Art of the Aegean Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:23 AM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
1
New cards
Anatolia
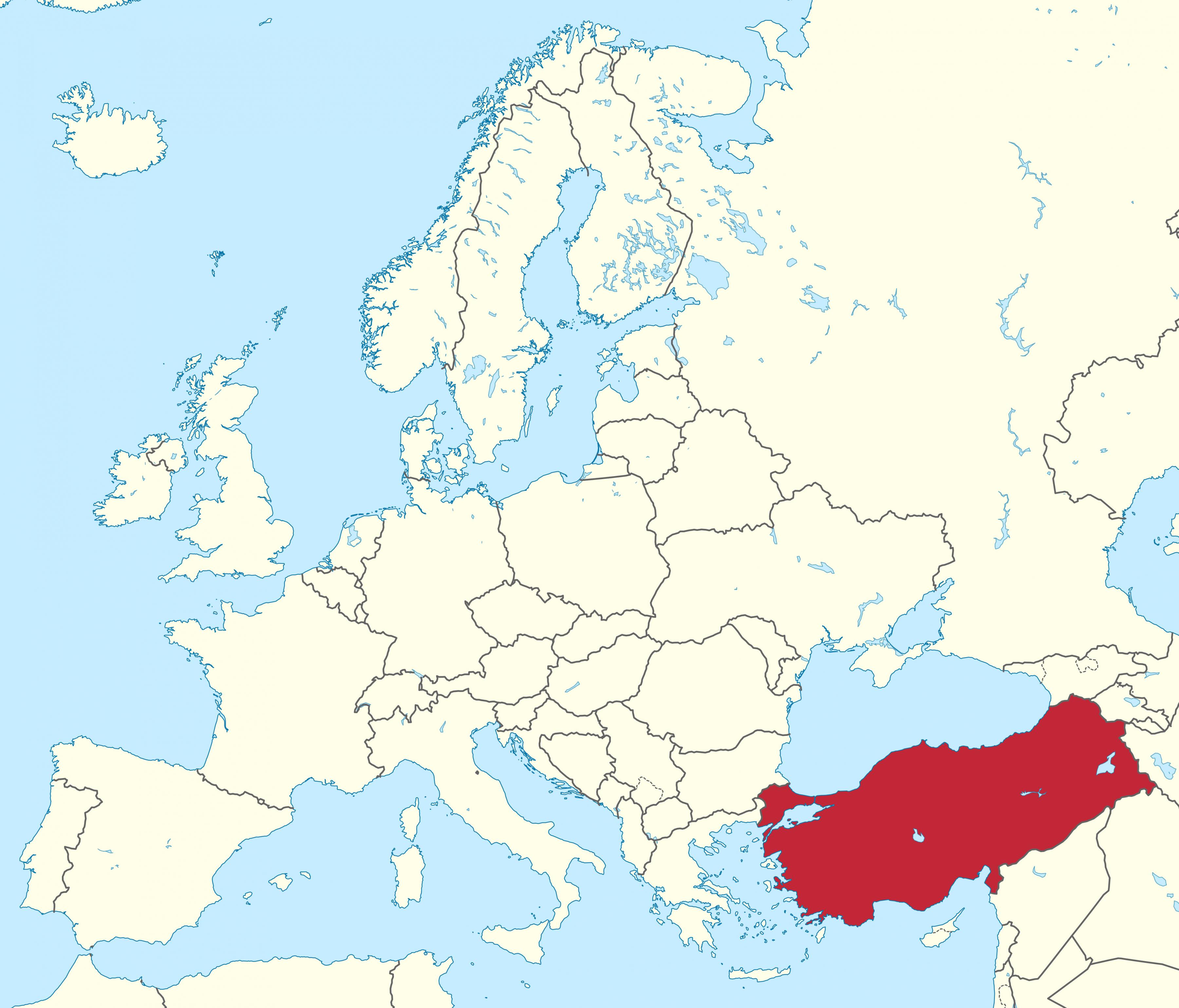
2
New cards
Crete
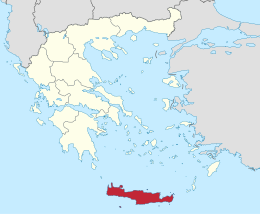
3
New cards
Cycladic Islands
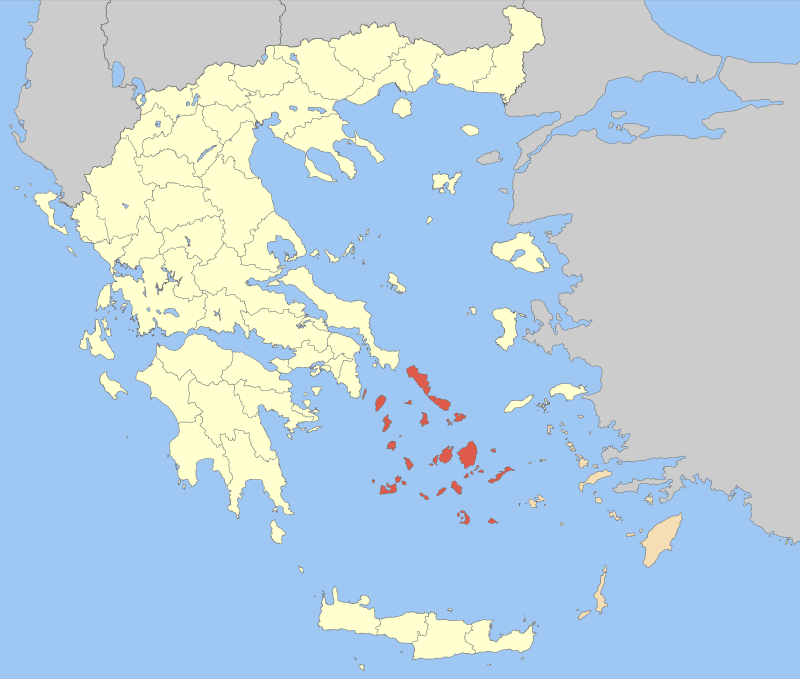
4
New cards
Dimini
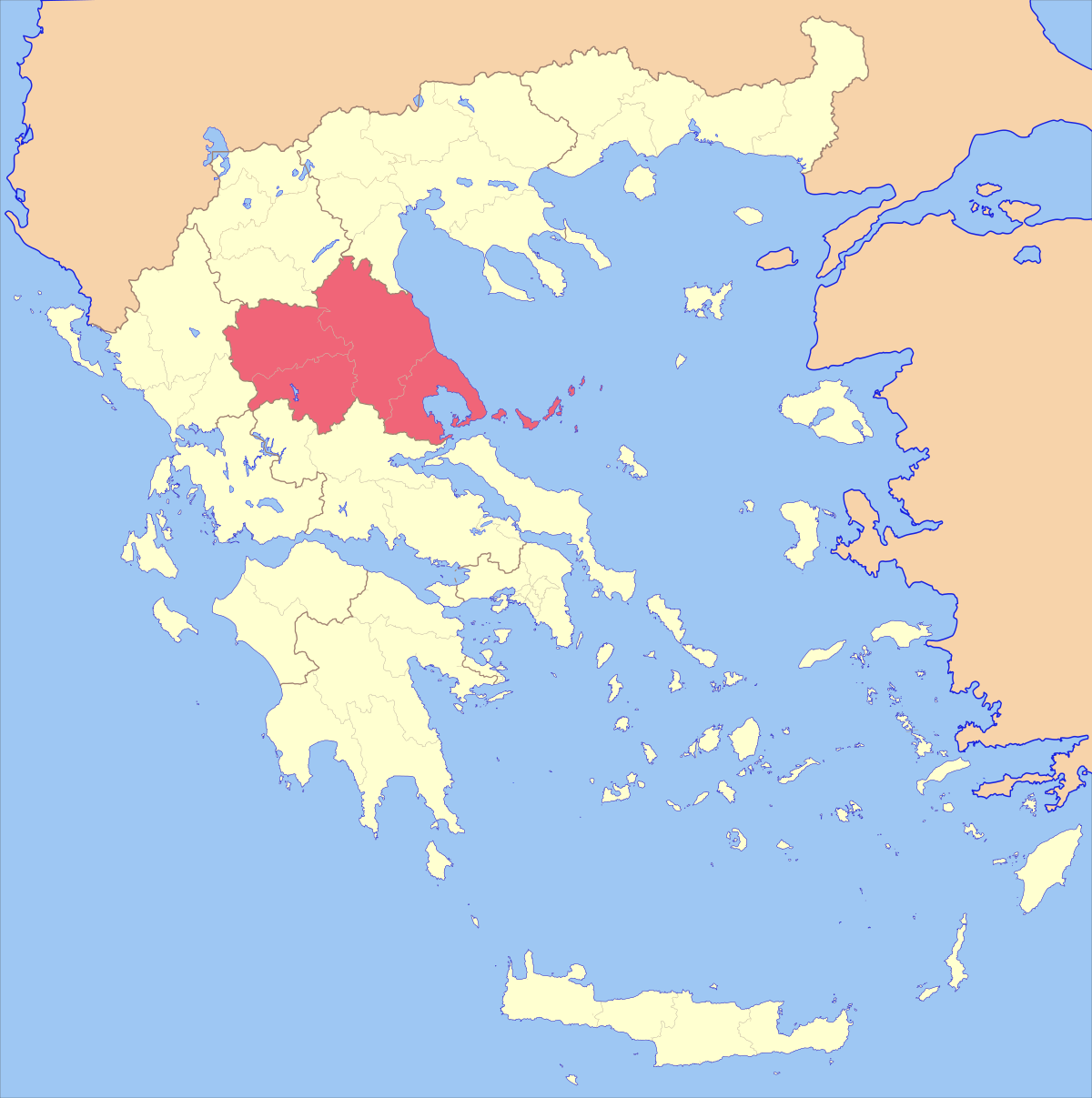
5
New cards
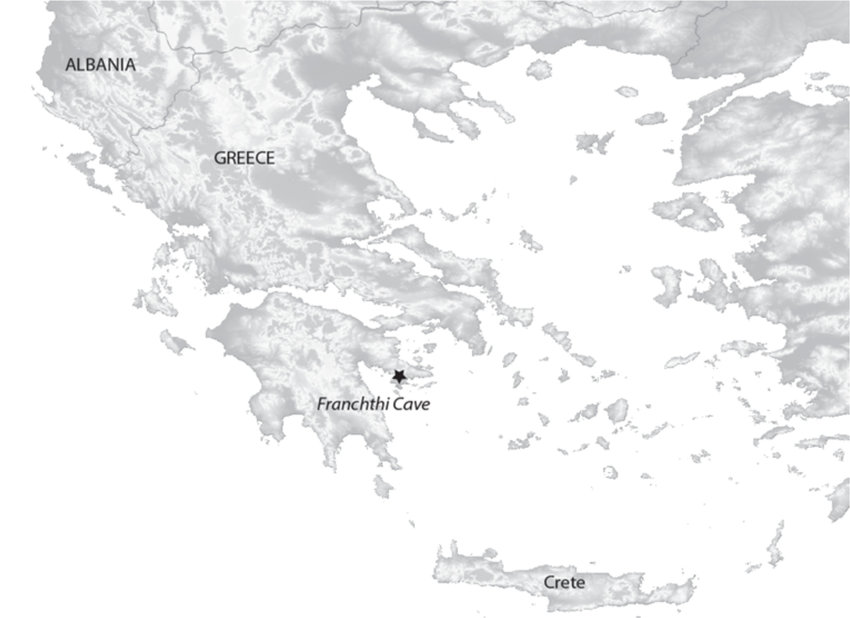
Franchthi Cave (map)
6
New cards
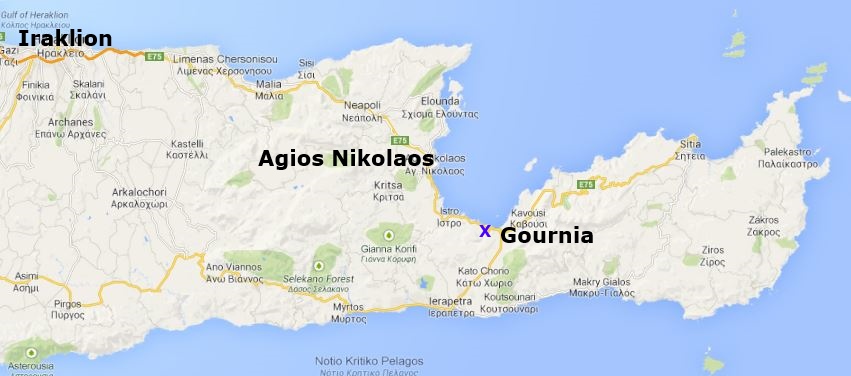
Gournia
7
New cards
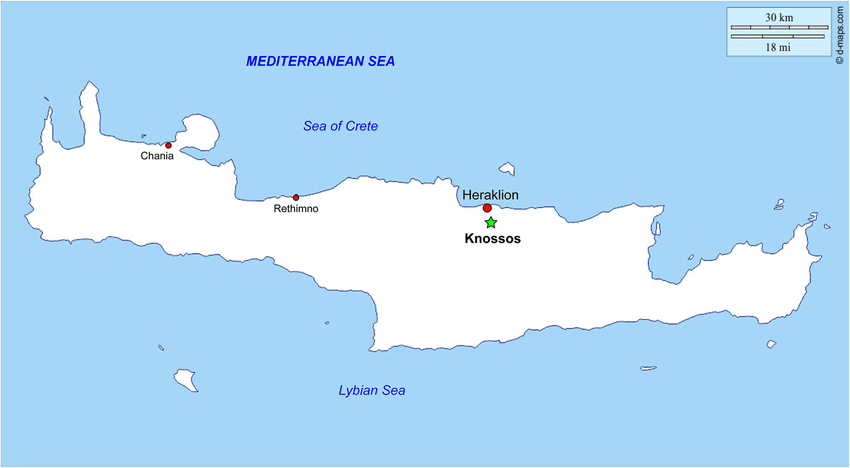
Knossos
8
New cards
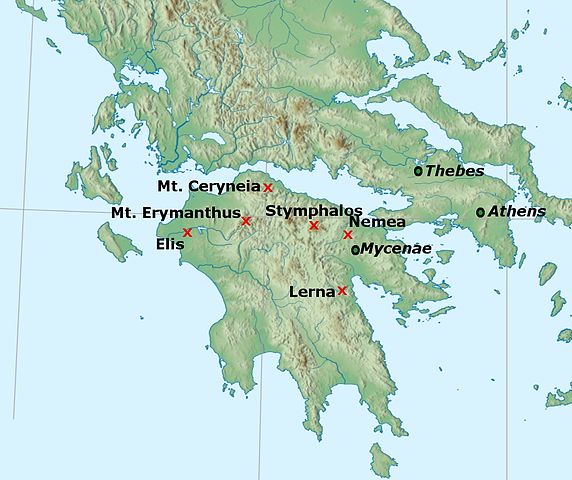
Lerna
9
New cards
Melos
10
New cards
Mycenae
11
New cards
Fournou Korifi
12
New cards
Peloponnese
13
New cards
Troy
14
New cards
Frying Pan
Cycladic art piece, not actually a frying pan, maybe a mirror?, symbolic spirals, long boats, etched bronze
15
New cards
Abrasion/Abrasives
material used to smooth/polish stone, mostly marble for sculpture, emery is common
16
New cards
Absolute Chronology
assigning exact dates to things (as opposed to relative chronology where you are estimating based on things before and after)
17
New cards
Abutting Walls
two walls that touch each other but were built at different times
18
New cards
Agglutinative Growth
how buildings get added on to over time with abutting walls
19
New cards
Attribution (to an artist/master)
saying a piece is from an ancient artist (whether it is or not) to give it higher monetary value, usually based on a set of similar characteristics
