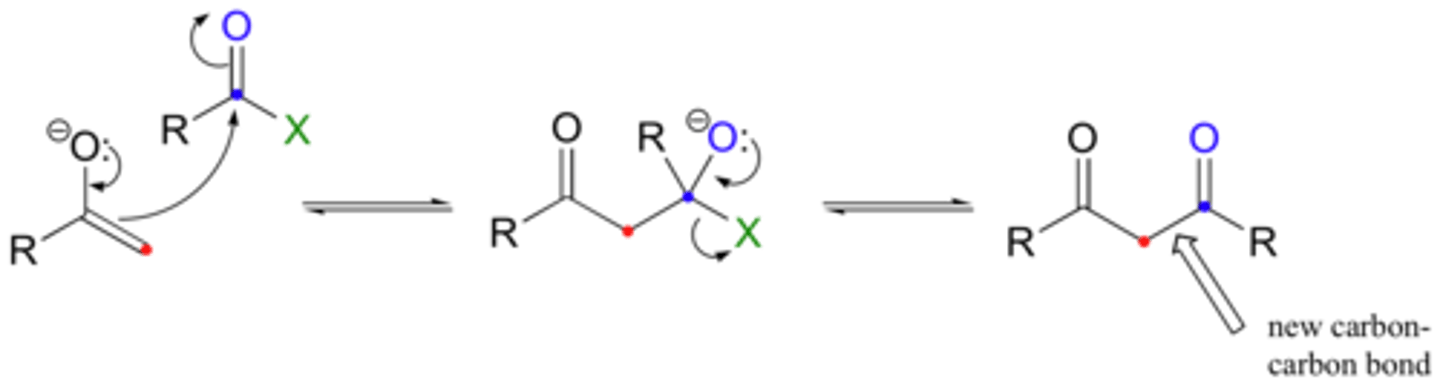
Nucleophilic Substitution
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Nucleophilic substitution
1. nucleophilic addition to acid derivative
