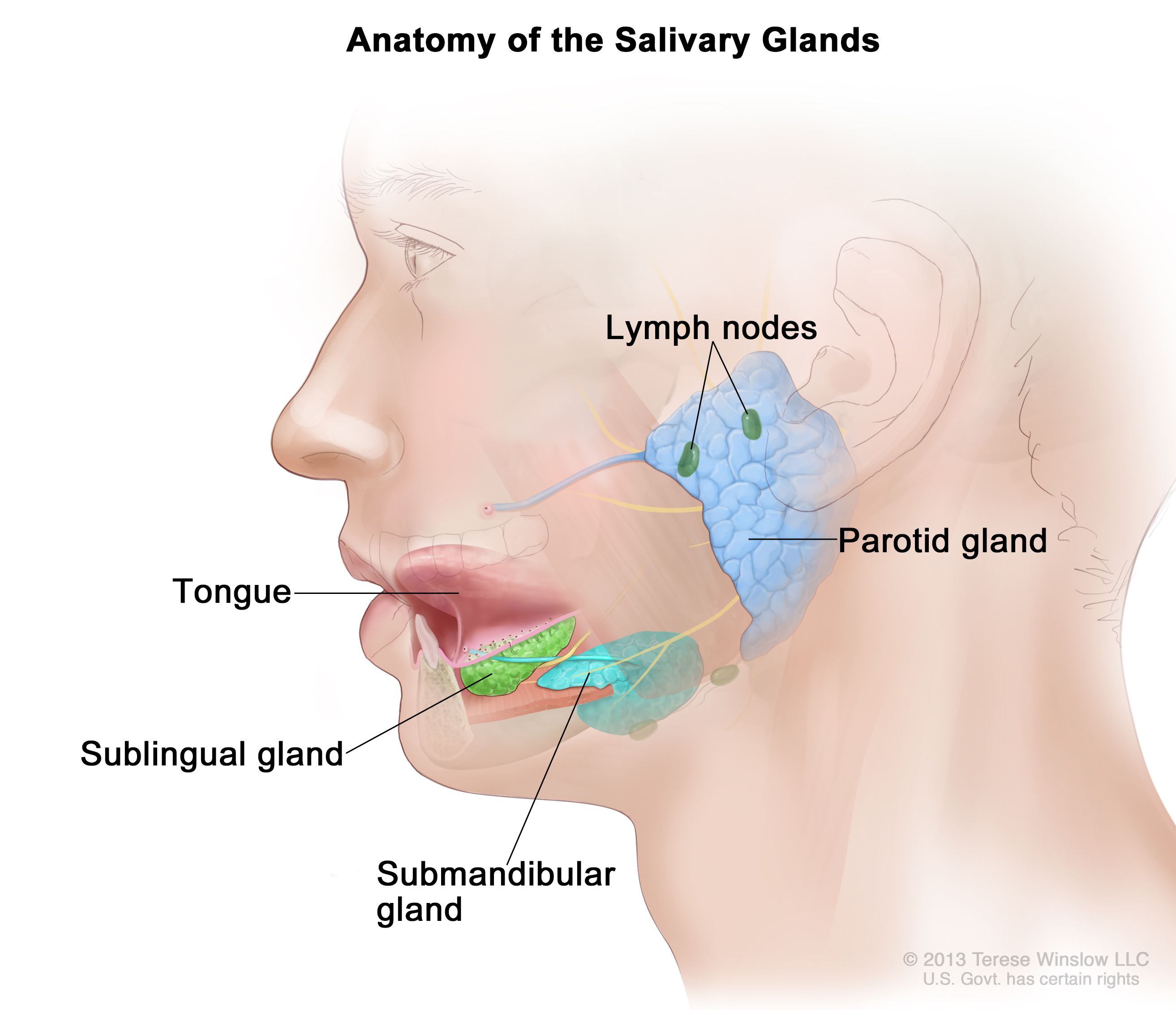
98
New cards
What enzyme in saliva starts digestion of complex carbohydrates?
amylase
99
New cards
what is secreted in the stomach that unwinds proteins?
hydrochloric acid
100
New cards
what enzyme digests proteins in the stomach?
pepsin