20
New cards
Bonding Walls
the way you lay brick and hold them together to keep the wall standing
21
New cards
Bronze
usually a copper and tin alloy that is shiny and can be molded and crafted into weapons, sculpture and practical wares
22
New cards
Bronze Age
the time after the copper age, in Greece (3,000-1050 BC)
23
New cards
Candiavervus
prehistoric Deer that Strasser talked a lot about in his article
24
New cards
Canon of Proportions
stencil used to make sure art carvings were equally proportional, Egyptians had them, unsure if Cyclades used them for their figurines
25
New cards
Cist Grave
a stone grave used to house the bodies of the dead, usually have grave goods and some sort of marker
26
New cards
Corridor House
Lerna, houses with long corridors on the sides with stairwells that lead to the 2nd story
27
New cards
Cycladic
the civilization that exists on the Cycladic Islands
28
New cards
Emery
abrasive stone used for smoothing marble
29
New cards
Ethnographic Parallel/Comparison
looking at current civilization practices and traditions to link archaeological evidence to an ancient practice or tradition
30
New cards
Folded-Arm-Figure (FAF)
Cycladic form of stone sculpture of a (typically) female figure with crossed arms
31
New cards
Franchthi Cave (term)
Southern Greek cave just above sea level with archaeological evidence dating back to the Paleolithic period (20,000 BC), but most known for the mesolithic burials and Neolithic architecture