2. pi donation
Result: nucleophile replaces another group or atom (the leaving group) in a molecule
pi donation
reverse of nucleophilic addition mechanistic step
acid derivatives
Compounds containing functional groups that can be converted to carboxylic acids by acidic or basic hydrolysis
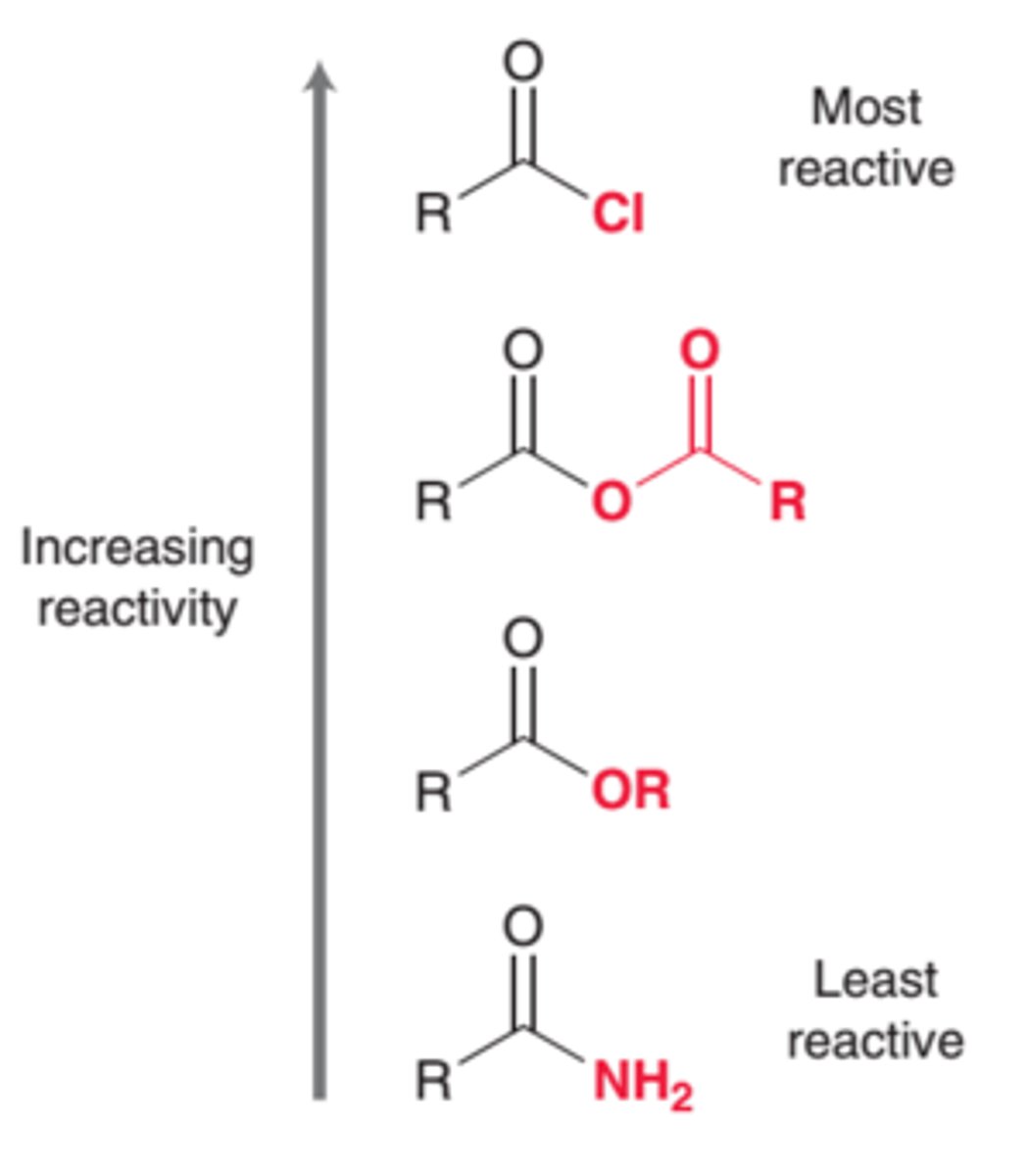
acid derivative reactivity
