NHA CCMA
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN)
A form provided to the patient when the provider believes Medicare will probably not pay for services needed.
Allowed Amount
The maximum amount a third-party will pay for a particular procedure or service.
Copayment
An amount of money that is paid at the time of medical service
Coinsurance
A policy provision frequently found in medical insurance whereby the policyholder and the insurance company share the cost of covered losses in a specified ratio, such as 80:20
Deductible
A specific amount of money a patient must pay out of pocket before the insurance carrier begins paying.
Explanation of Benefits
A statement from the insurance carrier detailing what was paid, denied, or reduced in payment; also contains information about amounts applied to the deductible, coinsurance and allowed amounts.
Participating Provider (PAR)
Providers who agree to write off the difference between the amount charged by the provider and the approved fee established by the insurer.
Medicare
Generally covers patients age 65 and older by Part A (hospitalization) or Part B (routine medical office visits) benefits
Tricare
Authorizes dependents of military personnel to receive treatment from civilian providers at the expense of the federal government.
CHAMPVA
Covers surviving spouses and dependent children of veterans who died as a result of service-related disabilities.
Medicaid
Provides health insurance to the medically indigent population through a cost-sharing program between federal and state governments for those who meet specific eligibility criteria.
Managed Care
Is an umbrella term for plans that provide health care in return for preset scheduled payments and coordinated care through a defined network of providers and hospitals
Worker’s Compensation
Protects wage earners against the loss of wages and the cost of medical care resulting from an occupational accident or disease as long as the employee is not proven negligent.
CMS-1500 Form
CMS-1500 forms are submitted by healthcare providers or suppliers (like doctors, clinics, or medical offices) to insurance companies or other payers to request payment for services. To complete it, the medical assistant needs the patient’s and guarantor’s personal and insurance details, as well as information about tests, treatments, procedures, and billing. The CMS-1500 has 33 fields, organized into three sections.