32
New cards
Ghost of Paint
basically the negative space left on a figure where paint was that protected the stone against the weathering and sun damage that happened to the rest of the statue
33
New cards
Hearth
a center fireplace in most dwellings (Tsoungiza had a clay one at the center)
34
New cards
Hellenic Arc
the stretch of the European continent that abuts the African continent and basically outlines Greece down to Crete and back up to Anatolia
35
New cards
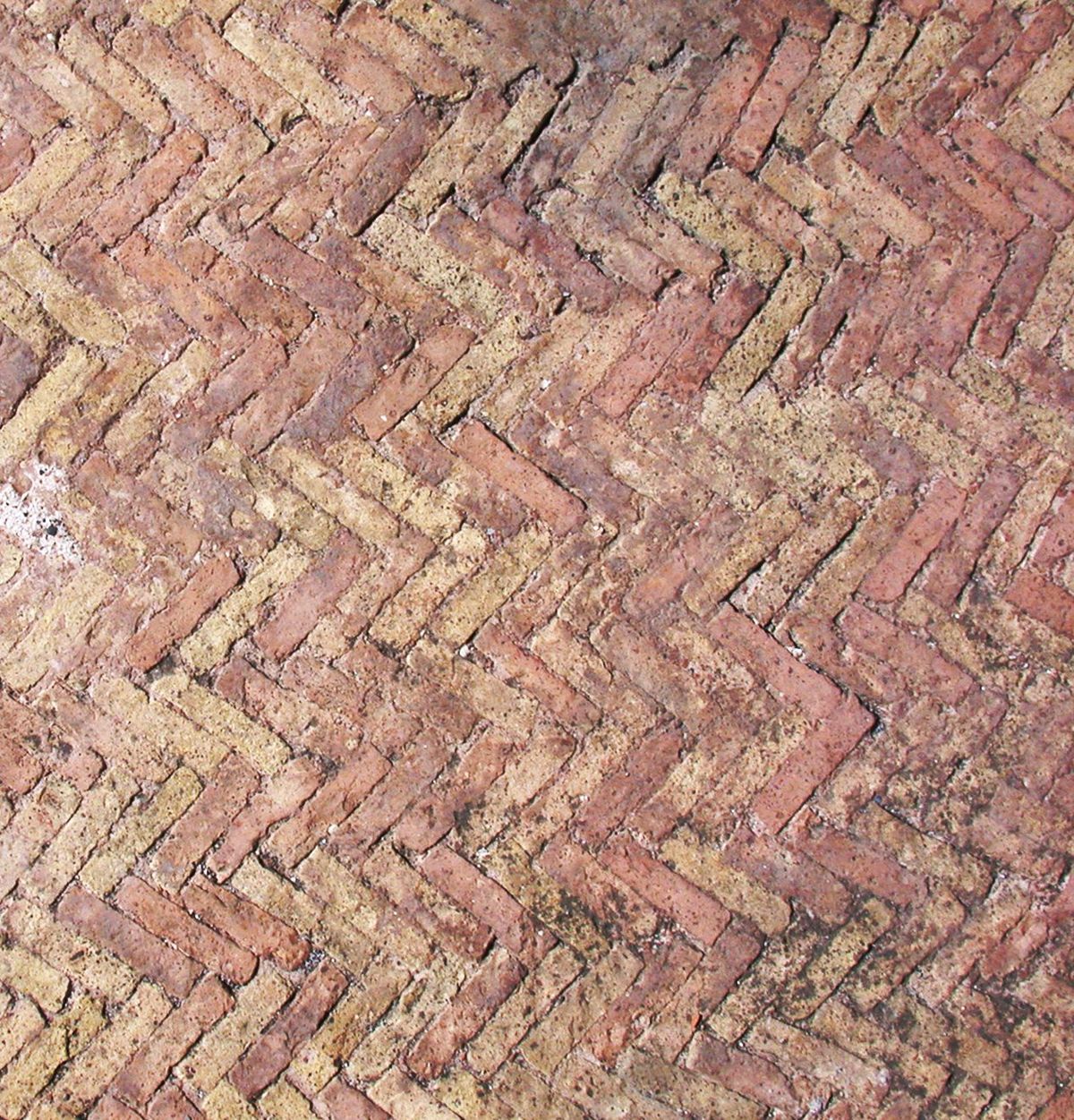
Herringbone Masonry
a specific alternating pattern of laying bricks that the house of the tiles used in Lerna

36
New cards
Incised Decoration
Keros-Syros Artifacts had this, basically you cut designs into pottery
37
New cards
Kernos (Kernoi)
multiple cups attached to a centerpiece that was used a multi-offering vessel
38
New cards
Longship
seen on the Cycladic frying pan, basically a long sailing vessel for traversing the Aegean Sea in the Bronze Age
39
New cards
Lyre-Shaped Head
seen on the Spedos variety of Cycladic figurines
40
New cards
Megaron
In Dimini, it's the largest room in the Mycenaean palace complexes that held lots of pots filled with goods and figurines
41
New cards
Mesolithic
Transitional period of the Stone Age between Paleolithic and Neolithic (8,000-5,000 BC)
42
New cards
Minoan
Ancient civilization based in Knossos on the island of Crete
43
New cards
Minos