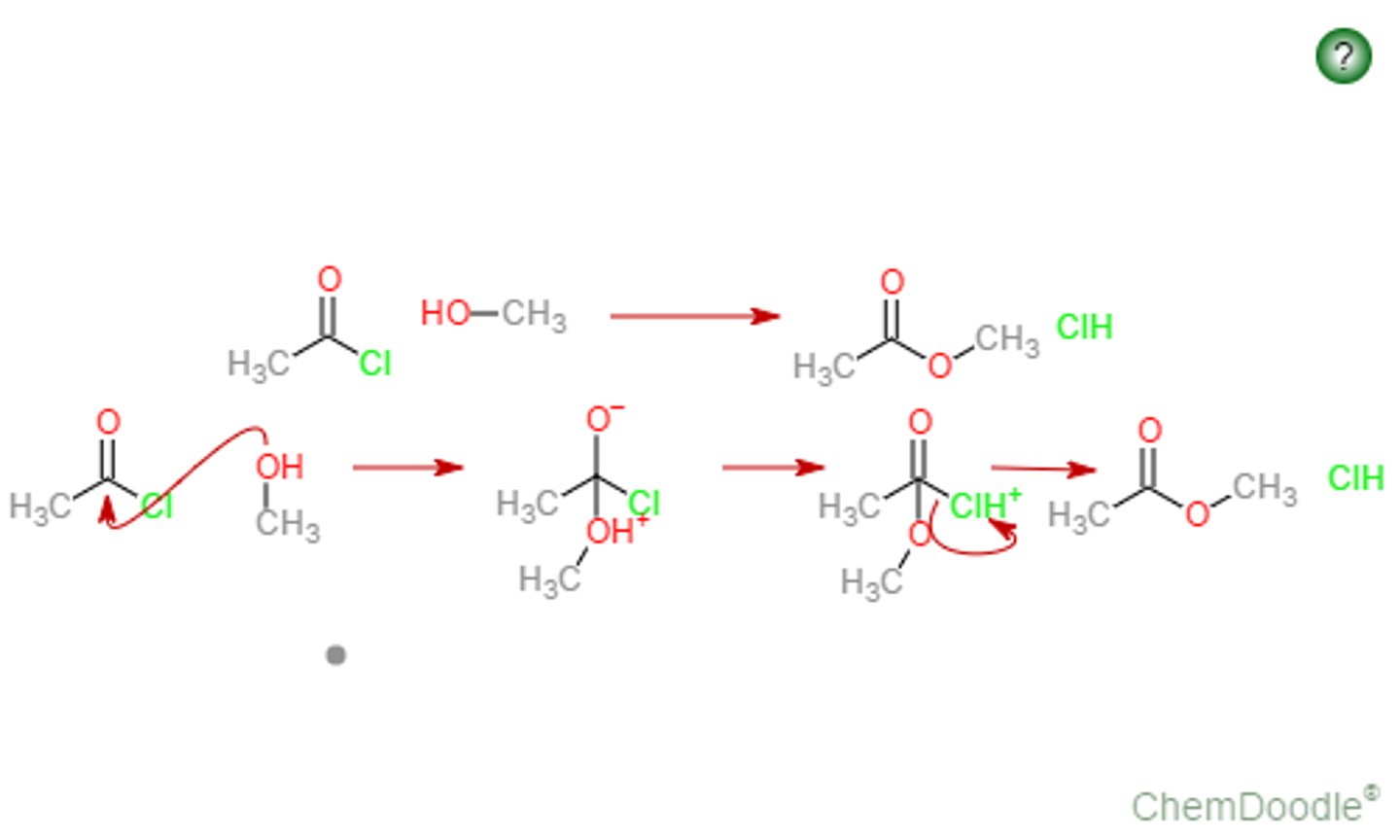
Mechanism for Acid Chloride to Ester
acid chloride to aldehyde
1. LiAl(OR)3H
2. H2O
acid chloride to alcohol
1) LAH
2) H2O