CMS-1500 Section 1
Carrier Block: contains the address of the insurance carrier and is located at the top of the form
CMS-1500 Section 2
Patient/Insured Section: Contains information about the patient or insured (if other than the patient); includes boxes 1-13
CMS-1500 Section 3
Physician/Supplier Section: contains information about the physician or supplier: includes boxes 14-33
Supine Position
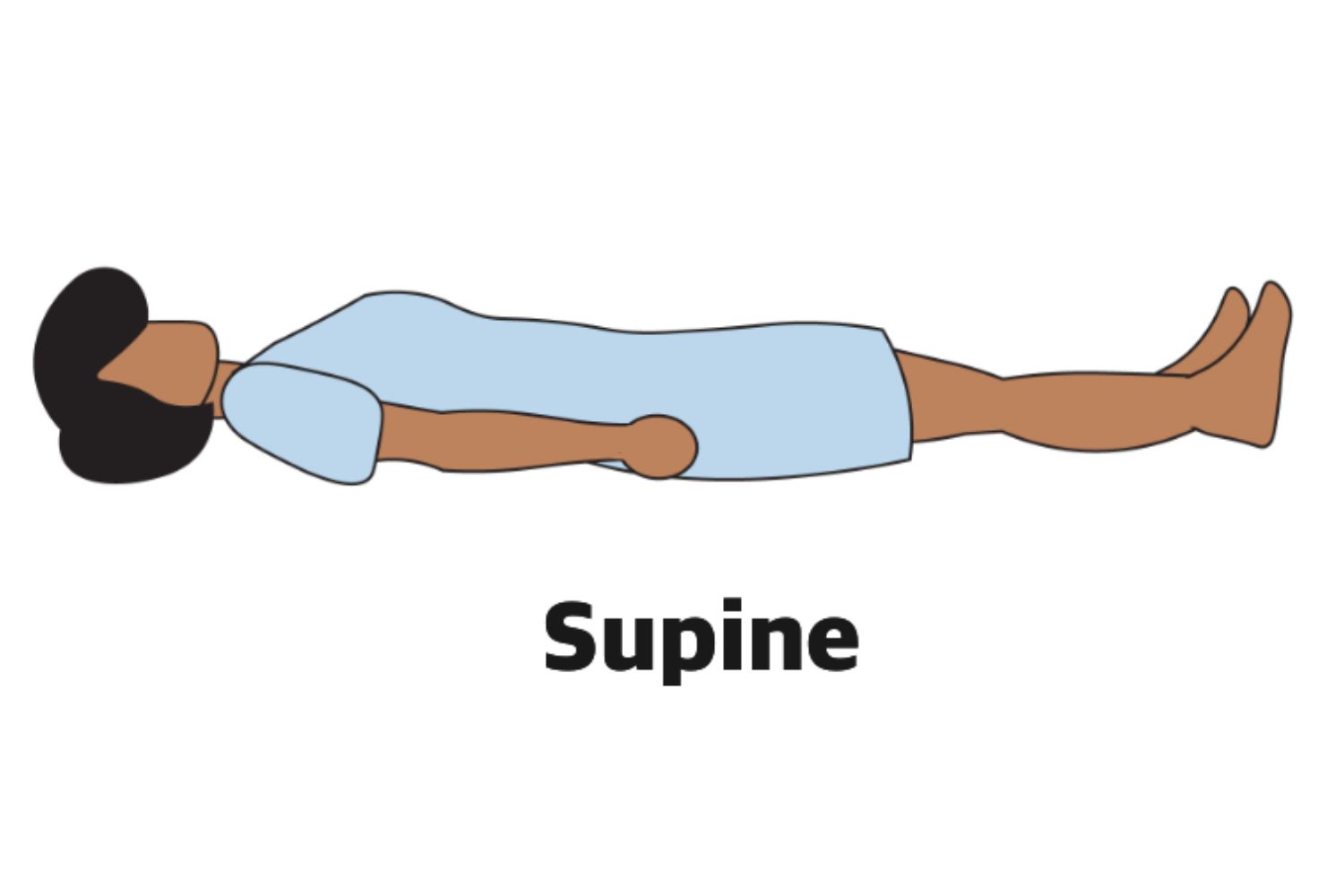
Dorsal Recumbent Position
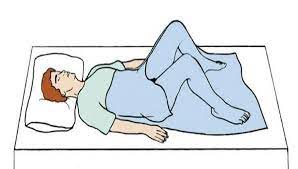
Sims Position
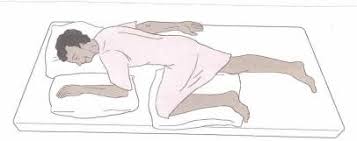
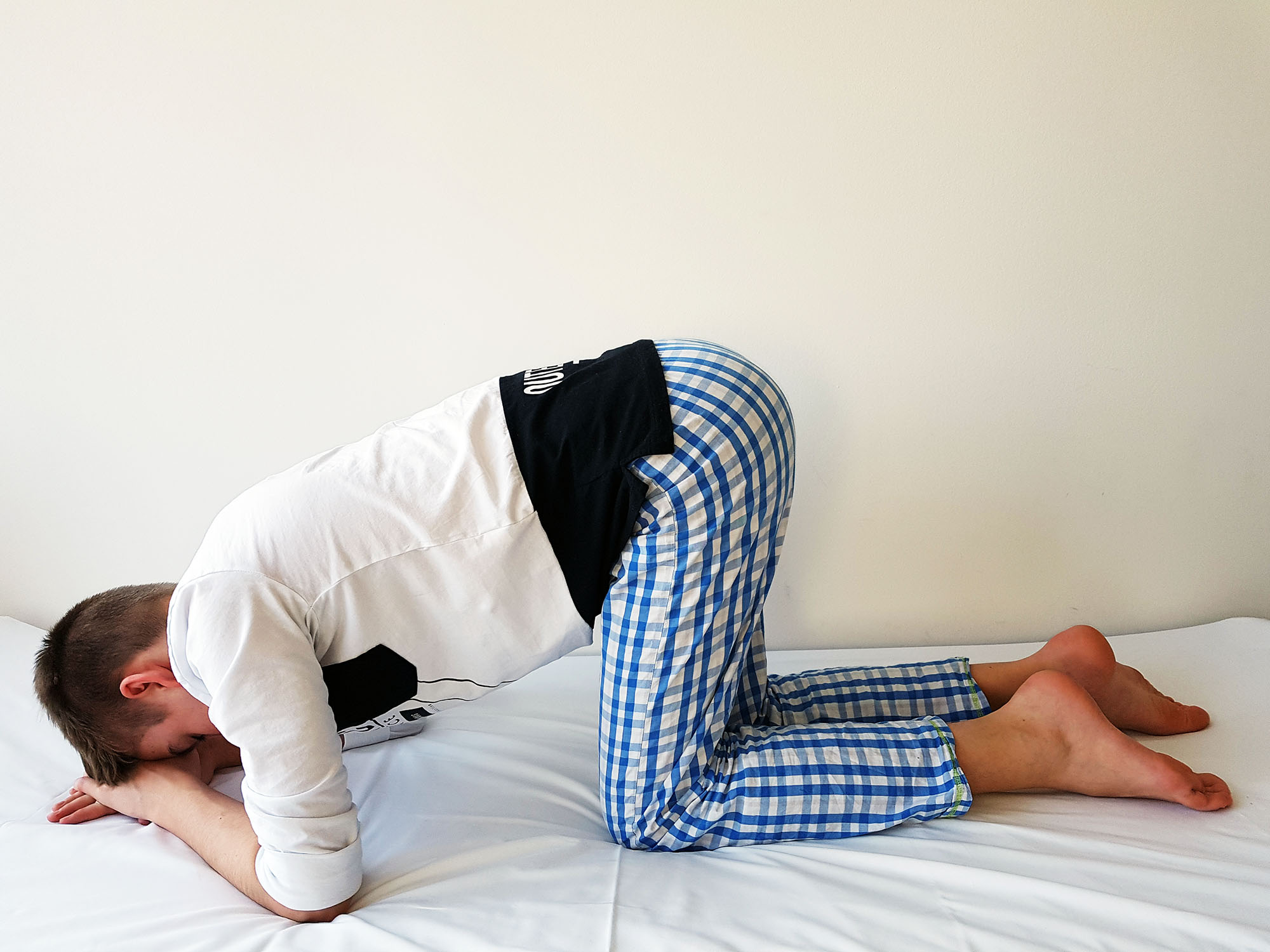
Knee-elbow position

Fowler’s Position
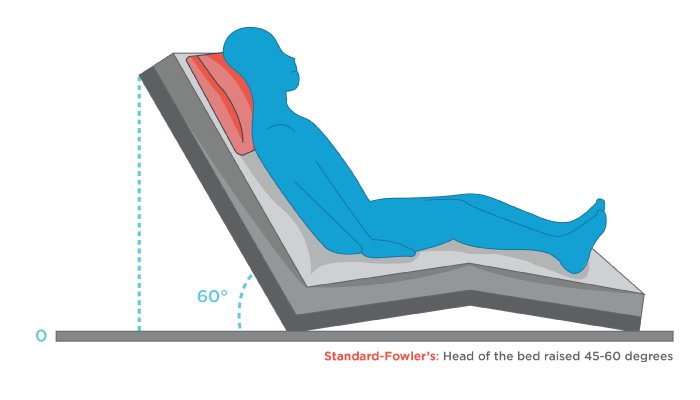
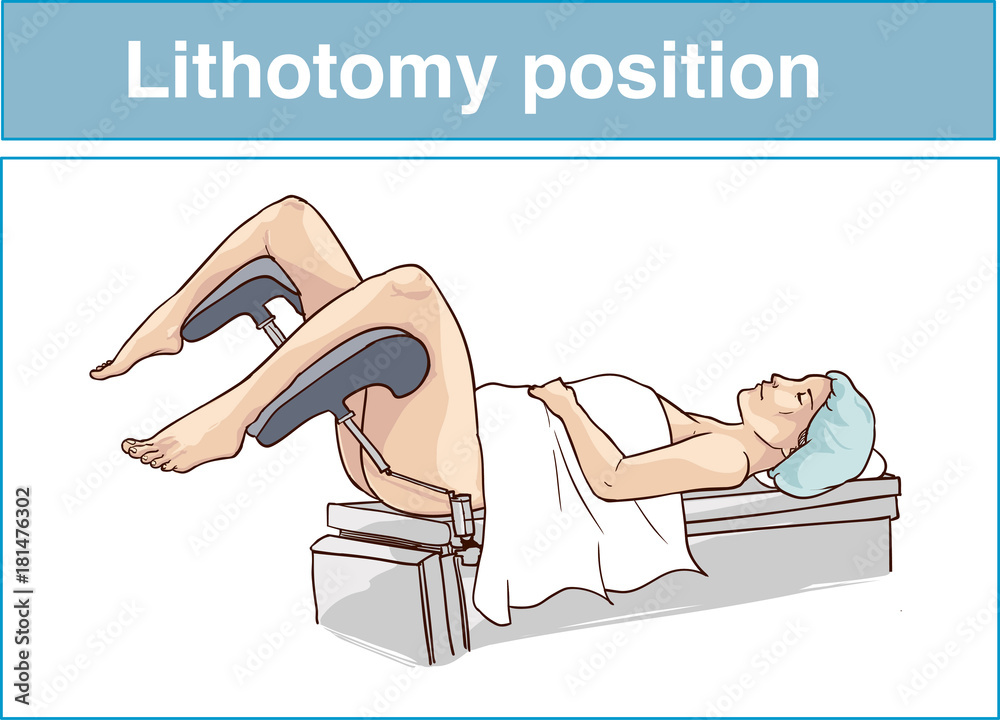
Lithotomy Position
Medication Schedules
Federal Controlled Substances Act (CSA) created five schedules for controlled substances, according to their potential for abuse and addiction. Only controlled substances are scheduled
Schedule I
Includes substances that have a high potential for abuse and no approved medical use in the US.