Ancient King of the Minoan civilization, known for starting the Minotaur legend
44
New cards
Minotaur
mythological half bull/half human that lived in the labyrinth below King Minos's tower and ate the yearly tribute of 12 athenian's every year until Theseus killed him
45
New cards
Mudbrick
the method of sun-drying mud into bricks to use for infrastructure, we have some at the House of the Tiles because they got fired and preserved when it burned down
46
New cards
Naturalistic Art
The Minoan practice of decorating their fresco with many examples of natural depictions such as animals, foliage and landscapes
47
New cards
Neolithic
The settling down of nomadic groups at the end of the Stone Age before the Bronze Age, find a lot of inhumations, stone tools and early buildings (6000-3000 BC)
48
New cards
Obsidian
Volcanic glass that can be chipped into very sharp and very useful tools
49
New cards
Paleolithic
Earliest part of the Stone Age since they hadn't yet developed ways of smelting metals, nomadic peoples, mostly find camp site remains and stone tools (300,000-6,000 BC)
50
New cards
Peloponnese (term)
Southern region of Greece where the Mycenaean culture was based
51
New cards
Petroglyph
Paleolithic form of art done by carving into a stone wall
52
New cards
Pithos (Pithoi)
a large ceramic vase used for storing things
53
New cards
Prepalatial Period
the early Minoan period from 3000-1900BC
54
New cards
Provenance
where did you buy the artifact from, who owned it before you, what museums has it been in