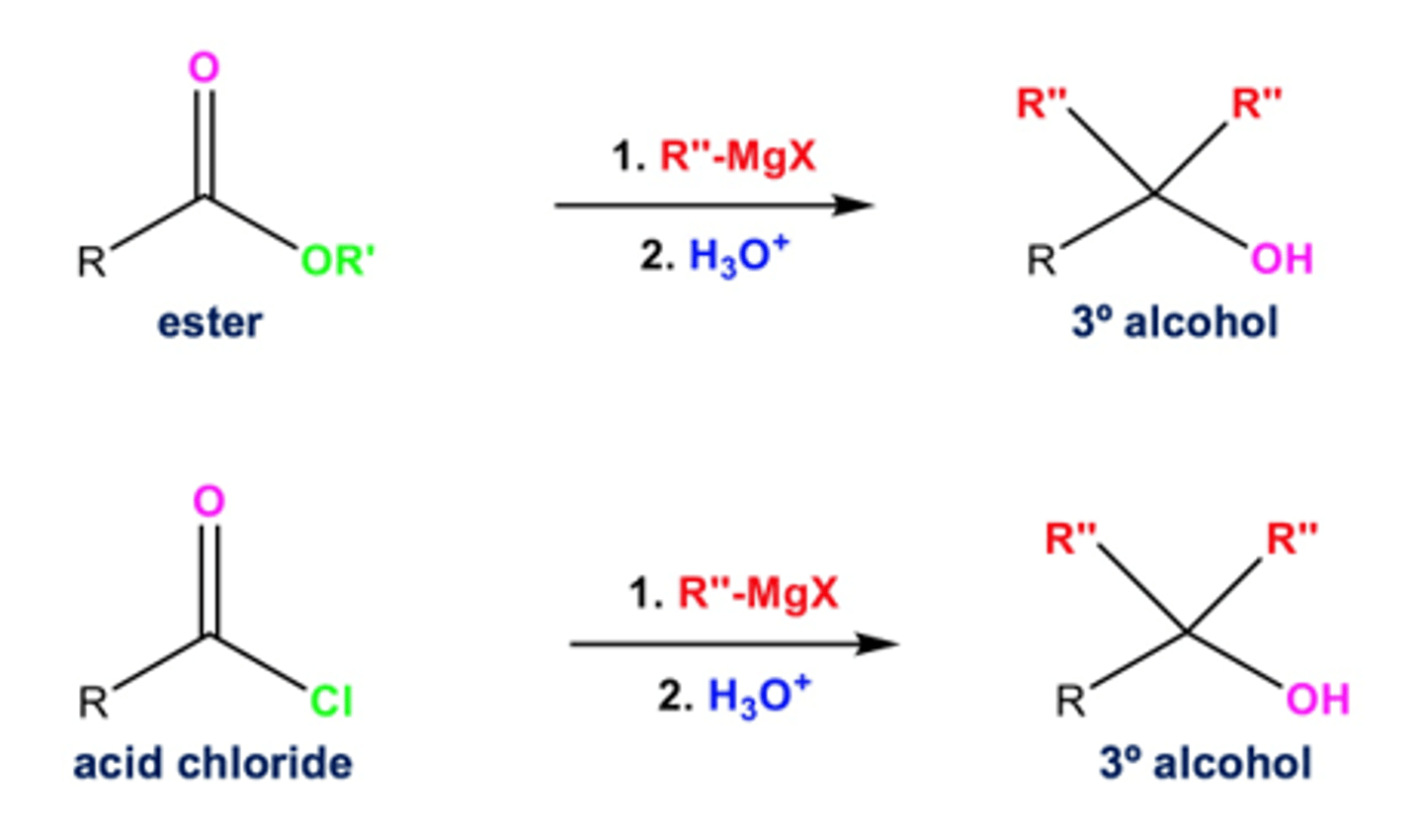
acid derivatives to tertiary alcohol
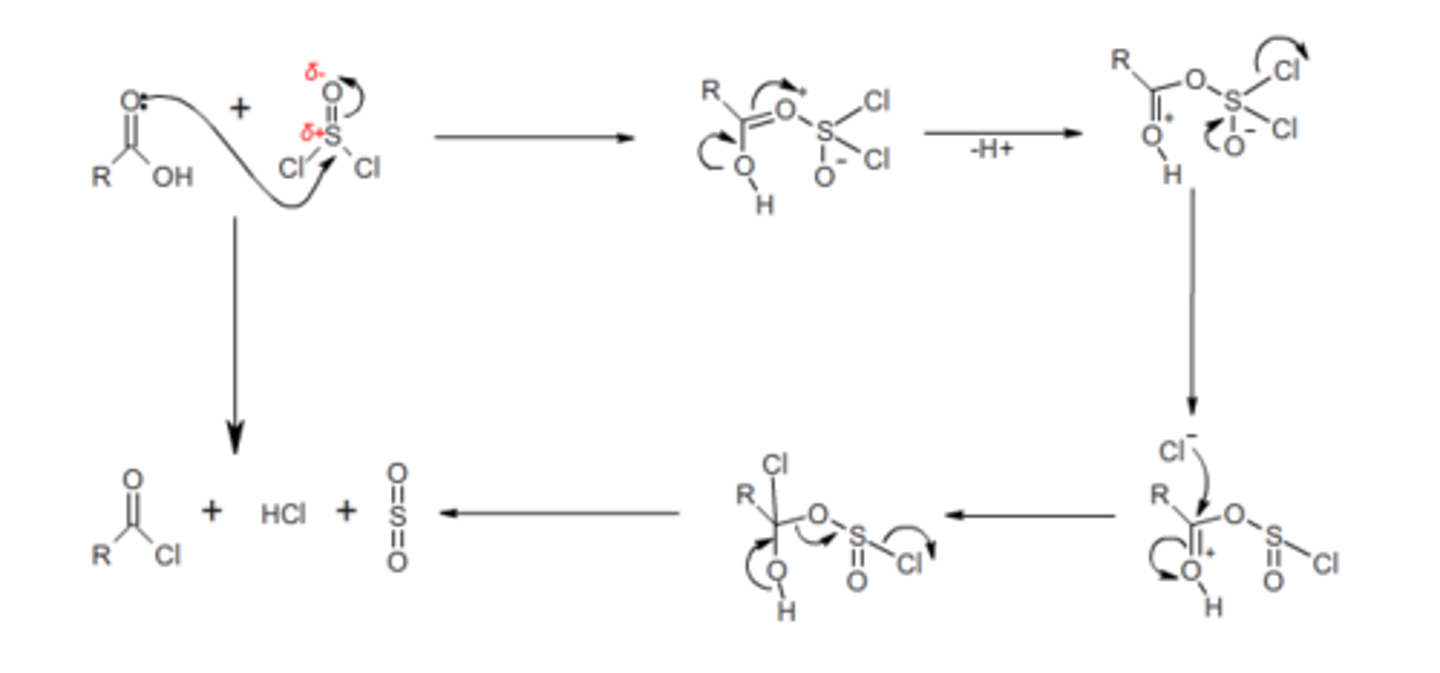
carboxylic acid to acid chloride
SOCl2
carboxylic acid to ester
1. SOCl2