Schedule II
Includes substances that have a might potential for abuse, are considered dangerous, and can lead to psychological and physical dependence. Providers must give patients a handwritten prescription with no refills. In health care facilities, staff must keep these in a secure, locked cabinet or stage separate from other meds.
Schedule III
Includes substances that have a moderate to low potential for physical and psychological dependence. Providers must give patients a handwritten prescription. They may refill them five times in 6 months.
Schedule IV
Includes substances that have a low potential for abuse and dependence. Providers must sign prescriptions for these substances, and patients may refill them five times in 6 months. Staff members may authorize refills over a phone.
Schedule V
Includes substances that contain limited quantities of some narcotics, usually for antidiarrheal, antitussive, and analgesic purposes. Providers must sign prescriptions for these substances, and patients may refill them five times in 6 months. Staff members may authorize refills over the phone.
Household Value: 15 drops (gtt)
Apothecary value: 15-16 minims
Metric: 1 mL
Household Value: 1 teaspoon (tsp)
Apothecary value: 1 dram
Metric: 5 mL
Household Value: 1 tbsp
Apothecary value: 4 dram
Metric: 15 mL
Household Value: 1 fluid oz, 2 tbsp
Apothecary value: 8 dram,1 oz
Metric: 30 mL
Household Value: 1 cup
Apothecary value: 8 oz
Metric: 240 mL
Household Value: 1 pint
Apothecary value: 1 pint
Metric: 480 mL
Household Value: 1 quart
Apothecary value: 1 quart
Metric: 960 mL
Household Value: 1 gallon
Apothecary value: 1 gallon
Metric: 3,830 mL
Household Value: 2.2 lb
Apothecary value: 2.2 lb
Metric: 1 kg
Route: Epidural
Location: Epidural space (spine)
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: Intra-Arterial
Location: Arteries (to break up clots)
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: Intra-Articular
Location: Within a joint space
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: Intradermal
Location: Skin of the upper chest, forearms, upper back
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: yes
Route: Intramuscular (IM)
Location: Deltoid, vastus lateralis, ventrogluteal muscles
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: yes
Route: Intraosseous
Location: Bone Marrow
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: Intraperitoneal
Location: Peritoneal Cavity (abdomen)
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: intrapleural
Location: Pleural space (lungs)
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: Intrathecal
Location: Subarachnoid space (brain)
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: Intravenous (IV)
Location: Major veins, most often in arms and hands, or via central venous access devices
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: no
Route: Subcutaneous
Location: Under the skin of the abdomen, anterior thighs, upper outer arms, upper back (under shoulder)
Medication Formulations: Injectable liquid
CCMA permitted to administer: yes
Classifying Solubility of Vitamins
their absorption, transportation, storage, and excretion depend on the availability of the substance in which they dissolve in.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins
A, D, E, K
Water-Soluble Vitamins
B1, B2, B3, B6, folate, B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, C
Erikson’s Stages of Psychological development
Trust vs. Mistrust
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt
Initiative vs. Guilt
Industry vs. Inferiority
Identity vs. Role Confusion
Intimacy vs. Isolation
Generativity vs. Stagnation
Ego Integrity vs. Despair
The Grief Cycle
Denial → Anger → Bargaining → Depression → Acceptance