55
New cards
Provenience
where did the artifact come from, meaning what grave, what site, what country
56
New cards
Pubic Triangle
a geometric depiction of female genitalia that appears on many Stone Age/EBA art pieces
57
New cards
Pyxis
a grave good little jar that could have been for cosmetics
58
New cards
Rectilinear Plan/Layout
a building design theme that consists primarily of straight lines, right angles, and square or rectangular shapes
59
New cards
Relative Chronology
placing things into time periods based on things that are definitely older and definitely newer to give it a relative date (as apposed to absolute chronology which has an actual year attached to it)
60
New cards
Representational Art
an art style that employs the use of signs that stand in for and take the place of something else
61
New cards
Rubble Masonry
masonry that uses irregularly shaped stones, sometimes minimally worked or selected for similar size (basically they just stack a bunch of stones that are close enough to the same size)
62
New cards
Sauceboat
Lerna type of ceramic pottery that could have been used for anything, but it kind of looks like a gravy boat
63
New cards
Schematic or Abstract Art
art that is usually very geometric and only vaguely resembles what it is representing
64
New cards
Seal
a tool with carvings on one end that you would press into wax or clay to leave the impression
65
New cards
Seal Impression
the impression left in wax or clay from a seal
66
New cards
Socle
the lower foundational part of the fortification wall that projects above the floor level
67
New cards
Stamped Decoration
seen in the Cycladic frying pans, carved into bronze by nailing designs into the soft metal or clay
68
New cards
Stamped Spirals
the spirals are symbolic of a journey and are made using the stamped decoration technique
69
New cards
Stratigraphy
layers of archaeological material that lets us relative date the various levels
70
New cards
Symmetry
an image that is duplicated on two sides of an axis
71
New cards
Terracotta
fired clay
72
New cards
Vasiliki Ware
Minoan pottery that looks like a tea pot
73
New cards
Zoomorphic
art representing animal forms or gods of animal form
74
New cards
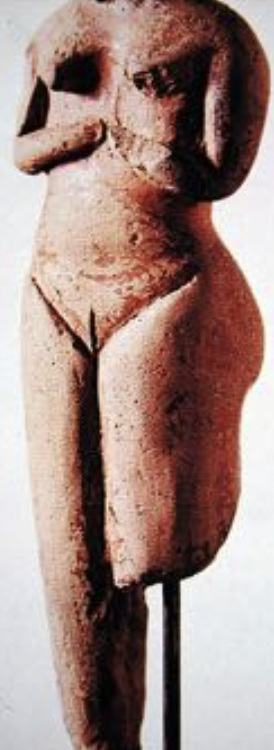
Lady of Lerna
Neolithic, terracotta, found in Lerna 1 house along with 10 graves
75
New cards
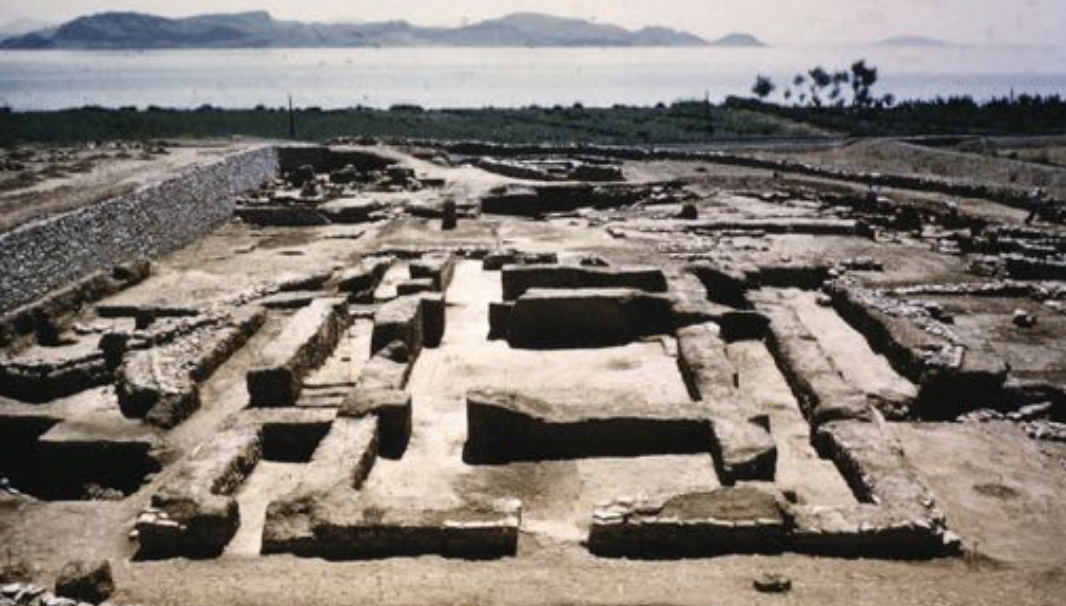
House of Tiles, Lerna
Early Helladic, 2-story corridor house made of stone base and mud brick, plaster on inner walls, terracotta tiles, burnt down and fired everything which is why we have it

76
New cards
Seals and Seal Impressions, Lerna
Early Helladic, found in the house of tiles, found both the carved seals and the seal impressions in fired clay
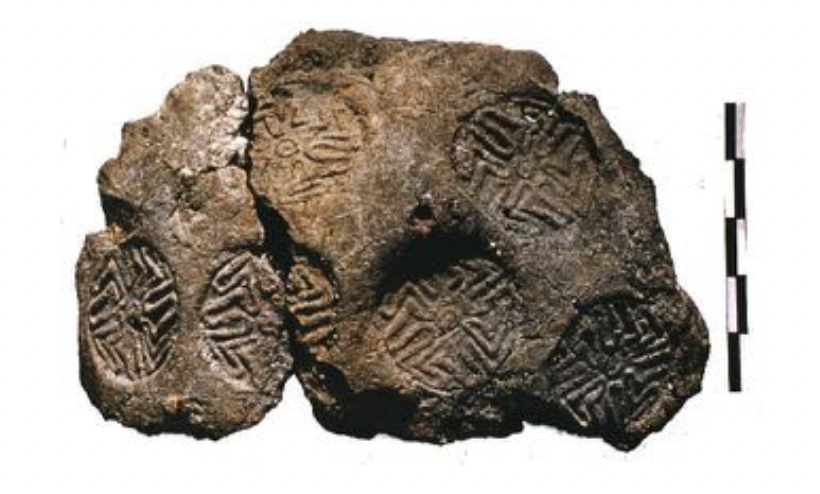

77
New cards
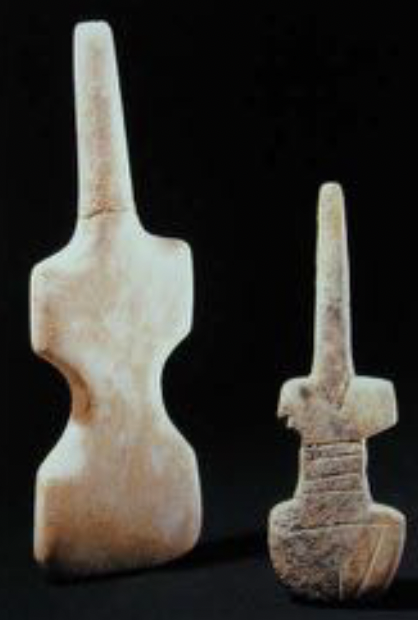
Cycladic Figurines - Schematic/Violin
marble, Grotta-Pelos Culture, ca. 3100/3000 - 2650 B.C.