2. Alcohol
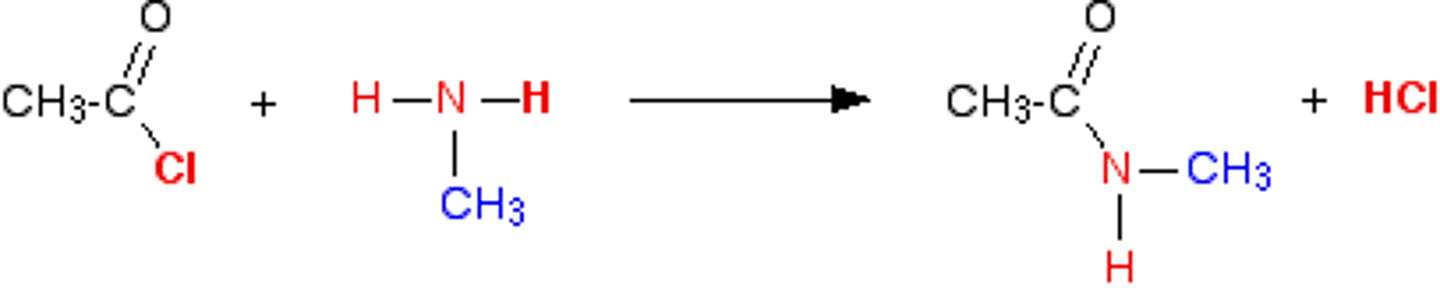
acid chloride to amide
NH3
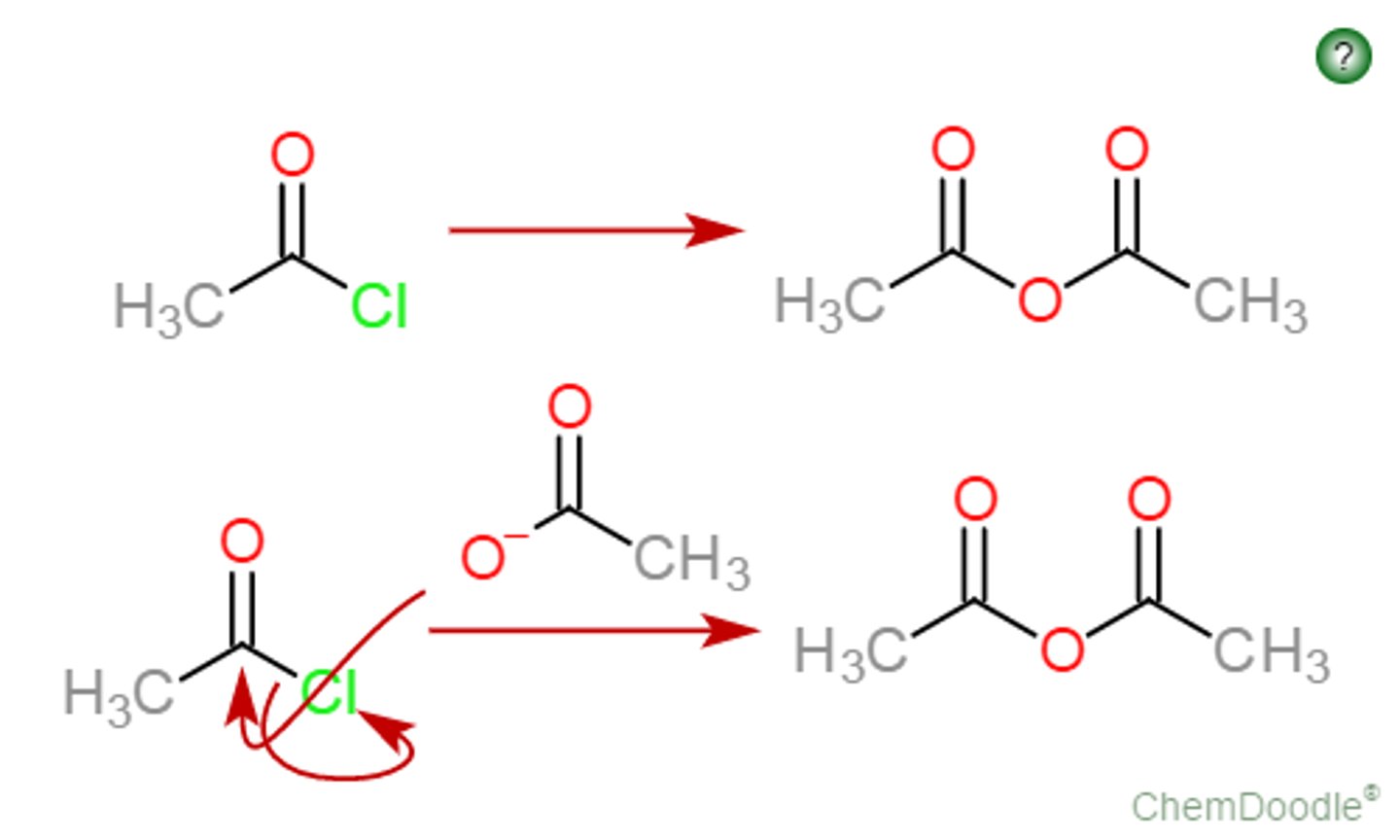
Acid Chloride to Anhydride
R'COOH, R'COO-
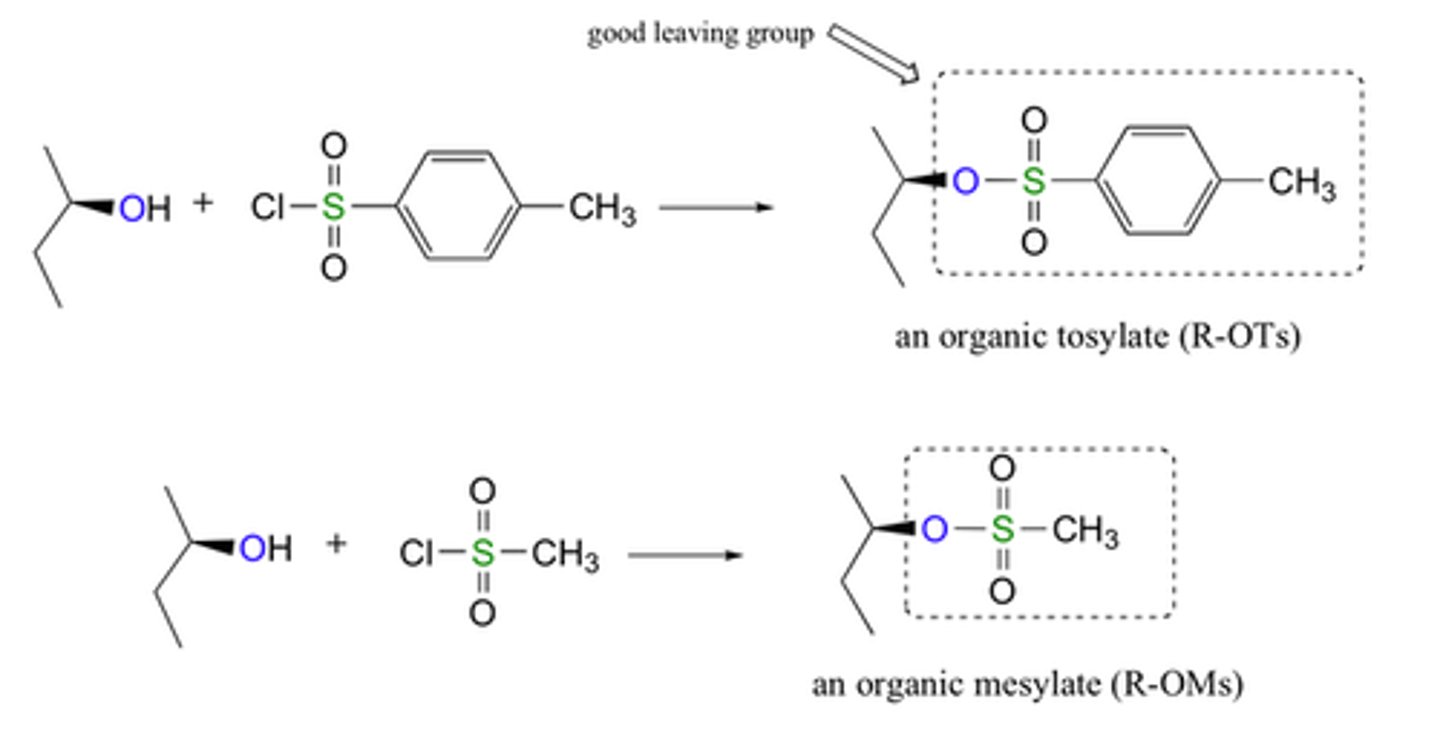