78
New cards
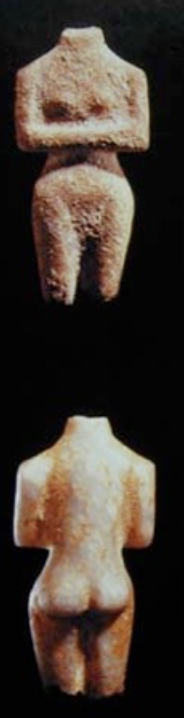
Cycladic Figurines - Plastiras
marble, Grotta-Pelos Culture, ca. 3100/3000 - 2650 B.C.
79
New cards
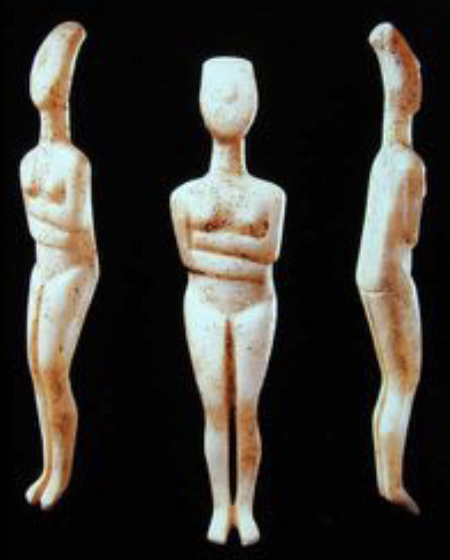
Cycladic Figurines - Spedos
marble, Keros-Syros Culture ca. 2650-2450/2400 B.C.

80
New cards
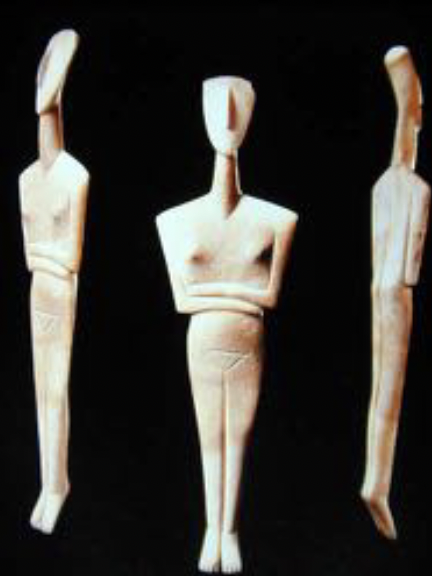
Cycladic Figurines - Dokathismata
marble, developed from the Spedos variety

81
New cards
Cycladic Figurines - Non-Canonical Varieties
marble, they don't fit into a particular canon, musicians, men with baldrics, women with different hand placement

82
New cards
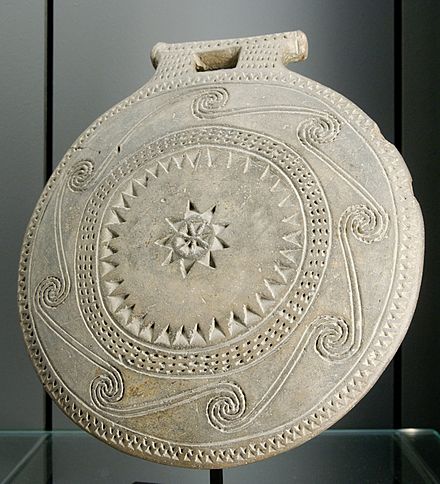
Cycladic Frying Pans - Kampos Group
clay, incised decoration, transitional between the ECI Grotta-Pelos and ECII Keros-Syros Culture, maybe center represents the sun

83
New cards
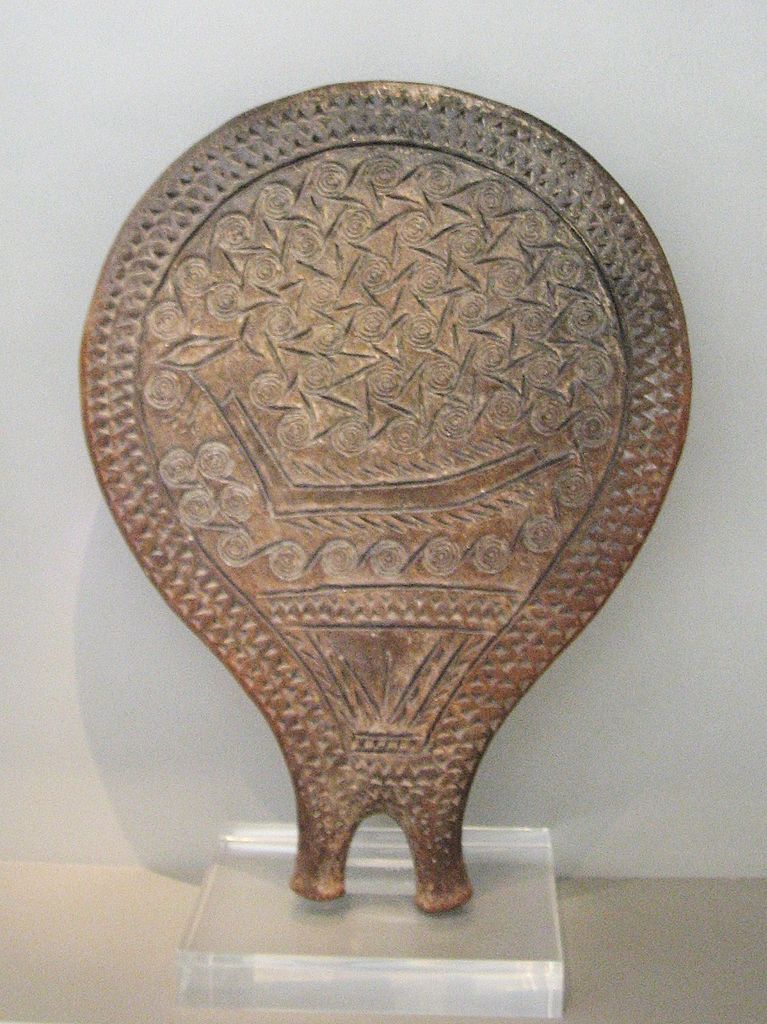
Cycladic Frying Pans - Keros-Syros
clay, depiction of a long boat, swirls depict wind/water/journeying, pubic triangle at the bottom

84
New cards
Potter's Disks, Fournou Korifi
Pre-Palatial, Early Minoan IIA, basically used to shape wet clay, but it didn't spin how we think of a potter's wheel, it was more just a plate

85
New cards
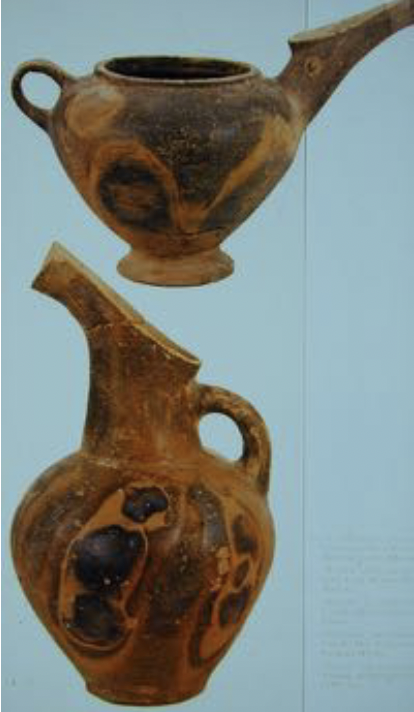
Vasiliki Ware Pottery
Pre-Palatial, Early Minoan IIB, basically a pitcher, made to look like stone even thought its terracotta, also had painted designs

86
New cards
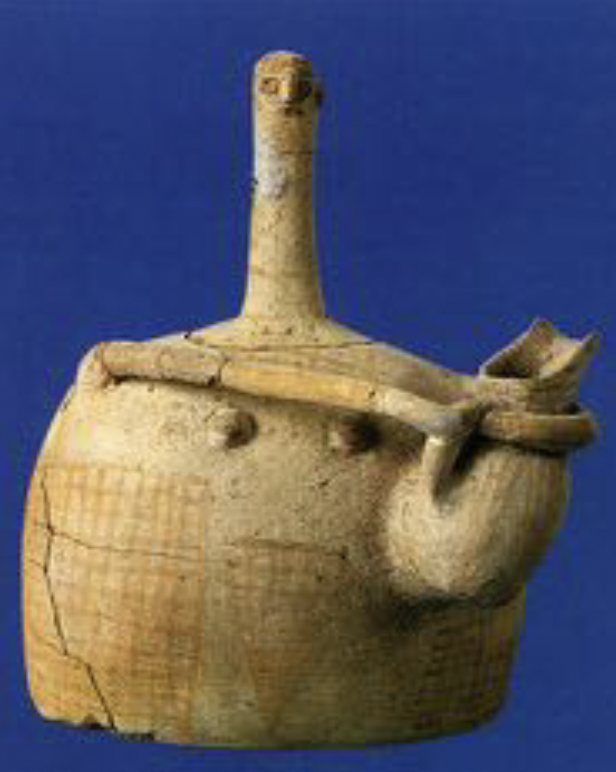
Myrtos Goddess
Pre-Palatial, Early Minoan II, (not the turtle goddess), found in room 92, maybe a votive figure, has an apron painted on, could have a pubic triangle

87
New cards
Essay Question 1
Applying what you have learned from lectures, readings, and class discussions, compare and contrast the roughly contemporary Early Bronze Age sites of Lerna (in southern Greece) and Myrtos Phournou Koryphi (in eastern Crete) in terms of history, development and architectural forms. What does the study of the material culture (art & artifacts) and the built environment (architecture) suggest about their respective cultures, communities, and social identities?
88
New cards
Essay Question 2
Applying what you have learned from lectures, readings, and class discussions, discuss the interpretation of Cycladic Folded-Arm-Figures. How have these objects been interpreted by art historians? What kinds of evidence have scholars used, and what are some of the pros and cons of their approaches? In particular, compare and contrast the approaches and interpretations of G. Hoffman and E. Hendrix. (HINT: Read BOTH articles!)