Alcohol to sulfonate ester
sulfonyl chloride
Hydrolysis of amides
NaOH
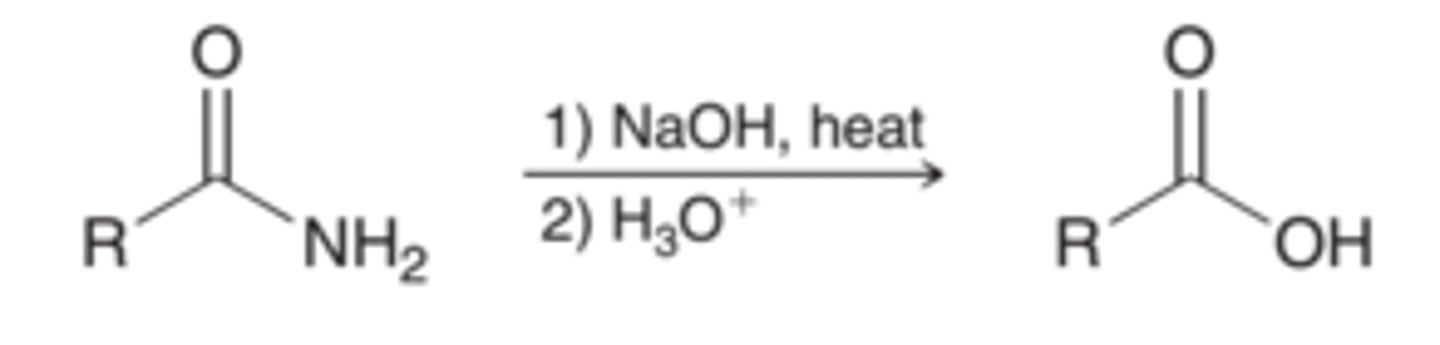
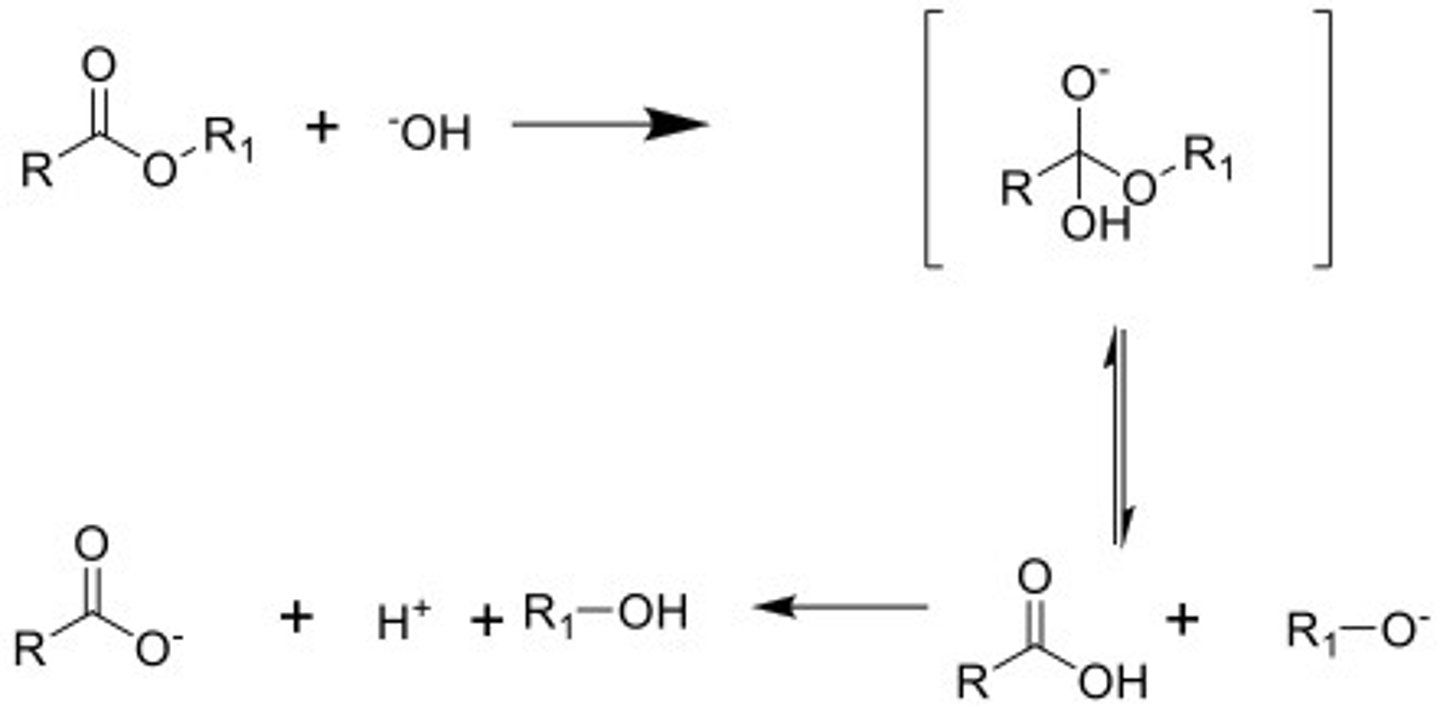
Hydrolysis of esters
NaOH
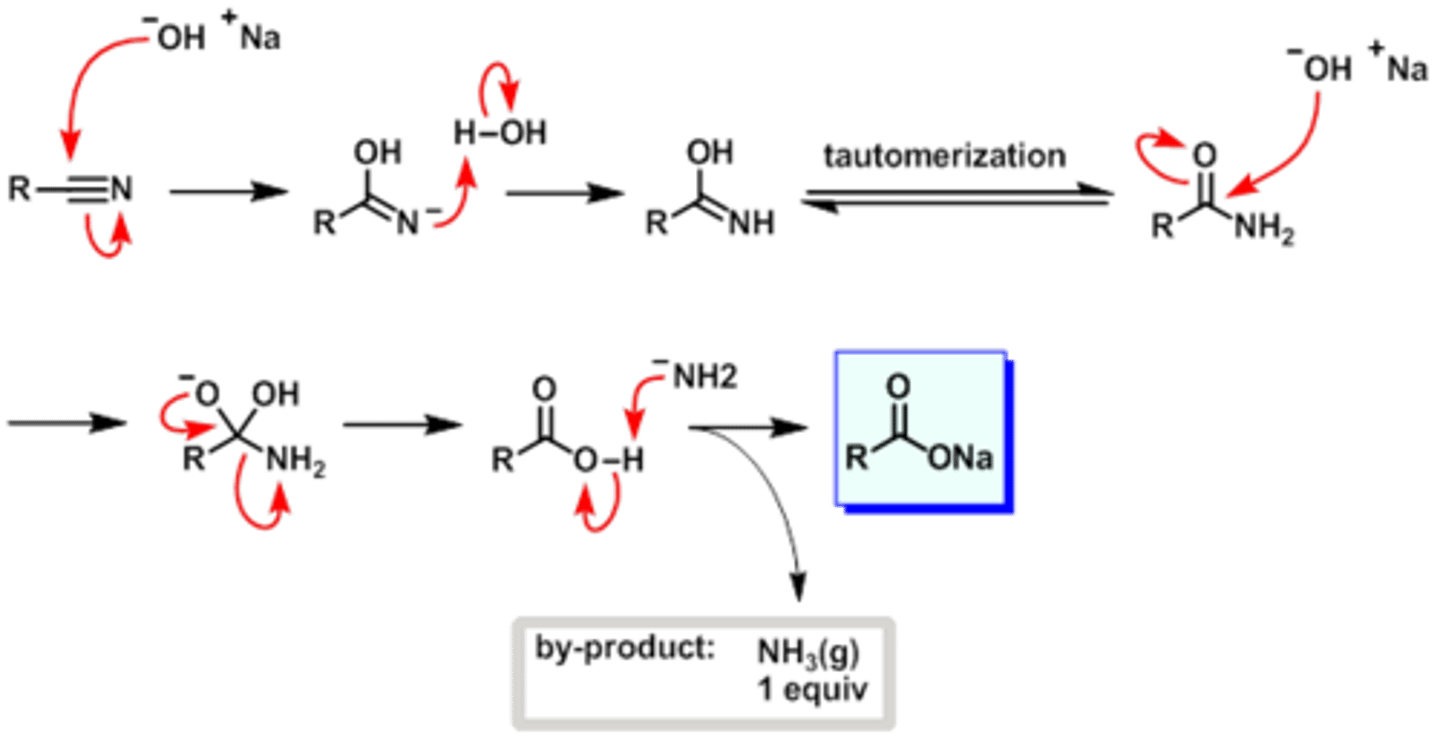
basic hydrolysis of nitriles
NaOH
Claisen Condensation
enolate ion of one ester acts as nucleophile attacking another ester